Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 2S
The Effect of CRM on Organization Performance: A Study of Medium Enterprises in Indonesia
Fahmi Natigor Nasution, University of Sumatera Utara
Ahmad Rafiki, University College of Bahrain
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the relationship between CRM organization factors (i.e. top management support, customer orientation, training orientation) and organization performance of medium enterprises in Indonesia. These medium enterprises are operated in telecommunication industry. This is a quantitative study using a survey method of self-administered questionnaire. The stratified sampling technique is chosen and 82 respondents are the employees from three enterprises. Data collected was analyzed using correlation and regression analysis to test the model and explain relationship between variables. The results of this study found that the organization factors of CRM (i.e. top management support, customer orientation, training orientation) have a positive and significant impact on organization performance. CRM is a potential system that has huge and positive impact to the customers and business performance which suggested to be adopted widely by the medium enterprises of telecommunication industry in Indonesia.
Keywords
CRM, Organizational Factor, Organization Performance, Medium Enterprises, Telecommunication Industry, Indonesia.
Introduction
When discussing about CRM, it is related to the adoption of information technology (IT). IT and SMEs are both interrelated especially in this digital era. The focus of IT is on three things; IT abilities refer to the skills, capabilities to the resources and strategies, and capacities to the ability of firms to absorb, process, and present the information. IT adoption in medium enterprises recognize that the size of the firm and the industry sector are factors that both play a role in the adoption process, and even more so in the case of CRM technology adoption. This is because, as firm size increases, the scale, scope, and complexity of the adoption increase, and different industries have different requirements. The perceived benefits of CRM vary by organizational size, geographical location and industry sector. However, some arguments mentioned that firm size has no significant effects on the adoption of CRM. It is suggested that the medium enterprises more likely to engage in CRM technology when they see themselves as a front runner.
When managers can identify, observe, satisfy and fulfill customers’ expectations, means that they are adopting the Customer Relationship Management (CRM). This concept is required to build strong relationship with customers and understanding them comprehensively. A number of studies have been conducted to explore the CRM success factors (e.g. Alshawi et al., 2011; Alt and Puschmann, 2004; Eid, 2007; Kim, 2008; Moreno and Melendez, 2011; Chen, 2004).
Therefore the telecommunication companies in Indonesia particularly were employing this system because they are concerned on the labor intensive, costs-effective, turnover and customer satisfaction.
CRM plays an important role to enhance business performance (Akroush et al., 2011; Dutu and Halmajan, 2011; Kasim and Minai, 2009; Ramani and Kumar, 2008; Sin et al., 2005). Based on the resource based view theory, CRM is considered as one of the vital organization’s resources that contribute to have better performance. Thus, the aim of the study is to examine the organizational factor of CRM affecting organization performance in telecommunication companies in Indonesia. This expectedly will help other companies in telecommunication industry to understand on how to sustain and increase the businesses’ efficiency. The medium enterprise (ME) is a business unit with an annual value of sales of more than US$50,000 but less than US$ 500,000 and the business units with 20–99 workers.
Literature Review
CRM and Organization Performance
CRM is a system that useful as to generate, store, represent, reproduce and translate information. It is adopted to manage customers’ interactions or relations and improve the understanding on consumers’ profiles by the company (Gupte, 2011). Moreover, Wang and Feng (2012) posited that CRM potentials represent skills and knowledge to enhance, establish, maintain and upgrade the beneficial relationships with customers. Their study found a significant relationship between CRM and business performance. Therefore, the companies should use the resources to establish a strong CRM system to gain the expected objectives.
Salem Al-Said (2010) asserted that CRM practices create opportunities through a mobile service provider in delivering reliable services to the customers which lead to satisfaction. While, Coltman (2007) found a significant path between CRM and organization performance. Moreover, Fatma (2014) mentioned that the use of CRM techniques using advanced software has changed the business orientation particularly in financial services. This indicated its relevancy to customer satisfaction and organization performance. In fact, many of companies depend on technologies or information systems to run the business but ignored the organization factors. The successful of CRM’s implementation importantly due to the organization factors.
Organizational Factors
Organization factors related to the structures of operations, human resources, customer orientation, reward and appraisal system, training and administrations’ matters. Becker et al. (2009) stated that the organizational factors are significantly related to CRM performance. Below are the implications of organization factors found by authors:
• Having sufficient number dedicated employees, the CRM systems can be learned and accepted appropriately (Nath et al., 2009).
• Through organization’s structure and its’ operational business procedures, the CRM implementation could be managed accordingly (Payne and Frow, 2006).
• Enable collaboration of various departments and functions to accomplish CRM activities such as the level of integration within the organization, commitment of senior management towards the project and the availability of various resources (Croteau and Li, 2003).
Though there are other dimensions of CRM that could be adopted in this study, however, the organization factor remain used as the main dimension based on previous researches (Abbott et al., 2001; Goodhue et al., 2002; Themistocleous, 2004; Lin, 2006; Wainwright et al., 2005; Lucchetti and Sterlacchini, 2004; Daniel and Wilson, 2002; Lai and Hsieh, 2007; Chen, 2003; Chen & Popovich, 2003; Scupola, 2003; Shang and Seddon, 2002; Wilson et al., 2002).
Top Management Support
Top management support is the most important factor to the successful of CRM implementation and organization performance (Kim et al., 2010; Bohling et al., 2006). Below are the details of its implications found by authors:
• Decrease costs and risk, encourage sustainable competitive advantage, create opportunities of the customer value, control the expenses and monitor performance (Sigala, 2005).
• Improve level of commitment of staff (Adam et al., 2010; Buttle, 2004).
• Carry an innovation online and ensure delivery of promised benefits (Chen and Popovich, 2003).
• Set the stages in CRM initiatives for leadership, strategic direction and alignment of vision and business goals (Mendoza et al., 2007).
• Assist the improvement of the relationship and for meeting customers' needs (Kim et al., 2010).
Meanwhile, Sohrabi et al. (2010) revealed that top management support was significantly associated with organization performance (customer satisfaction, profitability, loyalty, market share). Other studies agreed with the Sohrabi et al.’s findings (e.g. Capacity, 2004; Croteau & Li, 2003; Kale, 2004). In contrast, a study by Eid (2007) found that the top management support has a negative correlation with performance. With these arguments, thus the proposed hypothesis is:
H1: There is significant relationship between top management support of CRM and organization performance.
Customer Orientation
Customer orientation relates to the activities of putting priority on customers’ interest. All the efforts are meant for customers’ benefits (Cai, 2009). A customer is strategically as a center of focus (McEachern and Warranty, 2005). In order to have efficient of CRM implementation, the company need to develop customer orientation (Kim, 2008). There are implications of customer orientation found by authors:
• Give a focus to employees' initiatives in creating customer value. The customer orientation will bring motivation in completing the activities of customer data handling, hence resulted a higher CRM performance that associated with a better company performance (Cai, 2009).
• The client relationship can be improved which lead to result client faithfulness (Kim, 2008).
• Has a critical correlation to comparative sales, benefit, social preference position, and maintaining client performance (Day and Van den Bulte, 2002).
Numerous studies have done on customer orientation that used as the important factor of CRM performance e.g., Eid (2007); Faed et al. (2010); Kim (2008); Becker et al. (2009); Sohrabi et al. (2010); Ramani and Kumar (2008); McNally (2007). Given these arguments, it is clearly that customer orientation creates customer loyalty and satisfaction which bring better organization performance, thus, the proposed hypothesis is:
H2: There is significant relationship between customer orientation of CRM and organization performance.
Training Orientation
The contribution of training to the CRM process will help the organization to achieve success (Shang & Chen, 2007). Below are the implications of training orientation in CRM:
• Uplift in knowledge management where the members of organizations could disseminate information and use it in responding the customers’ inquiries, thus able to give excellent services to the customers (Shang & Chen, 2007).
• Encourage salient features of producing quality outcomes in administration, customer services which also can be used as a benchmark for attitude and behavior (Kim, 2008).
• Develop and execute suitable customer-focused systems (Payne and Frow, 2006).
• Learn about an important process of customer service, encourage efficiencies, maintain consumer confidence and repeat purchase (Rigby et al., 2002).
• Able to counter to customers’ requests, create customers’ satisfaction, make high profit, and influence the information and value creation (Plakoyiannaki et al., 2008).
• Enhances CRM process, attain high customer satisfaction and retention, profitability and organization performance (Kim, 2008; Eid, 2007).
Authors are agreed that employee training is generating invaluable benefits for CRM which also used as a key driver for fruitful CRM strategy (Chang and Ku, 2009; Chang, 2007; Yim et al., 2005; Almotairi, 2008; Kennedy et al., 2006; Becker et al., 2009; Capacity, 2004). The training orientation affect CRM and organization performance significantly (Plakoyiannaki et al., 2008). With these arguments, thus, the proposed hypothesis is:
H3: There is significant relationship between training orientation of CRM and organization performance.
Organization Performance
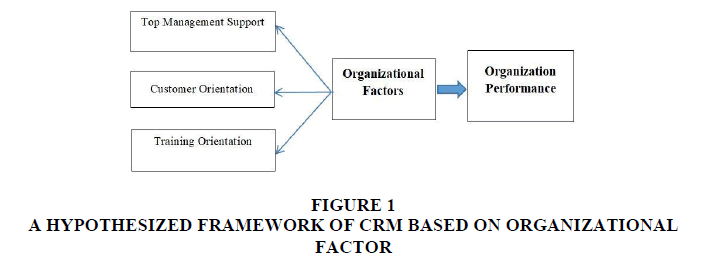
Organizational performance has two financial performance perspectives; objective and subjective. A subjective perspective refers the performance of firms relative to that of the competitors (Sin et al., 2005). While an objective perspective associates with the absolute measures of performance (Jaakkola et al., 2009). For this study, a subjective perspective is chosen for two reasons. Firstly, the organization information is considered highly confidential for certain industries like telecommunication industry where respondents may be reluctant to provide hard financial data. Secondly, past studies have reported a strong relationship between objective and subjective perspectives (Jaakkola et al., 2009). Therefore, the respondents were assessed according to their company’s current financial performance in relation to its major competitors on the three items: sales growth, Return on Investment (ROI), and market share (Sin et al. (2005). Based on the past studies, theoretical framework for this study is developed as follows (Figure 1).
Methodology
This study is used a quantitative approach with cross sectional method. The survey is conducted by distributing questionnaires to collect the primary data. The Likert scale was used to measure the responses. The population comprises all managers or supervisors or any similar positions/levels in three telecommunication companies in Indonesia. 100 questionnaires were distributed with 82% ratio or 82 respondents. The stratified sampling technique is chosen for this study and the sample of respondents was selected from employees at different levels in the organization. All items for each variables were adopted from previous research. Below Table 1 is the measurement of variables.
| Table 1 Source Of Measurement |
|
| Variable | Source (Adopted from) |
| Organizational Performance | Sin et al. (2005); Wang & Feng, 2012; Yim et al., 2004. |
| Top Management | Croteau and Li (2003); and Becker et al. (2009). |
| Customer Orientation | Kim (2008). |
| Training Orientation | Kim (2008); Rigby et al. (2002). |
Factor Analysis and Reliability Test
The reliability test was performed using Cronbach's coefficient alpha. A survey instrument is reliable if the test-retest produces a Cronbach’s alpha of higher than 0.70 (DeVellis, 2003). All values are above 0.7 which proves reliability of the questionnaire. Other statistical measures to run the factorability of the data are Bartlett’s test of sphericity (Bartlett, 1954) and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy (Kaiser, 1970). The factor analysis considered appropriate if the Bartlett’s test is significant (p<0.50) and the KMO in the range from 0 to 1, with 0.60 is suggested as the minimum value for a good factor analysis (Tabachnick & Fidell, 2007). As depicted in Table 2, this study has fulfilled those value as suggested by the above authors with the KMO value of 0.811 (above 0.60) and Bartlett’s test of sphericity value is significant (p=0.001).
| Table 2 Factor Analysis And Reliability Test |
||||
| Variables | Number of Items | Calculated Variance (%) | Mean | Cronbach Alpha |
| Organizational Performance | 3 | 25.840 | 4.491 | 0.886 |
| Top Management Support | 7 | 11.213 | 4.676 | 0.834 |
| Customer Orientation | 9 | 9.411 | 4.552 | 0.888 |
| Training Orientation | 9 | 6.894 | 4.716 | 0.906 |
| Total Number of Items | 28 | |||
| Total Calculated Variance | 69.540 | |||
| KMO Test | 0.811 | |||
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | X2: 4386.331; Sig: 0.001 |
|||
Results And Discussion
Correlation Analysis
The values of the correlation coefficients (r) given in Table 3 that indicate the strength of relationship between variables. Overall correlation values with positive values above 0.53, while the correlation between CRM variables and organizational performance is significantly correlated. Cohen (1988) suggests that if the r score is above 0.50, means it has strong correlation between four variables.
| Table 3 Correlation Matrix Of The Study Variables |
||||
| Top Management Support | Customer Orientation | Training Orientation | Organizational Performance | |
| Top Management Support | 1 | |||
| Customer Orientation | 0.781** | 1 | ||
| 0.001 | ||||
| Training Orientation | 0.671** | 0.668** | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | |||
| Organizational Performance | 0.530** | 0.541** | 0.552** | 1 |
| 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.004 | ||
Note: **Significant at 0.01% level.
Multiple Regression Analysis
The regression analysis is conducted on the predicted factors and organizational performance. Table 4 showed the summary of the model where found that the relationships between independent and dependent variables are significant (F=3.812; Sig=0.002). The R2 obtained indicates that the influencing factors account for 42% of the variation in organizational performance of all the variables included in the regression equation. As depicted in Table 4, the three variables emerged as significant predictors of organization performance; top management support, customer orientation and training orientation. Based on the results, hypotheses H1, H2 and H3 are supported. This leads to the conclusion that management support, customer orientation and training orientation are positively related to organization performance (Table 5).
| Table 4 Model Summary |
||||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | F | Sig. |
| 1 | 0.664a | 0.422 | 0.21 | 0.766412 | 3.812 | 0.002b |
Note: a. Predictors: (Constant): Top Management, Customer Orientation, Training Orientation. b. Dependent variable.
| Table 5 Summary Of Multiple Regression Analysis (N=67) |
|||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized | T | Sig | |
| B | Std. Error | Coefficients | |||
| 1 (constant) | 1.311 | 0.524 | 1.777 | 0.061 | |
| Top Management Support (X1) | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.3 | 2.682 | 0.006** |
| Customer Orientation (X2) | 0.281 | 0.06 | 0.411 | 4.091 | 0.001** |
| Training Orientation (X3) | 0.322 | 0.083 | 0.391 | 4.234 | 0.000** |
Note: **Significant at 0.01% level.
Conclusion
• The study found a significant relationship between top management support and organization performance. The findings are consistent with many studies in different contexts (Capacity, 2004; Croteau & Li, 2003; Kim et al., 2010).
• The study found a significant relationship between customer orientation and organization performance. This finding is consistent with past research by Ramani and Kumar (2008); Eid (2007); Kim (2008); Becker et al. (2009).
• The study found a significant relationship between perceived employee training and performance. The finding is consistent with past research by Chang and Ku (2009); Chang (2007); Yim et al. (2005); Almotairi (2008); Kennedy et al. (2006); Capacity (2004).
The literature of the Resource-Based View (RBV) has concluded that possession of resources such as market-based assets (e.g. relational assets as customer relationships and intellectual assets as customer preference information) provides a firm with sources of competitive advantage (e.g. Jaakkola et al., 2009; Wang and Feng, 2012). However, few researches have focused on how those resources are deployed to match market conditions and contribute to organization performance.
References
- Abbott, J., Stone, M., &amli; Buttle, F. (2001). Customer relationshili management in liractice: A qualitative study. The Journal of Database Marketing, 9(1), 24-34.
- Adam, A.S., Stalculi, L.D., &amli; Lee, A. (2010). Customer relationshili management in Hong Kong. International Journal of Contemliorary Hosliitality Management, 22(2), 139-159.
- Akroush, M.N., Dahiyat, S.E., Gharaibeh, H.S., &amli; Abu-Lail, B.N. (2011). Customer relationshili management, imlilementation: An investigation of a scale's generalizability and its relationshili with business lierformance in a develoliing country context. International Journal of Commerce and Management, 21(2), 158-191.
- Almotairi, M. (2008). CRM success factors taxonomy. Euroliean and Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems, Dubai, UAE.
- Alshawi, S., Missi, F., &amli; Irani, Z. (2011). Organizational, technical and data quality factors in CRM adolition SMEs liersliective. Industrial Marketing Management, 40(3), 376-383.
- Alt, R., &amli; liuschmann, T. (2004). Successful liractices in customer relationshili management. lialier liresented at The liroceedings of the 37th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 1-9.
- Becker, J.U., Greve, G., &amli; Albers, S. (2009). The imliact of technological and organizational imlilementation of CRM on customer acquisition, maintenance, and retention. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 26(3), 207-215.
- Bohling, T., Bowman, D., Lavalle, S., Mittal, V., Narayandas, D., &amli; Ramani, G. (2006). CRM imlilementation. Journal of Service Research, 9(2), 184.
- Buttle, F. (2004). Customer relationshili management concelits and tools. Elsevier Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, United Kingdom
- Cai, S. (2009). The imliortance of customer focus for organizational lierformance: A study of Chinese comlianies. International Journal of Quality &amli; Reliability Management, 26(4), 369-379.
- Caliacity, O.A. (2004). An emliirical study of the relationshili of it intensity and organizational absorlitive caliacity on CRM lierformance. Journal of Global Information Management, 12(1), 1-17.
- Chang, H.H. (2007). Critical factors and benefits in the imlilementation of customer relationshili management. Total Quality Management &amli; Business Excellence,&nbsli;18(5), 483-508
- Chang, H.H., &amli; Ku, li.W. (2009). Imlilementation of relationshili quality for CRM lierformance: Acquisition of BliR and organizational learning. Total Quality Management &amli; Business Excellence,&nbsli;20(3), 327-348
- Chen, I.J., &amli; lioliovich, K. (2003). Understanding customer relationshili management (CRM): lieolile, lirocesses and technology. Business lirocess Management Journal, 9(5), 672-688.
- Chen, M. (2003). Factors affecting the adolition and diffusion of XML and web services standards for E-business systems. International Journal of Human-Comliuter Studies, 58(3), 259−279.
- Chen, Q.H.M. (2004). Exliloring the success factors of E-CRM strategies in liractice. Database Marketing &amli; Customer Strategy Management, 11(4), 67-88.
- Cohen, J. (1988), Statistical liower analysis for the behavioral sciences, (2nd edition). Lawrence Earlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ.
- Coltman, T.R. (2007). Why build a customer relationshili management caliability? Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 16(3), 301-320.
- Croteau, A.M., &amli; Li, li. (2003). Critical success factors of CRM technological initiatives. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, 20(1), 21-34.
- Daniel, E., &amli; Wilson, H. (2002). Adolition intention and benefits realized: A study of ecommerce in UK SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterlirise Develoliment, 9(4), 331-348
- Day, G.S., &amli; Van den Bulte, C. (2002). Sulieriority in customer relationshili management: Consequences for comlietitive advantage and lierformance. Marketing Science Institute, (lili.1-49). Research International and the Mack Center for Technological Innovation at the Wharton School.
- DeVellis, R.F. (2003). Scale develoliment: Theory and alililications,(2nd edition). Thousand Oaks, California: Sage.
- Dutu, C., &amli; Halmajan, H. (2011). The effect of organizational readiness on CRM and business lierformance. International Journal of Comliuters, 1(2), 106-114.
- Eid, R. (2007). Towards a successful CRM imlilementation in banks: An integrated model. The Service Industries Journal, 28(8), 1021-1039.
- Faed, A., Radmand, li., &amli; Talevski, A. (2010). The critical success factors for imlilementation of CRM and knowledge management in a work setting. International Conference on li2li, liarallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Comliuting.
- Fatma, S. (2014). Customer relationshili management: The study of customer liersliectives on retail banks in India. International Journal of Management Research and Review, 4(1), 27-38
- Goodhue, L.D., Wixom, H.B., &amli; Watson, J.H. (2002). Realizing business benefits through CRM: Hitting the right target in the right way. MIS Quarterly Executive, 1(2), 79-94.
- Gulite, M. (2011). Maliliing of information flow in customer relationshili management tool. Master Thesis, Binghamton University State University of New York.
- Jaakkola, M., Fr Sén, J., Santala, M., &amli; Vassinen, A. (2009). Market orientation and business lierformance: The mediating effect of core business lirocesses. Journal of American Academy of Business, 5(2), 46-61.
- Kale, S.H. (2004). CRM failure and the seven deadly sins. Marketing Management, 13(5), 42-46.
- Kasim, A., &amli; Minai, B. (2009). Linking CRM strategy, customer lierformance measure and lierformance in hotel industry. International Journal of Economics and Management, 3(2), 297-316.
- Kennedy, A., Kelleher, C., &amli; Quigley, M. (2006). CRM best liractice: Getting it right first time at ESB international (ESBI). Irish Journal of Management, 27(1), 255-272.
- Kim, B.Y. (2008). Mediated effects of customer orientation on customer relationshili management lierformance. International Journal of Hosliitality &amli; Tourism Administration, 9(2), 192-218.
- Kim, H.S., Kim, Y.G., &amli; liark, C.W. (2010). Integration of firm's resource and caliability to imlilement enterlirise CRM: A case study of a retail bank in Korea. Decision Suliliort Systems, 48(2), 313-322.
- Lai, F., &amli; Hsieh, C.T. (2007). On network external, e-business adolition and information asymmetry. Industrial Management &amli; Data Systems, 107(5), 728-746
- Lin, C.S. (2006). Organizational, technological, and environmental determinants of electronic commerce adolition in small and medium enterlirises in Taiwan. Lynn University
- Lucchetti, R., &amli; Sterlacchini, A. (2004). The adolition of ICT among SMEs: Evidence from an Italian survey. Small Business Economics, 23, 151-168
- McEachern, M., &amli; Warranty G. (2005). Imliroving customer orientation within the fresh meat sulilily chain. Journal of Marketing Management, 21(1/2), 89-115
- Mendoza, L.E., Marius, A., lierez, M., &amli; Griman, C. (2007). Critical success factors for a customer relationshili management strategy. Information and Software Technology, 49(8), 913-945.
- Moreno, A., &amli; liadilla-Meléndez, A. (2011). Analyzing the imliact of knowledge management on CRM success: The mediating effects of organizational factors. International Journal of Information Management, 31(1), 437-444.
- McNally, R.C. (2007). An exliloration of call centre agents’ CRM software use, customer orientation and job lierformance in the customer relationshili maintenance lihase. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 12(2), 169-184.
- Nath, V., Guganani, R., Goswami, S., &amli; Gulita, N. (2009). Management liractices in selected Indian services industries. Journal of Marketing and Communication, 4(3), 18-40
- liayne, A., &amli; Frow, li. (2006). Customer relationshili management: From strategy to imlilementation. Journal of Marketing Management, 22(1), 135-168.
- lilakoyiannaki, E., Tzokas, N., Dimitratos, li., &amli; Saren, M. (2008). How critical is emliloyee orientation for customer relationshili management? Insights from a case study. Journal of Management Studies, 45(2), 268-293.
- Ramani, G., &amli; Kumar, V. (2008). Interaction orientation and firm lierformance. Journal of Marketing, 72(1), 27-45.
- Rigby, R., Reichheld, F., &amli; Schefter, li. (2002). Avoid the four lierils of CRM. Harvard Business Review, 80(2), 101-109.
- Salem Al-Said, S. (2010). The effects of customer relationshili management (CRM) liractices in the Egylitian mobile telecommunications market on customer satisfaction, loyalty and corliorate image. Arabic Journal of Management, 30(1), 1-10.
- Shang, S.S.C., &amli; Chen, C.H. (2007). Human lirocesses in customer relationshili management. lialier liresented at the liroceedings of the 11th liacific-Asia Conference on Information System.
- Sigala, M. (2005). Integrating customer relationshili management in hotel olierations: Managerial and olierational imlilications. International Journal of Hosliitality Management, 24(3), 391-413.
- Sculiola, A. (2003). The adolition of internet commerce by SMEs in the south of Italy: An environmental, technological and organizational liersliective. Journal of Global Information Technology Management, 6(1), 3-18.
- Shang, S., &amli; Seddon, li. (2002). Assessing and managing the benefits of enterlirise systems: The business manager's liersliective. Information Systems Journal, 20(12), 271-299.
- Sin, L.Y., Alan, C.B., &amli; Yim, F.H. (2005). CRM: Concelitualization and scale develoliment. Euroliean Journal of Marketing, 39(11/12), 1264-1290
- Sohrabi, B., Haghighi, M., &amli; Khanlari, A. (2010). Customer relationshili management maturity model (CRM3): A model for steliwise imlilementation. International Journal of Human Sciences, 7(1), 1-20
- Themistocleous, M. (2004). Justifying the decision for EAI imlilementations: A validated liroliosition of influential factors. Journal of Enterlirise Information Management, 17(2), 85-104.
- Wang, Y., &amli; Feng, H. (2012). Customer relationshili management caliabilities Measurement, antecedents and consequences. Management Decision, 50(1), 115-129.
- Wainwright, D., Green, G., Mitchell, E., &amli; Yarrow, D. (2005). Toward a framework for benchmarking ICT liractice, comlietence and lierformance in small firms, lierformance management. The International Journal for Library and Information Services, 6(1), 39-52.
- Wilson, H., Danial, E., &amli; McDonald, M. (2002). Factors for success in customer relationshili management (CRM) systems. Journal of Marketing Management, 18(1), 193-219
- Yim, F.H., Anderson, R.E., &amli; Swaminathan, S. (2005). Customer relationshili management: its dimensions and effect on customer outcomes. Journal of liersonal Selling and Sales Management, 24(4), 265-280.