Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 1
The Relationship between Green Human Resources Management and Companies Wellbeing A Study on Jordanian Companies
Dina Alkhodary, Middle East University
Citation Information: Alkhodary, D. (2022). The relationship between green human resources management and companies wellbeing a study on jordanian companies. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 26(1), 1-11.
Abstract
Purpose of the study: HR activities play an important role in preserving environmental resources and ensuring sustainability by implementing Green HR practices and creating a shared organizational culture in which employees, Green Management demonstrates that organizational performance is linked with minimizing environmental footprints as well as increasing social and environmental awareness. The purpose of this study is to look into the relationship between Green Human Resources Management (Green HRM) and company well-being. The author has subdivided organizational well-being into three sub-variables, which are as follows: (Employee organizational commitment, Employees Eco-friendly behavior and Environmental performance). The primary research hypothesis is that there is a link between Green HRM and company well-being. A comprehensive online questionnaire was distributed to 300 Jordanian business respondents as part of the methodology. After analyzing 278 valid questionnaires, the study's data was examined using SPSS. The significant observation endorses the research hypotheses, indicating a link between Green Human Resources Management and company well-being; additionally, the research findings show that Green HRM policies and practices have a positive relationship with employees' organizational commitment, eco-friendly behavior, and environmental performance. Applications of this study: The study's findings are applicable to a wide range of business sectors concerned with new practices in HRM, greening, and sustainability, as well as business practices that promote corporate well-being. The researcher suggests that more research be conducted on green HRM and company well-being, as well as the application of this study to other sectors in Jordan. This study is remarkable because it investigates the relationship between green HRM and a company's well-being, which is a relatively new topic in Jordan.
Keywords
Green HRM, Employee Organizational Wellbeing, Employee Organizational Commitment, Eco-friendly Behavior, Environmental Performance, Sustainability.
JEL Classifications
O15, R11, Q56.
Introduction
One of the main international trends currently is Substantiality, in which nations as well as companies, individuals aim to reserve resources and apply friendly practices, green HRM is one of the implications which companies apply nowadays to facilitate its social responsibilities as well as to prevent its knowledge capital in a way to link the traditional HRM practices with corporates social responsibility as well as to create a culture of sustainability and promote applying sustainable practices (Rani, 2014). Green HRM consists of HRM practices towered organizations resources and environmental resources, in which the companies apply business practices that maintain the environmental wellbeing and encourages their employees to adopt the same organizational culture. The new millennials are aware of the importance of the environment most likely more than the previous one, and they prefer to work with organizations that adapting the sustainable culture (Alzgool, 2019). Job sharing, teleconferencing, flexible working hours, sharing cars, telecommuting, E-filling, E-recruitment, online training, paper recycling, online jobs all are examples of the modern HR practices which result for Green HRM in which he companies minimize the operation cost, enhance employees life, as well as reduce the times needed to perform the tasks on another hand all these practices support reserving the companies and environment resources and achieve suitability (Rahoo et al., 2020). However, sustainability is a nation, HR practices could have a significant role in preserving the environment resources by applying Green HR practices as well as make it a shared organizational culture in which employees enhance their green practices and increase their organizational commitment. Green management acted in the 1990s and is common in the 2000s, Green Management shows that organizational performance is linked with minimizing footprints on the environment as well as enhancing social and environmental awareness (Lee et al., 2009). Green management is the balance between economic growth and natural environment conservation to help preserve the right of the future generation to live (Daily & Huang, 2001). Pollution reservation, corporate social responsibility as well as product stewardship as common practices for international companies (Úbeda-García et al., 2021). Organizations have to embrace changes as and when occur according to the wellbeing of human resources and to set goals or objectives such as strategies based on the experience and avoid future problems. The organization strategies are set to accomplish the desires of the human resources which are considered Green HRM and the distribution of the other resources in an accurate method at the accurate period to spread the predetermined strategies. There are lots of developments in the field of HR management due to the era of Strategic Green Human Resources Management in the organization as well as in the life cycle stage of human resources (Santhanam et al., 2021). The term Green HR has become the trendy word within every field of business, this is also a new topic in recent research works since the awareness on environmental challenges management and sustainable approach development has been increasingly growing globally. Green HR is one of the great and important deals that helps improve and encourage employee satisfaction, which adds value to the organization's sustainability and enhances employees' skills and retention level in the particular organization. Green HRM incorporates environmental consciousness and the social and environmental well-being of both the organization and employees in a broader context (Paramita & Ray, 2021).
Technical Literature Review
Green-HRM
HRM systems are characterized as a sequence of activities, processes, and functions attempting to attract, continuing to develop, and preserving organizations' human resources, while promoting sustainable traditional HR activities, processes, and functions in order to improve environmental reservations while also accomplishing organizational efficiency (Jeronimo et al., 2020). Green HRM is the combination of corporate ecological management with HRM, some practices like avoid wasting paper, and using porcelain cups for tea (Rwashedeh, 2021), Green HRM refers to enhance the employee's commitment and responsiveness towered solving problems by applying sustainable practices and solutions referred as it is refers to environments friend topics to archives efficiency in work (Rain, 2014), Green HRM refers to organizations policies and practices which relates to applying online, electronic practices in a way to reduce the time and cost as well as to enhance productivity and sustainability like applying online recruiting and interviewing, online training, online meeting, electronic performance appraisal (Daily & Huang, 2001), business plays a sign environmental on environment sustainability since Green HRM practice environment carbon footprint , thus the role of organization is significant should alerted about the advantages of the new technology by producing and environment-friendly products and services (Liu, 217). Green HRM is significant for environmental performance, thus the concern should concern about the development of its technology or start applying a modern system in which it could reserve its resources, time, effort, and cost, Green HRR could not be achieved successfully without significant employees' acceptance and commitment to the environmental organizational culture (Sheikh et al., 2019). Employees must believe in their company's commitment to sustainability. Green HR practices are a part of an organization's long-term strategies, and they can help guide that insight. For older personnel, green hiring is critical, while green training is appropriate for younger staff. This is referred to as "organizational justification for sustainability" The year 2020 (Jeronimo et al., 2020). Green HR practices boost an organization's revenue, cost-cutting, and branding, Some techniques such as online environmental training and an E-performance management system for monitoring an employee's environmental performance, may help organizations implement green HRM, Employee engagement, participation, and turnover will all improve, as will the ability to recruit employees who are environmentally conscious (Rahoo et al., 2020).
Remote working lead to several green planned initiatives which in turn cause pollution control, power savings, reduce food wastage, paperless work environment, it is important for the organizations to realize the green saving Some companies deciding to either totally work remotely or work on a hybrid model involving more than half the employees working from home and the rest from office, the scope for a continued environmental saving is very high. To adapt to Green HRM, the HR department needs an executive sponsor like the CEO and aggressively push to implement the green initiatives (Santhanam et al., 2021). Green HRM is a tool for implementing corporate social responsibility programs related to environmental preservation, as well as reassuring professionals about environmentally friendly behavior and innovative environmental creativity. Because green issues and the development of the green economy are critical, it is critical for businesses to raise awareness of Green HRM practices among CEO's, managers, and human capital authorities (Tsymbaliuk et al., 2021).
Green HRM policies and practices are associated with positive employee attitudes and behaviors, which reduces firms' ecological impact and improves sustainability of the business. Green HRM method employed staffs' green dedication and pro-environmental behaviors (Ansari, 2021). Top management should make sure the implementation of Green HRM policies aimed at improving environmental performance by the use of green knowledge management. Additionally, decision-makers should focus on the protection and improvement of about their employees' knowledge, as employees are green human capital. Managers should also communicate knowledge with key stakeholders in order to better identify and address their ecological consequences (Jahan, 2021). Because of the recent development of numerous environmental issues, governments worldwide have directed industries and organizations to focus on an environment protection program in addition to their business operations. Many organizations around the world have combined Green HR policies as part of HRM with traditional socially responsible plans to increase employee awareness of their responsibilities towards environmental management. As incredible abuse of natural resources continues to humiliate the environment, governments in emerging nations have come up with a variety environmental safety guidelines to confirm (Mukherjee, 2020), As a result, and in goal is to contribute to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals for 2019, organizations' green HRM practices are attempting to focus on improving employees' green behavioral patterns. Human misbehavior would be to blame for climate change because it wastes resources and harms the ecosystem. Ethical leadership on individuals' green behaviors, along with the mediating role of green HRM practices and the moderating recognition of self-green initiatives, are all critical for an organization's environmental success (Islam, 2020).
Green human resource management improves employees' sustainable and environment behavior; thereby, businesses should create connection between human resource sustainability and green issues, as well as employees' organizational commitment (Kim et al., 2019).
Green human resource management improves employees' eco-friendly behavior; therefore, it is critical for businesses to establish links between human resource management and environmental issues, as well as employees' organizational commitment. Kim et al. (2019) defines formalized Present research findings reveal that GHRM practices influence employees' green commitment and PEBs. Moreover, the results also suggest that green commitment mediates the relationship between GHRM and PEBs. In the end, theoretical contributions and implications were discussed.
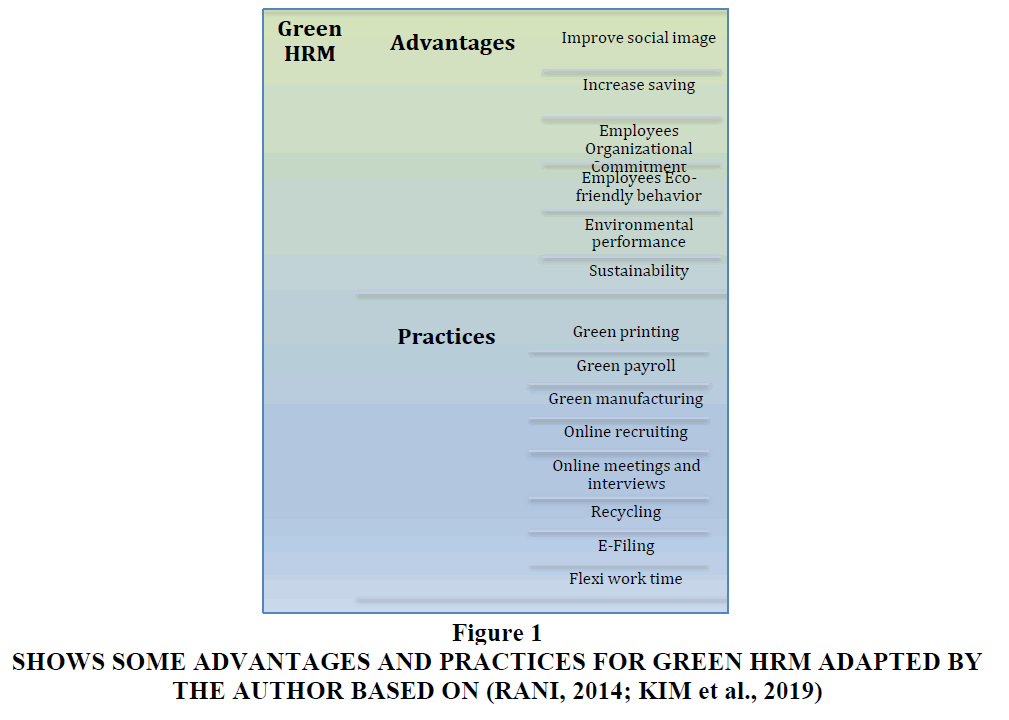
Present research findings reveal that GHRM practices influence employees' green commitment and PEBs. Moreover, the results also suggest that green commitment mediates the relationship between GHRM and PEBs. In the end, theoretical contributions and implications were discussed. Present research findings reveal that GHRM practices influence employees' green commitment and PEBs. Moreover, the results also suggest that green commitment mediates the relationship between GHRM and PEBs. In the end, theoretical contributions and implications were discussed in the Figure 1.
Figure 1 Shows Some Advantages and Practices for Green HRM Adapted by the Author Based on (RANI, 2014; KIM et al., 2019)
Corporates Wellbeing’s
Organizations nowadays are looking beyond their financial performance, organizations are looking to achieve a reputation through social responsibility programs, sustainability practices, as well as greening thus its, applies many policies and practices to ensure the success of social responsibility initiative, first by adopting a common culture which emphasizes the employee's eco-friendly behaviors, second by enhancing the employee's organizational commitment and last by improving the organizational environment performance (Kim et al., 2019).
Employees’ Organizational Commitment
Ecologic organizational commitment is involved with environmentally friendly behavior in the workplace, which refers to flexible activities performed by employees within an organization that are not compensated or required and are aimed at environmental sustainability (Daily et al., 2009) Strategic human resource management, also known as Green HRM, has a strong relationship with employee organizational citizenship behavior (Paillé et al., 2014; Luturlean et al., 2021), eco-friendly behavior practices are necessary to compensate for the inadequacy of organizational citizenship behavior. Environmentally behavior emphasizes particular actions such as energy demand, water consumption, and waste reduction, along with individual action to reduce one's negative impact on the environment (Kollmuss & Agyeman, 2002). This study anticipates that Green HRM will have a considerable relationship with Employees' Organizational Commitment, based on the discussion and synthesis presented above.
Eco-friendly Behavior
Phetvaroon (2019) Green employee behavior was used as a dependent variable, and different authors classified it in various ways, such as green in-role behavior or environmental behavior. Staff commitment to the organization increases their willingness to go above and beyond their assessments. Previous research has shown that there is a significant positive relationship between commitment and organizational commitment (Podsakoff et al., 2014). Employees' environmental behavior is influenced by their employer's commitment (Bishop et al., 2000). Employees with high organizational commitment defined their tasks more broadly and, as a result, engaged in unselfish behavior, a generous helping behavior, because there is a positive relationship between loyalty and altruistic environmental attributes. Employees who are emotionally invested in their institutions are more likely to develop altruistic OCB because they want to be good citizens in good organizations. Organizational commitment and environmental behavior have a strong relationship (Carmeli, 2005) (Liden et al., 2003), this study anticipates that Green HRM will have a significant influence on the employees' environment protection, based on the prior discussion and formulation.
Organizational Environmental Performance
Few empirical studies have determined the relationship between employees' commitment towered environmental behavior and environmental performance; however, According to a few research, workers' ecologic commitment behavior is a direct driver of sustainability impact; thus, employees' ecologic actions, such as waste reduction, should help firms achieve and enhance their sustainability objectives (Paillé et al., 2014; Daily et al. 2009). Green HRM is essential for Pakistan because it can be used to reduce the impact on the natural surroundings, which will support the nation's economic ecological systems in the long term. Tahir et al. (2020), by supplementing environmental management policies and practices, the impulsiveness of sustainable and environment behavior can improve environmental performance (Roy et al., 2013). Given the previous discussion and synthesis, this study anticipates that Green HRM will have a positive relationship with financial Sustainability practices.
Framework for Research
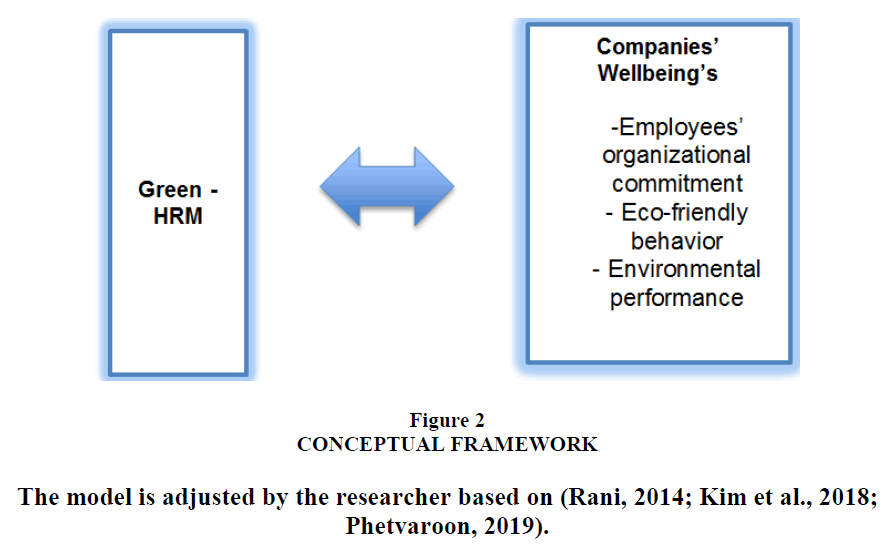
The conceptual framework depicted in Figure 1 includes the independent variable Green HRM to measure Green HRM and the dependent variable Companies well-being (Employees organizational commitment, Eco-friendly behavior, and Environmental performance) (Rani, 2014). Formalized adverbial adverb (Kim et al., 2019; Paillé et al., 2014; Podsakoff et al., 2014) Figure 2.
Figure 2 Conceptual Framework
The model is adjusted by the researcher based on (Rani, 2014; Kim et al., 2018; Phetvaroon, 2019).
The Problem of the Study
The following are the study's main hypotheses:
H1: Green HRM and company well-being are linked in Jordan.
H1.1: Green HRM and employee organizational commitment are linked in Jordan.
H1.2: Green HRM and environmentally friendly behavior are linked in Jordan.
H1.3: Green HRM and environmental performance are linked in Jordan.
Collection of Research Data Methodology
The research population consists of human resources employees from Jordanian businesses. The sample size for the study is 278 people who are familiar with the concept of green human resource management, and the questioner scale is (5 strongly agree, 4 agree, 3 neutral, 2 disagree, and 1 strongly disagree). Thirty statements were tested, 11 about Green-HRM and 19 about company wellness, with three scopes: organizational commitment, sustainable and environment behavior, and environmental performance.
Analysis and Results
The researcher used the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, a first-generation statistical package, to test the hypotheses and answer the research questions (SPSS). The Cronbach's Alpha test was used to test the reliability and consistency of the data collection tool, as well as multiple and simple regression analysis to test the research hypotheses. To answer research questions, the researcher used means, frequencies, and standard deviations; the tables below show the results of data collection from questionnaire respondents.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability refers to the degree to which a variable is consistent in what is proposed to be assessed (Keyworth, 2020). Cronbach's alpha of 0.70 or higher indicates high scale reliability (Ventura-León, 2020). As a consequence, Table 1 shows the reliability test as well as Cronbach's Alpha, which were used to test the dependability of the items while evaluating each variable: Green HRM and company wellness (employee organizational commitment, employee sustainable and environment behavior, and environmental performance), all values above the required minimum of 0.70.
| Table 1 Reliability Summary | ||
| Variables | Number of Statements | Values of Alpha |
| Green HRM | 11 | 0.922 |
| Employees’ organizational commitment | 6 | 0.904 |
| Eco-friendly behavior | 6 | 0.856 |
| Environmental performance | 7 | 0.899 |
| Overall | 30 | 0.958 |
The Cronbach's alpha reliability test was used to assess the questionnaire's internal consistency, which measures how closely the questions and variables are related to one another. The results show that the study's measurement is reliable because the alpha values are equal to or greater than 0.70, so it is accepted (Goodboy et al., 2020).
The mean and standard deviation values for each variable, as well as the results of the correlations between these variables, are shown in Table 2. Ratner (2020) defines a moderately positive (negative) correlation as values between (0.30 and 0.70). Table 2 demonstrates the positive correlations between independent and dependent variables.
| Table 2 Expressive Analysis and Connection Matrix | ||||
| Dimensions | Green HRM | Employees’ organizational commitment | Eco-friendly behavior | Environmental performance |
| Mean | 3.8937 | 3.7854 | 3.9532 | 3.574 |
| SD | 0.732 | 0.867 | 0.757 | 0.889 |
| Green HRM | 1 | 0.669** | 0.646** | 0.568** |
| Employees’ organizational commitment |
0.669** | 1 | 0.825** | 0.669** |
| Eco-friendly behavior | 0.646** | 0.825** | 1 | 0.663** |
| Environmental performance | 0.568** | 0.669** | 0.663** | 1 |
Discussion
The link between Green HRM and Employees' organizational commitment is statistically significant, according to the findings of regression analysis (table3) (sig. >0.05). As a result, H1.1: Green HRM and employee organizational commitment are linked in Jordan is supported. To put it another way, Green HRM has a positive and significant relationship with employee loyalty to the firm. Furthermore, because (sig. >0.05), the relationship between Green HRM and Employees' organizational commitment is statically significant (R2=.448), Green HRM explains 44.8 percent of the change in Employees' organizational commitment, since (sig. >0.05), the connection between Green HRM and Employees’ organizational commitment is statically significant because (sig. > 0.05).
| Table 3 Regression Analysis | |||||||||
| Independent Variables | Dependent Variable | ||||||||
| Corporates Wellness | |||||||||
| Employees Organizational Commitment |
Eco-friendly Behavior | Environmental Performance | |||||||
| R | Adjusted R2 | Sig. | R | Adjusted R2 | Sig. | R | Adjusted R2 | Sig. | |
| Green HRM | 0.669 | 0.448 | 0.000 | 0.646 | 0.418 | 0.000 | 0.568 | 0.322 | 0.000 |
| **p <.01 (N=500) | |||||||||
As a result, hypothesis H1.2: Green HRM and environmentally friendly behavior are linked in Jordan is also supported. In Jordan, there is a link between Green HRM and environmentally responsible behavior. Are positively and significantly related to one another (R2=0.418). As a result, 41.8 percent of the change in Green HRM may be attributed to eco-friendly behavior. According to regression analysis results, the link between Green HRM and environmentally friendly behavior is statistically significant (sig. > 0.05). Furthermore, Green HRM and environmental performance are favorably related (R2=.322). As a result, hypothesis H1.3: Green HRM and environmental performance are linked in Jordan is also supported. Jordan has a link between Green HRM and environmentally conscious behavior, Are strongly linked (R2=0.418). As a result, 0.322 percent of the change in Green HRM may be explained by environmental performance. The link between Green HRM and environmental performance is statistically significant (sig. > 0.05), according to the outcomes of regression analysis. Plus, environmental performance and green HRM are favorably related (R2=.322). As a result, environmental performance accounts for 32.2 percent of the variance in Green HRM. As a result, hypothesis H1: Green HRM and company well-being are linked in Jordan is supported. In other words, Green HRM and has a positive and significant relationship with Jordanian businesses' well-being.
Conclusion
According to the study, there is a strong relationship between Green HRM and company wellness (Employees' organizational commitment, Employees' Eco-friendly behavior, and Environmental performance), which is consistent with the previous findings (Rani, 2014; Kim et al., 2019; Paillé et al., 2014; Podsakoff et al., 2014). Green HRM is important for organizational environmental performance, social responsibility, and sustainability; therefore, businesses should be concerned about the advancement of technology or begin implementing a modern system that allows them to save resources, employees, and operations time, effort, and cost. Green HRM could not be accomplished successfully without significant employee acceptance and commitment to the environmental organizational culture; it could be accomplished by providing employees with new awareness sessions that emphasize the importance of environmental sustainability., as well as Green HRM, needs support from top management and create a special culture of greening, sustainability as well as eco-friendly behavior. Employees' commitment is essential if the companies would like to be excellent on Greening practices since the employee's commitment towered the organizational culture guarantee the applying the greening practices, as well as eco-friendly behavior. Organizational environmental performance in Jordanian companies could be more effective in Green HRM if they invest more in systems and technology as well as adding more valuable training and orientation about greening concepts as well as enhancing the role of the HR department as an infrastructure for employees to deploy the Greening culture as well as raise awareness level among top management, employees and HR professionals about environmental impact.
Acknowledgement
The author is grateful to the Middle East University, Amman, Jordan for the full financial support granted to this research project.
References
Alzgool, M. (2019). Nexus between green HRM and green management towards fostering green values. Management Science Letters, 9(12), 2073-2082.
Carmeli, A. (2005). The relationship between organizational culture and withdrawal intentions and behavior. International Journal of Manpower.
Islam, T., Khan, M.M., Ahmed, I., & Mahmood, K. (2020). Promoting in-role and extra-role green behavior through ethical leadership: mediating role of green HRM and moderating role of individual green values. International Journal of Manpower.
Lee, A.H., Kang, H.Y., Hsu, C.F., & Hung, H.C. (2009). A green supplier selection model for the high-tech industry. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(4), 7917-7927.
Luturlean, B.S., Prasetio, A.P., Anggadwita, G., & Hanura, F. (2021). Does work-life balance mediate the relationship between HR practices and affective organizational commitment? The perspective of the telecommunication industry in Indonesia. International Journal of Learning and Intellectual Capital, 18(2), 154-172.
Paramita, P., & Ray, A.P. (2021) Green HR Practices: A Solution to Environmental Challenges.
Rani, S. (2014). Green HRM: Practices and strategic implementation in the organizations. International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication, 2(11), 3633-3639.
Sheikh, W.A.H.I.D.U.L., Islam, M.S., & Rahman, F.A.R.H.A.N.A. (2019). Implementing Green Human Resource Management: Cost-Effective Strategies and Tools. Journal of Entrepreneurship Organization Management, 8, 264.