Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 3
The Relationship between Human Resource Management Strategies and Regulator Restraint: Evidence from Iraq
Dijla Mahdi Mahmoud, Middle Technical University
Abstract
The purpose of the research is to identify the type of relationship between resource management strategies and Regulatory restraint, Wasit textile industries was selected for textile industries and leather as a society to the research for being one of the organizations that suffer from the problem of the increasing number of employees and intentional sample research sample was (011) questioners. Distributed (35) of them among the managers and department heads and (65) employees in the company’ s departments. The research adopted five strategies for human resources management (job analysis and design, staffing and recruitment strategy, strategy performance evaluation, Training strategy human resource planning strategy) and the research adopted three strategies of regulatory restraint strategies (employees reduction strategy, work redesign strategy, systematic strategies). The research found a set of conclusions: a large surplus worker and the company’s need to redesign jobs. The research also reached a series of recommendations notably reengineering coefficient in accordance with modern environmental pledges to restore the company's products to the market and meet the market competition of the goods covered and the advancement of the Iraqi industry to occupy a competitive position in the Iraqi environment at least.
Keywords
Human Resource Management Strategies, Job Analysis and Design, Staffing and Recruitment Strategy, Regulatory Restraint
Introduction
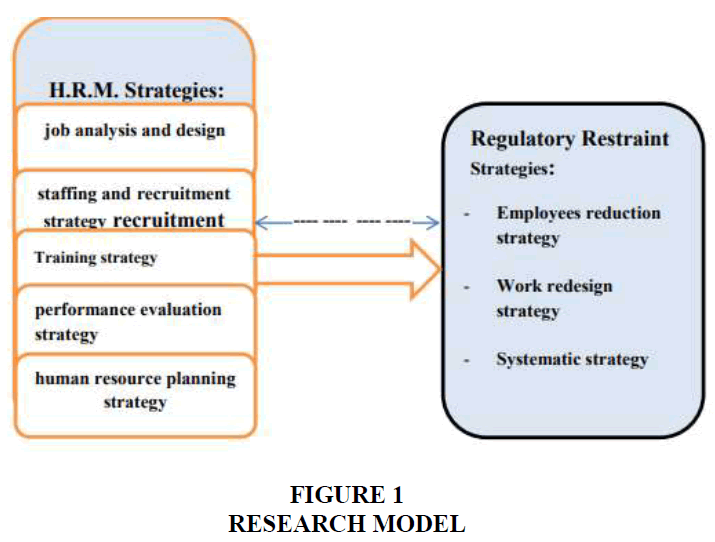
Usually business organizations seeking excellence and lasting success in its performance, in order to maintain a competitive position with other organizations seeking the same goal. In order to achieve such deliberate strategies organizations contribute to achieving the goals required rate under rapid changes today, and therefore the ability of any organization on competition lies in its success in attracting qualified persons capable of creativity and innovation, and maintain them and train them and triggered what They can achieve a competitive advantage for the organization. Studies have confirmed the importance of the role of human resources management strategies to achieve it. Therefore, the problem that embraced two variables: human resource management strategies included five indicators: (Job analysis and design strategy (Appendix Table 1A), staffing and recruitment strategy (Appendix Table 1B), training strategy human resource planning (Appendix Table 1C) performance evaluation strategy (Appendix Table 1D) and strategic human resources planning (Appendix Table 1E) as the independent variable. Either the dependent variable is regulatory restraint strategies have included three indicators (employees reduction strategy, work redesign strategy, systematic strategies).
This basis the research hypotheses were formulated. The research was divided into four chapters: the first axis: research methodology the second episode: theoretical framework section III: practical side topic IV: conclusions and recommendations (staff reduction strategy and redesign strategy and systemic strategy).
And because Iraqi organizations they have become in recent years reside under the environment of market dumping case and the absence of customs protection, companies are no longer able to cope with this new reality and became the Iraqi organization live amid sagging problem and disguised unemployment, to appointing workers according to the political and social conditions. Also, production processes and work system no longer keep pace with what's going on in the evolving global and regional companies’ years of Iraq for many years according to the political and social conditions. According to the kind of problems the company in question operates and produces according to the indicators and benchmarks are not based on scientific bases in human resource management. This leads to the problem of sagging career and disguised unemployment and low productivity of the company and stop the treatment for several years in the presence of competing products at lowest prices and highest quality. Based on the above the research problem formulated the question: What is the nature of the relationship between human resource management strategies (Appendix 1) and regulatory restraint strategies (Appendix 2)?
The result of this study will show the nature of the relationship between HRMS and regulatory restraint in the most important industrial Iraqi company.
The Research Importance
1. Reduce the aggravation of problems and administrative difficulties for the advancement of Iraqi industry to keep pace with the competitive market.
2. Organizational strategy has become the leading choice for many companies to reduce direct costs and increase efficiency, productivity, profitability and competitiveness.
3. Try to find ways that will contribute to fuelling the company's motivations and emphasize the importance of human resources management strategies and their role in leading the company toward success.
Literature Review and Previous Studies
Human resources definition concept: Are the causative agent of added value to organizations and sustainability source for competitive advantage (Al-Saedy, 2017). People working in organizations with a view to achieving organizational strategies and business design and production of goods and services (Braton & Gold, 2003). So, we can define it as human energies that can achieve success and that contribute to achieving efficiency and effectiveness of the organization.
Human Resources Management Concept
Is responsible for developing the organization’s policies and procedures and directions of personnel and other administrative duties (Decenzo & Robbins, 1999) and the department that works to achieve the goals of individual and organizational goals and the right investment for human resources and to achieve the best use of their potential and achieve their goals efficiently and effectively.
Human Resources Management Strategies
The process of developing a strategy for human resources management functions in accordance with the organization’s strategy and opportunities and external threats and strengths and weaknesses in order to increase the organization's ability to achieve success and stay in a business environment (Al-Saedy, 2017). It was the strategic approach to human resources management which concerns all regulatory activities affecting the behavior of individuals and helps the organization to achieve its goals (Inyang, 2010). Also (Armstrong, 2009) refers It was the method for making decisions about the intentions and plans of the organization in the form of policies and programmers on human resources. Based on the above, we could define the strategy of human resource as the selection of the appropriate strategies for human resources management that is compatible with the organization’s strategy to increase the organization's ability to achieve the competitive superiority.
The human resources management strategy, programs and policies and existing systems in the workplace, affecting the performance of the individual and the community drastically reflected on the performance of the organization and includes the following practices: hiring, training, development, performance evaluation, compensation (Braton & Gold, 2003). Al-Saedy (2017) had pointed that the most common strategies in the regulatory are:
1. Job analysis and design strategy: Job Analysis & Design Strategy is the process of obtaining detailed information about these works and job design strategy is making the tasks assumed collected with others in a particular job (supporter). Job analysis process provides information relevant to each of the human resource management and organization and the workers themselves is so important (Al-Saedy, 2017):
a) Planning human resources needs of the organization.
b) Job design and define their functions.
c) The choice of the most efficient wage and salary rates evaluate the effective performance develop training programs with the performing standards for each function.
2. Staffing and recruitment strategy: A process that the organization get on appropriate human resources in quantity and quality, so this strategy in the light of the process of job analysis and human resources planning based on determining the number of jobs, knowledge, qualifications and skills required. Al-Hety (2003) indicates that the hiring process is one of the functions carried out by the department of human resources efficiently and effectively and successfully. The performance success determines the course activities in the organization whether marketing or financial and research productivity.
3. The training strategy: Is the starting point for training activities within organizations and to link closely with the strategic plans of the organization it is a prerequisite to be training should be more effective and achieve the goals of the organization (Al-Saedy, 2017). The training also contributes to maintaining the competitive position of the organization and improves productivity using training programmers to help achieve high levels of production flexibility and high quality (Harris et al., 2003).
4. Performance strategy: It is formal organizational process implemented by comparing actual performance of individual or team with the expected performance according to the substantive or personal items which makes it a key role in human resources management and development. As the organization’s performance evaluation strategy not working alone it is a part of an integrated system of care to identify successful value-added utilization of human resources (Braton & Gold, 2003). Performance evaluation steps include the following: Determined performance standards, measuring performance, comparing actual performance standards, discussion of evaluation findings with personnel affirmative action and corrective action (Al- Saedy, 2017).
5. Human resources planning strategy: Study human resources based on the main activities, structures and what is the nature of the future tasks and functions foreseen what movement of workers, as well as the actions of the external labor market, uncontrolled new professions some of them are new and some of them do not and this needs to conduct rational forecasting to be rational in predicting to interview the professions with the skills they must possess.
Regulatory Restraint Strategies
The literature refers to several concepts of the regulatory restraint we review:
1. Organizational process of reducing the size of the organization and human resources in order to reduce operational costs and improve the competitive position of the organization to adapt to the surrounding environment (Chen & Wang, 2012).
2. A management strategy to reduce the area and volume of work to improve financial performance (Gomez et al., 2005).
3. Organizational restraint is the strategy by with the organization can improve its efficiency and effectiveness and improve its competitive position.
4. Objectives and importance of organizational restraint: Organizational restraint determined: Gandolf (2005) maximizing leadership, reducing bureaucracy, accelerate decision-better communication, reducing costs, increased productivity.
5. Forms of regulatory restraint: Gandolf (2005) that can distinguish between three main forms of regulatory restraint permanent: Permanent reduction, to encourage the employees of the organization as a whole or in part, reduction due to actual or future events.
Regulatory Restraint Strategies
Agree on the strategies that take place through the regulatory process by three strategies: strategies to reduce the resources and strategy to redesign jobs and systemic strategy (Gandolf, 2005):
1. Human resources reduction strategy: Focus on reducing the number of employees in the organization through a range of policies such as: Natural decline: (to retirement, death, resignation) and using this policy when conditions rapid reduction organization and the great work force. Early retirement: for ages near retirement age and without financial cost and of this own volition. Reduction of wages for a certain period until improvement is usually preceded by a policy of attrition or early retirement incentives.
Redistributing or transportation and training occupations need organization or transfer to other departments or branches of the organization. Reduction by the board: strong and take rates this method to enjoy working with diverse skills and high capacities (Evans et al., 2005). Demobilization: taking into account the laws and trade systems and link the demobilization plan needs.
2. Work redesign strategy: Work redesign strategy reducing the normal work or activity by reducing the number of administrative levels and unnecessary sections, and includes the following policies (Al-Saedy, 2017):
a) Cancel unnecessary jobs. Incorporate units and task forces-redesign of jobs reduced working hours.
b) Close a branch or exclude some production lines.
3. Regular strategy (overall): A lifestyle and an ongoing process as the basis for continuous improvement and require the following policies: organizational culture change. The participation of workers in steps. Continuous improvement and development of processes and activities (Gandolf, 2005; Wilkinson, 2004). Change the attitudes and values of employees. Change from the bottom up: from the base to the lower to upper management levels. Formatting between external parties such as customers and suppliers and laws and legislation and government here we note that previous strategies are not alternative strategies, but the organization could apply together.
Strategy are identified according to the organization’s activities, and noted that the regular strategy used for future results while reducing human resources aims to achieve immediate results, either redesign work be medium-term results and non-governmental organizations to find out where you can make improvements.
Implement Regulatory Restraint
Job done process requires five steps: (Cummings & Worly, 2001):
1. Clarify the organization’s strategy.
2. Evaluation phase.
3. Implement of size organization.
4. Behavioral implications for human resources.
5. Implementation of the process of renewal and growth of the organization.
In spite of what we have mentioned, previous studies and literature have dealt with different views on the relationship and impact of HRMS on the performance of organizations and companies surveyed, including the study Koon (2015) the impact of strategic human resource management on employee outcomes in private and public limited companies in Malaysia: This study investigates the interaction effects of two business strategies and human resources management practices (recruitment and selection and tanning, development, compensation and performance management, employment security and work life balance) on employee outcomes . Show that HRM practices mediate the interaction of business strategy and HRM practices mediate the interaction of business strategy and employee outcomes. Furthermore, the effects of business strategy and HRM practices strategy and HRM Practices on employee outcomes in public limited companies are only slightly different from the ones implemented in private limited companies. Specifically, the moderation analysis shows invariance between differentiation strategy and variance in low cost strategy. But Renata & Lucia (2016) try to find the relationship between human resource management and organizational performance. The results study showed a positive relationship between HRM practices and performance, in line with the literature. However, we point out some methodological issue such as the difficulty of isolating the HR practices from its context, the failure to consider the temporality of this relationship, and the comparison between from difference industries.
Another tries from Al Adresi & Darun (2017): Determining relationship between Strategic human resource management practices and organizational commitment. The main purpose of the article is investigating the relationship between SHRM. And organizational commitment and subsequently testing based on data from 52 oil and gas companies in Libya. The findings using structural equation modeling revealed that employees are more committed to the organization when they get best SHRM. It was shown that the employees are more concerned of their job security and dynamic working environment. Employees with the help of organizational support will be able to contribute to enhance organizational commitment.
Ahmed (2018) researched: Impact of Human Resource Management Strategies in the development of Organizational Innovation (OI). This study concerned the nature of direct and indirect relationship between SHRM and development organizational innovation in commercial banks. To achieve this, a sample 335 managers were selected at the main centers and all branches in the capital of commercial banks on Al Yamen by using a survey list to gather the necessary data. The results showed a direct correlation between the practice HRMS and development OI.
This study is concerned with finding the relationship between human resources management strategies on regulatory restraint strategies. The need of the Iraqi organization to review the reality of its human resources, which is suffering from increasing the size of its staff due to the current conditions in Iraq. Research hypotheses clarify the practical side of research.
Research Hypothesis and Model
Based on finding from the literature review, the following research hypothesis:
H1: There is significant correlation for job analysis and design on regulatory restraint strategies.
H2: There is significant correlation for staffing and recruitment strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H3: There is significant correlation for evaluating performance strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H4: There is significant correlation for Training strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H5: There is significant correlation for human resource planning strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H6: There is significant effect for job analysis and design on regulatory restraint strategies.
H7: There is significant effect for staffing and recruitment strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H8: There is significant effect for evaluating performance strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H9: There is significant effect for training strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
H10: There is significant effect for human resource planning strategy on regulatory restraint strategies.
To test the above hypotheses, the following research model was adopted (Figure 1):
Data Collection Methods
1. The theoretical side: To obtain data and information the research adopted the available foreign and Arab sources and the internet which related to the subject of the research.
2. The practical side: A questionnaire was designed in three parts, the first measures to demographic of describing the sample, while the second includes the variables of SHRM. The third was devoted to the measurement of the variables of regulatory restraint. For the validity of the study tool, nine professors and business expert were presented to receive proposals and make necessary adjustments. A total of (100) hand-held questionnaire distributed to selected sample of (35) of them to senior administrations, head departments and (65) to employees in various departments, the entire questionnaire were retuned. On research variables using (Likert) measurement to answer the questionnaire.
3. Statistical analysis: indicators were used to describe the characteristics of the research:
a) Cronbach Alpha coefficient (Cronbach’s Alpha): this procedure is used to measure the internal consistency of the study to verify the genuineness of performance.
b) Suitable paragraph with the scale by scale item rest correlation.
4. Methods of descriptive statistics (Descriptive Statistics): number of statistical indicators is used to describe the characteristics of the study sample vocabulary:
a) Frequency distribution of questionnaire statement and through which being recognized on the general direction of the sample for each variable separately.
b) The Mean and which identify the average respondents answer on each paragraph.
5. Evidentiary statistical techniques and program Amos (Inferential Statistics):
Use the following methods and tests are used to verify the study hypotheses and tested:
a) Amos effect size charts.
b) Path analysis choose optimal model CP.
c) Analysis of correlation coefficients.
Society and the Research Samples
To achieve the goal of the research was selected one Iraqi industrial companies Wasit textile and leather to be a place for research and for being one of the most important industrial companies in southern Iraq and suffering from the problem of increasing personnel. Below Table 1 illustrates the research sample description by, age, education, years of service and job site.
| Table 1 The Distribution of the Research Area According to the Age Location, Qualification and the Length of Service | |||
| Job Position | Number | Person’s Number | Ratio |
| Laboratory Manager | 4 | 4% | |
| Head of Department | 10 | 10% | |
| Official Division | 21 | 21% | |
| Employees in departments | 65 | 65% | |
| Total | 100 | 100% | |
| Age | Number | Person’s Number | |
| 30-21 | 25 | 25% | |
| 40-31 | 34 | 34% | |
| 50-41 | 41 | 41% | |
| Total | 35 | 100% | |
| BA | 22 | 22% | |
| Qualification | Technical Diploma | 50 | 50% |
| High school | 28 | 28% | |
| Total | 100 | 100% | |
| Length of service | 15-5 | 15 | 15% |
| 25-16 | 33 | 33% | |
| 35-26 | 52 | 52% | |
| Total | 100 | 100% | |
Research Methodology
Reliability Test
Test consistency and internal consistency of the scale used in the study
There are several ways to verify the consistency of the measure main including cronbach- Alpha to ensure internal consistency of metrics, have been using cronbach Alpha coefficient (Alpha Cronbach) has been used, which takes values between zero and one, if there is no data in the value of the operand is equal to zero, conversely if there is full data reliability coefficient is equal to 1. That increase the coefficient Alpha cronbach means greater credibility of data from reverse sample results on the study. The decline in the value of (0.60) evidence of reduced internal fortitude (Cooper & Schindler, 2008).
Test the sincerity scale (item test correlation)
A scale measures the interaction of answers within each paragraph of answers and interconnectedness of each paragraph with a measure as a whole and the higher the value of the scale, the greater the validity of the phrase.
The above Table 2 shows that the values of Cronbach Alpha all phrases are greater than 60% these values means a high degree of internal consistency of terms whether for each term individually or all words variable, where the value of Cronbach alpha of 0.83 variable. It is steadily rising and then arguably we rely on answers that variable in achieving the objectives of the study and analyze the results. We also note the value of the correlation of the expressions with the positive value of the value of (0.26) positive response and positive consistency in selection and analysis of vocabulary.
| Table 2 The Results Cronbach-Alpha and Consistency of the Paragraph with the Scale/A: Human Resources Strategies | |||
| S. No | Independent Variables | Cronbach Alpha | Reliability Test |
| 1 | The management makes the job analysis according to changes in the internal and external environment | 0.81 | 0.67 |
| 2 | The management analysis of internal and external environment for the identification of human resources in terms of number and quality, compared with the company's strategic requirements | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| 3 | The management is careful on job design to match the company's competitive strategy. | 0.81 | 0.66 |
| 4 | The management is depending on the performance evaluation results as a basis for modifying the strategic plans for the management of financial resources. | 0.80 | 0.71 |
| 5 | The Management is careful to assign human resources capable of achieving strategic company goals. | 0.82 | 0.53 |
| 6 | The management is kept to set the staffing requirements according to company strategy. | 0.83 | 0.38 |
| 7 | The Management is careful t to identify jobs in light of the process of job analysis and human resources planning | 0.83 | 0.33 |
| 8 | Careful management to identify clear criteria to evaluate and improve the training strategy | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| 9 | The management is reviewing the strategic plan when changes in the internal and external environment. | 0.82 | 0.42 |
| 10 | The management towards training and development strategy to achieve the company mission. | 0.83 | 0.33 |
| 11 | The management is careful management to assess the actual performance against the benchmark of expected performance | 0.82 | 0.49 |
| 12 | The management plans to deal with the projected gap between existing skills of future needs | 0.83 | 0.34 |
| 13 | The management develops plans that correspond to the needs of human resources in accordance with future posts. | 0.82 | 0.48 |
| 14 | Human resources Management needs analysis of the number and type in light of current awareness and future direction of the company. | 0.83 | 0.39 |
| General standard | 0.83 | 0.26 | |
The above Table 3 shows that the values of Cronbach-Alpha: (0.84) for variables. It is high stability and then arguably we rely on answers that variable in achieving the objectives of the study and analyze the results. We also note with words the positive value which reached (0.35). The positive answers and interaction consistency in selection and analysis of vocabulary.
| Table 3 The Results Cronbach-Alpha and Consistency of the Paragraph with the Scale/B: Regulatory Restraint Strategies | |||
| S. No | Supported Variable | Cronbach Alpha | Reliability Test |
| 15 | Management uses natural decline when conditions require a reduction of human resources. | 0.844 | 0.399 |
| 16 | The employees understand working reassign units and other departments when needed | 0.820 | 0.658 |
| 17 | The employees wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. | 0.828 | 0.569 |
| 18 | The employees wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. | 0.826 | 0.599 |
| 19 | The employees wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. | 0.845 | 0.372 |
| 20 | The employees Doesn't mind when personnel assigned to work more than one job in order to move the full performance capabilities of the unused hand and achieve the company's goals. | 0.845 | 0.368 |
| 21 | The employees understand the company closed one of its branches or production lines for compensation paid by the company to employees who are excluded | 0.818 | 0.669 |
| 22 | The employees helped management implementing philosophy of continuous improvement on different elements in the Organization | 0.826 | 0.602 |
| 23 | The management care to improve operations and the reference check with companies carrying out the same activity. | 0.816 | 0.715 |
| 24 | The management is interested in studying the different levels of personnel proposals before making decisions on organizational career. | 0.836 | 0.489 |
| General standard | 0.84 | 0.35 | |
Results
Data Analysis
Human resources strategies: The Table 4 also shows the order of variable for both human resources strategies as soon as by a member of the research sample.
| Table 4 Frequency distribution of respondent’s response to paragraphs human resource m. strategies | ||||||||||||
| No. Variable X | Don’t agree at all | Don’t agree | Agee to some extent | Agree | Agree completely | Total | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 1 | 6 | 6% | 4 | 4% | 11 | 11% | 77 | 77% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 2 | 1 | 1% | 9 | 9% | 13 | 13% | 77 | 77% | - | - | 100 | 100% |
| 3 | - | - | 5 | 5% | 21 | 21% | 73 | 73% | 1 | 1% | 100 | 100% |
| 4 | 1 | 1% | 9 | 9% | 16 | 16% | 67 | 67% | 7 | 7% | 100 | 100% |
| 5 | 2 | 2% | 5 | 5% | 47 | 47% | 42 | 42% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
| 6 | 8 | 8% | 8 | 8% | 69 | 69% | 21 | 21% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 7 | 1 | 1% | 6 | 6% | 58 | 58% | 30 | 30% | 5 | 5% | 100 | 100% |
| 8 | - | - | 6 | 6% | 38 | 38% | 46 | 46% | 10 | 10% | 100 | 100% |
| 9 | 2 | 2% | 8 | 8% | 24 | 24% | 63 | 63% | 3 | 3% | 100 | 100% |
| 10 | - | - | 10 | 10% | 20 | 20% | 64 | 64% | 6 | 6% | 100 | 100% |
| 11 | - | - | 4 | 4% | 27 | 27% | 60 | 60% | 9 | 9% | 100 | 100% |
| 12 | 1 | 1% | 3 | 3% | 28 | 28% | 65 | 65% | 3 | 3% | 100 | 100% |
| 13 | - | - | 1 | 1% | 32 | 32% | 65 | 65% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 14 | 1 | 1% | 5 | 5% | 41 | 41% | 51 | 51% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
Regulatory restrain strategies: Table 5 also shows the order of variable for both regulatory restraints as soon as by a member of the research sample.
| Table 5 Frequency Distribution of Respondents Response to Paragraphs: Regulatory Restrain | ||||||||||||
| No. Variable Y | Don ’ agree at all | Don’t agree | Agee to some extent | Agree | Agree completely | Total | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 15 | - | - | 8 | 8% | 46 | 46% | 44 | 44% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 16 | - | - | 7 | 7% | 25 | 25% | 64 | 64% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
| 17 | 2 | 2% | 6 | 6% | 21 | 21% | 69 | 69% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 18 | - | - | 6 | 6% | 39 | 39% | 53 | 53% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 19 | - | - | 4 | 4% | 60 | 60% | 32 | 32% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
| 20 | - | - | 6 | 6% | 61 | 61% | 31 | 31% | 2 | 2% | 100 | 100% |
| 21 | - | - | 7 | 7% | 24 | 24% | 60 | 60% | 9 | 9% | 100 | 100% |
| 22 | - | - | 4 | 4% | 28 | 28% | 64 | 64% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
| 23 | - | - | 5 | 5% | 19 | 19% | 72 | 72% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
| 24 | 2 | 2% | 2 | 2% | 35 | 35% | 57 | 57% | 4 | 4% | 100 | 100% |
Hypothesis Testing: Correlation Analysis
It means examining the relationship between two variables, and its primary goal is to determine the relationship between variables, form zero degree (no correlation) to link (perfect correlation). As defined Rodgers & Nicewander (1988):
R=1 Extreme Fully
0<R<1 Extreme
R=0 No Relationship
-1>R>0 Reverse
R= -1 Perfect Reverse.
The subsidiary hypothesis testing for the purpose of verifying hypotheses first major premise subsidiary correlation data were calculated (Pearson) learn and determine the strength of the relationship between variables.
Through the above Table 6 indicators evidenced the existence of positive relationships between moral significance strategies and organizational strategies (job analysis and design, staffing and recruitment, where it’s a direct correlation is positive except the relationship between evaluation performance and regulatory restraint strategies inverse relationship.
| Table 6 Showing the Strength of Correlation Between Research Variables | ||||
| S. No | Text of Hypothesis | Correlation Coefficient | Level Moral | Interpretation of Relationship |
| H1 | There is significant correlation for job analysis and design on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.28 | 0.04 | Extreme positive relationship |
| H2 | There is significant correlation for staffing and recruitment strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.46 | 0.001 | Extreme positive relationship |
| H3 | There is significant correlation for Evaluating performance strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.16 | 0.01 | Extreme positive relationship |
| H4 | There is significant correlation for Training strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | -0.05 | 0.5 | Negative inverse relationship |
| H5 | There is significant correlation for human resource planning strategy (Appendix Table 1E,) on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.23 | 0.03 | Positive Moral relationship |
The Subsidiary Hypothesis Testing
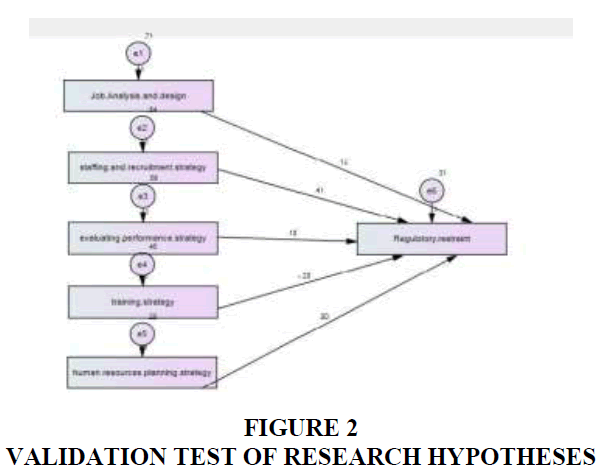
For the purpose of verifying hypotheses major premise subsidiary effect size was calculated by analyzing the CP track and draws an outline.
Through the above Table 7 indicators evidenced the existence of positive significance effect between strategies and organizational strategies (job analysis and design, staffing and recruitment, Evaluating performance strategy, human resource planning). While the effect of training strategy has had negative effect, indicating that this strategy has not affected regulatory restraint.
| Table 7 Showing the Magnitude of the Effect Between the Research Variables by Analyzing the Path CP | |||||
| S. No | Text of the hypothesis | Estimate | S.E | SIG | Interpretation of Hypothesis |
| H6 | There is significant effect for job analysis and design on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.117 | 0.067 | 0.04 | Significant positive effect |
| H7 | There is significant effect for staffing and recruitment strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.414 | 0.076 | 0.01 | Significant positive effect |
| H8 | There is significant effect for Evaluating performance strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.103 | 0.075 | 0.017 | Significant positive effect |
| H9 | There is significant effect for Training strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | -0.282 | 0.083 | - | Significant negative effect |
| H10 | There is significant effect for human resource planning strategy on Regulatory restraint Strategies. | 0.001 | 0.107 | 0.03 | Significant positive effect |
We can see through Figure 2, the analysis of the path and tend of impact HRMS variables on Regulatory Restraint Strategies: (SSPS- AMOS Analysis)
The results of the hypotheses which indicate that there is significant positive effect of HRMS in R.R. we used AMOS analysis test (Tables 6 and 7. These tables show the significant connotation which illustrates analysis of the path correlation and effect relationship between the independent variables (x) and to dependent variable (y) as Figure 2.
Discussion and Conclusions
The research shows an enlarge staffs of the general company for textile industries and leather in Wasit and there are redundant staffs. The company management did not realize the importance of early retirement and didn’t realize the importance of the transition from the professions or other sites. Achieve human resource reduction strategy of fast payouts to tackle inflation in the cadres of the company; this strategy has advanced to other strategies. Didn’t care about company cost leadership strategies as showing it downgrades policy promotion and advertising and product excellence policy. The company efficiency as its shifts down when applying the regulatory restraint strategies nowadays, if it turns out that the company's financial performance wanes by applying these strategies. To enhance pricing policy and development and distribution policy through applying these strategies. Human resources strategies yielded positive relationships strategies with moral significance with regulatory restraint strategies. Human resources strategies have achieved positive effect relationship with moral significance regulatory restraint strategy. Performance appraisal strategy showed correlation and inverse negative effect with regulatory restraint strategies, indicating that the management company didn't care about performance appraisal could reduce the need for regulatory retrain.
Attention to human resource as one of the main pillars in leading the company toward the distinction and success. Further expansion of interest in strategies for human resources and give it a strategic dimension. Activation of the company regulatory restraint as its works in the short, medium and long term. The importance of evaluating the performance and its continuous impact on the process of regulatory restraint. The need for coordination with external parties to ensure alternative employment opportunities for the staffs that the company tries to get rid of them being moral responsibility about those who provide services for many years. Redistribution of the cadres in light of company environmental updates and tech developments.
Need for reengineering processes and functions to suit the actual need of human resources and get rid of the lines that do not add value and do not pay the financial performance of the company for the better. The design of advertising and advertising campaigns to promote their products, especially in light of intense competition and lack of protection for the Iraqi product to market.
Recommendations
Buildings of discussion of finding and conclusions, the researcher recommend the company:
1. Human resources management must have a strategic vision that is capable of meeting challenges and selecting competent and capable human resources.
2. On the management of service organizations or profitability, understanding the basic factors of regulatory restraint to eliminate the inflation of human resources.
Appendix 1
The Questionnaire
General Data:
Age:
Qualification:
Function:
Length of Service:
Human Resources Strategies
| Appendix Table 1A Job Analysis and Design Strategy | |||||
| Response Replies | |||||
| Questions | Very Agree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | Not Agree |
| The management the job analysis according to changes in the internal and external environment | |||||
| The management analysis of internal and external environment for the identification of human resources in terms of number and quality, compared with the company’s strategic requirements | |||||
| The management Careful on job design to match the company’s competitive strategy. | |||||
| The management is dependent on the performance evaluation results as a basis for amending the strategic plans for the management of financial resources. | |||||
| Appendix Table 1B Staffing AND Recruitment Strategy | |||||
| Replies | |||||
| Questions | VeryAgree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | NotAgree |
| The Management Careful to assign human resources capable of achieving strategic company goals. | |||||
| The management Define t staffing requirements according to company strategy. . | |||||
| The Management Careful t to identify jobs in light of the process of job analysis and human resources planning | |||||
| Appendix Table 1C Training Strategy | |||||
| Replies | |||||
| Questions | Very Agree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | Not Agree |
| Careful management to identify clear criteria to evaluate and improve the training strategy. | |||||
| The management is reviewing the strategic plan when changes in the internal and external environment. | |||||
| Heading towards a strategy management training and development towards the company mission. | |||||
| Appendix Table 1D Evaluating Performance strategy | |||||
| Replies | |||||
| Questions | Very Agree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | Not Agree |
| The management Careful management to assess the actual performance against the benchmark of expected performance | |||||
| The management plans to deal with the projected gap between existing skills of future needs | |||||
| Appendix Table 1E Human Resource Planning Strategy | |||||
| Replies | |||||
| Questions | Very Agree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | Not Agree |
| Develop management plans that correspond to the needs of human resources in accordance with future posts. | |||||
| Human resources Management needs analysis of the number and type in light of current awareness and future direction of the company. | |||||
Appendix 2
Regulatory Restraint Strategies
| Questions | Very Agree | Agree | Agree to Some Extent | Disagree | Not Agree |
| Resort management to use attrition when circumstances require reduction of human resources | |||||
| Understand the working management reassign units and other departments when needed | |||||
| The workers wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. T | |||||
| The workers wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. | |||||
| The workers wished to diverse skills through redeployment and other departments. | |||||
| The management Doesn't mind when personnel assigned to work more than one job in order to move the full performance capabilities of the unused hand and achieve the company's goals. | |||||
| Employees understand the company closed one of its branches or production lines for compensation paid by the company to employees who are excluded | |||||
| Help employees perform management philosophy of continuous improvement on different elements in the Organization | |||||
| Care management to improve operations and the reference check with companies carrying out the same activity. | |||||
| The Department is interested in studying the different levels of personnel proposals before making decisions on organizational career. |
References
- Ahmed, A. (2018). The impact of human resources management strategies on development organizational innovation. Al-Jazera Journal, 1, 125-161.
- Al Adresi, A., & Darun, M. (2017). Determining relationship between strategic human resources management practices and organizational commitment. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 9, 1-9.
- Al-Hety, K. (2003). Human resources management. Dar Wael for publishing, Jordan, Aman.
- Al-Saedy, M. (2017). Thinking of human resources strategy. Dar Safa for Publishing First Education, Jordon, Aman, 49-189.
- Armstrong, M. (2009). Human resource management: Theory and practice (10thed.). Personal Management, Hand books, Cambridge University.
- Braton, J., & Gold, J. (2003). Human resources management: Theory and practice (3rd ed.). Great Britain.
- Chen, C.Y., & Wang, G.L. (2012). Exploring organizational downsizing of Taiwanese armed forces upon psychological impacts of their retained personal. Journal of Business Research-Turk, 4/1, 5-23.
- Cooper, D., & Schindler, P. (2008). Business research method (10th ed.). McGraw Hill.
- Cummings, T.G., & Worley, C.G. (2001). Worley essentials of psychological testing. Harper & Rows.
- Decenzo, D., & Robbin, S. (1999). Human resource management. Houghton Mifflin Company, USA, p: 3.
- Evans, G., Gunz, H., & Jall, R. (2005). Downsizing and the transformation of organization career system. Management, 2(3), 127.
- Gandolf, F. (2005). How do organization impalement downsizing? An Australian and New Zeal and Study Contemporary Management Research, 1(1), 58.
- Gomez, M., Luis, R., Balkin, D.B., & Carly, R.L. (2005). Management (2nd ed.). Published by McGraw-Hall Irwin Enc.
- Harris, K.R., Graham, S., & Mason, L.H. (2003). Self-regulated strategy development in the classroom: Part of a balanced approach to writing instruction for students with disabilities. Focus on Exceptional Children, 35(7), 1.
- Inyang, B.J. (2010). Strategic human resource management (SHRM): A paradigm shift for achieving sustained competitive advantage in organization. International Bulletin of Business Administration, 7(23), 215-243.
- Koon, V.Y. (2015). The impact of strategic human resource management on employee outcomes in private and public limited companies in Malaysia. Journal of Human Values, 21(2), 75-86.
- Renata, P., & Lucia, B. (2016). The relationship between human resources management and organizational performance. BBR-Brazilian Business Review, 13(3), 90-110.
- Rodgers, J., & Nicewander, A. (1988). Thirteen ways to look at the correlation coefficient. The American Statistician, 42, 59-66.
- Wilkinson, A. (2004). Downsizing right sizing or dumb sizing? Quality and human resources, in the management ofsustainability. TQM Journal, (5), 7.