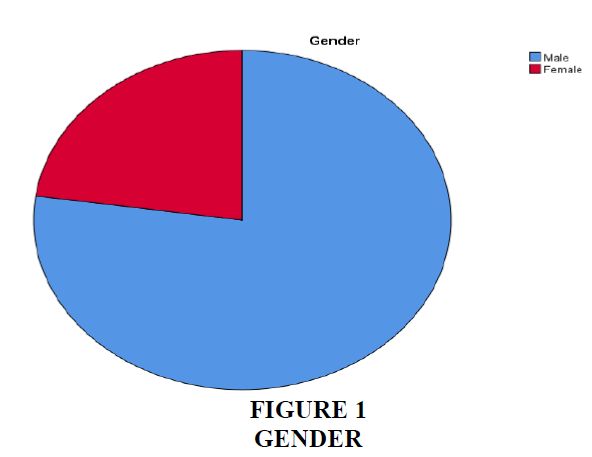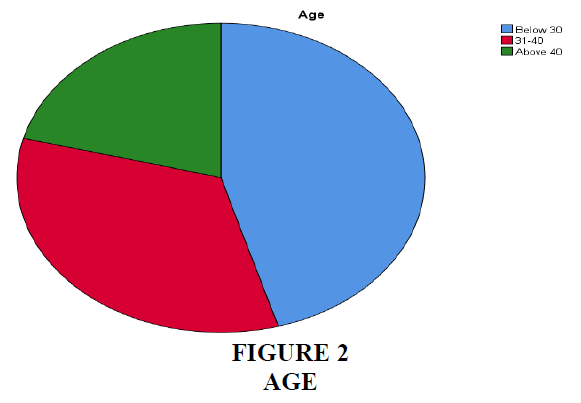Research Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 6S
To Study an Impact of Customer Relationship Management on Brand Loyalty in Special Reference with Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd
Vijaya E, National Institute for MSME (ni-msme), An Organization of Ministry of MSME, Government of India
Balaji Vejju, FST, ICFAI Foundation for Higher Education, Hyderabad Siriman Naveen, Woxsen University, Hyderabad
Gowri Kusuma Pinjarla, Siva Sivani Institute of Management, Hyderabad
Citation Information: Gondane, V.A., Waghmare, G., & Chavan, A. (2024). To study an impact of customer relationship management on brand loyalty in special reference with star health and allied insurance co ltd. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(S6), 1-14.
Abstract
The research investigates the impact of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) on brand loyalty in the Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd. The study aims to explicate the refinement dynamics shaping brand loyalty. By investigating real-world an empirical data, the research seeks to provide insights into the crucial role CRM plays in strengthening customer relationships and, therefore enhancing the brand loyalty. Also Study found a link between CRM implementation and customer happiness. The result of the study reveals that CRM has a positive and significant impact on brand loyalty. On the other hand, implementing a CRM strategy is likely to impact customer satisfaction and knowledge. Moreover, Customer engagement gave a significant influence on brand loyalty so Customer satisfaction emerged as the strong factor which influences brand loyalty. Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd emphasis on customer relationship management as a strategic tool to enhance their brand loyalty which achieve the customer value and build a strong bond in between company and customer due to the trust, commitment and customer satisfaction which predicts the brand loyalty.
Keywords
Customer Satisfaction, Brand Loyalty, Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Relationship Marketing.
Introduction
Customer happiness is a fundamental component of current marketing comprehension. Businesses may exist as long as they can fulfil the demands of their consumers and provide customer satisfaction. One method of facilitating consumer happiness is to determine and satisfy the consumer's wants and requirements. As a result, it is critical in our very competitive climate to maintain constant touch with customers and continuously monitor their changes Buttle & Maklan, (2019).
Marketing has shifted from a transactional to a relationship-based approach. Consumers become partners, and the company must commit to long-term partnerships via quality, service, and innovation. Relationship marketing is simply a marketing paradigm shift away from an acquisition/transaction focus and towards retention/relationships focus. Relationship marketing (relationship management) is a corporate philosophy and strategic orientation that focuses on retaining and enhancing current customers rather than gaining new consumers. This idea suggests that many consumers and corporate customers would rather establish a long-term connection with one company than switch between suppliers in their quest for value. Based on this notion and the fact that it is typically considerably cheaper to keep an existing customer than to recruit a new one, savvy marketers are developing efficient customer retention tactics (Valarie A.Zeithaml, Mary Jo Bitner, 2003) The first three phases in the marketing process—understanding the market and customer demands, developing a customer-driven marketing strategy, and putting together a marketing program—all lead up to the fourth and most essential step: developing lucrative customer relationships. Customer relationship managements possibly are the most essential notion in modern marketing. Some marketers consider it as a customer data management activity only (a practice called CRM). According to this definition, it entails keeping precise information on individual customers as well as managing customer "touch points" carefully in order to maximize customer loyalty. Most marketers, however, define customer relationship management in a broader sense. Customer relationship management, in its broadest meaning, is the process of establishing and maintaining profitable customer relationships by providing greater customer value and satisfaction. It covers all areas of gaining, retaining, and developing consumers (Kotler and Gary Armstrong, 2004).
Customers' access to different means of information and data distribution, as well as presenting items for product selection in a highly competitive market, has weakened their loyalty to providers. As a result, one of the most critical challenges in the durability and stability of firms in terms of competitiveness and profitability is how to successfully interact with consumers and ensure their longevity (Kotler, 2005). Furthermore, considering that customer expectations have risen in recent years in today's customer-oriented company environment, customer relationship management is a must.
A company's success is mainly determined by its ability to attract customers to its brands. It is very important for a company's existence to keep its present consumers and make them loyal to the brand. Brand loyalty has been one of the most pressing concerns in the marketing world in recent years (Kotler, 2009); Ndubisi & Wah, (2005).
A service, like physical things, must meet the demands of purchasers, according to Jobber and Lancaster (2009). Yet, because they cannot be stored or shown, the advantages are less tangible than with physical things, and enjoyment is obtained through activities. Insurance services are examples of intangible products. Several different types of insurance policies are available on the market to help reduce the chance of loss. These insurance businesses only sell promises to compensate the insured for unintentional loss or damage caused by insured risks. Insurance services are viewed as a risk management tool. Researchers in risk management and insurance contend that there is no uniform definition of risk, but there are two characteristics that all definitions share: indeterminacy and loss. Most definitions include uncertainty about the result and the chance that the conclusion will be undesirable; a lack of understanding about the future and the likelihood of some negative consequence. As a result, the most widely recognized definition of risk is "a circumstance in which there is a chance of an undesirable divergence from a desired outcome that is expected or hoped for" (Vaughan and Vaughan, 2008). Relationship marketing is a strategy that focuses on maintaining and enhancing current customer connections. Many studies have been undertaken to investigate the impact of relationship marketing on customer loyalty, satisfaction, and profitability. To succeed or simply survive, companies need a new philosophy, according to Kotler (2005). Companies must be customer-centered- they must deliver superior value to their target customers, they must become adept at building customer relationships, not just building products, and they must be skilled in market engineering, not just product engineering. As a result, the purpose of this research is to investigate the influence of relationship management on brand loyalty in the insurance sector in the instance of Star Health Insurance Company.
CRM Intervention
• There is a need to investigate the influence of the customer relationship management concept on brand loyalty in the insurance industry.
• Creating a network of loyal and delighted consumers is crucial for many businesses' survival (Kotler, 2004). In this case, branding is utilized to develop a competitive position by addressing one of branding's goals, such as repeat sales or loyalty (Lamb, 2008). According to a study performed by (Nebyou 2014) on the Indian private banking business, customer happiness is one of the most important influencers on brand loyalty. According to the findings, the consumer's sense of security in his or her connection with the bank brand is critical. It is built on the customer perception that the brand is trustworthy and concerned about the consumer's best interests. As a result, brand trust emerged as a strong predictor of brand loyalty.
• Another study published in a British publication (www.eajournals.org) discovered that CRM strategy had a favorable influence on bank customers' brand commitment and loyalty behaviors. Yet, continuance loyalty outweighed affective loyalty in terms of consumer advocacy activities. According to the report, customer relationship management approach aids in gaining customer brand commitment and loyalty. Hence, persistence characteristics are appropriate for forecasting advocacy intentions of Nigerian bank consumers. The article by (Abel, 2016) aimed at determining the factors of consumer brand loyalty in United Bank S.C. revealed that customer satisfaction plays a vital role in maintaining customer brand loyalty.
• Customer: Customers are organizations, people, and corporations that use insurance goods and services.
• Customer Relation Management (CRM): might be described as the formation and upkeep of long-term relationships between a company and its customers.
• Customer satisfaction: is the sense of satisfaction gained by a buyer after acquiring an item or service acknowledged. Chang and Chungiang (2004) Couldwell, (1998).
• Insurance: is an instrument for reducing uncertainty.
• Premium: the amount of money that an insurer costs a policy holder for the risk transfer.
• Trust: as occurring when one party has faith in the dependability and integrity of an exchange partner Hamdallah & Evelyn Assabil (1996).
• Commitment: refers to an insurer's and its employees' efforts to provide customers with the desired levels of service. It also represents the insurance company's customer orientation and CRM initiatives in terms of values, attitudes, and beliefs.
• Loyalty: The seller's impression of the consumer's good attitude about the product as demonstrated by repurchase. 67.
• Communication: Communication, particularly timely communication, entails assisting in the resolution of disagreements and matching conceptions and expectations in order to increase mutual trust in a partnership.
• Brand loyalty: Brand loyalty is a strong commitment to better services or items repurchased in the future to obtain the same brand despite prospective rivals' marketing efforts and their affects.
The Indian Insurance Industry Today
In terms of the industry, LIC, New India, National Insurance, United Insurance, and Oriental are the only government-controlled entities that rank high in terms of both market share and contribution to the Indian insurance sector. Agricultural Insurance Company Ltd specializes in crop insurance, while Export Credit Guarantee of India specializes in credit insurance. Others are private insurers (both life and general) that have formed a joint venture with international insurance corporations to launch their insurance operations in India.
Because of this partnership with global markets, India's insurance sector has only grown significantly, with a large present market share. In 2000, India authorized private enterprises in the insurance market, limiting FDI to 26%, which was extended to 49% in 2014. According to IRDAI, the Insurance Laws (Amendment) Act, 2015 increases the Foreign Investment Cap in an Indian Insurance Company from 26% to an Explicitly Composite Limit of 49% while ensuring Indian ownership and control.
Health Insurance in India
Health insurance is a rising sector of the Indian economy. The Indian healthcare system is one of the most extensive in the world, with almost 1.3 billion potential beneficiaries. In terms of income and employment generation, India's healthcare business has quickly become one of the most significant industries in the country. In 2018, one hundred million Indian homes (500 million individuals) lacked health insurance. In 2011, the health sector received 3.9% of India's gross domestic product.
There are policies available that protect both individuals and families. Health insurance accounts for 5-10% of this 3.9%, employers responsible for roughly 9%, and personal expenditure accounts for an amazing 82%. Based on its 71st round of surveys, the NSSO published the study "Key Indicators of Social Consumption in India: Health" in 2016. According to a poll conducted in 2014, more than 80% of Indians are uninsured, with just 18% (government financed 12%) of the urban population and 14% (government funded 13%) of the rural population covered by any type of health insurance.
Since its inception in 1986, the health insurance sector has developed dramatically, owing mostly to economic liberalization and increased public awareness. According to the World Bank, more than a quarter of India's population has access to some type of health insurance by 2010. There are both independent health insurers and government-sponsored health insurance companies. Until recently, the General Insurance Corporation of India and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDAI) had launched an awareness campaign for all sectors of the public to increase awareness and eliminate delay in purchasing health insurance.
In terms of density, the health insurance industry is roughly 10%. India has one of the lowest health insurance penetration rates in the world, with just 18% of people in urban areas and 14% in rural regions covered by any type of health insurance policy. One of the primary causes for poor health insurance uptake and coverage is a lack of competition in the market. To foster competition, the IRDAI, which is in charge of insurance policies in India, can establish health circles similar to telecom circles.
Policy price range: Insurance firms provide health insurance plans ranging from 5,000 for micro-insurance policies to 5 million (US$63,000) and above. Health insurance coverage typically range in price from $100,000 (US$1,300) to $500,000 (US$6,300).
The policyholder who takes out the insurance can claim tax deductions under Section 80D of the Income-tax Act.
Company Profile
Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd is an international health insurance firm based in Chennai, India. The firm offers health, personal accident, and international travel insurance directly as well as via other channels including as agents, brokers, and online. Star Health is also heavily involved in financial services, having long-standing relationships with a variety of institutions.
Commencing operations in 2006 as India’s first Standalone Health Insurance provider, Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd is providing sterling services in Health, Personal Accident and Overseas Travel Insurance etc. Our efforts have always been on service excellence and product innovation with a focus on delivering the best to our customers.
Star Health has underwritten a gross written premium of Rs.6865 Cr during the FY 2019-20 and has built up a promising path with an appreciable net worth of Rs.1889 Cr, as on 31st March 2020.
Currently Star Health has 12800+ employees and 640+ branch offices all over India Tables 1-3.
| Table 1 Insurance Provided by Star Health Insurance Company | ||
| HEALTH INSURANCE | ACCIDENT INSURANCE | TRAVEL INSURANCE |
| Individual Health Insurance | Personal Accident Cover Policy | Overseas Individual Travel Insurance |
| Health Insurance for Family | Family Accident Cover Plan | Student Travel Insurance |
| Health Insurance for Parents | Corporate Travel Insurance | |
| Maternity Insurance | ||
| Diabetes Safe Insurance Policy | ||
| Top Up Health Insurance | ||
| Star Out Patient Care Insurance Policy | ||
| Star Hospital Cash Insurance Policy | ||
| Table 2 Survey Response | |
| Sample Size | 110 |
| Distributed Questionnaires | 150 |
| Returned and Correctly Collected Surveys | 110 |
| Response Rate | 73.33 |
| Table 3 Gender of Respondents | |||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Male | 85 | 77.3 | 77.3 | 77.3 |
| Female | 25 | 22.7 | 22.7 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 110 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
Problem of the Study
1. Brand loyalty is one of the most pressing concerns confronting businesses today. Because of the enormous growth in rivalry and concentration of markets, developing loyal customers has become more vital. Companies strive to acquire and satisfy consumers while also establishing long-term relationships through customer loyalty (Gremler, 1996).
2. As a result of the growing competition in the business, insurance firms operating in India are under pressure. To keep their consumers, they use a variety of techniques.
3. Customers' expectations and attitudes regarding basic services are changing as customer demand rises. Their expectations and views are rapidly changing, requiring service providers to adjust their marketing approach to meet the needs of their target customers. In 2019/20, SHICO achieved the top performance in the industry. Yet, in competitive business, keeping, pleasing, and gaining new customers is becoming increasingly difficult for SHICO.
The Importance of the Research
• In its primary business, Star Health Insurance Company has achieved the top results in the industry over the past two years. To maintain this performance in a competitive context, competent marketing strategy and implementation are required. The goal of this study was to offer managers with information and guidance to help them make the best brand decisions in order to meet the company's goals. Furthermore, it provides top-level managers and staff with information regarding customers' perceptions of the company's service.
Literature Review
Nevertheless, increasing focus is placed on customer relationship management, which is defined as "a set of corporate approaches that are attentive and controlling customer behavior by managing relationships via meaningful communication in order to improve customer turnover" (Swift, 2000). In these cases, the customer relationship is characterized as a multidimensional construct comprised of four behavioral components: primary customer focus, CRM organization, knowledge management, and technology-based CRM in order to successfully deploy the CRM for boosting customer loyalty (Sadek 2011).
CRM is defined by Kotle r& Keller (2005) as the practice of carefully maintaining specific information on individual customers and all customer "touch points" in order to maximize loyalty. These touch points include any and all occasions when a customer interacts with the Brand, Product, or Service. (Zablah, Ballenger, and Johnnston 2004) proved that there are five points of view for defining CRM by synthesizing the many definitions of CRM proposed by different scholars. The method, strategy, philosophy, ability, and technology are the points of view Parvatiyar & Sheth (2001); Payne & Frow, (2005).
Evolution of CRM
Customer relationship management is not a new idea; in the literature, it is commonly referred to as one-to-one marketing; nonetheless, it is now practicable thanks to advancements in business software technology.
As customers have become more aware of their purchasing power, businesses have had to suffer the consequences of their mistakes in customer interactions. According to (Bose R. 2002), enterprises must listen to their customers in order to maintain their market presence. As a result, businesses realized that adopting customer-centric marketing may help them succeed. Numerous reasons aided CRM's quick development and evolution. One was the development of advanced computer and telecommunications technology, which enabled manufacturers to engage directly with end customers. The expansion of the service economy was another driver. Because services are often generated and supplied at the same time and location, the function of service marketing has been diminished (Berry & Parsurman 1991).
Customer expectations are evolving dynamically as a result of new technology and the increasing availability of superior product features and services. Consumers are less ready to make trade-offs or concessions in product and service quality. In the environment of ever-changing customer expectations, cooperative and collaborative relationships with consumers appear to be the most sensible strategy to keep track of and correctly influence their shifting expectations (Sharma, 2016).
Meskerem (2015) investigated the influence of relationship marketing on customer loyalty in Commercial Bank of Ethiopia, and her findings revealed that relationship marketing is connected to customer loyalty in Commercial Bank of Ethiopia. Mobayyeni et al. (2016) evaluated the impact of an internet relationship marketing approach on customer happiness and trust, with the internet service quality of Saman Bank branches in Tabriz acting as a moderator. According to the findings, online relationship marketing has a good and significant influence on consumer happiness and trust.
Sayed (2011) researched the association between effective customer relationships and brand equity enhancement in the Melli Bank banking business in West Azerbaijan. The findings revealed that in the banking business, there is a considerable positive association between good customer relationships and the promotion of brand equity and its components (brand awareness, brand image, perceived quality, and brand loyalty). Siyafsaokak et al. (2015) investigated the impact of links between brand value characteristics and brand briefness on customer responses to the banking sector. The findings revealed that the connection between brand awareness and perceived quality had a positive and direct influence.
According to Sanchez Garcia et al. (2007), trust and dedication are the most important components in determining communication quality. According to Garbarino and Johnson (2009) and Smith (1998), the quality of a connection is built via satisfaction, trust, and commitment.
In a research named "The Connection between Customer Relationship Management and Commitment and Loyalty to the Brand," Andy Fred, Lynn Tello, and Aydyka (2016) discovered that CRM strategy aids in consumer commitment and loyalty to the company. Chacha (2016) discovered that a long-term relationship with consumers leads to customer retention and loyalty in research titled "Customer Relationship Marketing and its Effect on Customer Retention: A Case Study on Commercial Banks in Tanzania Oliver, (1999); Öztaysi et al. (2011).
Research Methodology
Objectives: General Objectives
• To evaluate the impact of customer relationship management on brand loyalty at Star Health Insurance.
Specific Objectives
• To investigate the influence of trust on brand loyalty.
• To investigate the impact of commitment on brand loyalty.
• To investigate the impact of communication on brand loyalty.
• To investigate the effect of consumer satisfaction on brand loyalty.
Hypothesis of the Study
H1: There is significant positive relationship between trust and brand loyalty.
H2: There is significant positive relationship between commitment and brand loyalty.
H3: There is significant relationship between communication and brand loyalty.
H4: There is significant positive relationship between satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Research Design
Study is descriptive and exploratory in nature
Sample Size
A total of 110 customers from the Pune branch were included in the group sampled for this study. In order to conserve resources, the researcher made the assumption that customers would be easily accessible.
Sampling and Sampling Technique
Non-probability convenient random sampling was utilized in the study as a sample method. Inherently, convenience sampling is a non-probability sample technique.
Primary Data
Primary data refers to all data obtained primarily for this study utilizing a questioner. A questionnaire technique with a five-point Likert Scale will be used to obtain primary data from customers.
Secondary Data
As a result, this secondary data will be gathered from annual reports, as well as other printed materials such as proposals and other research papers from the firm. Other data sources include books, papers, and journals that are directly related to this topic.
Data Collection Methodology
This study's input was gathered through the use of questioning (survey) and interview methodologies, therefore both quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed. As a result, respondents were given questionnaires to indicate their level of agreement or disagreement with the indicated claims.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Response Rate
The surveys were physically given to Star Health Insurance Pune subscribers. With a 95% response rate assumed, 150 questionnaires were circulated, however only 110 were correctly filled and useable, resulting in a 73.33% response rate Figures 1-4.
Respondents Profile
The demographic profiles of the respondents are compiled and provided in this section.
Interpretation - According to the preceding data, the majority of respondents are male, accounting for 77.3% of all respondents.
Interpretation - The age group of responders is shown in the table 4 and pie chart 2 above. A large proportion of responders (45.5%) are between the ages of below 30. The remaining age groups are under 31 to 40 and over 40, with 33.6% and 20.9%, respectively. As a result, the bulk of responses are from the ages of below 30.
| Table 4 Age of Respondents | |||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Below 30 | 50 | 45.5 | 45.5 | 45.5 |
| 31-40 | 37 | 33.6 | 33.6 | 79.1 | |
| Above 40 | 23 | 20.9 | 20.9 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 110 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
Respondents' Marital Status
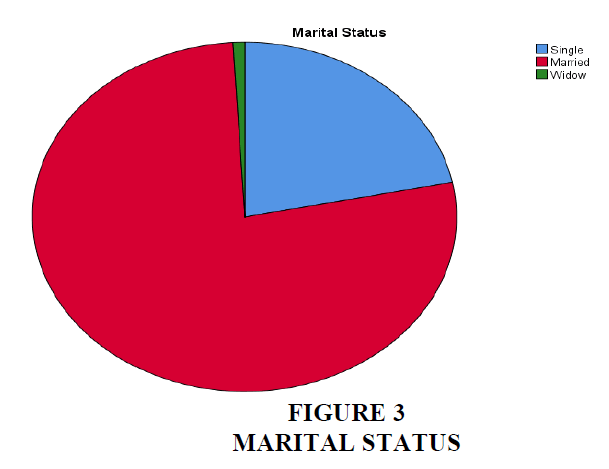
Interpretation - According to the Table 5 and pie chart 3, which details respondents' marital status, married people make up the majority of the company's customers (77.3%), followed by single people (21.8%). Widows receive a 0.9% share of the remaining respondents. The majority of responders are married people.
| Table 5 Marital Status | |||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Single | 24 | 21.8 | 21.8 | 21.8 |
| Married | 85 | 77.3 | 77.3 | 99.1 | |
| Widow | 1 | .9 | .9 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 110 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
Education Level
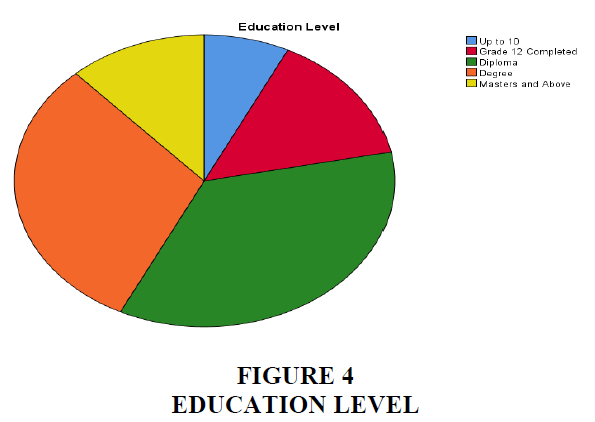
Interpretation - According to the Table 6 and Figure 4, the key to operating any business with a basic and/or moderate degree of expertise and entering into any commercial arrangement is education. As a result, the company's customers' educational levels at the Diploma, Masters, and above levels have been evaluated and presented as follows. With a valid percent of 35.5%, diploma holders make up the majority of Star Health Insurance SHIC's customers.
| Table 6 Education Level | |||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Up to 10 | 8 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 |
| Grade 12 Completed | 16 | 14.5 | 14.5 | 21.8 | |
| Diploma | 39 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 57.3 | |
| Degree | 34 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 88.2 | |
| Masters and Above | 13 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 110 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
Reliability
Table 7 represents Reliability test Cronbach's Alpha is applied on 21 scaled items to understand reliability value of 110 samples, Cronbach's Alpha value is .910, it show items has excellent internal consistency hence items are excellent to have further research study.
| Table 7 Reliability Statistics | ||
| Cronbach's Alpha | Cronbach's Alpha Based on Standardized Items | N of Items |
| 0.910 | 0.912 | 21 |
Hypothesis Testing: Regression
To solve the research issues, four hypotheses were developed for this study. As a result, regression analysis was performed to examine the effect of the independent factors (trust, commitment, communication, and customer satisfaction) on the dependent variable (Brand Loyalty).
Table 8 represents there is 89.6% impact of Brand Loyalty on all four variables of study
| Table 8 Model Summary | ||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
| 1 | .947a | .896 | .893 | .51507 |
Table 9 represents Analysis of One way Anova in this tried to understand the relationship between Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication and Brand Loyalty of SHICO, hence it accepts alternate hypothesis is accepted associated with Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication with 0.000 level of significance.
| Table 9 Anovaa | ||||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 241.198 | 4 | 60.300 | 227.289 | .000b |
| Residual | 27.856 | 105 | .265 | |||
| Total | 269.055 | 109 | ||||
b. Predictors: (Constant), Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication
Table 10 represents Regression analysis and understanding the Coefficients seeks relationship between Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication and Brand Loyalty of SHICO Swaminathan, (2004).
| Table 10 Coefficientsa | ||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | -.090 | .129 | -.696 | .488 | |
| Trust | .807 | .060 | .861 | 13.390 | .000 | |
| Commitment | .134 | .062 | .125 | 2.159 | .033 | |
| Communication | -.654 | .055 | -.742 | -11.911 | .000 | |
| Customer Satisfaction | .740 | .058 | .700 | 12.784 | .000 | |
Hence when applied Multiple regression analysis then it is fount that Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication is having impact on Brand Loyalty of SHICO with respective level of significance 0.000, 0.033, 0.000, 0.000So that following alternate all hypothesis are accepted
H5: There is significant positive relationship between trust and brand loyalty.
H6: There is significant positive relationship between commitment and brand loyalty.
H7: There is significant relationship between communication and brand loyalty.
H8: There is significant positive relationship between satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Findings
It concludes and summarizes the major findings of the study. It also discusses the implication of the present study, new idea embodied, limitations, and the scope for further research. As the study has examined the dimensions of CRM and its impact on brand loyalty in Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd.
This study shows that CRM strategy and customer loyalty are strongly related to retention. Instead of depending only on its resources, CRM must always be modified to achieve customer satisfaction.In turn, corporate administrators will implement new CRM protocols for the practical usage, contact and documentation of customer data. Such instructions must be combined with specific CRM targets and monitored by the relevant agency.The definition of the CRM company describes the steps to explain concrete results. Therefore, all consumers must provide their personal information to support workers with smooth and efficient processes as clearly as possible.Managers must also establish strategies and consistent design points for the development and maintenance of consumer acquisitions. They should also create a supervisory regulation system that allows them to closely track the achievement of customer association objectives across all customer contact points and strategies.
This study shows that CRM strategy and customer loyalty are strongly related to retention. Instead of depending only on its resources, CRM must always be modified to achieve customer satisfaction.In turn, corporate administrators will implement new CRM protocols for the practical usage, contact and documentation of customer data. Such instructions must be combined with specific CRM targets and monitored by the relevant agency. The definition of the CRM company describes the steps to explain concrete results. Therefore, all consumers must provide their personal information to support workers with smooth and efficient processes as clearly as possible.Managers must also establish strategies and consistent design points for the development and maintenance of consumer acquisitions. They should also create a supervisory regulation system that allows them to closely track the achievement of customer association objectives across all customer contact points and strategies.
1) Demographic study interrelates the company's customers' educational levels at the Diploma, Masters, and above levels have been evaluated and presented as follows. With a valid percent of 35.5%, diploma holders make up the majority of Star Health Insurance SHIC's customers.
2) Major findings of the study shows that there is a positive relationship between trust and brand loyalty, commitment and brand loyalty, communication and brand loyalty and satisfaction and brand loyalty.
3) Customer relationship management must be modified to achieve the trust so as the customer satisfaction. Hence it accepts alternate hypothesis is accepted associated with Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, and Communication with 0.000 level of significance. After applying multiple regression analysis from table 10 it is fount that Customer Satisfaction, Trust, Commitment, Communication is having a powerful impact on Brand Loyalty.
4) The effect of the independent factors (trust, commitment, communication, and customer satisfaction) on the dependent variable (Brand Loyalty) which represents there is 89.6% impact of Brand Loyalty on all four variables of study.
5) CRM should is one of the high octane strategy and not just an application of management. Customer satisfaction has emerged as a very influential factor to gain the brand loyalty.
Recommendation
Star Health and Allied Insurance Co Ltd must use customer relationship management as a strategic tool and include in the strategic plan which may contribute a great success to the company. Employee training and customer feedback in intervals can allow company to bring new strategies which can have a positive impact on brand loyalty in future years. Better communications and trust will create happy customers.
Discussion and Conclusion
The result shows that trust, commitment, communication leads to customer satisfaction hence it has a positive impact on Brand loyalty. All above factors to be interlaced and concluded that customer relationship management had an impact on brand loyalty. Trust, commitment and communication all the factors are essential and for customer satisfaction. Study has concluded the positive impact on Brand loyalty. So company needs to focus on how customers can be more satisfied which can affect the overall CRM. As Customer relationship management plays crucial role and a better way to build up a long term relationship which leads into Brand loyalty. This can be used further a strategy to create close relationship with customers in business value chain for mutual benefit, which proactively solve the problems aroused in the business and to enhance brand loyalty of the company. Research has shown that happy & satisfied customers can improve company’s success with a trust, commitment and better communication with their valued customers.
References
Buttle, F., & Maklan, S. (2019) Customer relationship management: concepts and technologies. Routledge.
Chang & Chungiang (2004). The causes and consequences of relationship quality in online commerce. Journal of Marketing Research 17, 460-469.
Couldwell, C. (1998). A war for data day. Computing, 64-6.
Hamdallah & Evelyn Assabil (1996). Customer Relationship Management Techniques at Hotels in Ghana's Ashanti Region, 20-29.
Kotler & Gary Armstrong, (10th Edition) (2004). Marketing fundamentals. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
Kotler (2005). Marketing mix the firm's range of marketing instruments, 8-10.
Kotler, P. (2009). Marketing management. Pearson Education India.
Ndubisi, N. O., & Wah, C. K. (2005). The roots of relationship marketing and consumer happiness are subjected to a factorial and discriminant analysis. International Journal of Bank Marketing 542-557.
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of marketing, 63(4_suppl1), 33-44.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Öztaysi, B., Sezgin, S., & Fahri Özok, A. (2011). A measurement tool for customer relationship management processes Industrial Management & Data Systems, 111(6), 943-960.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Parvatiyar & T.N. Sheth (2001). "Emerging Practice, Process, and Discipline in Customer Relationship Management." 3, 1-8, Journal of Economic and Social Research.
Payne, A., & Frow, P. (2005). A strategic framework for customer relationship management Journal of marketing, 69(4), 167-176.
Sayed H. (2011). Customer relationship management and its impact on marketing performance. International Journal of Business and Social Science 235.
Sharma, R.K. (2016). An empirical inquiry on measuring customer perceived service quality for life insurance services.
Swaminathan, S. (2004) Customer relationship management (CRM): its aspects and impact on customer outcomes. Personal Selling & Sales Management, 20, 250-276.
Received: 25-Mar-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14661; Editor assigned: 27-Mar-2024, PreQC No. AMSJ-24-14661(PQ); Reviewed: 29-May-2024, QC No. AMSJ-24-14661; Revised: 26-Jun-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14661(R); Published: 28-Aug-2024