Research Article: 2022 Vol: 25 Issue: 6S
The Theoretical Rooting Of Human Resource Development, Kaizen Methodology, and Sustainable Performance
Maysoon Ahmad Abu Jassar, The World Islamic Sciences and Education University
Mohammed Mufaddy Al-Kasasbeh, The World Islamic Sciences and Education University
Citation Information: Jassar, M.A.A., & Al-Kasasbeh, M.M. (2022). The theoretical rooting of human resource development, kaizen methodology, and sustainable performance. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 25(S6), 1-10.
Keywords
Human Resource Development, Kaizen Methodology, Sustainable Performance
Abstract
Kaizen methodology is based on the perfection and improvement of work, as well as continuous change. It ensures that human resource development preparedness is based on integrated and continuous practices, as well as readiness for effective, stable, and productive human potential at organizations for current and future action.
It raises awareness for the organizations by providing employees with more skills and knowledge and ensures systematic administrative methods to monitor and judge the relative value of the per capita income.
Kaizen technique and self-control are crucial and feasible administrative tools that allow for the identification of activities and actions that are not beneficial to the processes of accomplishing the organization's goals and sustaining performance.
Introduction
Human resource development's major goal is to help the organization achieve its vision and mission by increasing capacity and integrating the organizations and employees' goals and interests (Abu Al-Hajjaj, 2010). The significance of knowledge of human resource development as an integrated and comprehensive process based on initiating behavioral change and knowledge linked to work via managerial practices and rendering support to organizations and employees in order to attain maximum potential and make the most of integration, effectiveness, most advantageous deployment of resources and interdependence to ensure the capability to continuously withstand difficulties (Matthews et al., 2008). The notion of sustainable performance is personified in renewal, continuity, most advantageous conservation and utilization of resources, and enhancing the quality of human life (Al-Shammari, 2020).
Kaizen is a method of continuous improvement based on the principle of "doing one's best with what you've got." (Al-Darmaki & Al-Dhafari, 2017).
Working better and more professionally and committing to self-discipline at the individual, group, organization, and society as a whole is one of the ingredients for the success of sustainable organizations in order to bring about comprehensive development, and the advancement of necessary services and infrastructure, and other ways and mechanisms.
Dimensions of Human Resource Development
Regardless of how preoccupied they are with getting their current job done, employees are thinking about their professional futures, and they are aware that continuing their education will lead to increased responsibility and advancement. They responded by providing opportunities for employees to gain practical experience in developing the skills, they need when they are needed. The importance of careful planning for employees, building their skills, and carefully selecting planning methods is considered suitable for development, with a focus on educational and training programs to help employees build human resources and reach sustainability (Noe et al., 2016).
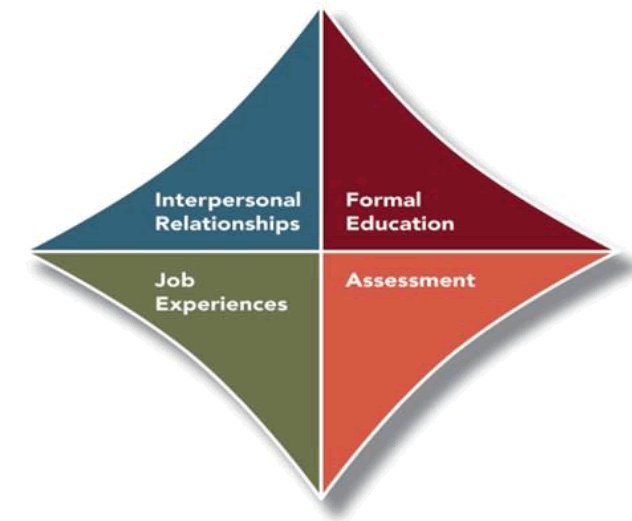
Figure (1) illustrates the dimensions of human resource development.
Figure 1: Dimensions of Human Resource Development
Source: Noe, Raymond A, Hollen beck, John R, Gerhrty, Barry, & Wright, Patrick M. (2016). Fundamentals of human resource management (6th ed.). Mc Graw-Hill.
Formal Education
The organization uses a variety of formal education programs to train employees both inside and outside of the workplace, including workshops designed specifically for company employees as well as short-term courses offered by universities, academic programs, and consultants, to help workers gain a degree in a science-related field of expertise (Hamad & Globe, 2020).
Assessment
Assessment is a critical component of developing high-performance organizations, which are defined as the most competitive, best, and fastest organizations through the use of a reliable, fair, and straightforward wide system for managing human resource performance; and through staff development and training. (Dessler, 2014).
Assessment is one of the strategies by which employees are developed. It involves obtaining information about their communication methods, abilities, and behavior from a variety of sources such as colleagues, clients, managers, and supervisors; and drawing inferences as feedback on them. The organization selects employees with administrative skills to evaluate managers' strengths and weaknesses and then uses the assessment to identify managers who are qualified for executive positions at a higher level, in addition to monitoring team members' weaknesses, strengths, and communication styles. The assessment provides an opportunity for employees' development by facilitating their development process and sharing the evaluation's findings with employees with the goal of identifying and addressing employees' weaknesses and reinforcing their strengths through attendance at professional training courses to enhance their skills and gain new job experiences, in addition to developing plans for self-development to improve employees' performance. As one of the developmental evaluation tools for performance, personality tests are used to evaluate employees' personality types and skills, communication patterns, employee behavior, and methods of working with others (Noe et al., 2016).
Job Experiences
When it comes to increasing productivity, Aziz & Al-Dalawi (2018) feel that education institutions and programs that ensure an improvement in productivity for working individuals are the best sources of acquiring new skills and information.
In addition to what is directly relevant to the job, employment experience comprises a variety of negative and good interactions, tasks, and practical attitudes. Human resources development is necessary when employees lack the experience and skills required to perform their jobs effectively, necessitating the development of new skills and the acquisition of more advanced knowledge, which must then be applied with a level of mastery and dedication that is distinct from the rest of the workforce. It is possible to develop human resources through experience by recognizing the most important work-related activities such as conflict resolution, customer service, data analysis and ending a failed process and congeniality with supervisors as prior events, which affected the managerial methods of employees because of what they learned from these experiences (Noe et al., 2016).
Interpersonal Relationships
By influencing and creating functional patterns marked by innovation, support, flexibility, and the promotion of work integration, human resource development plays a critical role in supporting sustainable performance and professional life.
For example, according to Hynes (2012), interpersonal relationships play an important role in promoting employee participation and achieving organizational objectives. The organization rewards those employees who work hard and positively influence their coworkers through the evaluation of the best performance, including moral incentives such as promotion, which enhances interaction and communication.
A variety of measures are taken by the company to facilitate communication between workers at various managerial levels who are capable of adjusting their behavior in response to changes in their emotional stability and who have a strong desire to succeed and the strength to improve their experiences through communication and interaction with colleagues who have practical experience gained through practice (Noe et al., 2016).
Performance Sustainability
As a sign of an organization's goodwill toward the environment, its resources, and its stakeholders, it considers the interests of its consumers, employees, local community, and future generations.
With the goal of reinforcing the capitalist ecosystem, it is the best system for allocating and utilizing resources among employees, customers, and shareholders in order to achieve the maximum profitability and maximum productivity of workers as well as values as an enhancing factor for continuity and survival. According to objective and scientific principles, it is a way to identify the areas in the company that must be addressed and given attention in order to achieve positive results and future planning, as well as the degree of need for resources (Qarah & Qasimi, 2020).
We've reached an era of sustainable performance where governments and society are increasingly demanding that organizations adapt the way they conduct their operations; Amid the current financial and economic crisis organizations have realized the importance of including them in sustainable performance indicators and adopting sustainable performance practices, in addition to the increased awareness of organizations that their sustainability depends on the economic and social conditions in which they operate and that the growth of financial instruments in the long term is critical for their continuity.
Kaizen methodology
While the validity of Kaizen technique is based on the pursuit of perfection and improvement in performance, it is also true that any physical action that is not motivated by an internal sense of motivation will fail.
By establishing standards and attaining them in personal, social, and work environments, Imai (1986) describes kaizen as a continual improvement process that helps small things operate better. Everyone, both managers and employees alike, is a part of Kaizen's continual development. The word kaizen is made up of two parts: Kai, which means change, and zen, which means better. Employees' superiority, adaptability, and flexibility are a result of this fundamental truth, which is why the company is able to quickly react to changing market and consumer needs.
Kaizen, according to Barraza & Davila (2014) can be defined as a collection of personal values that help you to grow as a person, which assumes that our way of life needs to be constantly and unstoppably improved.
The Theoretical Rooting of Human Resource Development, Kaizen Methodology, and Sustainable Performance
Human resource development and sustainable performance:
Developing human resource is seen as an expression of the organization's aspirations to improve performance and productivity in the short and long term. It also contributes to its achievement and practices that encourage employees to improve themselves by thinking and taking initiative and it gives them the power to provide maximum production capacity that is characterized by quality and distinction (Matthews et al., 2008, 42).
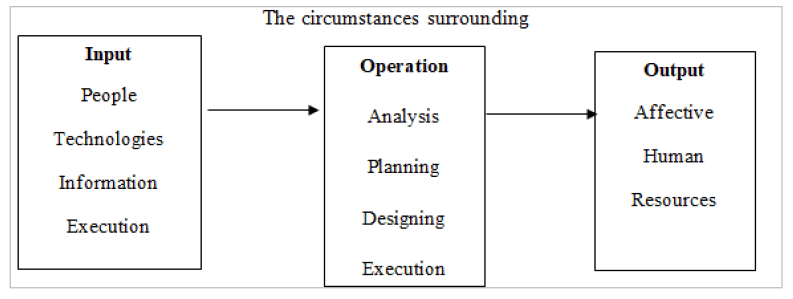
In the view of Al-Asnawi and Al-Sayed,. (2020, 280) the human resource development system begins with a study of the organization's goals, strategies, and policies, as well as an analysis of the role of the human resource to achieve the goals and the extent to which the strategies and policies are consistent with each other; There must be a renewed awareness and clear understanding of the organization's human resources in order to implement an integrated strategy for developing their capabilities and expertise. The open system model is the intellectual framework that underpins human resource development processes, in addition to behavioral orientations and intellectual characteristics that support or contradict the activation of activities and requirements for success and the achievement of expected and sustainable performance and the objectives of the organization, as demonstrated in Figure (2).
Figure 2: The Open System Model of the Intellectual Framework for Development Processes
Source: Al-Asnawi, Jalal Farouk, & Al-Sayed, Ibrahim. (2020). Creative management. House of Science and Faith for Publishing and Distribution.
There is a possibility of affecting efficiency and effectiveness by using improvement approaches to system operations and improving the level of required outputs and emphasizing its evaluation criteria, as well as clarifying the importance of self-balancing the elements of inputs, processes and outputs, when considering human resource development as an open system (Al-Asnawi & Al-Sayed, 2020).
In many firms, positive human resource development methods have been proved to boost employee performance, which in turn improves the overall performance of the organization. Perhaps this belief stems from the fact that an organization's success and growth are heavily dependent on its employees, making it critical to elevate human resource development from a tactical to a strategic position, where it can play an important role in the overall growth of the organization. Instead of simply developing them in the traditional manner, it is critical that the process be transformed into one that provides more advanced development services that contribute to skill development in an effective manner, increasing the effectiveness of human resource development by adding to the overall strategy of the organization (Rajashekara & Biradar, 2017).
It is important to remember that progress and long-term success go hand in hand. To put it another way, sustainable performance is the result of the continuous improvement in environmental and social performance of a business unit; and that it is a result of the administrative practices of the organization in the areas of sustainability in it.
Staniskis & Arbaciauskas (2009) also point out that sustainable performance is influenced by the philosophy of sustainable development, which aims at both economic and social prosperity. According to Al-Mashhadani & Al-Nuaimi (2017) quality, training and education are essential for long-term success. Because the human element and its energies play such an important role in sustainable performance processes, they are of paramount relevance. In order for a company to achieve sustainable performance, it must first have the right processes and materials in place. This is ultimately reflected in the level of human resource development. Economic development in developed countries.
Nations and organizations are enriched by the abundance of human capital. Physical capital and natural resources, despite their importance and necessity, do not always benefit in the long term if the human element is not well trained and prepared; This is because human is able to use these resources and harness them in production processes to obtain maximum satisfaction and meet the needs of societies in order to achieve prosperity.
It has been said by Abboud (2008) that human resource development program is focused on creating and sustaining long-term jobs in a green economy that respects the environment, people rights, and the economy. Green entrepreneurship is today's new economic dynamic.
To continue to see the environment as a secondary function of the economy, Brandler (2015) argues that it must be considered a fundamental system and the economy as a subordinate one. To begin, it is important to note that economic rearrangement affects all levels and sectors of society and the economy as a whole. It also affects the entire supply chain, from farm to fork to consumer. Because the goal is to ensure that nothing is wasted and that everything is seen as a source of worth, the distribution method should not place an undue strain on ecosystems or limit consumer values to the destruction of products. Human resources must be developed at the same pace as the company's performance to ensure long-term viability. The deteriorated institution and the surrounding environment can be restored via careful management of the existing resources and human and environmental capabilities.
People can use the available energy to their fullest potential to achieve freedom and happiness when the social dimension of sustainable performance is considered, as demonstrated by Leignel, et al., (2019). Human resource development for sustainable performance is defined by Rabie (2015) by focusing on the social component because it is the dimension that makes growth a means of social cohesion and development. Through economic and sociological analyses, Kodden (2020) has developed a new concept of unemployment that considers the possibility that work and unemployment could be altered by the idea of employment that includes growth and training. Studies show that the high rates of development and progress in developing countries have reduced the formality of employment, until it is noticed that there are different types of unemployment such as voluntary, administrative and technical employment and employment of certificate holders. It is also noted that new concepts of work have emerged because technology has advanced, including telecommuting and rotating shifts, amongst other things in other words, social mobility, distribution equality, public involvement, cultural diversity, and institution sustainability are all components of the social system.
Based on the above, it is concluded that human resource development is directly related to sustainable performance for the following reasons:
1- Sustainable performance does not simplify the environmental system for ease of control, but rather considers the development aspect in conjunction with environmental preservation.
2- Long-term performance is dependent on the coordination and integration of human resource development policies and initiatives.
3- Sustainable performance is concerned with the time dimension, which is the foundation of long-term development, which is dependent on analyzing present possibilities, which is always planned.
4- Human resource development is concerned with employees' performance both inside and outside of enterprises.
5- Human resource development aims to improve employees' quality of life through long-term performance goals that emphasize on the interactions between the organization's activities, society, and the environment.
6- Human resource development leads to long-term economic growth while protecting natural capital and achieving basic development goals.
7- Human resource development contributes to the unification of stakeholders' efforts through strategic partnerships between organizations in the public and private sectors on agreed-upon understandings, programs, and initiatives that contribute to the improvement of the economic and social reality of all current and future societal groups.
8- Human resource development and sustainable performance emphasize the significance of examining economic, political, social, and administrative circumstances with a more broad and predictable vision.
Human Resource Development and Kaizen Methodology
In organizations, employees are viewed as the driving force behind success because of their intellectual and motivational prowess. The success of a company is directly linked to the performance of its workforce. Employees' quality and style of work, as well as their persistent search for continuous improvement, motivates the organization to attain greatness and head towards the future (Jubairaat, 2019).
The relationship between human resources and Kaizen methodology could be summarized as follows:
1. The fundamental tenet of kaizen is that the employee possesses perceptual capabilities and that nothing happens free except that with hard work and constant education, the employee can achieve better and sustainable performance.
2. Continuous improvement is a competitive advantage; it is achieved through a relentless pursuit of continuous improvement, by completing the smallest tasks well, by obtaining the greatest levels of performance, and by pursuing the objective of zero faults.
3. Continuous improvement of operations is a critical component of professional ethics and achieving peak performance, with continuous improvement focusing on resolving issues and ensuring the happiness of all consumers, including staff.
4. People are most closely associated with processes that are undergoing improvement because they identify the improvements that need to be made.
5. The essence of continuous improvement is the constant improvement of all aspects involved in the conversion of inputs to outputs. Work practices, employee attitudes, and performance all benefit from improvement.
6. Everything and anything that an employee accomplishes is evaluated on a continuous basis (Jiblac, 2021).
7. Employees must understand that their jobs are contingent upon the organization's survival and continuity, which is contingent upon the quality of services provided to all stakeholders in order to ensure the organization's long-term viability, as well as the impact on job satisfaction and employee financial security.
8. Because the organization's life and continuation are contingent on the quality, offered, overall quality management must progress in lockstep with institutional development (Deming, & Hagstrom, 2009/1960).
9. Kaizen empowers people by demonstrating their cognitive competence while accomplishing their duties (Al-Bouhi et al., 2018).
10. Achieving excellence through employees requires a shift in perspective, and given that working with employees is done through them, organizations must develop the skills and capabilities of their human resources, as any progress is contingent on continuing education and training.
11. One of the most effective administrative techniques is performance measurement, which offers information about an employee's performance.
12. Participation in information that helps to performance improvement, in addition to participation in information by all employees, which entails accountability for company results. (Al-Aoushen, 2017).
Kaizen methodology and sustainable performance
Kaizen is one of the most important methods of interest to the organization that wants to raise the level of performance and its sustainability; therefore, kaizen is one of the most important methods of interest to the organization. It is focusing on customer needs; kaizen emphasizes improving all services for target communities, as well as improving procedures and changing the work environment and enhancing communication and communication in organizations, as well as reducing losses as much as possible with the goal of anticipating the effects of deviation in operations and correcting errors and eliminating their causes (Al-Bouhi, 2018). Kaizen is characterized by the great driving forces of loyalty and belonging among workers and the forces of feeling a sense of job and social security and the strength of decisions that are taken from the base. This is in addition to the power of leadership that guides, develops and works to find radical solutions for issues, as well as the power of cooperation, which crystallizes in the quality of output and sustained performance. Aoushen (2017). According to Sultan & Mezher (2019); Jassim (2018), the most essential recommendations include trying to document all information connected to improvement in order to improve it and create this information when necessary, which adds to boosting performance levels. For this reason, it is imperative that the groundwork is laid before a continuous improvement process can begin, so that the targeted populations may receive high-quality services, while all stakeholders are satisfied. Kollenburg & Wouters (2018) concluded that continuous improvement supports the acceleration of improvements in labor productivity and that it is necessary to deal with social changes in order to achieve further improvement, which in turn can lead to an increase in labor productivity at the overall level, and that Kaizen leads to sustainable results. According to Yang et al., (2016), continuous improvement practices require frontline employees to constantly make changes and solve problems, and highlight the operational improvement skills of frontline employees, which enhances their creativity and leads to the development of and development of their skills, thus improving performance and its sustainability.
Conclusion
As a critical and effective administrative tool, Kaizen technique aids in the identification of activities and actions that do not contribute to the achievement of the organization's goals. Improved processes result from the discovery of these activities, which promotes long-term performance sustainability (including social, environmental, and economic performance). The organizations benefit greatly from kaizen methodology, which promotes long-term performance sustainability. Therefore, the Kaizen methodology could play the moderating role between human resource development and performance sustainability.
References
Abu Al-Hajjaj, Y. (2010). The arts and skills of human resource management and development. Arab Book House for Publishing.
Al-Asnawi, J.F., & Al-Sayed, I. (2020). Creative management. House of Science and Faith for Publishing and Distribution.
Al-Bouhi, R.A.A., & Al-Masry, I.J. (2018). Quality in education. House of science and faith for publication and distribution.
Al-Darmaki, A., & Al-Dhafari, H. (2017). Total quality management, human resources and institutional performance. Qandeel Printing, Publishing and Distribution.
Al-Mashhadani, B.N., & Al-Nuaimi, N.S.H. (2017). Evaluating the sustainable performance of economic units using the balanced score card, an intervention in the Fourth Scientific Conference on the Orientalization of the future prospects for the economy of the Kurdistan Region of Iraq in the light of current changes. Nowruz University: Iraq.
Al- Mawajdah, A. (2019). The role of information technology in supporting sustainable performance in electronic business organizations: an applied study in electronic business organizations in Jordan. Unpublished Master's Thesis, Middle East University: Amman.
Al-Shammari, M.S. (2020). Sustainability within the framework of development: a future vision for sustainable development in Iraq. Kufa Studies Center Journal. 57, 1-35.
Al-Aoushen, M.b.S. (2017). Kaizen the Japanese methodology for continuous improvement the Japanese experience in management and performance improvement secrets of Japanese management. King Fahd National Library during publication.
Aziz, G.A.K., & Al Dalawi, I.M. (2018). Knowledge management and human resource development in the General Secretariat of the Central Library. Journal of the College of Education for Girls. 29 (1), 1727-1746.
Barraza, M.F.S., & Dávila, J.Á.M. (2014). Assessing the design, management and improvement of Kaizen projects in local governments. Business Process Management Journal 20(3).
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed At
Abboud, N. (2008). The Green Dimension of Business: Environmental Responsibility for Businessmen. Dar Al-Warraq for Publishing and Distribution.
Brandler, S., & Roman, C.P. (2015). Group work: Skills and strategies for effective interventions. Routledge.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed At
Deming, E., & Hagstrom, R. (2009). Total quality management: foundations, principles and applications. (Translated by Hind Rushdie). Kunouz for publishing and distribution. (1960).
Dessler, G. (2014). Human Resource Management. (Translated by: Muhammad Abdul-Mutaal and Abdul-Mohsen Judeh). Dar Al-Marikh Publishing House. (Original publication year 2007).
Hamad, E.O., & Globe, N.A. (2020). The importance of training in the development of human resources methods and means: an analytical theoretical study. Literature Journal. 134 (9), 415-428.
Hynes, G.E. (2012). Improving employees’ interpersonal communication competencies: A qualitative study. Business communication quarterly, 75(4), 466-475..
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed At
Imai, M. (1986). Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success. McGraw-Hill Education.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed At
Jiblac, A. (2021). Quality Management. Syrian Virtual University. Creative Commons.
Jassim, A.A.-A. (2018). The role of leadership and pioneering thinking in enhancing the quality of banking service: An exploratory study on a sample of Iraqi private sector bank officials in Najaf Governorate. Kufa Adab Journal, 36, 293-338.
Jubeirat, S. (2019). Human performance in organizations. Dar Osama for Publishing and Distribution.
Kodden, B. (2020). The Art of Sustainable Performance A Model for Recruiting, Selection, and Professional Development. Springer Nature Switzerland.
Kollenburg, T.V., & Wouters, S. (2018). The future of continuous improvement. Conference: European Lean Educators Conference 2018, October 16, 2020.
Leignel, J., Me?nager, E., & Yablonsky, S. (2019). Sustainable enterprise performance: a comprehensive evaluation method. ISTE, Ltd.
Matthews, J.J., Mignson, D., & Surtees, M. (2008). Human Resource Development. (Translation: Ola Ahmed Salah). Cairo:The Arab Nile Group. (The Year of original Publication 2004).
Noe, R.A., Hollen, b.,, John, R., Gerhrty, B., & Wright, P.M. (2016). Fundamentals of human resource management (6th ed.). Mc Graw-Hill.
Qarah, A.H., & Qasimi, K. (2020). The role of the role of human capital in achieving sustainable performance in economic institutions: An applied study on a group of economic institutions. The Wilayat of M'sila. Knowledge Aggregates Journal, 6(1), 181-196.
Rabie, M. (2015). Sustainable Community Development: A Theory of Economic Development and Sustainable Development. Al-Yazuri Scientific Publishing and Distribution House.
Rajashekara, G.R., & Biradar, B.S. (2017). Human resource development in Indian software technology libraries: A study with special reference to library professionals training and development facilities. The Clarion, 6(1), 44-50.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Staniskis, J.K., & Arbaciauskas, V. (2009). Sustainability Performance Indicators for Industrial Enterprise Management. Environmental Research, Engineering and Management, 2(48), 42-50.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Sultan, A.F., & Mezher, A.A. (2019). The impact and relationship of continuous improvement and creativity management in raising the level of performance - an analytical study of a sample of private banks in the province of Qadisiyah. Rafidain Development Journal, (13).
Yang, Y., Lee, P.K.C., & Cheng, T.C.E. (2016). Continuous improvement competence, employee creativity, and new service development performance: A frontline employee perspective. T.C.E. International Journal of Production Economics, 171, 275-288.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Received: 04-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. JMIDS-22-11688; Editor assigned: 06- Apr -2022, PreQC No. JMIDS-22-11688 (PQ); Reviewed: 10-Apr-2022; QC No. JMIDS-22-11688; Revised: 18-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. JMIDS-22-11688 (R); Published: 30-Apr-2022