Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 2S
The Effect of the Corporate Governance and Financing Decision on Financial Performance and Firm Value of the Banking Industry Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange
Syahriyah Semaun, IAIN Parepare
Keywords
Corporate Governance, Financing Decision, Financial Performance and Firm Value
Citation Information:
Semaun, S. (2022). The Effect of the Corporate Governance and Financing Decision on Financial Performance and Firm Value of the Banking Industry Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S2), 1-10.
Abstract
The aims of this research are: (1) to analyze the effect of corporate governance on financial performance; (2) to analyze the effect of financing decisions on financial performance; (3) to analyze the effect of corporate governance on firm value: (4) to analyze the effect of financing decisions on firm value; (5) to analyze the effect of financial performance on firm value. The population in this research is banking industry listed in Indonesian Stock Exchange 38 companies. Samples are 28 companies, in the period 2015 to 2019. The analysis technique in research used the program Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Based on results of data analysis show that: (1) corporate governance has a significant negative effect on financial performance; (2) financing decisions have a significant positive effect on financial performance; (3) corporate governance have a negative not significant effect on firm value; (4) financing decisions have a significant positive effect on firm value; (5) financial performance have a positive not significant effect on firm value.
Introduction
Good corporate management aims to provide adequate protection and treat shareholders and other interested parties fairly. Corporate governance is a system used to direct and control the company's business activities. Corporate governance regulates the duties, rights, and obligations of parties in the organization to the company's life, including shareholders, the board of directors, managers, and all members of non-shareholder stakeholders. In the financing policy, financial managers must consider and analyze the combination of various sources of funds that are economical for the company to finance multiple investment needs and business activities. Sources of funding consist of loan or debt capital and own capital. The use of each type of capital has a different effect on the company's net income. The use of money from loans will reduce net income because they have to pay interest. The amount of interest is used as a tax deduction borne by the company, while the use of own capital whose compensation is in the form of dividend payments taken from net profit after tax. The combination of various sources of funds reflects the financial structure and capital structure of a company. 1 The optimum capital structure is a balance of long-term debt and equity with a minimum average cost of capital. The company's financial performance is one of the factors seen by potential investors to determine stock investment. It becomes imperative for every company to maintain and improve its financial performance to survive and be in demand by investors. The financial statements issued by the company are a reflection of the company's economic performance. 2 The financial report serves as a means of information, a tool for management accountability to the company owner, describing the indicators of the company's success and as material for consideration in decision making (Harahap, 2004).
The company's financial performance is one factor that potential investors see to determine investment shares. 3 It becomes imperative for every company to maintain and improve its financial performance to survive and be in demand by investors. The financial statements issued by the company are a reflection of the company's economic performance. The financial report serves as a means of information, a tool for management accountability to the company owner, describing the indicators of the company's success and as material for consideration in decision making (Harahap, 2004). The higher this ratio means the more efficient the use of own capital by the company's management. 4The increase in this ratio from year to year in the company represents an increase in the company's net profit. The rise in net profit can indicate that the company's value rises because the increase in net income a company is concerned with would cause the stock price to rise, which also means the increase in the company's value. 5
Method
The population of this research is all banking companies that go public and are listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) during the 2015 – 2019 periods. The total population is 38 banks. At the same time, the sampling technique used in this research is purposive sampling. 6 The criteria for selection in this study are banking companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in 2015 - 2019. Companies that present and publish financial statements during the 2015 - 2019 research year do not experience losses during 2015 - 2019.
Data Analysis Method
The analytical method used in this research is Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) as follows:
1. Causality tiered, e.g., corporate governance affects the financial performance and then onwards affects the enterprise value of the banking industry.
2. The variables analyzed have latent variables. They are unobservable, for example, the value of a firm whose indicators are formative, as if they are variables that affect the latent variable. If one hand increases, it does not have to be followed by the rise in the other indicators in one latent variable.
The SEM model in this study is used to analyze the effect of corporate governance and financing decisions on financial performance and firm value, 7 with the following formulation:
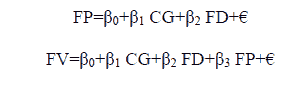
Description:
FP=Financial Performance
CG=Corporate Governance
FD=Financing Decision
FV=Firm Value
β0=Intercept
€= Error term
Variable Operational Definition
1. Corporate governance variables, the indicator as follows:
Managerial ownership describes share ownership by management, which is measured by the percentage of shares owned by management.
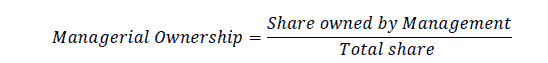
Institutional ownership describes the ownership of shares by institutional investors, measured by the percentage of shares owned by institutional investors.
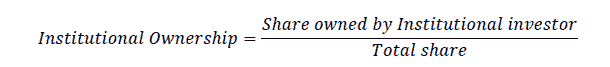
Board of Directors, in this research, were obtained from several boards of directors in the company.
Independent Commissioner measured using the proportion of independent commissioners sitting on the board of commissioners.
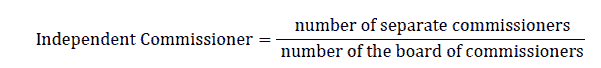
2. Financing Decision variables, the indicator as follows:
Debt Ratio (DR) or known as Leverage Ratio. In this study, the debt ratio will be measured by comparing total liabilities compared to total assets owned by the company.
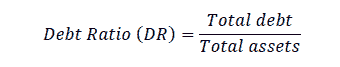
Debt to Equity Ratio describes the relativity of funding sources obtained from total debt compared to total equity.
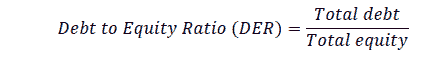
Long Term Debt to Total Equity describes the proportion of long-term debt to the company's equity.
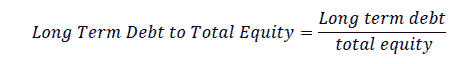
3. Financial performance variables, the indicator as follows:
The quick ratio this ratio is used to measure the ability of banks to fulfill the obligation to withdraw third party funds from the most liquid assets.
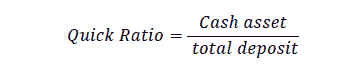
Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) is used to measure the ability of banks to fulfill loan withdrawals from depositors through repayment of loans given.
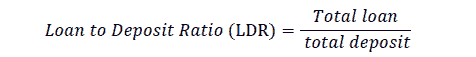
Return on Assets (ROA), this ratio shows the ability of management to manage all assets owned to generate pre-tax profits.
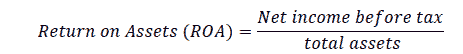
Return on Equity (ROE), this ratio measures the ability of banks to generate net income from equity owned.
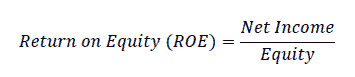
Non-Performing Loan (NPL) describes the ratio of total non-performing loans to total loans.
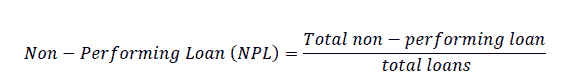
4. Firm Value variables, the indicators as follows:
Market to Book Value of Assets (MBA) shows that the company's growth prospects are reflected in market prices.
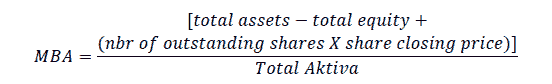
Price to Book Value (PBV) measures a company's value by comparing the share market price to its book value.
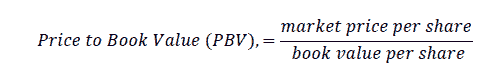
Price Earning Ratio (PER) is the ratio between the stock's closing price per share to net income per share.
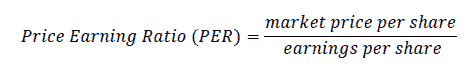
Tobin’s Q, shows market appreciation of the company's ability to generate profits.
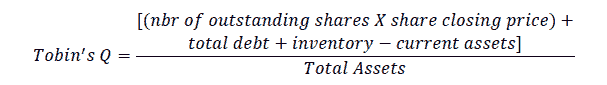
Results and Discussion
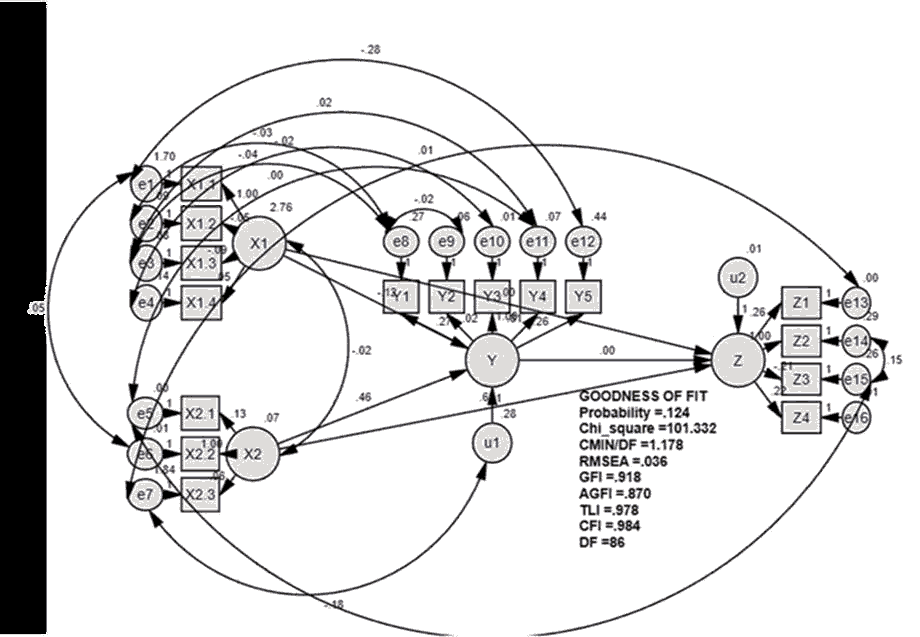
The results of the SEM analysis in the form of a path diagram are shown as follows: as shows in Figure 1.
The model test results shown in the figure above are evaluated based on the goodness of fit indices in table 1 below. The criteria for the model and the critical value that have data suitability are presented. 8
| Tabel 1 Evaluation Criteria Goodness Of Fit Indices Overall Model |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| The goodness of fit index | Hasil Model | Cut-off Value | Remarks |
| Chi-square | 1,01,332 | Expected smeller | Good Model |
| Probability | 0,124 | = 0,05 | Good Model |
| RMS | 0,036 | = 0,08 | Good Model |
| GFI | 0,918 | = 0,90 | Good Model |
| TLI | 0,978 | = 0,95 | Good Model |
| CFI | 0,984 | = 0,95 | Good Model |
| CMIN/DF | 1,178 | = 2,00 | Good Model |
The evaluation of the proposed model shows that the assessment of the model on the construct as a whole turns out that there are no critical violations from various criteria. Table 1 above shows that the result value has met the fit criteria so that the SEM model is appropriate to use. 9 After obtaining the overall model is declared fit, the significance test of the effect on the construct is carried out. This test uses the value of Critical Ratio (CR) or Probability (P) on standardized regression weights. The relationship between variables is said to have a significant effect if the P-value is 0.05 (5%). 10 The direct effect analysis to evaluate the effect of each construct on the immediate effect is the coefficient of all coefficient lines with one-pointed arrows on the test results presented. To find out how much influence between variables, an analysis of the direct power and indirect influence and the total effect is carried out. 11 as shows in Table 2.
| Tabel 2 Direct Effect, Indirect Effect Andtotal Effect Between Variable |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.No | Variable | Prob | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | Remarks | ||
| Independent | Intervening | Dependent | ||||||
| 1 | Corporate Governance | - | Financial Performance | 0,019 | -0,340 | - | -0,340 | Negative, Significant |
| 2 | Financing Decision | - | Financial Perfomance | 0,024 | 0,214 | - | 0,214 | Positive, Significant |
| 3 | Corporate Governance | Financial Performance | Firm Value | 0,732 | -0,015 | - | -0,015 | Negative, not Significant |
| 4 | Financing Decision | Financial Performance | Firm Value | 0,001 | 0,920 | 0,001 | 0,921 | Positive, Significant |
| 5 | Financial Performance | - | Firm Value | 0,982 | 0,001 | - | 0,001 | Positive, not Significant |
Mathematical models in the form of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) obtained the formula as follows:
- The effect of corporate governance and financing decision on financial performance, the formula as follows:
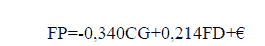
- The effect of corporate governance, financing decision, and financial performance on firm value, the formula as follows:
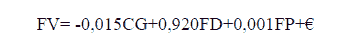
Description:
FP=Financial performance
CG=Corporate governance
FD=Financing decision
FV=Firm value
€=Error term
a. The Effects of Corporate Governance on Financial Performance
SEM analysis shows that corporate governance has a negative and significant effect on financial performance, as shown in table 2. The regression coefficient value is -0.340 with a p-value of 0.019 or less than 0.05. The value of the regression coefficient shows a different direction as hypothesized. 12 It means that considerable corporate governance will burden financial performance, so this research hypothesis is rejected. The results support Purweni Widhianningrum, Nik Amah (2012); Roza Mulyadi (2016), which show that Good Corporate Governance is proxied by the independent board commissioners' size significant adverse effect on financial performance. 13 The research object is the same as this research, namely the banking industry listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange. This study shows that a relatively large percentage of independent commissioners will reduce financial performance. Research strengthens the argument that more personnel on the board of commissioners can impact the poorer performance of the company (Yermack, 1996; Jensen, 1993).
b. The Effect of Financing Decision on Financial Performance
SEM analysis shows that the results follow the proposed hypothesis 2; namely, funding decisions have a positive and significant impact on the financial performance of the banking industry. It can be seen in table 2, where the regression coefficient value is 0.214 with a p-value of 0.024 or less than 0.05. 14 The coefficient values indicate the same direction as hypothesized. It means that better funding decisions will improve financial performance, so hypothesis 2 of this study is accepted. The results support Melinda Stefani Harefa (2015) research results, showing that capital structure has a positive and significant effect on financial performance and firm value. 15 This research strengthens the validity of MM's capital structure theory. The addition of debt can increase its ability to earn profits because more funds are available for its operations. The addition of debt results in an additional cost of capital is smaller than the company's benefits. The effect of taxation compensates for the extra cost of capital. 16
c. The Effect of Corporate Governance on Firm Value
SEM analysis shows that corporate governance has a negative and insignificant effect on firm value. It can be seen in table 2, where the regression coefficient value is -0.015 with a p-value of 0.732, which is greater than 0.05. The coefficient value shows a different direction from the hypothesized, so hypothesis 3 of this study is rejected. 17 It means that the corporate governance of the banking industry does not contribute to firm value. The results support Stefan Cristian Gherghina, et al., (2014), who found a lack of a statistically significant relationship between corporate governance ratings and firm value. It means that corporate governance is not a moderating variable of firm value. 18
d. The Effect of Financing Decision on Firm Value
SEM analysis shows that funding decisions have a positive and significant effect on firm value, as shown in table 2, where the regression coefficient value is 0.921 with a p-value of 0.001, which is smaller than 0.05. It means that the right financing decision will increase the value of the company. Therefore, hypothesis 4 of this study is accepted. The results support Mokhamat Ansori, et al., (2010), who found that financing decisions have a positive and significant effect on firm value. This study strengthens the validity of the trade-off theory (Myers, 1984), which emphasizes the principle of benefits and costs of capital. As long as the benefits are greater than the cost of money, the company tends to increase debt for productive investment activities. 19
e. The Effect of Financial Performance on Firm Value
Answering the problem formulation and hypothesis 5 can be observed from the SEM analysis, which shows that financial performance has a positive and no significant effect on firm value. It can be seen in table 21, where the regression coefficient value is 0.001 with a p-value of 0.982, more significant than 0.05. It means that financial performance does not have a substantial effect on firm value. 20 Therefore, this research hypothesis 5 is rejected. The results support Niyanti Anggitasari, et al., (2012) research results, who found that financial performance as proxied by ROA did not significantly affect the firm value as proxied by Tobin's Q. 21
Conclusion
Based on the results of the SEM analysis conducted on 28 banking companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in 2015-2019, the conclusions are as follows:
1. Corporate governance has a negative and significant effect on financial performance. It means that excellent corporate government will burden financial performance. One argument states that more personnel on the board of commissioners can result in the worse version of the company.
2. Financing decisions have a positive and significant impact on the financial performance of the banking industry. It means that better financing decisions will improve financial performance.
3. Corporate governance has an insignificant and adverse effect on firm value. It means that the corporate governance of the banking industry does not contribute to firm value.
4. Financing decisions have a positive and significant effect on firm value. It means that the right financing decision will increase the value of the company.
Financial performance has a positive and insignificant effect on firm value. It means that economic performance is not the only variable that directly affects the value of the company.
Endnotes
- Alas an-excuse that can be used as the basis for a divorce in accordance with Article 39 (2) Republic Act. Number 1 of 1974 concerning Marriage and Article 116 of Presidential Instruction Number 1 of 1991 concerning KHI are: a. One of the parties commits adultery or becomes a drunkard, compactor, gambler and so on which is difficult to cure; b. one of the parties leaves the other for 2 (two) consecutive years without the permission of the other party and without a valid reason or for other reasons against his will; c. One of the parties gets a prison sentence of 5 (five) years or a heavier sentence after the marriage takes place; d. One of the party’s commits cruelty or serious harm that is harmful to the other party; e. One of the parties has a disability or illness which results in the inability to carry out his obligations as husband/wife; f. Between husband and wife there are continuous disputes and quarrels and there is no hope of living in harmony again in the household; g. Husband violates Ta'lik Talak; h. Religious conversion or apostasy that causes disharmony that occurs in the household.
- Syahrizal Abbas, Mediation in the Perspective of Shari'ah Law, Customary Law, and National Law, p. 153.
- Makassar KPTA data, 2009.
- Sugiono, Administrative Research Methods, p. 91.
- Read further, if the population is large, and it is impossible for the researcher to study everything in the population, for example, due to limited funds, manpower, and time, the researcher can use samples taken from that population. What is learned from the sample, the conclusions will be applicable to the population? Sugiono, Administrative Research Methods, p. 91.
- This technique is used when the population has members/elements that are not homogeneous and proportionally stratified. Sugiono, Administrative Research Methods, p. 93.
- Hj. Harijah Damis, Deputy Chairperson of the Makassar Religious Court, Interview, at the Makassar PA office on 15 July 2014.
- Marhumah, Justice Seeker at the Makassar Religious Court, Interview, July 15, 2014 at the Makassar Religious Court office.
- Presented by H. Muhtar Gani, Judge Mediator of the Watansoppeng Religious Court during an interview on March 25, 2014.
- These three factors were conveyed during an interview with Muh. Yasin, Chairman of the Sidrap Religious Court on March 25, 2014.
- Slamet Muttaqin, Mediator Judge at the Sidrap Religious Court, Interview, 25 May 2014.
- Slamet Muttaqin, Judge Mediator at the Sidrap Religious Court, Interview, 25 May 2014.
- H. Makka A., Mediator Judge at Polewali Religious Court, Interview, April 8, 2014.
- Hj. Sulastri Kasim, Mediator Judge of the Sidrap Religious Court, Interview, 6 December 2013.
- H. Makka A., Mediator Judge at Polewali Religious Court, Interview, April 8, 2014.
- [16] Abdul Samad, Deputy Chairperson of the Polewali Religious Court, Interview, 17 December 2013.
- Abdul Manan, Ethics of Judges in the Administration of Justice, A Study in the Islamic Justice System, (Jakarta: Kencana, 2007), p. 177.
- Roihan A. Rasyid, Procedural Law of Religious Courts, New Edition (Cet. VI, Jakarta: Rajawali Pers, 1998), p. 97-98.
- Hj. Harijah Damis, Deputy Chairperson of the Makassar Religious Court Class IA, Interview, July 15, 2014 at the Head of the Makassar Religious Court.
- Abdul Sama, Deputy Chairperson of the Polewali Religious Court, Interview, March 11, 2014 at the Polewali Religious Court office.
- Muhtar Gani, judge of the Watansoppeng Religious Court, Interview, July 15, 2014 at the Watansoppeng Religious Court office.
References
Alam, S. (2019). Reconstruction of marriage zonation in Islamic law perspective. Legal Scientific Journal LEGALITY, 27(2), 161-176.
Allen, S., & Hawkins, A.J. (2017). Theorizing the decision making process for divorce or reconciliation. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 9(1), 50-68.
Amato, P.R. (2010). Research on divorce: Continuing trends and new developments. Journal of marriage and family, 72(3), 650-666.
Currie, A. (2011). Religious and cultural belief systems regarding death and the deceased body and their potential to impact upon forensic practice: Eastern religious belief systems and Maori culture. Pathology, 43(1), S25.
Durkheim, E. (2008). The elementary forms of the religious life. North Chelmsford, Massachusetts: Courier Corporation.
Tiara Sari, O. (2013). The effect of investment decisions, funding decisions and dividend policy on company value. Management Analysis Journal, 2(2).
Bambang, R. (2001). Basics of corporate spending. Fourth, Seventh Printing: BPFE, Yogyakarta.
Brealey, M.M. (2008). Fundamentals of corporate financial management, (Fifth Edition). Erlangga Publisher.
Brigham, E.F. (2014). Fundamentals of financial management book 1 (Eleventh Edition). Translated by Ali Akbar Yulianto. Jakarta: Salemba Four Publishers.
Emirzon, J. (2006). Regulatory driven principles of Good Corporate Governance (GCG) in regulating business activities in Indonesia. Sriwijaya Journal of Management & Business, 4(8).
Harahap, S.S. (2004). Critical analysis of financial statements, (First Edition). Fourth Print. PT. Raja Grafindo Persada. Jakarta.
Homaifar, J.Z., & Omar, B. (1994). An empirical model of capital structure: Some new evidence. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, 21, 1-14.
Ikatan Akuntansi Indonesia (2002). Financial accounting standards. Salemba Empat, Jakarta.
Jensen, M.C. (1986). Agency cost of free cash flow, corporate finance, and takeovers. American Economic Review, 76, 232-329.
Jensen, M.C. (1993). The modern test of effect of board size on firm efficiency. Economics Letter, 54, 259 -264.
Jensen, M., & Meckling, W.H. (1976). The theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency cost, and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305-360.
Jensen, G.R., Fonal, P.S., & dan Thomas, S.Z. (1992). Simultaneous determination of insider ownership, debt, and dividend policies. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 247-263.
La Porta, R., Lopez-de-Silanes, F., Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. (1998). Law and finance. Journal of Political Economy, 106, 1115-1155.
Megginson, W.L. (1997). Corporate finance theory. Addison-Wesley Educational Publishers Inc.
Meilinda, S.H. (2015). Analysis the influence of good corporate governance and capital structure to firm value with financial performance as intervening variable (Study at manufacturing companies that listed at Indonesia stock exchange). Retrieved from https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/77038/ MPRA Paper No. 77038.
Modigliani, F., & Miller, M. (1958). The cost of capital, corporation finance, and the theory of investment. American Economic Review, 48(3), 261-297.
Modigliani, F., & Miller, M. (1961). Dividend policy, growth and the valuation of shares. Journal of Business, 34, 411-433.
Modigliani, F., & Miller, M. (1963). Corporate income taxes and the cost of capital: A correction. The American Economic Review, 53, 433-443.
Mitton, T. (2002). A cross-firm analysis of the impact of corporate governance on the East Asian financial crisis. Journal of Financial Economics, 64, 215-241
Myers, S.C. (1977), Determinate of corporate borrowing. Journal of Finance Economics, 147-175.
Myers, S.C. (1954). The capital structure puzzle. Journal of Finance, 39(3), 575-572.
Myers, S.C., & Nicholas, S.M., (1964). Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information that investor do not have. Journal of Financial Economics, 13.
Niyanti, A.S.M. (2012). The influence of financial performance on company value with disclosure of corporate social responsibility and good corporate governance as moderating variables. Diponegoro Journal of Accounting, 1(2).
Purweni, W.N.A. (2012). The effect of good corporate governance mechanism on financial performance during the financial crisis of 2007-2009. Journal of Accounting Dynamics, 4(2), 94-102.
Roza, M. (2016). The effect of corporate governance on financial performance. Accounting journal, 3(1).
Shleifer, A.V. (1986). Large shareholders and corporate control. Journal of Political Economy, 94, 461-488.
Stefan, C.G., & Georgeta, V.I.T. (2014). A study on the relationship between corporate governance ratings and company value: Empirical evidence for S&P companies. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 6(7).
Sucipto. (2003). Financial performance assessment. Journal of Accounting, University of North Sumatra Undergraduate Program.
Sudiyatno, B. (2010). The role of company performance in determining the effect of macroeconomic fundamental factors, systematic risk, and company policy on company value. Disertasi: Universitas Diponegoro Semarang.
Tri Kartika, P.F.M. (2012). The effect of financial performance, good corporate governance on food and beverage company value. Journal of the Faculty of Economics.
Triyono, K.R., & Rina, A. (2013). The effect of dividend policy, ownership structure, debt policy, profitability and firm size on firm value in manufacturing companies on the Indonesia stock exchange. Pandanaran University, Semarang: Journal of the Faculty of Economics.
Weston, J.F., & dan Brigham, E.F. (1995). Fundamentals of financial management, (Ninth Edition). Jakarta: Erlangga Publisher.
Yermack, D. (1996). Higher market valuation of companies with small board of directors. Journal of Financial Economics, 40, 185-211.
Lukito, R. (2006). Religious ADR: Mediation in Islamic family law tradition. Al-Jami’ah: Journal of Islamic Studies, 44(2), 325-346.
McKoski, R.J. (2010). Re-establishing actual impartiality as the fundamental value of judicial ethics: Lessons from big judge Davis.
Nolan-Haley, J. (2012). Mediation: The new arbitration.
Shaydullin, R.R., & Baranov, S.Y. (2014). Mediation in Islamic law (Sharia) and its use in some countries of the islamic world.
Sujarweni, V.W. (2014). Research methodology: Complete, practical, and easy to understand. Yogyakarta: Pustakabaru press.
Taufik, A. (2021). The settlement principles and effectiveness of divorce by mediation of Islamic civil perspective: A critical review of the Supreme Court regulation. Justicia Islamica, 18(1), 168-188.
Tjersland, O., Gulbrandsen, W., & Haavind, H. (2015). Mandatory mediation outside the court: A process and effect study. Conflict Resolution Quarterly, 33(1), 19-34.
Wahab, R. (2002). Understanding qualitative research methods.