Review Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 4
The Effect of Telecommuting on Productivity : A Meta-Analysis
Shweta Tewari, Dayananda Sagar University
Citation Information: Tewari, S (2023). The effect of telecommuting on productivity: a meta-analysis. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(4), 1-7.
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to bring clarity to the existing research by reviewing and synthesizing the literature. Even more central, the relationship between telecommuting and productivity will be evaluated empirically using meta-analysis techniques. A review of the relationship between telecommuting and productivity is done by keeping four goals in mind: (1) to identify a comprehensive list of studies that have examined the relationship between telecommuting and productivity;(2) to review the studies from the quantitative perspective ;(3) to provide information the effect sizes; and (4) to assess the generalizability of the telecommuting effect on productivity across settings and subjects, including differences in research design. Design/Methodology/Approach: A meta-analysis is a useful tool for assessing the overall impact of a body of literature in instances where multiple researchers have examined the same relationship between variables. The technique has taken on increased importance in the medical research community (for its ability to provide an assessment of the outcome of several clinical trials, for example), and has contributed to the implementation of evidence-based healthcare(Sutton et al 2000).For example, recent meta-analytical studies have provided conclusive evidence of a relationship between weight reduction and lowering blood pressure (Neter et al. 2003) Findings: Major research has been made in the area of the effect of telecommuting on productivity, including previous narrative reviews. A recent study by Greta Onken-Menke, Stephan Nuesch, and Claudia Kroll, indicates that FWPs increase organizational attractiveness hence contributing to employer branding. Flexible work schedules and sabbaticals (but not telecommuting) increase organizational commitment and all FWPs decrease turnover intention. Our understanding of the issue concerning the effect of telecommuting on productivity is not well known, however, because these past consolidation efforts did not provide a conceptual framework combined with a quantitative analysis summarizing the results of prior studies. To understand thoroughly what past research has found regarding the relationship between telecommuting and productivity, a review should incorporate all types of research, including, qualitative, survey, experimental and econometric designs. Originality/Value: A comprehensive review encompassing all the existing published literature is needed to fully understand the exact impact of telecommuting on productivity. However, to date, there has been no quantitative integration (i.e. meta-analysis) study. To fill this void, the current research provides a quantitative integration of possible available published research conducted to determine what impact, if any, telecommuting has on productivity.
Literature Review and Hypothesis
Because previous research and reviews on the effect of telecommuting on productivity have reported mixed results, the effectiveness of telecommuting has been a point of controversy. The current research is a quantitative integration (meta-analysis) of the available published telecommuting research conducted to determine what impact, if any, telecommuting has on productivity. Results of the meta-analysis show that telecommuting has a significant effect on productivity. Telework has been associated with some negative outcomes, especially when employees telework a majority of the time. show that employees experience isolation when they telework for a longer duration of time. Additionally, they also report higher levels of family-to-work conflict Alpers et al. (2021), Brittany & MacDonnell (2012).
In addition, lower levels of coworker satisfaction. These mixed results show that the study of telecommuting requires more attention and that its effects are not fully known. On the other hand, several primary studies suggest telecommuting results in positive outcomes. Telework has been shown to have beneficial relationships with job satisfaction, supervisor-rated performance, work–family balance, and reduced stress and turnover intentions (Fonner & Roloff 2010; Gajendran & Harrision 2007; Golden & Veiga 2005; Golden et al.2006; Hill et al. 2003).
While telecommuting is one of the most researched and controversial factors involving productivity, the influence of telecommuting on productivity has long been a matter of debate(For example Walther 1992,Klaus and Bass 1982).So despite the proliferation of studies on the subject of telecommuting and productivity, no clear consensus exists regarding the impact of telecommuting on productivity of employees. Because of the mixed findings from decades of research and the lack of consensus regarding this relationship, there is disagreement about the exact impact of telecommuting on productivity and hence the effectiveness of telecommuting Campbell & Heales (2016), Clark (2007), Da et al. (2022).
Today's, adaptability is progressively perceived as a vital apparatus of giving an approach to oversee space, time, and workers all the more viably inside the vulnerability of condition and the down turning of worldwide economy. It moved toward becoming as a key arrangement received to build up a more grounded, increasingly practical firms with submitted, progressively profitable workers. As indicated by (Apgar, 1998) offering adaptability is beneficial system that human asset the executives can help make powerful relationship among workers and friends objectives. On the off chance that organizations can support individuals targets, the constructive outcome can prompt long haul productivity and viability to the firm by accomplishing business objectives (Greenhaus and Parasuraman 1997). A few researchers, for example, (Bird, 2006; Jacobs and Gerson, 2004; Cullbreath, 2010; Lewis et al,, 2008 ,Kang et al., 2006, Palmeri, 2013) have demonstrated that adaptable work plans were effective as they can profit the two representatives and businesses. Work environment rehearses that can enable representatives to deal with their work-individual lives have raised the enthusiasm of numerous analysts and professionals Gajendran (2017).
Among those practices adaptable work courses of action in particular have been touted as key that can furnish specialists with opportunity and self-rule to adjust their work and non-work obligations. Also, it's commonly considered as work choices that permit adaptability regarding when and where work is finished (Rau and Hyland, 2002). There has been an ongoing pattern in business and data innovation (IT) to end up more naturally upright (Green). In the wake of analyzing the maintainability activities of 30 extensive companies, Nidumolu, Prahalad, and Rangaswami (2009) inferred that supportability gives association and mechanical developments that will result in extra incomes and benefits. "We will meet our social commitment, however society will pay for it," said Jim Parker, Caterpillar VP of conveyance in the Americas (Gordon, 2011). Cost decrease is without a doubt an advantage that each association can appreciate. Organizations can likewise help spare expenses greenly through exercises, for example, working from home and virtual gatherings Hallman et al. (2021).
As indicated by Dennis Pamlin from the World Wildlife Fund, "Expanding virtual gatherings and working from home today could, with no sensational measures, help to spare in excess of 3 billion tons of CO2 emanations in a couple of decades; this is proportionate to around half of the current U.S. CO2 discharges" (Buttazzoni, Rossi, Pamlin, and Pahlman, 2009). Associations are likewise discovering that working from home is an extraordinary method to spare expenses into thea large number of dollars. It was accounted for that AT&T spared an expected $550 million by working from home (Nidumolu et al., 2009). Furthermore, AT&T assessed that their remote workers spared about 5.1 million gallons of fuel (Buttazzoni et al., 2009). Virtualization and other union procedures with PC equipment helped Citi spare $1 million on power and cooling costs by merging 15% of its 42,740 servers Ivasciuc et al. (2022).
Working from home that can be perceived as the capacity of individuals to get to work from remote area by utilizing PCs (Mamaghani, 2006). It imagined as an approach to limit the firm expense. What's more, it can possibly enhance representative efficiency while wiping out the time consumptions of physical driving by enabling individuals to work from outside the organization area (Siha and Monroe, 2006). It might move toward becoming as an answer for help individuals suit family-work commitments, diminish cutbacks, enhance representative duty and faithfulness, create cheerful and profitable laborers, lastly bolster the hierarchical execution Jöllenbeck et al. (2022).
Numerous researchers, for example, (Allen, 2001; McNall et al, 2010; Maxwell, 2007; Siha and Monroe, 2006; Palmeri, 2013; Cullbreath, 2010; Lambert, 2008, Allen et al, 2013) revealed positive relationship between those game plans as free factor and diverse ward factors like, work fulfillment, hierarchical execution, work family, efficiency, benefit, non-appearance, and work family balance. As indicated by Jin and Wu (2011), the advantage of teleworking not just brought down the expense of obliging representatives with office space yet additionally enhanced participation, assurance, and consequently productivity. USPTO runs 17 working from home projects, the two biggest of which are the Trademark Work-At-Home (TWAH) program and the PHP Koyama et al. (2021).
Ruth (2008) likewise examined the impacts of working from home on representative profitability, surveyed points of view from supervisors, office colleagues, and remote workers of the ramifications of working from home on efficiency. As indicated by the outcomes, members of the program displayed a noteworthy increment in compelling, duration, and standardizing duty in respect to a control gathering; in any case, in teleworking conditions that permit working only at home, authoritative responsibility was comparable to that of the control gathering. Mello (2007) investigated the commonness of and advantages and restrictions related with telecommuting and gave a proposal on the most proficient method to execute telecommuting.
As per Mello (2007) regardless of the all-around recorded ecological, societal, business representative relationship, teleworking can have some negative consequences for an association if not actualized deliberately. Recognizing and tending to the difficulties of working from home is vital to understand the potential advantages of teleworking. Lal and Dwivedi (2009) tested the normal statements concerning social separation. The creators examined and talked about how home laborers utilize their cell phone for social-cooperation purposes. The outcomes challenge the basic declarations concerning social disengagement inside the home-working writing. In the following area of the writing audit, the connection between occupation fulfillment and working from home will be discussed.
Fonner and Roloff (2010) tested suppositions with respect to the esteem and need of regular eye to eye work environment association by expanding upon a hypothetical system for the results of working from home. Franco and Gary (2011) recommended that with chose people, legitimate structure, and adequate criticism components set up, the selection of working from home has the ability to fortify an association's primary concern and give an unmistakable advantage to its representatives.
The current review and meta analytical tests of hypotheses are organized around the effects of telecommuting on productivity.
H1: Telecommuting has a significant effect on productivity.
H2: Telecommuting does not have a significant effect on productivity.
Review Procedures
Subjectively exploring examination is one technique for outlining research results. Be that as it may, one issue with subjective survey ,in logical inconsistency to a meta-examination, is that it doesn't consider the issues of impact estimate in each investigation, nor does it consider the nature of the study(Franke and Andrews 2003).Thus all things considered, when issues, for example, these are taken into account ,the discoveries of a subjective audit could be switched or nullified(Goldberg 2003).Therefore a superior method of outlining research results is to direct a meta-investigations, which factually or quantitatively cumulates inquire about discoveries.
The discourse of the examination technique is composed as pursues. To start with, the writing accumulation method is clarified. At that point the impact estimate calculation Is depicted. At last, the investigation of results under meta-examination is laid out.
Literature Compilation Technique
Over 60 years of empirical research on the effect of telecommuting on productivity will be reviewed and synthesized in this study. The search of relevant studies began with thorough computerized searches using EBSCOhost.In addition , the search examined the business source premier, academic search premier, PROQUEST Documents Next journals containing research on telecommuting were examined. The search produced approximately 100 published articles on telecommuting. Studies included meta analytical studies as well from various aspects.
Following Grewal er al (1997),the subsequent types of articles were not included in the meta-analysis because they do not provide necessary information :conceptual and/or review pieces(e.g. Lancaster and Lancaster 2003a;nelson 2006) and studies in which the empirical or the conceptual domains does not provide statistics that can be converted to the r statistic effect size.
Effect Size Computation
The effect size may be viewed as the relationship of strength ,or the magnitude of a relation.(Cohen 1977) defines effect size as the degree to which the phenomenon is present in the population or the degree to which the null hypothesis is false. Therefore the effect size is some specific nonzero value in the population in that the larger the value, the greater the degree that the phenomenon under study is manifested. For each study included in the quantitative review, The actual result (At F , or a mean and standard deviation) was converted into the zero-order product moment correlation coefficient m which is an easily interpretable ,scale free ,effect size metric (Hedges and Olkin 1985;Hunter and Schmidt 1990).
Results Analysis
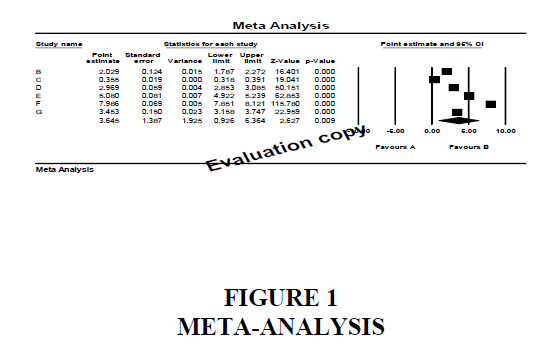
The objective of this study was to discover whether telecommuting has an effect on productivity of employees. To this end a meta-analysis using 6 studies was conducted. Please refer to Figure 1.
Virtually all studies have mean differences over 0.0,which means that telecommuting has higher influence over telecommuting positively. The effects seem to be reasonably consistent .The confidence interval for most studies overlaps the mean effect size.The fixed effect model would be more appropriate if all the studies were virtual replicates of each other. This is not the case, which is not the case here since the study populations varied in numerous(if unknown) ways. The random effects model would be more appropriate if the study vary in ways that may impact effect size. Therefore, we will use the random effects model.
A quick view of the plot suggests that telecommuting effect on productivity was always on a high or higher side .The observed effects are pretty consistent ,in that the confidence intervals for all studies overlap the mean effect size except one. The summary effect is 3.645 with a CI of 0.926-6.364.The summary effect has a z –value 2.627 a p-value 0.009.Thus we can reject null hypotheses. At the same time the magnitude of the mean difference is relatively modest.
The confidence interval tells us that the mean effect size falling the range of 0.926 – 6.364.It tells us nothing about how widely the true effect size varies from study to study. This is an important issue hence we need to distinguish between various possibilities such as-
➢ The mean is about 3 points higher
➢ That telecommuting sometimes has mean 0points higher, sometimes 3 points higher sometimes 5 times higher ,sometimes 7 or more points higher.
To address this we not only need the mean difference but also the standard deviation of the differences. Heterogeneity shows a test of null hypothesis that the true effect is identical in all the studies and that 100% of the variation in the observed effects is due to sampling error.
Summary
This analysis includes six studies where persons who telecommuted were compared with those who did not and their productivity was analyzed. Effect size was the difference in mean of productivity.
Is Telecommuting Related To Productivity?
The pooled difference in means is 3.645, which means that people who telecommuted had larger effect on productivity than those who did not telecommute.
These studies were samples from a universe of possible studies defined by certain inclusion/exclusion rules as outlined in full paper. The confidence intervals for the mean difference is 0.926-6.364 which tells us that mean difference that mean difference in the universe could fall anywhere in the range. This range does not include a difference of zero, which tells us that the true difference is probably not zero.
Similarly, the z-value for testing the null hypothesis is 2.627,with a corresponding p-value of 0.009.We can reject the null that telecommuting has no effect on productivity positively and conclude that telecommuting effects productivity positively.
Does The Effect Size Vary Across Studies?
The observed effect size varies somewhat from study to study, but a certain amount of variation is expected due to some error. We need to determine if the observed variation falls within the range that can be attributed to sampling error (in which case there is no evidence of variation in true effects) or if it exceeds that range.
References
Alpers, S.E., Skogen, J.C., Mæland, S., Pallesen, S., Rabben, Å.K., Lunde, L.H., & Fadnes, L.T. (2021). Alcohol consumption during a pandemic lockdown period and change in alcohol consumption related to worries and pandemic measures. (2021). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1220.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Brittany, H.M., & MacDonnell, R. (2012). Is telework effective for organizations?: MRN. Management Research Review, 35(7), 602-616.
Campbell, J., & Heales, J. (2016). Factor structure of individual consequences for teleworking professionals. Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 20.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Clark, L.A. (2007). Relationships between the big five personality dimensions and attitudes toward telecommuting (Order No. 3264816). Available from ProQuest One Business. (304825713).
Da, S., Silje, F.F., Wara, I., Christensen, M., & Siw, T.I. (2022). To change or not to change: A study of workplace change during the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 1982.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gajendran, R.S. (2017, Jan 15). Unlocking the promise of telecommuting: A technological revolution is gradually liberating the modern workplace by unchaining work from place. Business Today.
Hallman, D.M., Leticia, B. J., Mathiassen, S.E., Heiden, M., Svensson, S., & Bergström, G. (2021). Working from home during the COVID-19 outbreak in sweden: Effects on 24-h time-use in office workers. BMC Public Health, 21, 1-10.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ivasciuc, I.S., Epuran, G., Vu??, D.R., & Tesca?iu, B. (2022). Telework implications on work-life balance, productivity, and health of different generations of romanian employees. Sustainability, 14(23), 16108.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jöllenbeck, M., Maloku, O., Berling, I., Stamer, T., & Ochsmann, E. (2022). Healthy mobile work: The relationship of a participative work agreement and workplace health management-qualitative results of a longitudinal study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7526.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Koyama, S., Tabuchi, T., Okawa, S., Kadobayashi, T., Shirai, H., Nakatani, T., & Miyashiro, I. (2021). Changes in smoking behavior since the declaration of the COVID-19 state of emergency in japan: A cross-sectional study from the osaka health app. Journal of Epidemiology, 31(6), 378-386.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 07-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13208; Editor assigned: 08-Feb-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13208(PQ); Reviewed: 08-Apr-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13208; Revised: 20-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13208(R); Published: 21-May-2023