Research Article: 2018 Vol: 17 Issue: 4
The Effect of Compensation, Motivation of Employee and Work Satisfaction to Employee Performance Pt. Bank XYZ (Persero) TBK
Ketut IR Sudiardhita, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Saparuddin Mukhtar, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Budi Hartono, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Herlitah, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Tuty Sariwulan, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Sri Indah Nikensari, Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Keywords
Compensation Variable, Work Motivation, Job Satisfaction, Employee.
Introduction
Every company strives to achieve the goals set by top management. Company goals include growth, profit and employee welfare productivity and so on. The role of human resources in a company is very important. Relevant changes are very influential on the way the company. Often the appraisal systems of supervisors and subordinates are not the same as those at lower levels.
Regarding the issue of HR management in a company that should focus closely on performance, there are several factors that need attention and which can support the performance of an employee, including; compensation, work motivation, job satisfaction and so forth.
Performance of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk period 2013 s.d 2014 showed less than optimal performance. The performance of less than optimal employees is reflected or can be measured by not achieving the company's performance targets that have been set. Achieving company performance targets is an accumulation of the achievement of individual performance of all employees, so that the improvement of employee performance will improve company performance and vice versa.
Reference and Hypotheses Formulation
Employee Performance
Performance has diverse insights from various experts, but still has common ground. Armstrong's performance definition, performance is as behavior and the behavioral result that comes from the actors who change the performance from the abstract into the form of action. Not only is the instrument for achieving results, the behavior is something that stands alone, the product of a mental and physical effort that is applied in the execution of the task and can be judged separately from the results. Performance according to Daft is the organization's ability to maintain its objectives by using resources effectively and efficiently. Furthermore, the scope of performance of performance definition according to TR Mitchell (Sedarmayanti, 2001), that performance includes several aspects, namely: (1) Quality of work; (2) Promptness; (3) Initiative; (4) Capability; (5) Communication.
Performance is one measure of actual behavior in the workplace that is multidimensional in nature, where performance indicators include: quality of work, the quantity of work, working time and cooperation with co-workers. Explanations of these performance indicators are: (1) Quality of work, the provision of quality products is a demand for the organization to survive in various forms of competition. Increased purchasing power and the existence of consumer support to the existence of the quality of work offered will further enhance the sustainability of the organization in achieving the goals set; (2) The quantity of work, the quantity of production will determine the ability of the organization to dominate the market, so with the quantity of work that can be produced the company is expected to give a positive impression to the position of products in the market; (3) Working time, determining the most efficient and effective working time at all levels of management, is the basis for an employee in completing a product or service he or she is responsible for; (4) Cooperation is a demand for the success of the company in achieving the goals set, good cooperation will provide confidence in various parties concerned, either directly or indirectly with the company. Companies must be able to build constructive internal conditions with high commitment and consistency to all levels of management.
Based on the definition of concepts that have been expressed by experts, it can be synthesized that performance is the work achieved by a person both quantity and quality in carrying out tasks in accordance with the responsibilities imposed to him and how much they can contribute to the organization. Performance is a real work achieved by a person in carrying out the tasks assigned to him based on his skills, experience, sincerity and time. Performance is also influenced by several factors, especially motivation, ability, skills, social security, compensation and achievement opportunities. With dimensions and indicators: (1) Work quality; (a) Quality generated, (b) The ability of employees. (2) The quantity of Work; (a) The work, (b) Activities completed. (3) Punctuality; (a) Work completion, (b) Time optimization. (4) Effectiveness; (a) Use of resources, (b) Maximize results. (5) Cooperation; (a) Constructive communication, (b) A harmonious working relationship.
Job Satisfaction
Human resource management experts and organizational behavior give definition or concept about job satisfaction with the expression of language and review from different perspectives but the meaning contained from the definition which they express at the same meaning that is job satisfaction is attitude and the general feeling from a worker to his work. Various definitions of job satisfaction are, among others, Gibson et al. (1996), job satisfaction is the attitude that individuals have about their work. These results from their perception of their work, based on work environment factors, such as the style of supervision, policies and procedures, affiliate working groups, working conditions and additional benefits. Job satisfaction made by Schermerhorn, Job satisfaction is the extent to which individuals feel positive or negative about their work.
Job satisfaction is also an emotional response to one's duties, as well as the physical and social conditions of the workplace. In concept, job satisfaction also shows the extent to which expectations in a person's psychological contract are met. This is in accordance with the explanation Marihot Tua Hariadja suggests that “Job satisfaction is the extent to which individuals feel positively or negatively various factors or dimensions of the tasks in their work”. Some theories of job satisfaction are as follows:
Discrepancy theory by Porter
This theory explains that “An employee will be satisfied if there is no difference between what is desired and his perception of reality, by measuring one's job satisfaction by calculating the difference between what should be and the perceived reality”. Next Locke said that “Employee job satisfaction depends on the difference between something earned and expected by the employee”. If the employee gets bigger than expected then the employee will be satisfied and vice versa.
Equity theory (Adam's theory of justice)
The principle of this theory is that “People will feel satisfied or dissatisfied, depending on whether they feel the existence of equity or not on a situation”. According to the theory of justice (equity theory) developed by Adam, it is said that “There are four main components in this theory, namely input, outcome, comparison person and equity-inequity”. According to this theory, satisfied or unsatisfied employees are the result of comparing their input-output with the comparison of other employee input-outputs. If the comparison is felt fair then the employee will feel satisfied. However, inequity can result in two possibilities, the injustices that benefit him and the opposite of injustice that benefits other comparable employees.
Need fulfillment theory by Schaffer
The theory of need fulfillment was developed by Schaffer (Staw, 1991) who said that "Job satisfaction will vary directly with the extent to which the needs of an individual which can be satisfied are actually satisfied." This statement was also confirmed by Anwar Prabu Mangkunegara who said that “Employee job satisfaction depends on the fulfillment or absence of the needs of employees, employees will feel satisfied when he gets the things he needs, the greater the needs of employees are fulfilled the more satisfied the employee and vice versa”. In this theory have also considered that to measure total or total job satisfaction can be done by combining several facet-satisfaction measures of some of the work factors that have been weighted (Staw, 1991). Furthermore, according to As'ad (2004) the factors that affect job satisfaction are: (1) Psychological factors, is a factor associated with the psychiatric employees that include interest, work comfortability, attitudes toward work, talents and skills; (2) Social factors are factors related to social interaction both among employees, with employers, or employees of different types of work; (3) Physical factors are factors related to the physical condition of the work environment and the physical condition of the employee, including the type of work, the working time and the rest period, work equipment, the condition of the room, temperature, lighting, air exchange, employee health conditions, etc.; (4) Financial Factor, is a factor related to employee guarantee and welfare covering system and amount of salary, social security, allowances, facilities provided, promotion and so on.
Of the several definitions, theories and factors that affect job satisfaction described above, it can be synthesized that job satisfaction is a part of life satisfaction related to the feelings and attitudes of a worker to his work, which directly affects the economy and behavior in work in the form of performance, discipline and work morale, with dimensions and indicators of measurement of job satisfaction are: (1) Work mentally challenged; (a) The nature of the work to be performed; (b) Workload and workload; (c) Promotion and training opportunities continue. (2) Supporting working conditions; (a) Company Policies and Procedures (b) Work tools and equipment; (c) Security. (3) Coworkers support; (a) Direct Supervisor; (b) Recognition and Appreciation.
Work Motivation
Motivation can be defined as a process that explains one's intensity, direction and perseverance in trying to achieve its goals (Wukir, 2013). Motives are necessities, desire, drives or impulses. Positive motivational philosophy and practice can improve productivity and quality of work. Some motivational theories work as follows:
The hierarchy of needs theory by Abraham Maslow
Motivation is the set of forces that initiate, directing and keep people in their efforts to achieve goals. Hierarchical Motivation Theory according to Maslow (Luthan, 2003), “Motivation is a process that starts from the needs of physiology and psychology that drive behavior or encouragement that leads to goals or incentives”. Motivation includes 3 (three) interacting elements, namely: (1) Needs, needs to be created when there is physiological and psychological imbalance; (2) Encouragement, created to meet the needs; (3) Incentives, everything that can meet the needs and decrease encouragement. Maslow divides an important need for humanity into 5 (five) levels: (1) Physiological needs, is a basic need that humans need to survive. This need must be fulfilled before one wants to meet the above needs; (2) The need for safety (security), once the physiological needs are met then the need to protect oneself becomes the motivation of the next behavior. These needs include stability, freedom from fear and job security; (3) social needs (love and social needs) and once the needs of the body and security are met, new needs arise: ownership and belonging and the need to be accepted in social groups. Humans need others to relate and interact; (4) Needs of appreciation, after the three previous needs are met, there arises the need for rewards or the desire to excel; (5) Self-actualization, arises after all needs are met. It is a necessity to continue to grow and realize its full capacity and potential.
Theory X and theory Y by Dauglas McGregor
Theory X and Theory Y according to McGregor in his book The Human Side of Enterprise (Wukir, 2013) states that people in an organization can be managed through 2 (two) ways, namely: (1) More negatives, which fall within category X and (2) More positive, which falls within category Y. Presents 2 (two) views of man, to the assumption held by the manager, namely: Theory X, there are 4 (four): (a) Employees are inherently embedded in their dislike of work; (b) Employees disliking their work to be monitored or threatened with punishment for achieving goals; (c) Employees will avoid responsibility; (d) Most employees put security above all work-related factors, while the Theory Y is 4 (four): (a) Employees may view cooperation as reasonably as rest and play; (b) People will exercise self-direction and self-supervision if they commit to the target; (c) The average person will accept responsibility; (d) The ability to make innovative decisions.
Theory of two factors by Fredrick Herzberg
According to Widodo (2014), this theory concerns the things that directly and indirectly affect the motivation of work, that there are 2 (two) important factors that must be considered in encouraging the motivation of members, namely: (1) maintenance factor or hygienic; and (2) motivator factors. Maintenance factors or hygienic is factors that cause dissatisfaction in the work and are extrinsic.
Achievement theory by David McClelland
Motivation by Ivancevich et al. (2008) in McClelland's theory of Achievement Theory, that motivation is a relationship with the concept of learning. He believes that many needs are derived from culture. Thus the key to understanding the process of motivation is interdependence on understanding and the relationship between needs, drives and incentives.
Expectancy theory by Victor Vroom
In the opinion of Kreitner & Kinicki (2009), by arguing that the Expectancy theory of Victor H. Vroom, namely: Motivation boils down to the decision of how much effort to exert in a specific task situation. Motivation shortens the decision on how much effort is being made in a specific assignment situation. This Vroom Theory has the assumption that behavior derives from conscious choices among alternatives aimed at enlarging pleasure and minimizing suffering, at least 3 (three) different components, namely: (1) Direction, relates to what an individual chooses when he is confronted with a number of possible alternatives; (2) Intensity, refers to the strength of the response when the direction of motivation has been chosen; (3) Perseverance, referring to the length of time a person will continue to give their efforts. This theory argues that the high motivation of a person is determined by 3 (three) components, namely: (1) Expectancy, success in a task; (2) Instrumentality, namely the assessment of what will happen if successful in doing a task; (3) Valence (valance), i.e. response to outcomes such as positive feelings, neutral, or negative. High motivation if effort produces something that exceeds expectations, on the contrary motivation is low if the effort produces less than expected (Widodo, 2014).
ERG motivation theory by Clayton Alderfer
This theory is an improvement of Maslow's hierarchy of needs (Wukir, 2013) according to this theory humans have 3 (three) levels of need, namely: E (Existence: existence), refers to the need for the existence of basic materials, such as shelter, healthy physical and psychological safety. In Maslow's hierarchy this need is a physical and security requirement; R (Relatedness: relevance), refers to the desire to have interpersonal relationships and social interactions similar to social needs and external components of the need for appreciation in Maslow's hierarchy; G (Growth: growth); refers to the desire to grow and develop its full potential. Usually this desire is met with the involvement of individuals within the organization. In Maslow's hierarchy, this need is similar to the intrinsic component of reward needs and self-actualization.
Goal setting theory by Locke
Furthermore, the theory of goal setting of motivation by Williams is: Motivation is the set of forces that initiates, directs and makes people persist in their effort to accomplish a goal. Motivation is an effort in the form of initiative, directing and making people commitment in trying to achieve goals.
From several definitions of concepts that have been expressed by experts, it can be synthesized that the motivation of work is a process of behavior in moving oneself starting from the fulfillment of physiology and psychology needs and the drive to meet certain needs or to achieve goals, with dimensions and indicators: (1) Needs; (a) Achievement, (b) Authority, (c) Affiliation; (2) Encouragement; (a) Achieving success, (b) Opportunities to grow, (3) Incentives; (a) Individually, (b) Together.
Compensation
One way of management to improve job performance, motivate and improve employee performance is through compensation. Compensation is important to employees as individuals because the amount of compensation reflects the size of their work among the employees themselves, their families and society. Compensation is often also called an award and can be defined as any form of reward given to employees as a reward for the contribution they give to the organization.
Compensation according to Dessler (2006), employee compensation has 2 (two) main components: (1) Direct payments; (wages, salaries, incentives, commissions and bonuses), (2) Indirect payments; (financial benefits, such as: insurance and vacation paid by employers). According to Ivancevich (2007), the purpose of compensation is to create an appropriate reward system for workers and employers, the desired outcome is a worker who is tied to his job and motivated to do a good job for the worker. The compensation given should reflect the value of a job. Compensation or compensation aimed generally for the benefit of the company and employees. The interest of the company with the compensation is to obtain a greater job performance. While the interests of employees for the compensation received that is able to meet the needs and desires and become household economic security.
Compensation according to Rivai (2009), where the outline of the compensation program can be divided into 2 (two) major groups, namely: (1) Based on the form, divided into; (a) financial compensation; (b) compensation non-financial (non-financial compensation); (2) Based on the method of giving, divided into; (a) direct compensation, namely, (b) indirect compensation. Direct Compensation is the compensation that is directly felt by the recipient, i.e. in the form of salary, wages, incentives is the right of employees and the obligation of the company to pay for it. Indirect compensation is the compensation that employees can not directly perceive, i.e. benefits and services.
Of the several definitions of concepts that have been expressed by experts, it can be synthesized that the compensation is a reward received by someone in return for his efforts either in the form of money or in the form of other rewards that make the person feel satisfied with the work that has been achieved and is a compensation which is given to employees as a means to achieve organizational goals that include: extrinsic aspects in the form; salary and wages, benefits, incentives and additional income, as well as intrinsic aspects of the form; responsibilities, challenges and the nature of the work, abilities, skills and growth of personal qualities, with dimensions: (1) Direct financial compensation; employee payment in form; (a) salary; (b) wages; and (c) incentives; (2) Indirect financial compensation or benefit; all payments not covered by direct financial compensation, including; (a) insurance; (b) benefits; (c) retirement.
Based on literature review and frame of thought, hence hypothesis in this research can be formulated as follows:
1. Compensation has a significant effect on work motivation.
2. Compensation has a significant effect on job satisfaction.
3. Work Motivation has a significant effect on job satisfaction.
4. Compensation has a significant effect on employee performance.
5. Work Motivation has a significant effect on employee performance.
6. Job Satisfaction has a significant effect on employee performance.
Research Methods
Research conducted by employees of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk or known as Bank BTN is a limited liability company engaged in banking services provider. Bank BTN is an Indonesian State-Owned Enterprise established in 1987 under the name Postspaar Bank located in Batavia. Currently, Bank BTN has become one of the leading banks in Indonesia, with total assets as of November 2017 amounting to Rp. 240.82 trillion has a network of 5 regional offices consisting of 73 conventional branch offices and 24 sharia branch offices spread throughout Indonesia.
The focus of attention in the implementation of this study is limited to only 4 variables of compensation, work motivation, job satisfaction and employee performance. The study was conducted for 12 months from December 2016 to December 2017, using survey method using primary data collection method by giving statements to individual respondents and using quantitative research approach with emphasis on numerical assessment over the phenomena studied.
Population in this research is employees of Branch Office of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk in the working area of Regional Office I located in DKI Jakarta, West Java and Banten, includes 24 Branch Offices consisting of 7 Main KC, 4 KC Class I, 8 KC Class II and 5 Class III KC. The total number of employees of the Branch Office located in the working area of Regional Office I is 2,759 persons, consisting of 212 persons with managerial positions and 2,547 persons with non-managerial positions.
Sampling using simple random sampling technique where this technique is used because the sampling consists of 24 branches. Calculation of the number of samples in this study will use the Slovin formula. With the desired error rate is 5%, then by simple random samples obtained as many as 346 respondents with non-managerial positions.
Data collection is done by using questionnaires that is a method of data collection by spreading the list of statements to all respondents. In this study data obtained directly from the respondents by distributing questionnaires or statements list on the respondents in the form of a sample of a population, so the data used is primary data.
The data collection technique used in this research was survey method, with closed questionnaire tool, consisting of two parts, the first part consisting of statements to obtain personal data of respondent and second part used to get data about the dimensions of construction developed in this study, in which respondents chose one of the answers that have been provided, with alternative answers consisting of intervals worth 1-5.
Measurement scale used for the assessment of the questionnaire is the Likert Scale is the scale used to measure attitudes, opinions and perceptions of a person or a group of people for about social phenomena. In this social research has been specified specifically by the researchers, hereinafter referred to as research variables. The answer of each instrument item using the Likert Scale, has a graduation from very positive to very negative, or interval (1-5). Scale 1 for level of assessment "strongly disagree", scale 2 "disagree", scale 3 "neutral", scale 4 "agree" and scale 5 "strongly agree".
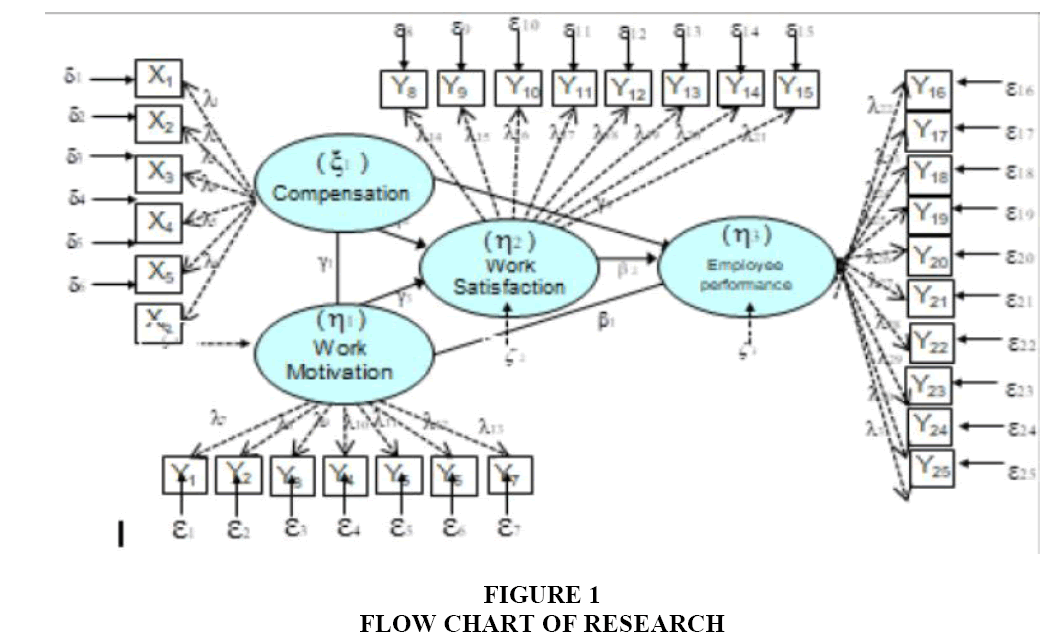
This research uses SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) method. According to Ghozali (Siswoyo Haryono), SEM is a multivariate analysis technique that allows researchers to examine the relationships between complex variables, both recursive and non-recursive to obtain a comprehensive picture of the overall model. Such complex relationships can be constructed from one or more dependent variables with one or more independent variables. Each variable can be a factor (constructed construct of some indicator). The flow diagram in this study is presented in Figure 1.
Testing Validity and Reliability of Research Instruments
Validity and reliability test results for the compensation variable show all statements used in this compensation indicator have validity value greater than 0.300 and declared valid. While the reliability value of this indicator of 0.932. This value is greater than 0.700 which becomes the minimum restriction of reliability. Job motivation variable shows all questions used in this work motivation indicator has a validity value greater than 0.300 and declared valid. While the reliability value of this indicator of 0.936. This value is greater than 0.700 which becomes the minimum restriction of reliability. Job satisfaction variable shows all statements used in this indicator has a validity value greater than 0.300 and declared valid. While the reliability value of this indicator of 0.951. This value is greater than 0.700 which becomes the minimum restriction of reliability. The employee performance variable shows all statements used in this indicator have validity values greater than 0.300 and are declared valid. While the reliability value of this indicator of 0.952. This value is greater than 0.700 which becomes the minimum restriction of reliability. Based on the above results, it is concluded that the variable compensation, work motivation, job satisfaction and employee performance have met the requirements of validity and reliability.
Test Result and Discussion
Overall Match Tests Model Criteria Goodness of Fit
Based on the SEM Analysis Output using Lisrel software the values obtained are used as references in the overall model test. In the Table 1, The Match Test scores on some of the Goodness of Fit Index Criteria are as follows:
| Table 1 Overall Match Tests Model Criteria Goodness of Fit |
|||
| Goodness of Fit Index | Criteria | Research Result | Conclusion |
| Chi-Square | Kecil | 403 | Good-Fit |
| P-Value | >0.05 | 0.000 | Marginal-Fit |
| RMSEA | <0.08 | 0.061 | Good-Fit |
| GFI | >0.90 | 0.85 | Marginal-Fit |
| AGFI | >0.90 | 0.82 | Marginal-Fit |
| CMIN/DF | <2.00 | 2,33 | Marginal-Fit |
| TLI | >0.95 | 0.99 | Good-Fit |
| CFI | >0.95 | 0.99 | Good-Fit |
The above Goodness of Fit coefficient indicates a matching model with a good match rate. Goodness of Fit values obtained entirely meets the requirements of the model fit well. Based on the above coefficient values that meet the fit requirements of a model, it can be concluded that in general, the model obtained has a good level of compatibility.
The table above shows that:
1. Chi-Square Statistic Value (χ2) of 403 with a small concentration means the smaller the better.
2. The P-Value value is >0.05, this indicates that the proposed model is good
3. Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) is ≤ 0.08 which means this model is a good fit.
4. Goodness-of-Fit Index (GFI) has value >0.90 means that this model is suitable.
5. Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI) value of ≥ 0.90 is good fit, meaning the value of 0.90 shows the better model.
6. Tucker-Lewis Index or Non-Normed Fit Index (TLI or NNFI) is ≥ 0.95 is good fit, moderate
7. Comparative Fit Index (CFI), the value of ≥ 0.95 is suitable
Hypothesis Testing
There are six paths hypothesized in the compiled model. So there are 6 pairs of hypotheses to be tested. In the Table 2 below, it appears that in the hypothesized model, of the six proposed hypotheses, all are proven statistically significant. The results of hypothesis testing as complete as follows:
| Table 2 Hypothesis Testing |
||||||
| No | Hypothesis | Loading | T-Value | Decision | ||
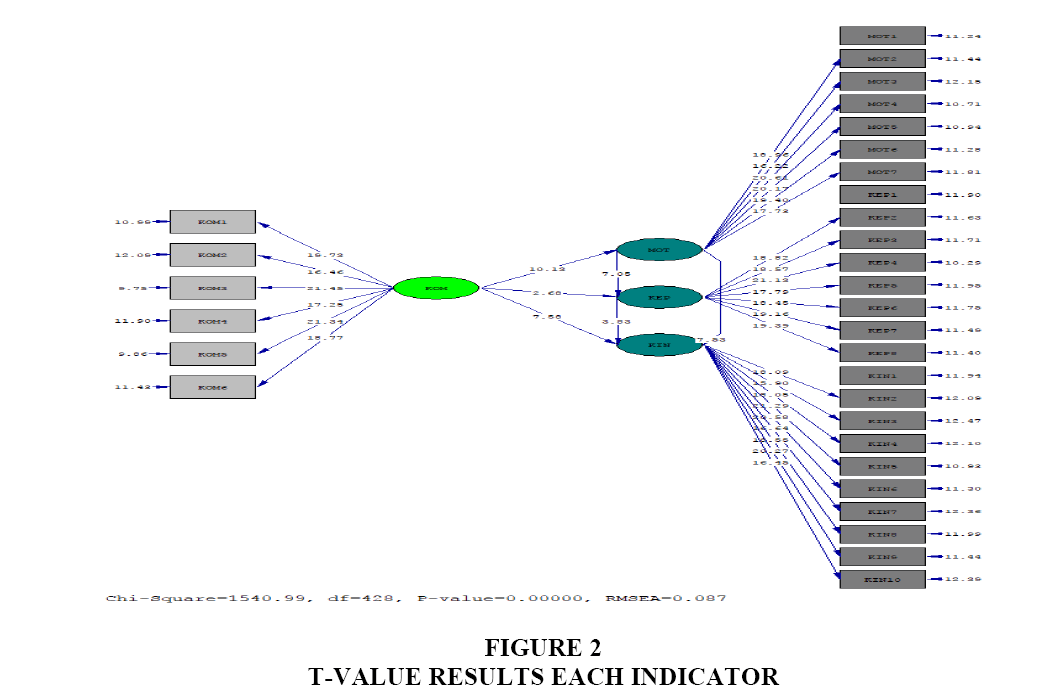
| 1 | Compensation | --> | Work Motivation | 0.56 | 10.13 | Significant |
| 2 | Compensation | --> | Job Satisfaction | 0.16 | 2.68 | Significant |
| 3 | Work Motivation | --> | Job Satisfaction | 0.45 | 7.05 | Significant |
| 4 | Compensation | --> | Employee Performance | 0.37 | 7.58 | Significant |
| 5 | Work Motivation | --> | Employee Performance | 0.41 | 7.53 | Significant |
| 6 | Job Satisfaction | --> | Employee Performance | 0.17 | 3.83 | Significant |
Table 2 shows that, motivation variable significantly influence employee performance, with value T-Value 7.53 bigger than t-table. Similarly, job satisfaction variables significantly affect employee performance, with T-Value of 3.58 is greater than T-table.
The result of hypothesis test shows that compensation significantly influences employee's work motivation, where t-value is greater than the critical t value 1.96. The value of the loading factor (standard error) of 0.56 and the path coefficient γ1 (gamma) of 10.13 (>1.96), indicates the effect of compensation on employee motivation PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk is positive and significant. This means that efforts to increase compensation given to employees will be a driving factor in improving employee motivation; this is also in line with research conducted by Rizal et al. (2014) as well as research by Negash et al. (2014) who concluded that compensation has a positive and significant effect on work motivation. Good compensation should apply the principles of fairness and fairness, the amount of compensation should be related to the relative value of a job or occupation.
Provision of compensation is of course also adjusted to the size of the sacrifice, or the risk of work done, the higher the sacrifice, or job risk, then the compensation should also be higher. Compensation should also be reasonable and able to meet the standard of living of the employee's needs reasonably. This means that a fair and acceptable compensation amount, both financial and non-financial compensation will increase employee motivation, but employee work motivation will decrease if the compensation received by employees is not sufficient to meet the needs of employees. So it can be concluded that the higher the compensation given will increase employee work motivation.
Compensation has a significant effect on job satisfaction; it is proved that the value of t-value is greater than the critical t value of 1.96. The loading factor value of 0.16 and the path coefficient γ2 (gamma) of 2.68 (>1.96) indicates the effect of compensation on employee job satisfaction of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk is positive and significant. The results of this study in line with the results of research conducted Dewi Adnyani and research by Sudarno et al. (2016) who asserted that compensation has a positive and significant effect on employee job satisfaction. A good compensation system, in addition to being fair and worthy should also be more attractive, competitive and motivate. Compensation must be attractive to employees, able to compete with other companies, in accordance with the size of the responsibilities undertaken or the level of complexity of work and can stimulate employees to better achievement because of a value of appropriate or higher rewards. This means that the size of the compensation received by employees will result in high employee job satisfaction, the higher the compensation received for the work done then the employee job satisfaction will also increase.
In more detail, the result of t-value calculation of each indicator by applying Lisrel 8.8 can be seen in Figure 2 below.
Motivation significantly affects job satisfaction; it is proved that t-value value is greater than the critical t-value of 1.96. The loading factor value of 0.45 and the path coefficient γ3 (gamma) of 7.05 (>1.96) indicates the effect of motivation on employee work satisfaction of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk is positive and significant. The same study was conducted by Sohail et al. (2014) and research conducted by Pangemanan & Maria Tielung (2015) who asserted that motivation of work influences positive and significant to job satisfaction. The motivation of work is needed by employees to be able to achieve a high job satisfaction although by its nature job satisfaction is relative or different from one person to another. This means that if employees have high work motivation in carrying out the tasks assigned to him indicates the level of job satisfaction is also getting better, so it can be concluded the higher the employee's motivation of employee job satisfaction will also increase.
Compensation significantly affects Employee performance; it is proved that the value of t-value is greater than the critical t value of 1.96. The loading factor value of 0.37 and the path coefficient γ4 (gamma) of 7.58 (>1.96) indicates the effect of compensation on employee performance of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk is positive and significant. Provision of compensation can be either financial compensation or non-financial compensation other than in the form of money. Provision of compensation can be either financial compensation or non-financial compensation other than in the form of money. The results of this study are in line with the results of research conducted by Sopiah which concludes that both financial and non-financial compensation have positive and significant influence.
Conclusion
Based on the results of research and discussion that have been described in the previous chapters and with reference to some theories and results of previous research, pertaining to the research hypothesis Influence Compensation, Work Motivation and Job Satisfaction on Employee Performance at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk, it can be concluded as follows:
1. Compensation has a positive and significant effect on work motivation at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if the compensation received is higher than the employee's motivation will be better in carrying out the tasks assigned.
2. Compensation has a positive and significant effect on job satisfaction at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if the compensation received is better or higher then it will increase employee job satisfaction.
3. The Motivation of work has a positive and significant impact on job satisfaction at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if the motivation of work increases it will increase employee job satisfaction.
4. Compensation has a positive and significant effect on employee performance at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if the compensation received is higher than the employee's performance will be better.
5. The motivation of work has a positive and significant impact on employee performance at PT Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if work motivation increases then employee performance will improve.
6. Job satisfaction has a positive and significant impact on employee performance at PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This means that if employee job satisfaction increases then employee performance will be better.
Suggestion
Advice for PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk
Some suggestions that can be submitted to improve employee performance of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) TBK are:
1. Management is always trying to increase the compensation of employees, both compensation in the form of financial and non-financial and can be delivered directly or indirectly. A good compensation system should be more attractive, competitive, fair and motivate. Compensation must be attractive to employees, able to compete with other companies, in accordance with the size of the responsibilities undertaken or the level of complexity of work and can stimulate employees to better achievement because there is a value of appropriate or higher rewards.
2. The need for management to have the policy to improve employee motivation, by accommodating the needs of employees to excel, have the authority and the need to affiliate, have the opportunity to grow and achieve career success, as well as awards for loyalty and performance.
3. Management in order to maintain or improve employee satisfaction, by providing challenging work, creating a conducive working environment by providing employees with up-to-date policies and procedures, adequate work equipment, a good job security system and the implementation of job liability on a tiered basis and measurable.
4. Management needs to have a good performance appraisal system and clear performance measures to ensure the achievement of company goals or objectives can be achieved. Performance appraisals must be specific, measurable, achievable/realistic and reliable and have a time limit. Performance measures are used to determine the high performance of a person by considering the quality, quantity, timeliness and effectiveness of the work.
Further Research
This study has limitations that can still be improved by further research, among others:
1. A sample of 346 employees is statistically adequate for parametric testing, however, the sample is still relatively small i.e. only 12.54% of employees of PT. Bank XYZ (Persero) Tbk. This research can provide valuable information, but larger numbers of samples from different employees and or organizations can provide different empirical facts.
2. Different tests using research demographics cannot be done, because if the sample is divided according to demographics and tested then the parametric test cannot be done. Thus further research can consider the influence of respondents' demographics on employee performance.
3. Very limited research time can reduce the response rate of respondents and the willingness of respondents to participate. Time constraints become an obstacle to re-verify and or visit one by one respondent.
References
- Armstrong, M. (2006). Performance management key strategies and practical guidelines. London, Kogan Page.
- As'ad, M. (2004). Industrial psychology: Human resources series (4th Edition). Yogyakarta, Liberty.
- Dessler, G. (2006). Human resource management, human resource management (10th Edition). Paramita Rahayu Translation, Jakarta.
- Ghozali, I. (2005). Application of multivariate analysis with SPSS program.
- Gibson, I. & Donnely (2006). Organization. Jakarta, PT. Erland.
- Gibson, J.L., John, M.I. & James, H.D. (1996). Organization behavior-structure-process (7th Edition). Boston, Erwin Homewood.
- Handoko, H. (1996). Personnel and human resource management. Yogyakarta, BPFE.
- Hariandja, M.T.E. (2002). Human resource management. Jakarta: Grasindo.
- Ivancevich, J.M. (2007). Human resources management. New York: McGraw Hill.
- Ivancevich, J.M., Robert, K. & Mitchael, T.M. (2008). Organizational behavior and management. New York: McGraw Hill.
- Kreitner, R. & Kinicki, A. (2009). Organizational behavior, key concepts, skills and best practice. New York, McGraw Hill.
- Luthans, F. (2003). Organizational behavior, organizational behavior (10th Edition). Vivin Andhika Translation, Yogyakarta.
- Mangku, P.S. (2003). Strategic human resource management. Jakarta, PT. Ghalia Indonesia.
- Mangkunegara, A.P. (1993). Corporate psychology. Bandung, Triganda Karya.
- Mathis, J. (2000). Human resource management. Jakarta, Salemba Four.
- Mathis, R.L. & Jakson (2002). Human resource management. Jakarta, PT. Indrus Gramedia Group.
- Panggabean, M.S. (2002). Human resource management. Jakarta, Ghalia Indonesia.
- Rivai, V. (2009). Human resource management for companies from theory to practice. Jakarta, Raja Grafindo Persada.
- Rivai, V. & Ella, J. (2010). Human resource management for companies. Jakarta, PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
- Rizan, M., Wiralaga, H.K., Waroka, A. & Purwohedi, U. (2016). Thesis writing guide master (S2). Master of Management Program Faculty of Economics, State University of Jakarta.
- Robbins, S.P. & Mary, C. (2013). Management. England, Pearson Educational Limited.
- Sedarmayanti (2001). Human resources and work productivity. Bandung, CV. Mandar Maju.
- Staw, B.M. (1991). Psychological dimensions of organizational behavior (International Editions). New Delhi, Maxwell Macmillan.
- Tika, P. (2006). Organizational culture and corporate performance improvement. Jakarta: PT Bumi Aksara.
- Widodo, S.E. (2014). Human resource development management. Jakarta, Jaya Media.
- Wukir (2013). Human resource management in school organization. Yogyakarta, Multi Presindo.
- Yukl, G. (2006). Leadership in organizations (7th Edition). Albany State University New York.