Research Article: 2018 Vol: 22 Issue: 1S
The Role of Financial Sustainability to Reduce the Financial Crisis, Through the Interactive Role of the Strategic Scenario: An Analytical Study in the Sector of Commercial Banks Listed in the Iraq Stock Exchange
Ammar Nazar Mustafa Al-Dirawi, University of Basrah
Qasim Mohammed Dahash, University of Basrah
Abstract
Iraq is an oil dependent economy, and country 90 percent revenue is coming from the export of oil. The recent volatility in oil prices has adversely affected the economic growth of Iraq. The prime objective of the current study is to explore the impact of financial sustainability on financial crisis. In addition to that, we have also investigated the indirect and direct impact of strategic scenarios such as portfolio diversification strategies on the financial crisis. The financial crisis is measured as the growth in real gross domestic product. Whereas, the financial sustainability is measured as an index of profitability, liquidity, and efficiency, the diversification to loan, non-interest income, and investment are taken as proxies of strategic scenarios. The ordinary least square, and hierarchical regression method is used to achieve the research objectives of the current study. The results of the study have shown a great deal of agreement with the hypothesized result. The financial sustainability has significant positive impact on economic growth of Iraq. Similarly, the concentration to loan, and diversification investment has significant positive impact on economic growth. Where is the diversification non-interest income having significant negative impact on economic growth? The 26 banks out of total listed banks are the final sample of the study. Data of eight years from 2008 to 2017 is taken form the annual reports and world bank data base. The findings of the study will be helpful for the practitioners, researchers and policy makers in understanding the role of financial sustainability and strategic scenarios of banks in fostering the economic growth.
Keywords
Financial Sustainability, Financial Crisis, Economic Growth, Iraq.
Introduction
The subprime crisis is one of the ordeals of latest century and has given many lessons to learn. The revival of global economy was inevitable, but the lessons learned from this crisis are of great importance. One of the lessons learned is trickle-down effect of any burst in a globally integrated financial system, which calls for revolutionary amendments in global financial market regulations. Since the start of 1970s, in its development process, the concept of financial globalization has experienced a real boom which is mainly origin from the massive technological advancement, financial innovation and liberalization and with floating exchange rate system. All these changes are considered under the situation of increasing risk-taking capabilities in the environment of financial market with the increasing severity of financial crisis as well.
The concept of financial crisis has threatened the economic, political and social stability in various region and continue as one of the most significant risk factors. Such type of crisis and level of uncertainties are objecting the present financial system with its limitation and failure. Such limitations are of deep concerned at both national and international level due to the flow of capital from one region to another. Since 1929, when the US stock market has suffered financial losses and shocks, global economy has experienced numerous crisis and collapse in financial terms. The time duration of 1929 is known as the great depression for the development of the economy. Besides, some other financial crisis like shocks tankers from 1973 to 1979, debt crisis in region of Latin America in 1980s, monetary crisis in European financial system from 1992-93, Mexican crisis from 1994-95, Asian financial crisis from 1997-98 and Russian financial crisis of 1998 are very much significant. Additionally, crisis in Brazil from 1998-99, in Turkey, internet bubble and crisis in 2001 named as Argentina crisis and the crisis of sovereign in the Eurozone 2010 are very much significant to discuss. But among all these, the financial crisis in the year 2007, which are initially known as credit crisis are the most severe in nature after the great depression. In US due to instability in financial globalization, various steps have been taken by the government to control the severity of these crisis. The Basel Committee for the supervision of banking firms have also played significant role to reduce the possibility of upcoming of such event. Besides all these measures, one of the most significant measures which need great attention is the reform in international financial system. Such reforms are very much necessary and significant as it can be considered as ethical finance which can be major part of reform which can find its inspiration in Islamic finance.
Financial sustainability is defined as the consistency of firms in generating the positive outcomes that not only covers cost but also accelerate the firm growth. The aftermaths of subprime crisis have revealed the fact that the firms with financial sustainability were least affected from financial crisis (Gofman, 2017). The financial stability of any corporation is seen as the ratio of income to expenditures, which helps in determine the level of cash at firm disposal (Keister, 2018). The financial stability which is dependent upon a sound financial system helps in normalizing any state of crisis.
Iraq has recently through a crisis situation when in 2014 fall to 60 percent in two consecutive years from 2014 to 2106. However, during same time period the financial sector grown sustainably. And through this suitability of banking sector the Iraq has managed to survive from the state of crisis (Allen et al., 2018). Therefore, this study is being carried out on the sample of Iraqi banks in knowing how the sustainability of these banks helps the financial system in avoiding and normalizing the state of crisis. In addition to that it is also interested in knowing that how the strategic scenarios of banks interact this relationship. The Iraqi financial sector is a dominant sector of Iraqi stock exchange.
Literature Review
Financial Sustainability
In a globalized economy, defining and establishing the financial sustainability has become a challenge for organizations of all sizes and types (Haas & Lelyveld, 2014; Claessens & Horen, 2015). The reason why financial sustainability is so important is its impact on the overall financial system (Acemoglu et al., 2015). The aftermath of financial crisis has made it realized to the world that the financial sustainability is a key to avoid and mange such crisis situations (Ocampo, 2018). Sustainable Development (SD) defines as the growth that fulfils the demand of the current population without jeopardizing the propensity of later generations to satisfy their own demands (Hák et al., 2018). SD provides an ethical understanding of three dimensions of sustainability and encourages a company to work towards balancing between economic, environmental and social sectors. SD, after the Rio Summit, became a blueprint for a new approach integrating environmental and social issues in company operations and working towards the triple bottom line (Elkington, 1998).
The new sustainability approach receives attention from most countries and helps translate proposed rules and regulations into action. These rules and regulations establish indicators to determine the sustainability concept to facilitate its application in countries generally and companies specifically. Countries increasingly have adopted SD as the main development strategy to enhance both environmental and social performance to increase economic growth. SD contributes to CS; the ability of managers to set out the main issues they should focus on; environmental, social and economic performance, and provides general social goals for both companies and governments to work towards with respect to sustainability performance (Wilson, 2003).
The growth of literature debate about SD during the last two decades has shifted from the general aspect of protecting the environment to corporate strategy towards corporate sustainability. Therefore, the literature has brought new definitions of corporate sustainability; evolving from the original definition of SD. Salzmann, Ionescu-Somers, and Steger (2005) defined corporate sustainability in line of a smart and profit-making business counterpart of social and environmental causes, created by the company’s main and alternative activities. Meanwhile, Deloitte, and Touche (1992) defined corporate sustainability from a different perspective. They defined it as “adoption of business strategies and activities that meet the needs of companies and its stakeholders today while protecting, sustaining and strengthening human and natural resources that will be necessary in the future”. Often, definitions of corporate sustainability have insisted upon including social and environmental issues to a company’s activities and concern for stakeholders needs by integrating these issues into business strategies. Financial performance is a terminology that mostly recurs in the domain of business, no matter what the industry is. In retrospect, a company’s achievement was evaluated on its financial performance, regardless of other factors that might have pursued in the quest for market dominance. Waddock and Graves (1997) defined performance by stating that corporate performance was the ability of a company to reach its goals by using resources effectively and also comprised the output of management operational strategy and the implementation of that strategy into the company plan leading to performance measurement. In line with Waddock and Graves (1997), the Carton and Hofer (2006) defined company performance as “a measure of the change of the financial state of an organization, or the financial outcomes that result from management decisions and the execution of those decisions by members of the organization”.
Financial Crisis
The concept of financial crisis can be defined as the situation when there is break in overall financial system which can increase the severity of moral hazards in overall financial market (Lins et al., 2017; Colander et al., 2014). Under such situation, financial markets are not able to transfer the funds in an effective way from agent to fund borrower. Such crisis also sharps the contraction of various economic activities and hurts the working of financial markets as explained by (Mishkin, 2017).Various formats are identified in existing body of literature for financial crisis. However, three major types of crisis are very much significant to discuss here. These are the sudden top crisis which are also known as capital account or in the form of balance of payment, debt crisis and finally the banking crisis as well. these types can be classified from various dimensions but they can overlap in these types as explained by (Claessens et al., 2014; Basheer et al., 2018). Financial crisis has various and severe effects in different regions of the globe. In their study, (Reinhart & Rogoff, 2009) have summarized the financial crisis in four major types which are as follow.
Monetary Crisis
Such type of crisis is normally known as the currency level crisis and occurs at the time when speculative attack on a currency and it leads to immediate drop in the value of that currency (Aguiar et al., 2015). Due to such crisis central banks must face a lot because it must increase the level of foreign reserves with the large amount of interest margin to protect the domestic currency.
Banking Crisis
Banking crisis are also known as the financial panic which refers to that situation in which the market loses the confidence from the investors like in the banks and various agents start to withdraw their deposit (Marshall et al., 2018). The core motivation to secure their deposit and to place it into some secure place or another institution. Such crises are due to low quality of loans which becomes worthless at the time of crisis in the market.
Debt Crisis
The portion of debt crisis occurs when the borrowers in the market place stop paying their debt obligation either in the form of principle or interest. Such types of loans are linked to private sector or public or both which has sovereign potential risks (Acharya et al., 2018; Becker et al., 2017).
Financial Market Crisis
Such type of crises is also known are bubble burst and come into existence as a result of strong speculative operations which has some ultimate consequences in the form of low asset valuation and loss of confidence from the various lending officer (Goh et al., 2015). Such crisis causes a slowdown the working of real economic sector.
The global financial crisis simply means the worth economics’ situation in the world, caused by the mortgage market credit in US in 2007-2008. In other meaning, the global financial crisis is a difficult business environment to succeed in since potential consumers tend to reduce their purchases of goods and services until the economic situation improves (Avery & Brevoort, 2015). Reid et al. (2017) states, the financial engineering instruments in the form of subprime mortgage were causing the financial crisis in the US. Subprime mortgage or letter of credit housing (mortgage) low interest in 2001-2005 led to the increasing demand for home (boom in the housing market).
Subprime mortgage is a letter of credit that can be traded by mortgage giver (mortgage lenders) to another party (collateral debt swap) with interest specific, such as commercial banks. Bank then sells as a portfolio the mortgage to the investment as a bank. The liquidity is needed that make the bank sells the house confiscated with low prices. The inability of the banks to make a profit will disturb the optimal payment of subprime mortgage derivatives that also will disturb the confidence of investors (Basheer, 2014). Finally, in order to not undermine the liquidity badly, investors are comprised of the large company branches which having the small branches around the world. However, lately, some companies’ anticipation eventually went bankrupt because the sale of derivatives does not meet the liquidity needs of this situation shake the US stock market and Europe until finally in Asia (Reid et al., 2017; Javed & Basheer, 2017).
The Causes of Financial Crises
There are various circumstances and causes of these stated financial crises. Some of these factors causing a situation of crisis are linked to microeconomic and some are of macro in nature. in the discussion of interim report of 1998, various factors have been discussed which create a situation of financial crisis. For instance, it is explained in the report that financial instability is due to macroeconomic instability (Basheer et al., 2019). Besides various fiscal and monetary policies cause a reactivation of loan and significant amount of debts, which increase the level of investment in nonproductive sector. Such investment can increase the price of the assets and monetary policies must play their role for the correction of price. Such factors finally slow down the economic activity and decline in the real value of collateral and increasing level of receivable ratios. In addition, from the turbulence of financial sector of an expansion of credit, capital influence from abroad with the collapse of financial market can cause of financial crisis. Financial sector fragility is reflected through lax credit policies and inequity in the balance sheet of banks. However, the component of capital flow is strongly related to the epidemic of various financial crisis. At the time of crisis, short term credits are riskier and have great portion of withdrawal when the cost of such transaction is low. But the cost of foreign investment is very much high during the time of such crisis. Considering the portfolio theory, the diversification to non interest activities, diversification to investment and concentration to lending are used as strategic scenarios.
Methodology
Data source
Data of four fiscal years (2010-2017) is collected from annual reports of the banks. Initially, the entire listed bank in Iraqi Stock Exchange was the target sample. However, later firms with missing data and liability financing more than the total asset value or negative value of equity are excluded from the analysis and the final sample is comprises of 26 banks with 208 firm’s year observations.
Methodology
To achieve the objective the current study has adopted the panel data methodology. The panel data methodology advocates the polling of observation into smaller units of cross-sectional nature over many intervals of time or time periods. One of the advantages of this method is that it provides more detailed, comprehensive authentic findings which are not possible with other simple analysis such as time series or cross-sections. The general form of panel model is as follow:
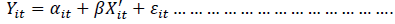 (1)
(1)
In our case, as our sample is spread of 6 years from 2012to 2017 and the total number of firms is 100, therefore
i=1 ,……………………., 26, t =1 ,…………………, 8
The error vector is given by:
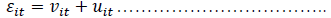 (2)
(2)
Where, it v the individual is the effect of each of the industrial companies and it u is the error which assumes a normal distribution.
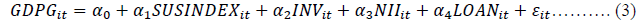
Hierarchical multiple regression model is a minor extension form of classical linear multiple regression (Hair et al., 2006). Hierarchical multiple regressions allow another variable between independent the ent and dependent variable to depend on the level of another independent variable. (i.e., the moderator) (Bisbe & Otley, 2004). It is an appropriate method for detecting the effects of moderating variables. This method improves the attempts of ordinary linear regression estimation by adding a third variable in the model.
The moderator hypothesis is accepted or rejected on the basis if outcome the of the interacting term is significant or insignificant. Baron and Kenny (1986) also highlighted that there may be direct as significant ant relationship between path a and path b with outcome variable, but these paths are conically not relevant to test the moderating effect. The linear model of moderated relationship defines by Hair et al. (2006) is as follow:
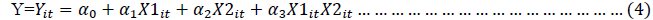
Where,
α0= Intercept
α1X1= Linear effect of X1
α2X2 = Linear effect of X2
α3X1 X2= Moderating effect of X2 on X1
Thus, following Baron and Kenny (1986) and Hair et al. (2006) the equations Moderating the moderating impact of dividend payout in the relationship between cash flow from operation, capital expenditures, earnings before interest and tax and cash flow moderating model for this study are as follows:
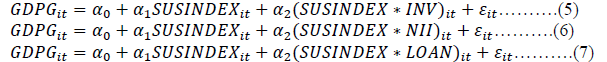
Where, for each company (i) and each year (t); GDPG is a proxy of economic growth and alternatively of financial crisis.SUSINDEX is sustaiabity index developed by the factor analysis of three key factors namely profitibity, efficency, and liquidity, INV is the ratio of investmnet to total asset , NII, is the ratio of non intrest income to total assets, and LOAN is the ratio of total advances to total aset.
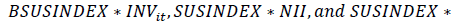
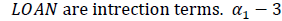 are coefficients of concerned variables and εit
is random
error term for the ith firm of time t.
are coefficients of concerned variables and εit
is random
error term for the ith firm of time t.
Pre-test Specifications
To decide between the panel data fixed effect random effect or pooled OLS we have used are-test specification tool known as Breusch and Pegan Lagrangian Multiplier (LM) test. This is a test which is used for the purpose of selecting the most fitting model between random effect and pooled OLS. The results of the test var (u)=0, Chi2(01)=0.00 and Probability>Chi2=1.00. The results of Breusch and Pegan Lagrangian Multiplier (LM) test shows that, the probability value of Breusch and Pegan lagrangian multiplier test (1.0000) is not significant. This leads to non-rejection of the null hypothesis, which means that there is no entity effect in the model. Thus, the test perfectly suggests that pooled OLS is the most efficient and appropriate.
Results And Discussion
Correlation Analysis
The result of the correlation analysis is discussed in Table 1. The results indicate that the board size and Audit committee independence are positively related to audit committee budget. Whereas, the competency of the audit committee and board independence are in negative relation to audit budget.
| Table 1 Correlation Analysis |
|||||
| GDPG | SUSINDEX | INV | NII | LOAN | |
| GDPG | 1 | ||||
| SUSINDEX | 0.5379* | 1 | |||
| INV | -0.3242** | 0.1353* | 1 | ||
| NII | -0.2027 | -0.2322 | 0.186 | 1 | |
| LOAN | 0.3210** | 0.2359** | -0.0117* | -0.2914* | 1 |
Direct Results
The prime objective of the current study is to investigate the impact of financial sustainability on the financial crisis. In addition to that we are also interested in knowing the impact of strategic scenarios such as diversification to non-interest income, investments and concentration on loan on economic growth of Iraq. The finding of the study is discussed in Table 2.
| Table 2 OLS Regression Results |
|
| Dependent Variable:GDOG | (3) |
| SUSINDEX | 0.723*** |
| (0.139) | |
| INV | 0.732*** |
| (0.121) | |
| NII | -0.437** |
| (0.052) | |
| LOAN | 0.527** |
| (0.137) | |
| R2 | 0.812 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.824 |
| F-statistic | 20.247 |
| Prob. (F–Statistics) | 0.000 |
| S.E of Regression. | 0.099 |
| Number of firms | 26 |
The result of the study show that the financial sustainability has significant positive impact on the economic growth, similarly, the diversification to investment and concentration to loan both are in positive and significant relationship with economic growth. However, diversification to non-interest income appeared in a negative relationship with economic growth and relationship is significant
Results of the Hierarchical Multiple Regression Model
The results of the hierarchical Multiple Regression Model is shown in Table 3. The direct results have shown consistency with the finding of direct results presented in Table 2. The dividend payout appears as a strong moderator in all models.
| Table 3 Results Of The Hierarchical Multiple Regression Model |
|||
| Dependent Variable:GDPG | (5) | (6) | (7) |
| SUSINDEX | 0.241*** | ||
| (0.029) | |||
| INV | 0.342*** | ||
| (0.012) | |||
| NII | -0.351** | ||
| (0.023) | |||
| LOAN | |||
| BSUSINDEX*INV | 0.388** | ||
| (0.126) | |||
| SUSINDEX * NII | -0.676* | ||
| (0.177) | |||
| SUSINDEX * LOAN | 0.258*** | ||
| (0.018) | |||
| Number of firms | 26 | 26 | 26 |
Note: *, **, *** denote statistical significance the 0.10%, 0.05% and 0.01% level respectively.
The direct results hierarchical multiple regression model of the current study has shown a great deal of agreement with the OLS results. The indirect results of BSUSINDEX*INV, and SUSINDEX*LOAN are positive and significant. Whereas the relationship between SUSINDEX*NII, and GDPG is negative and significant. The results of results hierarchical Multiple Regression Model has shown a great deal of agreement with our hypothesized results.
CONCLUSION
Financial stability provides the necessary level of competitiveness of the corporation, by creating an uninterrupted process of production and sale of finished products. Financial stability determines the reliability of the corporation, displays the safety margin, which becomes for its protection during periods of instability of the world market. According to the definition of the United Nations, the development of society is sustainable, that is, it can be sustained over a long period of time if it can meet the needs of present generations without damaging the opportunities that remain for future generations to meet their needs. Sustainability performance is an integrated achievement of social, environmental and economic performance measures (Schaltegger & Burritt, 2006; Schaltegger & Wagner, 2006). Indeed, the economic performance basically excludes from the presents study as the challenge is to consider the social and environmental issues in company operations All trials in measuring and facilitating sustainability issues that would result in heightened business achievement should observe the link between a company’s sustainability performance as well as its financial performance. There is no doubt that nonmarket issues such as social and environmental issues can have a substantial impact on a company’s economic performance.
Few years ago, the global financial crisis had been started from the United States and some developed countries. It has also impacted the financial crisis in some Asian countries. Alasrag (2010) said that the crisis since July 2007 can attract by the liquidity crisis because the United States lost their confidence in mortgage credit market. Usmani (2010) also stated the same things if the financial crisis in 2007-2008 can be stop the whole economic around the world rapidly. The global financial crisis gave bad impact not only for non-bank but also for the financial in bank. The global financial crisis in the United States affected some countries like Russia, Denmark, United Kingdom, France, and Germany, then also in Asia Pacific countries like China, Taiwan, Singapore, Japan, and Australia. This situation automatically impacted Indonesian investment industries in finance institution in the United State. Financial industry or non-banking which were allocate their assets for getting income by capital share or obligation in foreign finance instrument, for examples City group, UBS, Merril Lynch, American International Group (AIG), etc., (Reid et al., 2017). He also stated that, the direct impacts of the global financial crisis are the decrease of the liquidation and the increase of the commodity prices.
The result of the study show that the financial sustainability has significant positive impact on the economic growth, similarly, the diversification to investment and concentration to loan both are in positive and significant relationship with economic growth. However, diversification to non-interest income appeared in a negative relationship with economic growth and relationship is significant. The direct results hierarchical multiple regression model of the current study has shown a great deal of agreement with the OLS results. The indirect results of BSUSINDEX*INV, and SUSINDEX*LOAN are positive and significant. Whereas the relationship between SUSINDEX*NII, and GDPG is negative and significant. The results of results hierarchical Multiple Regression Model has shown a great deal of agreement with our hypothesized results. Thus, we can conclude that in the current conditions of global market development, the role of financial stability of multinational companies is increasing. The key to winning a significant market share is cash and financial leverage to influence fluctuations in the global market. That is why it is already impossible to count on stability without having the opportunity to participate in global finance. Only world-class financial systems have the opportunity to either approach, for some time, financial stability, or apply all the levers to destabilize it in their favor.
References
- Acemoglu, D., Ozdaglar, A., & Tahbaz-Salehi, A. (2015). Systemic risk and stability in financial networks.American Economic Review,105(2), 564-608.
- Acharya, V.V., Eisert, T., Eufinger, C., & Hirsch, C. (2018). Real effects of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe: Evidence from syndicated loans.The Review of Financial Studies,31(8), 2855-2896.
- Aguiar, M., Amador, M., Farhi, E., & Gopinath, G. (2015). Coordination and crisis in monetary unions.The Quarterly Journal of Economics,130(4), 1727-1779.
- Alasrag, H. (2010). Enhance the competitiveness of the Arab SMEs in the knowledge economy.
- Allen, F., Carletti, E., Goldstein, I., & Leonello, A. (2018). Government guarantees and financial stability.Journal of Economic Theory,177, 518-557.
- Avery, R.B., & Brevoort, K.P. (2015). The subprime crisis: Is government housing policy to blame?Review of Economics and Statistics,97(2), 352-363.
- Baron, R.M., & Kenny, D.A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,51(6), 1173.
- Basheer, M.F. (2014). Impact of corporate governance on corporate cash holdings: An empirical study of firms in manufacturing industry of Pakistan.International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies,7(4), 1371.
- Basheer, M.F., KhorramI, A.A.A., & Hassan, S.G. (2018). Patronage factors of islamic banking system in pakistan.Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal,22, 1-9.
- Basheer, M., Ahmad, A., & Hassan, S. (2019). Impact of economic and financial factors on tax revenue: Evidence from the Middle East countries.Accounting,5(2), 53-60.
- Becker, B., & Ivashina, V. (2017). Financial repression in the European sovereign debt crisis.Review of Finance,22(1), 83-115.
- Bisbe, J., & Otley, D. (2004). The effects of the interactive use of management control systems on product innovation.Accounting, Organizations and Society,29(8), 709-737.
- Carton, R.B., & Hofer, C.W. (2006).Measuring organizational performance: Metrics for entrepreneurship and strategic management research. Edward Elgar Publishing.
- Claessens, S., & Van Horen, N. (2015). The impact of the global financial crisis on banking globalization.IMF Economic Review,63(4), 868-918.
- Claessens, S., Kose, M.A., & Terrones, M.E. (2014). Understanding financial cycles. Macroprudentialism. VoxEU eBook, CEPR, London.
- Colander, D., Follmer, H., Haas, A., Goldberg, M., Juselius, K., Kirman, A., & Sloth, B. (2014). The financial crisis and the systemic failure of academic economics.The Economics of Economists: Institutional Setting, Individual Incentives, and Future Prospects,21(2-3), 344.
- De Haas, R., & Van Lelyveld, I. (2014). Multinational banks and the global financial crisis: Weathering the perfect storm? Journal of Money, Credit and Banking,46(1), 333-364.
- Elkington, J. (1998). Partnerships from cannibals with forks: The triple bottom line of 21st‐century business.Environmental Quality Management,8(1), 37-51.
- Gofman, M. (2017). Efficiency and stability of a financial architecture with too-interconnected-to-fail institutions.Journal of Financial Economics,124(1), 113-146.
- Goh, B.W., Li, D., Ng, J., & Yong, K.O. (2015). Market pricing of banks’ fair value assets reported under SFAS 157 since the 2008 financial crisis.Journal of Accounting and Public Policy,34(2), 129-145.
- Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., & Tatham, R.L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis, (seventh edition). Pearson.
- Hák, T., Janoušková, S., Moldan, B., & Dahl, A.L. (2018). Closing the sustainability gap: 30 years after “Our Common Future”, society lacks meaningful stories and relevant indicators to make the right decisions and build public support.Ecological Indicators,87, 193-195.
- International Institute for Sustainable Development, Deloitte & Touche, & Business Council for Sustainable Development (1992).Business strategy for sustainable development: leadership and accountability for the'90s. International Institute for Sustainable Development.
- Javed, M.A., & Basheer, M.F. (2017). Impact of external factors on bank profitability.EPRA International Journal of Research and Development,2(5), 1-11.
- Keister, T. (2018). The interplay between liquidity regulation, monetary policy implementation and financial stability.Global Finance Journal.
- Lins, K.V., Servaes, H., & Tamayo, A. (2017). Social capital, trust, and firm performance: The value of corporate social responsibility during the financial crisis.The Journal of Finance,72(4), 1785-1824.
- Marshall, N., Dawley, S., Pike, A., Pollard, J., & Coombes, M. (2018). An evolutionary perspective on the British banking crisis.Journal of Economic Geography.
- Mishkin, F.S. (2017). Rethinking monetary policy after the crisis.Journal of International Money and Finance,73, 252-274.
- Ocampo, J.A. (2018). International asymmetries and the design of the International financial system. InCritical Issues in International Financial Reform(pp. 45-74). Routledge.
- Reid, C.K., Bocian, D., Li, W., & Quercia, R.G. (2017). Revisiting the subprime crisis: The dual mortgage market and mortgage defaults by race and ethnicity.Journal of Urban Affairs,39(4), 469-487.
- Reinhart, C.M., & Rogoff, K.S. (2014). Recovery from financial crises: Evidence from 100 episodes.American Economic Review,104(5), 50-55.
- Salzmann, O., Ionescu-Somers, A., & Steger, U. (2005). The business case for corporate sustainability: Literature review and research options.European Management Journal,23(1), 27-36.
- Schaltegger, S., & Wagner, M. (2006). Integrative management of sustainability performance, measurement and reporting.International Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Performance Evaluation,3(1), 1-19.
- Schaltegger, S., Bennett, M., & Burritt, R. (Eds.). (2006).Sustainability accounting and reporting(Vol. 21). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Usmani, M. T. (2010). Present financial crisis, causes and remedies from Islamic perspective. InPost-crisis reforms, Davos forum, source: www. muftitaqiusmani. com.
- Waddock, S.A., & Graves, S.B. (1997). The corporate social performance-financial performance link.Strategic Management Journal,18(4), 303-319.
- Wilson, M. (2003). Corporate sustainability: What is it and where does it come from.Ivey Business Journal,67(6), 1-5.