Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 2
The effect of financial literature, parents social economic and student lifestyle on students personal financial management
Ismail, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Hyronimus Rowa, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Noudy Tendean, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Tun Huseno, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Sri Hartati, Institut Pemerintahan Dalam Negeri
Citation Information: Ismail., Rowa H., Tendean N., Huseno T., Hartati S. (2022). The effect of financial literature, parents social economic and student lifestyle on students personal financial management. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 26(2), 1-10.
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to analyze The Effect of Financial Literature, Parents Social Economic and Student Lifestyle on Students Personal Financial Management. In this study using quantitative methods and data analysis techniques Structural Equation Modeling Equation Modeling using SmartPLS 3.0 software. The sample selection method uses nonprobability sampling methods. Online questionnaires were sent to respondent’s as many as 230 student questionnaires, the next step is to evaluate the returned questionnaires, namely the 220 returned questionnaires and 10 questionnaires did not return. Based on the results of data analysis using SmartPLS, it was found that Financial Literature had a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Literature on Students variable would have a significant effect on increasing the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Financial Literature variable would have a significant effect on the decrease in the Students Personal Financial Management variable. Student Lifestyle has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect on increasing the Student Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect on the decrease in the Student Personal Financial Management variable. Parents Social Economics has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Parents Social Economic variable will have a significant effect on increasing the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Parents Social Economic variable will have a significant influence on the decrease in the Students Personal Financial Management variable.
Keywords
Financial Literature, Parents Social Economic, Student Lifestyle, Students Personal Financial Management
Introduction
In this era of industrial revolution and digital literacy, Indonesia needs to prepare many of the needs of its people to import and export from other countries. With the increasing number of needs, people must be able to manage or respond to each individual's personal finances. According to Co?kun et al. (2020) Money is often a source of considerable problems; this is because almost all human activities involve money. Seeing how important money is in human life, it triggers people to feel that they cannot live without money. Therefore, as humans who are very dependent on money, we must also be able to control and manage our finances properly and wisely. One of the various ways to manage finances is how from yourself you can control every expense. According to Al-Bahrani et al. (2020), Ameer and Khan (2020), Ço?kun and Dalziel (2020) when expenditures occur continuously and are indefinite in their entirety until someone finds it difficult to control them, this is because a person's level of financial literacy is still fairly poor or low. According to Chuah et al. (2020) Individual financial knowledge can be expected to influence a person's individual attitude. And according to Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) financial knowledge leads to developments in financial decision making and determination. Human life will be happy if it succeeds in achieving what it wants and dreams of. The success and happiness of human life can be defined by various measures, such as the career path or position that has been achieved, the assets that have been collected, and the preparation of the next generation. In this day and age, many Indonesians still have difficulty managing their personal finances. This happens because people do not understand financial literacy.
According to Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) stated that knowledge about finance at the youth level such as college students and school students is still very small, although through learning at school, learning related to various fields of financial knowledge has been explored. The millennial generation's lack of understanding of financial literacy is an important problem faced by them. Teenagers like to try new things due to high curiosity. According to Iramani and Lutfi (2021), Panos and Wilson (2020) this is due to the learning process about finance that is less than ideal and optimal for adolescent students, which of course must be tested for truth in further research. At the age of adolescence consumptive behavior begins to form because teenagers tend to follow the times or trends. A common symptom that often occurs in students is that they are still busy hunting for identity and have not been able to determine their priorities in consumptive activities. Because they have not been able to determine their priorities, most teenagers are still too quick to make decisions so that they do not think long about what is needed more than what they want. Even the largest consumer market falls to the age range of 21 to 30 years. According to Panos and Wilson (2020) Students with high economic parents tend to be more easily influenced by a consumptive lifestyle. This is because all their needs and desires can be easily fulfilled. The youth group is one of the potential markets for producers. Therefore, teenagers must also be smart to deal with their finances wisely. According to Iramani and Lutfi (2021), Johan et al. (2021), Panos and Wilson (2020) there are several internal factors and external factors, one of which is socio-economic characteristics and financial knowledge.
The main reason suspected to cause personal financial management in this research is the level of financial literacy. Knowledge of finance and expertise in practicing it is called financial literacy. According to Philippas and Avdoulas (2020), Radianto et al. (2021), Thomas and Subhashree (2020) Management is defined as organizing in the treatment of money, while control is the activity of controlling activities related to financial management. The treatment of sound financial management is shown in the activities of designing, processing and controlling these finances. According to Thomas and Subhashree (2020) a person's position in the environment related to other individuals on their rights and responsibilities in interacting and resources is called socioeconomic status. There is also the upper economic status, which is the position of the individual measured based on his wealth, where if the property is able to meet the tertiary needs, on the contrary the lower economic status where if the assets do not meet their daily needs and are still below the average of society in general. Students, whose parents' economic status is at the top level, will have more opportunities to use the momentum in developing their personal financial skills. This is because their parents can meet the needs of students. On the other hand, students will be more careful and think long in using their money if their parents' socioeconomic status is low. According to Philippas and Avdoulas (2020), Radianto et al. (2021), Thomas and Subhashree (2020) Lifestyle can be implemented through one's daily life, one's interests, and opinions. Lifestyle is also referred to as a personal attitude as individuals run their lives, control their money, and optimize the time and opportunities they have, as well as the way a person interacts with the environment and others. If the community is not capable and tenacious in controlling themselves in today's global competition period so that they can follow the flow of the globalization wave, one of the examples that is easily exposed to the direct effects of globalization is the millennial generation. Based on the output by research reviewed and he explained that students' personal financial management is influenced by lifestyle factors.
According to White et al. (2021), Xiao et al. (2020) financial literacy is the ability to make estimates and effective measures about managing the use of money. While Al-Bahrani et al. (2020) explains that financial literacy is a way for each individual's ability to carry out economic or financial information obtained and then made an evaluation of financial planning, financial accumulation, pensions, and debt. Socio-economic status is defined as the condition or condition of individuals in the community environment related to other individuals such as their relationships, rights, and obligations in interacting with the environment and resources. The level of parents' economic status according to Co?kun et al. (2020) consists of economic status which is a condition or condition of a person as measured by the level of his wealth which is sufficient to meet his daily needs and has an income that is above the average of society in general, while on the contrary, the economic status is lower where his wealth is still lacking to fulfill his needs. Daily needs and have an income below the average in general. There are various aspects of the variables that have been disclosed by Al-Bahrani et al. (2020), Ameer and Khan (2020), Ço?kun and Dalziel (2020) namely parents' education, income, and occupation. Lifestyle is often defined through one's activities, one's interests, and personal opinions. And more can be described by a person's treatment of the environment and others, namely about the way they live, allocate their money, and spend their time. According to Co?kun and Dalziel (2020) as well as according to Al-Bahrani et al. (2020), which states that lifestyle is defined as the way individuals socialize in their community expressed through their activities, interests, and opinions. Management is an activity starting from planning, processing, directing, to examining the efforts of organizational members. Meanwhile, according to Ameer and Khan (2020), Ço?kun and Dalziel (2020) financial management is defined as a technique to balance a person's consumptive lifestyle with his productive lifestyle, for example saving, doing business, or investing. And the meaning of financial control is the design, organization, and control of activities related to finance. Financial management aims to avoid conditions that are difficult to meet the needs and conditions of more expenditure than income. The purpose of this study is to analyze The Effect of Financial Literature, Parents Social Economics and Student Lifestyle on Students.
Method
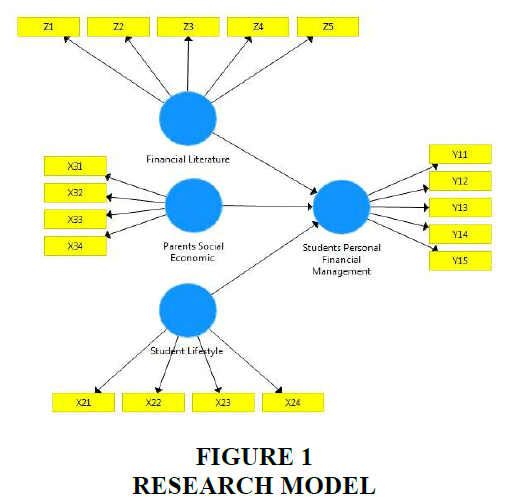
In this study using quantitative methods and data analysis techniques Structural Equation Modeling Equation Modeling using SmartPLS 3.0 software. The sample selection method uses non-probability sampling methods. Online questionnaires were sent to respondent’s as many as 230 student questionnaires, the next step is to evaluate the returned questionnaires, namely the 220 returned questionnaires and 10 questionnaires did not return. Based on theoretical studies and previous studies, the research model is structured as follows in Figure 1:
The hypotheses in this study are as follows:
H1: There is a positive and significant influence of Financial Literature on Students Personal Financial Management
H2: There is a positive and significant influence of Parents Social Economic and Student Lifestyle on Students Personal Financial Management
H3: There is a positive and significant influence of Student Lifestyle on Students Personal Financial Management
Results and Discussion
According to Purwanto et al. (2021) reliability is a measure of the internal consistency of indicators of a construct that shows the degree to which each indicator shows a general latent construct. According to Purwanto et al. (2020) the reliability requirement is a measure of the stability and consistency of the results (data) at different times. To test the reliability of the construct in this study used the value of composite reliability. A variable is said to meet construct reliability if it has a composite reliability value > 0.7 and Cronbach's Alpha value > 0.6 has a good level of reliability for a variable (Purwanto et al., 2021). The composite reliability value of each indicator can be seen in table 1 below.
| Table 1 Reliability | ||
| Variables | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability |
| Financial Literature | 0.924 | 0.949 |
| Parents Social Economic | 0.770 | 0.941 |
| Student Lifestyle | 0.995 | 0.996 |
| Students Personal Financial Management | 0.926 | 0.943 |
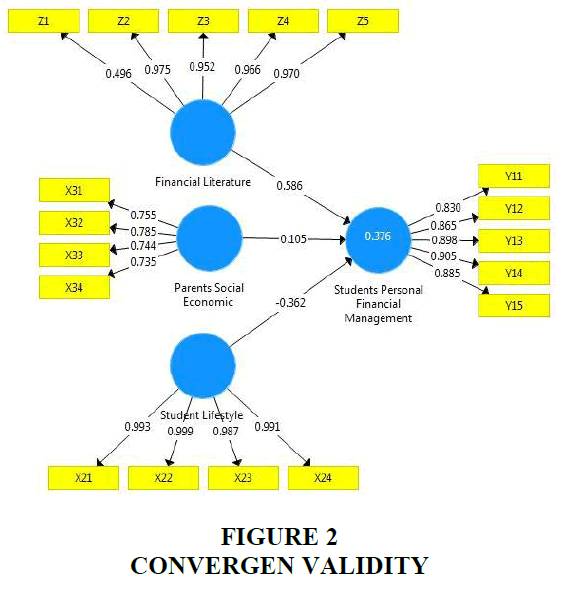
In Table 1, it can be seen the results of the reliability test analysis using the SmartPLS tool which states that all composite reliability values are greater than 0.7, which means that all variables are reliable and have met the test criteria. Furthermore, the value of cronbanch's neglect also shows that all values of cronbanch's neglect are more than 0.6 and this indicates that the level of reliability of the variable has also met the criteria. According to Purwanto et al. (2020) the validity test is intended to measure the extent to which the accuracy and accuracy of a measuring instrument performs the function of its measuring instrument or provides appropriate measurement results by calculating the correlation between each statement with a total score. In this study, the measurement validity test consisted of convergent validity and discriminant validity. Measurement can be categorized as having convergent validity if the loading factor value is > 0.7 (Purwanto et al, 2021). Figure 2 shows that all loading factors have a value of > 0.7, so it can be concluded that all indicators have met the criteria for convergent validity, because indicators for all variables have not been eliminated from the model.
Discriminant Validity
Based on Table 2, the AVE value for all variables is > 0.50. So it can be said that the measurement model has been valid with discriminant validity. In addition, discriminant validity was also carried out based on the Fornell Larcker criteria measurement with the construct. If the construct correlation in each indicator is greater than the other constructs, it means that latent constructs can predict indicators better than other constructs (Purwanto et al., 2020).
| Table 2 AVE | |
| Variables | AVE |
| Financial Literature | 0.796 |
| Parents Social Economic | 0.570 |
| Student Lifestyle | 0.985 |
| Students Personal Financial Management | 0.970 |
Structural Model (Inner model)
The structural model (inner model) is the pattern of the relationship between the research variables. Evaluation of the structural model is by looking at the coefficients between variables and the value of the coefficient of determination (R2). The coefficient of determination (R2) essentially measures how far the model's ability to explain variations in the dependent variable is. In this study, the adjusted r-square value (adjusted R2) is used, because it has more than two independent variables.
In table 3 it can be explained that the adjusted R2 value of the independent variable Financial Literature, Parents Social Economic. Student Lifestyle The dependent variable of Students Personal Financial Management is 0.376. This value is categorized as moderate, so it can be concluded that the two independent variables have an influence and a moderate level of the independent variable Financial Literature, Parents Social Economic. Student Lifestyle the dependent variable of Students Personal Financial Management is 37.6% while the remaining 52.4% is influenced by other variables not discussed in this study.
| Table 3 R-Square Adjusted | |
| Variables | R-square adjusted |
| Students Personal Financial Management | 0.376 |
Hypothesis Test
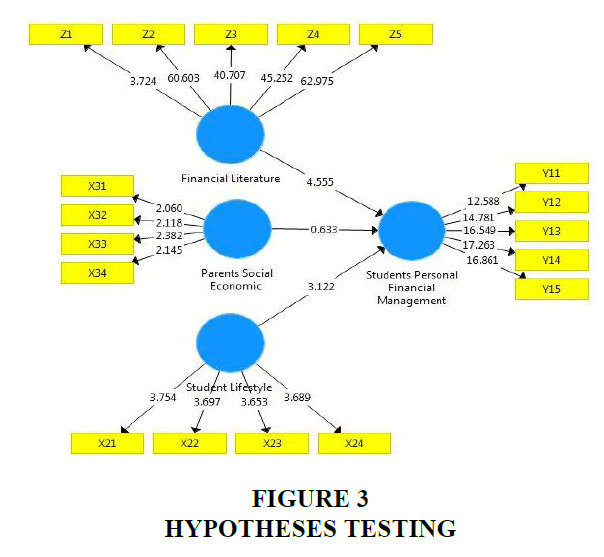
According to Purwanto et al. (2021) after a research model is believed to be fit, a hypothesis test can be performed. The next step is to test the hypothesis that has been built in this study. The following are the results of the data test using bootstrapping. Hypothesis testing in this study can be known through regression weight by comparing the p-value with a significance level of 5% (α=5%). The hypothesis is said to be significant if it has a probability value (p-value) < 5% in Table 4 and Figure 3.
| Table 4 Hypotheses Testing for Direct Effect | ||
| Hypotheses | P - Value | Result |
| Financial Literature -> Students Personal Financial Management | 0.000 | Significant |
| Parents Social Economic -> Students Personal Financial Management | 0.000 | Significant |
| Student Lifestyle -> Students Personal Financial Management | 0.000 | Significant |
Relationship Financial Literature on Students Personal Financial Management
Based on the results of data analysis using SmartPLS obtained p value 0.000 < 0.050 so it can be concluded that Financial Literature has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Literature on Students variable will have a significant effect on an increase in the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Financial Literature variable will have an effect. Significant to the decrease in the Student Personal Financial Management variable. These results are in line with the research conducted by Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) that Financial Literature has a positive and significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management. It concludes that personal management can be influenced simultaneously by variables of financial literacy, socioeconomic status, and lifestyle. Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) says that how to manage finances is something that must be owned by someone. Parent's economic circumstances or conditions can also affect the flow of personal financial processing in students. Students with parents with sufficient income will have more opportunities when optimizing their financial arrangement, this can happen because parents can meet the needs and desires of children easily compared to students whose parents' economic status is low, students will be more careful in using and more economical to meet their needs. As a student who has studied finance at school, he must be able to manage his personal finances. According to Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) Lifestyle can be interpreted as the whole life of a person who relates to the environment and each other. The luxurious lifestyle is not only applied by teenagers whose economic level is upper middle class. However, even teenagers with low economic levels are the same. They are willing to not spend their pocket money for days to collect money to buy luxury items such as the latest Smartphones, expensive make-up, watching movies to concerts, and walking to the mall. According to Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) The treatment of luxurious living makes it difficult for individual needs to be fulfilled in order to fulfill their desires. This is because they are seen following the trend and not out of date. This unfavorable lifestyle can be overcome by going through the role of parents towards children, and also being able to control finances effectively and calculatingly.
Relationship of Parents Social Economic on Students Personal Financial Management
Based on the results of data analysis using SmartPLS obtained p value 0.000 < 0.050 so it can be concluded that Parents Social Economics has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Parents Social Economic variable will have a significant effect on an increase in the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Parents Social Economic variable will gives a significant effect on the decrease in the Student Personal Financial Management variable. These results are in line with the research conducted by Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) that Parents Social Economic has a positive and significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management.
This study is in line with the research of Radianto et al. (2021), Thomas and Subhashree (2020) proves that the financial behavior of students is influenced by their level of financial literacy. In his research states, someone with knowledge and ability to control finances well will show treatment in financial decisions such as when to save, invest, and use credit cards. In the research of Iramani and Lutfi (2021), Johan et al. (2021), Panos and Wilson (2020) shows that students' personal financial management is influenced by their financial literacy, which means students who have high financial knowledge will be able to easily manage their personal finances. On the other hand, students who have little knowledge of finances find it difficult to manage their personal finances. However, this study is not in line with the research of Philippas and Avdoulas (2020), Radianto et al. (2021), Thomas and Subhashree (2020) which proves that student financial management is not influenced by their financial literacy
Relationship Student Lifestyle on Students Personal Financial Management
Based on the results of data analysis using SmartPLS obtained p value 0.000 < 0.050 so it can be concluded that Student Lifestyle has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect on increasing the Student Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect. To the decrease in the Student Personal Financial Management variable. These results are in line with the research conducted by Chuah et al. (2020), Cherney et al. (2020), Humaidi et al. (2020) that Student Lifestyle has a positive and significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management. The output of this research is in line with the research of Philippas and Avdoulas (2020), Radianto et al. (2021), Thomas and Subhashree (2020) which proves that a child's personal finances can be caused by the level of the parents' economic status. The higher the literacy level and income of parents, the higher the level of pocket money managed by students so that the needs and desires of students are more easily met. It can be explained if students with high parental education and more than adequate income can manage their personal finances easily. On the other hand, students with low parental education, parents who have less income will be careful and save with their expenses. However, this research is not in accordance with the research presented by Thomas and Subhashree (2020) which proves that students' financial management is not caused by their socioeconomic status. This research supports the research of Thomas and Subhashree (2020) who found that the high and low levels of development in managing students' personal finances were influenced by lifestyle. Factors that cannot be separated from personal financial management activities are individual lifestyles. White et al. (2021), Xiao et al. (2020) millennial generation consumers are the most experience-hungry consumers. In fact, it is not only students with sufficient economic level of parents who can only show off the experience, students with low economic level of parents are also willing to collect their pocket money for days to enjoy their desires such as going to the mall with their friends, eat at expensive restaurants, buy luxury and branded goods. This unfavorable lifestyle can be overcome through the role of parents towards children, and also being able to manage finances properly and wisely.
Conclusion
Based on the results of data analysis using Smart PLS, it was found that Financial Literature had a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Literature on Students variable would have a significant effect on increasing the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Financial Literature variable would have a significant effect on the decrease in the Students Personal Financial Management variable. That Student Lifestyle has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect on increasing the Student Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Student Lifestyle variable will have a significant effect on the decrease in the Student Personal Financial Management variable. Parents Social Economics has a significant effect on Students Personal Financial Management, an increase in the Parents Social Economic variable will have a significant effect on increasing the Students Personal Financial Management variable and a decrease in the Parents Social Economic variable will have a significant influence on the decrease in the Students Personal Financial Management variable.
References
References
Chuah, SC, Kamaruddin, JN, & Singh, JSK. (2020). Factors affecting financial management behaviour among university students. Malaysian Journal of Consumer and Family Economics, 25, 154-174.
Purwanto, A, Asbari, M, & Santoso, TI. (2021). Marketing Research Data Analysis: Comparison of Results between Amos, SmartPLS, WarpPLS, and SPSS for Large Samples. Journal of Industrial Engineering & Management Research, 2(4), 216-227.
Purwanto, A, Asbari, M, & Santoso, TI. (2021). Social and Management Research Data Analysis: Comparison of Results between Amos, SmartPLS, WarpPLS, and SPSS for a Medium Sample Size. International Journal of Social and Management Studies, 2(4), 43-53.
Purwanto, A, Purba, JT, Bernarto, I, & Sijabat, R. (2021). The Influence of Servant, Digital and Green Leadership on Manufacturing Industry Performance through Mediation of Organizational Commitment. Journal of Management and Entrepreneurship Inspiration Research, 5(1), 1-13.
Purwanto, A, Purba, JT, Bernarto, I, & Sijabat, R. (2021). Effect of Management Innovation, Transformational Leadership, and Knowledge Sharing On Market Performance of Indonesian Consumer Goods Company. Management Application Journal, 19(2).