Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 6
The financial contagion of novel corona virus SARS-COV-2 on Skechers U.S.A., Inc
Shaista Alvi, Amity University Dubai
Citation Information: Alvi, S. (2021). The financial contagion of novel corona virus SARS-COV-2 on Skechers U.S.A., Inc. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(6), 1-12.
Abstract
The study is of the financial performance of SKECHERS U.S.A., INC pre- and post-COVID--19 outbreak. The Novel B-coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID -19) shock in December 2019 has a near standstill effect on the global economy with lockdowns and quarantine policies announced by sovereign states. SKECHERS U.S.A., INC (NYSE: SKX) manufactures and sells branded lifestyle footwear for men, women, and children, under the Skechers Performance brand name. A descriptive exploratory design to perform financial analysis that compares Pre-COVID-19 period financial year ending 31st December 2017 to 31st December 2019 compared to Post-COVID-19 financial year ending 31st December 2020 the secondary data collected from the published financial statement including but not limited to consolidated balance sheet, consolidated income statement, consolidated cash flow, and consolidated statement of equity. The financial analysis was conducted with financial tools of ratio analysis and trend analysis for the period to measure the firm’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations, the impact on profitability, activity ratios, and solvency ratios. DuPont analysis was conducted for an in-depth analysis of profitability. Thereafter, Altman Z- score analysis was also undertaken to predict the financial distress which indicates that the company has a grey area.
Keywords
Financial statement; Skechers; Comparative analysis; COVID-19; Ratio analysis; Z-Score; DuPont analysis; Activity; Profitability and solvency ratios.
Company Background
SKECHERS U.S.A., INC. was founded by Robert Greenberg and Michael Greenberg (Skechers Executive Team, 2021) in 1992 in California and reincorporated in Delaware in 1999 with its headquartered in Manhattan Beach, CA. The group design and market Skechers-branded lifestyle footwear for men, women, and children, and performance footwear for men and women under the Skechers performance brand name. They also design and market men's & women's Skechers branded lifestyle apparels, and license their Skechers brand to others for accessories, leather goods, eyewear, and scrub manufacturers, among others. The company and its subsidiaries serve its customers in the USA, Asia, Europe, Canada, Central America and South America through its domestic wholesale, international wholesale & direct-to-consumer segments (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020).
The company has Class “A” common stock traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol "SKX" with 500,000 shares as authorized capital (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020). At the financial year ending 2020, the group had 3,891 Skechers stores around the world (Skechers Press release, 2020), including 2,570 distributors, licensee, and franchise stores with total sales of ~USD 4.59 Billion and net income of~ USD 98 Million with a total balance sheet footing of ~USD 5.8 Billion with total employees of 11.700 (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020).
Statement of the Problem
To explore the influence of COVID-19 on Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries financial performance and also compare it with pre-COVID-19 financial parameters having special reference to profitability, solvency, short-term liquidity, operational activities and financial distress analysis.
Research Objective
The aims are to perform the financial analysis and interpretation of the financial statements and explore the contagion on financial performance on the NYSE listed company Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries by:
1. Pre and post-COVID-19 global pandemic comparative detailed analysis on liquidity, activity, leverage, profitability ratios of the company
2. To evaluate the Bankruptcy Risk of the company due to the COVID-19 global pandemic
3. Identifying financial survival techniques of the company
4. Suggest appropriate recommendations on problems, strategies, and solutions.
Literature Review
Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) was recognized by the People’s Republic of China was declared by the Director-General World Health Organization as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) under the International Health Organization amendment of 2005 in the second meeting of the Emergency committee (Sharma, 2020) Sovereign states had taken austerity measures to prevent and reduce the effect of spreading the pandemic by imposing lockdown and quarantine orders. The consequences of the COVID -19 global pandemic on the retail sector had a divergent effect on traditional street-side shops compared to virtual shops, essential store compared to inessential store and small compared to large enterprises (OECD, 2020). Because of termination of business order, stay home directive for the workforce, manufacturing units shut down leading to the declining global trade which nearly came to sojourn affecting the survival of industries related to textiles, clothing, leather, and footwear (ILO Sectoral Brief, 2020). According to World Bank, the pandemic had created the grim recession worst since World War II in 1870 with the global economy was expected to contract by 5.2% in 2020 (Global Economic Prospects, 2020). To measure and ascertain the previous year and prospective financial position of a company is facilitated by the financial statement. To inform the financial health of a company it compromises four statements (i) Balance Sheets; (ii) Income statements; (iii) Cash Flow statements; and (iv) Statements of shareholders' equity (Fraser et al., 2016).
Financial statement analysis enables the company to evaluate the risk and prospects (Subramanyam & Wild, 2009). To benchmark the financial facts the financial ratios are employed as quantitative relations in measuring unit of coefficient (Coff.) or percentage. The financial ratio is an analytical tool for the financial health of the company and is classified into four groups of ratios namely liquidity ratio, activity ratio, leverage ratio, and profitability ratio. Even though, the independent ratios or as a part of the classification measure the liquidity, efficiencies metrics, financing structure, solvency, and profitability, DuPont analysis highlights the positive and negative financial condition and identifies the causes of issue in the performance of the company by investigating into the relationships of financial ratio to derive the overall return to shareholders (Fraser et al., 2016).
There are various studies to predict financial distress or bankruptcy; however, two studies have gained significance. Firstly, the univariate model of William Beaver indicated that the following ratios in chronological order of cash flow /total debt, Return on Assets (ROA), Total Debt/Total Assets (Debt ratio) predicted financial failure. Secondly, to predict bankruptcy multivariate model used the weighted five financials ratio developed by Edward I. Altman in 1968 which was called Altman's Z-score (Gibson, 2008).
Methodology
Research Design
The study has an exploratory Quantitative Descriptive design with a rationale to analyze the effects of global pandemic COVID -19 on the financials of SKECHERS U.S.A., INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES. A longitudinal analysis is also conducted on the aforementioned mentioned financials to analyze the financial metrics of the company thereby measuring the repercussions of this global pandemic.
Data Collection
The secondary data is collected from the company’s Website, Annual Reports, Sec filing over a financial period from 2017 to 2020 (Skechers Annual report, 2019; Skechers Press release, 2020; Skechers Form 10-K, 2020; Skechers Executive Team, 2021; Skechers website (2021).
Research Methods
The paper specifically studies for the period financial year ending 31st December 2020 as post-COVID-19 and pre-COVID-19 for three years from the financial year ending 31st December 2017 to 2019:
1. Consolidated Balance Sheets
2. Consolidated Statements Of Earnings
3. Consolidated Statements Of Comprehensive Income
4. Consolidated Statements Of Equity
5. Consolidated Statements Of Cash Flows
6. Notes To Consolidated Financial Statement
The financial analysis tools applied for evaluating the financial data were:
1. The Financial Ratios were calculated which facilitated the comparison and scrutinizing of the absolute financial data. The following financial ratios were categorized and implemented to measure the various financial aspects concerning:
a) Profitability
b) DuPont Analysis
c) Liquidity
d) Activity
e) Leverage
f) Altman’s Z score
2. Trend Analysis was undertaken to evaluate and compare the performance of the SKECHERS U.S.A., INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES over the financial period of 2017-2020.
Financial Analysis of Skechers U.S.A., Inc
The financial analysis is undertaken on the Consolidated Audited financials is based on the audited year-end (12 M) financials for FYE 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020. The Financials are audited by BDO USA, LLP and the audit is in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States)-PCAOB (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020) (Table 1).
| Table 1 Profitability | ||||||
| Parameters | Formula | MU | Audited FY 2020 | Audited FY 2019 | Audited FY 2018 | Audited FY 2017 |
| Gross Profit Margin | Gross profit*100 /Sales |
% | 47.63% | 47.72% | 47.90% | 46.56% |
| Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) Margin | EBIT*100 /Sales |
% | 3.72% | 10.03% | 9.43% | 9.39% |
| Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA) Margin | EBITDA*100 /Sales |
% | 6.83% | 12.17% | 11.79% | 11.71% |
| Net Profit Margin | Net profit*100 /Sales |
% | 3.18% | 8.19% | 8.00% | 5.65% |
| Return on Equity(ROE) | Net Profit*100 /Book Value Equity |
% | 5.36% | 16.85% | 16.96% | 12.07% |
| Return on Assets(ROA) | Net profit*100 /Total Assets |
% | 2.52% | 8.73% | 11.50% | 8.60% |
Sales
The Company recorded for the Financial Year Ending (FYE) 2020, 2019, 2018 & 2017 revenue of USD 4,597.40 Million, USD 5,220.10 Million, USD 4,642.10Million, (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020) USD 4,164.20 Million (Skechers Annual report, 2019). The trend analysis of Sales indicated that the company had negative growth of 12 % in the FYE 2020 compared to positive growth of 12 % & 11% in FYE 2019 & 2018 respectively.
It pointed out that COVID- 19 affected Sales growth of FYE 2020 that were recorded in absolute terms of USD 4,597.40 Million (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020) as compared to a higher pre-COVID -19 Sales levels of USD 4,642.10 Million FYE 2018 (Skechers Annual report, 2019), indicating a setback of sales that reached even below the 2018 level of activities.
Gross Profit Margin
As the Company does not own or operate any manufacturing facilities, the products are produced by independent contract manufacturers located primarily in Asia mainly in China & Vietnam. The cost of goods sold mainly includes the cost of footwear purchase from the manufacturers, duties, tariffs, quotas, freight, broker cost and storage cost, etc (Skechers Annual report, 2019). Hence the company was able to maintain Gross Margin at previous levels.
However, in absolute terms, Gross Profit decreased in the Financial Year Ending (FYE) in 2020 to USD 2189.80 Million as compared to USD 2491.20 Million, USD 2223.60 Million, (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020) and USD 1938.88 Million (Skechers Annual report, 2019) for the FYE 2019, 2018, 2017 respectively.
EBITDA
The COVID -19 Impact was also witnessed by a decrease in EBITDA in absolute terms in the Financial Year Ending (FYE) 2020 to USD 312.80 Million compared to USD 635.10 Million, USD 547.40 Million, and USD 487.50 Million for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively. The expenses related to warehouse distribution and also, as the company acquired Mexico unit the Depreciation & Amortization expenses increased due to stock compensation which included extraordinary payment concerning legal settlement (Skechers Annual report, 2019). Considering the above facts among other expenses the warehouse and distribution expense due to COVID shock as the company increased warehouse outlets which are functioning to clear up the inventory resulting in the all-time low EBITDA margin at 7% in the FYE in 2020 compared to 12% for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017.
EBIT
Due to increase in interest expense due to additional borrowings in absolute terms in the Financial Year Ending (FYE) 2020 to USD 16.3 million compared to USD 7.5Million, USD 5.8 Million, and USD 6.7Million for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively.
In addition, Royalty income decreased in FYE 2020 to USD 16 Million compared to USD 22.4 Million, USD 20.5 Million for FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively. EBIT Margin stood at reduced levels of 4% in the FYE 2020 compared to 10% for the FYE 2019 and 9% for FYE 2018 & 2017.
Net Profit
Due to the low EBIT and sales turnover the company also experienced a decreased profitability in joint ventures due to pandemic. In addition, the company was benefited by the decrease in the effective tax rate in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 was 5.5% n compare to FYE 2019 to 17.5 % which was primarily due to changes in the ownership structure of our international operations and related benefits provided by the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security ("CARES") Act (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020).
The net profit margin during the pandemic period of the FYE 2020 was lowest at 3% compared to 8%, 8% 6% for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively.
ROA
Return On Assets over the years have fluctuated with the lowest in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 recording 3% mainly due to increase in assets and low net profits which compared for the FYE 2019,2018 & 2017 which stood at 9%,12% & 9% respectively. It has been seen that the asset turnover has decreased over to 0.79 x during the FYE 2020, from 1.07x, 1.44x, 1.52x for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively (Table 2).
| Table 2 Dupont Analysis | ||||||
| Parameters | Formula | M u | Audited | Audited | Audited | Audited |
| FY2020 | FY2019 | FY 2018 | FY 2017 | |||
| Net Profit | USD Million | 146.20 | 427.30 | 371.30 | 235.10 | |
| Total sales | USD Million | 4,597.40 | 5,220.10 | 4,642.10 | 4,164.20 | |
| NPM | Net Profit *100 /Sales | % | 3.18% | 8.19% | 8.00% | 5.65% |
| Total Sales | USD Million | 4,597.40 | 5,220.10 | 4,642.10 | 4,164.20 | |
| Total Assets | USD Million | 5,812.40 | 4,892.90 | 3,228.30 | 2,735.10 | |
| Asset Turnover | Sales / Total Assets | Coff. | 0.79 | 1.07 | 1.44 | 1.52 |
| Total Assets | USD Million | 5,812.40 | 4,892.90 | 3,228.30 | 2,735.10 | |
| Equity | USD Million | 2,725.70 | 2,536.10 | 2,189.30 | 1,948.20 | |
| Equity Multiplier | Total Assets /Equity | Coff | 2.13 | 1.93 | 1.47 | 1.40 |
| DuPont Analysis -ROE | (NPM× Asset Turnover × Equity Multiplier?) | % | 5.36% | 16.85% | 16.96% | 12.07% |
This indicates that the company is not efficiently utilizing its assets during the pandemic period coupled with generating lower profit in FYE 2020 as a percentage (%) of its assets.
ROE (Return on Equity) in the financial year ending (FYE) 2017 stood at 12.07% with Net profit Margin and Asset Turnover majority contributing to it. In the FYE 2018, ROE increased to 16.96% mainly on account of improved Net Profit Margin, with a marginal increase in the company’s Leverage. However, in the FYE 2019, the ROE dropped marginally to 16.85% even though Net Profit Margin improved to 8.19% and increased the use of Leverage by 0.46x, however, it is to be noted that the Asset Turnover decreased by 0.37x during this period. In the FYE 2020, the Net Profit Margin decreased by 5.01% and Asset Turnover Ratio decrease by 0.28x compared to the FYE 2019, however, the use of Leverage increased by 0.20x indicating the increased risk in operation, hence, it can be assumed that due to global pandemic COVID-19, both the Operating Risk and Financing Risk was increased.
Current Ratio
As per trend analysis the current ratio has been decreasing in the financial year ending (FYE) 2018, and 2019 to 2.91x and 2.28x respectively. In the FYE 2020, it increased to 2.76x mainly on account of an increase in Cash & Cash Equivalent of USD 1.37 Billion, an increase of USD 545.9 Million as the company considers all highly liquid debt instruments with original maturities of three months or less to be Cash Equivalents (Skechers Form 10-K, 2020). The company had an outstanding in the Money Market payments of USD 423 million compared to USD 162.5 Million, USD158.6 Million, nil for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively (Table 3).
| Table 3 Liquidity Ratio | ||||||
| Parameters | Formula | MU | Audited FY 2020 | Audited FY 2019 | Audited FY 2018 | Audited FY 2017 |
| Current Ratio | Current Assets/Current Liabilities | Coff. | 2.76 | 2.28 | 2.91 | 3.52 |
| Quick Ratio | Current Assets-Inventory/Current Liabilities | Coff. | 1.92 | 1.41 | 1.89 | 2.06 |
Quick Ratio
The trend in the quick ratio is similar to the current ratio. In the financial year ending (FYE) 2020, the company decreased its inventory by USD 53 Million (Table 3).
Overall the above ratios indicate that the company's short-term liquidity is sufficient to meet the short-term debts.
Operating Ratio
As per the last four years, the company trends indicate that the working capital cycle days have increased to 266 days in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 compare to 197 days, 194 days and 185 days for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively. The above table indicates that Inventory Days have significantly increased in FYE 2020 to 154 days compared to 143 days, 130 days and 143 days in FYE 2019 for nil for the FYE 2018 & 2017 respectively (Table 4).
| Table 4 Operating Ratio | ||||||
| Parameters | Formula | MU | Audited FY 2020 |
Audited FY 2019 |
Audited FY 2018 |
Audited FY 2017 |
| Working capital Cycle Days | Inventory turnover days + Receivable turnover days - Payable turnover days | days | 266 | 197 | 194 | 185 |
| Inventory Turnover Days | Inventory*365/Cost of Good Sold | days | 154 | 143 | 130 | 143 |
| Receivable Turnover Days | Receivable*365 /Net Sales | days | 55 | 49 | 44 | 38 |
| Payable Turnover Days | Payable*365/Cost of Good Sold | days | 113 | 102 | 103 | 83 |
In addition, the Receivables Days have steadily increased in FYE 2020 to 55 days from FYE 2017 in the FYE 2020 compared to 49 days, 44 days, and 38 days for the FYE 2019, 2018 and 2017 respectively indicating an increased credit period which was availed by customers.
The company has also stretched the Payment to Suppliers over the years from 2017 to 2020. In FYE 2020 it had 113 days Payment to Supplier position as compared to 102 days, 103 days, and 83 days for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively.
Overall it can be inferred that in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 the pandemic had affected negatively (-) the Collection Period for Receivables, increase in Stock Turnover and increase in Supplier Credit provided by its suppliers which resulted in increased Working Capital Cycle further resulting in a delayed cash conversion cycle for the company.
Debt Equity Ratio (DER) & Solvency Ratio
Debt/Equity Ratio
The aforementioned table indicates that the Debt/Equity Ratio has been on an increasing trend to 1.13x in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 compared to 0.93x, 0.47x, 0.40x for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively. In the FYE 2019, DER was increased due to recording of an operating lease in the Balance Sheet during that financial year, however, in the FYE 2020, the company has net long-term borrowings of USD 616.6 million indicating that the company has increased its borrowings as steps to maintain Liquidity which was required because of the global pandemic effects on the business (Table 5).
| Table 5 Debt Equity Ratio (DER) & Solvency Ratio | ||||||
| Parameters | Formula | MU | Audited FY 2020 |
Audited FY 2019 |
Audited FY 2018 |
Audited FY 2017 |
| DER Ratio | Total Liabilities /Book value Equity | Coff. | 1.13 | 0.93 | 0.47 | 0.4 |
| Debt Ratio | Total Liabilities /Total Assets | Coff. | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.29 |
| Interest Coverage | EBIT/Interest Expense | Coff. | -10.49 | -69.81 | -75.47 | -58.36 |
| Total Liabilities /Tangible Networth | Current liabilities +Long Term Liabilities)/Tangible Networth** | Coff. | 0.6 | 0.49 | 0.31 | 0.26 |
Debt Ratio
In consonance, with the above ratio the Debt Ratio has also been on an upward trend at 0.53x in the financial year ending (FYE) 2020 compared to 0.48 x, 0.32 x, 0.29 x for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively.
Total Liabilities /Tangible Net worth (TOL/TNW)
The ratio has been on an upward trend to 0.60 x in the financial year ending 2020 compared to 0.49 x 0.0.31 x and 0.26x towards which indicates maintaining adequate solvency of the business.
Interest Coverage Ratio
This ratio has been fluctuating during the period of analysis. It had an increase in financial year ending (FYE) 2018 and thereon had shown negative (-) growth to reach at 10 x in the FYE 2020. This is mainly due to the company increasing borrowing in FYE 2020 therefore a high-interest expense is exhibited.
Altman Z Score
Wherein X1 = Working Capital/Total Assets ratio; X2 = Retained Earnings/Total Assets ratio; X3= Earnings before Interest and Taxes/Total Assets ratio; X4 = Market Value of Equity/Book Value of Total Debt ratio; X5 = Sales/Total Assets ratio (Altman, 1968).
In the financial year ending (FYE) 2020, the Z score was 0.0293x as per the classification the company falls in the Grey Zone which in between the risk of distress and non-distress zones, inferring a moderate probability of bankruptcy compared to 0.0409x, 0.0527x, 0.0788x for the FYE 2019, 2018 & 2017 respectively, indicating that the company was in a safe zone and financially sound health. The Z-Score has deteriorated, which may be due to global pandemic COVID-19. It is a difficult situation to predict its failure, given that there are greater possibilities of recovery of the overall financial health of the company, post-global pandemic COVID-19 effects on the global economy directing it to a healthy global business environment (Table 6).
| Table 6 Altman Z Score | |||||
| Parameters | MU | Audited FY 2020 |
Audited FY 2019 |
Audited FY 2018 |
Audited FY 2017 |
| X1 is the Working Capital/Total Assets ratio | Coff. | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.55 |
| X2 is the Retained Earnings/Total Assets ratio | Coff. | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| X3 is the Earnings Before Interest and Tax/Total Assets ratio | Coff. | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| X4 is the Market Value of the Equity/Total Liabilities ratio | Coff. | 1.80 | 2.83 | 3.42 | 7.52 |
| X5 is the Total Sales/Total Assets ratio | Coff. | 0.79 | 1.07 | 1.44 | 1.52 |
| Zscore * | Coff. | 0.02924 | 0.04089 | 0.05273 | 0.07875 |
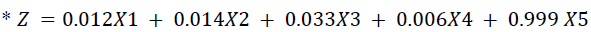
During the financial year ending (FYE) 2017 to 2020, it is observed that the coefficient (Coff) of working capital/total assets have been on decreasing trend in the pre-COVID -19 period, however, in post-COVID-19 in FYE 2020 is increased due to the increase in Total Assets which indicates that the company has been investing in Assets as well as it improved the Working Capital indicating a sound short term financial health.
Retained earnings/total assets had approximately remained stable during the financial year ending (FYE) 2017 to 2018, however, the declining trend was observed thereon demonstrating reliance on debt for financing the business as the profit retained were not sufficient to plough back for business.
a) EBIT/Total Assets have been on a declining trend
b) Equity/Debt has decreased by more than 700%
c) Sales/Assets recorded a deteriorating Trend
Hence, closer surveillance and monitoring of the financial performance of the company is suggested in that the event the global pandemic COVID-19 continues.
Discussion and Conclusion
The study was an evaluation of the financial health of Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries to measure the repercussion of a pandemic. To achieve the objective of the comparative analysis was undertaken for the period 2017 to 2020 with the pre-COVID-19 period being 2017, 2018 & 2019 and global pandemic COVID-19 FYE 2020 by applying the following Ratio & Trend Analysis:
a) Liquidity - Current Ratio & Quick Ratio
b) Profitability - Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin, EBITDA Margin, EBIT Margin, DuPont Analysis
c) Solvency - Debt Equity Ratio, Debt Ratio, TOL/TNW, and Altman's Z- score
d) Operational - Working Capital Days, Receivable Turnover Days, Inventory Days, and Payable Days
The Trend Analysis as demonstrated with tables indicates the changing trend over the period of this study
Although the company's business has been profitable during the global pandemic COVID-19 crisis, the contagion of a global pandemic on the financial performance of the company has affected operational activities with increased Cash Conversion, Lower Profitability, and increased indebtedness of the company indicating considerable Operating and Financial risk.
The company needs to increase its sales and increase profitability which can be plough back into the business and taking appropriate measures towards long term and short term indebtedness.
Moreover, the company also requires focusing on operational efficiency by the collection of receivables and increased turnover of inventory with effective working capital management strategies.
The above analysis is specific to the financial performance of Skechers U.S.A., Inc., therefore, further research is required for industry and peer group analysis and develop a financial model based on a larger sample and extending the period of study drawn from various countries for generalization of results and setting the norms for the industry. The financial model should be based on sensitivity analysis considering the worst-case scenario which includes internal and external factors affecting the industry for a prolonged period of 3 to 5 years with a substantial decline in liquidity and profitability parameters. This will enable the investors and governments to make their decision enabling the firms to garner the support of the stakeholders and plan for the future in the best possible way as a proactive measure instead of a reactive measure.
Limitations of Study
The following are the limitation has been experienced in conducting this study:
1. The study is based on secondary data including financial statements published for 2017-2020 in a public domain and has no access to the company’s internal information.
2. The Analysis and Interpretation on the factors based on the financial information.
3. Change in accounting policy and tax policy may have an impact on the analysis of financials.
4. There can be marginal calculation errors or differences in the tables exhibited in this study.
5. Time constraint is a major factor.
6. The external environment is dynamic and the analysis is based on the past financial performance of the company.
7. The analysis and interpretation of the financials is a subjective view of the researcher.
References
- Altman, E. I. (1968). Financial ratios, discriminant analysis and the prediction of corporate bankruptcy. The Journal of Finance, 23(4), 589-609.
- Fraser, L. M., & Ormiston, A. (2016). Understanding financial statement, 11th edition. Pearson.
- Gibson, C. (2008). Financial reporting and analysis: Using financial accounting information. Cengage Learning. Financial Reporting & Analysis. South-Western, Cengage Learning.
- Global Economic Prospects (2020). Global Economic Prospects, June, 2020. Retrieved from World Bank https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2020/06/08/covid-19-to-plunge-global-economy-into-worst-recession-since-world-war-ii
- ILO Sectoral Brief (2020). COVID-19 and the textiles, clothing, leather and footwear industries. Retrieved from https://www.ilo.org/sector/Resources/publications/WCMS_741344/lang--en/index.htm
- OECD (2020). The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. COVID-19 and the retail sector: impact and policy responses. Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/covid-19-and-the-retail-sector-impact-and-policy-responses-371d7599/
- Sharma, N. C. (2020, Jan). WHO declares coronavirus as Public Health Emergency of International Concern. Retrieved from https://www.livemint.com/news/world/who-declares-coronavirus-as-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-11580432732667.html
- Skechers Annual Report (2019). Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries. Annual report. Retrieved from https://d1io3yog0oux5.cloudfront.net/_7545ff0e897d3dddce61574941849fc9/skx/db/437/3330/annual_report/2019+Annual+Report.pdf
- Skechers Executive Team (2021). Skechers, about. Retrieved from https://about.skechers.com/executive-team/
- Skechers Form 10-K (2020). Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries 2020 FORM 10-K. Retrieved from https://investors.skechers.com/financial-data/all-sec-filings/content/0001564590-21-009442/0001564590-21-009442.pdf
- Skechers Press Release, (2020). Skechers U.S.A., Inc. and Subsidiaries (2021, February 4). Skechers Announces Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2020 Financial Results (press release). Retrieved from https://d1io3yog0oux5.cloudfront.net/_7545ff0e897d3dddce61574941849fc9/skx/news/2021-02-04_Skechers_Announces_Fourth_Quarter_and_Full_Year_474.pdf
- Skechers website (May, 2021). About Skechers USA. Retrieved from https://about.skechers.com/
- Subramanyam, K. R., & Wild, J. J. (2009). Financial Statement Analysis. New York: McGraw Hill.