Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 1S
The Impact of Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership and Accounting Information System towards the Good Corporate Governance Implementation and its Implication on Fertilizer Distributors' Performance (Survey on Fertilizer Distributor in Indonesia).
Achmad Tossin Sutawikara, Padjadjaran University
Sri Mulyani, Universitas Padjadjaran Bandung and Universitas Singaperbangsa
Karawang Yudi Azis, Padjadjaran University
Ida Farida, Padjadjaran University
Keywords
Internal Audit, Accounting Information System, Ethic, GCG, Structural Equation Modeling, Fertilizer Distributor
Abstract
This research conducts the test on how big the impact of internal audit, ethical leadership and accounting information system towards the Good Corporate Governance (GCG) implementation and its impact on fertilizer distributor performance. This research used descriptive analysis and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)-Lisrel statistical method. The data was collected through questionnaires distributed to and returned from 208 fertilizer distributor in Indonesia as the respondents. The result showed that the role of internal audit, ethical leadership and accounting information system gave positive and significant impact either partially or simultaneously towards GCG. The result also showed ethical leadership and GCG gave a positive and significant impact on distributor's performance. Yet, internal audit and accounting information system did not give a positive and significant impact on distributor's performance.
Introduction
Research Background
GCG is a concept that refers to the process of achieving decision and their implementation that can be accounted for collectively (Mulyani et al., 2018). GCG orders the task assigning, the rights and obligation of the involved parties toward the company, including the shareholders, board of directors, managers, and non-shareholder stakeholder. Yet, the study by Al-ahdal et al., (2020) finds that GCG elements such as transparency and revelation have negative insignificant impact on company performance.
Stakeholder theory explains the interconnected between GCG and performance. Stakeholder theory states that the success of an organization can be valued from the organization ability in creating value-added to all involved parties. Besides, the companies which always strive to fulfill the expectancy of involved parties tend to create more impact on company performance (Donaldson & Preston, 2020). GCG is a mechanism that keeps transparent, accountable, responsible and fair production and distribution to all stakeholders that impact upon company performance. The GCG implementation is supported by various factors that drive the success of the GCG implementation process. Internal audit, ethical leadership and the quality of information systems are critical factors for the success of GCG in in order to improve performance (Harrison & Wicks, 2013).
Internal audit is the party who conducts the independent activity, provides objective assurance, provides consultation to add value and improves organizational operations. Internal audit helps an organization to achieve its goals by taking a systematic and disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control and governance processes (Danescu, Prozan & Prozan, 2015). An effective internal audit function is believed to be able to provide support for improving GCG, risk management and management control. Internal audit is a support for the commissioner audit committee, director and management to develop GCG (Mahzan & Yan, 2014).
Trust, value and leaders' acts are the corporate governance standard and ethical decision making (Banerji, 2014). Ethics in corporate governance refers to company policy in process related to daily operations of the company. The study conducted by Pilkien, Alonderien, Chmieliauskas, Saulius & Müller (2018) states that horizontal leadership power is closely related to governance in a job through trust and control. Chukwujioke (2018) states that there is a positive relationship between Ethical Leadership, Corporate Governance and Organizational Performance. Even Wu, Huang & Gong (2020) states that Ethical Leadership and governance planning are important elements in developing artificial intelligence in China.
Accounting Information is one means for decision making in the company. For the sake of the company, the wider use of information technology is required. Information quality is a level in which data that has been processed by the information system has meaning for its users, in the form of facts and useful values. Information quality consists of relevance and reliability, which are the two primary qualities that make accounting information useful for decision making (Susanto, 2017).
The importance of studies on the determinant elements becomes more crucial to be done in an object like fertilizer distributor. BPK RI states that in its fertilizer distribution, there are some things that do not comply with the provisions. According to an auditor, irregularities are found during the distribution of subsidized fertilizer done by PT PSP as the producers until lines IV, which derail from regulation approved by the Ministry of Agriculture. The Ministry of Agriculture Andi Amran Sulaiman has once estimated the loss experienced by farmers due to a syndicate of illegal fertilizer producers and distributors with amount IDR720 billion from 2007 to April 2016 (BKP Legal Information Section, 2017).
Police officers who are also part of the Fertilizer Control Commission have also found irregularities in the distribution of fertilizers. Pidie Police investigators found that there were parties who controlled subsidized fertilizers even though they did not have a business license as a fertilizer distributor or retailer; and subsidized fertilizer retailers who have retailed the subsidized fertilizers at different designated locations (Zulkarnaen, 2019).
Based on the phenomena that have been described, to ensure that the company is doing well, the company must be able to create a system that can increase the efficiency and productivity of the company by eliminating any existing waste. In other words, management must be able to use strategies to maintain or improve its market position. One strategy is to use technology to get better performance. One strategy is to use technology to achieve better performance.
Identification of Problem
The identification of the problem in this study is: how big the impact of internal audit, ethical leadership, accounting information system towards distributors' performance through the application of GCG simultaneously and partially?
Literature Review
Internal Audit
Internal audit according to Guidance Task Force (GTF) in (Sawyer's, 2003) defines the internal audit as a consulting activity and objective confidence that is managed independently within the organization and is directed by a value-added philosophy to improve the operational in a company. Such audits assist the organization in achieving its objectives by applying a systematic and disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management processes, adequacy of controls, and organizational management. Internal audit is a dynamic and evolving profession that anticipates changes in its operating environment and adapts to changes in organizational structures, processes and technology. Arens (2009) defines internal audit as an independent consulting action and objective which is designed to elevate the value and operational.
The Institute of Internal auditors (2020) similarly defines internal audit as independent consulting activity and objective designed to elevate the value and operational. Internal audit helps the organization in achieving its goal by applying the systematical and disciplined approach to evaluate and increase the effectiveness, risk-governance process, control adequacy, and organization governance. Internal audit is done by the professionals who possess a deep understanding of business culture, system and process. The internal audit will guarantees whether internal control is adequate to mitigate the risk, has an effective and efficient governance process, as well as the purpose and the goal of the organization are achieved.
Ethical Leadership
From an evolutionary perspective, an ethical factor can be the key factor of successful leadership. In an organization, leadership is valued if the leadership functions are carried out based on ethical principles. Ethical leadership will create a more comfortable working environment and vertical-horizontal conflict can be avoided. This is because organizational actors are aware of the existence of guidelines in the form of ethical principles that limit their behavior and actions.
Brown, Trevino & Harrison (2005) define ethical leadership as the demonstration of proper normative behavior through personal acts and interpersonal relationship. The ethical leadership plants, motivates and equip the employees with a sense of responsibility. Ethical leadership practices open communication, clears with its responsibility and clear with expectation on all employees.
Ethical leadership includes the prevalent working environment where the employees feel more spirited in placing their efforts with motivation and commitment (Piccolo et al., cited in Ilyas & Ashaq, 2020). Ethical leadership is defined as principles, beliefs and values, to differentiate right and wrong, which reflects the roots of organizational attitude that form the basis of leader that affects the employees in achieving the organization's goal (Al-Sharafi & Rajiani, 2013).
Accounting Information System (AIS)
The system has components in the form of subsystems. Each subsystem is designed to achieve one or more goals. The goal will not be achieved if the goal of each subsystem is inconsistent with others and the system as a whole. Therefore, in doing the job, the components in a system must be mutually integrated with each other (Mulyani et al., 2018). Meanwhile, Susanto (2017) defines the system as a group in both physical and non-physical form interrelated with each other and work together harmoniously to achieve a certain goal. Accounting information is information resulted from the accounting process. There are an accounting information and non-accounting information. What categories the information as accounting is when the information related to the acts or economy event with money as the goal. Accounting information in the company consists of financial accounting information and management accounting information (Susanto, 2017). Utilization of the system also has a positive impact on the decision-making process (Septriadi, 2020).
Good Corporate Governance (GCG)
Forum for Corporate Governance in Indonesia (FCGI) defines GCG as a set of regulations that control the relationship among shareholders, company managers, creditors, government, employees, as well as the internal and external parties related with rights and obligations; in other words, a system that controls the company. The purpose of GCG is to create an additional value for all important parties (stakeholders). GCG according to (Sutedi, 2011) is a process and structure used by the core of the corporate (stakeholders, commissioners, supervisors and directors) to elevate the success rate and the company accountability in long term aspect by preserving the stakeholders' interest following the regulations and ethical values. Article 1 Letter KEPMEN BUMN No. KEP-117/M-MBU/2002 date 31 July 2002 on the application of GCG on BUMN states that GCG is a process and structure used by the core of BUMN to elevate the success and the accountability by realizing the stakeholder values in long term aspect through preserving the other stakeholders' interest following the regulation and ethical values.
Performance
According to Keban (2008) performance is often defined as the appearance, demonstration or achievement that comes from the job performance or actual performance of the work performance or achievement to be achieved. Upper Echelon Theory in Saragih & Mulyani (2018) says organization performance and strategy can be seen as the reflection of the top management’s conduct. Performance is an important factor in organizational life. Performance is an organizational effort to produce something (Setyaningsih et al., 2020)
Steers & Mowday (2004) state that organization performance as the level that shows how far the work implementation can be carried out in order to achieve the goal (Keban, 2008) states that performance in an organization is defined as the degree of accomplishment or the level of accomplishment for the company's goal in a continuous cycle.
The Impact of Internal Audit on GCG Implementation
The study by Kusmayadi (2012) explained that internal audit that uses independent measures, professional skills, scope of work, the implementation of investigation, internal audit management simultaneously give a significant impact on GCG implementation in BUMN Tbk in Indonesia. Kontogeorgis (2018) found that internal audit is closely related to company governance. Besides, internal audit is a tool that can strengthen the GCG implementation. The study conducted by Ganda, Saputra & Yusuf (2019) showed the positive and significant relationship between internal audit and company governance. Based on this fact, it can be concluded that the effectiveness of the internal audit will push the emergence of better company governance.
The Impact of Ethical Leadership towards GCG Implementation
The study conducted by (Khalid, 2014) which tested the relation between ethical leadership, corporate governance and public and private company governance in Pakistan found the positive and significant relationship between ethical leadership and corporate governance in public and private corporations in Pakistan. Chukwujioke (2018) conducted a study on the role of ethical leadership towards corporate governance, corporate social responsibility and organization performance in Nigeria. The study used the primary data taken from a survey on bank employees in Nigeria. Based on double linear regression analysis, the result shows that ethical behavior brings positive and significant impacts on corporate governance.
Ermongkonchai (2010) found that ethical leadership has a positive impact on developing corporate governance. The similar study was done by the company (Kwakye, Yusheng, Ayamba & Osei, 2018) who studied the ethical leadership on corporate governance in Ghana in which the result reveals the active role of ethical leadership on the success of corporate governance in Ghana. The different result found by (Zvavahera & Ndoda, 2014) which showed that ethical leadership has negative impact on GCG implementation.
The Impact of AIS on GCG Implementation
Study done by (Uyar, 2017) on the impact of AIS on corporate governance in corporate in Turki showed that positive and significant result. (Napitupulu, Situngkir & Harun 2017) conducted the study on the quality of AIS towards the BPR governance in Medan. The qualitative method is used in explaining the role of the good quality of the AIS. Based on the result, it is known that the quality of the AIS plays a role in producing transparent, accountable, and accounted for the financial report. This makes the decision taken will be unbiased. The same result is also found in a study done by Rachmawati (2019) who finds the positive and significant effect of AIS on Bank Perkreditan Rakyat governance in Central Java.
The Impact of GCG Implementation on Distributor’s Performance
Wang (2014) conducted a study on the relation between corporate governance, management accounting and organization performance in corporate in Southeast Asia. The data gained through questionnaires. Based on the testing result with partial least square method, it is known that corporate governance has a positive and significant impact on organization performance. Besides, the result also reveals that management accounting mediates the relation between corporate governance and organizational performance. In the context of education, (Yudianto et al., 2021) good university governance has positively and significantly influence on university performance in Indonesia.
The study done by (Adebayo et al., 2014) was about the relationship between corporate governance and performance on corporate listed in stock exchange in Nigeria. The result showed that corporate governance has a positive and significant impact on performance. Besides, the study was done by (Kamau et al., 2018) showed that Corporate Governance has a positive and significant impact on organizational financial institute performance in Kenya. However, the contradicting result is found by (Haufe, Muschter, Siegert & Böttcher, 2018) who found that corporate governance harms the performance.
The Impact of Internal Audit on Performance
The support of internal audit elevates the sense of responsibility in executive directors and employees and other parties (Eighme & Cashell cited in Gros, Koch & Wallek, 2017). Internal audit department gives reliable service, objective and neutral to management, the board of directors, audit committee, while the important parties hold interest in investment withdrawal, growth, strong leadership, reliable financial performance report and corporate business practice (Ljubisavljevi? & Jovanovi?, 2011).
Prevention and detection of fraud by internal auditors have the role in assessing the effectiveness of an organization; provide input on continuous improvement in performance (Mulyani, 2020). The internal audit gives a big contribution in achieving the corporate goal and strategy implementation in achieving those (Ljubisavljevi? & Jovanovi?, 2011). Besides, the function of internal audit is responsible for strengthening the management and internal audit (Hutchinson & Zain, 2009). Internal audit plays an important role in helping the management to achieve better performance and its purpose is to help the performance become better.
The Impact of Ethical Leadership on Performance
(Assaed et al., 2016) states that ethical leadership plays an important role in developing the organization. This is because the leaders consider every plan and business decision, effectiveness and an on-time decision by taking into account the organizational leadership, in wide specter and in crucial aspect during the business process. So, ethical leadership plays an active role in elevating the organization performance.
(Assaed et al., 2016) studied ethical leadership on organization performance mediates by corporate social responsibilities. The study was done in the banking sector in Pakistan. Random sample technique was used to determine the sample in the study. Significant testing was done to show that ethical leadership has a positive and significant impact on organizational performance. Besides, corporate social responsibilities mediate the relation between ethical leadership and organizational performance. Similarly, an empirical study done by (Mohiuddin & Hossain, 2016) showed the close relationship between ethical leadership and organizational performance.
The Impact of AIS on Distributor Performance
Suzan, Mulyani, Sukmadilaga & Farida (2019) found the success of information system implementation has a direct positive impact on the organizational performance measured with balanced scorecard. According to Chenhall, Hall & Smith (2013) a different AIS design supports organization with different strategy that elevate the organization performance.
The more investment in AIS will make the corporate culture more flexible and stronger which will make the organization capable of facing any changes in the business. AIS is a system that uses organizational financial data, but combine technique and accounting control with that corporate governance has a positive and significant impact on performance. Besides, the study was done by (Kamau et al., 2018) showed that Corporate Governance has a positive and significant impact on organizational financial institute performance in Kenya. However, the contradicting result is found by (Haufe, Muschter, Siegert & Böttcher, 2018) who found that corporate governance harms the performance.
The Impact of Internal Audit on Performance
The support of internal audit elevates the sense of responsibility in executive directors and employees and other parties (Eighme & Cashell cited in Gros, Koch & Wallek, 2017). Internal audit department gives reliable service, objective and neutral to management, the board of directors, audit committee, while the important parties hold interest in investment withdrawal, growth, strong leadership, reliable financial performance report and corporate business practice (Ljubisavljevi? & Jovanovi?, 2011).
Prevention and detection of fraud by internal auditors have the role in assessing the effectiveness of an organization; provide input on continuous improvement in performance (Mulyani, 2020). The internal audit gives a big contribution in achieving the corporate goal and strategy implementation in achieving those (Ljubisavljevi? & Jovanovi?, 2011). Besides, the function of internal audit is responsible for strengthening the management and internal audit (Hutchinson & Zain, 2009). Internal audit plays an important role in helping the management to achieve better performance and its purpose is to help the performance become better.
The Impact of Ethical Leadership on Performance
(Assaed et al., 2016) states that ethical leadership plays an important role in developing the organization. This is because the leaders consider every plan and business decision, effectiveness and an on-time decision by taking into account the organizational leadership, in wide specter and in crucial aspect during the business process. So, ethical leadership plays an active role in elevating the organization performance.
(Assaed et al., 2016) studied ethical leadership on organization performance mediates by corporate social responsibilities. The study was done in the banking sector in Pakistan. Random sample technique was used to determine the sample in the study. Significant testing was done to show that ethical leadership has a positive and significant impact on organizational performance. Besides, corporate social responsibilities mediate the relation between ethical leadership and organizational performance. Similarly, an empirical study done by (Mohiuddin & Hossain, 2016) showed the close relationship between ethical leadership and organizational performance.
The Impact of AIS on Distributor Performance
Suzan, Mulyani, Sukmadilaga & Farida (2019) found the success of information system implementation has a direct positive impact on the organizational performance measured with balanced scorecard. According to Chenhall, Hall & Smith (2013) a different AIS design supports organization with different strategy that elevate the organization performance.
The more investment in AIS will make the corporate culture more flexible and stronger which will make the organization capable of facing any changes in the business. AIS is a system that uses organizational financial data, but combine technique and accounting control with methodologies through IT to track the external and internal report, financial report and trend analysis which will affect the performance (Grande, Estébanez & Colomina, 2011).
(Chang et al., 2019) states that AIS plays an important role in elevating the organizational effectiveness within globally competitive environment. A financial report is still an important source of data for external important parties. Even though its continuous growth and its uses on a larger scale, accounting practices cannot offset the technological advances and the economic growth, which later consistently affect the significance of accounting information (Onaolapo & Odetayo, 2013) says that major accounting fraud reported in developed countries, the changing economy, and some empirical studies show the decrease the significance of accounting information. However (Onaolapo & Odetayo, 2013) concluded in their study that the AIS still possesses relevant value.
Soudani (2012) found that the AIS has a positive impact on the organizational performance in corporate listed in the Dubai stock exchange. A study was done by (Alnajjar, 2017) on the impact of AIS on organizational performance. This study involved 115 UMKM in Uni Emirate Arab. Based on the statistical result, it can be concluded that the AIS gives a positive and significant impact on organizational performance. Besides, (Dmour et al., 2017) found that AIS and organizational performance has a positive and significant relation.
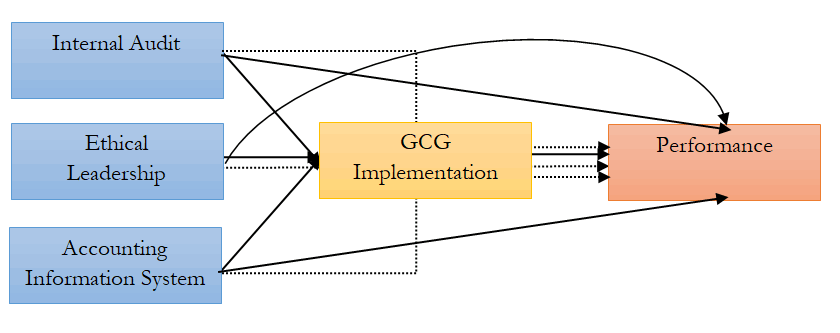
Based on the explanation above, the theoretical framework is drawn below.
Figure 1 : The Impact of Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership And AIS Toward Good Corporate Governance And Its Impact on Fertilizer Distributor Performance
Hypothesis
Hypothesis 1:
1. Internal audit has a positive impact on GCG implementation.
2. Ethical leadership has a positive impact on GCG implementation.
AIS have a positive impact on GCG implementation.
Hypothesis 2:
1. Internal audit has a positive impact on distributor performance.
2. Ethical leadership has a positive impact on distributor performance.
3. AIS have a positive impact on distributor performance.
4. GCG implementation has a positive impact on distributor performance.
Hypothesis 3:
1. Internal audit has a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation.
2. Ethical leadership has a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation.
3. AIS have a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation.
Hypothesis 4:
Internal audit, ethical leadership and AIS simultaneously have a positive impact through GCG implementation.
Hypothesis 5:
Internal audit, ethical leadership and AIS simultaneously have a positive impact on distributor performance.
Hypothesis 6:
Internal audit, ethical leadership and AIS simultaneously have a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation
Method
Object of the Study
Objects in this study are internal audit, ethical leadership, AIS, GCG implementation and distributor performance.
Operationalization Research Variable
| Table 1 Operationalization Varible |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | Indicator(s) | Item |
| Internal audit -Nurhayati, (2017) - Boynton et al., (2002) |
1. Compliance test 2.Verification 3.Protection of assets, 4.Appraisal of control, 5.Appraising performance, 6.Recommending operating improvements 7.Consulting activity |
1-7 |
| Ethical Leadership (Chukwujioke, 2018) | 8.Fairness, 9.Integrity, 10.Ethical guidance, 11.People oriented power sharing, 12.Role clarification 13.Concern for sustainability. |
8-13 |
| AIS Halimatusadiah (2014) (Uyar, 2017) |
14.Policy and procedures of accounting records 15.Difference staff of recording and verify 16.Document always signing by different staff 17.Procedure of existing account 18.Supplementary financial report 19.Financial analyst report used in decision making 20. Performance evaluation by financial analysis report 21.Recorded transaction follow the accounting standard 22.Financial reporting in line with accounting standard 23.Budgeting system 24.Operating budget 25.Operating budget used in decision making |
14-25 |
| GCG Implementation (Uyar, 2017) |
26.Employees know the corporate plan. 27.The goal of organization is clear. 28.Business operations do not depend on a person. 29.Rights for opinion during meeting. 30.Diversity in internal audit member 31.Clear job description, rights and responsibilities 32.Every top management has their own success plan. 33.Planning a good meeting agenda. 34.Have a code of conduct. 35.Standard retrieval system. 36.Job description for every position. 37.Have clear and complete meeting minutes. 38.Fair remuneration policy within the corporate. 39.Employees chosen based on objective criterion. 40.Employees’ performances are rated fairly. 41.Employees’ placement is based on job requirement. 42.Performance rating is referred to standard and clear regulation. |
26-42 |
| Fertilizer distributor performance (Wiklund, 1999) (Stam & Elfring, 2008) |
43.Market share 44.Profit 45.Sales growth 46.Resolutions of agent complaints 47.Amount and types of fertilizer 48.Employees growth 49.Employees competence 50.Turn over employees |
43-50 |
Data Analysis
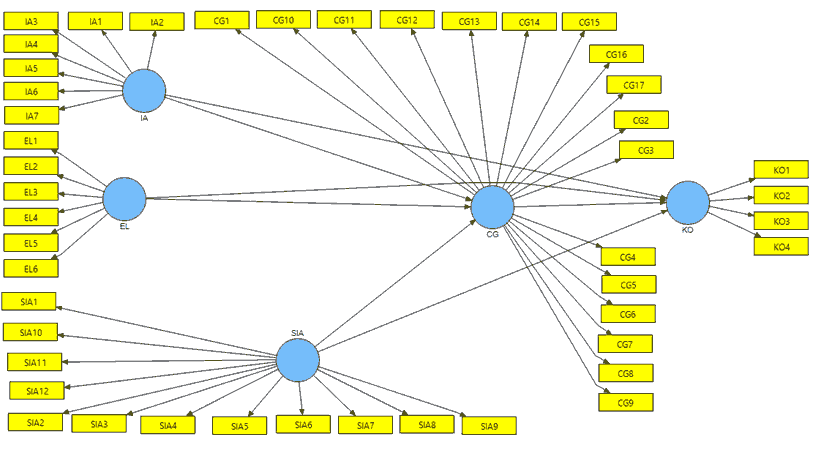
After the model is developed theoretically, next the flowchart is arranged which purpose is to test the impact of free variables (independent/exogenous variables) towards the bound variables (dependent/endogenous variables) whether it is in partial or simultaneous impact. The research method formed in a theoretical study is shown in figure 2 below.
Figure 2 : Conceptual Method on Impact of Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership And AIS on GCG Implementation And Its Impact on Distributor Performance
Result and Discussion
Descriptive Analysis
From 208 questionnaires, categorization is done on respondents’ answer based on the score of the answer. The score categorization is done based on maximum and minimum score divided with the preferred number of categories. The respondents' answer for each statement items is categorized into 5 categories such as very good, good, enough, not good, and bad with the calculation below.
• Maximum score index =Highest scale=5
• Minimum score index =Lowest scale=1
• Interval range =[maximum score - minimum score] : 5 =(5 –1): 5 =0, 8
Below is the calculation result of average scores, deviation standards and relative frequency from each variable:
| Table 2 Analysis of Research Score Variables |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NNo | Variable | Real score | Max score | Avg score | % Realization | %GAP | Criteria |
| 1 | Internal audit | 5343 | 7280 | 3.67 | 73.39 | 26.61 | Baik |
| 2 | Ethical leadership | 4913 | 6240 | 3,94 | 78.73 | 21.27 | Baik |
| 3 | Accounting information | 9368 | 12480 | 3.75 | 75.06 | 24.94 | Baik |
| 4 | GCG implementation | 12765 | 3536 | 3.61 | 72.20 | 27.80 | Baik |
| 5 | Distributor performance | 6684 | 9360 | 3.57 | 71.41 | 28.59 | Baik |
Based on table 2, all variables have total score with average criteria is categorized as good.
Analysis of Path Coefficient
Calculation result of path coefficient can be seen in figure 3: H
The Impact of Internal Audit on GCG
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows that internal audit has a positive and significant impact on GCG implementation. This is proved based on tcount score is higher compared to ttable; hence at the error rate of 5%, it is decided to accept the hypothesis. This means that GCG can be elevated if internal audit effectiveness is elevated.
The Impact of Ethical Leadership on GCG
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about ethical leadership has positive and significant impact toward GCG implementation. This is proved by score tcount variable ethical leadership (4, 81) is higher than ttable (1, 64). Due to the score of tcount higher than ttable, the error rate is 5 %. This means that GCG can be elevated if ethical leadership is elevated.
The Impact of Using AIS toward GCG
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of the hypothesis about the use of AIS has a positive and significant impact on GCG. It is proved by the score tcount AIS variable (9, 72) is higher than ttable (1, 64). Due to the score of tcount is higher than ttable, the error rate is 5 %. This means that GCG can be elevated if the support of AIS is elevated.
The Impact of Internal Audit on Distributor Performance
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about internal audit does not have positive and significant impact on distributor performance. It is proved by the score tcount internal audit variable (0, 54) lower than ttable (1, 64). Thus, the error rate is 5 %.
The Impact of Using Ethical Leadership toward Distributor Performance
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about ethical leadership has a positive and significant impact on distributor performance. It is proved by the score tcount ethical leadership variable (1, 90) higher than ttable (1, 64). Thus, the error rate is 5 %. This means the more impact given by ethical leadership, the more elevated distributor performance will be.
The Impact of Using AIS on Distributor Performance
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of a hypothesis about the use of AIS does not have a positive and significant impact on distributor performance. It is proved by the score tcount AIS variable (-0, 69) lower than ttable (1, 64). Thus, the error rate is 5 %.
The Impact of GCG Implementation on Distributor Performance
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about the GCG implementation has positive and significant impact on distributor performance. It is proved by the score tcount higher than ttable. Thus, the error rate is 5 %.
The Impact of Internal Audit on Distributor Performance through GCG Implementation
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about internal audit has a positive and significant impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. The testing shows the direct and indirect impact. The direct impact of internal audit on distributor performance has a lower score than indirect impact (0.02<0.0677).
The Impact of Ethical Leadership on Distributor Performance through GCG Implementation
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about ethical leadership has positive and significant on distributor performance through GCG implementation. The testing shows the direct and indirect impact. Direct impact of ethical leadership on distributor performance is lower than indirect impact (0, 12 < 0, 2896).
The Impact of Using AIS on Distributor Performance through GCG Implementation
The result of the path coefficient significance test on structural model shows the result of hypothesis about using AIS has a positive and significant impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. The testing shows the direct and indirect impact. The direct impact of AIS on distributor performance is lower than indirect impact (-0, 69 < 0, 2356).
The Impact of Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership, AIS on GCG
Because R2 has a positive score of 0.71 and close to 1, it is decided to accept that internal audit, ethical leadership, AIS have a positive impact on GCG.
The Impact of Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership, AIS on Distributor Performance
Because RTsup has a positive score of 0.48 and close to 1, it is decided to accept that internal audit, ethical leadership, AIS have a positive impact on distributor performance.
The Impact of Using Internal Audit, Ethical Leadership, AIS toward Distributor Performance through GCG
Based on R2 has a positive score of 0.62 and close to 1, it is decided to accept that internal audit, ethical leadership, AIS have a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG.
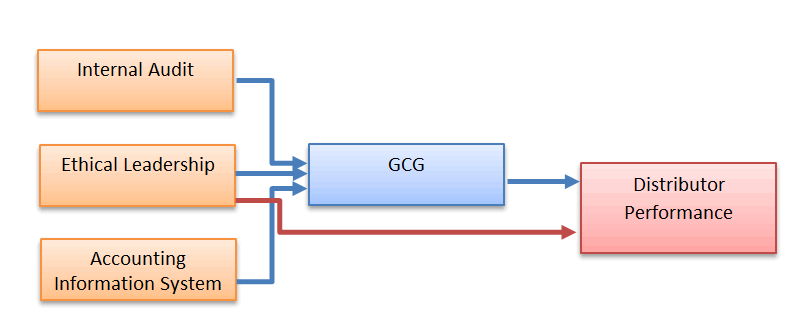
Based on the hypotheses testing above, the findings signify that internal audit and AIS have yet to give a positive and significant impact on distributor performance while ethical leadership has direct relationship with distributor performance. Therefore, the research framework model befitting the findings can be drawn below:
| Table 3 Summary on Path Coefficient Estimation and Statistical Test |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Hypotheses(Ha) | Path(Relations) | t count Score ( =1,64 ) | Impact | Hypotheses Conclusion (H1) |
||
| Direct | Indirect | Total | ||||
| H1a | IA → GCG | 1,76 | 0,09 | - | 0,09 | Accepted |
| H1b | KB → GCG | 4,81 | 0,32 | - | 0,32 | Accepted |
| H1c | SIA → GCG | 9,72 | 0,52 | - | 0,52 | Accepted |
| H2a | IA → KIN | 0,54 | 0,02 | - | 0,02 | Rejected |
| H2b | KB → KIN | 1,90 | 0,12 | - | 0,12 | Accepted |
| H2c | SIA → KIN | -0,69 | -0,04 | -0,04 | Rejected | |
| H2d | GCG → KIN | 8,56 | 0,53 | 0,53 | Accepted | |
| H3a | IA → GCG → KIN | 0,02 | (0,09 x 0,53)=0,0477 | 0,0677 | Accepted | |
| H3b | KB → GCG → KIN | 0,12 | (0,32 x 0,53)=0,1696 | 0,2896 | Accepted | |
| H3c | SIA → GCG→ KIN | -0,04 | (0,52 x 0,53)=0.2756 | 0,2356 | Accepted | |
| Alternative Hypotheses(Ha) | Path(Relations) | R² (+) | Direct | Indirect | Total | Hypotheses Conclusion (H1) |
| H3 | IA, KB, SIA → GCG | R²=0.71 | Accepted | |||
| H4 | IA, KB, SIA → KIN | R²=0.48 | Accepted | |||
| H5 | IA, KB, SIA →GCG →KIN | R²=0.62 | Elevated | Accepted | ||
Discussion
The result of hypothesis testing has been done by using a statistical approach. The discussion on those hypotheses can be seen below.
Hypothesis 1a
The internal audit impacts GCG implementation. This is because the internal audit has become an integrated part of GCG implementation. Internal audit proves to be helpful to management distributor in identifying the weaknesses, failures, and inefficiencies from several programs planned by the concerned corporate. Internal audit also helps the transparency, accountability, responsibility, independence, and fairness from a distributor who performs his function as a fertilizer supply chain for farmers. This result confirms the empirical findings by Kusmayadi (2012) who found that internal audit has a significant impact on GCG implementation in BUMN Tbk in Indonesia. Kontogeorgis (2018) also found out that internal audit is closely related to corporate governance. Internal audit is a tool to strengthen GCG implementation.
Hypothesis 1b
Ethical leadership has a significant impact on GCG implementation. This means the way the distributor stakeholders in handling the collective action from an ethical point of view in the majority and the way to avoid the vandalism by ensuring the correct control in controlling power, authority, and responsibility have been done well. Ethical kindness of leaders has becomes an integrated part in GCG implementation. Leader distributors have become the role model and able to push the application of distributor management system more responsibly.
This result supports the previous findings by Keselman (2012) who said ethical leadership has a role in GCG by helping in motivating, increasing work productivity, employees attitude, and giving the self-satisfaction for the employees themselves Khalid (2014) also found out the positive and significant relationship between ethical leadership and corporate governance in public and private corporations in Pakistan. Further, Chukwujioke (2018) also confirmed the existence of empirical facts from ethical behavior which has a positive impact on corporate governance.
Hypothesis 1c
The use of the AIS has a significant impact on GCG. This means the AIS has become the system that processes data and transactions to produce useful information to plan, control, and operate the fertilizer business in a better way. The AIS integration is efficient in producing information flexibility, increasing the quality of financial reports, giving information on time and reliable to support the planning and decision making in fertilizer distributor business. This is also caused by the support from PT. Pupuk Indonesia in distributor AIS from producers, distributors until the supplier.
The hypothesis result also confirms the study by Uyar (2017) who found the positive and significant impact from the AIS toward corporate governance in corporate in Turkey. Napitupulu, Situngkir & Harun (2017) also found out that high quality of information system plays the role in resulting transparent, accountable and responsible financial reports. This will result into unbiased decision taken by stakeholders. The empirical findings also stated in a study by Rachmawati (2019) who said AIS has a positive and significant impact toward management of Bank Perkreditan Rakyat (BPR) in Central Java.
Hypothesis 2a
Internal audit does not have positive and significant impact on performance. This is based on interviews results that say internal audit in the field is limited to watch dog style; finding offenses, mistakes and it is not enough as solutions over the operational and distributor performance. With the limited internal auditor staff and the work emphasis on the safety aspects of fertilizer distribution from leakage cases and the increase in HET prices, the scope of internal audit work is still unable to assist distributor management in achieving good performance by introducing a systematic approach to improving performance.
The results shows different angle from study by Ahmad (2018) who found the positive and significant relationship between internal audit and organizational performance. In contrast, this result supports the study by Nurhayati (2017) who found that internal audit does not have significant impact on organizational performance. In order to make audit to has relation with performance, Picket (2006) said from the first audit planning, internal audit must be done with risk-based audit so it could be used in real life to handle risks which emerged from demands for better performance and the rivalry intensity. The risks faced by the company include market risk, risk of failure to meet customer needs, and risk of failure to meet stakeholder interests. Internal audit, which is expected to mitigate company risks, also faces risks in its implementation effectiveness such as:
a. Doing the wrong audit
b. Using the wrong audit approach
c. Violating professional standards
d. Doing work at the wrong time
e. Issuing wrong reports and giving wrong basis.
Risk based audit proposed by Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) pushes the performance through management and money control. The audit team is asked to support the operational management by helping manage the risk SOX offence or any rules that will affect the performance (Picket, 2006).
Hypothesis 2b
Ethical leadership from distributor has been able to lead and guide the member towards goal and purposes advantageous for the distributors, members, stakeholders, and people. The head of distributors possesses an ethical value such as honest, trustworthy, fair and attentive. The head also practice transparency and involve in open discussion, promote and appreciate the ethical values in his members. The result confirms Assaed, et al., (2016) who found that ethical leadership plays an important role in developing the organization. Along with these findings, the empirical study done by (Mohiuddin & Hossain, 2016) showed that ethical leadership is closely related to performance.
Hypothesis 2c
AIS do not have a positive impact on distributor performance due to its limitation as administrative; merely as the means to control the operational activities. AIS have yet able to be the enabler or the supporting factor, so the improvement with more useful features in decision making such as an informative dashboard is required. With the improvement in AIS functions, it is expected from AIS to become the alternative practice in meeting the monitoring function and auditing that will facilitate a distributor to improve risk-based improvement. An effort from the cultural aspect is also necessary so that AIS infestation becomes the lever to achieve stronger, more flexible and more persistence corporate culture in facing the fast-changing environment.
This result contradicts the findings by (Suzan et al., 2019) who found that the success in implementing AIS has direct and positive impact toward organizational performance measured with balanced scorecard. Chenhall, Hall & Smith (2013), said that different AIS design will support the organization with a different strategy which will elevate organizational performance.
Hypothesis 3a
Internal audit has a significant impact on performance through GCG implementation. Even though internal audit does not have a direct positive and significant impact on performance, with the intermediary from GCG implementation, internal audit can be the determinant in distributor performance. For internal audit to contribute to distributor performance, the changes in behavior and mindset must be changed from bystander into a partner during operational. Partner during distributor operational is in line with the GCG principle (transparent, accurate, responsible, and free of conflict of interest and naturally serving information).
Hypothesis 3b
Ethical leadership has a significant positive effect on the performance of fertilizer distributors through the implementation of GCG. The results of this study empirically confirm that the ethical leadership of fertilizer distribution through the application of GCG can be the determinant for distributor to achieve the goals and business targets. Distributor leaders who practice ethical behavior as honest, trustworthy, fair and caring people, with the support of governance, have implications for overall distributor performance.
Hypothesis 3c
The AIS has a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. Even though the AIS have yet to directly determine the performance, by making AIS integrated with GCG, distributor performance will be elevated holistically. AIS is not supposed to be a mere operational application required by producers, Pupuk Indonesia, and the Ministry of Agriculture but also become the strategic tool during decision making.
Hypothesis 4
Internal audit, ethical leadership and AIS simultaneously have positive and significant impact toward GCG implementation. This means these three variables have a contribution in forming better management for the distributor. These findings support the study by Kusmayadi (2012) who finds that internal audit, AIS, and ethical leadership simultaneously have a significant impact on GCG implementation on BUMN Tbk in Indonesia.
Hypothesis 5
The result shows that internal audit, ethical leadership, and AIS simultaneously have positive and significant impact on distributor performance. This means these three variables have contributions in improving better distributor performance. It is noted that even though partially speaking internal audit and AIS are not the important factors for distributor performance, however, in whole organizational context these two insignificant variables must be put into consideration and their quality must be preserved.
Hypothesis 6
Internal audit, ethical leadership and accounting system information simultaneously have a positive and significant impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. This means the model, holistically speaking, is an elaboration capable with explaining operational and distributor performance. Distributor management must pay attention to five variables tested in this study to ensure the going concern of distributor corporate. For internal audit to become more useful for performance, an update and the understanding of internal audit and its function as a partner are necessary. Besides, upgrading accounting system information into a friendlier version in decision making is required for its function is not supposed to be limited.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusion
Based on the phenomena, formulation of the problem, hypotheses, and findings done to the distributors, it can be concluded that:
1) Internal audit impacts the GCG implementation because it helps management distributor in identifying weaknesses, failures, inefficiencies from several programs that have been carried out by concerned corporate.
2) Ethical leadership has a significant impact on GCG implementation because ethical values practiced in the organization will ensure the GCG implementation in a better way. The way the distributor stakeholders handle the collective action from the ethical point of view in the majority and the way they avoid the vandalism by ensuring the correct control in controlling power, authority, and responsibility have been carried out ethically.
3) AIS have a significant impact on GCG implementation because AIS has become a system, which processes the data and transaction, to produce useful information to plan, control and operate the fertilizer business well. It is efficient in improving the information generating flexibility, increasing the financial report quality, giving on time and reliable information that supports the planning and decision making in fertilizer distributor business, supported by Pupuk Indonesia Corporate in AIS distributor from producer until supplier.
4) The internal audit does not have a significant impact on performance because its function is similar with watchdog. With the limitation on the safety aspect and the risk of leakage, internal audit has yet to help distributor management to achieve better performance.
5) Ethical leadership has been able to lead and guide the members toward the goal and purposes that will be advantageous to the involved parties because the leader practices the ethical values, transparency, involves in open discussion, promote and appreciate the ethical values among members.
6) AIS do not have a positive impact on distributor performance for it is still limited as administrative. AIS role can be elevated with more useful features in decision making such as an informative dashboard. Any improvement on AIS function will facilitate a distributor to improve risk-based improvement. An effort from the cultural aspect is necessary so that AIS infestation becomes the lever to achieve stronger, more flexible and more persistence corporate culture in facing the fast-changing environment.
7) The internal audit does not have a direct positive and significant impact on performance. For internal audit to contribute to distributor performance, the changes in behavior and mindset must be changed from bystander into a partner during operational. Becoming a partner during distributor operational is in line with the GCG principle.
8) Ethical leadership has a significant positive effect on the performance of fertilizer distributors through the implementation of GCG. The results of this study confirm empirically that the ethical leadership of fertilizer distribution through the application of GCG can be the determinant for the fertilizer distributor to achieve its goals and business targets. Practicing ethical values with the support of GCC will have implications for overall distributor performance.
9) AIS have a positive impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. Even though the AIS has yet to directly determine the performance, by making AIS integrated with GCG the distributor performance, distributor performance will be elevated holistically. AIS are not supposed to be a mere operational application but also become the strategic tool during distributor management decision making.
10) Internal audit, ethical leadership and AIS simultaneously have positive and significant impact toward GCG implementation. They contribute in forming better management for the distributor.
11) Internal audit, ethical leadership, and AIS simultaneously have positive and significant impact on distributor performance. They contribute in improving better distributor performance. Even though partially speaking internal audit and AIS are not the important factors for distributor performance, however, these two insignificant variables must be put into consideration and their quality must be preserved.
12) Internal audit, ethical leadership and accounting system information simultaneously have positive and significant impact on distributor performance through GCG implementation. This means the model, holistically speaking, is an elaboration capable in explaining operational and distributor performance. Distributor management must pay attention to five variables tested in this study to ensure corporate going concern.
Limitation of the Study
This study has yet to reveal all variables that impact GCG which affect distributor performance. It is hoped further study is conducted on other variables such as commitment from organization, culture organization, internal control and others so that the distributors' role can be optimalized in ensuring availability, accuracy, and price suitability in supporting the productivity of the national agricultural sector.
References
- Adebayo, M., Ibrahim, A.O., & Bakare. (2014). Good corporate governance and organizational performance: An empirical analysis Journal, I., & Vol, S. S. Department of Accounting and Finance Faculty of Management Sciences Lagos State University Nigeria Department of Economics Faculty, 4(7), 170–178.
- Ahmad, B.O. (2018). The effect of internal audit on organizational performance: An empirical exploration of selected Jordanian banks. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting, 9(14), 137–144.
- Al-ahdal, W.M., Alsamhi, M.H., Tabash, M.I., & Farhan, N.H.S. (2020). The impact of corporate governance on financial performance of Indian and GCC listed firms: An empirical investigation. Research in International Business and Finance, 51(August 2019), 101083.
- Al-sharafi, H., & Rajiani, I. (2013). Promoting organizational citizenship behavior among employees - The role of leadership practices. International Journal of Business and Management, 8, 47–54.
- Alnajjar, D.M. (2017). Impact of accounting information system on organizational performance: A study of SMEs in the UAE. Global Review of Accounting and Finance, 8, 20–38.
- Apago PDF Enhancer Apago PDF Enhancer. (2009).
- Assaed, D., Butt, A., Naseer, A., & Ayaz, M. (2016). Impact of ethical leadership on organizational performance and mediating role of corporate social responsibility: Evidence from banking sector of Pakistan. 2.
- Literature Review. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, 5(6), 25–37.
- Banerji, P. (2014). Ethical preferences of transformational leaders: An empirical investigation. (June).
- Bank, K. (2012). Determination of internal audit in realizing good corporate governance and its implications, 16(1), 147–156.
- Brown, M., Treviño, L., & Harrison, D. (2005). Ethical Leadership: A social learning perspective for construct development and testing. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 97, 117–134.
- Bumn, G.P., Heryana, T., & Novrita, V. (2009). 961–972.
- Chang, Y.T., Chen, H., Cheng, R.K., & Chi, W. (2019). The impact of internal audit attributes on the effectiveness of internal control over operations and compliance. Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics, 15(1), 1–19.
- Chenhall, R.H., Hall, M., & Smith, D. (2013). Performance measurement, modes of evaluation and the development of compromising accounts. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 38(4), 268–287.
- Chukwujioke, K. (2018). Effect of ethical leadership on corporate governance, performance and social responsibility : As study of selected deposit money banks in Benue State, Nigeria, 2, 19–35.
- Danescu, T., Prozan, M., & Prozan, R.D. (2015). The valances of the internal audit in relationship with the internal control–Corporate governance. Procedia Economics and Finance, 26(15), 960–966.
- Dmour, A., Al-Fawaz, K., Aldmour, R., & Al-lozi, N. (2017). Accounting information system and its role on business performance: A theoretical study. Journal of Management and Strategy, 8, 79.
- Donaldson, T., & Preston, L.E.E.E. (2020). The stakeholder theory of the corporation: Concepts, Evidence, and Implications Author (s): Thomas Donaldson and Lee E. Preston Source: The Academy of Management Review, 20, 1, 65-91.
- Ganda S.I., & Yusuf, A. (2019). The role of internal audit in Corporate Governance and contribution to determine audit fees for external audits. Journal of Finance and Accounting, 7(1), 1–5.
- Grande, E.U., Estébanez, R.P., & Colomina, C.M. (2011). The impact of Accounting Information Systems (AIS) on performance measures. The International Journal of Digital Accounting Research, 11, 25–43.
- Gros, M., Koch, S., & Wallek, C. (2017). Internal audit function quality and financial reporting: Results of a survey on German listed companies. Journal of Management and Governance, 21(2), 291–329.
- Harrison, J.S., & Wicks, A.C. (2013). Stakeholder theory, value, and firm performance. Business Ethics Quarterly, 23(1), 97–124.
- Haufe, H., Muschter, K., Siegert, J., & Böttcher, H. (2018). EndNote. Scientia Horticulturae, 239, 26–34.
- Hutchinson, M., & Zain, M. (2009). Internal audit quality, audit committee independence, growth opportunities and firm performance. Corporate Ownership and Control, 7.
- Kamau, G., Aosa, E., Machuki, V., & Pokhariyal, G. (2018). Corporate governance, strategic choices and performance of financial institutions in kenya, 13(7), 169–178.
- Keselman, D. (2012). Ethical leadership. Holistic Nursing Practice, 26(5), 259–261.
- Khalid, W. (2014). The study of relationship among ethical leadership and organizational performance in corporate governance in the Public and private sectors of Islamabad/Rawalpindi, Pakistan. European Journal of Business and Management Www.Iiste.Org ISSN, 6(14), 153–162.
- Kontogeorgis, G. (2018). The role of internal audit function on corporate governance and management, 8(4), 100–114.
- Kwakye, O., Yusheng, K., Ayamba, E.C., & Osei, A.A. (2018). Impact of ethical behavior on corporate governance of firm’s performance in Ghana. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 6(06), 456–466.
- Ljubisavljevi?, S., & Jovanovi?, D. (2011). Empirical research on the internal audit position of companies in Serbia. Economic Annals, 56(191), 123–141.
- Mahzan, N., & Yan, C.M. (2014). Harnessing the benefits of corporate governance and internal audit: Advice to SME. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 115(Iicies 2013), 156–165.
- Mohiuddin, G., & Hossain, M. (2016). Ethical leadership: Its issues and impacts in organization. International Journal of Islamic Management and Business, 2(2), 1–9.
- Mulyani, S., Suzan, L., Sagara, Y., Kasim, E.Y., Karya, C.D., Azizah, Z.N., & Maulidina, A.M. (2018). Accounting information systems: Applications in the public sector. A Practical Guide to the Analysis and Design of AIS Implementation in the Public Sector, 285.
- Mulyani, S., Munir, D.A., Akbar, B., Yosep, M., & Sudrajat. (2020). The significance of the internal control system implementation on village government performance, 36, 1278-1291.
- Napitupulu, I.H., Situngkir, A., & Harun, A. (2017). Achieving good corporate governance in rural banks: Contribution of quality Accounting Information Systems, Effectiveness of Internal Controls and ….
- Onaolapo, A.A., & Odetayo, T.A. (2013). Effect of accounting information system on organizational effectiveness: A case study of selected construction companies in Ibadan, Nigeria. American Journal of Business and Management, 2(1), 183.
- Pilkien, M., Alonderien, R., Chmieliauskas, A., Saulius, Š., & Müller, R. (2018). The governance of horizontal leadership in projects, 36, 913–924.
- Receipt, A.D., Asset, C., Model, P., & Added, E.V. (2018). Frequently used symbols and units. In Fundamentals of Electroceramics.
- Rusman. (2017). The effect of state property management on the quality of the Aceh government's financial reports (Study at the Aceh Revenue and Wealth Service) Sties, 8(1), 66–80.
- Septriadi, D., Mulyani, S., Zarkasyi, W., & Sukmadilaga, C. Management Accounting Information System in Gas Station Business, 25(2), 244-254.
- Setyaningsih, S.D., Mulyani, S., Akbar, B., & Farida, I., (2020). Influence of internal control implementation on performance with financial reporting quality as the intervening variable. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology
- Saragih, T.A.A., & Mulyani, S. (2018). Analysis of differences in the performance of local governments led by regional heads with entrepreneurial and non-entrepreneurial backgrounds. BanqueSyar'i, 4, 69–86.
- Soudani, S. (2012). The usefulness of an accounting information system for effective organizational performance. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 4.
- Stam, W., & Elfring, T. (2008). Entrepreneurial orientation and new venture performance: The moderating role of intra- and extra industry social capital. Academy of Management Journal, 51(1), 97–111.
- Steers, R.M., & Mowday, R.T. (2004). The future of motivation theory, 29(3), 379–387.
- Susanto, A. (2017). Accounting information system understanding concepts structured.
- Sutedi, A. (2011). Good corporate governance.
- Suzan, L., Mulyani, S., Sukmadilaga, C., & Farida, I. (2019). Empirical testing of the implementation of supply chain management and successful supporting factors of management accounting information systems.
- International Journal of Supply Chain Management, 8(4), 629–641.
- Keban, Y.T. (2008). Six Strategic Dimensions of Public Administration, 305.
- The Institute of Internal Auditors. (2020). About Internal Auditing.
- Uyar, A. (2017). Impact of the accounting information system on corporate governance: Evidence from Turkish non-listed companies impact of the accounting information system on corporate governance, 11(1), 9–27.
- Wang, D.H. (2014). Linkages among corporate governance, management accounting practice and organizational performance: Evidence from a Southeast Asian Country. Romanian Economic and Business Review, 9(1), 63–81.
- Wiklund, J. (1999). The sustainability of the entrepreneurial orientation- performance relationship (1992), 37–48.
- Wu, W., Huang, T., & Gong, K. (2020). Ethical principles and governance technology development of AI in China. Engineering.
- Yudianto, S., Mulyani, M., Fahmi., & Winarningsih, S. (2021). The influence of good university governance and intellectual capital on university performance in Indonesia. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 10(1), 57-57
- Zvavahera, P., & Ndoda, G.R. (2014). Corporate Governance and Ethical Behavior: The case of the Zimbabwe Broadcasting Corporation. Journal of Academic and Business Ethics, 9, 1–9.