Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 4S
The Impact of Strategic Foresight on Organizational Performance at Private Iraqi Commercial Banks
Mohammed AbdulFattah Hammad, Amman Arab University
Rashad Mohammad Al-Sa'ed, Amman Arab University
Citation Information: Hammad, M.A., & Al-Sa'ed, R.M. (2022). The Impact of Strategic Foresight on Organizational Performance at Private Iraqi Commercial Banks. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S4), 1-11.
Abstract
The study aimed to examine the impact of strategic foresight dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), on organizational performance (internal operations, learning and growth, customer satisfaction), at private Iraqi commercial banks, the questionnaire was used as a main tool to collect The data where the researcher distributed (126) questionnaires to the researched sample, (115) were retrieved represent (91.26 %), of the total distributed questionnaires to achieve the objectives of study. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences” (SPSS.V.25) used. The study revealed a number of results, the most prominent of which was the presence of a statistically significant effect at the significance level (a=0.05), of strategic foresight on organizational performance in Iraqi private commercial banks. The study was keen to present a set of recommendations, the most prominent of which was the development of the concept of strategic foresight among the leaders of banks, as well as the enhancement of the concept of organizational performance among employees.
Keywords
Strategic Foresight, Organizational Performance, Iraqi Private Commercial Banks, Iraq
Introduction
Since the beginning of its formation, the whole world has witnessed continuous changes, whether they are natural due to climatic factors, formative to the earth, or abnormal changes caused by man and what he seeks to achieve. Was it governmental or non-governmental, especially profitable and non-profit ones, from planning and continuous follow-up to control the changes that occur around it by acquiring strengths and employing them in the field in which it operates, avoiding weaknesses and places of imbalance that affect them, as well as trying to gain opportunities and work to end external threats. The events resulted in a number of variables and developments in the field of business organizations, which made it necessary to take measures and decisions to confront the dangers and challenges of the future. The future direction of any organization and the identification of its goals that it always seeks to achieve depends to a large extent on the identification, description and knowledge of future situations through strategic foresight, as The integration between strategic foresight through its curricula and capabilities and the extent to which the organization has the appropriate strategy will lead the organization to achieve the desired organizational performance, which leads it to creativity and excellence in the field in which it operates (Naama & Abdel Rahim, 2021).
Research Problem
All banks seek to achieve outstanding organizational performance as it is the main indicator that reflects the ability of banks through their use of their available financial, human, material and information resources in an effective and efficient manner, as the level of organizational performance depends primarily on the actions of managers and their interaction with employees, due to their direct contact with operational processes in addition to the degree Productive efficiency and the level of dealing with customers, which requires the management of banks to follow modern management concepts instead of the old or traditional methods of management. Entrepreneurial behavior based on the behaviors followed. The researcher inferred the problem of the study through his review of many previous research and studies, including the study (Khaled & Younis, 2014), which talked about the intensity of competition in the services provided by private banks in order to obtain a greater number of clients, so it was necessary to go towards their internal environment, especially focusing On organizational performance (Hussain & Al-Mamouri, 2016), which recommended more research and study on strategic foresight and organizational performance.
Theoretical Framework
Foresight can create the vision of future organizations or future research in organizations as well as enhance the ability to face and respond to external change (Rohrbeck, 2012). As for it was considered that foresight is critical to the success of organizational performance in environments with rapid change and are especially important in plans with greater complexity and real uncertainty.
Strategic Foresight
The concept of strategic foresight has taken great interest by many researchers and scientists until it has become more widespread, especially with the increasing speed of changes in various fields in the world, as their focus on it as a purposeful thinking and vision by organizations for a positive impact in the future through a purposeful scientific method to explore the future (Hamad, 2019). Strategic foresight is an organized scientific endeavor, through which it aims to formulate a set of conditional predictions that contain the main features and pillars of the conditions of a particular society or organizations during a certain period of time (Kadduri & Al-Alousi, 2018), foresight is the ability to predict how you might interpret the future, which means that it is an important and crucial strategic ability for effective planning at the long level (Peter & Jarratt, 2013). Iden, et al., (2017), sees the use of foresight as a personal force as the ability to predict. (Kuosa, 2014), saw that foresight is not a prediction, but rather a demonstration of a full set of future alternatives through which problems in organizations can be addressed. Foresight is a set of practices that support the exploration of new business by identifying drivers of change (perception) (Rohrbeck & Højland, 2017). Strategic foresight is to enhance the organization’s ability to understand emerging risks and opportunities, and motives, which constitute a possible, reasonable, and potential or preferred future space, so that the organization can make informed and better equipped decisions. (Arokodare, 2020) strategic foresight is the ability of companies to implement actions that reflect critical decision-making and to be aware and able to perceive and interpret weak signals and infer the course of relevant actions (Sarpong, et al., 2015), Horlesberger, et al., (2016) stressed that strategic foresight is a future dialogue related to thinking about the future and discussing its formations in order to enhance decision-making and future dynamic ability. This study aims at how organizations explore how to identify, anticipate and manage imbalances, prepare for an uncertain future and work to maintain a distinct competitive position, as well as conduct continuous survey and interpretation of reactions to these changes (Rohrbeck & Gemünden, 2008).
Organizational Performance
In the literature, performance is a fundamental and important concept for business organizations in general. It is also considered one of the important issues that concern management in most developed and developing countries, because the growth of real income in most developed countries, as well as rising the standard of living in them depends mainly on the high efficiency of performance. On the level of civilizational and economic progress (Abd AL-Rahman, 2018). Performance can be counted as that action that leads to the completion of the work as planned to be accomplished, and is characterized by comprehensiveness and continuity, and in this sense it is the main determinant of the success of the organization and its survival in the target markets (Al-Haidari, 2017). As for (Liao & Wu, 2009), they indicated that performance is a recurring topic in most branches of management and is of interest to academics, researchers and managers. Although the importance of the concept of performance is widely recognized, the treatment of performance in a research environment can be one of the most complex issues facing the academic researcher today with the increasing volume of literature on the topic of performance. (Hadijah & Ramdani, 2020) clarify that the organizational performance is the overall work results achieved by the organization. Since the achievement of the organization's goals refers to its organizational performance, meaning to what extent the organization can reach its goals in relation to the goals that were previously set. Organizational performance is of great importance for organizations in the past, present and future, as its importance stems from the fact that it helps them to communicate with the surrounding environment of the organization. Its ultimate goal and purpose is organizational performance and is considered a reflection of individual or organizational productivity (Faeq & Abd, 2018).
(Friedman & Shraibman, 2018), they pointed to the importance of organizational performance, through which it is known which of the strategies to be followed in the future, as well as an indicator or measurement that the organization can by knowing the extent to which the objectives set in the future are achieved. Liao & Wu (2009), they indicated that performance is a recurring topic in most branches of management and is of interest to academics, researchers and managers. Although the importance of the concept of performance is widely recognized, the treatment of performance in a research environment can be one of the most complex issues facing the academic researcher today with the increasing volume of literature on the subject of performance, and performance can be defined according to the opinions of a group of researchers and writers.
Research Model and Hypotheses
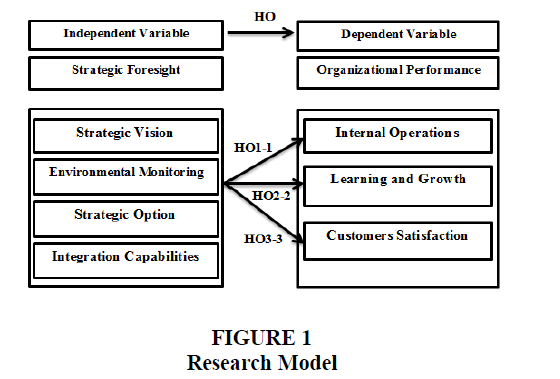
Based on previous studies (Amniattalab & Ansari, 2016; Hamad, 2019; Al-Hasnawi, 2020; Paliokaite et al., 2014; Nima & Abdel Rahim, 2021; Al-Zwyalif, 2012; Haddadin, 2014; Ibrahim, 2017; Al-Ghabban, 2009; Manhal & Zaid, 2020; Abdullah & Abdul Qadir, 2019; Rafiq et al., 2020). Researchers present the proposed model which Strategic Foresight as an independent variable, and Organizational Performance as a dependent variable. Figure 1 clarified the formulated model and the correlative between the research dimensions.
Based on the study problem and its questions, the following hypotheses were formulated:
The Main Hypothesis HO: There is no statistically significant impact at the level of significance (a=0.05), for strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), on organizational performance with its dimensions (internal operations, learning and growth, customer satisfaction) at private Iraqi commercial banks.
The following sub-hypotheses are derived from the main hypothesis:
HO1-1: There is no statistically significant impact at the significance level (a=0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), on the internal operations at the Iraqi private commercial banks.
HO2-2: There is no statistically significant impact at the significance level (a=0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), on learning and growth at the Iraqi private commercial banks.
HO3-3: There is no statistically significant impact at the level of significance (a=0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, capabilities of integration), on customer satisfaction at the Iraqi private commercial banks.
Research Methodology
The study aimed to know the impact of strategic foresight represented by its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), on organizational performance, represented by its dimensions (internal operations, learning and growth, customer satisfaction), in private Iraqi commercial banks, and the study relied on the approach Analytical descriptive, as the study was applied in private Iraqi commercial banks on a sample of its members, which included (the director, the assistant director, heads of departments, and managers of administrative divisions), which numbered (126) individuals, and the questionnaire was used as a main tool for data collection, where the researcher distributed (126), a questionnaire on the researched sample, and (115) were retrieved, a questionnaire valid for statistical analysis, with a percentage of (91.26%) of the total distributed questionnaires.
Analysis and Results
Validity and Reliability of the Measurement Items
To test the clarity of the questionnaire and ensure consistency between the elements and variables, a comprehensive review was thoroughly conducted by academic arbitrators from Amman Arab University and arbitrators from Iraqi universities in various disciplines in business administration. The questionnaire was submitted to (10) arbitrators, including (4) faculty members at Amman Arab University and (6) teachers from Iraqi universities, where suggestions were taken into account from the researcher. For (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016), reliability should be (0.60) or higher to indicate sufficient convergence or internal consistency. The results shown in Table (1) are acceptable levels as suggested by (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
| Table 1 Stability Coefficient Kronbach Alpha For The Study Instrument |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Cronbach's alpha | ||
| Independent Variable: Strategic Foresight | |||
| 1 | Strategic Vision | 0.928 | |
| 2 | Environmental Monitoring | 0.858 | |
| 3 | Strategic Option | 0.911 | |
| 4 | Integration Capabilities | 0.921 | |
| Strategic Foresight 0.972 | |||
| Dependent variable: Organizational performance | |||
| 1 | Internal Operations | 0.880 | |
| 2 | Learning and Growth | 0.926 | |
| 3 | Customers Satisfaction | 0.930 | |
| Organizational performance 0.962 | |||
| The questionnaire in general 0.980 | |||
The values of Cronbach's alpha, which ranged between (0.858-0.972), for the study variables and dimensions, which are greater than (0.70), and this indicates that the variables and dimensions have appropriate internal consistency, while the internal consistency coefficient of Cronbach's alpha for the scale in total was (0.980), It enjoyed a high evaluation, and these results indicate that the study scale (resolution), enjoyed a good level of stability, and this is evidence of the extent of its internal consistency in addition to the stability of its paragraphs. As for honesty, it is the degree to which the scale measures the purpose for which it was designed or for which it was developed the results in Table (7) indicate that they ranged between (0.926-0.986), which is a good percentage (Table 2).
| Table 2 Variation And Variance Amplification Factor Test |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | VIF | Tolerance |
| Strategic Vision | 2.924 | 0.3420 |
| Environmental Monitoring | 2.731 | 0.3660 |
| Strategic Option | 2.541 | 0.3940 |
| Integration Capabilities | 2.558 | 0.3910 |
The Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) test, for all variables, is less than (10), and ranges between (2.541-2.924), and the Tolerance test, ranged between (0.3420-0.3940), and this is an indication of a correlation Among the independent variables (Multi-collinearity), and it was also confirmed that the data follow a normal distribution by calculating the Skewness coefficient, where the values were more than the value (0), means more than (1).
Testing Hypotheses
Main Hypothesis H01
The value of the correlation coefficient for the independent variable (strategic foresight), and the dependent variable (organizational performance), together amounted to (0.670), and the value of the coefficient of determination (r2), (0.819), meaning that the model explained (81.9%), of the total variance in (organizational performance), the rest is explained by other factors (Table 3 & 4).
| Table 3 Summary Of The Model For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight On Organizational Performance |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Standard Standard (R) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Rate factor (R) | Standard Error |
| 1 | 0.670 | 0.819 | 0.47450 | 0.658 |
| Table 4 Results Of Multiple Regression Analysis Of The Impact Of Strategic Foresight On Organizational Performance Anova |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Data Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Squares | The Calculated F Value | Sig. |
| 1 | Regression | 50.365 | 4 | 12.591 | 55.924 | 0.000 |
| The error | 24.766 | 110 | 0.225 | |||
| Total | 75.131 | 114 | ||||
Regression variance analysis of the impact of strategic foresight on organizational performance, where the calculated F value appears, which indicates the suitability of the model to the regression test and that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables reached (55.924), at a significance level of (0.000), and the decision rule states that the model is appropriate if The value of the level of significance (sig), was less than (0.05), and thus the null hypothesis was rejected and the alternative hypothesis was accepted, which is that there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α ≤ 0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, And the strategic choice, capabilities of integration), in organizational performance in its dimensions (learning and growth, internal operations, customer satisfaction), in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks (Table 5).
| Table 5 Transaction Results For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight On Organizational Performance |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-standard Transactions | Standard Coefficients | T Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Standard Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | Constant | 0.376 | 0.219 | 1.713 | 0.090 | |
| strategic vision | 0.024 | 0.083 | 0.028 | 0.294 | 0.769 | |
| environmental monitoring | 0.273 | 0.091 | 0.273 | 3.017 | 0.003 | |
| strategic choice | 0.147 | 0.086 | 0.148 | 1.696 | 0.093 | |
| Integration capabilities | 0.435 | 0.082 | 0.467 | 5.333 | 0.000 | |
| Table 6 Model Summary For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Learning And Growth Dimension |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Correlation Coefficient (R) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Rate Factor (R) | Standard Error | ||
| 1 | .8290 | .6870 | .6760 | .476300 | ||
The values of the moral significance amounted to (0.090, 0.769, 0.003, 0.093, 0.000), sequentially, as the results showed that (environmental monitoring, and integration capabilities), had a significant impact on organizational performance in Iraqi private commercial banks, in While both (strategic vision and strategic choice), they have no significant impact on organizational performance in private Iraqi commercial banks, and this indicates the existence of a problem in strategic vision and strategic choice in private Iraqi commercial banks. The table shows that the most influential dimensions in organizational performance in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks were the dimension (integration capabilities), and the value of Beta was (0.467), followed by the dimension (environmental monitoring), where the value of Beta was (0.273).
Testing the Sub-Hypothesis H01.1: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for the strategic foresight in its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice and integration capabilities) in the dimension of learning and growth in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks (Table 6).
| Table 7 Multiple Regression Analysis Of The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Learning And Growth Dimension Anova |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Data Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Squares | The Calculated F Value | Sig. |
| 1 | Regression | 54.772 | 4 | 13.693 | 60.357 | .0000 |
| The error | 24.955 | 110 | 0.227 | |||
| Total | 79.727 | 114 | ||||
The value of the correlation coefficient for the independent variable (strategic outlook), and the dependent variable (the learning and growth dimension), together amounted to (0.829), and the value of the coefficient of determination (r2), F (0.687), meaning that the model explained (68.7%), of the variance Total in the (learning and growth dimension).
Table 7 shows the analysis of regression variance for the impact of strategic foresight in the learning and growth dimension, where it shows the calculated F value, which indicates the suitability of the model to the regression test, and that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables reached (60.357), at a significance level (0.000), and states The decision base is based on considering the model appropriate if the value of the level of significance (sig), is less than (0.00), and thus the null hypothesis was rejected and the alternative hypothesis was accepted, which is that there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05), for the strategic foresight in its dimensions (Strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), in the dimension of learning and growth in Iraqi private commercial banks.
It is clear from the statistical results presented in Table 8, that the values of the significant significance amounted to (0.193, 0.020, 0.051, 0.628, 0.000), sequentially, where the results showed that (environmental monitoring, and strategic option), They have no significant impact on the learning and growth dimension of the Iraqi private commercial banks, while (strategic vision and integration capabilities) had a significant impact on the learning and growth dimension in private Iraqi commercial banks, and this indicates the existence of a problem in environmental monitoring and strategic choice among Iraqi private commercial banks in learning and growth. The table shows that the most influential dimensions in the dimension of learning and growth in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks were (integration capabilities), and the value of Beta was (0.493), followed by the dimension (strategic vision), where the value of Beta was (0.215).
| Table 8 Transaction Results For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Learning And Growth Dimension |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-Standard Transactions | Standard Coefficients | T. value | Sig. | ||
| B | Standard Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | Constant | 0.288 | 0.220 | 1.310 | 0.193 | |
| Strategic Vision | 0.196 | 0.083 | 0.215 | 2.358 | 0.020 | |
| Environmental Monitoring | 0.179 | 0.091 | 0.174 | 1.969 | 0.051 | |
| Strategic Choice | 0.042 | 0.087 | 0.041 | 0.486 | 0.628 | |
| Integration Capabilities | 0.473 | 0.082 | 0.493 | 5.775 | 0.000 | |
The second sub-hypothesis H02.2: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), in the dimension of internal operations in the Iraqi private commercial banks investigated (Table 9).
| Table 9 Summary Of The Model For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Dimension Of Internal Operations |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Correlation Coefficient (R) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Rate Factor (R) | Standard Error | |
| 1 | .7640 | .5840 | .5690 | .606370 | |
The value of the correlation coefficient of the independent variable (strategic foresight), and the dependent variable (the dimension of internal operations), together amounted to (0.764), and the value of the coefficient of determination was (R2), (0.584), meaning that the model explained (58.4%), of the variance The total is in the (learning and growth dimension), while the rest is explained by other factors (Table 10).
| Table 10 Multiple Regression Analysis Of The Impact Of Strategic Foresight On The Internal Operations Dimension Anova |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Data Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Squares | The Calculated F Value | Sig. |
| 1 | Regression | 56.760 | 4 | 14.190 | 38.593 | .0000 |
| The Error | 40.445 | 110 | 0.368 | |||
| Total | 97.205 | 114 | ||||
Regression variance analysis of the impact of strategic foresight in the dimension of internal operations, where the calculated F value appears, which indicates the suitability of the model to the regression test and that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables reached (38,593), at the level of significance (0.000), and the decision rule states that the model is appropriate If the value of the level of significance (sig), is less than (0.05), and thus the null hypothesis was rejected and the alternative hypothesis was accepted, which is that there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α ≤ 0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring Strategic choice, integration capabilities), in the dimension of internal operations in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks (Table 11).
| Table 11 Transaction Results For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Internal Operations Dimension |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-standard Transactions | Standard Coefficients | T. value | Sig. | ||
| B | standard error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | Constant | 0.202 | 0.280 | 0.721 | 0.472 | |
| Strategic vision | 0.075 | 0.106 | 0.074 | 0.705 | 0.482 | |
| Environmental monitoring | 0.395 | 0.116 | 0.346 | 3.408 | 0.001 | |
| Strategic choice | 0.176 | 0.110 | 0.156 | 1.592 | 0.114 | |
| Integration capabilities | 0.444 | 0.104 | 0.419 | 4.259 | 0.000 | |
The values of the moral significance amounted to (0.472, 0.482, 0.001, 0.114, 0.000), sequentially, the results showed that each of the (strategic vision, and strategic choice), have no significant effect on the internal operations of the Iraqi private commercial banks, in While all (environmental monitoring, and integration capabilities) had a significant impact on the dimension of internal operations in private Iraqi commercial banks, and this indicates the existence of a problem in the strategic vision and strategic choice of private Iraqi commercial banks in internal operations, as the table shows that the most influential dimensions In the dimension of the internal operations in the Iraqi private commercial banks investigated was the dimension (capabilities of integration), and the value of Beta was (0.419), followed by the dimension (Environmental Monitoring), where the value of Beta was (0.346).
The Third sub-hypothesis HO3-3: There is no statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring, strategic choice, integration capabilities), in the dimension of customer satisfaction in the Iraqi private commercial banks surveyed.
The value of the correlation coefficient for the independent variable (strategic foresight), and the dependent variable (customer satisfaction dimension), together amounted to (0.724), and the value of the coefficient of determination (r2), (0.525), meaning that the model explained (52.5%), of the variance Total in (customer satisfaction dimension) (Table 12 & 13).
| Table 12 Summary Of The Model For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Dimension Of Customer Satisfaction |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Correlation Coefficient (R) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Rate Factor (R) | Standard Error | |||
| 1 | .7240 | .5250 | .5080 | .589410 | |||
| Table 13 Results Of Multiple Regression Analysis Of The Effect Of Strategic Foresight In The Dimension Of Customer Satisfaction Anova |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Data Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Squares | The Calculated F Value | Sig. |
| 1 | Regression | 42.201 | 4 | 10.550 | 30.369 | .0000 |
| The error | 38.214 | 110 | 0.347 | |||
| Total | 80.415 | 114 | ||||
Regression variance analysis of the impact of strategic foresight in the dimension of customer satisfaction, where the calculated F value appears, which indicates the suitability of the model to the regression test and that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables reached (30.369), at the level of significance (0.000), and the decision rule states that the model is appropriate If the value of the level of significance (sig), is less than (0.05), and thus the null hypothesis was rejected and the alternative hypothesis was accepted, which is that there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05), for the strategic foresight with its dimensions (strategic vision, environmental monitoring Strategic choice, integration capabilities), in the dimension of customer satisfaction in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks (Table 14).
| Table 14 Transaction Results For The Impact Of Strategic Foresight In The Dimension Of Customer Satisfaction |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-standard transactions | Standard coefficients | T. value | Sig. | ||
| B | Standard Error | Beta | ||||
| 1 | Constant | 0.202 | 0.280 | 0.721 | 0.472 | |
| Strategic Vision | 0.075 | 0.106 | 0.074 | 0.705 | 0.482 | |
| Environmental Monitoring | 0.395 | 0.116 | 0.346 | 3.408 | 0.001 | |
| Strategic Choice | 0.176 | 0.110 | 0.156 | 1.592 | 0.114 | |
| Integration Capabilities | 0.444 | 0.104 | 0.419 | 4.259 | 0.000 | |
The values of the moral significance amounted to (0.021, 0.640, 0.031, 0.041, 0.000), sequentially, the results show that (strategic vision), has no significant effect on customer satisfaction with Iraqi private commercial banks, while each of the (Environmental monitoring, strategic choice, and integration capabilities) had a significant impact on customer satisfaction in private Iraqi commercial banks, and this indicates the existence of a problem in the strategic vision of private Iraqi commercial banks in the customer satisfaction dimension, as the table shows that the most influential dimensions in The dimension of customer satisfaction in the researched private Iraqi commercial banks was the dimension (capabilities of integration), and the value of Beta was (0.403), followed by the dimension (Environmental Monitoring), where the value of Beta was (0.238), and in the third place came the dimension (strategic option), The Beta value is 0.216.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The results of the descriptive analysis showed that the independent variable (strategic foresight), was the general arithmetic mean (mean), and that the highest arithmetic mean of the dimensions is the dimension (integration capabilities), with an arithmetic mean of (3.624), followed by the dimension (strategic choice), where the mean value reached The arithmetic (3.591), followed by the dimension (strategic vision), where the arithmetic mean reached (3.550), followed by the last dimension (environmental monitoring), with an arithmetic mean of (3.487). This study agreed with the study (Hamad, 2019), as well as the study (Qaddouri & Al-Alousi, 2018), as well as the study (Nama & Abdel Rahim, 2021). The results of the descriptive analysis showed that the dependent variable (organizational performance), was the general arithmetic mean (average), and that the highest arithmetic mean of the dimensions is the dimension (internal operations), with an arithmetic mean of (3.55), followed by the dimension (customer satisfaction), with an arithmetic mean It reached (3.529), followed by the last dimension (learning and growth), with an arithmetic mean of (3.477). This study agreed with the study (Manhal & Zaid, 2020), as well as the study (Al-Ghabban & Hussein, 2009), as well as the study (Abdullah & Abdel-Qader, 2019).
After reviewing the results that were reached after analyzing the data obtained, the researcher presented a set of recommendations that serve the management of private banks and benefit from them, and shed light on the aspects that they suffer from. The researcher recommends further development of the concept of strategic foresight among the leaders of Iraqi private banks, as the results showed that the general average of strategic foresight was a medium degree. The researcher also recommends the management of Iraqi private commercial banks to reconsider the strategic vision in terms of clarity, future perceptions and environmental changes to provide renewed visions. The researcher also recommends the management of Iraqi private commercial banks to reconsider the strategic option in terms of choosing alternatives in a way based on innovation and continuous learning in order to improve the opportunities of competitive banks and provide the best services to satisfy customers. In addition, the researcher recommends reconsidering environmental monitoring methods and developing them through more training and learning programs for the managers of these banks in order to choose the best strategic alternative to keep in their growth and continuity of these banks and their competition at the local and regional levels.
References
Abdel, R., & Abbas, H.E. (2018). Oriented total quality management and its impact on institutional performance – The modifying role of organizational culture: Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Business Administration, College of Graduate Studies: Sudan University of Science and Technology.
Abdul Qadir, N., & Abdullah, A. (2019). The impact of the entrepreneurial leader’s behavior on organizational performance: An exploratory study in the Basra Oil Company. Journal of Administrative Studies, 14(28), 202-223.
Al-Haidari, D.A. (2017). The effect of applying the philosophy of total quality management on organizational performance from the point of view of the internal customer/a comparative study: Master’s thesis (unpublished), Administrative Technical College/Baghdad, Central Technical University, Iraq.
Amniattalab, A., & Ansari, R. (2016). The effect of strategic foresight on competitive advantage with the mediating role of organisational ambidexterity. International Journal of Innovation Management, 20(03).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Arokodare, A. (2020), Strategic agility: Achieving superior organizational performance through strategic foresight. Global Journal of Management and Business Research, 20(3).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Faeq, T.A., & Abd, A.M. (2018). The role of strategic intelligence in enhancing organizational performance: An exploratory research for the opinions of the administrative leaders of the University of Fallujah. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 107(24), 108-127.
Haddadin, R. (2014). The effect of customer relationship management on organizational performance using the balanced scorecard: A field study in Jordanian commercial banks, Department of E-Business, College of Business, Middle East University, Jordan.
Hamad, A.R. (2019). The impact of strategic foresight on the quality of strategic decisions: An analytical study of the opinions of senior leaders at the University of Kufa. Iraq: University of Kufa.
Højland, J., & Rohrbeck, R. (2018). The role of corporate foresight in exploring new markets–evidence from 3 case studies in the markets. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 30(6), 734-746.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Hussein, A., & Al-Mamouri, A. (2016). The model path for auditing the performance of the supervisory role of the Central Bank of Iraq on private banks according to the standards of the supreme bodies for financial control and accounting. Journal of Accounting and Financial Studies, applied research in the Federal Office of Financial Supervision - Iraq, 2-36.
Ibrahim, S. & Esa, M. (2017). A study on enterprise risk management and organizational performance. Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology(IJCIET), 8(10), 184-196.
Iden, J., Leif, B.M., & Gunnar, E.C. (2017). The nature of strategic foresight research: A systematic literature review. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 116(1), 87-97.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Kaddouri, F., & Al-Alusi, W. (2018). The role of strategic foresight in achieving organizational excellence according to the perspective of strategic flexibility. Journal of Kirkuk University for Administrative and Economic Sciences, 8(1), 113-140.
Khaled, I., & Younis, Z. (2014). Achieving organizational performance according to human resources management: An exploratory study on a sample of private banks. Al-Danner magazine, Al-Mamoun University College, (6), 402-443.
Kuosa, T. (2014). Towards strategic intelligence: Foresight, intelligence, and policy-making. Dynamic Futures.
Liao, S., & Wu, C. (2009). The relationship knowledge management, organizational learning, and organizational performance. International journal of business and management, 4(4), 64-76.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Nehme, A.H., & Abdel Rahim, S. (2021). The impact of strategic foresight capabilities in green creativity: An exploratory study for the general company for food products. Journal of Economics and Administrative Sciences, 27(125).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Paliokait?, A., Pa??sa, N., & Sarpong, D. (2014). Conceptualizing strategic foresight: An integrated framework. Strategic change, 23(3-4), 161-169.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Peter, M.K., & Denise, G.J. (2013). The practice of foresight in long-term planning. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 101(2013), 49-61.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Ramdani, M., & Hadijah, S. (2020). The influence of knowledge management on organizational performance with ERP implementation as mediator. Dinasti International Journal of Management Science, 1(4), 455-462.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Rohrbeck, R. (2012), Exploring value creation from corporate-foresight activities. Futures, 44(5), 440-452.
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Rohrbeck, R., & Gemünden, H.G. (2008). Strategic foresight in multinational enterprises: building a best-practice framework from case studies. Emerging Methods in R&D Management Conference (pp. 10-20).
Sarpong, D. Amstéus, M.N., Amankwah-Amoah, J., & Appiah, G. (2015). On the influence of organizational routines on strategic foresight. Foresight, 17(5).
Crossref, Google Scholar, Indexed
Received: 18-Dec-2022, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-10988; Editor assigned: 20-Dec-2022; PreQC No. ASMJ-22-10988 (PQ); Reviewed: 03- Jan-2022, QC No. ASMJ-22-10988; Revised: 09-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. ASMJ-22-10988 (R); Published: 25-Jan-2022