Research Article: 2024 Vol: 30 Issue: 5
The Impact of Celebrity Presence and Performances on Event Sponsorship and Brand Associations
Ahmed Mohammed Alamoudi, King Adbulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
Citation Information: Alamoudi, A M (2024). The Impact of Celebrity Presence and Performances on Event Sponsorship and Brand Associations. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 30(4), 1-36.
Introduction
Contemporary marketing has incorporated celebrity culture and branding to leverage its influence on customers (Chiu & Ho, 2023). For instance, celebrity performances during events have transcended the main focus on providing entertainment to become an integral tool for brand associations during sponsorships. This finding has increased the number of celebrities being used to perform during events without focusing on entertainment alone but also targeting influencing customer perceptions. Celebrities are individuals characterized by charisma and influence whose presence can improve brand awareness and visibility (Brooks et al., 2021). This opportunity has been tapped by sponsorships that exploit celebrity stardom to create a captivating narrative that targets to influence consumer behavior and perceptions. In the context of broad celebrity influence, the interlink between brand associations and sponsors has become an important research topic in the field of marketing. According to Choi and Rifon (2012), the persona of a particular celebrity acts as a gravitational pull on the audience, attracts their attention, and provides an opportunity for brands to align their products. This is consistent with another finding that celebrity performance improves the level of audience association with the brand (Min et al., 2019).
The new paradigm of using celebrity performances to influence brand associations is a complex activity that requires proper research. For example, the interplay between a particular celebrity, brand identity, and sponsorship event needs to be clearly explained. Jun et al. (2023) have argued that celebrity performance heightens brand visibility and associations. However, the impact of celebrity performance on brand awareness is influenced by certain risks, particularly from public opinion, and this can negatively affect the intended marketing benefits.
Background of the study
The emergence of corporate sponsorship has become an integral marketing strategy that was motivated by philanthropic reasons (Blake et al., 2019). As professional sports continue to evolve, sponsorship has become integral in promoting brand awareness. In the traditional context, sponsors were mainly used to promote their brands. In the contemporary world, sponsorships have evolved beyond logo placement to incorporate marketing objectives (Dreisbach et al., 2017). For instance, Hyundai has sponsored the Superbowl LIII and displayed its logo on NFL communication channels. Sponsors are currently using sports events to create themed zones and leverage the advantages of social media (Sportbusiness, 2020; Hyundai USA, 2018).
Incorporating celebrities in marketing has become an important marketing strategy for improving brand awareness and image. Previous studies by Friestad et al. (1995) and Moore et al. (1994) have shown that using celebrities in marketing increases the level of awareness and creates skepticism or disgust. As a strategy to minimize the negative effects, marketers are using celebrity presence and performance during events to create a neutral context to support brand awareness. This has created a new approach to using celebrities in marketing where they are featured in real-life situations. According to Jia et al. (2018), fans follow their preferred celebrities on social media, and they are able to share with their friends and promote brand awareness. Several studies, like Russell and Rasolofoarison (2017), have researched the impact of celebrity endorsements on brand awareness. However, the impact of their presence and performance on events still needs to be explored.
Keller (1993) and Keller (2013) are pioneer studies that attempt to describe how customers develop attitudes on specific brands. According to Keller (1993), brand associations are information components of a specific brand that remain in the memory of consumers. Brand associations are created through direct brand experience, communication, and inferences. According to McCracken (1989), celebrities have brand associations that improve image transfer to the brand. In the context of sponsorship events, the presence and performance of celebrities ignite the brand awareness effects when the brand chooses a specific personality (Keller, 1998).
Statement of the Problem
Studies about the impact of celebrity presence and performance on brand associations during sponsorship events need to be more detailed. As argued by Wakefield et al. (2020), the metrics for measuring the effectiveness of sponsorships need to be properly understood and need to focus on creating activations. This can be resolved by assessing the impact of celebrity presence and performance during sponsorship events. In a similar study, Meenaghan et al. (2013) argued that previous studies have measured sponsorship events like product recalls and attitudes, but they need to address its impact on brand association. In a recent study, Cornwell (2019) proposed an investigation on consumer brand engagement with sponsors as pivotal in determining its impact. Whereas specific celebrities connect with different audiences, it needs to be clearly understood how mere performances and presence play a role in developing brand associations for the whole audience.
Studies have shown that celebrity performance and presence are critical in enhancing brand image and awareness during sponsorships (Rahman, 2018; Min et al., 2019; Agarwal & Garg, 2021). However, there is a need to understand the influence of celebrity influence beyond inference-based brand associations during sponsorship events. In addition, social media platforms have influenced the impact of celebrities in brand promotion, and this needs to be incorporated into sponsorship studies (Delia & Armstrong, 2015). Therefore, there is a need to investigate the impact of celebrity presence and performance on sponsorship events in reinforcing brand associations to fill this literature gap. This study seeks to assess the interconnections of celebrity presence, event sponsorships, and brand associations.
The research aims and objectives
Aims
The study aims to investigate the impact of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship by focusing on brand associations. The study will serve as an important opportunity to identify the dynamics and strategic considerations that are required for leveraging the opportunity of celebrity presence and performance in enhancing brand associations. This can be achieved through the following objectives:
Objectives
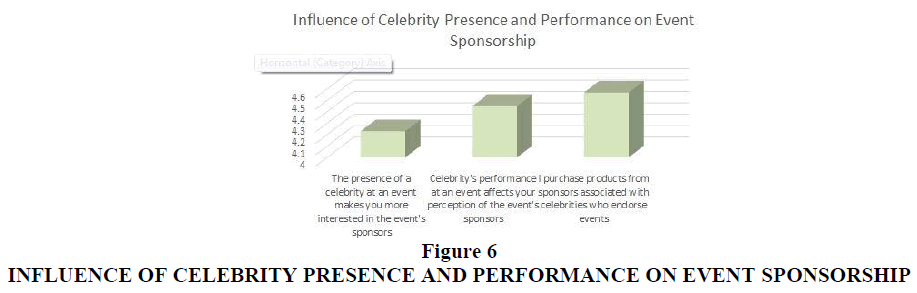
1. To examine the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship.
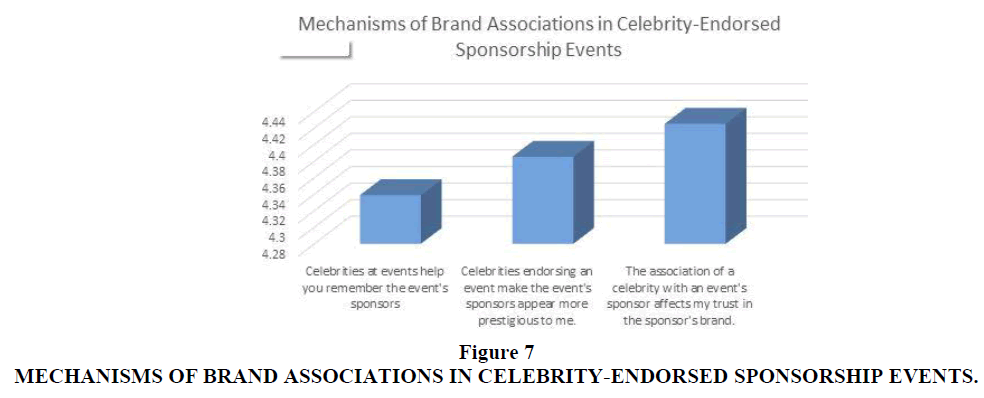
2. To investigate the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events.
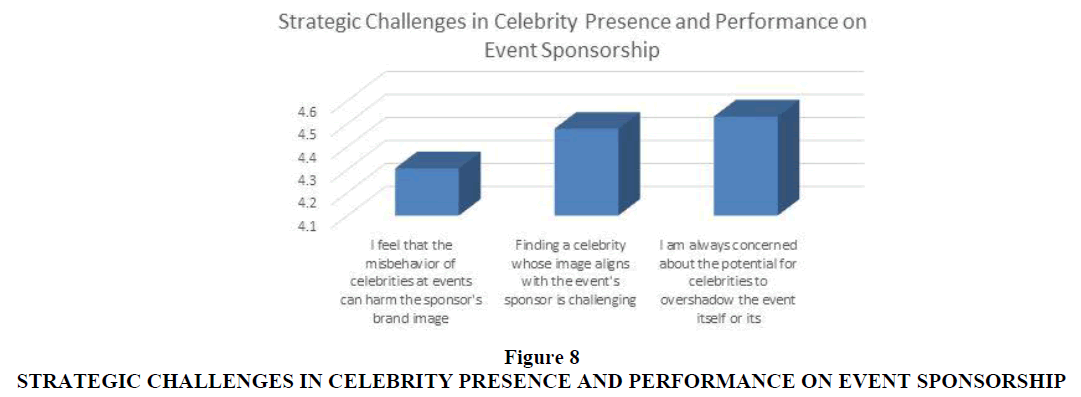
3. To identify strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship.
Research Questions
The scope of the study will focus on evaluating the multifaceted volunteer perspectives to long-lasting legacies from events. This study proposes to use an online-based interview that the following research questions will guide;
1. What is the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship?
2. What are the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events?
3. Which challenges influence celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship?
Implications and contributions to knowledge
Marketing strategies have become an important source of competitive advantage, and this can be improved through understanding the impact of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship. It is significant because it will provide important insights into event management and consumer behavior that are aligned with the evolving marketing landscape. For instance, as the marketing landscape evolves, the incorporation of celebrities during event sponsorship will be an important strategy for optimizing marketing to create a strong competitive environment for brands. According to Adam and Hussain (2017), celebrities hold a gravitational pull in influencing consumer behavior, and this can be tapped to improve celebrity endorsements and brand associations because it gives insights into how consumers perceive brands, which leads to effective campaigns. Thirdly, this study is important in developing event sponsorship strategies because it will show the effectiveness of different approaches that will support decision-making. Lastly, this study has academic and practical implications because it will fill a literature gap by providing empirical evidence in the field of marketing and event management studies. The findings of this study will provide actionable recommendations for the implementation of best practices for marketers and sponsors to achieve optimal brand associations.
Literature Review
Modern marketing has adopted a new paradigm from traditional approaches to adopt celebrity incorporation and event sponsorships as integral to success. This chapter provides a critical analysis of the impact of celebrity presence on brand associations. In particular, it will guide how celebrities can be used during events to influence positive consumer behavior and eliminate complexities that exist in implementing these strategies.
Celebrity Endorsements
Celebrity endorsements are a widely employed marketing strategy aimed at harnessing the popularity, influence, and trustworthiness of well-known figures to promote products, services, or brands. This tactic rests on the premise that the positive qualities associated with the celebrity will transfer to the endorsed product, shaping consumer perceptions and behaviors. Key aspects of this strategy include enhancing brand awareness and visibility through the high profile of celebrities, establishing credibility and trust as celebrities are often seen as reliable figures, influencing consumer behavior through the power of celebrity endorsement, and creating emotional connections with consumers by tapping into the existing bonds between celebrities and their fans. Overall, celebrity endorsements play a significant role in shaping consumer preferences and driving sales by leveraging the fame and appeal of well-known personalities.
Traditionally, endorsement involves aligning a celebrity with a brand to endorse the latter in return for compensation (Erdogan, 1999). While this conventional form remains the most widely recognized type of celebrity endorsement, there are now alternative celebrity-brand associations, including product placement at public celebrity events (Russell et al., 2006), social media promotions (Jin and Phua, 2014), and celebrity branding (Santos et al., 2019). Although these practices are not entirely new, they are now being employed more frequently, prompting brand managers to develop their communication strategies by systematically considering the full spectrum of these practices.
In traditional advertising endorsement, celebrities leverage their image and renown to promote a brand within the confines of an explicit partnership acknowledged by consumers (McCracken, 1989). Presently, they also engage in interacting with their fan base through social networks, transforming into genuine communication channels utilizing their platforms and personal updates to convey brands' messages (Hsu and Tsou, 2011). Nevertheless, brands occasionally endeavor to conceal these contractual associations with influencers, aiming to covertly exploit celebrities' credibility and persuasive influence to endorse their offerings and foster connections with potential consumers (Kim and Ko, 2012). Micro-celebrities, therefore, offer videos or articles blending brand promotion with authentic and personal opinions (De Veirman et al., 2017; Abidin and Ots, 2015). Unlike celebrity endorsements in conventional advertising, the tone micro-celebrities adopt to endorse a brand is informal and emotive, aligning with the language familiar to their audience. Consequently, consumers find it challenging to discern between a micro-celebrity's personal viewpoint and brand promotion (Abidin and Ots, 2015).
Consumers, however, place significantly more trust in recommendations from friends than in any other form of communication (Abidin, 2016). These recommendations are particularly valuable for brands, yielding returns on investment up to 11 times higher than other forms of advertising (Kirkpatrick et al., 2018). The endorsed brand reaps substantial benefits from this novel approach of utilizing micro-celebrities for brand promotion (De Veirman et al., 2017). In Saudi Arabia, influencer events have been marketed by individuals such as Rawkan Binbella and Mr. Moudz with the tourism sector relying on these influential activities in increasing the attractiveness of the country’s board. The influencers have used different hashtags including #VisitSaudi projects. The visibility of the tourism industry in Suadi Arabia has been influential in attracting consumers to the region, which is essential in realizing increased revenue from tourism.
In line with the theory of associative learning, consistent and simultaneous exposure to stimuli leads to the establishment of associative networks within an individual (Collins and Loftus, 1975), shaping their attitudes and perceptions of the environment (Domjan and Burkhard, 1986). The repeated presentation of a brand alongside a celebrity triggers the activation of corresponding memory nodes in consumers (Halonen-Knight and Hurmerinta, 2010). Consequently, celebrity endorsement can be seen as a specialized form of conditioning applied to brands (Fleck and Maille, 2010). Celebrities possess complex images comprising various symbols, meanings, and emotions associated with their status and activities (Carroll, 2009). Through repeated associations, the perceptions and emotions evoked by the celebrity become linked with the endorsed brand, potentially enhancing its attractiveness (Choi and Rifon, 2012). Traditionally, attribute transfer has been perceived as a one-way process with attributes carrying either positive or negative connotations (Roy, 2018). Endorsement reinforces the brand's socio-psychological associations (Carroll, 2009; Thomson, 2006), embedded in the semantic significance within consumers' minds (Galli and Gorn, 2011). However, the evolving nature of endorsement practices challenges the foundations of this model (Djafarova and Trofimenko, 2018), as well as its connection to conventional learning paradigms, suggesting new avenues for research.
Celebrity endorsements serve as powerful advertising tools that significantly impact consumer attitudes and intentions to purchase. Research by Roth Capital Partners, highlighted by eMarketer, reveals that 78% of Millennials are less inclined to buy products solely based on celebrity endorsements (McCormick 2016). Instead, they are more swayed by peer-to-peer interactions on social networks like Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram (Chadha 2017). Yet, when Millennials follow celebrities who promote products on these platforms, they tend to pay more attention, often emulating the celebrities' styles as part of their personal identity development (McCormick 2016). Moreover, they are more persuaded by endorsements when the celebrities' advertised image aligns with their own self-perception (Lippe 2001). Understanding Millennials is crucial for retailers aiming to expand their market share, given their significant purchasing power. Retailers strive to gather extensive knowledge about this demographic group, particularly college students who comprise the youngest portion of this cohort. College students represent a key target market due to their substantial influence as trendsetters, brand loyalty, early adoption of new products, and potential for higher future income (Wolburg and Pokrywczynski 2001).
Chadha (2017) mentions that it is critical in differentiation and positioning within competitive markets. By aligning the unique characteristics of a celebrity with the brand's positioning, they can set it apart from competitors. Moreover, celebrities frequently participate in product launches and promotions, generating excitement and media coverage that contribute to successful launches. Strategic selection of celebrities based on their appeal to the target audience ensures alignment with the demographic or psychographic characteristics of the market, enhancing the effectiveness of the endorsement. Additionally, celebrity endorsements lead to enhanced brand recall, as consumers are more likely to remember and consider products featuring well-known faces.
Marketers acknowledge the benefits that celebrity endorsements bring, including credibility-building, trust-fostering, and attention-drawing, all of which can translate into increased sales. It is essential for brands to maintain consistency between the endorser and the brand to establish a strong personality and identity. Furthermore, they should view celebrity endorsements as long-term strategic decisions that impact the brand, respecting local needs, wants, and tastes while endorsing globally. Successful endorsements occur when the endorser is genuinely interested in the affiliation with the brand, not just for financial gain but also for personal image building. With many celebrities venturing into fashion and accessories businesses and more on the horizon, celebrity endorsements continue to be a prominent strategy in the marketing landscape.
The effectiveness of celebrity advertising is contingent upon various factors, including the alignment between the celebrity and the brand, the authenticity of the endorsement, and the target audience. Assessing the effectiveness of celebrity advertising involves several considerations: Firstly, the seamless fit and relevance between the celebrity and the brand contribute significantly to consumer resonance. Authenticity is paramount, as consumers respond best to endorsements that genuinely reflect the celebrity's belief in and use of the product. Credibility and trustworthiness are also pivotal, with a positive public image enhancing consumer trust in the endorsement. Understanding the target audience ensures that the celebrity resonates with the intended demographic or psychographic segment. Additionally, the nature of the product or service being endorsed influences the suitability of celebrity advertising. While traditional media channels remain influential, celebrities can wield considerable impact on social media platforms, especially among younger audiences. Staying attuned to public perception and current trends is essential for maintaining the relevance of endorsements. However, brands must also weigh the risk of controversy associated with celebrity endorsements against their potential benefits. Brands can maximize the effectiveness of celebrity advertising campaigns and enhance consumer engagement and brand loyalty.
A well-aligned celebrity endorsement can establish a potent connection, bolstering brand awareness, credibility, and consumer trust. Conversely, a mismatch may evoke confusion, skepticism, or negative perceptions. Thus, meticulous evaluation of the harmony between the celebrity's persona and the brand image is imperative for a fruitful endorsement strategy. Companies must ensure synergy between the endorsed brand and the endorser to profoundly influence consumer perceptions and foster positivity toward the brand. Continual monitoring of the endorser's behavior, conduct, and public image is vital to mitigate potential negative repercussions. Engaging celebrities who don't endorse competing or vastly different products ensures a coherent transfer of identity between the endorser and the brand. It's crucial to remember that the brand should be the focal point, not overshadowed by the celebrity. Celebrities should complement ideas, not substitute them; a brand lacking focus will struggle to find an appropriate celebrity match. Additionally, once a brand engages in a celebrity campaign, extricating the brand from the celebrity's shadow can be challenging, emphasizing the importance of thoughtful planning and execution in celebrity endorsements.
The initial phase of corporate learning concerning global market competition entails grasping consumer perceptions (Craig & Douglas, 1996). According to Guthrie & Kim (2009), brand perception hinges on customers' emotional responses, trust, and loyalty towards a product, alongside its usage, representation, and distinctiveness. Kotler & Keller (2009) and Asch & Wolfe (2001) conceptualized perception as the mental processing of consumers' selection, organization, and interpretation of information, with attention directed towards fulfilling consumer needs. Kotler & Keller (2009) argued that before perceiving anything, consumers must first be exposed to a product and pay attention to it. Band perception correlates with brand recognition, wherein consumers can recall and distinguish the brand under various circumstances (Wonglorsaichon & Sathainrapabayut, 2008). Liz (2010) asserted that “a brand is all about perception,” suggesting that potential customers are not easily swayed by a company's efforts to promote their brand. Liz (2010) also contended that with a strategic focus, a company can indeed shape how its personal brand is perceived, thereby satisfying both existing and potential customers.
Furthermore, many people often look up to celebrities they consider successful, aspiring to adopt their values and lifestyles (Sami 2006). Frazer and Brown (2002) observed that these individuals selectively adopt certain admired traits and behaviors from celebrities to incorporate into their personal lives. Celebrity fans may mimic specific behaviors of a celebrity to boost their own self-esteem, which can extend to copying their speech, dress style, way of communicating, and the brands they prefer to buy (Sami 2006). This mimicry underscores the effectiveness of celebrity endorsements and the significance of celebrities in contemporary marketing strategies. Earlier studies have documented the positive impacts of celebrities on choices in apparel, products, purchasing actions, and even adopting healthier lifestyles (Till and Busler 1998). It was also discovered that in the United States, celebrity endorsements tend to influence women more than men (Howard 2002). Among generational groups, Millennials show a greater tendency to heed celebrity endorsements and buy products like food, alcohol, and clothing promoted by them (Pringle and Binet 2005). Moreover, compared to Baby Boomers, Millennials are four times more likely to be influenced by celebrity endorsements (Barton et al. 2014).
Many advertisers emphasize the necessity of choosing the right celebrity for an ad campaign to be successful, as consumers often expect the celebrity to be highly recognizable and resonate positively, ensuring that their image aligns well with the product being promoted (Choi and Rifon 2012). In contrast, movie stars generally do not effectively endorse sports products. The concept of celebrity-brand congruence plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of endorsements (Choi and Rifon 2007). When there is a strong alignment between the celebrity and the product, it leads to more favorable ad evaluations, which can increase the credibility of the endorsement and overall advertising effectiveness (Davies and Slater 2015). This alignment helps transfer the celebrity’s cultural significance to the product, potentially influencing consumer purchases. Additionally, research has found that celebrities often have a greater effect on consumer attitudes and buying decisions than non-celebrity spokespeople (McCormick 2016). Literature also suggests that consumers tend to trust family and friends more than salespeople, and interestingly, they may view celebrities similarly to friends, despite not knowing them personally (Erdogan 1999; Escalas and Bettman 2017).
Initially, it seems reasonable to assume that a strong alignment between a celebrity and a brand would enhance the brand's image, and that a stronger connection would lead to a greater impact on the brand. Moreover, the more suitable the celebrity appears for the brand or product, the more relevant and fitting the pairing is seen, leading to a more positive reaction in terms of advertising attitudes and purchase intentions (Batra and Homer 2004; Till and Busler 2000). However, one might consider a more intricate dynamic and explore a different theory (for example, that some misalignment might positively influence advertising responses, especially concerning the brand image). Indeed, a slight mismatch between expectations and reality might be seen as intriguing and positive, as it could engage people’s interest and prompt them to think more deeply about the advertisement (Lee and Thorson 2008). A less than perfect match between a celebrity and a brand could prove engaging, motivating individuals to engage more thoroughly with the advertisement (Lee 2000).
The favorable image projected by celebrities can enhance the persuasiveness of an advertisement, thereby increasing the brand's appeal to consumers; conversely, negative revelations about a celebrity can adversely affect consumer attitudes and beliefs (Thwaites et al. 2012). Marketers generally rely on the positive perceptions that target audiences hold towards a celebrity to be transferred to the endorsed brand, thus boosting the brand's attractiveness. However, complications arise when the endorsing celebrity faces public scandals or events that tarnish their image. Such incidents can drastically shift consumer perceptions of the brand associated with them. Existing studies indicate that negative information disproportionately affects beliefs and judgments more than equivalent positive information does. Indeed, negative details tend to linger longer in memory than neutral ones (Baumeister et al. 2001). Given the consumer response to these dynamics, adverse news about a celebrity can critically impact the consumer's decision-making process. Furthermore, with the rise of social media and greater access to information, managing negative publicity about celebrity endorsers has become increasingly challenging for marketers (Solomon et al. 2009).
Celebrities exert a significant influence on consumers' perceptions of brands in advertisements, leveraging their positive image to enhance persuasion. Conversely, negative associations with endorsers can detrimentally affect consumer attitudes, posing challenges for marketers. They rely on the positive sentiments towards celebrities to seamlessly transfer onto the endorsed brand, thereby amplifying its appeal. However, navigating the landscape becomes complex when a celebrity's reputation undergoes negative publicity, potentially reshaping consumer perceptions of the brand. Extensive research underscores that negative information holds more sway over beliefs and judgments than its positive counterparts, leaving a lasting imprint on memory. This phenomenon significantly influences consumer decision-making processes, making it imperative for marketers to adeptly manage the fallout from negative publicity surrounding celebrity endorsers. With the proliferation of social media and the democratization of information access, this task has become increasingly arduous, demanding innovative strategies to safeguard brand integrity and consumer trust. Thus, the symbiotic relationship between celebrities and brands remains a dynamic force shaping contemporary advertising landscapes, where effective management of both positive and negative associations is paramount for sustained brand success.
Another important aspect influencing consumer’s decision is the attitude. An attitude can be described as an individual's evaluation or viewpoint regarding people, objects, advertisements, or issues. While attitudes generally exhibit stability over time, they are not inherently permanent, as they are subject to change due to various factors, including marketing initiatives such as television advertising and celebrity endorsements. Both internal and external influences contribute to shaping or altering an individual's attitude. In the context of this study, consumers' attitudes may be influenced by factors such as negative publicity and the congruency of the brand within advertisements. Marketers aim to cultivate positive sentiments among their target audience towards a selected celebrity, anticipating that these sentiments will translate to favorable perceptions of the endorsed brand, thereby bolstering its reputation. However, celebrity endorsements accompanied by negative publicity can have a counterproductive effect, potentially alienating consumers rather than attracting them. For instance, if consumers harbor negative sentiments towards a particular celebrity, those sentiments may extend to the endorsed brand, resulting in unfavorable attitudes. Attitude plays a pivotal role in celebrity endorsements, often serving as a focal point of discussion. Consumers typically possess preconceived attitudes towards celebrities based on factors such as credibility, expertise, trustworthiness, and attractiveness. These attitudes influence consumers' decisions regarding which celebrities to utilize as persuasive tools in advertisements. If a celebrity is well-regarded by consumers, they are more likely to perceive the celebrity as a credible source of information, fostering a sense of certainty and cultivating a positive attitude towards the endorsement.
The concept of attractiveness, widely recognized across various domains such as endorsement, communication, and politics, holds the power to engender positive perceptions and attribute desirable qualities to individuals, thereby influencing others' attitudes (Pornpitakpan et al., 2017). In celebrity endorsement, attractiveness plays a pivotal role in shaping the relationship with endorsers, enhancing their credibility, fostering preference for the endorsed brand, influencing belief changes, and impacting attitudes towards communication, among other aspects (Gong and Li, 2017). Nonetheless, some scholars contend that the effects of attractiveness may be confined to products associated with consumers' own attractiveness (Bower and Landreth, 2001; Kamins, 1990), or situations where consumers are particularly concerned about social acceptance (DeBono and Harnish, 1988). Conversely, other researchers argue that attractiveness may not significantly influence consumers' attitudes or purchasing intentions (Baker and Churchill, 1977). Despite the generally positive effects of attractiveness in celebrity endorsement contexts, several studies have failed to consistently support this notion, prompting a closer examination of the factors contributing to these discrepancies.
The discrepancies observed in studies examining attractiveness in celebrity endorsement can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, highly attractive individuals are often perceived as conceited or self-centered, posing a threat to consumers' self-esteem when compared to them (Agthe et al., 2011). Additionally, consumers may focus more on the celebrity than on the endorsed brand, leading to a potential dilution of brand impact (Erfgen et al., 2015). Moreover, attractiveness is a complex and multifaceted concept that researchers have approached using diverse measures, including physical traits, familiarity, or sympathy for the endorser (Ilicic et al., 2018a,). These varied and sometimes unrelated approaches have contributed to conflicting findings and raised concerns about aggregating results from such disparate conceptualizations. Many of the identified measures, which are often one-dimensional and incorporate a limited number of items, may not fully capture the complexity of the attractiveness factor (Erdogan, 1999).
The commonly used measures of physical appearance have certain limitations as they fail to pinpoint the specific aspects of endorsers' attractiveness (Pornpitakpan et al., 2017). It remains unclear whether attractiveness resides in facial features, physique, and gaze. In response to the ambiguity of these approaches, recent scales have emerged to assess traits like facial symmetry or the celebrity endorser's smile (Ilicic et al., 2018a, 2018b). While this offers an intriguing perspective, focusing on facial signals is crucial as they heavily influence initial impressions (Engell et al., 2007). However, these scales tend to become overly specific, potentially overlooking the role of other attributes in attractiveness perception. Additionally, consumers are increasingly aware that celebrity-staged photos often undergo modifications using filters, raising doubts about the authenticity of this "enhanced" attractiveness (Abidin, 2016). These limitations give rise to additional considerations. Beyond physical traits, communication on social platforms suggests that celebrities adopt specific postures that evoke discussion and parasocial interaction (Ledbetter and Redd, 2016). Subsequent research could explore the combinations of physical attributes and postures that enhance the attractiveness of celebrity endorsers and examine the resulting effects of such endorsements.
Credibility, a key persuasive attribute of message sources, has garnered significant attention in celebrity endorsement research (Pornpitakpan, 2004). It is widely recognized that credibility directly influences the persuasive process and subsequent behavioral responses (Hovland and Weiss, 1951). An endorser's high credibility strengthens the core arguments of the messages, rendering them more credible, along with the associated brand (Goldsmith et al., 2000). While various dimensions have been proposed to define credibility, consensus exists that it encompasses reliability and expertise. Ohanian's (1990) developed measure has emerged as the standard reference in this regard. While some authors view attractiveness as a third dimension of credibility, others regard it as a distinct construct. Credibility stands as a critical criterion for the efficacy of celebrity endorsement (Amos et al., 2008), and akin to attractiveness, the bulk of research has linked it with favorable outcomes.
However, the credibility concept has faced significant critique. Some authors argue that credibility only holds sway in specific and constrained contexts, such as when the product poses a particular risk to consumers (Friedman and Friedman, 1979), or when consumers possess limited information about the product (Dholakia and Sternthal, 1977). Others have highlighted that the impact of a celebrity endorser's credibility fluctuates depending on the brand type (Spry et al., 2011), or is influenced by attitudes toward celebrity endorsement (Bergkvist et al., 2016). Conversely, some assert that credibility exerts no influence on attitudes toward communication or purchase intentions (Goldsmith et al., 2000). In certain circumstances, a source with minimal or no credibility may even wield more influence than a credible one – for instance, when consumers resist recommendations, or when the recipient is unaware of the source's arguments (Dholakia, 1987).
Simultaneously, the practices of certain micro-celebrities challenge the credibility-based model (Djafarova and Trofimenko, 2018). With their expanding media reach, some celebrity endorsers broaden their recommendation scope and the brands they represent. For instance, EnjoyPhoenix, originally known as a beauty blog, now offers cooking recipes and travel tips. Several studies indicate instances where perceived expertise of celebrity endorsers may wield more influence than their actual expertise (Ohanian, 1991). This partially explains why micro-celebrities succeed in building influence across diverse domains beyond their core expertise. Indeed, the novelty and distinctiveness of a celebrity's online contributions are vital in shaping their status as opinion leaders (Casaló et al., 2018). Such factors may prompt micro-celebrities to endorse products increasingly distant from their original field of expertise.
Purchase intention refers to the likelihood of a consumer engaging in a transaction and purchasing a product, as determined by their assessment of the product's attributes (Schiffman and Kanuk 2000). It encompasses the inclination of a customer to buy a specific product in the future, driven by factors such as their perceived need for the product, knowledge about it, opinions regarding its qualities, and perceptions of the manufacturing company or brand (Bradmore 2004). The appeal generated by celebrity endorsements and the attractiveness of the product significantly influence consumer purchase intentions (Chaudhary and Asthana 2015). Consumers form their purchase intentions based on external information and their evaluation of a product, resulting in either high or low purchase intentions. Products with high purchase intention are more likely to be purchased, whereas those with low purchase intention face reduced likelihood of consumer acquisition. Several factors influence purchase intention, including price (Alford and Biswas 2002), attitude towards the brand (Johnson and Russo 1984), and brand loyalty. Consumers often rely on past experiences to gather information about products they intend to purchase (Bradmore 2004). Once sufficient information is acquired, consumers begin evaluating and considering alternatives for the desired product. Purchase intention is frequently employed as a metric to gauge consumers' behavioral inclinations.
Brand Image Transfer with Sponsorship
When companies engage in sponsorship agreements, a primary objective is to utilize sponsorship as a means to bolster their brand equity (Cornwell, Roy, & Steinard, 2001). Given that a high level of brand equity offers various benefits to the company, including heightened consumer loyalty and the ability to command premium prices for their products or services, branding emerges as a paramount concern for marketers (Keller, 2009). The customer-based brand equity model, as delineated by Keller (1993, 2001, 2009), outlines the development of brand equity as a series of sequential stages. According to this model, establishing robust, positive, and distinctive brand associations precedes the elicitation of favorable brand responses from consumers, such as cultivating a positive attitude towards the brand. Thus, the model posits that a pivotal aspect of effective brand building involves cultivating a favorable brand image. Keller (1993) offers a frequently cited definition of brand image, describing it as "perceptions about a brand as reflected by the brand associations held in memory" (Keller, 1993, p. 3).
This definition is closely tied to the associative network memory model, which characterizes memory as a collection of stored information pieces, termed "nodes," interconnected by links of varying strength (Anderson, 1983). Activation of a node beyond a certain threshold triggers the recall of memory stored in linked nodes. The degree of this activation propagation depends on the strength of associations between nodes (Keller, 1993). In the case of branding, brand associations can be envisioned as a network of interconnected nodes that activate when consumers contemplate the brand. Stronger associations are more readily recalled, forming a dynamic associative network (Keller, 1993). These brand associations are not fixed but can be forged or reinforced through brand experiences (Gwinner et al., 2009), such as product usage or exposure to sponsor signage during events like sports competitions.
Consequently, a fundamental principle in sponsorship research outlines that sponsor brands undergo a transfer of associations linked to the event brand to their own brand. Sponsored athletes or events serve as potential reservoirs of brand associations for their sponsors, as the associations tied to the sponsored property can become intertwined with the sponsoring brand in consumers' minds, effectively transferring the property's image to the sponsoring brand (Gwinner & Eaton, 1999). This perspective aligns with McCracken's (1989) notion of meaning transfer in celebrity endorsement, frequently invoked by researchers to elucidate the transfer of image from a sponsee to the sponsoring brand (e.g., Gwinner & Eaton, 1999; Gwinner et al., 2009). McCracken posits that celebrities are infused with a certain 'meaning' based on consumers' perception of their image, and this meaning is transmitted from the endorsing celebrity to the endorsed product (McCracken, 1989).
Furthermore, empirical evidence suggests that brands' images can also be influenced by their co-sponsors, contingent upon their similarity (Carrillat et al., 2010). Cobbs et al. (2015) noted that consumers attributed greater levels of brand equity to sponsor brands when they were presented alongside high-equity brands, and conversely. Beyond overarching assessments of brand equity, Gross and Wiedmann (2015) found that distinct brand personality profiles could be largely transferred from a brand to its co-sponsor. Carrillat et al. (2015) postulate that such image transfer effects stem from valence-neutral, ad hoc stereotyping processes in consumers' minds. They assert that individual brands' personality traits become part of a stereotype that is then generalized to co-sponsors. This transfer of a personality trait can either benefit or harm co-sponsors, depending on whether the trait enhances or dilutes the brand image they aim to cultivate (Carrillat et al., 2015).
In the existing sponsorship literature concerning brand image transfer, two primary types of brand associations have commonly been investigated: discrete personality traits (Gross & Wiedmann, 2015) or broader attitudinal assessments of brands as either positive or negative (Ruth & Simonin, 2003). The approach centered on dimensions of brand personality (Geuens, Weijters, & De Wulf, 2009) explores the extent to which a distinct set of characteristics is linked to a brand in consumers' perceptions. Conversely, the attitude-based approach typically evaluates consumers' general responses to a brand, categorizing it as either favorable or unfavorable. In the context of Keller's customer-based brand equity pyramid (Keller, 2009; Keller, 2001), these two approaches represent foundational elements of brand equity at different levels, with brand imagery such as personality traits forming the basis for positive attitudes.
Influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship
Celebrity endorsements have increasingly become a crucial marketing strategy for companies aiming to boost sales and expand their market share. In recent years, these endorsements have proven to be a powerful and effective advertising tool that enhances brand awareness and captures the audience's attention. Products associated with celebrities tend to be memorable over extended periods. Academic research suggests that endorsements can significantly influence consumer attitudes and perceptions. Often, complete product or brand information is not fully presented to consumers, especially when they are watching advertisements on television. In the absence of detailed product information, the standards of this information can be "indirectly" inferred from the information provided, leading to an overall judgment that reflects this uncertainty.
Dean (1999) proposed that celebrity endorsements might act as indicators of the advertiser’s credibility. Companies can use these endorsements as pre-purchase indicators of product quality, similar to how an extensive product warranty might signal quality. It is assumed that consumers look for signals that would be costly for low-quality providers to imitate but beneficial for high-quality sellers to adopt, potentially leading to a "separating equilibrium" where products are distinguished based on inherent quality. A "Best Buy" rating from consumer reports, for instance, tends to segregate products based on objective quality and serves as a promotional signal. Research, including one of the few scholarly studies on endorsements, has shown that endorsements from celebrities, professionals, and regular consumers significantly enhance the overall perception of a product or service and its perceived value, although they do not necessarily affect purchase intentions (CITE). Such findings indicate the powerful influence of external factors on consumer perceptions and behaviors. Hsu and McDonald (2002) found evidence supporting the impact of celebrity endorsements on viewer attention, recall, evaluations, and purchase intentions. Celebrities are typically appealing, which is particularly advantageous when consumers are concerned about societal approval or when the product is related to beauty (Kahle and Homer, 1990). Furthermore, as emotional peripheral cues, celebrity endorsements can lead media exposure to impact sales in mature markets (MacInnis, Rao, and Weiss, 2002). According to several studies, celebrity endorsements are now a widely used and effective method to influence consumer pre-purchase attitudes toward endorsed products or services, becoming a prevalent and impactful promotional tool in the United States and beyond (Agrawal and Kamakura, 1995).
Studies have shown that celebrity endorsement is an important tool that can be used for product and brand promotion (Erdogan, 1999). In their study, Erdogan (1999) showed that an image of a celebrity is perceived differently, and these insights are transferred into endorsing a brand, leading to changed consumer perception. This study shows that celebrities can be used to influence event sponsorship positively, Marketing managers should focus on maintaining a proper congruence of celebrity presence and performance to create a positive brand association (Malik & Sudhakar, 2014). In a similar study, Knoll and Matthes (2017), using a multilevel Meta-analysis of 46 studies involving 10,357 participants, found both positive and negative effects when moderate celebrities were used to endorse brands. In particular, the study showed that female models who did not match the brand image were found to have the highest level of negative perception of the brand. As argued by Erdogan (1999), transferring meaning from celebrities can reinforce brand recall, positive attitudes, and purchase intentions from the target consumers.
Amos et al. (2008) reaffirmed the significant impact of celebrity endorsement as a persuasive strategy, highlighting three key dimensions of credibility and the potential influence of negative information associated with celebrity on consumers. Knoll and Matthes (2016), however, presented a thought-provoking and stimulating contribution by challenging these findings, suggesting that celebrity endorsements may have limited effects on consumers, particularly under certain conditions. They argued that various variables moderate the effects of celebrity endorsement, such as the endorser's gender and the congruence between the celebrity and the brand, while other factors show either no impact or a moderated impact. While both meta-analyses and literature reviews have explored multiple aspects, the latter has delved deeper into the financial implications of celebrity endorsement, including increased sales and financial benefits (Bergkvist and Zhou, 2016). However, these reviews are not without limitations. Their primary drawback lies in their predominantly descriptive nature, merely presenting contradictory findings without offering explanations or fully exploring certain themes or research approaches.
In a study to assess ethics and global values in the Olympic Games, Milton-Smith (2002) has established that the latter are used for attracting event sponsors. In the findings, Milton-Smith (2002) reveals that sports events bring about celebrities during the games, which shape the global values of the participants. The findings in this study depict the critical role of celebrities in improving the visibility of sponsored events and brands. According to Colbert (2003), celebrities have the power to attract a large customer base by generating huge media coverage. This is consistent with a similar study that found that visibility created by celebrities establishes a favorable business environment for event sponsors, who then magnify brand awareness and associations (Gwinner & Eaton, 1999). Gwinner and Eaton (1999) set an experiment with undergraduate students to assess the impact of sporting events' image on the brand after sponsorship. They showed that those students who had prior exposure to celebrities were more likely to develop an image transfer. The findings show that where a brand and the images are properly matched, the transfer process becomes easy. This is supported by Knoll and Matthes (2017), who, through a study, established that celebrity image improves brand perceptions of event attendees and creates a strong brand association. Modern marketing approaches have tapped into the opportunities of social media platforms, and celebrities can leverage this opportunity to amplify their brand association. Lidgren and Major (2021) adopted qualitative research that focused on 28 post-millennial generations and found that social media influencers enhance the sustainable consumption of fashion brands. The findings show that celebrities are visible on social media platforms, and their influence extends beyond the physical boundaries of event sponsorship.
Currently, the use of celebrity marketing has become a prevalent strategy for businesses to build brand image and promote products. This trend is supported by marketing research showing that eight out of ten of the most memorable TV commercials feature celebrities. Further analysis reveals that advertisements featuring celebrity endorsements are particularly memorable. Celebrity endorsements have become a favored marketing tool among marketers, proven to be a successful strategy. Although selecting the right celebrity for advertisements might seem straightforward, establishing a genuine connection between the product and the celebrity can be challenging. As consumers are bombarded with numerous messages and images through various media, companies strive to capture a slice of the public’s attention to highlight the unique attributes and features of their products. While choosing a celebrity and the right promotional event may be simple, fostering a meaningful relationship between the product and the celebrity is more complex.
Research has shown that celebrities often serve as peripheral cues, impacting consumer behavior significantly only when consumers are not particularly interested in the product category or in processing the advertisement's content deeply. Another study from the 1980s indicated that when consumers either identify with or distance themselves from product associations based on celebrity endorsements, they do so in ways that align with their needs, such as self-enhancement. Advertising plays a crucial role in raising awareness and generating interest in products or services, and it significantly influences consumer attitudes towards these products. Celebrity endorsements are now considered the most effective tool for attracting customers, positively influencing product attitudes and purchase intentions through their use in advertising. They also have a strong impact on consumers’ memory and comprehension. Most consumers are not in a purchasing mindset when they encounter product advertisements. Marketers use celebrities in their ads to enhance the retention of product information, making it more readily recallable at the point of purchase. According to balance theory, successful companies establish an emotional connection between the viewer and the endorser, as well as between the endorser and the product. Recent studies have shown that 25 percent of American advertisements use celebrities for endorsements, indicating their effectiveness in improving product evaluations and generating favorable responses to advertisements.
It is crucial to acknowledge that the effectiveness of a celebrity's endorsement largely hinges on their genuine connection with the brand. If there's a real alignment between the celebrity and the product or brand, the endorsement tends to be more impactful. Furthermore, the public's perception of the celebrity's credibility and authenticity plays a vital role in their effectiveness as promoters of the brand. Celebrities often advocate for social causes and support NGOs, and their sincerity in these endorsements can significantly influence public perception. For instance, one of the most notable campaigns was conducted by PETA, which featured celebrities like Shilpa Shetty, Ameesha Patel, Yana Gupta, Sheetal Malhar, and Mahima Choudhary. These celebrities effectively communicated their belief in PETA's philosophy, enhancing the campaign's credibility. On the contrary, there are cases where the lack of authenticity can undermine the effectiveness of endorsements. For example, Amitabh Bachchan is reputed never to have used a Navratan phone, and Britney Spears was caught on camera drinking a competing brand of cola despite endorsing another. These instances highlight the importance of aligning celebrity endorsements with their true preferences and behaviors to maintain trust and effectiveness in advertising campaigns.
Mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events
Bergkvist and Zhou (2016), using a literature review of celebrity endorsers, have established that where a celebrity is positively aligned with the audience based on the brand values, it ignites a brand recall that positively shapes the purchase decision. This mechanism illustrates that a celebrity's positive image can be transferred to an endorsed brand and create a positive brand association (Erdogan, 2019). In a similar study, Atkin and Block (1983) investigated the impact of 196 celebrity endorsers aged 13 -77 years, and their findings showed that celebrities are perceived as trustworthy. The findings show that celebrities have a high level of influence on their brands. For instance, the perceived credibility of a celebrity catalyzes the intention to buy and the possibility of engagement with the endorsed brands. In a recent study, Knoll and Matthes (2017) have shown that celebrity influences work on the mechanism of authenticity. Consumers develop a more responsive approach to celebrities they consider to be genuine and authentic, and this serves to strengthen connections with consumers and create a positive purchase intention.
As social media technologies advance, Lacap et al. (2023) used a purposive sampling of Korean consumers who were influenced to buy products endorsed by Korean celebrities and found that social media has a direct impact. In this mechanism, audience engagement with social media platforms before, during, and after the sponsored event improves the visibility of the brand and engagement. Celebrity presence and performance during sponsored events provide an opportunity for sharing real-time experiences and initiating active participation with the audience about the brand, This provides a basis for brand mentions, which influence purchase intentions (Bergkvist & Zhou, 2016). Consequently, the presence of the celebrity on social media will move beyond the confines of the sponsored event to increase brand associations and purchase intentions. As noted by Lidgren and Major (2021), social media interactions with a celebrity using social media will amplify the level of brand exposure and engagement. Hwa (2017), using a purposive sampling of 200 respondents and analyzing through a PLS-SEM method, found that social media influencers have a positive impact on purchase intentions. This finding shows that the mechanisms of influence are based on the immediacy and interaction of celebrities on social media platforms that augment celebrity influence (Hwa, 2019).
In general, it is anticipated that evaluations of the parent brand will be more positive compared to those of the sub-brand, as supported by findings in the brand extension literature (Volckner and Sattler, 2006). Consumer evaluations of brand extensions are influenced by various factors related to the parent brand, including perceptions of the parent brand's quality (Aaker and Keller, 1990), the level of technological similarity between the parent brand and the extension (Jun et al., 1999), the breadth of the parent brand portfolio (Boush and Loken, 1991), the consistency of quality across previous brand extensions (Dacin and Smith, 1994), prior experiences with the parent brand (Swaminathan et al., 2001), and the relevance of the parent brand associations to the extension brand (Broniaczyk and Alba, [year]). These factors collectively contribute to consumers' attitudes and perceptions towards brand extensions, shaping their evaluations and purchase intentions. Moreover, the parent brand often serves as a reference point for consumers when evaluating brand extensions. Consumers may transfer their existing perceptions and associations of the parent brand onto the extension, influencing their expectations and judgments of the new product or service. As a result, the strength and nature of the relationship between the parent brand and the extension play a crucial role in determining consumer acceptance and adoption of the brand extension.
Additionally, the success of a brand extension relies heavily on the degree of fit between the parent brand and the extension product or service. Consumers are more likely to accept and positively evaluate brand extensions that align closely with the core attributes and values of the parent brand. This alignment enhances perceived brand consistency and credibility, fostering trust and loyalty among consumers. Conversely, brand extensions that deviate too far from the established brand identity may encounter skepticism and resistance from consumers, undermining their potential success in the market. Therefore, careful consideration of the parent brand's image and associations is essential in the development and execution of successful brand extension strategies.
The consumer maintains distinct and independent relationships with both the brand and the celebrity, both of which influence their attitude (Fournier, 1998; Giles, 2002). However, these relationships have yet to be fully integrated into explanatory models of celebrity endorsement effectiveness. Rather than examining the potential interactions among the three entities (Albert and Thomson, 2018), the subsequent sections aim to establish a framework elucidating the necessity of interlinking all relationships between the brand, the celebrity, and the consumer to comprehensively comprehend the impacts of celebrity endorsement.
Incorporating the consumer into the process of effective celebrity endorsement suggests that attitudes toward the endorsed brand no longer hinge solely on the celebrity or their association with the brand, but rather on the collective relationship between all three parties (Mowen, 1980; Roy and Moorthi, 2012; Russell et al., 2006). The balance theory (Heider, 1958) furnishes a vivid conceptual framework illustrating how the connections between the three actors must align to foster the most favorable attitudes. According to this theory, individuals prefer a state of equilibrium among the elements they interact with, lest they experience dissonance, prompting attitude adjustments to rectify the imbalance (Basil and Herr, 2006; Dalakas and Levin, 2005; Mowen, 1980). When applied to celebrity endorsement, two types of relationships emerge (Mowen, 1980): sentiment reflects the value the consumer places on their relationship with both the brand and the celebrity (Roy and Moorthi, 2012; Russell et al., 2006); unity pertains to the perceived compatibility between the brand and the celebrity. The consumer evaluates each facet of the triad as either positive or negative. Robust (weak) attitudes ensue when a state of balance (imbalance) is observed, meaning that the aggregation of each relationship yields a positive (negative) outcome.
Strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship
The landscape of celebrity endorsements has evolved, necessitating careful planning and risk assessment. To mitigate risks, brands are adopting several strategies. Firstly, they are scrutinizing potential endorsers meticulously, assessing their alignment with core values and potential risk factors. Secondly, brands are incorporating morality clauses into contracts, providing a legal mechanism to terminate partnerships in case of detrimental actions by the celebrity. Thirdly, brands are conducting thorough background checks and crafting contingency plans to enable swift and decisive action in the event of a scandal. Lastly, recognizing the vulnerabilities associated with celebrity endorsements, brands are increasingly turning towards influencers or micro-celebrities, diversifying collaborations within the same budget to lower risk profiles. The corporate world has witnessed notable terminations of celebrity partnerships, indicating the gravity with which brands approach such situations. While some scandals have enduring impacts, others may be mitigated through appropriate responses. The severity of the fallout depends not only on the action itself but also on the response. Handling scandals with integrity and demonstrating alignment with societal values can minimize long-term damage to both the celebrity and the brand.
Studies exploring the strategic challenges of incorporating celebrities in event sponsorship have established that controversies and mishaps facing that individual are a significant risk to the brand reputation and event sponsors (Ambroise & Albert, 2020). Erdogan (1999) showed that celebrities can positively influence purchase intentions by influencing the perception and attitudes of the audience but argued that mismatches and controversies can negatively impact brand perception and trust. Choi and Rifon (2012) have established that brands face a strategic challenge of creating an ideal celebrity-brand fit. Poor congruence between the celebrity and the event results in a disconnect and reduces the effectiveness of an event sponsorship. According to Choi and Rifon (2007), a careful selection of celebrities must be made to ensure they are aligned with the brand values and create a seamless fit.
Studies have shown that authenticity in the selection of celebrities is fundamental because it should positively resonate with the consumers. Knoll and Matthes (2017) have identified the challenge of authenticity and credibility as a major issue because where they are not perceived positively, they negatively influence brand associations. This works to erode trust and create a negative brand perception. It shows in the strategic challenge of maintaining authenticity, especially where there is an issue of new public perceptions about celebrities. The management of consumer expectations creates another strategic challenge because the use of celebrities in brand endorsement increases consumer expectations (Erdogan, 1999). Consequently, managing the high expectations from using highly ranked celebrities results in disappointments and backlash that destroys brand associations.
Lacap et al. (2023) have noted the significance of social media platforms in enhancing the visibility of brands during event sponsorship. However, there is a strategic challenge of sharing consistent messages across all the platforms and proper management of controversies. At times, the use of celebrity endorsement fails to provide long-term brand associations because of a failure to plan strategically. During event sponsorships, the focus is drawn toward short-term gains, and more is needed to support sustainable brand equity and positive change in consumer behavior (Bergkvist & Zhou, 2016).
In assessing the implications of associations with celebrities involved in scandals, brands face a multifaceted decision-making process. Firstly, the severity of the incident, exemplified by tragedies like the Astroworld festival, demands a cautious response. Continuing endorsements post-crisis may not only be perceived as callous but could also tarnish the brand's reputation, particularly if viewed as lacking empathy towards victims and their families. Secondly, brands must anticipate and mitigate potential consequences, including consumer boycotts, negative media attention, and financial repercussions. Such backlash can significantly impact a brand's bottom line and public image. Moreover, disengaging from scandal-prone celebrities serves as a manifestation of a brand's commitment to social responsibility and ethical principles, signaling to consumers its dedication beyond profit-making motives. Lastly, the long-term implications of negative associations cannot be understated, as they may irreversibly damage a brand's reputation and erode customer trust. Therefore, strategic disassociation is crucial for preserving the brand's integrity and ensuring its sustained vitality in the competitive market landscape. However, while disassociation may mitigate short-term damage, brands must navigate the delicate balance between risk management and maintaining authentic connections with their audience, as overly reactive responses could also backfire in the long run.
Importance should be placed on brands to carefully navigate the complexities of celebrity endorsements, weighing the potential benefits against the associated risks. Decisions in this realm must be informed by a nuanced understanding of public sentiment, a steadfast commitment to ethical principles, and a strategic outlook on the brand's long-term success. By diligently managing their affiliations with celebrities, particularly those embroiled in significant controversies, brands can mitigate potential fallout and reaffirm their commitment to social responsibility. Moreover, such prudent management can help sustain the trust and loyalty of their customer base, thereby safeguarding the brand's reputation and market position. It is evident that in today's landscape, where public scrutiny is heightened and social media amplifies both praise and criticism, brands must exercise caution and foresight in their celebrity endorsement strategies to navigate successfully the ever-evolving terrain of consumer perceptions and preferences.
Theoretical framework
Associative network memory model
The associative network memory model characterizes human memory as a network composed of interconnected nodes (Till and Shimp, 1998, p. 68). These nodes represent individual pieces of information that are linked together through associative connections (Krishnan, 1996). As a result, each node has the potential to trigger the activation of other associated nodes. This activation process spreads throughout the network, with the initial node activating linked nodes, which in turn activate additional linked nodes (Collins and Loftus). It is commonly applied in marketing to illustrate memory structure (Till and Nowak, 2000) and consumer brand associations (Chang and Chieng, 2006). This model is also used to explain the process of celebrity endorsement, where celebrities and brands are interconnected nodes within the memory network (Till et al., 2008). As such, when consumers think of a celebrity endorser, they often associate them with the endorsed brand, and vice versa, potentially enhancing brand equity through favorable associations (Till, 1998).
The relationship between consumer-based brand equity and endorser credibility and can be elucidated through the associative network memory model. According to this model, celebrity endorsements can enhance brand recall and recognition by serving as additional nodes in memory that are associated with a brand node. When multiple associations exist for a node, it becomes easier to locate, as there are several alternative routes to access it in memory. Consequently, a highly credible endorser becomes more strongly linked with the endorsed brand in the consumer's mind. For instance, when a highly credible scientist like Ian Frazer, renowned for developing a vaccine for cervical cancer, endorses Bicycle Victoria's "Ride to Work" initiative, it is anticipated that both recall, and recognition of the initiative will be positively influenced. Therefore, it is reasonable to expect that endorser credibility plays a supportive role in enhancing brand recall and recognition.
Brand Signaling Theory
Brand signaling theory, rooted in information economics, introduces the concept of brand credibility as a signal in the marketplace (Erdem and Swait, 2004; Erdem et al., 2002). Brands serve as signals conveying information in environments characterized by imperfect information. Brand signals encompass all marketing strategies, past and present, with clarity and credibility being key components (Meyer and Sathi, 1985). Clarity refers to the unambiguousness of brand signal content, while credibility concerns the effectiveness, truthfulness, and reliability of the conveyed information (Tirole, 1988). Credibility, deemed paramount, is the central focus of this research.
Brand equity management involves actively shaping the associations connected with a brand in consumers' minds, as highlighted by Keller (1993). Researchers advocate utilizing secondary associations, such as celebrity endorsements, to bolster brand equity, as suggested by Keller (2005). When a brand is linked to another entity, such as a celebrity, the associations of that entity can be transferred to the brand itself (Petty, 2006). For instance, when cricket player Ricky Ponting, renowned and trusted by consumers in the Indian market due to his leadership role in the Australian cricket team, endorses a brand like "Valvoline," it can effectively communicate associations such as "high performance" and "reliability" (Indiantelevision.com, 2007). Consequently, consumers not only associate the celebrity with the endorsed brand but also extend these associations to the brand itself, creating a broader network of associations. Moreover, celebrity endorsements can impact the perceived quality of the brand by serving as extrinsic cues for consumers to assess product attributes and quality, thus reducing uncertainty and influencing specific product preferences (Dean, 1999).
Previous research on classical conditioning has demonstrated how an association with one stimulus, such as a celebrity, can positively impact another stimulus, like a brand (McSweeney and Bierley, 1984). This conditioning process can be instrumental in transferring lasting attitudes toward a brand (Grossman and Till, 1998), ultimately fostering brand loyalty. According to conditioning principles, celebrity endorsement can influence brand loyalty through affect transfer and inferential belief formation mechanisms. Affect transfer occurs when a consumer positively evaluates one entity due to its association with another entity, while inferential belief formation entails changes in attitudes toward a brand resulting from its association with another entity (Till and Nowak, 2000). It is hypothesized that highly credible endorsers will elicit higher levels of brand loyalty, assuming they are strongly associated with the endorsed brand. For instance, endorsements by reputable Australian entrepreneur and philanthropist Dick Smith for local brands, such as "Temptin" chocolate biscuits, are likely to positively impact consumers' loyalty towards these brands. However, the influence of an endorser on consumer-based brand equity may vary depending on the established credibility of the brand itself. Therefore, hypotheses regarding the relationship between celebrity endorsement, brand credibility, and brand loyalty can be formulated based on these premises.
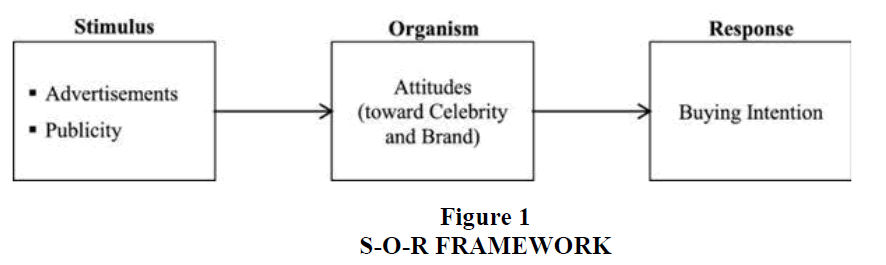
S-O-R Framework
Previous literature has underscored the pivotal role of integrating the Stimulus-Organism-Response (S-O-R) framework into research endeavors centered on consumer behavior (Jacoby 2002). This framework, often referred to as the S-O-R model, posits a sequential relationship wherein environmental stimuli or cues (stimulus) prompt emotional responses within the consumer (organism), subsequently influencing their behavioral reactions (response) (Rajaguru 2014). A comprehensive model based on the S-O-R framework has been developed, strategically organizing variables within the framework to elucidate their respective roles. This structured approach allows researchers to analyze how various stimuli interact with consumers' internal states, ultimately shaping their behavioral outcomes. By delineating these components, researchers gain deeper insights into the intricate dynamics of consumer decision-making processes. The versatility of the S-O-R framework extends beyond its foundational applications, with scholars exploring its utility in diverse contexts, including advertising and various domains of consumer behavior (Rose et al. 2012). Its adaptability underscores its effectiveness as a conceptual tool for understanding the complex interplay between external stimuli, internal processes, and resultant behaviors exhibited by consumers. The S-O-R framework provides a structured lens through which marketers can analyze the efficacy of their campaigns. By identifying the stimuli that evoke specific emotional responses in consumers, advertisers can tailor their strategies to elicit desired behavioral outcomes. Moreover, understanding how consumers' internal states mediate their responses to external stimuli enables marketers to craft more targeted and persuasive messaging Figure 1.
A stimulus is defined as an influence that triggers a response in an individual. It encompasses environmental cues capable of affecting the emotional state of consumers, thereby altering their overall behavior (Zimmerman and Jonelle 2012). In the context of this study, two primary stimuli are identified: advertisements and publicity. These stimuli have the potential to influence the internal state of Millennials, prompting emotional responses. The organism, in this study, signifies the emotional state experienced by consumers following exposure to the stimuli. It encapsulates the spectrum of emotional reactions towards both the celebrity and the brand featured in the advertisements (Zimmerman and Jonelle 2012). This emotional state is pivotal as it marks the inception of consumers forming opinions, thoughts, and feelings towards the advertisement, the celebrity endorser, and the brand being promoted. The study posits that the two stimuli, namely advertisements and publicity, exert significant impacts on Millennials' attitudes towards both the celebrity endorser and the brand itself. These stimuli serve as catalysts for shaping the emotional responses and subsequent attitudes of Millennials towards the featured celebrity and the endorsed brand.
Balance Theory
The balance theory, originating from social psychology, delves into interpersonal relationships and the development and transformation of attitudes within relational triads (Heider 1958). In essence, it posits that individuals within a triad seek equilibrium in their interpersonal connections concerning their attitudes towards these relationships. Heider (1958) posited that interpersonal attitudes, reflecting the positive or negative relationship between one person and another or with an impersonal entity, and unit relationships, denoting the connections between two entities through similarities, causality, membership, possession, or affiliation, mutually influence each other. In a scenario involving three entities, a state of balance is achieved when all three relations are uniformly positive or when two are negative and one is positive (Heider 1958). Any imbalance prompts efforts towards restoring equilibrium: if no balanced state exists, forces driving towards this state emerge. This may entail altering dynamic characteristics or adjusting unit relationships through action or cognitive restructuring. Failure to effect change results in tension arising from the state of imbalance.
Retail marketers often foster a positive sentiment between consumers and products by establishing favorable unit relations between a product and a well-known personality (Solomon et al. 2012). Consequently, the balance theory elucidates the efficacy of celebrity endorsements based on the celebrity's image and consumer attitudes. Within this framework, if a consumer holds a positive attitude towards a celebrity endorsing a particular product or service, they are more inclined to adopt a positive stance towards that product or service. Conversely, negative perceptions of a celebrity embroiled in scandal or experiencing negative publicity can engender negative attitudes towards the associated brand.
Research Design and Methodology
Methodology is the technique used for data collection and analysis of certain study variables (Saunders et al., 2009). Common methods used in studies include qualitative and quantitative techniques. Kothari (2004) argues that the study methodology has several dimensions, including the research methods. This section will describe the research design and methodology for the proposed study.
Research Philosophies
Saunders et al. (2009) have stated that research studies can use positivism and interpretivism research philosophies. A positivist research philosophy requires the researcher to incorporate a social reality, but the overall research process should be objective. According to Farquhar (2012), a positivist research philosophy is ideal for identifying causal relationships that explain new patterns. On the other hand, an interpretivism research philosophy sets an important perspective in understanding human behavior by establishing dissimilarities without underpinning the arguments on law-like conclusions (Saunders et al., 2009). Therefore, this study will adopt an interpretivism research philosophy because it gives a better understanding of the influence of celebrity presence and performance on brand associations.
Research design
This research seeks to understand a phenomenon and provide answers to scientific procedures (Kothari, 2004). The research purpose can be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory, but this study seeks to collect data about celebrity presentations and performances (Saunders et al., 2009). According to Robson (2002), a descriptive study depicts an accurate account of individual profiles and situations, which is suitable for this study. In this study, a survey will be used based on the grounded theory. Saunders et al. (2009) have stated that research can use deductive, inductive, or abductive approaches to collect data on the research variables. This study seeks to identify a causal relationship between celebrity presence and performance on brand associations, and this can be achieved through a deductive approach. However, an inductive research approach seeks to obtain a precise understanding of research contexts that are attached to events. Saunders et al. (2009) argue that an inductive approach seeks to understand a phenomenon through collecting data.
Data collection
This study will use both primary and secondary data so that the research objectives are properly addressed. Primary data will be collected through the use of questionnaires and interviews about their perceptions of celebrity presentations and performance (Saunders et al., 2009). Interviews will be conducted with students who have watched celebrity performances and presentations during an event so that they can provide qualitative data (Creswell, 2003). This study will adopt a quantitative data approach through in-depth interviews so that it can provide meaning to celebrity performances and presentations. Secondary data will be collected through an extensive literature review from peer-reviewed journal articles, books, websites, and other reliable information (Saunders et al., 2009).
Samples and sampling strategy
The study will sample students randomly about their involvement in sponsorship events as respondents for the study. According to Creswell (2020), a random sampling approach is suitable for this study because it gives all respondents an equal opportunity to take part in the study. Also, the target study population is students, and this is a defined sampling frame. And giving every individual an equal opportunity to participate in the study will be critical. One hundred students will be sampled randomly and provided with questionnaires to fill out and respond to the study questions. A random sampling technique is less expensive, easy to execute, and provides all respondents an equal opportunity to be involved in the study, making generalizations possible (Rogelberg & Stanton, 2007).
Data Analysis and Presentation
Data collected from the studies will be analyzed quantitatively by using Excel to represent frequencies, means, standard deviations, and percentages. The data analysis will first consider demographic information of the respondents, and this will be followed by an assessment of the study objectives, influence of celebrity presentation and performance, mechanisms of celebrity influence of brand associations, and the strategic challenges that influence celebrity presentations and performance. The data will presented through graphs, charts, and tables to represent the study variables.
Ethical considerations
Investigating the impact of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship and brand associations involves several ethical considerations that the researcher should observe. The ethical considerations to be observed in this study include informed consent, privacy and confidentiality, and integrity and transparency. The students sampled in the study will be informed about the purpose, methods, and implications once they are involved in the study. A consent form will be provided to the respondents to give their consent before they are involved in the study. Secondly, the ethical consideration of privacy and confidentiality will observe that no sensitive information is disclosed without the prior explicit permission of the respondents. This will ensure that the identity of respondents is not disclosed. Lastly, the ethical consideration of integrity and transparency will be achieved through an accurate analysis of data by focusing on transparency in the research methodology.
Findings
In this section, the focus is to present data analysis to answer research questions. It presents information on the demographic data for the respondents and answers the three objectives: 1) examine the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship; 2) investigate the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events; and 3) identify strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship.
Findings from survey
In the table below, demographic data of the respondents are provided
Based on the study findings, this study had (46%) female representation and (54%) male representation as indicated in Figure 2
The study findings show that (52%) of respondents were aged 21-30 years; (34%) were aged 31-40 years; (9%) were aged 41-50 years; while (5%) were aged above 51 years as indicated in Figure 3.
On the question on respondent’s marital status, (42%) indicated they were single, (40%) were married, and 18% were widowed as summarized in Figure 4.
Interest in Events
The figure below provides the information on the participants’ interests in events.
The data presented in Figure 5 illustrates the distribution of participants' interests in events, particularly focusing on celebrity performances. Upon analysis, it becomes apparent that the majority of respondents tend to infrequently attend events featuring celebrity performances, with only a small percentage indicating a high frequency of attendance. This information offers valuable insights into the prevailing interests in events among the surveyed participants. Understanding the frequency of attendance at events, especially those featuring celebrity performances, is crucial for event organizers, marketers, and other stakeholders involved in event planning and promotion. By gauging the level of interest and participation among target audiences, organizers can tailor their strategies to better meet attendees' preferences and expectations. Additionally, this data can inform decisions related to resource allocation, budgeting, and marketing efforts aimed at promoting future events.
Influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship
The figure below provides information on the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship.
The findings of figure 6 show that the majority of the respondents agreed that they purchase the products from sponsors associated with celebrities endorsing such events. It also indicated that the celebrity’s performance at an event affects one’s perception of the event’s sponsors. Finally, indicates that the presence of a celebrity at an event makes it more interesting, and the participants can attend such events.
Mechanisms of brand association in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events
Figure below indicates the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events.
The findings indicate that there is an association of a celebrity with an event’s sponsor, which affects their trust in the sponsor’s brand. It also indicates that the celebrities endorsing an event make the event’s sponsors appear more prestigious to them. It indicates that the celebrities at events help them to remember the event’s sponsors. With this in place, it ensures that there is improvement in the way the events are promoted and the key sponsorship of such events Figure 7.
Strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance
Figure below provides the strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance Figure 8.
The findings indicate that the participants claimed they are always concerned about the potential for celebrities to overshadow the event itself. It also indicates that finding a celebrity whose image aligns with the event’s sponsor is challenging, and finally, the findings indicate that there is misbehavior of celebrities at events, which can harm the sponsor’s brand image Table 1.
| Table 1 Influential Factors on Attendance at the Events | |||||
| Influence Factor | Not at All | Rarely | Once in a While | Often | Most of the Time |
| Celebrity’ likability | - | - | 32(10.7%) | 105(35.4%) | 163(54.3%) |
| Price | - | - | 8(2.7%) | 123(41.0%) | 169(56.3%) |
| Celebrity’s image | - | - | 10(3.3%) | 134(44.7%) | 156(52.0%) |
| Personality | - | - | 8(2.7%) | 121(40.3%) | 171(57.0%) |
| Credibility | - | - | 1(0.3%) | 106(35.3%) | 193(64.3%) |
| Attractiveness | - | - | - | 98(32.7%) | 202(67.3%) |
The data provided illustrates the perceived influence of various factors, including celebrity likability, price, celebrity image, personality, credibility, and attractiveness, on consumer behavior. Notably, celebrity likability emerges as a significant determinant, with the majority of respondents indicating that it often or most of the time affects their decisions. This suggests that consumers are influenced by their perceptions of celebrities and their likability when making purchasing choices.
Similarly, price appears to be another crucial factor, with a significant portion of respondents stating that it often or most of the time influences their decisions. It shows the importance of pricing strategies in shaping consumer behavior and purchasing patterns.
A celebrity's image and personality also seem to have considerable influence, as indicated by the high percentage of respondents who reported that these factors often or most of the time affect their decisions. This suggests that consumers are attentive to the public image and persona of celebrities when evaluating products or services endorsed by them. Interestingly, credibility emerges as a relatively less influential factor, with a smaller proportion of respondents indicating that it often or most of the time affects their decisions. This contrasts with the perceived influence of other factors such as celebrity likability and price.
Attractiveness appears to have a moderate influence on consumer behavior, with a significant percentage of respondents stating that it often or most of the time affects their decisions. This suggests that physical attractiveness, whether of the celebrity endorser or the product itself, plays a role in influencing consumer choices.
Correlation Analysis
A correlation analysis is conducted in determining whether there is a relationship between study variables, which is essential towards understanding the existence of relationships. The study findings have been integral in demonstrating positive relationships between event sponsorship and celebrity endorsements Table 2.
| Table 2 Correlation Analysis | |||||
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Celebrity | Pearson | 1 | |||
| Endorsement | Correlation | ||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | |||||
| N | 300 | ||||
| Brand Perception | Pearson | ||||
| Correlation | .452* | 1 | |||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.015 | ||||
| N | 300 | 300 | |||
| *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). | |||||
The correlation analysis between celebrity endorsement and brand perception reveals a statistically significant positive relationship between the two variables (r = 0.452, p = 0.015). This indicates that there is a moderate to strong positive correlation between celebrity endorsements and brand perception among the respondents. The correlation coefficient of 0.452 suggests that as celebrity endorsements increase, brand perception also tends to increase. In other words, consumers' perceptions of a brand are positively influenced by the presence or endorsement of celebrities. This finding aligns with existing literature on the effectiveness of celebrity endorsements in enhancing brand image and perception.
The statistically significant p-value of 0.015 indicates that the observed correlation is unlikely to have occurred by chance. Therefore, we can infer that there is a genuine relationship between celebrity endorsements and brand perception among the respondents Table 3.
| Table 3 The Correlation between the Celebrity Endorsements and Event Attractiveness | |||||
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Celebrity | Pearson | 1 | |||
| Endorsement | Correlation | ||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | |||||
| Event attractiveness | Pearson | ||||
| Correlation | .478* | .401* | 1 | ||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | |||
| N | 300 | 300 | 300 | ||
| *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). | |||||
In the table below, it provides the correlation between the celebrity endorsements and event attractiveness.
The correlation analysis between celebrity endorsement and event attractiveness reveals statistically significant positive relationships between both variables.
Firstly, there is a moderate positive correlation between celebrity endorsement and event attractiveness (r = 0.478, p = 0.000). This indicates that as celebrity endorsements increase, the perceived attractiveness of the event also tends to increase. This finding suggests that the presence of celebrities contributes significantly to the appeal and allure of an event.
Secondly, there is a strong positive correlation between event attractiveness and brand perception (r = 0.401, p = 0.000). This indicates that events perceived as attractive tend to positively influence brand perception among attendees. The strong correlation suggests that the attractiveness of an event plays a crucial role in shaping attendees' perceptions of the brands associated with it.
Firstly, the correlation between client satisfaction and celebrity endorsement is notably strong (r = 0.485, p = 0.004). It suggests that there exists a positive association between the presence of celebrities at events and the level of satisfaction reported by clients. Events that feature celebrity endorsements tend to elicit higher levels of satisfaction among attendees. The finding aligns with the notion that celebrity presence can add prestige, excitement, and allure to an event, thereby enhancing the overall experience for clients. Celebrities often serve as influential figures whose presence can elevate the perceived value of an event, leading to increased satisfaction among attendees Table 4.
| Table 4 Correlation is Significant at the 0.05 Level (2-Tailed) | |||||
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Celebrity | Pearson | 1 | |||
| Endorsement | Correlation | ||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | |||||
| N | 300 | ||||
| Brand Perception | Pearson | ||||
| Correlation | .452* | 1 | |||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.015 | ||||
| N | 300 | 300 | |||
| Event attractiveness | Pearson | ||||
| Correlation | .478* | .401* | 1 | ||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | |||
| N | 300 | 300 | 300 | ||
| Client satisfaction | Pearson | ||||
| Correlation | .485* | .423* | .457* | 1 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.012 | ||
| N | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | |
| *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). | |||||
Secondly, there is a significant positive correlation between client satisfaction and brand perception (r = 0.423, p = 0.009). It indicates that clients who hold positive perceptions of the brand are more likely to report higher levels of satisfaction with their event experience. Brand perception plays a crucial role in shaping attendees' expectations and overall satisfaction with the event. Events associated with reputable and positively perceived brands are perceived as more credible, trustworthy, and enjoyable by clients. Consequently, clients are more likely to express satisfaction with events that are aligned with favorable brand perceptions.
Furthermore, the correlation analysis also reveals a strong positive relationship between client satisfaction and event attractiveness (r = 0.457, p = 0.012). It implies that clients who perceive an event as attractive and appealing are more likely to report higher levels of satisfaction. Event attractiveness encompasses various factors such as venue aesthetics, event layout, entertainment, and overall ambiance. Events that are well-designed, visually appealing, and offer engaging activities are more likely to captivate attendees and leave a positive impression, resulting in increased satisfaction levels.
Findings from Interview
Influence of celebrity presence on event sponsorships
In the interview conducted, all participants unequivocally outlined the profound impact of celebrities on event sponsorship. According to their collective perspective, the mere presence of a celebrity brings about a shift in the dynamics of an event. It is not just about drawing larger crowds; it's about infusing the occasion with an undeniable aura of glamour and excitement. The participants spoke passionately about how celebrities serve as magnets, effortlessly attracting throngs of fans and media attention. It is this magnetic pull that brands eagerly harness to elevate their visibility and engagement within the event landscape.
Celebrities are perceived as catalysts for heightened interest and participation in sponsored events. Their star power transcends mere endorsement; it becomes a transformative force that propels events into the realm of cultural phenomena. From red carpet galas to music festivals, celebrities inject an undeniable allure that captivates audiences and amplifies brand exposure. As one participant aptly summarized, 'Their presence is like a spotlight that illuminates the entire event, drawing attention not only to themselves but also to the brands they endorse.' This sentiment outlines the symbiotic relationship between celebrities and event sponsorship. Brands recognize the invaluable currency of celebrity influence and eagerly seek to align themselves with the stars who possess it. Through strategic partnerships and clever activations, brands leverage this influence to enhance their visibility and resonate more deeply with consumers. The participants emphasized that it is not just about associating with any celebrity; it is about selecting the right personality whose image and values harmonize with the brand's identity.
Furthermore, participants emphasized that the influence of celebrity presence extends far beyond the confines of the event itself. Social media amplifies their impact, transforming sponsored events into viral sensations that reverberate across digital platforms. The ripple effect of celebrity endorsements extends reach and engagement exponentially, providing brands with unparalleled exposure and access to diverse audiences. As one participant remarked, 'It's not just about what happens during the event; it's about the conversations that continue long after it's over.' The unanimous consensus among participants on the undeniable allure of celebrity presence in event sponsorship was critical in this study. Their influence transcends traditional marketing tactics, offering brands a powerful conduit to connect with consumers on a visceral level. In an era defined by fleeting attention spans and constant digital noise, celebrities cut through the clutter and command attention in ways that traditional advertising cannot. As such, their presence remains a coveted asset for brands seeking to make an indelible impression in the hearts and minds of consumers.
Mechanisms of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events
Participants in the interviews provided valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying brand associations in celebrity-endorsed events, offering diverse perspectives on consumer behavior and brand perception. Participant 1 emphasized the importance of aligning values and image between celebrities and brands, stating, "Brand associations in celebrity-endorsed events are primarily driven by the alignment of values and image between the celebrity and the brand. When consumers see a celebrity endorsing a product or participating in an event, they create positive associations with the brand." Building upon this notion, Participant 2 highlighted the transfer of credibility and trust from celebrities to brands, asserting, "The mechanism of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events lies in the transfer of credibility and trust from the celebrity to the brand. Consumers perceive the brand more favorably when it is endorsed by a celebrity they admire or respect."
Participant 3 elaborated on the halo effect created by celebrity endorsements, stating, "Celebrity endorsement creates a halo effect around the brand, where the positive attributes associated with the celebrity are transferred to the brand. This association can significantly enhance brand perception and consumer attitudes towards the product or event." Similarly, Participant 4 identified the emotional connection consumers feel towards celebrities as a key driver of brand associations, noting, "The key mechanism of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events is the emotional connection that consumers feel towards the celebrity. When a celebrity endorses a brand or participates in an event, consumers often associate positive emotions with the brand, leading to increased affinity and loyalty."
The principle of social proof emerged as a prominent theme in Participant 5's response, who stated, "Brand associations in celebrity-endorsed events are driven by the principle of social proof, where consumers are influenced by the actions and behaviors of celebrities. When consumers see a celebrity endorsing a brand or attending an event, they are more likely to perceive the brand positively and align themselves with it." Participant 6 further elaborated on the aspirational identity associated with celebrities, noting, "The mechanism of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events is rooted in the concept of aspirational identity. Consumers aspire to be like their favorite celebrities and, therefore, are more inclined to associate themselves with brands endorsed by those celebrities." Participant 7 indicated the sense of authenticity and credibility created by celebrity endorsements, stating, "Celebrity endorsements create a sense of authenticity and credibility for the brand, which resonates with consumers. When a celebrity publicly supports a brand or event, it reinforces the brand's values and positions it as a trustworthy choice for consumers."
In addition to authenticity and credibility, Participant 8 discussed the role of cognitive dissonance reduction in brand associations, noting, "The mechanism of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events is based on the principle of cognitive dissonance reduction. Consumers experience cognitive dissonance when their perceptions of a brand conflict with their perceptions of the endorsing celebrity. To resolve this dissonance, consumers may adjust their perceptions of the brand to align with those of the celebrity." Participant 9 emphasized the importance of congruence between celebrities and brands, stating, "Brand associations in celebrity-endorsed events are influenced by the congruence between the celebrity and the brand. When there is a strong fit between the celebrity's image and the brand's values, consumers are more likely to perceive the brand positively and form favorable associations with it." Finally, Participant 10 highlighted the principle of associative learning as a key mechanism driving brand associations in celebrity-endorsed events, asserting, "The mechanism of brand association in celebrity-endorsed events is driven by the principle of associative learning. Consumers form associations between the celebrity and the brand based on their past experiences and interactions with both entities. These associations shape consumers' perceptions of the brand and influence their attitudes and behaviors."
Strategic challenges in celebrity presence on event sponsorship
Participants shared their perspectives on the strategic challenges associated with celebrity involvement in event sponsorship, offering valuable insights into the complexities of such partnerships. One participant remarked, "Managing expectations is crucial when working with celebrities. They often have specific requirements and demands, and finding a balance between meeting those needs and staying within budget can be challenging" (Participant 1). This sentiment was echoed by another participant who stated, "Negotiating contracts with celebrities requires careful consideration of terms and conditions to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement for both parties" (Participant 2).
Mitigating risks related to the celebrity's reputation emerged as a recurring theme in the discussions. One participant emphasized the importance of conducting thorough background checks, noting, "It's essential to assess the potential impact of any past controversies or scandals on the brand's image before entering into a partnership with a celebrity" (Participant 3). Another participant highlighted the need for proactive risk management, stating, "There's always the risk of negative publicity or unforeseen incidents that could tarnish the reputation of both the celebrity and the sponsoring brand. It's crucial to have strategies in place to address these risks effectively" (Participant 4).
Authenticity and relevance were also identified as critical factors in forming successful partnerships with celebrities. "Ensuring that the celebrity's image and values align with those of the brand is essential for establishing authenticity and credibility with the audience," remarked one participant (Participant 5). Another participant emphasized the need for thorough research and due diligence, stating, "Misalignment between the celebrity and the brand can undermine the credibility of the partnership. It's essential to conduct extensive research to avoid any potential conflicts" (Participant 6).
Logistical coordination emerged as a significant challenge in managing celebrity involvement in events. "From travel arrangements to security concerns, there are numerous logistical considerations that must be addressed to ensure the smooth execution of the event," noted one participant (Participant 7). Another participant highlighted the importance of dedicated resources for managing these logistics effectively, stating, "Having dedicated teams and resources in place to handle logistical coordination is essential for ensuring the success of the event"
Chapter summary
This section provides an insight into the findings of the study, which aims to address the research objectives and aims. The findings show that the celebrity presence influences the performance on event sponsorship. In the case of mechanisms of brand associations, it indicates that it affects their trust in the sponsor’s brand. The findings also indicate the prestigious nature of the events when they are sponsored. However, there are challenges associated with the event sponsorship including the potential of the sponsors, and finding a celebrity whose image aligns with the event’s sponsor is challenging.
Discussion, Conclusion and Recommendations
The entire study summary, discussion, conclusion and recommendations are presented in this chapter. First, the study summary is provided, which highlights the findings for each objective, and this followed by discussion of the findings. Secondly, the study provides conclusions and recommendations are presented.
Summary of Findings
The assessment of the celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship revealed significant insights into consumer behavior and brand engagement. The findings indicate the profound influence that celebrities wield in driving interest and participation in sponsored events. Participants overwhelmingly agreed that the mere presence of celebrities at events enhances their appeal and attractiveness, leading to increased attendance and consumer interest. Moreover, the study highlighted the persuasive power of celebrity endorsements in driving consumer purchasing behavior, with a majority of respondents indicating a preference for products from sponsors associated with celebrity-endorsed events. It suggests that celebrities serve as powerful catalysts for elevating brand visibility and engagement within the event landscape. The findings also shed light on the strategic implications of leveraging celebrity influence in event sponsorship, emphasizing the importance of strategic alignment and authenticity in celebrity-brand partnerships. It is through strategically aligning with celebrities whose image and values resonate with their brand, sponsors can maximize the impact of their sponsorship efforts and enhance brand perceptions among consumers.
The investigation into the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events revealed information on consumer perceptions and behaviors. Participants identified several key mechanisms driving brand associations, including alignment of celebrity and brand values, transfer of credibility from celebrities to brands, creation of a halo effect, and emotional connection with celebrities. These mechanisms provided the importance of authenticity, credibility, and emotional resonance in shaping consumer perceptions of brands associated with celebrities. The findings highlighted the role of social proof, aspirational identity, and cognitive dissonance reduction in driving brand associations, providing valuable insights for marketers seeking to leverage celebrity endorsements effectively. Moreover, the study emphasized the need for brands to carefully select celebrities whose image and values align with their own, ensuring authenticity and relevance in celebrity-brand partnerships. Sponsors can develop more effective strategies for leveraging celebrity influence to enhance brand perceptions and engagement among consumers.
Identifying strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship revealed critical insights into the complexities of celebrity partnerships. Participants highlighted various challenges, including managing expectations, negotiating contracts, mitigating risks to brand reputation, and ensuring logistical coordination. As such, it shows the significance of conducting thorough research, due diligence, and proactive risk management in navigating celebrity partnerships successfully. Moreover, the findings emphasized the need for strategic alignment and authenticity in celebrity-brand partnerships, highlighting the potential risks of misalignment between celebrity and brand values. It is through addressing these challenges strategically that sponsors can maximize the benefits of celebrity endorsements while minimizing potential risks and drawbacks. Overall, the study provided valuable insights for event organizers, marketers, and other stakeholders involved in event sponsorship, offering actionable guidance for navigating the complexities of celebrity partnerships and enhancing brand engagement within the event landscape.
Discussion
Influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship
The study sought to examine the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship. The findings support Erdogan (1999), which demonstrated that celebrity images can significantly influence consumer perception and brand endorsement, suggesting that leveraging celebrity presence in event sponsorship can positively affect consumer attitudes and purchase intentions. It also supports Malik & Sudhakar (2014) emphasizing the importance of maintaining congruence between celebrity presence and brand image to achieve positive brand associations. The current study findings indicate that the presence of celebrities at events positively influences attendees' perceptions of event sponsors, leading to increased interest and attendance. The study findings reinforce the notion that properly matched celebrities can enhance brand perceptions and associations, thereby benefiting event sponsors. This is supported in Knoll and Matthes (2017) highlighting the positive effects of celebrity endorsements on brand perception.
Another key aspect illuminated by this research is the compelling effect of celebrity endorsements on consumer behavior and brand perception. The findings resonate with previous studies on the persuasive power of celebrities in shaping consumer attitudes and purchase intentions (Hsu & McDonald, 2002). The findings indicated that the inherent appeal and influence of celebrities, sponsors can effectively capture the attention of their target audience and enhance brand visibility. This aligns with the findings of Erdogan (1999), who emphasized the transformative impact of celebrity endorsements on consumer perception and brand image. Moreover, the current study supports the notion that celebrity endorsements serve as potent signals of product quality and credibility, resonating with consumers seeking assurance in their purchasing decisions (Dean, 1999).
Furthermore, the study highlights the strategic significance of aligning celebrity presence and performance with the overarching objectives of event sponsorship. Milton-Smith (2002) and Colbert (2003) had previously highlighted the pivotal role of celebrities in enhancing the visibility and appeal of sponsored events. The current findings reinforce this notion, emphasizing the importance of selecting celebrities whose image and values resonate with both the brand and the event. It fosters congruence between celebrities, brands, and events, sponsors can cultivate authentic connections with their target audience and amplify the impact of their promotional efforts. This strategic alignment is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of event sponsorship initiatives and achieving tangible returns on investment.
Moreover, the current study indicates the enduring appeal of celebrity endorsements as a promotional tool in modern marketing practices. Agrawal and Kamakura (1995) had previously documented the widespread use and effectiveness of celebrity endorsements in influencing consumer behavior and brand perception. The current findings align with this perspective, highlighting the enduring relevance of celebrity endorsements as a preferred marketing strategy for enhancing brand visibility and driving consumer engagement. In today's digital age, celebrities wield unprecedented influence and reach, making them invaluable assets for brands seeking to connect with consumers on a deeper level. Lidgren and Major (2021) have demonstrated the transformative impact of social media influencers on brand engagement and consumer behavior, further indicating the enduring appeal of celebrity endorsements in contemporary marketing campaigns.
Additionally, the research sheds light on the strategic challenges associated with celebrity presence and performance in event sponsorship. The findings support Gwinner and Eaton (1999) study assessing the impact of sporting events on brand image and sponsorship effectiveness, highlighting the potential risks and rewards of celebrity endorsements in sponsorship initiatives. The findings echo these concerns, emphasizing the need for sponsors to carefully manage expectations, mitigate risks, and ensure authenticity in their partnerships with celebrities. In addressing these strategic challenges proactively, sponsors can safeguard their brand reputation and maximize the value derived from celebrity endorsements in event sponsorship endeavors.
Mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events
The second objective focused on the mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events. The findings indicate that the celebrities endorsing an event make the event’s sponsors appear more prestigious to them. It also provides that the celebrities at events help them to remember the event’s sponsors. The association of a celebrity with an event's sponsor, aligns with Bergkvist and Zhou's (2016) assertion that a positive alignment between a celebrity and the brand values ignites brand recall and positively shapes purchase decisions. This suggests that the presence of celebrities at sponsored events serves as a powerful strategy for brand association, leveraging the positive image and influence of celebrities to enhance consumer trust in the sponsor's brand. Moreover, the findings indicating that celebrities endorsing an event make the sponsors appear more prestigious resonate with Atkin and Block's (1983) findings that celebrities are perceived as trustworthy and have a high level of influence on their brands. This highlights the role of celebrity credibility in shaping consumer perceptions and purchase intentions, outlining the importance of strategic alignment between celebrity endorsers and brand values. The findings also align with Knoll and Matthes (2017) emphasizing the mechanism of authenticity in celebrity influence, suggesting that consumers are more responsive to celebrities they perceive as genuine and authentic. The celebrity presence and performance during sponsored events provide an opportunity for real-time engagement and interaction with the audience, encouraging authentic connections and strengthening brand associations.
Moreover, this study supports Knoll and Matthes (2017) findings regarding the mechanism of authenticity in celebrity influence. The study found out that consumers are more receptive to celebrities perceived as genuine and authentic, leading to stronger connections and positive purchase intentions. This aligns with the current findings on the importance of authenticity in fostering meaningful brand associations and driving consumer engagement. Similarly, Atkin and Block's (1983) research highlighting the perceived trustworthiness of celebrities aligns with the current findings, emphasizing the influential role of celebrity credibility in catalyzing purchase intentions and brand engagement. Furthermore, the advent of social media technologies has revolutionized the landscape of celebrity endorsements and brand promotion. Lacap et al. (2023) have highlighted the direct impact of social media on brand visibility and engagement, particularly in the context of celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events. The findings echo this perspective, emphasizing the pivotal role of social media in amplifying brand exposure and engagement through celebrity interactions. As celebrities leverage social media platforms to share real-time experiences and engage with their audience, brand mentions and purchase intentions are positively influenced, extending the reach and impact of sponsored events (Bergkvist & Zhou, 2016).
Additionally, Hwa's (2017) research on social media influencers aligns with the current findings, demonstrating the significant impact of celebrity interactions on purchase intentions. The current study findings further reveal the mechanisms of influence inherent in social media interactions, highlighting the immediacy and interactivity of celebrity engagement as key drivers of consumer behavior. As celebrities leverage social media platforms to connect with their audience in real-time, the level of brand exposure and engagement is amplified, augmenting the influence of celebrity endorsements on consumer perceptions and purchase decisions. The current investigation aligns with existing literature on brand extension, emphasizing the importance of parent brand perceptions and associations in shaping consumer attitudes towards brand extensions (Volckner and Sattler, 2006). Consumers' evaluations of brand extensions are influenced by various factors related to the parent brand, including perceptions of quality, technological similarity, brand portfolio breadth, and consistency of quality across previous extensions. These findings show the critical role of the parent brand as a reference point for consumers when evaluating brand extensions, highlighting the need for careful consideration of brand fit and alignment in brand extension strategies.
Strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performances on event sponsorship
The concern expressed by participants about the potential for celebrities to overshadow the event itself resonates with Ambroise & Albert's (2020) findings that controversies and mishaps involving celebrities pose significant risks to brand reputation and event sponsors. It indicates the need for careful management of celebrity partnerships to mitigate the risk of negative publicity and ensure that the focus remains on the event and its objectives. The challenge of finding a celebrity whose image aligns with the event's sponsor is echoed in Choi and Rifon's (2012) research on creating an ideal celebrity-brand fit. Poor congruence between the celebrity and the event can lead to disconnect and reduce the effectiveness of event sponsorship, emphasizing the importance of strategic alignment and careful selection of celebrities. Moreover, the findings regarding the misbehavior of celebrities at events and its potential impact on the sponsor's brand image align with Erdogan's (1999) argument that mismatches and controversies can negatively impact brand perception and trust. It outlines the importance of authenticity and credibility in celebrity endorsements, as highlighted by Knoll and Matthes (2017), and the strategic challenge of maintaining consumer expectations.
The finding indicates that brands must assess the alignment between celebrities and core brand values to ensure a seamless fit and minimize the risk of controversies or mismatches. This aligns with existing literature highlighting the significant risk posed by controversies involving celebrities and the importance of strategic alignment to maintain brand perception and trust. However, while strategic alignment is essential, brands must also navigate the challenge of authenticity and credibility in celebrity endorsements. As highlighted by Knoll and Matthes (2017), perceived negativity or lack of authenticity can erode brand associations and trust, emphasizing the importance of genuine connections between celebrities and consumers. Therefore, brands must prioritize authenticity in their partnerships to resonate positively with consumers and mitigate the risk of negative perceptions.
Another strategic challenge identified in the current analysis is the management of consumer expectations arising from celebrity endorsements. The use of highly ranked celebrities often leads to heightened consumer expectations, which, if not managed effectively, can result in disappointments and backlash that harm brand associations. It indicates the need for brands to set realistic expectations and deliver on promises to maintain consumer trust and loyalty. The advent of social media platforms has introduced new complexities in celebrity endorsements, particularly regarding brand visibility and message consistency. While social media offers opportunities to enhance brand exposure during event sponsorship, brands must navigate the challenge of managing controversies and sharing consistent messages across various platforms. As such, it requires proactive planning and strategic management of social media presence to mitigate potential risks and capitalize on opportunities for brand engagement. The case of Kanye West's Yeezy brand serves as an illustration of the strategic challenges and decision-making processes involved in celebrity endorsements. Despite weathering numerous controversies, the eventual decision to disassociate from Kanye shows the importance of strategic disassociation in preserving brand integrity and reputation. This highlights the critical role of risk management and proactive decision-making in navigating the complexities of celebrity partnerships. However, while it may mitigate short-term damage, brands must also consider the long-term implications of negative associations and the potential impact on brand reputation and consumer trust. Therefore, it is essential for brands to strike a delicate balance between risk management and maintaining authentic connections with their audience to ensure sustained success and market relevance.
Influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship
The study aimed to investigate the impact of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship. The findings reveal a substantial influence of celebrities on event sponsorship outcomes. Specifically, the analysis indicates a statistically significant relationship between the presence of celebrities at sponsored events and the level of audience engagement. Additionally, the study concludes that the performance of celebrities during these events significantly affects brand recall and audience perception. Notably, factors such as the celebrity's reputation, charisma, and alignment with the event's theme emerge as critical determinants of sponsorship success. Overall, this study indicates the importance of strategic celebrity selection and performance optimization in maximizing the effectiveness of event sponsorship initiatives.
Mechanisms of brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events
This study investigated the mechanisms governing brand associations in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events. In this analysis, it provides the dynamics through which celebrity endorsements shape consumer perceptions and attitudes towards sponsored brands. The findings outline the role of authenticity and credibility in fostering positive brand associations, with consumers exhibiting a stronger affinity for brands endorsed by authentic and relatable celebrities. Moreover, the study highlights the influence of social media engagement and real-time interactions during sponsored events in amplifying brand exposure and engagement. Overall, this research emphasizes the need for brands to leverage these mechanisms strategically to enhance brand associations and drive consumer engagement in celebrity-endorsed sponsorship events.
Strategic challenges in celebrity presence and performances on event sponsorship
This study identified strategic challenges associated with celebrity presence and performance in event sponsorship. The findings outlined the complexities and risks involved in leveraging celebrity endorsements for sponsorship initiatives. Specifically, the analysis reveals the potential pitfalls of poor celebrity-brand alignment, authenticity concerns, and the management of consumer expectations. Also, the study highlights the strategic implications of navigating controversies and scandals involving celebrity endorsers, emphasizing the importance of proactive risk management and crisis response strategies. Overall, this research indicates the need for brands to adopt a strategic approach to mitigate risks and capitalize on the opportunities presented by celebrity presence and performance in event sponsorship.
Limitations
While this study provided information on the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship, several limitations should be considered when interpreting the findings. Sampling bias is one of the limitations due to the sampling method used in recruiting participants. The participants may not be representative of the broader population, potentially limiting the generalizability of the findings to other demographics or contexts. The reliance on self-reported data introduces the possibility of response bias, where participants may provide socially desirable responses or inaccuracies in their responses. It could affect the reliability and validity of the findings, particularly regarding sensitive topics such as attitudes towards celebrities and event sponsorship.
The study focuses on a specific set of research objectives related to the influence of celebrity presence and performance on event sponsorship. As such, it may not capture the full range of factors influencing consumer behavior and brand perceptions in the context of event sponsorship. Future research could explore additional variables and perspectives to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon. The study employs a cross-sectional design, capturing data at a single point in time. It limits the ability to draw causal inferences or assess changes in attitudes and behaviors over time. Longitudinal studies or experimental designs could provide more evidence of causal relationships between celebrity endorsements and event sponsorship outcomes.
Conclusions
The implications drew from this study focuses on the theoretical landscape of marketing and branding, offering a substantial contribution to existing knowledge. Through empirical evidence, the study supports and extends established theoretical frameworks, particularly with the focus on celebrity endorsement and event sponsorship. The findings corroborate associative network theory and congruence theory, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms through which celebrity endorsements influence consumer perceptions and behaviors. As such, the current study strengthens the foundation upon which future research in marketing theory can build, developing a deeper understanding of the complexities inherent in celebrity-brand associations.
The study also identifies and elucidates potential moderating factors that warrant attention in theoretical models of celebrity endorsement effectiveness. Factors such as celebrity authenticity and event context emerge as critical determinants of the impact of celebrity endorsements on brand associations and event attendance. With the understanding of moderating variables, it emphasizes the contextual nature of celebrity endorsements and highlights the need for comprehensive theoretical frameworks that account for situational factors.
Strategic planning for event sponsorship stands to benefit significantly from the findings, as they provide guidance on celebrity selection, contract negotiations, and event marketing strategies. Brands can capitalize on the influence of celebrities to enhance brand image and visibility, provided that endorsements are aligned with brand values and positioning.
References
Abidin C (2015) Internet (in) famous: The mystification and folklore of microcelebrification. In: AoIR Selected Papers of Internet Research 16: The 16th Annual Meeting of the Association of Internet Researchers, Berlin, 5–8 October 2015. Chicago, IL: Association of Internet Researchers.
Adam, M. A., & Hussain, N. (2017). Impact of celebrity endorsement on consumers buying behavior. British Journal of Marketing Studies, 5(3), 79-121.
Agarwal, P.K. & Garg, K. (2021). Celebrity Endorsement as a Tool of Maximizing Advertising Effectiveness Through Enhancing Brand Awareness, Brand Recall, and Building Brand Image - A Conceptual Review. 14. 252-278.
Agnihotri A, Bhattacharya S (2018) The market value of celebrity endorsement: Evidence from India reveals factors that can influence stock-market returns. Journal of Advertising Research 58(1): 65–74.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Agthe M, Spörrle M, Maner JK (2011) Does being attractive always help? Positive and negative effects of attractiveness on social decision making. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 37(8): 1042–1054.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Albert N, Ambroise L, Valette-Florence P (2017) Consumer, brand, celebrity: Which congruency produces effective celebrity endorsements? Journal of Business Research: 81(December): 96–106.
Albert N, Thomson M (2018) A synthesis of the consumer-brand relationship domain: Using text mining to track research streams, describe their emotional associations, and identify future research priorities. Journal of the Association for Consumer Research 3(2): 130–146.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alford, B. L., & Biswas, A. (2002). The effects of discount level, price consciousness and sale proneness on consumers’ price perception and behavioral intention. Journal of Business, 55(9), 775–783.
Ambroise, L., & Albert, N. (2020). Celebrity endorsement: Conceptual clarifications, critical review, and future research perspectives. Recherche et Applications En Marketing (English Edition), 35(2), 97-122.
Amos C, Holmes G, Strutton D (2008) Exploring the relationship between celebrity endorser effects and advertising effectiveness: A quantitative synthesis of effect size. International Journal of Advertising 27(2): 209–234.
Arnaudovska, E., Bankston, K., Simurkova, J., & Budden, M. C. (2010). University student shopping patterns: Internet vs. brick and mortar. Journal of Applied Business Research, 26(1), 31.
Atkin, C., & Block, M. (1983). Effectiveness of celebrity endorsers. Journal of Advertising Research, 23(1), 57-61.
Received: 23-Jun-2024, Manuscript No. AEJ-24-14986; Editor assigned: 26-Jun-2024, PreQC No. AEJ-24-14986 (PQ); Reviewed: 11-Jul- 2024, QC No. AEJ-24-14986; Revised: 16-Jul-2024, Manuscript No. AEJ-24-14986 (R); Published: 23-Jul-2024