Research Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 4S
The Effect of eWOM, Online Review & Rating, and Advertising Information & Value on Consumer′s Preference and their Loyalty for Brands
Lalit Kumar, Shri Guru Ram Rai University
Monika Bangari, Shri Guru Ram Rai University
Citation Information: Kumar, L., & Bangari, M. (2023). The effect of ewom, online review & rating, and advertising information & value on consumer’ preference and their loyalty for brands: a study with special focus on working women and cosmetic products. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 27(S4), 1-16.
Abstract
In today's digital world, digital media advertisement is increasingly becoming an important factor in influencing consumer brand preference and brand loyalty. Through digital media platforms such as online review ratings, electronic word of mouth and advertisement information and values, brands are able to create an emotional connection with customers that can ultimately lead to increased brand preference and loyalty. The objective of this research is to determine how ads on digital media (such as online review ratings (ORR), electronic word of mouth (EM), and advertising information and value (AV)) have on brand preference & brand loyalty. This results of research revealed advertising in digital media has a substantial effect on brand preferences as well as their brand loyalty. It was discovered that online review ratings, electronic word of mouth, and the advertisement information and value all had a positive impact on a consumer's preference for a brand, while online review ratings and the advertisement information and value had influence on brand loyalty. According to results of research, it seems that advertising on digital media could be an effective tool for increasing brand preference and brand loyalty. It is suggested that marketers should use digital media advertisement more effectively to attract customers and increase their loyalty.
Keywords
Advertising Information & Value, Online Reviews & Ratings, eWOM, Brand Preference, Brand Loyalty.
Introduction
The advent of digital media advertising in the manner of online reviews, electronic word-of-mouth, and also advertisement information also values has had a significant impact on consumers' proclivities towards certain brands as well as their commitment to those brands. Since consumers are increasingly reliant on digital media to influence their choices, businesses have been forced to alter their marketing tactics in order to make the most of the power that is offered by the many new channels. This study explores the effect that advertising in digital media has on brand preferences and brand loyalty, with the goal of understanding how companies can effectively use digital media advertising like online review rating, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information and value to increase their market share and improve customer loyalty (Hanaysha, 2016) Online reviews allow consumers to share their experiences with a particular brand, which can then be used by other consumers to make informed decisions about their purchases. Electronic word of mouth refers to sharing of thoughts and experiences about a brand or product through online platforms such as blogs, forums, and social media sites (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010).
Through advertisements, companies are able to provide consumers with info about their products or services, which can help create a positive image of the brand (Widayat et al., 2022).
Studies found that brand loyalty and brand preference have a major role in marketing (Tsai et al., 2015). (Lakmali et al., 2022) Brand preference is a measure of how much a consumer prefers a particular brand compared to its competitors. It is usually determined by the consumer’s perception of brand’s quality in addition to its ability in meet their needs. (Yi et al., 2022) Brand loyalty, on the other hand, is the degree to which a consumer continues to purchase the same brand over time. Brand loyalty is typically measured by the consumer’s frequency of purchase, their willingness to pay more for brand, also amount of effort they are willing to put into finding the product. Moreover, (Hidayanti et al., 2018) some previous research supported the idea that brand preference served as a predictor of brand loyalty. In order to better understand preference and loyalty, the present study is looking at effect of online review ratings, electronic word-of-mouth, advertisement information, and values on brand preference and brand loyalty.
Theoretical Background and Hypothesis development
Digital media advertising has become a major part of contemporary marketing strategies and that it has the potential to influence consumer preferences and loyalty. The authors found that digital media advertising can influence consumer preference by creating positive associations with the brand, increasing the visibility of the brand, and providing information about the brand. Furthermore, digital media advertising has been found to positively affect brand loyalty by increasing customer confidence in the brand and providing an avenue for customer feedback. Many of the authors mentioned about online review rating and electronic word of mouth on brand, some of them are discussed below.
(Chakraborty & Bhat, 2018) used structural equation modelling to analyze consequence of online trust assessments on brand equity as well as ramifications of this impact on customer behavior. this evaluation was done to determine how online reviews affect brand equity dimensions. (Vo et al., 2022) in this research, author evaluated the influence of online review rating on the hotel sector. The research looked at the following elements that influence guest online reviews: passenger input, hotel management reaction, plus brand loyalty. According to findings of study, the investigation found that the choice process of the consumers was the single most significant component in the online behavior of customers' reviews themselves towards the hoteliers' service quality in order to promote positive customer satisfaction in dealing with online communication. (Zablocki, 2018) In this piece of research, the author presented a conceptual model that investigates in depth the connection that exists between the qualities of online reviews and brand attitudes. The model makes aid in comprehending the role of circumstance elements on brand attitudes within the setting of online communication by providing this context.
(Muka et al., 2021) had investigated the impact that marketing activities conducted through social media have on a company's overall brand recognition, image, and loyalty to the brand. In addition, research has shown that a company's brand awareness as well as its brand image takes significant influence on customer's commitment to the brand. (Sijoria et al., 2019) had examined the relationship among the antecedents of EM and consumer-based brand equity (CBBE) in the context of branded hotels. (S et al., 2017) discussed "The Effect of Advertising on Brand Preference in Kerala's Consumer Durables Market," which is one of the most competitive marketplaces in Kerala. Advertising is an important tool that everyone brand in this industry to combat the severe competition. (Lema, 2016) had investigated the influence that advertising information has on consumers' brand preferences in the beer brand market in the city of Adama. This study ultimately suggested appropriate actions for businesses to take in the process of refining their advertising strategies as a means of overcoming the intense competition that is currently present in the market.
(Perera et al., 2019) wanted in order to get a handle on the part that electronic word of mouth marketing plays in the development of e-loyalty. In addition, the authenticity of the information, the usefulness of the context all played a role in strengthening the connection between word of mouth marketing through the internet and e-loyalty. (Rialti et al., 2017) was to investigated the factors of Brand loyalty intention and EM by concentrating on customer gender disparities. The research showed that male consumers' intentions to remain loyal to a business are influenced by their engagement in social media.
(Awareness et al., 2018) was to evaluated the customer attachment to brand loyalty in Grab Indonesia, and electronic word of mouth. According to the findings, endogenous factors are considerably and favorably affected by exogenous variables such as online advertising, EM, customer attachment (brand loyalty). (Ebrahim, 2020) was to evaluate the influence that social media marketing efforts, often known as SMM, have on customer loyalty, specifically as assessed by a customer's level of trust and equity in the company. The direct effects on customer loyalty are mediated by trust in the brand, while the indirect effects on brand equity are mediated directly by trust in the brand.
Research gap: There is little research that has evaluate impact of digital media advertisement (online review rate, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information, and value) on brand preference and brand loyalty in the context of the modern digital media landscape. The majority of the currently available research concentrate on advertising on social media marketing and also the effect it has on brand equity & loyalty. It is not apparent how these factors affect the choice process of consumers, nor how successfully advertising via digital media can generate long-term brand preference and brand loyalty.
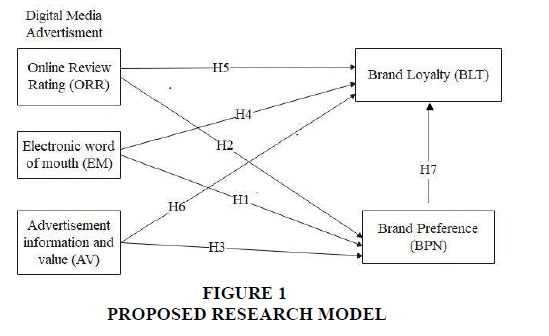
The effect of digital media advertisement (online review rating, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information and value) on brand preference & brand loyalty. The research hypotheses are based on this analysis of the existing literature. The main hypothesis is “There is no positive significant impact of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating as well as Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty and Brand preference”.
Digital Media Advertisement and Brand Loyalty
Digital media advertisement includes online reviews, electronic word of mouth, and advertisement information and value. In digital media advertisement, we considered dimensions like identity, conversation, sharing, presence”. According to (Ducoffe, 1995), The "degree to which people disclose their identity in a social media arena" is what the Identity functional block analyses and explains.” (Akbar et al., 2023) conversations block of honeycomb model "the degree to which one user interact with other users on a social media system. (Khan & Jan, 2019) Sharing block, distribute, and receive material. Social media users exchange views, photographs, videos, links, and more. (Rani et al., 2022) The degree to which users are able to detect whether or not other users are accessible is indicated by the presence building component. The following study hypotheses have been created in order to ascertain the effect that advertising through digital media has on consumer brand loyalty.
H1: There is a positive significant impact of electronic word of mouth on Brand loyalty
H2: There is a positive significant impact of Online Review Rating on Brand loyalty
H3: There is a positive significant impact of Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty
Brand preference & brand loyalty have become increasingly important topics for marketing scholars and practitioners. Both are essential for the success and sustainability of a company in a competitive market (DAM, 2020). Brand preference and loyalty are affected by many different factors, including product features, price, and quality. In addition, the internet and digitalization have drastically changed the way customers search for products and services and how companies interact with and reach their customers.
Online Review Rating, EM, Advertisement Information and Value on Brand Preference
According to (Akbar et al., 2023), Digital media is one of the web programmes that attempts to allow consumers to contribute their opinions, expertise, and prior experiences through social media platforms, content areas, & blogs. Another internet-based programme with the same goal is wikis. According to (Ducoffe, 1995), social media has a substantial beneficial influence on brand preference. Online review ratings are one of the most important factors influencing brand preference. Electronic word-of-mouth (EM) is another important factor influencing brand preference. EM refers to online conversations between consumers about products and services. Advertising information and value also play a key role in influencing brand preference.
The following hypotheses are presented based on the preceding discussion:
H4: There is a positive significant impact of electronic word of mouth on Brand preference
H5: There is a positive significant impact of Online Review Rating on Brand preference
H6: There is a positive significant impact of Advertisement information and value on Brand preference
Brand Preference & Brand Loyalty
(Ebrahim et al., 2016) expressed at the option assessment stage of the consumer decision-making process (Amofah, 2015) Brand Loyalty is studied in (Bobâlc? et al., 2012) marketing research literature as a component of one generic loyalty or four dimensions “cognitive, affective, and action loyalty scale”. The authors concentrated primarily on the behavioral part of loyalty, which was seen as a process of recurrent purchases(Vongurai, 2020). When Day introduced the notion of two-dimensional loyalty, this method analyzed brand loyalty in terms of outcomes rather than motives. As a result, we proposed below hypothesis:
H7: There is a positive significant impact of Brand preference on Brand loyalty.
Methodology
The main purpose of the study is to investigate the impact of digital media advertisement (online review rating, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information and value) on brand preference and brand loyalty. This study mainly focused on three variables, those are digital media advertisement, brand preference, brand loyalty. From these variables, online review rating, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information and value are the independent variables, brand preference and brand loyalty are the dependent variable.
Survey Measures
The survey measurement items of the constructions from past investigations were examined through and modified so that they would fit the parameters of the current study. The level of agreement was determined utilizing a 5-Likert scale, range from "1 = completely disagree" to "5 = completely agree."
Brand Preference
In this specific piece of study, a scale had four individual components, was put to use. The scale was used to measure the level of satisfaction that individuals had with their experiences with the company. each item was given a rating out of five points. Each of the items' questions was crafted with the intention of measuring a distinct feature of a consumer's affinity for a certain brand.
Brand Loyalty
In this particular research, Cognitive Loyalty Scale consists of two questions regarding the customer's degree of awareness, recognition and preference of the brand. The Action Loyalty Scale consists of three questions regarding the customer's level of repeat purchasing, recommending and switching behavior. The Affective Loyalty Scale consists of five questions regarding the customer's emotional attachment and satisfaction with the brand. All ten items were combined to form a Brand Loyalty Scale.
Online Review Rating, Electronic Word of Mouth, Advertisement Information and Value
In the current research, we used some queries to reflect the sub constructs of online review rating, electronic word of mouth and also advertisement information and value for the main construct i.e., digital media advertisement. There is a diverse set of queries pertaining to each and every object, all of which are dependent on the dimensions.
| Table 1 Description Of Latent Construct |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Construct | Item | Scale | Reference |
| BPN1 | This is a brand that I believe would be intriguing to me. | (DAM, 2020) (Luxton et al., 2015) | |
| Brand Preference (BPN) | BPN2 | This brand is my top choice when compared to others of its kind. | |
| BPN3 | When all other factors are considered equal, I prefer this cosmetic brand. | ||
| BPN4 | In general, I prefer this cosmetic brand | ||
| Brand Loyalty (BLT) | BLT1 | In the not-too-distant future, I also plan on purchasing this particular brand. | (Bobâlc? et al., 2012) |
| BLT2 | It is my intention to purchase other items manufactured by this brand. | ||
| BLT3 | Those who want my opinion and recommendations should consider purchasing this brand. | ||
| BLT4 | When I talk to other people about this brand, I only say good things about it. | ||
| BLT5 | When I am in the market for cosmetic items, I always go to this particular business first. | ||
| BLT6 | I decided to buy this particular brand since I have a lot of faith in it. | ||
| BLT7 | I am glad that I decided to purchase this brand rather than any of the other ones. | ||
| BLT8 | In comparison to other brands, I like these particular cosmetics. | ||
| BLT9 | As compared to other brands, I feel a stronger connection to this one. | ||
| BLT10 | As compared to other brands, I am much more intrigued by this specific brand. | ||
| Online Review Rating (ORR) | ORR1 | I put a lot of stock in the testimonials that were provided by customers. | (Akbar et al., 2023) |
| ORR2 | I plan to make purchases when I've read the most recent reviews of the items. | ||
| ORR3 | I want to purchase items since the feedback provided by customers is not fabricated in any way. | ||
| ORR4 | Correct information may be found on social media platforms in the form of product reviews. | ||
| ORR5 | I often hear or read evaluations of items from other people or on social media, and as a result, I intend to buy products that are reviewed there. | ||
| ORR6 | The majority of customers that review Scarlett Whitening products gave them bad feedback. | ||
| ORR7 | I have made up my mind to purchase the items after reading or hearing reviews from other individuals or on social media. | ||
| Electronic Word of Mouth (EM) | EM1 | Only the internet reviews that provide information that is pertinent to me am I going to bother reading them. | (Toni, 2022) |
| EM2 | My choice to buy anything is impacted by how trustworthy the website is that offers the reviews. | ||
| EM3 | My choice to buy anything is impacted by how reliable the website is that offers the customer ratings and comments. | ||
| EM4 | If the author's geographical location is comparable to mine, I am more likely to believe the product review. | ||
| EM5 | My choice to buy anything is influenced by an argument as long as it can provide sound evidence to back up its valence. | ||
| EM6 | My choice to buy anything is significantly influenced more by favorable comments made on internet shopping sites. | ||
| EM7 | If a reviewer discusses a product, I'm interested in buying using technical jargon and vocabulary, I consider that person to be knowledgeable. | ||
| AV1 | Advertising is useful | (Ducoffe & Ducofje, 2012) | |
| Advertisement information and value (AV) | AV2 | People are informed about items when they have a need for the information, which is provided via advertisements. | |
| AV3 | Advertisements often omit vital information about the items they promote. | ||
| AV4 | Advertisements are deceitful | ||
| AV5 | Information that is pertinent to items is provided via advertisements. | ||
| AV6 | There is too much advertising | ||
| AV7 | Advertisements are entertaining | ||
| AV8 | Advertisements are pleasing | ||
| AV9 | Advertising is irritating | ||
| AV10 | Advertisements lie | ||
| AV11 | Information that is current and relevant about items is provided via advertising. | ||
| AV12 | Advertisements insult people's intellect | ||
| AV13 | Advertising is enjoyable | ||
| AV14 | Advertising is important | ||
| AV15 | Advertising is valuable | ||
Data Analysis
Data screening and the identification of univariate outliers were done prior to the analysis. On the basis of maximum-minimum, descriptive and frequency analysis has been done for missing values. First, all of the statistical measures have been computed, including means, standard deviations, as well as correlations. To evaluate the hypotheses, a second-stage SEM procedure was used in the second step.
The first stage was a test to see whether the study's self-report measures were all different and independent from one another (Alder et al., 2006). In order to solve the issue of model identification, sub constructs were employed to assess employee brand advocacy and employer branding, employing a second-order factor confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) method to evaluate each model independently.
In the second step, you'll examine a pre-defined model that specified the associations between the various constructions. An overall CFA is then performed utilizing all variables to determine relationships and differences across constructs by explaining how each construct emerges in the model. This is done by looking at indicators for model fit as well as factor loadings(ten Brummelhuis et al., 2012)
Data Analysis and Result
The statistical information relevant to the information gathered from the research study's respondents is presented in this chapter. This chapter also includes discussion of the research study's statistical findings. The researcher discusses the conclusions that were derived from the quantitative data. The information was first added to an Excel spreadsheet, and then it was brought into SPSS 24.0 for analysis. As a consequence of this, the outcomes of the present investigation were analyzed utilizing the SPSS programme. The number 500 was chosen as the size of the study's sample. As independent factors, the study looked at online review ratings, electronic word of mouth, and the information and value provided by advertisements. As a dependent variable, the researchers focused on customer loyalty to certain brands. By a process of reliability analysis, Cronbach's alpha was utilized to evaluate the degree to which the data has an internal coherence. Confirmatory factor analysis is a method that falls under the umbrella of factor analysis. (CFA) has as its primary goal the establishment of an understanding of the fundamental connections that exist between the variables that are being assessed. To provide a concise summary of the data, descriptive statistics are used. Variables are often represented by the mean value followed by their standard deviation (mean SD). Finding the connection between the dependent and independent variables may be accomplished via the use of regression analysis. For the purpose of structural equation modelling (SEM), also known as "path diagramming," which depicts the relationship between a dependent variable (one that is not seen) and independent variables, path diagrams are used (those that are seen).
| Table 2 Descriptive Statistics & Pearson’s Correlation Coefficients For The Study Variables |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construct | No. of items | Mean | SD | EM | ORR | AV | BLT | BPN |
| Electronic word of mouth (EM) | 7 | 3.44 | 0.95 | 1 | .506** | .909** | .889** | .898** |
| Online Review Rating (ORR) | 7 | 3.59 | 0.84 | 1 | .372** | .142 | .371** | |
| Advertisement information and value (AV) | 15 | 3.52 | 0.92 | 1 | .921** | .976** | ||
| Brand loyalty (BLT) | 10 | 3.59 | 0.70 | 1 | .938** | |||
| Brand preference (BPN) | 4 | 3.50 | 0.90 | 1 | ||||
Table 1 & 2 reveals the Statistics that are descriptive & Pearson's correlation coefficients for the variables in the research the fact that the factor Online Review Rating has a high mean value of 3.59 indicates that the majority of respondents agreed with it. In contrast, the fact that the factor EM has the lowest mean value of 3.44 indicates that respondents answered neutrally when asked about the electronic word of mouth factor.
According to the findings presented above, there was a substantial positive linear link between brand loyalty and EM (r=0.889, p0.01) and advertisement information & value (r=0.921, p0.01). Furthermore, a significant positive linear association was found between brand preference and electronic word of mouth (r=0.898, p0.01), online review rating (r=0.371, p0.01), and advertisement information & value (r=0.976, p0.01). It was shown that a substantial positive linear association exists between a consumer's choice for a brand and their loyalty to that brand (r=0.938, p0.01). The significant value of Online Review Rating (r=0.142, p>0.05) which is greater than 0.05, it is reveals that there is significant relationship with Online Review Rating and Brand loyalty.
| Table 3 Factor Analysis Along With Reliability Analysis, Composite Reliability, Average Value Extract Analysis |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | α | CR | AVE | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
| Electronic word of mouth (EM) | 0.983 | 0.807 | 0.967 | ||||||
| Only the internet reviews that provide information that is pertinent to me am I going to bother reading them. | EM1 | 0.929 | |||||||
| My choice to buy anything is impacted by how trustworthy the website is that offers the reviews. | EM2 | 0.924 | |||||||
| My choice to buy anything is impacted by how reliable the website is that offers the customer ratings and comments. | EM3 | 0.924 | |||||||
| If the author's geographical location is comparable to mine, I am more likely to believe the product review. | EM4 | 0.898 | |||||||
| My choice to buy anything is influenced by an argument as long as it can provide sound evidence to back up its valence. | EM5 | 0.884 | |||||||
| My choice to buy anything is significantly influenced more by favorable comments made on internet shopping sites. | EM6 | 0.865 | |||||||
| If a reviewer discusses a product, I'm interested in buying using technical jargon and vocabulary, I consider that person to be knowledgeable. | EM7 | 0.865 | |||||||
| Online Review Rating (ORR) | 0.963 | 0.705 | 0.943 | ||||||
| I put a lot of stock in the testimonials that were provided by customers. | ORR1 | 0.84 | |||||||
| I plan to make purchases when I've read the most recent reviews of the items. | ORR2 | 0.861 | |||||||
| I want to purchase items since the feedback provided by customers is not fabricated in any way. | ORR3 | 0.838 | |||||||
| Correct information may be found on social media platforms in the form of product reviews. | ORR4 | 0.835 | |||||||
| I often hear or read evaluations of items from other people or on social media, and as a result, I intend to buy products that are reviewed there. | ORR5 | 0.828 | |||||||
| The majority of customers that review Scarlett Whitening products gave them bad feedback. | ORR6 | 0.827 | |||||||
| I have made up my mind to purchase the items after reading or hearing reviews from other individuals or on social media. | ORR7 | 0.826 | |||||||
| Advertisement information and value (AV) | 0.991 | 0.893 | 0.992 | ||||||
| Advertising is useful | 0.986 | ||||||||
| People are informed about items when they have a need for the information, which is provided via advertisements. | AV1 | 0.984 | |||||||
| Advertisements often omit vital information about the items they promote. | AV2 | 0.983 | |||||||
| Advertisements are deceitful | AV3 | 0.979 | |||||||
| Information that is pertinent to items is provided via advertisements. | AV4 | 0.977 | |||||||
| There is too much advertising | AV5 | 0.977 | |||||||
| Advertisements are entertaining | AV6 | 0.969 | |||||||
| Advertisements are pleasing | AV7 | 0.969 | |||||||
| Advertising is irritating | AV8 | 0.966 | |||||||
| Advertisements lie | AV9 | 0.915 | |||||||
| Information that is current and relevant about items is provided via advertising. | AV10 | 0.913 | |||||||
| Advertisements insult people's intellect | AV11 | 0.913 | |||||||
| Advertising is enjoyable | AV12 | 0.894 | |||||||
| Advertising is important | AV13 | 0.881 | |||||||
| Advertising is valuable | AV14 | 0.857 | |||||||
Table 3 reveals the Factor analysis along with Reliability analysis, Composite Reliability, Average Value Extract analysis. A factor analysis is performed using all twenty-nine of the assertions. The total of twenty-nine assertions have been condensed down to three components using the principal component analysis construction method. Electronic word of mouth, online review ratings, and the Advertisement information and value provided by advertisements make up the three components. In order to evaluate the degree of internal consistency that exists within each component, the research makes use of the Cronbach's alpha approach. The reliability analysis reports to measurements for each factor are included in the table below. Cronbach's alpha scores may range from 0.963 to 0.991, It demonstrates that there is a significant degree of consistency within each of the individual elements. Displays both the Convergent Validity Test as well as the Discriminant Validity Test for your perusal. Both the Composite Reliability (CR) and the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) should be larger than or equal to 0.5, and the Composite Reliability (CR) should be >=0.7. Since all of the AVE values in this situation are larger than 0.5 and the CR value is 0.9, which is greater than equal to 0.7, it may be concluded that both convergent & discriminant validity are present Table 4.
Hypothesis
H01: There is no positive significant impact of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating and Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty and Brand preference
H11: There is a positive significant impact of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating and Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty and Brand preference
| Table 4 Association Between Digital Media Advertisement, Brand Loyalty And Brand Preference |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DV | Independent Variables | Unstandardized Coefficients | R Square |
T value |
P value |
|
| Beta | SE | |||||
| BLT | (Constant) | 1.128 | .061 | 0.864 | 18.444 | 0.000** |
| Electronic word of mouth | .231 | .033 | 7.095 | 0.000** | ||
| Online Review Rating | .017 | .017 | 0.994 | 0.321 | ||
| Advertisement information and value | .491 | .031 | 15.693 | 0.000** | ||
| BPN | (Constant) | .119 | .047 | 0.853 | 2.560 | 0.000** |
| Electronic word of mouth | .060 | .025 | 2.411 | 0.006** | ||
| Online Review Rating | .012 | .013 | 4.168 | 0.001** | ||
| Advertisement information and value | .905 | .024 | 37.998 | 0.000** | ||
Dependent Variable: BLT: Brand loyalty, BPN: Brand preference, **p<00.01
The relationship that exists between advertisements in digital media, brand loyalty, and brand preference is shown in the table that is located above. According to the significant value (p-value less than 0.01), brand loyalty is dependent on factors such as online review ratings, electronic word of mouth, and advertisement information and value. Moreover, Electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating, and the advertisement information and value could be able to explain 87% of the variation in Brand loyalty (R2 value = 0.866). Also, the beta coefficients for electronic word of mouth (0.171) and online review rating (0.051), and advertisement information and value (0.517) are all positive. It demonstrates that an increase in the value of electronic word of mouth, online review ratings, along with advertisement information and value will lead to an increase in brand loyalty if these factors are valued more highly. In a similar vein, the significant value (p-value less than 0.01) demonstrates that a consumer's preference for a brand is dependent on factors such as online review ratings, electronic word of mouth, and the advertisement information and value. Moreover, Electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating, & advertisement information and value may be able to explain 85% of the variation in Brand choice (R2 value = 0.853). Also, the beta coefficient for electronic word of mouth is positive (0.047), while the online review rating beta coefficient is positive (0.012), and the advertisement information and value beta coefficient is positive (0.910). It demonstrates that an increase in the value of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating, and Advertising information and value will lead to an increase in Brand preference if these factors are valued more highly.
H02: There is no positive significant impact of Brand preference on Brand loyalty.
H12: There is a positive significant impact of Brand preference on Brand loyalty.
| Table 5 Association Between Brand Preferences On Brand Loyalty |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DV | Independent Variables | Unstandardized Coefficients | R Square |
T value |
P value |
|
| Beta | SE | |||||
| BLT | (Constant) | 1.044 | 0.044 | 0.880 | 23.980 | 0.000** |
| Brand preference | 0.727 | 0.012 | 60.299 | 0.000** | ||
Dependent Variable: BLT: Brand loyalty, **p<0.01.
The association between Brand preferences on Brand loyalty is depicted in the above Table 5. Since the significance value was less than 0.01, we may deduce that brand preference is directly related to brand loyalty. In addition, one's preferences for a brand could be able to explain 88 percent of the variation in one's loyalty to a brand (R2 value = 0.880). Moreover, there is a positive value for the beta coefficient of brand preferences (0.727). It demonstrates that if a consumer's choice for a brand increase in value, then this will always result in a rise in that brand's loyalty Figures 1 & 2.
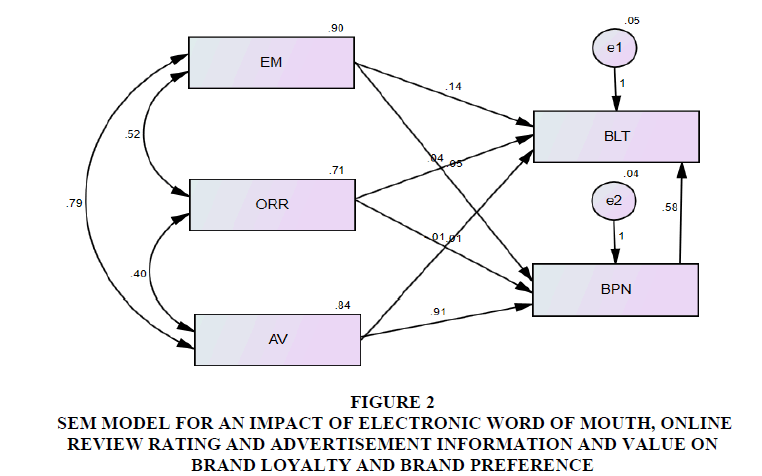
Figure 2: SEM model for an impact of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating and Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty and Brand preference.
| Table 6 Sem Path For An Impact Of Electronic Word Of Mouth, Online Review Rating And Advertisement Information And Value On Brand Loyalty And Brand Preference |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path | Unstandardized coefficient |
S. E | Standardized coefficient |
R Square | p-value | ||
| BPN | <--- | EM | 0.047 | 0.026 | 0.049 | 0.866 | <0.0001*** |
| BPN | <--- | ORR | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.011 | <0.0001*** | |
| BPN | <--- | AV | 0.910 | 0.024 | 0.925 | <0.0001*** | |
| BLT | <--- | AV | 0.010 | 0.055 | 0.013 | <0.0006*** | |
| BLT | <--- | EM | 0.144 | 0.03 | 0.195 | 0.853 | <0.0032*** |
| BLT | <--- | ORR | 0.044 | 0.016 | 0.053 | 0.862 | |
| BLT | <--- | BPN | 0.579 | 0.052 | 0.747 | 0.893 | <0.0001*** |
***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05
SEM path analysis for an influence of electronic word of mouth, Online Review Rating and Advertisement information and value on Brand loyalty & Brand preference is depicted in the Table 6. As a result of this work, it will be feasible to test all of the important pathways, and measurement errors and feedbacks will be able to be included into the model in a straightforward manner. The fit indices of a model show the model has a good fit when factors are judged to be significant at p values of less than 0.05. The extent to which the proposed model fits the available data was assessed by utilising global fit, which consisted of seven different fit indices, and r, which made it possible to examine how well the model suited the data The extent to which the proposed model fits the available data was evaluated to establish the model's level of compatibility with the data.
| Table 7 Model Fit Summary |
||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | Value | Suggested value |
| Chi-square value(χ2) | 4.037 | |
| Degrees of freedom (df) | 1 | |
| P value | 0.069 | P-value >0.05 |
| GFI | 0.994 | > 0.90 |
| RFI | 0.982 | >0.90 |
| NFI | 0.998 | >0.90 |
| IFI | 0.998 | > 0.90 |
| CFI | 0.998 | >0.90 |
| RMR | 0.004 | < 0.08 |
| RMSEA | 0.010 | < 0.08 |
The structural model, in terms of its quality of fit, was able to provide an acceptable representation of the sample data (2 (1) = 4.636, GFI (Goodness of Fit Index) =0.994; CFI (Comparative Fit Index) =0.998, RFI (Relative fit index) = 0.982 and NFI (Normed Fit Index) = 0.998, all of which are higher than the 0.90 threshold that was recommended. Similarly, RMR (Root Mean Square Residuals) =0.004 & RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation) =0.010 values are less than 0.08 crucial threshold Table 7.
Discussion
The importance of the study was to assess and define impact of digital media advertising (online review rating, electronic word of mouth, advertisement information and value) on brand preference as well as brand loyalty in a different context than previous studies. Most recent research focuses on these factors for many sectors, and this present study discussed these influences in the brand market. According to the present research findings, the seven hypotheses in the study model were accepted Table 8.
| Table 8 Structural Model Assessment |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Relationship | T-value | P-value | Decision |
| H1 | EM--> BLT | 7.095 | 0.000** | Accepted |
| H2 | ORR--> BLT | 0.994 | 0.321 | Rejected |
| H3 | AV-->BLT | 15.693 | 0.000** | Accepted |
| H4 | EM--> BPN | 2.411 | 0.006** | Accepted |
| H5 | ORR--> BPN | 4.168 | 0.001** | Accepted |
| H6 | AV-->BPN | 37.998 | 0.000** | Accepted |
| H7 | BLT-->BPN | 60.299 | 0.000** | Accepted |
The results of this analysis reveal the essential connection between digital media advertisement, brand loyalty and brand preference. The data suggests electronic word of mouth, online review rating, also advertisement information and value are all important components in predicting brand loyalty and preference. The p-value of less than 0.01 shows that the results are significant and that these three factors can explain a large percentage of the variance in both brand loyalty (87%) and brand preference (85%). The positive beta coefficients for all three variables indicate that higher values of these components result in higher levels of brand loyalty and preference. Overall, this analysis confirms the importance of digital media advertisement in influencing consumer brand loyalty and preference. Companies should consider investing in strategies such as enhancing their online presence, positive reviews, and advertisement information and value in order to improve customer loyalty and preference.
According to the findings of the significance test, here is high correlation among Brand preferences & Brand loyalty. A p-value that is less than 0.001 indicates that brand preferences are a significant factor in determining brand loyalty. Furthermore, the R2 value of 0.880 shows that Brand preferences can explain 88% of the variance in Brand loyalty, demonstrating that Brand preferences are a strong predictor of Brand loyalty. Additionally, the positive beta coefficient of 0.727 demonstrates that a rise in the brand preference will result in a rise in the loyalty to that brand. According to the findings of this investigation, brand preferences seem to have a considerable effect on brand loyalty.
Overall, this analysis reveals digital media advertisement shows significant role in influencing consumer brand loyalty & preference. The data shows that electronic word of mouth, online review rating, along with advertisement information and value are all important components in predicting brand loyalty and preference. Furthermore, the positive beta coefficients for all three variables indicate that higher values of these components result in higher levels of brand loyalty and preference. Thus, companies should consider investing in strategies such as enhancing their online presence, positive reviews, and advertisement information and value in order to improve customer loyalty and preference.
Implications
The implications of the digital media advertisement on brand preference and brand loyalty are numerous. Firstly, digital media advertisement can help to create a strong brand identity and enhance brand loyalty. By providing customers with relevant, up-to-date information and value, customers are more likely to form positive opinions of the brand and develop trust in it. Secondly, digital media advertisement can help to increase brand preference by creating a positive perception of the brand amongst customers. Customers may be more likely to view the brand as trustworthy and reliable if they are exposed to its digital media advertisement. Finally, digital media advertisement can also help to increase customer engagement and build relationships with customers. By providing customers with relevant content and engaging them in conversations, customers remain possible to become loyal towards the brand and remain loyal even when faced with competition from other brands.
Digital media advertisement provides great opportunities to build brand awareness and engage customers. It also provides consumers with more information and value that can help them make informed decisions. Online review ratings, electronic word of mouth, & advertisement information and value can help shape brand preference & brand loyalty. Consumers are more likely to trust a brand that has positive online reviews, electronic word of mouth, and advertisement information and value. This can lead to increased brand preference and loyalty. Marketers should take advantage of digital media advertising to create positive brand associations, build trust, and engage customers. They should also ensure that the information and value provided in their advertisements is relevant and accurate. Doing so can help increase brand preference and loyalty.
Limitations and Future research
There is a limit on how much advertisements on digital media may have on consumers' preferences towards brands and their loyalty to such brands. Digital media advertisement is dependent on a user’s exposure to it, which could be affected by factors such as the user’s browsing habits, the type of device used to access the advertisement, and the user’s online behavior. Furthermore, advertisements may be presented in an incomplete or biased manner, leading to a limitation in their effectiveness. Additionally, the availability of rival commercials, the user's familiarity with the brand, as well as the absence of interactive aspects in the advertisement may restrict the influence that digital media advertisement has on brand choice and brand loyalty. Finally, digital media advertisement may suffer from low user engagement and low levels of recall, which could limit its effectiveness.
The future research should also investigate how the perceptions of consumers towards digital media advertisement influence their brand loyalty and preference. The study should also concentrate on the influence that demographic parameters like age, gender, & income have on the effect that advertisements in digital media have on consumers' preferences for brands and their loyalty to those brands. In addition, the study needs to investigate the moderating influence that various digital media platforms have on the impact that digital media advertisements have on consumers' preferences and loyalty to certain brands. Moreover, it should explore the influence that advertisements in digital media have on consumer behavior in a variety of cultural settings.
References
Akbar, A. R., Kalis, M. C. I., Afifah, N., Purmono, B. B., & Yakin, I. (2023). The Influence of Product Packaging Design and Online Customer Review on Brand Awareness and Their Impact on Online Purchase Intention. South Asian Res J Bus Manag, 5(1), 10-18.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alder, G. S., Noel, T. W., & Ambrose, M. L. (2006). Clarifying the effects of Internet monitoring on job attitudes: The mediating role of employee trust. Information & management, 43(7), 894-903. Amofah, O. (2015).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
An assessment of the influence of service marketing mix on customer choice of restaurant in Kumasi. Biomass Chem Eng, 49(23-6), 22-23.
Bobâlc?, C., G?tej, C., & Ciobanu, O. (2012). Developing a scale to measure customer loyalty. Procedia Economics and Finance, 3, 623-628.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables (Vol. 210). John Wiley & Sons.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chakraborty, U., & Bhat, S. (2018). The effects of credible online reviews on brand equity dimensions and its consequence on consumer behavior. Journal of promotion management, 24(1), 57-82.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dam, T. C. (2020). Influence of brand trust, perceived value on brand preference and purchase intention. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(10), 939-947.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ducoffe, R. H. (1995). How consumers assess the value of advertising. Journal of current issues & research in advertising, 17(1), 1-18.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ebrahim, R. S. (2020). The role of trust in understanding the impact of social media marketing on brand equity and brand loyalty. Journal of Relationship Marketing, 19(4), 287-308.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ebrahim, R., Ghoneim, A., Irani, Z., & Fan, Y. (2016). A brand preference and repurchase intention model: the role of consumer experience. Journal of Marketing Management, 32(13-14), 1230-1259.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hanaysha, J. (2016). The importance of social media advertisements in enhancing brand equity: A study on fast food restaurant industry in Malaysia. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 7(2), 46.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hidayanti, I., & Nuryakin, N. F. (2018). A study on brand commitment and brand trust towards brand loyalty of branded laptop in Indonesia. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 12(3).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural equation modeling: a multidisciplinary journal, 6(1), 1-55.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jöreskog, K. G., & Sörbom, D. (1981). LISREL 5: analysis of linear structural relationships by maximum likelihood and least squares methods;[user's guide]. University of Uppsala.
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Business horizons, 53(1), 59-68.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khan, M. F., & Jan, A. (2019). A measure of social media marketing: Scale development and validation. Jindal Journal of Business Research, 8(2), 158-168.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lakmali, M. G. T., Samaraweera, G. C., Narayana, N. M. N. K., & Laksiri, W. M. R. (2022). Effect of Marketing Mix Antecedents on Consumer Brand Preference of Milk Powder. Tropical Agricultural Research, 33(3), 260-270.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Luxton, S., Reid, M., & Mavondo, F. (2015). Integrated marketing communication capability and brand performance. Journal of advertising, 44(1), 37-46.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Perera, C. H., Nayak, R., & Long, N. V. T. (2019). The Impact of electronic-word-of mouth on e-loyalty and consumers’e-purchase decision making process: A Social media perspective. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 10(4), 85-91.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rani, A., Toni, M., & Shivaprasad, H. N. (2022). Examining the effect of electronic word of mouth (eWOM) communication on purchase intention: A quantitative approach. Community & Communication Amity School of Communication, 15(8), 2456-9011.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rialti, R., Zollo, L., Pellegrini, M. M., & Ciappei, C. (2017). Exploring the antecedents of brand loyalty and electronic word of mouth in social-media-based brand communities: do gender differences matter?. Journal of Global Marketing, 30(3), 147-160.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sijoria, C., Mukherjee, S., & Datta, B. (2019). Impact of the antecedents of electronic word of mouth on consumer based brand equity: a study on the hotel industry. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 28(1), 1-27.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Steiger, J. H. (1989). EzPATH: causal modeling: a supplementary module for SYSTAT and SYGRAPH: PC-MS-DOS, Version 1.0. Systat.
Tsai, Y. C., Chang, H. C., & Ho, K. C. (2015). A study of the relationship among brand experiences, self-concept congruence, customer satisfaction, and brand preference. Contemporary Management Research, 11(2).
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
VONGURAI, R. (2020). Factors affecting customer brand preference toward electric vehicle in Bangkok, Thailand. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(8), 383-393.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yi, L., Khan, M. S., & Safeer, A. A. (2022). Firm innovation activities and consumer brand loyalty: A path to business sustainability in Asia. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 942048.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 18-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13360; Editor assigned: 28-Jan-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13360(PQ); Reviewed: 30-Feb-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13360; Revised: 28-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13360(R); Published: 09-Apr-2023