Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
The Contribution of the Quality of Management Information Systems to Customer Orientation, an Exploratory Study at the Universities of Cihan and Nowruz
Niebal Younis Mohammed, Northern Technical University
Thanoon Y. Thanoon, Northern Technical University
Maryam Adnan Alkahrbjee, Northern Technical University
Abstract
The current study sought to determine the quality of management information systems & their contribution to customer orientation at two private universities located in Dohuk Governorate: Cihan & Nawroz. From this point of view, the study problem was identified by the following question: Does the quality of management information systems contribute to customer orientation in the two universities surveyed? In order to answer this question, the researchers adopted the descriptive & analytical approaches, in addition to adopting several hypotheses to address the subject from all its aspects. To test the validity of these hypotheses, a questionnaire was prepared for this purpose. The universities of Cihan & Nawroz were chosen as a research site for the current study. The opinions of a sample of (303) employees of the two universities were surveyed, & the data was analysed using a number of statistical methods using computer software (SPSS) & (AMOS). The study reached a number of conclusions, the most important of which are: The existence of a significant correlation relationship between the quality of management information systems at the macro level & the orientation towards customers in the two institutions investigated. The results of the field study confirmed that the quality of management information systems at the macro level contributes to a positive impact in enhancing customer orientation in the two institutions surveyed. Accordingly, the researchers presented a set of recommendations consistent with these conclusions.
Keywords
Quality of Management Information Systems, Customer Orientation
Introduction
The business environment of organizations is characterized by a world of rapid change dominated by the information and communication revolution. The orientation towards customers is considered a vital artery that contributed to the success of the various organizations, as the increasing number of organizations in light of economic and technological developments led to an increase in competition among them. Therefore, the orientation towards customers resulting from this development has become of interest to organizations in order to confront competitors. So, customers must be understood to allure and retain the largest possible number of them. The interest has increased in building long-term relationships with customers and managing those relationships effectively to satisfy their needs and desires. To achieve all this, the organization must have solid information systems to create value for customers. The main benefit of using the quality of information systems oriented towards customers comes from accurate and complete information and the system that provides speed and accuracy in dealing with customers as well as the quality of service provided to customers. The rest of the paper is organized in five sections. The first section explains the study's methodology. The second section covers the theoretical background. The third section covers the field part of the study and data collection. The fourth section is dedicated to the discussion of results, and study concludes with the conclusions and recommendations in its final section.
Research Methodology
This section discusses the methodology used in this research and as follows.
Research Problem
Customers represent the ultimate goal of the operations of business organizations. The continuity of the organization depends on customers as they are the key to the success and failure of the organization. In order for the organization to survive and continue, it must provide services of high value to its customers as this will also bring success. As the most important thing that an organization should possess is high quality information systems. The good systems that organizations seek to possess represent a material wealth that enables them to enter the competitive market through the widest doors. Hence, we can say that the success of organizations depends on the rate of efficiency of the systems in making successful decisions. This is because the quality of information is considered as the cornerstone of decisions. The study problem can be formulated in the following questions:
Does the quality of management information systems contribute to customer orientation?
Does the quality of management information systems affect customer orientation?
Objectives of the Study
The research seeks to achieve the following:
Contributing to the theoretical strand of the two dimensions of the study: the quality of management information systems and customer orientation.
Revealing the nature of the correlation and impact between the quality of management information systems and customer orientation.
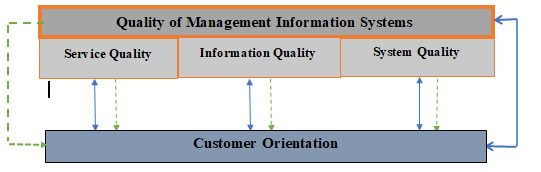
The Suggested Research Model
References: designed by the researchers.
Refers to an effect
Refers to a Correlation
Research Hypotheses
There is no significant correlation between the quality of management information systems and customer orientation in the two organizations surveyed. The following sub-hypothesis emerges from it:
There is no significant correlation between each dimension of the quality of management information systems individually and orientation towards customers.
There is no significant effect of the quality of management information systems on customer orientation. The following sub-hypothesis emerges from it:
There is no significant effect for each dimension of the quality of management information systems on the orientation towards customers.
Study Limitations
The limitations of this study include the following:
Time limits: The study was limited to the time period in which the questionnaire was distributed and the results analyzed from 3/14/2021 to 06/30/2021.
Spatial boundaries: The study was limited to the private universities of Nawroz & Cihan in the governorate of Dohuk due to the cooperation of the two universities’ administrations with researchers.
Limitation of Study
The study was limited its number of respondents because it came with the unexpected the Covid-19 pandemic that swept the region forcing the region into lockdown and two investigated universities to take prevention and safety measures . For these reasons the researcher faced difficulties in contacting all university employees and the choice of sample was limited to those who had valid emails and internet access.
Theoretical Contribution
The theoretical contribution of the study is that deals with a contemporary and modern topic which integrates two concepts from different branches of knowledge in business management, namely, management information systems and customer orientation which meets one of the requirements recommended by Salamzadeh (2020) for papers with theoretically contributions by investigating a new relationship among different concepts. The choice of private universities as a field of study especially with regard to the concept of customer orientation meets another of the requirements stated in Salamzadeh (2020) by examining a previously tested theory of customer orientation in a new context represented by private universities instead of marketing businesses as to the researcher's knowledge this topic was not addressed in previous studies.
The Theoretical Framework
The Quality of Management Information Systems
Recent developments have led to the concept of systems acquire new connotations that keep pace with the environmental changes taking place. Simply, we can say that systems are an organized group of parts or sub-systems that are largely integrated to achieve the general goal as the systems contain different inputs that pass through a set of different processes. This is in order to provide specific outputs through which we can achieve the general goals (Nelson et al., 2005). Ramadhan (2018) has indicated that it is the integration of components, systems and sub-components of systems that are characterized by accuracy and the ability to customize all user needs. Riandi, et al., (2021) noted that they are the systems that achieve the requirements and expectations of the user by ensuring the quality of the design of the system in a way that in turn ensures the availability of useful information that contributes to raising the efficiency of decision-makers. Consistent with the foregoing, we believe that the concept of the quality of management information systems includes compliance with the standards and forms for all documents used to ensure the flow of information in the organization using standard and consistent templates based on the automated account that expresses a variety of networked systems. These systems consist of computers, communication devices and software systems that work in the framework of a technical organizational structure in order to achieve a high level of modern collaboration and a competitive advantage that adds value to the outputs of that organization.
Importance of the Quality of Management Information Systems
The increasing interest in management information systems has prompted many organizations to harness all their administrative and programming capabilities to research and evaluate information systems as they are the effective means to achieve the goals of the organization in the fastest time and with the least effort (Rodriguez & Casanovas, 2010). The importance of the quality of management information systems can be summarized as follows Delone & McLean (2016); Shniekat, et al., (2021)
Management Information Systems (MIS) quality works to counter pressures to reduce costs or increase production without increasing costs.
Improving the quality of products or services & staying in a competitive environment.
Information systems support rapid decision-making while planning, directing, & supervising the activities of the organization.
Because manual work in organizations waste time & resources, management information systems are widely used to save costs, and overcoming the obstacles of manual work
MIS make it easy to share knowledge among employees and connecting all organizational units.
The Dimensions of the Quality of MIS
The current study relied on the model adopted by DeLone & McLean (2003) because it proved that it is one of the most effective tools in ensuring the success of management information systems. The following is an explanation of each of the dimensions:
System quality: Koh, et al., (2020) indicated that system quality is the technical factors such as reliability, response time, ease of access to resources, and design of systems, as these factors are directly related to the system and affect the satisfaction of users in a positive way. Elmohadab, et al., (2017) stated that it includes all aspects such as hardware capabilities, software and policy procedures of an information system that can provide the information needs for users. Habib (2020) explained that it is the system that fulfils the requirements and expectations of the user, and in order for the system to be considered good, this system must be well designed and provide assistance and information to users.
Information quality: Bosse & Rogova (2019) indicated that the quality of information represents the degree to which the information meets the users' needs according to their external and subjective perceptions. Endraria (2020) stated that it represents a function of the value of the outputs produced by the system that the users perceive, as a great deal of information may have different characteristics. However, it is seen as determining the importance of information quality such as accuracy, timeliness of the output, reliability, completeness, conciseness, form and relevance. Regarding the importance of the quality of information, Azemi, et al., (2017) stated that it is a good model for many organizations as the quality of information contributes to identifying needs, directing targeted services and creating efficiency in daily work. We also have another statement on this issue by Caserio & Trucco (2020) who stated that the quality of information has significant economic effects on the organization because bad information can lead the organization to spend resources on ineffective projects. It can also lead to increased costs that are mainly related to wasting time for decision makers trying to find the most appropriate information for their needs.
Service quality: AL-Azzam (2015) indicated that service quality reflects comparing the performance of the service provided by the organization with the general expectations of customers of how the service will be, which is reflected in the organization’s evaluation of customers. Ramya & Kowsalya (2019) explained that it is the organization’s ability to keep customers because the organization strives to retain customers by building strong and sustainable relationships with them. This is done by providing services that exceed their expectations, which generates a state of satisfaction for them. The characteristics of service quality are as follows: Leonnard (2018).
Tangible: this is related to the physical condition and the availability of material facilities and human resources.
Reliability: this is related to the ability of service providers to deliver services in accordance with what they have promised.
Response: this concerns the ability of service providers to provide the best service to consumers.
Warranty: this deals with the knowledge and skills possessed by service providers.
Empathy: this deals with the personal concern that a service provider gives to consumers.
Customer Orientation
The Concept of Customer Orientation
Fellesson & Salomonson (2020) indicated that customer orientation is not an administrative activity, but a philosophy that must be applied and spread in all departments of the organization. This is in order to become an integral part of its main activities to serve customers and build long-term relationships with them. Li Sa, et al., (2020) stated that it is organizational commitment and job satisfaction that is able to read the needs of customers, which greatly affects the creation of knowledge to improve the final performance. Orientation towards customers is directly related to the performance of the organization. Mady (2020) explained that it is a system that consists of a set of cognitive integrative organizational constants. These depend on the degree of information processing related to customers in the organization and the presence of three levels that support the process of orientation towards customers: organizational levels, administrative levels, and levels of individuals. In line with the foregoing, we believe that customer orientation expresses a philosophy based on integrating everything related to customers in the organization’s activities and making it the starting point for work in order to achieve the organization’s primary goal, which is to achieve customer satisfaction. This in turn is reflected positively on increasing the profitability and market share of the organization and achieving sustainable competitive advantage.
The Importance of Customer Orientation
Customer-oriented organizations are in a better position to detect opportunities and develop long-term strategies and are able to accurately determine the importance of customers’ needs and note the change in demand (Kotler et al., 2018). Aziz, et al., (2020) explained that customer orientation leads to a deep understanding of customer problems & increases the organization’s ability to link market information with separate ideas & concepts and allows it to apply different ideas and concepts in unexpected ways to create new opportunities in the market. Therefore, the ability to process information as a result of orientation towards customers supports the structural alignment in the organization. He explained Nejati, et al., (2011) that the Customer orientation useful to predict customer buying behavior. He added Radović-Marković (2018) that the customers orientation important the business organization connects to its customers and offer them reasons revisit and repurchase by creating for them a unique experience.
Dimensions of Customer Orientation
The views of researchers about the dimensions of customer orientation vary in terms of their emphasis on some dimensions rather than others, but most researchers, including Zulu (2015); Mokhtaran & Komeilian (2016); Domi, et al., (2020) have agreed that the dimensions of customer orientation are as follows:
Developing and sustaining the relationship with customers: The process of developing and sustaining the relationship with customers plays an important role in ensuring the success of the organization. Nowadays, organizations can maintain themselves in the market in the long term by implementing strategies to create a long-term relationship with their customers Salem (2021). As Aka, et al., (2016) indicated that it is a strategic direction that focuses on maintaining existing customers and building a long-term relationship with them. Therefore, maintaining long-term relationships between the organization & customers is a way for organizations to be able to compete in the modern business environment. Ojiaku, et al., (2017) explained it as an integrated effort to identify, maintain and build networks with individual customers and to continually enhance the network for the mutual benefit of both sides through interactive, individual and value-added communications over a long period of time. Aldaihani & Ali (2019) identified a strategy used to develop & increase the profitability of the organization by establishing long-term relationships with customers in order to obtain many benefits, including the acquisition of new customers at the lowest costs.
Customer Satisfaction: The concept of customer satisfaction occupies an important place in marketing theories and practices, as it is the main result of marketing performance that links purchase and consumption processes with post-purchase phenomena such as brand loyalty, repeat purchase and change of situation. Therefore, it is expressed as the overall evaluation of the consumer or the beneficiary of the organization’s performance (Al-Ghamdi & Badawi, 2019). Safi & Alagha (2018) indicated that customer satisfaction expresses the positive response that customers feel towards their experience of the organization’s products. Dam & Dam (2021) explained that customers’ perceptions of happiness or frustration are due to the comparison between service performance and customers’ expectations. If the performance matches or exceeds expectations, then customers are satisfied, but if the performance is below expectations, then customers are dissatisfied and frustrated. Consequently, dissatisfaction is a negative outcome that affects the organization and its market position.
Dissemination of information for Customer: Ho, et al., (2020) indicated that dissemination of information expresses voices or a group of activities on social networking sites through which they show brands, and they are like offers by organizations to publish the details of their services to customers. Lis, et al., (2020) noted that it is a useful mechanism for sharing information with a large number of people at a specific time by sharing their thoughts and feelings, as this information may be true or false. With regard to the purpose of disseminating the information, it was clarified by Boutayeb, et al., (2020) that it is represented by the following:
The information is easily disseminated by any means orally such as emails, phone calls, social networks, etc. This is done with the help of advanced technologies to facilitate human communication.
Sharing the information that has been published by social media tools so that customers can determine the appropriateness of this information and then make a decision.
Customer value: Danurdara & Hidayah (2016) indicated that customer value expresses the difference between benefits and costs in certain service offerings. Alam & Perry (2002) stated that it is the product of a positive interaction between business and customers in order to create a benefit that in turn translates into a respiratory advantage that aims to delight and satisfy customers. Customers’ experience with the organization and the goods it produces stimulates their perception of value and preference towards the brand (Kuranga & Salau, 2020). As the value that the organization creates and comes to customers, whether it is the current customer or the future customer of the organization, is what determines the success of the organization. This success depends on the ways in which customers are retained and increased in number (Sánchez et al., 2019). He added Moghadamzadeh, et al., (2020) that the Customer participation in creation of value can be aided by information sharing that makes it possible for customers to share their information with business organization and aid in its efficiency in meeting, customers’ needs and preferences more perfectly.
Meeting the needs of customers: Majava, et al., (2014) referred to the needs of customers as the problems that customers intend to solve by purchasing or benefiting from a particular service. Camilleri (2018) defined it as something that customers’ needs and that generates satisfaction. For example, in the case of business travellers, the punctuality of the service is a good example of what constitutes customers’ need for it. However, in the event that the airline fails to provide a high level of commitment, you will lose customers to the competitors. However, it is not possible to put all the requirements of customers under the heading of need. For example, it can be said that the friendly attitude on the part of the cabin staff, despite it being simple, has a decisive influence on the passenger’s choice of an airline, so it should be classified as a desire rather than a need. So, desires are very important in today’s marketing because, in many markets, airlines can meet the needs of customers just like their competitors but it is the fulfilment of desires that differentiates the competitors. Timoshenko & Hauser (2019) explained that it is a description of what customers need and what they seek to obtain from the service provided to them.
Fieldwork
This study includes the following topics:
The description of organisation as the research community of this study and the justifications for its selection: Two universities of Nawroz & Cihan were selected as a field for the current research. Perhaps the most important justifications for choosing this organization as a field for study are the following:
faculty members in their various scientific titles and the staff in the organization in question have experience and knowledge of the systems used by the university, which can determine the answers to the questions contained in the questionnaire approved in the current study.
The importance of the strategic role played by the researched university by increasing intellectual and cultural awareness through providing distinguished educational services. This contributes to achieving levels comparable to the ranks of sober colleges.
Description of the respondents: A sample of (303) employees in the two universities was selected. Table (1) shows some characteristics of the research sample members as follows:
| Table 1 Description of The Respondents in Nawroz and Cihan Universities |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage | Number | Variables | |
| 24.4% | 74 | 1 – 4 | Years of service |
| 41.3% | 125 | 5 – 10 | |
| 23.1% | 70 | 11 – 15 | |
| 11.2% | 34 | + 16 | |
| 18.8% | 57 | Lower management | Nature of work |
| 56.1% | 170 | Central management | |
| 25.1% | 76 | Senior Management | |
Years of service: It is clear from Table (1) that the majority of individuals working in the two organizations surveyed have more than 5 years of service, as the percentage of individuals falling under this category reached (75.7%). This contributed to improving their experience and knowledge in the organization and the impact. It was evident through their handling of the questionnaire.
Nature of work: It is clear from Table (1) that (56.10%) of the respondents work in the middle management, which is the highest percentage among the individuals surveyed from the total sample, followed by the category of workers in the higher management, which is (25.10%). We find that employees in the minimum administration (18.80%). This is a good indicator because it indicates the multiplicity of administrative levels in the sample studied.
Measuring the correlation between the quality of management information systems and customer orientation.
Measuring the correlation relationship between the quality of management information systems combined and orientation towards customers: It is clear from Table (2) that there is a direct significant relationship between the quality of management information systems and orientation towards customers. In terms of the value of the correlation coefficient, this appeared equal to (0.760), and this value is significant based on the probability value (P-value) which appeared equal to (0.000) which is less than (0.05). Accordingly, the first main hypothesis is rejected and its alternative is accepted, which states that there is a significant correlation between the quality of management information systems and customer orientation.
| Table 2 Correlation Coefficient Between The Quality of Management Information Systems and Customer Orientation |
||
|---|---|---|
| Correlation | ||
| Customer orientation | ||
| Quality of management information systems | Pearson Correlation | 0.760** |
| P-value | 0 | |
| N | 303 | |
Measuring the correlation relationship between the dimensions of the quality of individual management information systems and the orientation towards customers: From the observation of the results of Table (3), we find that there is a direct significant relationship between the dimensions of the quality of individual management information systems and orientation towards customers. In terms of the values of the correlation coefficient for each of them, these values were significant based on the probability value (P-value) which appeared equal to (0.000) which is less than (0.05). Accordingly, the sub-hypothesis of the first main hypothesis will be rejected and its alternative will be accepted, which states that there is a significant correlation relationship for each dimension of the quality of MIS in customer orientation.
| Table 3 Correlation Coefficient Between Individual MIS Quality Dimensions and Customer Orientation |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation | ||||
| Dimensions of quality of management information systems | ||||
| System Quality | Information Quality | Service Quality | ||
| Customer orientation | Pearson Correlation | 0.667** | 0.678** | 0.692** |
| P-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| N | 303 | 303 | 303 | |
Measuring the impact of the quality of management information systems on customer orientation in the two organizations surveyed:
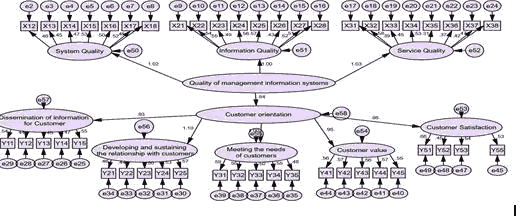
Measuring the effect of the overall dimensions of management information systems’ quality on customer orientation: Figure (2) of the structural equation modelling indicates the significance of the model that was designed in terms of high saturation values. The results of the statistical analysis in Table (4) of the regression analysis showed a direct and significant effect of the dimensions of the quality of management information systems combined in the dimensions of orientation towards customers combined in terms of the value of the regression coefficient of (0.984). This indicates that the higher the levels of quality of management information systems, the greater the orientation towards customers and this effect is significant in terms of the probabilistic value, which amounted to (0.020). This is less than (0.05), as well as the unit of signals for the confidence limits of the model. Through the foregoing, the second main hypothesis will be rejected and its alternative will be accepted, which is that there is a significant effect of the quality of management information systems combined in the orientation towards customers.
Figure 2:Structural Equation Modelling For The Impact of The Dimensions of The Quality of Management Information Systems Combined on Customer Orientation
| Table 4 Regression Analysis of The Effect of The Overall Dimensions of MIS Quality on Customer Orientation |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-value | 95% Confidence Interval | Estimate | SRW | Dependent variable | Direction of Effect | Independent variable | |
| 0.020 | 0.754 | Lower Bound | 0.984 | 0.843 | Customer orientation | → | Quality of management information systems |
| 0.907 | Upper Bound | ||||||
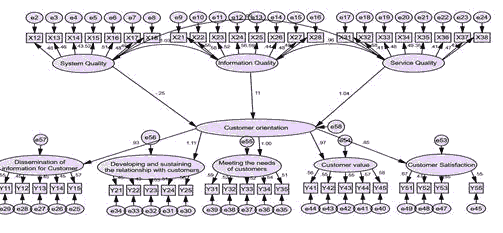
Measuring the effect of individual MIS quality dimensions on customer orientation: Figure (3) indicates the results of the statistical analysis for each dimension of MIS quality in customer orientation, the results of which are shown in Table (5) and as follows:
Measuring the effect of system quality on customer orientation: The results of the statistical analysis shown in Table (5) indicated that there was no significant effect of the system quality dimension on customer orientation, in terms of the probabilistic value that reached (0.438), which is greater than (0.05).
Measuring the effect of information quality on customer orientation: The results of the statistical analysis shown in Table (5) proved that there is a direct and significant effect of the information quality dimension on customer orientation, in terms of the probabilistic value that reached (0.0029), which is less than (0.05).
Measuring the impact of service quality on customer orientation: Table (5) shows that there is a direct and significant effect of the service quality dimension on customer orientation, as the value of the regression coefficient is (0.827). This indicates that the higher the service quality, the greater the orientation towards customers. This effect is significant in terms of the probability value, which appeared equal to (0.038), which is less than (0.05).
Figure 3: Structural Equation Modelling For The Impact of Individual MIS Quality Dimensions on Customer Orientation
| Table 5 Regression Analysis of The Effect Of Individual MIS Quality Dimensions on Customer Orientation |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-value | 95% Confidence Interval | Estimate | SRW | dependent Variables | Direction of Effect | Independent Variable | |
| 0.438 | -4.208 | Lower Bound | -0.285 | -0.250 | Customer orientation | → | System quality |
| 0.495 | Upper Bound | ||||||
| 0.0029 | 0.102 | Lower Bound | 0.117 | 0.114 | → | information Quality | |
| 2.619 | Upper Bound | ||||||
| 0.038 | 0.294 | Lower Bound | 0.827 | 1.041 | → | service Quality | |
| 3.619 | Upper Bound | ||||||
The findings of the current study are in agreement with Faryadras & Dashti (2016) who found that the quality of management information systems effectively contributes to the identification and application of customer orientation, as effective information systems contribute clearly to organizational decision-making on the total level, thus improving customer orientation. With regard to the effectiveness of management information systems and their quality characteristics. Management information systems quality helps in the speed of service delivery, increase the speed of work, reduce wastage of time in internal operations, enhance the speed of service provision and increase the quality of service provided to customers.
The finding of the current study also agree with (Masri et al., 2020), in which he found that the quality of management information systems leads to the provision of services that suit the needs and expectations of customers through its dependence on reliable information which is accessible by the customer at any time and place. Customer satisfaction, trust, and long-term customer relationships are affected by the quality of management information systems.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusion
1) The existence of a significant correlation relationship between the quality of management information systems at the total level and the orientation towards customers in the two organizations investigated.
2) The existence of a significant correlation relationship between each dimension of the quality of management information systems individually and the orientation towards customers.
3) The results of the field study confirmed that the quality of management information systems at the total level of the two organizations surveyed contributes to a positive and direct impact in enhancing customer orientation in the two organizations surveyed.
4) The results of the current study confirmed that there was no effect of system quality in enhancing customer orientation in the two organizations surveyed.
5) The study found that the quality of information and the quality of service had a significant effect in enhancing customer orientation.
Recommendations
1- The two universities surveyed should increase their focus on the quality of the system because it represents the cornerstone on which the quality of information and service quality are based. This in turn is positively reflected on the success of the organization in orientation towards customers by paying attention to modern programs and applications that support these systems.
2- There is necessity for the two universities surveyed to strive seriously and continuously to enhance the contributing and influencing factors in the decision-making process through the quality of the information provided by the organization because it is a main source of customer orientation.
3- The two universities surveyed should encourage their employees and develop their abilities to understand the quality of the used management information systems and work to enhance them through holding training courses to raise their level of efficiency and build their capabilities to understand more about everything that should be done to meet the needs of customers.
The two universities investigated should always work to add quality to the information and services provided to customers, to ensure renewal and keep pace with modern developments without indulging in stereotypes.
References
Aka, D., Kehinde, O., & Ogunnaike, O. (2016). Relationship marketing & customer satisfaction: A conceptual perspective. Binus Business Review, 7(2).
Alam, I., & Perry, C. (2002). A customer oriented new service development process. Journal of Services Marketing, 16 (6).
Al-Azzam, D. (2015). The impact of evaluating service quality dimensions on patient satisfaction: A study of private hospitals in Irbid City/Jordan. European Journal of Business and Management, 7.
Aldaihani, F.M.F., & Ali, N.A.B. (2019). Impact of relationship marketing on customers loyalty of Islamic banks in the State of Kuwait. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 8(11), 788-802.
Al-Ghamdi, S., & Badawi, N. (2019). Do corporate social responsibility activities enhance customer satisfaction and customer loyalty? Evidence from the Saudi banking sector. Cogent Business & Management, 6(1).
Azemi, N., Zaidi, H., & Hussin, N. (2017). Information quality in organization for better decision-making. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(12).
Aziz, N., Ismail, R., & Rahmana, I. (2020). The influence of customer orientation and marketing innovation towards SME performance in East Coast Malaysia: A proposed conceptual model. International Journal of Accounting, 5(28).
Bossé, É., & Rogova, G. (2019). Information quality in information fusion & decision making. New York: Springer.
Boutayeb, H., Bidah, S., Zakary, O., & Rachik, M. (2020). A new simple epidemic discrete-time model describing the dissemination of information with optimal control strategy. Discrete dynamics in nature & society, 2020.
Camilleri, M. (2018). Understanding customer needs & wants. In: M. Camilleri, ed., Travel Marketing, Tourism Economics & the Airline Product. Cham: Springer.
Caserio, C., & Trucco, S. (2020). The impacts of ERP integration on information quality. International Journal of Management & Information Technology, 15.
Dam, S., & Dam, M. (2021). Relationships between service quality, brand image, customer satisfaction, & customer loyalty. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics & Business, 8(3).
Danurdara, A., & Hidayah, N. (2016). Creating customer value & its implication to customer loyalty: An empirical study at star hotels in West Java, Indonesia. International Review of Management and Business Research, 5(2).
Delone, W., & MacLean, E. (2003). The DeLone & McLean model of information systems success: A Ten-Year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4).
DeLone, W., & McLean, E. (2016). Information systems success measurement. Foundations and Trends  in Information Systems, 2(1).
Domi, S., Capelleras, J., & Musabelliu, B. (2020). Customer orientation & SME performance in Albania: A case study of the mediating role of innovativeness and innovation behavior. Journal of Vacation Marketing, 26(1).
Elmohadab, M., Khalene, B., & Safi, S. (2017). Enterprise resource planning: Introductory overview. Paper presented at International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies (ICEIT), Rabat, Morocco, 15-18 November, 2017.
Endraria, E. (2020). Influence of information quality on the development of Covid-19 pandemic in Indonesian. Indonesian Journal of Social Sciences, 29(6).
Faryadras, P., & Dashti, N.S. (2016). Discussing the Impact of Management Information System (MIS) on improvement of efficiency and quality of services of hospitals: Case study: Tehran's Madayen Hospital. Rev. Eur. Stud., 8, 258.
Fellesson, M., & Salomonson, N. (2020). It takes two to interact “Service orientation, negative emotions & customer phubbing in retail service work. Journal of Retailing & Consumer Services, 54.
Habib, A. (2020). System quality, information quality, user satisfaction, & individual impact a study in using hospital information system In Indonesia. Doctoral Dissertation. Universitas Andalas.
Koh, J. & Kan, R. (2020). Perceptions of learning management system quality, satisfaction, and usage: Differences among students of the arts. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology.
Kotler, P., Armstrong, G. & Opresnik, M. (2018). Principles of marketing, (17th edition). New York: Pearson Education Limited.
Kuranga, M.O., & Salau, A.A. (2020). Impact of perceived service value on customer satisfaction in selected Nigerian commercial banks in Lagos metropolis. Fountain university Oshogbo. Journal of management, 5(2), 12-22.
Leonnard, L. (2018). The performance of SERVQUAL to measure service quality in private university. Journal on Efficiency and Responsibility in Education and Science, 11(1).
Li Sa, M., Choon-Yin, S., Chai, Y., & Aik Joo, J. (2020). Knowledge creation process, customer orientation & firm performance: Evidence from small hotels in Malaysia. Asia Pacific Management Review, 25(2).
Lis, T., Bajdor, P.,Grondys, K., & Ptak, A. (2020). The role of information relations in network organizations. European Research Studies Journal, 13(1).
Mady, S. (2020). The effect of entrepreneurial & customer orientation on service quality in hotels. Business and Entrepreneurial Review, 62(6).
Majava, J., Nuottila, J., Haapasalo, H., & Law, K. (2014). Customer needs in market-driven product development: product management & R&D Standpoints. Technology and Investment, 05(01).
Masri, N.W., You, J.J., Ruangkanjanases, A., Chen, S.C., & Pan, C.I. (2020). Assessing the effects of information system quality and relationship quality on continuance intention in e-tourism. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(1), 174.
Moghadamzadeh, A., Ebrahimi, P., Radfard, S., Salamzadeh, A., & Khajeheian, D. (2020). Investigating the role of customer co-creation behavior on social media platforms in rendering innovative services. Sustainability, 12(17).
Mokhtaran, M., & Komeilian, B. (2016). Exploring the effect of customer orientation on Dana insurance performance considering the intermediary role of customer relations and service quality management. International Review, (3-4).
Nejati, M., Salamzadeh, Y., & Salamzadeh, A. (2011). Ecological purchase behaviour: Insights from a Middle Eastern country. International Journal of Environment and Sustainable Development, 10(4), 417-432.
NELSON, R., Todd, P., & Wixom, B. (2005). Antecedents of information and system quality: An empirical examination within the context of data warehousing. Journal of Management Information Systems, 21(4).
Ojiaku, O., Aghara, V., & Obianuju, L. (2017). Effect of relationship marketing & relationship marketing programs on customer loyalty. International journal of Business and Management Review, 5(5)
Radović-Marković, M. (2018). Female entrepreneurship opportunity: Home-based genealogy business. Journal of Women's Entrepreneurship &Education, (3/4), 20-33.
Ramadhan, Y. (2018). Determinants of management accounting information systems quality on management accounting information quality. In: International Conference on Business, Economic, Social Science and Humanities (ICOBEST)..
Ramya, N., & Kowsalya, A. (2019). Service quality and its dimensions. EPRA International Journal of Research & Development, 7.
Riandi, M., Respati, H., & Hidayatullah, S. (2021). Conceptual model of user satisfaction as mediator of e-learning services and system quality on students individual performance. International Journal of Research in Engineering, Science and Management, 4(1).
Rodriguez, N., & Casanovas, J. (2021). A structural model of information system quality: An empirical research. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth Americas Conference on Information Systems.
Safi, F. & Al-Agha, M. (2018). The relationship between service quality & customer satisfaction. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 10 (8).
Salamzadeh, A. (2020). What constitutes a theoretical contribution? Journal of Organizational Culture, Communications and Conflict, 24(1), 1-2.
Salem, S. (2021). Do relationship marketing constructs enhance consumer retention? An empirical study within the hotel industry. SAGE Open, 11(2).
Sánchez-Gutiérrez, J., Cabanelas, P., Lampón, J.F., & González-Alvarado, T.E. (2019). The impact on competitiveness of customer value creation through relationship capabilities and marketing innovation. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 34(3).
Shniekat, N., Jawabreh, O., & Saleh, M.M.A. (2021). Efficiency & effect on the competitive advantage of Management Information Systems (MIS) in classified hotels in the city of petra; type of management as moderator. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20, 1-18.
Timoshenko, A., & Hauser, J. (2017). Identifying customer needs from user-generated content. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Zulu, S. (2015). The relationship between brand orientation, customer orientation, competitor orientation & Brand distinctiveness in South African Retailing. Business & Social Sciences Journal (BSSJ), 1(1).