Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 4S
The Effect of Leadership Patterns on Developing Administrative Creativity in Jordanian Telecommunications Companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) in Jordan
Yaser Issa Mahmoud Momani, Ajloun National University
Keywords
Leadership Patterns, Motivation, Administrative Creativity, Jordanian Telecommunications Companies (Umniah, Orange, And Zain)
Abstract
This study aimed to identify the effect of leadership patterns on stimulating administrative creativity in the official Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) in Jordan, and to achieve the objectives of the study, a descriptive analytical approach was used, where the study community was formed from the administrative staff of Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) ), their number are (3865) employees, and the study questionnaire was designed and distributed to the study sample that was withdrawn in a simple random way, where the number of sample individuals reached (387) employees, and (353) valid questionnaires for analysis were retrieved, representing (91%) from the study sample. Several results have been reached, the most prominent are: The existence of a statistically significant effect of leadership patterns (autocratic leadership pattern, transactional leadership pattern, reciprocal leadership pattern) on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain). There are no statistically significant differences about the study variables (autocratic leadership pattern, transactional leadership pattern, reciprocal leadership pattern) due to demographic variables (gender, age, academic qualification, years of experience at the university, length of service with the direct official, job title). The study concluded by presenting a number of recommendations, the most importantly are: Work to enhance the practice of the reciprocal leadership pattern and the transactional leadership pattern, by encouraging workers to invest their creative abilities and their participation in the decision-making process, and to work on allocating rewards to creative and idealistic workers, in order to encourage them to take the initiative, and from in order to explode their creative abilities and increase their motivation, as well as work to develop material and moral plans and programs that will raise the level of employee engagement with universities and their loyalty to them to ensure their continuity in work in the long term, and the need to develop and develop creative behavior among workers, and encourage innovative ideas that contribute to solving problems and providing alternatives.
Introduction
Leadership in modern management thought is considered one of the most important pillars of the success of the administration in all its tasks because it defines the strategies and policies that will be applied in the organization, and because effective leadership is the one which has the power and influence to implement and follow these strategies, as its success is measured by the efficiency of the team’s performance and its effective work. Successful leaders create an environment of mutual respect, define the directions and paths their employees will take to achieve their goals, and have the ability to entice people to join and follow them. Accordingly, one of the most important causes for the success of organizations is the roles of the leader, the patterns he adopts in planning, goal-making and policies for the organization, in addition to creating a spirit of cooperation between workers and seeking consultation and participation in the decision-making process and motivating them to innovate in order to achieve the desired goals, and implement the future strategy, through his behavior and leadership characteristics.
Creativity is a major requirement for any organization, because an organization that does not innovate at the present time will face a fate that leads to backwardness and demise, but it is noticeable in some organizations the existence of monotony and routine when employees perform their work, and therefore no creativity or distinction appears from them that contributes to pushing the wheel of development and progress for the better.
Looking at the elements of the creative process, the cornerstone is the factor from which the organization starts and develops, because organizations, no matter how technically advanced or possessed, remain hostage to the human minds that manage and work with them. Also, it must provide the appropriate environment for creativity, which in turn works on the leadership and brilliance of the organization.
Administrative creativity and its motivation is a skill that enables leaders to face various challenges and keep pace with rapid developments, and in order for Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain) to be able to achieve their strategies and goals that they seek, their leaders must focus and work on stimulating administrative creativity among their employees, because they are affected by creative skills and behaviors for leaders.
The administrative red tape and the adherence of some leaders to traditional leadership patterns may hinder the opportunities for development, improvement and creativity, diminish their abilities and potentials and weaken their motivation. As the leader's adoption of the appropriate pattern is one of the most important factors affecting creativity. Hence, this study came to identify the effect of leadership patterns on stimulating administrative creativity in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) in Jordan.
The Study Problem and Its Questions
Workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies suffer from many problems; Among the most prominent of them is the lack of an appropriate climate for creativity, as creativity is one of the important strategies that management pursues to solve problems. Therefore, identifying the prevailing leadership patterns and stating their role in creating and stimulating administrative creativity among employees represents the correct path to perform the work in a different and more productive way, and to treat problems in an unconventional, pioneering manner.
Accordingly, the problem of the study is summarized as the following main question:
The main question: Is there an effect of leadership patterns (autocratic leadership pattern, transactional leadership pattern, reciprocal leadership pattern) on stimulating administrative creativity with its community elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in the official Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain)?
Objectives of the Study
This Study Aims To Achieve the Following Objectives
- Explain the effect of leadership patterns (autocratic leadership pattern, transactional leadership pattern, reciprocal leadership pattern) on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements (originality, flexibility) in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
- Present a theoretical and field study on the impact of leadership patterns on stimulating administrative creativity with its components in its society for the companies of the study sample.
- Describe and diagnose the study variables represented by leadership patterns and stimulating administrative creativity with its elements in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
- Examine the correlation and impact relationships between leadership patterns and stimulating administrative creativity with its components combined in the companies, sample of the study.
Significance of the Study
The Importance of the Study Comes from the Following
- The importance of the topic you are studying, which discusses the impact of leadership patterns (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) on stimulating administrative creativity with its community elements (originality, flexibility) among workers.
- Effective leadership has become a major requirement for organizing the behavior of individuals, mobilizing their energies, embodying their creativity and directing it towards achieving the goals of Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) efficiently and effectively.
- This study contributes to enriching the local and Arab library with new and modern study in the field of administrative creativity and the impact of leadership patterns on it.
- Accessing valuable information and placing it in the hands of those interested in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain) to be used in choosing the appropriate leadership pattern that positively affects stimulating administrative creativity among employees, which contributes to the development and regulation of the work environment in these Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah and Orange and Zain).
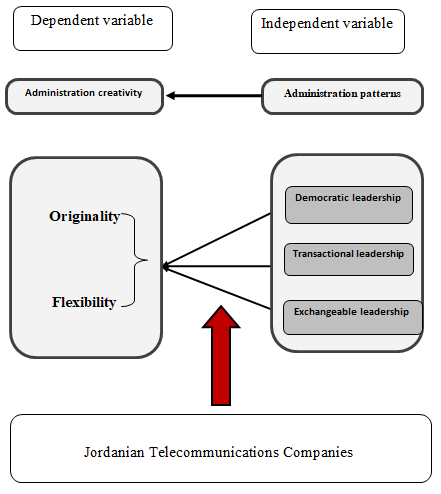
Study Model
To achieve the specific objectives of the study in determining the effect of the independent variables on the dependent variable, the researcher developed a model for the study, and Figure (1-1) illustrates the study model and its dimensions.
Figure 1: Study Model
Source: (Prepared by the researcher, based on the literature of previous studies (Saifi, 2016);(Al-Banna, 2017)
Study hypotheses
Based on the study problem and its questions, and in order to achieve the objectives of the study, the following hypotheses were formulated:
- Ha1 Main Hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for leadership patterns (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) on stimulating administrative creativity with its community elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah and Orange) And Zayn).
The following sub-hypotheses stem from it:
Ha1-1 the first sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) for autocratic leadership pattern on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
Ha1-2 the second sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) for transactional leadership pattern on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
Ha1-3 the third sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) for the reciprocal leadership pattern on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
Method and Procedures
Study Methodology
In order to reach the objectives of the study, the researcher adopted the descriptive and analytical approach with the aim of collecting and classifying data and analyzing it, in order to describe and analyze the variables of the study and its society, and it was presented in the form of tables. After using the (SPSS) program, reaching the results and recommendations of the study.
Study Population
The study population is represented by all the administrative workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain), they were (3300 employees).
Study sample
The study sample consisted of a number of administrators in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain), they were (387) employees, and the simple random sample was used where the study questionnaire was distributed to them to obtain the study data. (387) were a questionnaire on a random sample, and the total of the questionnaires recovered was (353), as they formed (91%) of the study sample.
Data Collection Sources
The researcher collected and analyzed scientific and practical study data by relying on two types of sources:
Secondary sources: These are data obtained from library sources and from the literature review of previous studies.
Primary sources: The researcher designed a scientific questionnaire to collect data on leadership patterns and administrative creativity in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
Study Tool
The researcher adopted a questionnaire that addressed all dimensions of the study variables, independent and dependent, in a way that enabled testing of the hypotheses of the study that were constructed, distributed and formed according to the sample members. In order to increase the degree of reliability and credibility of the data collected, the researcher relied on the measures contained in the previous studies in the study variables, whose reliability and credibility have been proven.
The researcher developed some expressions that were not mentioned in the previous studies and are necessary for measurement. The responses of the sample members were distributed to the items of the questionnaire according to the five-dimensional Likert scale.
Credibility of the Study Tool
The researcher tested the degree of apparent credibility in order to find out the questions related to each other, as the questionnaire was presented to those with experience and expertise and a group of referees including finance and business professors in a number of Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) in Jordan.
Stability of the Study Tool
Cronbach's Alpha coefficient was approved for internal consistency, in order to ensure the validity of the questionnaire as a tool for collecting data necessary for the current study, and that the values of the internal consistency coefficient, Cronbach's Alpha for all dimensions of the items of the study tool (the questionnaire). It ranged between (0.83 - 0.93), and the study also used statistical tests (Reliability test-Cronbach's Alpha) to verify the stability of the study tool, and the following table shows the results of those tests and the stability and internal consistency factors.
| Table 1 Internal Consistency Factor |
|
|---|---|
| Variables | Internal consistency factor |
| Independent variable / leadership patterns | |
| Democratic leadership | 0.81 |
| Transactional leadership | 0.90 |
| Transactional leadership | 0.85 |
| The dependent variable / administrative creativity | |
| administration creativity | 0.95 |
| originality | 0.93 |
| Flexibility | 0.93 |
| The overall total of items for the entire questionnaire | 0.94 |
Source: (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
It is noticed from the previous table that all the coherence parameters of the (Cronbach's Alpha) test were higher than the statistically acceptable level (60%), which indicates that there is a high internal consistency and stability for all the questionnaire axes, which may be attributed to the experience and knowledge of the respondents in the subjects of the study in addition to the clear and short items of the questionnaire, as the internal consistency coefficient for all the study items reached (0.94), which is a very high rate, and it is higher than the statistical acceptance factor (60%) to reflect the validity and credibility of the study tool.
Methods of Statistical Data Analysis
The questionnaire data were entered into the SPSS program in order to be processed according to the tests that achieve the purpose of the study, and specifically the following methods were used: Cronbach's Alpha, Variance, and Statistics Descriptive Measures Arithmetic mean, standard deviation, frequencies, percentages, multiple regression analysis, independent T-test, Avona, Pearson correlation matrix, and variance amplification factor and tolerance variance test.
Boundaries of the Study
The study boundaries were as follows:
- Spatial boundaries: This study was applied to Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
- Temporal boundaries: this study was completed during the year 2020.
- Human boundaries: The study was based on all the administrative workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain), and their number reached (3300) employees.
- Scientific boundaries (objective): This study discussed important topics, namely: leadership patterns (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) and administrative creativity with its combined elements (originality and flexibility) in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
Previous Studies
The researcher conducted a survey of previous studies on the subject of this study, and some studies that have a direct relationship to the subject of the study were benefited from, and among these studies the following:
- Bachioh's (2018) study entitled Leadership Patterns Prevailing at the University of Mohamed Lamine Dabbaghine in the Algerian city of Setif, according to the viewpoint of its faculty members. The study aimed to identify the nature of the leadership pattern prevailing at the Presidency of the University of Mohamed Lamine Dabbaghine (Setif 2) in Algeria, as seen by the faculty members at the university, and to find out if there are statistically significant differences in the perception of the faculty members in the university of the leadership pattern prevailing in the presidency, The university attributed to the variables (gender, specialization, job title, years of work experience, academic qualification, and experience in administrative work). In order to achieve this, the researcher designed a questionnaire consisting of (60) items divided into (3) areas and applied them to the study sample consisting of (125) faculty members from the study community. The statistical analysis software (SPSS) was also used. The study reached several results, the most importantly are: the sovereignty of democratic leadership and the absence of statistically significant differences in the faculty members ’view of the nature of the leadership pattern prevailing in the study variables. It presented a number of recommendations, the most important of which were: promoting the principle of collective leadership, especially with regard to planning and policy-making, encouraging individual pioneering work in implementing these policies to preserve the principle of reward and punishment, and the need for the university presidency to adopt the democratic model in management in all its aspects. The researcher benefited from this study in strengthening the theoretical side of the independent variable leadership patterns (autocratic leadership pattern).
Al-Jabour (2019) study, The Impact of Leadership Patterns on Organizational Citizenship Behavior of Workers in the Ministry of Endowments, Islamic Affairs and Resources. This study aimed to identify the effect of administrative leadership patterns (demographic leadership pattern, democratic leadership pattern, and free leadership pattern) on the organizational citizenship behavior of workers in the Ministry of Endowments and Islamic Affairs and Holy Places in Jordan. The researcher relied on the descriptive analysis approach, and the questionnaire as a study tool to collect data. The study population consisted of the administrative employees in the ministry center and its departments in Amman, and the study sample included (170) employees. The study reached several results, the most importantly are: The superiority of democratic leadership, followed by demographic leadership, and then free leadership. Among the most important recommendations of the researcher are: Promoting the democratic leadership practice and taking corrective measures to practice the demographic leadership pattern. The researcher benefited from this study in strengthening the theoretical side of the independent variable leadership patterns (autocratic leadership pattern).
Rafeh (2020) study, entitled Transactional Leadership and its Impact on Technological Crisis Management at Zain Telecom in Jordan. The study aimed to identify the reciprocal leadership and its impact on the management of technological crises in Zain Telecommunications Company in Jordan. The study community included the (250) administrators working in Zain Telecom in Jordan. The study questionnaire was designed and distributed to the study sample that was withdrawn in a simple random way, as the number of the sample was (152) administratively, and (124) valid questionnaires were retrieved for analysis, representing (81.6%) of the study sample. The study has reached several results, the most important of which are: that there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for reciprocal leadership in its combined and individual dimensions (ideal effect, intellectual stimulation, individual considerations, motivation) on technological crisis management (detection of warning signals, preparedness and prevention). Containing or limiting damages, restoring activity, learning) in Zain Telecom in Jordan The study recommended a number of recommendations, the most important of which are: Interest in promoting the concept of reciprocal leadership in the company through training courses that are held for the administrators working in it. The researcher benefited from this study in strengthening the theoretical aspect of the independent variable leadership styles (the reciprocal leadership style).
Brenyah & Tetteh (2016) Organizational Leadership Styles and Their Impact on Employees' Job Satisfaction: Evidence from the Mobile Telecommunications Sector of Ghana
The study aimed to determine the effect of different leadership styles on employee job satisfaction within the organization, as the study targeted employees of the telecommunications sector in Ghana, and the study was based on the descriptive and analytical approach as a method of study, and (400) questionnaires were filled out by employees. The search tool included a questionnaire, and to process the data, the statistical analysis program (SPSS) was used. The study concluded with several results, the most important of which are: There is a positive relationship between the reciprocal leadership factors represented by (individual consideration, inspiration and intellectual stimulation) and external satisfaction imposed on employees from their external surroundings. The study recommended a number of recommendations, the most important of which are: Paying attention to strengthening reciprocal leadership in the institution by involving workers in training courses.
The researcher benefited from this study in strengthening the theoretical side of the independent variable of leadership styles.
Elrehail, et al., (2018) “The Impact of Transformational Leadership On Innovation In Higher Education”
This study aimed to investigate the impact of the reciprocal leadership style on the process and innovation of products in higher education institutions in Jordan. As this study shows how the influence of leadership styles fluctuates on the spread of knowledge exchange as a prevailing rule in the organization. This study was applied to higher education institutions in northern Jordan, and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) techniques were used to analyze the data. This study found: that reciprocal leadership and knowledge exchange have a positive effect on creativity in higher education institutions.
The researcher benefited from this study in enhancing the theoretical side of the independent variable, leadership styles (reciprocal leadership style).
Bani (2018) "Emplyee Empoerment: Do Leaership Style Matter?: Empirical Study at Colleges of Al-Balqa'a Applied University"
This study aimed to identify the effect of leadership styles on empowering employees to empower employees at Al-Balqa Applied University. This study examined three leadership styles: reciprocity, transactional, and democracy and their impact on employee empowerment. Using the quantitative study method, the researcher applied a questionnaire as a study tool, and the study sample consisted of (233) participants. The researcher analyzed the responses to find out what leadership styles affected the employees most at Al-Balqa Applied University, and the researcher used statistical analysis (SPSS) to test the reliability and validity of the tool. Linear regression analysis was used to examine the hypotheses. The results of the study showed that there is an important effect between leadership styles and employee empowerment, as the reciprocal leadership style was the most influential, followed by transactional leadership and finally democratic leadership.
The researcher benefited from this study in enhancing the theoretical side of the independent variable leadership styles.
Badir (2019) the Impact of Leadership Style on the Innovation Process: Case of Mobile Phone Service Providers in Jordan
The current study aimed to determine the impact of the leadership styles practiced by leaders and chiefs in the three companies specialized in providing mobile services registered in Jordan - Umniah, Zain and Orange - on the innovation process from the point of view of subordinates. Then, identify the best of these patterns in terms of influencing the innovation process. In this study, the researcher adopted the analytical descriptive approach, and, through reviewing the study literature, he developed a questionnaire as a tool for data collection. The study sample consisted of (427) employees. The study revealed several results, the most important of which are: The reciprocal leadership style is the prevailing pattern in the study sample, followed by the democratic, then transformative, then free, and finally democratic leadership. The researcher benefited from this study in strengthening the theoretical aspect of the independent variable of leadership styles.
The Theoretical Framework of Study
Test Hypotheses for Study
Before analyzing and testing the study hypotheses, it is necessary to test the normal distribution and test (VIF) between the indicators of the independent variable and the dependent variable.
Test of Normal Distribution of Data
The normal distribution test of the data was performed based on the value of the Skewness coefficient, to test whether the data used in the analysis follow the normal distribution or not, and the results were as shown in Table (2)
| Table 2 Test The Normal Distribution of Data Based on The Value of The Coefficient of Skewness |
|
|---|---|
| coefficient of Skewness | |
| Democratic leadership style | -0.645 |
| Transactional Leading Pattern | -0.202 |
| Cross-leadership style | -0.392 |
| A | -0.337 |
| originality | -0.261 |
| Flexibility | -0.424 |
| administration creativity | -0.293 |
Source: (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
It is noticed from Table No. (2) That the Skewness coefficient for all paragraphs of the questionnaire was less than one, which means that the data follow the normal distribution.
Test the Suitability of the Study Model to the Used Statistical Methods
The linear correlation test was used with the aim of ensuring that there is no high correlation between the independent variables, by relying on the variance inflation factor (VIF) test and the Tolerance test for each of the independent variables, where the independent variables of the model must be independent between them. And to make sure of that purpose, we use this test, which is one of the ways to get rid of the problem of linear multiplicity, knowing that the coefficient of variance inflation must not be exceeded for the value (10), and the value of the allowable variance test must be greater than (0.05), and by calculating the previous coefficients for each The independent variables, the results obtained were listed in Table No. (3) the following:
| Table 3Test of The Variance Amplification Factor and the Permissible Variance of The Search Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| c | Variance Tolerance | variance inflation factor VIF |
| Democratic leadership style | .9830 | 1.018 |
| Transactional leadership style | .4660 | 2.147 |
| Reciprocal leadership style | .4630 | 2.158 |
Source: (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
Table (3) indicates that the values of the variance inflation test for all variables are less than (10), as they ranged between (1.018 - 2.158), while the value of the allowable variance test for all variables is greater than (0.05), where it ranged between (0.463 - 0.983), Thus, it can be said that there is no high correlation problem between the variables, and this indicates that there is no statistically significant correlation between the independent variables included in the (correlation) table, and this enhances the possibility of using them in the model, based on (Gujarati, 2004).
Pearson Correlation Coefficients between the Dimensions of the Independent Variable
The researcher used Pearson correlation coefficients between the dimensions of the independent variable, to ensure that there is no linear multiple correlation between the sub-variables in the independent variable, and the results were as shown in Table (4)
| Table 4 Pearson Correlation Matrix For Sub-Variables in The Independent Variable |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic leadership style | Transactional leadership style | Reciprocal leadership style | |
| Democratic leadership style | 1 | ||
| Transactional leadership style | .107 0* | 1 | |
| Reciprocal leadership style | .130 0* | .731 0** | 1 |
| ** Statistically significant at (α ≤0.01) level | |||
Source (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
Table (4) between the sub-variables of the variable is (0.731) the two variables (the reciprocal leadership style) and (the alternative leadership style), while the values of the correlation coefficient between the other independent variables were that, and this indicates the absence of the phenomenon of multiple linear correlation between the sub-variables For the independent variable, if all of them are less than (0.107), then they are free of multiple linear correlation problem.
Test the Study Hypotheses
For testing length measurement, during operation, steps and steps.
Main hypothesis: The effect of statistically significant at the level of significance (α≤0.05), of leadership styles (democratic leadership, transactional leadership) on leadership motivation (democratic leadership, transactional leadership).
And to identify the possibility of positive and acceptance of stimulating the performance of administrative work in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) on several methods to teach the variation of regression to the effect of leadership styles (democratic leadership, reciprocal leadership). The results were as follows in Table (5):
| Table 5 Linear Regression Analysis of The Effect of Leadership on Leadership Actions (General Democratic Leadership, Transactional Leadership) on Stimulating Construction in Jordanian Telecom Companies (Umniah, Orange, And Zain) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependant variable | Model summary | ANOVA | Coefficient | |||||||
| RCorrelation coefficient | R2Determination coefficient | Fcalculated | Freedom levelsDF | Sig.Fstatistical significance | statement | B | Standard mistake | tcalculated | Sig.tstatistical significance | |
| Administration creativity | 0.7490 | 0.5620 | 148.995 | 3 | 0.0000 | Democratic leadership style | 0.0240 | 0.0380 | 0.638 | 0.5240 |
| Transactional Leading style | 0.3590 | 0.0520 | 6.887 | 0.0000 | ||||||
| Cross-leadership style | 0.4760 | 0.0560 | 8.521 | 0.0000 | ||||||
Source (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
The results in Table (5) indicate that there is a statistically significant effect of leadership styles (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) on stimulating administrative creativity among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain), where the correlation coefficient reached ((R =0.749). Which indicates the existence of a statistically significant correlation relationship between the independent variables of community (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) and the dependent variable (administrative creativity) and it appeared that the value of the determination coefficient (R2 =0.562) indicates that the leadership styles combined (democratic leadership, Transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) interpreted (56.2%) of the variance in (managerial creativity) while the remainder is due to other variables that were not included in the model, and the value of (F =148.995) at a confidence level equal to (sig = 0.000) This confirms the significance of the regression at a significance level of α > 0.05.
It appears from the parameter table that the values of (B) at the dimension of (autocratic leadership style) reached (0.0240) and that the value of (t) was (0.6380) and in statistical terms it reached (0.524), indicating that this effect is not significant.
It appears from the transactions table that the values of (B) at the dimension of (the transactional leadership style) reached (0.3590) and that the value of (t) was (6.887) and in statistical terms it reached (0.000), which indicates that the effect of this dimension is significant, and this means that the increase in (Transactional leadership style) by one unit will increase (administrative creativity) by (0.3590).
It appears from the transactions table that the values of (B) in the dimension of (the reciprocal leadership style) reached (0.4760) and that the value of (T) was (8.521) and in statistical terms it reached (0.000), indicating that the effect of this dimension is significant, and this means that the increase in (Mutual leadership style) by one unit will lead to an increase in (administrative creativity) by (0.476). Based on the above, the first main hypothesis was accepted. That is, there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for leadership styles (democratic leadership, transactional leadership, reciprocal leadership) on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) .
From this hypothesis, the following sub-hypotheses are divided:
The first sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) of the autocratic leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
To verify the validity of the first sub-hypothesis, simple linear regression was used, and the results were shown in Table (6) as follows:
| Table 6 Results of Simple Linear Regression of The Effect of Autocratic Leadership Style on Stimulating Administrative Creativity Among Workers in Jordanian Telecommunications Companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Model summary | ANOVA | Coefficient | |||||||
| RCorrelation coefficient | R2Determination coefficient | Fcalculated | Freedom levelsDF | Sig.Fstatistical significance | statement | B | Standard mistake | tcalculated | Sig.tstatistical significance | |
| Administrative creativity | 0.119 | 0.014 | 5.028 | 1 | 0.026 | Demographic leadership style | 0.126 | 0.056 | 2.242 | 0.026 |
Source (prepared by the study in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
The results in Table (6) indicate a statistically significant effect of the autocratic leadership style on administrative creativity, as the correlation coefficient reached ((R =0.119) indicating a statistically significant correlation between the independent variable (autocratic leadership style) and the dependent variable (creativity It appeared that the value of the determination coefficient (R2 =0.014) indicates that (the autocratic leadership style) explained (1.4%) of the variance in (administrative creativity), while the remainder is due to other variables that were not included in the model. The value of (F =5.028) was reached at a confidence level equal to (sig =0.026), which confirms the significance of the regression at a significance level of α > 0.05
It appears from the parameter table that the values of (B) in the dimension of (autocratic leadership style) reached (0.1260) and that the value of (t) was (2.242) and in statistical terms it reached (0.026), indicating that the effect of this dimension is significant, and this means that the increase In (autocratic leadership style) by one unit, this will lead to an increase in (administrative creativity) by (0.126). Based on the above, the hypothesis was accepted. That is, there is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) for the autocratic leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
The second sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
And to verify the validity of the second sub-hypothesis, simple linear regression was used, and the results were shown in Table (7) as follows:
Results of simple linear regression of the effect of transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity among employees of Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
| Table 7 Results of Simple Linear Regression |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Model summary | ANOVA | Table of Coefficient | |||||||
| RCorrelation coefficient | R2Variance of limit | Fcalculated | Degree of freedomDF | Sig.F | statement | B | Standard mistake | Tcalculated | Sig.t | |
| Administrative creativity | 0.684 | 0.468 | 309.091 | 1 | 0.000 | Transactional leadership pattern | 0.687 | 0.039 | 17.581 | 0.000 |
Source (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
The results in Table (7) indicate a statistically significant effect of the transactional leadership style on administrative creativity, where the correlation coefficient reached (R =0.684), which indicates the existence of a statistically significant correlation relationship between the independent variable (the transactional leadership style) and the dependent variable (creativity It appeared that the value of the determination coefficient (R2 =0.468), which indicates that the (transactional leadership style) explained 46.8% of the variance in (administrative creativity), while the remainder is due to other variables that were not included in the model. A value of (F =309.091) at a confidence level equal to (sig =0.000). This confirms the significance of the regression at a significance level of α > 0.05.
It appears from the transactions table that the values of (B) at the dimension of (transactional leadership style) reached (.6870) and that the value of (t) was (17,581) and in statistical terms it reached (0.000), indicating that the effect of this dimension is significant and this means that the increase in (Transactional leadership style) by one unit will lead to an increase in (administrative creativity) by (0.687). Based on the above, the hypothesis was accepted. That is, there is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for the transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain)
The third sub-hypothesis: There is a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α≤0.05) for the reciprocal leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
And to verify the validity of the third sub-hypothesis, simple linear regression was used, and the results were shown in Table (8) as follows:
| Table 8 Results of Simple Linear Regression of The Effect of The Reciprocal Leadership Style on Stimulating Administrative Creativity Among Workers in Jordanian Telecommunications Companies (Umniah, Orange, And Zain) |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Model summary | ANOVA | Coefficient | |||||||
| RCorrelation coefficient | R2Variance of limit | Fcalculated | Degree of freedomDF | Sig.F | statement | B | Standard mistake | Tcalculated | Sig.t | |
| Administrative creativity | .7080 | .5010 | 352.735 | 1 | .0000 | Reciprocal leadership style | .7600 | .0400 | 18.781 | .0000 |
Source (prepared by the researcher in light of the results of SPSS statistical analysis)
The results in Table (8) indicate a statistically significant effect of the reciprocal leadership style on administrative creativity, where the correlation coefficient reached ((R =0.708), which indicates a statistically significant correlation relationship between the independent variable (reciprocal leadership style) and the dependent variable (creativity It appeared that the value of the coefficient of determination (R2 =0.501) indicates that (the reciprocal leadership style) explained (50.1%) of the variance in (administrative creativity) while the remainder is due to other variables that were not included in the model. The value of (F =352.735) was reached at a confidence level equal to (sig =0.000), which confirms the significance of the regression at a significance level of α > 0.05
It appears from the transactions table that the values of (B) at the dimension of (transactional leadership style) reached (0.760) and that the value of (t) was (18.781), and in statistical terms it reached (0.000), indicating that the effect of this dimension is significant, and this means that the increase in (Transactional leadership style) by one unit will lead to an increase in (administrative creativity) by (.7600). Based on the above, the hypothesis was accepted. That is, there is a statistically significant effect at the level of (α≤0.05) for the transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its elements combined among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain).
Findings and Recommendations
Search Results
The results of the study are presented below:
First: Administrative leaders in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain) practice each of the reciprocal leadership, transactional leadership, and democratic leadership to close degrees.
Second: The results showed a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α = 0.05) for leadership styles (autocratic leadership style, transactional leadership style, transactional leadership style) on stimulating administrative creativity with its elements together (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain). These results explain the nature of the relationship between the leadership style used by the leader and the level of motivation for managerial creativity among subordinates, and the creation of a competitive and innovative work environment. This result was in agreement with the results of the study (Waier 2015)
Third: The results showed a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α = 0.05) of the autocratic leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its community elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain). This result is in agreement with the results of (Al-Banna 2017) and (Al-Saifi 2016) research.
Fourth: The results showed a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α = 0.05) of the transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its community elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange, and Zain). This result is in agreement with the results of the study (Summer 2016).
Fifth: The results showed a statistically significant effect at the level of significance (α = 0.05) of the transactional leadership style on stimulating administrative creativity with its combined elements (originality, flexibility) among workers in Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain). This result differed with the results of (Khweldi 2016) study and agreed with (Waier, 2015) study.
Recommendations
After discussing the findings of the study, the researcher presents a number of recommendations, which are as follows:
1. Work to enhance the practice of reciprocal leadership and transactional leadership, by encouraging workers to invest their creativity and their participation in the decision-making process.
2. Work to build strong and solid relationships between the leader and university workers, which leads to an increase in their cooperation and participation in introducing new ideas in an innovative way.
3. Work to allocate bonuses for creative and idealistic workers, in order to encourage them to take initiative and to explode their creative talents and increase their motivation.
4. Working on laying down material and moral plans and programs that would raise the level of employee engagement with Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) and their loyalty to them to ensure their continuity in work in the long run.
5. The necessity of developing the creative behavior of workers and encouraging innovative ideas that contribute to solving problems and providing alternatives.
6. The necessity of increasing attention to the human element and providing an appropriate environment for workers, and working to raise their morale, informing them of the importance of their role in the university, and encouraging them to innovate and participate in the decision-making process.
7. The necessity of the official Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) to get rid of demographic leadership methods, in order to make room for workers in the process of expressing opinions, and to participate in the decision-making process.
8. Conducting a field study on the obstacles to administrative creativity and its causes among workers in the official Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain).
9. The need to create a department for administrative creativity in the official Jordanian telecommunications companies (Umniah, Orange and Zain) to encourage employees to be creative and distinguished.
References
References
Al-edenat, M. (2018). Reinforcing innovation through transformational leadership: the mediating role of job satisfaction. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 31(4), 810-838.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Avery, G. C., & Ryan, J. (2002). Applying situational leadership in Australia. Journal of Management Development, 21(4), 242-262.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Asnawi, A., Awang, Z., Afthanorhan, A., Mohamad, M., & Karim, F. (2019). The influence of hospital imageand service quality on patients’ satisfaction and loyalty. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 911-920.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Aziz, M.I., Adnan, A.A., Afthanorhan, A., Foziah, H., Ishak, S.I., & Rashid, N. (2019). The influence ofemployer value proposition in talent demand towards talent shortage in the Malaysian Islamic banking institutions: A SEM approach. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 843-850.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Al-Khamaiseh, Z., Halim, B.B.A., Afthanorhan, A., & Alqahtani, A.H. (2020). Exploring and developing items measuring Situational Leadership II (SLII). Humanities & Social Sciences Reviews, 8(2), 2020, 579-588.
Brenyah, R.S., & Tetteh, E.N. (2016). Organizational leadership styles and their impact on employees' job satisfaction: Evidence from the mobile telecommunications sector of Ghana. Global Journal of Human Resource Management, 4(4), 12-24,
Blanchard, K.H., Zigarmi, D., & Nelson, R.B. (1993). Situational Leadership® after 25 years: A retrospective. Journal of leadership studies, 1(1), 21-36.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Brislin, R.W. (1980). Cross-cultural research methods environment and culture. 47-82: Springer.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Church, A.H., & Waclawski, J. (1998). The relationship between individual personality orientation andexecutive leadership behavior. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 71(2), 99-125.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Crowe, A. (2013). Leadership styles questionnaire.
Dalila, D., Latif, H., Jaafar, N., Aziz, I., &Afthanorhan, A. (2020). The mediating effect of personal values on the relationships between attitudes, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control and intention to use. Management Science Letters, 10(1), 153-162.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Ebere, E., & Fragouli, E. (2015). Exploration of suitability of situational leadership in the oil and gas sector. Journal of Social Economics Research, 2(1), 10-30.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Elrehail, H., Okechukwu, L.E., Abdallah, A., & Amro, A. (2018). The impact of transformational leadership on innovation in higher education: The contingent role of knowledge sharing. Telematics and Informatics, 35(1), 55-67.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Forsyth, B., Rothgeb, J.M., & Willis, G.B. (2004). Does pretesting make a difference? An experimental test. Methods for testing and evaluating survey questionnaires, 525-546.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Graeff, C.L. (1997). Evolution of situational leadership theory: A critical review. The Leadership Quarterly, 8(2), 153-170.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hair, J.F., Gabriel, M., & Patel, V. (2014). AMOS covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM):guidelines on its application as a marketing research tool. Brazilian Journal of Marketing, 13(2).
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hair Jr, J.F., Wolfinbarger, M., Money, A.H., Samouel, P., & Page, M.J. (2015). Essentials of business research methods. Routledge.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Hersey, P., Blanchard, K.H., & Natemeyer, W.E. (1979). Situational leadership, perception, and the impact of power. Group & Organization Studies, 4(4), 418-428.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
ICG, C. e. M. T. (2013). Taking the Manager Coach Approach Further.
Mohamad, M., Afthanorhan, A., Awang, Z., & Mohammad, M. (2019). Comparison between CB-SEM and PLS-SEM: Testing and confirming the maqasid syariah quality of life measurement model. Journal of Social Sciences Research, 5(3), 608-614.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Majid, N.A., Zainol, F.A., Wan Daud, W.N., & Afthanorhan, A. (2019). Cooperative entrepreneurship in Malaysian secondary schools: A review of current practices. Journal of Social Sciences Research, 5(3), 812-818.