Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 6S
The Effect of Strategic Intelligence of Leaders on Organizational Innovation in Jordanian Industrial Companies
Husam Mahmmud Jamil Abu Hamour, Al-Balqa Applied University
Abstract
This research points to distinguish the affect leaders' strategic intelligence on organizational innovation in Jordanian mechanical companies. The study population included Jordanian mechanical companies, and the test comprised of (271) respondents from supervisors and workers at the upper and central regulatory levels in these companies. The research concluded that there is an impact of the components of the strategic intelligence of the leaders taken together (building vision, strategic focus, creativity capacity) on organizational innovation, and it was found that there is a high level of approval of the three dimensions from the sample's point of view. The study presented several recommendations, most notably the enhancement of the strategic intelligence practices of leaderships among managers and workers at the upper and central regulatory levels in Jordanian mechanical companies due to their clear impact on organizational innovation. That is by following the design of the company's mission within the framework of its vision in general terms that reflect the reason for its existence and its progress in written form.
Keywords
Strategic Intelligence of Leaders, Organizational Innovation, Jordanian Industrial Companies
Citation Information
Hamour, H.M.J.A. (2021 The effect of strategic intelligence of leaders on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 24(S6), 1-16.
Introduction
The strategic intelligence of leaders represents the degree of excellence in the leadership performance of the leaders of organizations in the areas of planning, attracting, and maintaining distinguished competencies, and this is related to the capacity of individuals or work groups to think and to act and impact others in a way that empowers these organizations to gain a competitive advantage (Arfat, 2017).
The literature has shown that organizational innovation has gotten to be the center of the authoritative prepare of any organization, as directors who oversee modern organizations must endeavor to create employees' capabilities, competence, the meaning of work, and self-direction to contribute to solving problems, and participate in the decision-making process, generate new ideas and work in the spirit of one distinguished and serious team to achieve better levels of performance at work. Consequently, organizational innovation must be at a level equivalent to the existing challenge. There must be innovation in administrative efforts, creating an integrated mix, and undertaking innovative activities that contribute to making the organization's performance in the best possible way (Daft, 2014).
Based on the foregoing, this study goals to identify the effect of leaders' strategic intelligence on organizational innovation; during a field study in Jordanian industrial companies, these variables constitute a strong pillar for research in the Jordanian industrial sector. The Jordanian industrial sector is considered one of the other business sectors most in need of such a study because of the intense competition from well-known international companies.
The Study Problem and its Questions
The researcher benefited greatly from the knowledge presentation that was the basis for the exploratory study that he carried out on several Jordanian industrial companies. He concluded that the problem lies in the fact that Jordanian industrial companies generally focus on traditional leadership methods and suffer from a weakness in adopting the strategic intelligence dimensions of leaders. It also complains of neglecting the issue of organizational innovation and capacity development. Also, these companies are more in need than other organizations of leaders with strategic intelligence. Hence, such a study is much needed because they are facing stiff competition from well-known global companies and are looking for more innovations to secure their place among those companies. Based on the foregoing, the purpose of this study can be achieved by answering the following questions:
The primary question: What are the recognitions of the test individuals of the key insight’s dimensions of the administrations within the Jordanian mechanical companies?
The second question: What are the respondents' recognitions of organizational development within the Jordanian mechanical companies?
The third question: Is there an impact of the leaders' strategic intelligence represented by (building the vision, strategic focus, the ability to innovate) on organizational innovation in the Jordanian industrial companies?
The Significant of the Study
The Theoretical Significant
The importance of the current study emerges from the intellectual enrichment that it may contribute to by tracing the theoretical literature and previous studies of concepts related to the main variables adopted in this study, whether independent or dependent, and represented by (strategic intelligence of leaders and organizational innovation) in the form that is an integrated conceptual framework for their relationship, characteristics, models and methodology of their studies, and because these variables are contemporary and have an influential nature in the life of contemporary organizations, which gives them efficient performance and continuous creativity.
Practical Importance
This importance comes from the possibility that the Jordanian industrial companies researched could benefit from their results to spread organizational innovation culture among their administrative leaderships, especially since this study is one of the rare studies as far as the researcher knows. Therefore, it is expected that the results of its results will benefit the researched Jordanian industrial companies by introducing them to the level of strategic intelligence of the leaders in them and the level of organizational innovation.
The Objectives of the Study
1. Identify the sample members' perceptions of the level of the strategic intelligence dimensions of the leaderships in the Jordanian mechanical companies.
2. Identify the sample members' perceptions of the level of organizational innovation in the Jordanian mechanical companies.
3. Identify the impact of the strategic intelligence of leaders on organizational innovation in Jordanian mechanical companies.
The Study Hypotheses
The researcher adopted the following main hypothesis: There is no statistically significant effect at (α≤0.05) level of the leadership's strategic intelligence (vision building, strategic focus, creativity ability) on organizational innovation in Jordanian mechanical companies. The following hypotheses are divided from it:
H1: There is no statistically significant effect of building the vision on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies.
H2: There's no factually critical affect of the key center on Jordanian mechanical companies' organizational advancement.
H3: There is no statistically significant effect of creativity on Jordanian industrial companies' organizational innovation.
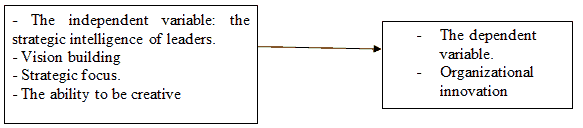
The Study Model
As shows in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The Study Model
Source: The sample prepared by the researcher based on the following references and studies:
- The independent variable: the strategic intelligence of leaders: The variables adopted by the study (Vera & Crossan, 2015), and the study (Sayed and Al-Sheikh, 2019).
- The dependent variable: organizational innovation: Variables adopted in the study (Victor, 2012), and the study (Vera & Crossan, 2015).
The Study Terms
Strategic Intelligence of Leadership
It is represented in Jordanian industrial companies' ability to find leaders who possess intelligence and knowledge to build future vision, strategic focus, and creativity. It is measured by the responses of the sample members to the items of the strategic intelligence scale of the leaders in the questionnaire, and that through the following dimensions:
- Vision Building: building the future path for the Jordanian industrial companies researched, which determines the destination they want to reach, the target center, and the type of resources and capabilities they plan to invest.
- Strategic Focus: It means focusing on thinking, tasks, efforts, and main requirements and managing time effectively to achieve the results targeted by the researched Jordanian industrial companies, away from the traditional and routine molds.
- The Ability to Innovate: That the Jordanian industrial companies researched constantly search for product development in a way that achieves great and new benefits for customers and works to achieve the maximum possible satisfaction of their needs and desires, and this requires carrying out new and modern research, administrative and marketing operations far from imitation, in addition to providing human resources, and material, financial and legal to conduct the process of modernization and development.
- Organizational Innovation: Jordanian industrial companies tend to develop new products or develop them and their success in providing those products, services, or new processes on an ongoing basis for their shareholders' benefit. Organizational innovation includes changes in the company's structure and operations to implement new management concepts and practices in it.
The Limits of the Study
- Temporal Limits: The study was completed during the period between (1-12-2019 until 5-1-2020).
- Spatial Limits: This study was applied in Jordanian industrial companies.
- Human Limits: It includes all managers and workers at the upper and middle management levels in these companies.
The Theoretical Framework
Strategic Intelligence of Leaders
Strategic leadership is described as the capacity to impact others to actualize daily decisions voluntarily that contributes to directing the organization in the long term while maintaining financial stability in the short term; strategic leadership also represents the ability of individuals or teams to think in an organized way, act well, and influence others (Beatty, 2010). Some view the concept of strategic leadership as those actions that focus mainly on defining long-term trends and the strategic vision and are based on communicating this vision to the relevant authorities; it represents the necessary strength that is based on the realization of that vision while having the ability to inspire others to go in the right direction (Crow, 2018).
Leaders' strategic intelligence is represented in developing employees' capabilities, urging them to accept changes, and directing them towards developing organizational behavioral patterns to achieve goals. It also helps to bring about a qualitative shift in the methods used in accomplishing tasks and adopting a positive behavior in carrying out duties and achieving goals, as well as the strategic intelligence of leaders plays a major role in the organization’s performance of its role in serving the local community as it works in it (Burns & Carpenter, 2008).
The researcher believes that the issue of raising the levels of strategic intelligence of leaders and the consequent decision-making and following the executive mechanisms in terms of acceptance or rejection by the subordinate and then the resultant success or failure is one of the fertile aspects of research and investigation, the strategic intelligence of leaderships is, in the end, a human art that needs a constant review in order to deal with it and present it more acceptably, this requires carrying out the exercise of the training process, which in turn has become an objective condition for the accomplishment of the task entrusted to the successful leader.
Accordingly, the leadership's strategic intelligence does not appear until after the administration has paid attention to the axes and roles that achieve its goals and objectives in the long run. These axes and roles are:
Building the Future Vision: The vision clarifies the main purpose of the organization’s existence in society, and the vision reflects the extent of the contribution that the organization can make to this community. The vision is also the mental image that the organization wishes to project about itself in others' minds and represents the organization's ambition and what it wants and desires to be in the future. To benefit from its mission, it must embody its vision in a tangible reality that its customers, employees, and suppliers see (Thomas, 2012).
Strategic Focus: The strategic focus policy, or the so-called management, focuses on several main axes, the most important of which is the focus on the strategic objectives of the organization in the scope in which it conducts its business, as well as the field of actual applications in one of the pillars on which the organization is based and focus on results as well. The policy of strategic focus is a post-stage of the strategic analysis stage. Upon completing the organization-wide strategic analysis process, strengths and weaknesses are identified, and opportunities and threats are identified (Al-Kurdi, 2011).
The Ability to Create: Creativity is a basic concept from the general concepts of creativity itself, and creativity in management science is related to new ideas, leadership and management of work teams, product development and improvement of services that are provided to clients, that is, creativity includes all known administrative functions, because of the complexity of the creative process, the thinkers and researchers approached various points of view to clarify what the concept of creativity is, so the difference in this theoretical concept came due to the different jurisprudence and the different scientific and cultural approaches, and the schools of thought to which these thinkers and researchers belong (Al-Hakbani, 2017).
The Organizational Innovation
For a long time, innovations remained an activity restricted to innovation centers or research and development departments in some large organizations, and even if this activity existed, it was seen as a wasteful activity with high costs. Still, this view has changed today, so organizations are gradually realizing the status of innovation and considering them important economic investments that guarantee the continuity, survival, and development of organizations. Innovation is the development and application of new ideas in the organization, and here is the word comprehensive development, as it covers everything from the new idea to the realization of the idea to bringing it to the organization and then applying it, innovation does not stop at the threshold of the new idea, but rather it is followed by practical application in the market or within the organization (Hassan, 2011).
Najm (2013) points out that organizational innovation means: “The organization’s ability to reach what is new adds more value and faster than competitors in the market. This definition means that the innovative organization is the first in comparison with competitors to come up with the new idea or concept: the first to reach the new product and the first to reach the market “.
Mustafa (2012) indicates that organizations of all kinds and forms have taken an interest in organizational innovation as an approach that helps them improve their level of performance. It can create and offer assistance amass individual aptitudes in considering and collective interaction through conceptualizing groups and increments the quality of choices that are made to address issues at the level of the organization or the level of its divisions and offices, within the different specialized, monetary, and promoting areas and those related to the social work environment.
The researcher believes that organizational innovation is new and different that distinguishes Jordanian industrial companies and gives them support in improving the level of performance, whether innovation is in the field of administrative or financial performance methods. An innovative treatment method is the innovation or use of a new method in presenting innovative products or undertaking a new organizational activity is innovation. Therefore innovation is linked to any action or new thing by the company, and it may be in the form of a new solution to an existing problem.
Previous Studies
The study of Víctor, et al., (2012) aimed to demonstrate the effects of transformational administration on organizational execution through learning and organizational innovation's energetic capabilities. The comes about uncovered that transformational authority influences organizational execution emphatically through organizational learning and advancement, and organizational learning impacts organizational execution emphatically, either straightforwardly or in a roundabout way through organizational innovation; organizational innovation affects organizational performance positively.
The study of Vera & Crossan (2015) aimed to identify the dimensions of strategic leadership, organizational learning processes, and their levels to describe how strategic leadership affects each element of the learning system. The study found that strategic leadership is sensitive to the past and dreamy of the future and focuses on executive work as a strategic activity, and it encourages open culture and flexible systems.
The study of Al-Husseini & Al-Beltagy (2016) aimed to study the impact of transformational leadership on the product and the innovation process, and the results showed that transformational leadership plays a pivotal role in enhancing the product and the innovation process and that the method would be ideal in the Iraqi educational context because it may enhance innovation development strategies.
A study of Abuzaid (2017) dealt with the impact of strategic intelligence and was studied through (foresight, vision and motivation on a pioneering approach. The aim was to study the impact of the strategy Intelligence information about the entrepreneurial trend. A study sample was taken for (36) diversified Jordanian financial services companies listed on the Amman Stock Exchange. Where the study sample includes all study population. A questionnaire was designed to collect the required data from the study sample and based on the results, organizations need to enhance strategic intelligence within them.
A study by Shehab, Buresh & Hathat (2017) aimed to shed light on the role of innovation in developing the competitive advantage of the enterprise and reached the importance that the institution has to rely on the adoption of innovation, especially concerning meeting the demands of customers concerning the products it offers, and this is what constitutes a continuation of its competitive advantage as a result of the continuous renewal of knowledge and experience.
The study of Joel, et al., (2018) aimed to develop and test a multi-level model linking transformational leadership and creativity in facing the challenges faced by team leaders in promoting individual and collective creativity. The results concluded that individuals had an indirect positive impact on individual creativity through individual skill development.
The study of Sayed Wal-Sheikh (2019) concluded a statistically significant effect of the strategic leadership practices represented in (building vision, strategic focus, creativity, strategic implementation, and strategic follow-up) in the marketing performance excellence in Jordanian private hospitals. Strategic leadership practices push the hospital to pay attention to excellence and achieve high marketing performance levels and a good reputation.
The study of Al-Janabi (2019) dealt with the strategic intelligence of leadership as one of the most prominent elements of human behavior, and its impact on organizational excellence in the presence of emotional intelligence as an intermediate variable, and concluded that there is an effect of strategic intelligence of leaders on organizational excellence in Iraqi banks with the presence of emotional intelligence as an intermediate variable.
Finally, the study of Al-Shamsi (2020) aimed to verify the level of the impact of transformational leadership on the organizational culture: the mediating role of organizational innovation in ministries in the United Arab Emirates from the point of view of employees in upper and middle management. The study found a statistically significant effect of transformational leadership in organizational culture through organizational innovation as an intermediate variable.
Study Methodology
Study Approach
This study is considered one of the field studies that followed the descriptive and analytical method and was completely dependent on the field survey of the study community, using a questionnaire that was specifically designed to serve the study's purposes and directions, and in line with the questions that the researcher adopted.
The Study Population and its Sample
The study population consists of all employees in the departments of Jordanian industrial companies. For the study, the random stratified sampling method was used, a sample consisting of thirty companies were selected from the study population of 63 companies, according to what was mentioned in the Amman Financial Market Bulletin for November 2019, and it was determined to include large companies and medium companies and from various activities to represent the study community in the companies. The inspection unit included managers working in upper and middle departments in the searched Jordanian industrial companies, and (10) questionnaires were distributed in each company. The number of distributed questionnaires reached (300), and (274) questionnaires were retrieved out of the total number of distributed questionnaires with a percentage of (91.3%) after the questionnaires were sorted, (3) questionnaires were excluded due to lack of validity and were incomplete. Thus, the sample settled on (271) respondents, with a percentage (90.3%) of the total distributed questionnaires.
The Study Tool
The researcher reviewed a number of previous studies and literature related to the subject of the study to design a questionnaire that included expressions related to leadership's strategic intelligence variables and organizational innovation. The researcher utilized the five-point Likert scale: Strongly agree (5 points), agree (4 degrees), neutral (3 degrees), disagree (two degrees), and strongly disagree (one degree).
As for the limits adopted by this study when commenting on the arithmetic mean, the researcher has identified three levels (weak, medium, and high) based on the statistical equations related to this aspect.
The Validity of the Study Tool
The researcher conducted a validity test to ensure the reliability of the study tool and the confidence in its results by presenting the questionnaire to a group of referees, university professors, and experts in administration and statistics to judge the extent of its apparent and logical validity and its validity as a tool for data collection.
The Reliability of the Study Tool
To ensure the validity of the questionnaire as a tool for collecting the necessary data for the study, the coefficient (Cronbach-Alpha) was used for the internal consistency of the items of the questionnaire as a whole, and it reached (93.2%), which is an appropriate and high-reliability rate.
It is noted from these values and as shown in Table 1 that the reliability coefficients for all the study variables were good and suitable for the study's purposes (Sekaran, 2016).
| Table 1 The Value Of The Reliability Coefficient Of Internal Consistency |
||
|---|---|---|
| Sequencing of the items | Variable | Cronbach coefficient alpha% |
| 1-30 | Strategic intelligence of leaders | 89.6 |
| 31-40 | Organizational innovation | 91.3 |
| 1-40 | The general rate of the reliability coefficient | 93.2 % |
Information collection methods: In this ponder, two sorts of data sources were depended on: essential sources and auxiliary sources, as follows:
First: Primary Data: These are data that the researcher relied on by designing a developed questionnaire to serve the subject of the study.
Second: Secondary Data: They are the sources of available data and information collected for other purposes, from library sources and from reviewing previous literature. These data strengthened the scientific frameworks and foundations to enrich the theoretical side of this study.
It is represented in the data obtained from libraries, scientific materials, specialized periodicals, publications, master's theses, and doctoral theses, especially those looking at leaders' strategic intelligence and organizational innovation.
Statistical Treatment
To answer the study questions, the following statistical analyze were used:
To answer the study questions, the following statistical analyze were used:
2. Multiple and basic direct relapse examination was utilized to test the impact of all autonomous factors collectively and independently on the subordinate variable, which is organizational development.
Results of the Study
Results related to the questions of the independent variable:
The Strategic Intelligence of Leaders
As shows in Table 2.
| Table 2 Arithmetic Means, Standard Deviations, And The Relative Importance Of The Vision Building Variable |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Items | Mean | STD | Relative importance | Rank |
| 1 | The company's management is keen to build the future path by making use of the results of the environmental analysis | 3.706 | 0.7310 | High | 7 |
| 2 | The company's management designs its mission within the framework of its vision in general terms that reflect the reason for its existence and its progress in written form. | 3.586 | 0.7183 | Moderate | 9 |
| 3 | The management of the company determines the strategic direction that serves to obtain a suitable competitive position. | 3.733 | 0.6224 | High | 6 |
| 4 | The company's management is keen to define the strategic directions and put them into practice | 3.626 | 0.8506 | Moderate | 8 |
| 5 | The company's management embodies the vision in a tangible reality that its customers perceive from its outstanding performance. | 3.946 | 0.6344 | High | 1 |
| 6 | The company's management determines the appropriate strategic alternatives through the participation of all administrative levels in the decision. | 3.800 | 0.6576 | High | 4 |
| 7 | The company's management focuses in its vision on the proper investment of the resources available to it | 3.893 | 0.6487 | High | 2 |
| 8 | The company’s management is making efforts to develop its position among other companies | 3.786 | 0.7586 | High | 5 |
| 9 | The company's management analyzes the external environment to find opportunities and threats and explores the internal environment to determine the strengths and weaknesses. | 3.853 | 0.7107 | High | 3 |
| 10 | The company's management is keen to build the future path by making use of the results of the environmental analysis | 3.706 | 0.7310 | High | 7 |
| Vision building | 3.770 | 0.2808 | High | ||
It appears that the answers of the sample members for the items of the vision building variable and the averages related to them came at a high level, as the arithmetic mean was (3.770) and a standard deviation (0.2808), and it ranged between (3.9467) and (3.5867). The item, "The company's management embodies the vision in a tangible reality that its dealer's touch with its outstanding performance," came first with a mean of (3.9467), which is higher than the general average, and a standard deviation of (0.63445). The item which states that “the company's management designs its mission within the framework of its vision in general terms that reflect the reason for its existence and its progress in written form” came last with an arithmetic mean of (3.5867), which is lower than the general average, and a standard deviation of (0.71836). The researcher believes that building a future vision is an important matter in organizational innovation in the Jordanian industry sector because this vision reflects the development of the future course of the company's work and determines its position as a strategic direction to provide products that live up to the customers' preferences.
Strategic Focus
As shows in Table 3.
| Table 3 The Arithmetic Means, Standard Deviations, And The Relative Importance Of The Strategic Focus Variable |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Items | Mean | STD | Relative Importance | Rank |
| 1 | The company's management focuses on implementing the vision and mission in the field reality. | 3.706 | 0.7123 | High | 7 |
| 2 | The company's management focuses on formulating the values that drive work in the realm of application as pillars of the organization. | 3.506 | 0.8442 | Moderate | 11 |
| 3 | The management of the company focuses on the strategic objectives of the society | 3.586 | 0.7183 | Moderate | 10 |
| 4 | The company's management is keen to scrutinize the vision and translate it into strategic actions through its plans | 3.733 | 0.6224 | High | 6 |
| 5 | Company management focuses on managing difficult tasks with a mind mixed with thoughtful emotions. | 3.626 | 0.8506 | Moderate | 9 |
| 6 | The company's management is keen to scrutinize the vision and divide the strategic business into plans and focus standards designed accordingly to the concept of strategic performance | 3.946 | 0.6344 | High | 1 |
| 7 | The company's management is keen to manage time away from the traditional and routine templates | 3.813 | 0.6716 | High | 4 |
| 8 | The management of the company is keen to focus on providing the main requirements to achieve its goals | 3.893 | 0.6487 | High | 2 |
| 9 | Company management sets standards for strategic performance | 3.786 | 0.7586 | High | 5 |
| 10 | The company’s management draws up a methodology for simplifying work procedures that contribute to achieving the goals. | 3.866 | 0.7039 | High | 3 |
| Strategic focus | 3.743 | 0.2691 | High | ||
The responses of the respondents to the items of the strategic focus variable and the averages related to them came at a high level, and that is from the sample's point of view, the general arithmetic mean was (3.743) and a standard deviation (0.2691), and it ranged between (3.9468) and (3.5067). The item “The company’s management is keen to scrutinize the vision and divide the strategic business into plans and focus standards designed according to the concept of strategic performance” came first with an arithmetic average (3.946), which is higher than the general arithmetic average, and a standard deviation of (0.6344). The item which states that “the company’s management focuses on formulating the values that drive work in the field of actual application as pillars of the organization” came last, with an arithmetic mean of (3.506), which is lower than the general arithmetic mean, and a standard deviation of (0.8442).
The researcher believes that organizational innovation in the Jordanian industry sector is based on focusing thinking, tasks, efforts, and the main requirements on achieving the company's results and based on scrutinizing his vision according to a list of strategic directions.
The Ability to Create
As shows in Table 4.
| Table 4 Means, Standard Deviations, And The Relative Importance Ofthe Creativity Variable |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Items | Mean | STD | Relative importance | Rank |
| 1 | The company is looking for developing new products that will achieve great benefits | 3.653 | 0.70698 | Moderate | 9 |
| 2 | The company is keen to conduct research operations that contain a kind of originality and renewal | 3.720 | 0.68891 | High | 7 |
| 3 | The company uses new methods or introduces developments in its marketing activities | 3.573 | 0.71986 | Moderate | 10 |
| 4 | The company attracts qualified and trained human resources to conduct the modernization and development process | 3.746 | 0.59487 | High | 6 |
| 5 | The company allocates material and financial resources for the necessary modernization and development process | 3.706 | 0.85065 | High | 8 |
| 6 | The company is keen to adopt new ideas in production processes and try to apply them at work | 4.000 | 0.54525 | High | 1 |
| 7 | The company makes changes to the technology it uses in the production | 3.853 | 0.67169 | High | 4 |
| 8 | The company is keen to develop and amend methods, procedures, and work methods in its policies and strategies in line with environmental requirements | 3.893 | 0.64877 | High | 2 |
| 9 | The company is keen on establishing and designing specialized departments or units to carry out specialized activities | 3.813 | 0.78316 | High | 5 |
| 10 | The company uses research and development methods of work to help solve the problems it faces | 3.880 | 0.71584 | High | 3 |
| The ability to be creative | 3.784 | 0.2536 | High | ||
It appears that the responses of the respondents to the items of the creativity variable and the averages and standard deviations related to them came at a high level, as the arithmetic mean was (3.784) and a standard deviation (0.2536), and it ranged between (4.000) and (3.573). The item “The Company is keen on adopting new ideas in production processes and trying to implement them at work” came first with a mean of (4.000), which is higher than the general arithmetic mean and a standard deviation of (0.5452). The item which states that "the company uses new methods or introduces developments in marketing activities" ranked last, with an arithmetic mean of (3.573) which is lower than the general arithmetic mean, and a standard deviation of (0.7198). The researcher believes that Jordanian mechanical companies' interests can contribute to achieving creativity in many aspects of their work and parts. Creativity cannot be achieved in the company as a whole without achieving this in other levels in it, which indicates that creativity has levels that must be achieved for the company to enjoy organizational innovation, which enables it to outperform its competitors (Table 4).
The Dependent Variable: Organizational Innovation
As shows in Table 5.
| Table 5 Means, Standard Deviations, And The Relative Importance Of The Organizational Innovation Var |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Items | Mean | STD | Relative importance | Rank |
| 1 | The company focuses on continuously developing new products or processes for the benefit of customers | 3.516 | 0.8397 | Moderate | 9 |
| 2 | The company is keen to make changes in its organizational structure to implement new management concepts and practices such as teamwork | 3.333 | 0.6644 | Moderate | 10 |
| 3 | The company has to prepare in advance to deal with any potential difficulties | 3.853 | 0.6083 | High | 3 |
| 4 | The services provided by the company are of added value. | 3.813 | 0.7295 | High | 5 |
| 5 | The company is making distinct and innovative efforts to provide services that satisfy customers. | 3.951 | 0.4932 | High | 1 |
| 6 | The company is constantly keen to improve the level of its products. | 3.693 | 0.6773 | High | 7 |
| 7 | The company is interested in innovating new ways and methods of presenting its products. | 3.853 | 0.5621 | High | 3 |
| 8 | The company seeks to take advantage of technological developments to provide the best products to the customers. | 3.893 | 0.7273 | High | 2 |
| 9 | The company is working on expanding the opportunities associated with offering its products to customers | 3.760 | 0.6943 | High | 6 |
| 10 | The company has the mechanisms to confront the information and communication technology revolution in innovative ways. | 3.623 | 0.6876 | Moderate | 8 |
| The dependent variable: organizational innovation | 3.728 | 0.2406 | High | ||
It appears that the answers of the study sample individuals for the items related to the dependent variable: organizational innovation and the means and standard deviations related to them came at a high level, as the mean was (3.728) and a standard deviation (0.2406). And it ranged between (3.951) and (3.333). The item “The Company is making distinguished and innovative efforts to provide services that satisfy customers” came first with a mean of (3.951) which is higher than the general arithmetic mean and a standard deviation of (0.4932). The item which states "the company uses new methods or introduces developments in marketing activities" ranked last, with a mean of (3.333), which is lower than the general mean, and a standard deviation of (0.6644) (Table 5).
The researcher believes that organizational innovation should benefit Jordanian industrial companies and be characterized by the generality of its effects and benefits because its success requires providing scientific and technological capabilities of scientific and technological knowledge, theories and market demand, and economic aid that transforms scientific and technological capabilities into products and services that meet market demand.
Testing Hypotheses
The main hypothesis states that: There is no statistically significant effect at (0.05 α) level of the strategic intelligence of leaders represented by (vision building, strategic focus, creativity capacity) on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies. To test the hypothesis, multiple linear regression analysis was used to find out this effect, as the results contained in Table (6) show the following:
| Table 6 Multiple Regression Analysis Of The Effect Of The Leaders' Combined Strategic Intelligence Variables On Organizational Innovation |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis of variance (ANOVA) | ||||||||
| Model | Sum of squares | df | Mean of squares | Calculated (F) | Sig | |||
| Regression | 220.919 | 3 | 73.639 | 38.411 | 0.000* | |||
| Residual value | 61.354 | 267 | 0.229 | |||||
| Total | 282.273 | 270 | - | |||||
| Coefficient’s analysis | ||||||||
| Variables of strategic intelligence for the leaders included in the regression model | Standard error | Standard transactions (Beta) |
Calculated (F) | Sig | ||||
| Fixed limit (0.325) | 0.055 | - | 5.25 | 0.000 | ||||
| Vision building | 0.267 | 0.376 | 7.783 | 0.000 | ||||
| Strategic focus | 0.238 | 0.319 | 6.219 | 0.000 | ||||
| The ability to be creative | 0.223 | 0.380 | 6.774 | 0.000 | ||||
| Correlation coefficient (R)=0.998, coefficient of determination (R2)=0.996, modified coefficient of determination (Adj R2)=424, *: Statistically significant at (0.05 =a) significance level. | ||||||||
It is evident from Table (6) that the three independent dimensions of the strategic intelligence of leaders, which were adopted as independent variables combined, i.e., the value of the coefficient of determination (R2) explains the percentage (99.7%) of the differences between the respondents of the study sample in organizational innovation. As the value of the modified coefficient of determination (Adj. R2). (0.424) Depending on the value of (F) for the model, which amounted to (38.411), and its level of significant significance (P), which amounted to (0.000), it turns out that the effect of these three dimensions on organizational innovation is statistically significant. It was found through the values of the standard transactions (Beta) shown in Table (7) that the variable of creativity was the most influential in organizational innovation, as the value of its standard parameter (β) reached (0.380), which is statistically significant, where the significant value (t) was (Sig) (0.000), which is less than the level of significance (0.05). It was followed by the variable of vision construction, where the value of the standard parameter (β) reached (0.376), which is statistically significant, where the value of (t) (Sig) (.000) which is less than the significance level (0.05), then came the technology variable. Finally, came the strategic focus variable and it was the least influential in organizational innovation, where the value of the standard parameter (β) was (0.319), which is statistically significant, where the value of (t) is significant (Sig) (0.000), which is the lower than the significance level (α≤0.05). Accordingly, the main nihilistic hypothesis of the study is rejected, and the alternative hypothesis is accepted, which states, “There is a statistically significant effect at (α≤0.05) level of the strategic intelligence of leaders represented by (vision building, strategic focus, and creativity capacity) on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies.” As for testing the hypotheses stemming from this hypothesis, the results showed the following:
- Rejects the first hypothesis and accepts the alternative hypothesis, which states that "there is a statistically significant effect of building a vision on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies”; Where the significant (t) value (Sig) was less than the significance level (0.05).
-Rejects the second hypothesis, which states that “there is a statistically significant effect of the strategic focus on organizational innovation in the Jordanian industrial companies, as the value (t) of the significant (Sig) was less than the level of significance (0.05).
- Rejects the third hypothesis, which states that “there is a statistically significant effect of creativity on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies,” as the value (t) of the significant (Sig) was less than the level of significance (0.05).
Discussion of the Results
The hypothesis test results indicated a statistically significant effect of the variables of strategic intelligence of the collective leaders, represented by (building vision, strategic focus, and creativity) on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies. This result is consistent with the result of the study (Vera & Crossan, 2015) that the dimensions of strategic leadership have the effect of strategic leadership in every element of the learning system. This result is also consistent with the result of a study (Víctor et al., 2012) which concluded that transformational leadership affects organizational performance positively through organizational innovation. It was also found that the leaders' strategic intelligence helps the company make distinct and innovative efforts to provide services that satisfy customers by taking advantage of technological developments to provide the best products to customers and interest in innovating new methods in presenting their products. In addition to making them ready in advance to deal with any potential difficulties. This result is also consistent with the result of the study of Sayed & Al-Sheikh (2019), which concluded that there is a statistically significant effect of strategic leadership practices in distinguishing marketing performance.
This result reflects the importance of the leaders' strategic intelligence, which has become an important focus on which the various activities in the company are based. In light of the growing duties and the large size of companies, and the complexity of their work, the urgent need to effect change and appropriate development in a manner that guarantees them to carry out the duties entrusted to them. This is a mission that can only be achieved under a conscious leadership that possesses intelligence, leadership skills, and strategic perceptions that enable it to mobilize efforts and direct the energies and manpower in the company to achieve the best level of achievement, organizational innovation, and the launch of innovative ideas that enhance companies' ability to provide products. The results of the sub-hypothesis test showed that:
First: The existence of a statistically significant impact on building the vision on organizational innovation in the Jordanian industrial companies. As for the arithmetic averages of the paragraphs related to this variable, it came at a high level, and it was found that the senior management in the company embodies the vision workforce able reality that its dealers touch with its distinguished performance. It focuses in its vision on the proper investment of the resources available to it and analyzes the external environment to identify opportunities and threats and analyze the internal environment to find out the strengths and weaknesses; the senior management also determines the appropriate strategic alternatives through the participation of all administrative levels in the decision. It is making efforts to develop the company's position among other companies. This result is consistent with the findings of the study of Al-Husseini & Al-Beltagy (2016), which showed that leadership plays a pivotal role in enhancing the product and the innovation process.
The researcher accepts that characterizing the key discernments of the company and creating a long-term vision for key expectation, in turn, reflects the individual sees of the cleverly and rousing pioneer in case the key pioneer can clarify his point of see and include his subordinates in it. He gets their bolster for his vital vision, which makes the leader's vital aim a idiosyncrasy.
Second: The existence of a statistically significant impact of the strategic focus on organizational innovation in the Jordanian industrial companies. The means of the items related to this variable came at a high level. It was found that the senior management in the company is keen to scrutinize the vision and divide the strategic work into plans and focus standards designed according to the concept of strategic performance. It is keen to focus on providing the main requirements to achieve its goals by drawing a methodology for simplifying work procedures that contribute to achieving the goals as well as showing that senior management is keen on managing time away from traditional and routine templates and is also keen to set standards for strategic performance in the company. It also focuses on thinking on the mechanisms of implementing the vision and mission in the real field. This result is consistent with the results of a study by Shahab, Buresh & Hathat (2017), which concluded its importance in focusing its strategic thinking on adopting innovation, especially concerning meeting customer demands.
This result indicates the need for leaders to focus strategically as a process characterized by continuous effectiveness. The leader can specifically influence the people who work with him and deliver the vital data for his choices.
Third: The existence of a statistically significant effect of creativity on organizational innovation in Jordanian industrial companies. It was found that the means of the items related to this variable came at a high level, and this result is consistent with the result of a study (Joel et al., 2018), which concluded that individuals had an indirect positive effect on individual creativity through the development of individual skills.
It turns out that the company is keen to adopt new ideas in the production and presentation of products and to try to implement them at work, and is also keen to develop and amend methods, procedures, and work methods in its policies and strategies in line with environmental requirements, and it uses research and development methods to help solve the problems it faces and make changes in the technology you use to produce and deliver products.
This result reflects the importance of researching the issue of advancing strategic leadership thinking and the consequent decisions and implementation mechanisms in terms of acceptance or rejection by the subordinate, and then what results from the success or failure of research operations need permanent revision to present it in its most acceptable form, which requires the ability to be creative.
Recommendations
The researcher recommends the need to enhance the strategic intelligence practices of leaderships among managers and workers at the upper and middle administrative levels in Jordanian industrial companies, due to their clear impact on organizational innovation, by following the following mechanisms:
1. Emphasizing the senior management by designing the company's mission within its vision in general terms reflects the reason for its existence and its progress in written form.
2. Emphasis on senior management to be keen on defining strategic directions and putting them into practice.
3. Emphasis on the senior management to be keen on building the company's future path by using the results of the environmental analysis.
4. Emphasizing the company's senior management by focusing on formulating the values that drive work in the actual application as pillars of the organization.
5. Emphasizing the company's senior management by focusing on managing difficult tasks with a mind mixed with thoughtful emotions.
6. The necessity for the senior management in the company to focus their thinking on implementing the vision and mission in the field reality.
7. Emphasizing the company's senior management the necessity of using new methods or introducing any recent developments in marketing activities while allocating the material and financial resources for the necessary modernization and development process.
8. The company searches for developing new products to achieve great benefits by translating strategy into actionable programs.
9. There is a need to conduct more research and studies on the topic of strategic intelligence and and organizational innovation in various sectors.
10. Organizations need to incubate and enhance strategic intelligence within them by strengthening capabilities to their senior management in formulating a clear vision
11. Adopting a common goal, implementing a clear vision, and increasing the ability to innovate.
Note: This research is supported by Al-Balqa Applied University - Deanship of Scientific Research and innovation.
References
- Abuzaid, A.N. (2017). Exploring the impact of strategic intelligence on entrepreneurial orientation: A practical study on the Jordanian diversified financial services companies. International Management Review, 13(1), 72-84.
- Al-Janabi, A. (2019). Strategic intelligence of leadership and its impact on organizational excellence in the presence of emotional intelligence as an intermediate variable, (An applied study on commercial banks in Iraq, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Gezira, Sudan.
- Al-Husseini, S., & Al-Beltagy, I. (2016). Transformational leadership and innovation: A comparative study of public and private higher education in Iraq, Publications of the Graduate School of Management, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, United Kingdom. Translated and edited by Al-Bayan Center for Studies and Planning.
- Hassan, R. (2011). The conduct of modern business organizations. University House for Publishing and Distribution, Alexandria, Egypt.
- Al-Haqbani, T. (2017). Creative orientation. Ain Shams Library, Cairo, Egypt.
- Sayed, A., & “Khaled Muhammad” K. (2019). The effect of strategic leadership on distinguishing marketing performance in Jordanian private hospitals. The Islamic University Journal of Economic and Administrative Studies, 27(2), 117-142.
- Al Shamsi, A. (2020). The impact of transformational leadership on organizational culture: The mediating role of organizational innovation in the ministries of the United Arab Emirates. Ph.D. Thesis, International Islamic Sciences University, Amman, Jordan.
- Al-Kurdi, A. (2011). The impact of focus and strategic implementation on human resources management in business organizations. Egyptian Step magazine, issued by the Arab Council for Development, (9), 132-149. Cairo
- Lashhab, A., Boresh, A., & Hathat, S. (2017). The role of innovation in developing the enterprise's competitive advantage: A field study of a civil engineering company in the wilaya of Ouargla. The Algerian Journal of Economic Development, 07/December 20.
- Mustafa, A. (2012). Human management (origins and skills). University House for Publishing and Distribution, Alexandria, Egypt.
- Najm, N. (2013). Innovation management. WAEL publishing and distribution house, Amman, Jordan.
- Arfat, Y., Rehman, M., Mahmood, K., & Saleem, R., (2017). The role of leadership in work engagement: The moderating role of a bureaucratic and supportive culture; Department of Management Sciences, Superior University, Lahore, Pakistan. Pakistan Business Review, 1(1), 688-7059
- Beatty, Q. (2010). Strategic command taking the long view for organizational success. Leadership in Action, 30(1), 3-7.
- Burns, J.M., & Carpenter, J. (2008). Organizational citizenship and student achievement. Journal of Cross-Disciplinary Perspectives in Education, 1(1), 51 – 58.
- Crow, W. (2018). Strategic leadership. N. Y. Simon & Schuster Press.
- Daft, R. (2014). Organizational theory and design. Thomson Learning, USA.
- Joel, F., & Hee, W. (2018). Enhancing employee creativity via individual skill development and team knowledge sharing: Influences of dual-focused transformational leadership9 Journal of Business Ethics, 46(1), 719
- Sekaran, U. (2016). Research methods for business, a skill-building approach. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York.
- Thomas, H. (2012). Strategic role in achieving competitive advantage. Management Review, Florida, 30(1), 19-37. Florida.
- Vera, D., & Crossan, M. (2015). “Strategic leadership and organizational learning.” Academy of Management Review, 29(2).
- Victor, J., Maria, M., & Leopold, G. (2012). Transformational leadership influences organizational performance through organizational learning and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 7(65), 1040-1050.