Review Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 5
The Challenges, Barriers and Advantages of Management Information System Development: Comprehensive Review
Hamzeh Ahmad Alawamleh, Al-Balqa Applied University
Kafa ALNawaiseh, Al-Balqa Applied University
Mohammad Shibly, Al-Balqa Applied University
Basel J. A. Ali, Al-Balqa Applied University
Citation Information: Alawamleh, H.A., ALShibly, M.H.A., Tommalieh, A.F.A., Al-Qaryouti, M.Q.H., & Ali, B.J.A. (2021). The challenges, barriers and advantages of management information system development: comprehensive review. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(5), 1-7.
Abstract
Often businesses do not capitalize on any of the possible advantages of Management Information Systems (MIS). Today, the growing growth of IT and its significant impact on the competitiveness of public and private organizations around the world, as well as the global push to use various forms of information systems, namely Management Information System (MIS), has caused developed countries to follow suit. According to the results, most organizations are shifting toward a greater competitive value of MIS. As a result, MIS administrators take a holistic approach to MIS and prioritize issues impacting the whole company over those affecting only the MIS department. The current study clarified the position, goal, function, meaning, philosophy, dimensions, advantages, and classification of MIS, as well as the organizations' challenges and barriers.
Keywords
Challenges, Advantages, Management Information Systems.
Introduction
Management information (IS) utilizes a broad variety of information technologies (IT's) to perform complex tasks, collaborate and counsel numerous actors in different operational and social environments, including computers, software, databases, networking networks and the Internet, mobile devices, among others. Therefore, all facets of information technology development, integration, operation, application and impact within organizations and societies are of general interest to the IT sector (Boell & Cecez-Kecmanovic, 2015; Ali et al. 2016 a & b). The efficiency of the use of the information system is the wide range of information that most organizational customers require. It has an impact on decision-making and corporate coordination assistance (Salameh et al., 2020). As a result, sound decision-making becomes essential to the survival of the company (Ali & Oudat, 2020).
MIS is an organized, diverse and automated information system which deals with the collection, maintenance and transmission of related information to support business management processes. The data of a company is distributed through the various departments. In a number of ways, data are analyzed to provide accurate and valuable management material, including graphs, diagrams, analyses and surveys. The MIS central storage of all consumer records. MIS is used by an organization at all times (Mishra et al., 2015). The information age has changed the functioning of traditional systems. IS has always reflected on manual processes the output pattern from the years (Ali et al., 2016a & b; Salameh et al., 2020). The question is, why are information management systems facing so many challenges? Consequently, it is important to consider the challenges in order to implement sound information management systems procedures. This study is therefore intended to recognize the problems of the MIS.
The Need for MIS
Any of the reasons for making a MIS structure are as follows (Karim, 2011):
• In order to make sound choices, policymakers need evidence. Management information systems allow for this to happen (MIS).
• Record tracking – Management information systems maintain track of all of an organization's financial operations and function as a repository for the transactions.
• MIS programs enhance collaboration both inside the organisation and outside it – workers in the company can obtain the necessary information on a day-to-day basis. Short Message Service (SMS) and e-mail allow consumers and vendors to contact an organization's MIS infrastructure.
MIS Compounds
There are the following major components (Romney et al., 2012):
• Users: individuals using the IT system.
• Data.
• Business Processes: defined procedure for recording, storing, and analyzing data.
• Hardware includes computers, workstations, networking facilities, printers, and so on.
• Software: there are applications that are used to manage records. These include spreadsheet applications, database tools, and so on.
Types of Information Systems
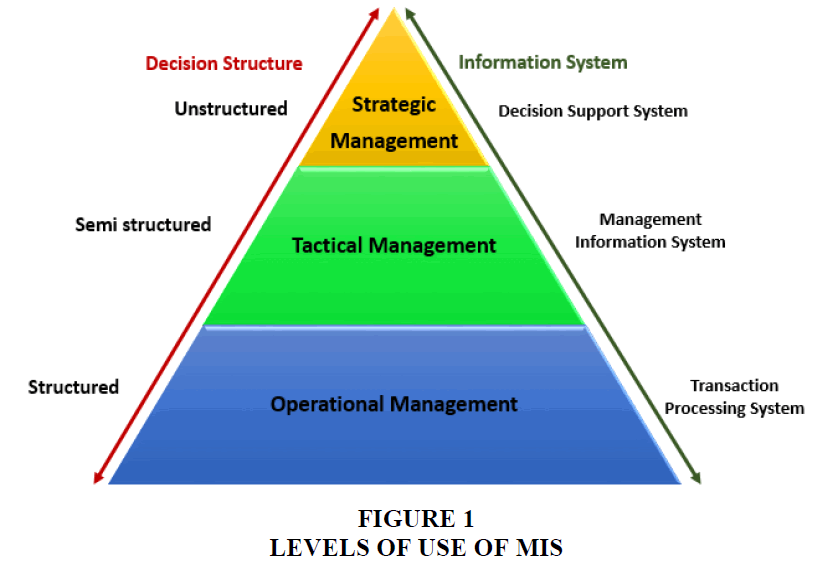
The way a customer selects its information system depends on its position the chart below (Figure 1) displays the organization's three main usage levels and the type of information system (Nayak et al., 2012).
• Transaction Processing Systems: used to keep everyday company accounts. An example in a point of sale is a transaction processing system (TPS). To track daily purchases, a point-of-sale machine is used.
• MIS: These systems help situational managers in the semi-structured decision-making process. The database system for transaction processing is fed into the information system (MIS).
• Decision support systems (SSD): Tools for decision taking are used for semi-structured decision-making by top-level managers. DSS systems also incorporate external data points, such as current industry capabilities, competitiveness and so on, with the output of the Management Information System.
Computerized Information System
Data is the lifeblood of every company. In order to make decisions, everyone in an organisation requires facts. An information system is a method of capturing, saving, and extracting data that is well-organized. Depending on the management's preference, this data may be recorded manually or electronically (Ali et al., 2016a & b). Time consuming, vulnerable to malfunction, lack of protection, data duplication, data inconsistencies, and lack of backups are some of the drawbacks of using manual information systems (Salameh et al., 2020). Computerized programs have been developed to resolve manual information systems weaknesses. The biggest difference between both an information system manual and a computerized system is that an electronic system records, maintains, analyses and collects information through software and hardware combinations.
Advantages
Although these computerized information systems are useful, they have the following advantages:
• A computerized information system has one of the most significant benefits of capturing and saving data fast. It processes information and collects information more quickly. This leads to a more constructive association between the client and the client.
• Improved data consistency - data authentication and verification controls are easier to implement in a computerized environment than in a manual system.
• Enhanced protection – the computerized information system will enforce other security mechanisms as well as controlling access to database servers such as user verification, biometric automation systems, access rights management and so on.
• Less information exchange – Stocking systems are created to prevent duplication of the records. This ensures that the other divisions will instantly access some modification of data in one branch.
• Enhanced recovery tools – Backups can be saved in the cloud with modern technologies, making it possible to restore information if data failure is achieved by hardware and software.
• Easy Information Access – most corporate managers can move when making informational decisions. Data can now be accessed from any location due to developments in internet and mobile technology.
The Challenges and Barriers of MIS
Babaei & Beikzad (2013); Almalki et al. (2017); Ali et al. (2016) are categorized into humanistic, organizational, and environmental considerations, and the main disadvantages and causes for loss and use of MIS in public institutions are as follows:
The Humanistic Factors
• Administrators and consumers need knowledge because they are unsure about what they expect and what information they need.
• A lack of knowledge of users' needs by designers (a lack of proper description and interpretation of needs)
• A lack of knowledge from managers and customers about the designer team's coordination process.
• The administrators and consumers were not included in the machine architecture.
• Administrators in software and information technology had a lack of comprehension.
• The majority of researchers and programmers (designers) are unfamiliar with the current system's working environment.
• The machine executors' unwillingness to adapt and their lack of recognition.
• The inaccuracy of the information gathered.
Organizational Considerations Include
• A lack of decent opportunities for administrators, customers, and device directors to participate and collaborate.
• A lack of study of current structures and processes prior to device construction
• A lack of assessment of existing capacity
• Education of specialist forces is in poor condition.
• A shortage of human capital in management and computing fields, as well as other necessary specializations (absorption issues)
• Inadequate user education and Inadequate and outdated documentation
• Inappropriate technology deployment
Environmental Considerations Include
• A lack of consistency criterion in developing-country information systems.
• A scarcity of qualified contractors to develop the structure and applications.
• A lack of protocols, methodology, and stages in the system's growth.
• A lack of environmental assessment of management information systems.
• Inadequate use of mass media to foster a philosophy of computer and information technology use.
• A shortage of appropriate MA preparation programmes in universities, as well as a lack of suitable human resource education in this regard.
• The lack of ratification of appropriate laws in the Islamic council parliament and government commission, as well as the significant issue in this regard.
• A lack of careful thought and proper investment in this region.
MIS Categories
A management information system is a broad term that refers to a variety of specialized programs. The major styles of structures are as follows (Al-Mamary et al., 2014):
• Executive Information System- (EIS): An EIS is utilized for senior management to make enterprise-wide decisions. Executives need high-level awareness as well as the opportunity to dig down if necessary.
• Marketing Information System- (MkIS): Marketing teams use MkIS to reflect on the progress of past and ongoing initiatives, as well as to plan future campaigns based on the lessons learned.
• Business Intelligence System- (BIS): A BIS is used in activities to render business choices based on the collection, incorporation, and analysis of data and information. This scheme is close to EIS in that it is used by lower-level managers as well as executives.
• Consumer Relationship Management- (CRM) Framework: A CRM system holds essential customer records such as past purchases, contact information, and revenue opportunities. CRM is often employed for communications, customer service, sales, and business development teams.
• Sales Force Automation System- (SFA): A specialized component of a CRM system that automates much of a sales team's operations. Contact management, lead generation and reporting, and order management are all options.
• Transaction Processing System- (TPS): A management information system (MIS) that processes payments and related details. A TPS is a point of sale (POS) device or a machine that allows a visitor to search for a hotel and see room options such as price range, bed style and number, or a swimming pool, and then choose and book it. Using the data produced, employees can report on usage habits and monitor sales over time.
• Knowledge Management System- (KMS): A KM system may be used to provide customer service by answering queries and troubleshooting problems.
• Financial Accounting System- (FAS): This MIS is utilized for organizations that deal with expenditures and accounting, such as accounts payable (AP) and receivable (AR) (AR).
• Human Resource Management System- (HRMS): This system manages staff performance reviews as well as payroll data.
• Supply Chain Management System- (SCM): Suppliers use SCM to monitor the flow of resources, machinery, and services from the moment they are ordered before the final product is shipped.
Literature Review
A management information system is used for both public and private organizations. A management information system (MIS) is a system that aids managers in making decisions to address problems that exist in both public and private organizations. By using MIS, executives may make wise decisions in terms of being able to fix existing problems while preventing the development of new problems that can jeopardize an organization's life. The presence of computer technologies has made a major beneficial contribution to the management information system, and MIS is also very important for representatives of a company or organization to make responsible decisions (Meiryani & RA Aryanti Wardaya Puspokusumo, 2020; Oudat & Ali, 2021; Oudat et al., 2021) In comparison to prior recognition, modern companies face tremendous significant risks as a result of globalization due to changing technological growth. Managing these threats was not a top priority for financial firms. As a result, many businesses see financial risks as a major challenge. According to a recent Ampofo (2020) paper, the study analyzed the record keeping process in order to elucidate the MIS problems at the UDS-Wa Campus. A vacuum remains to be filled due to a lack of literature in this field. The study is qualitative in nature, and forty (40) respondents were chosen by a purposive sampling process. The faculty consisted of six (6) administrative staff members, fourteen (14) senior and junior lecturers, and twenty (20) student delegates. According to the findings of the report, administrators, lecturers, and students was unable to perform regular reviews of the Management Information System by using the correct identification numbers and passwords. Furthermore, the study discovered that the home page and archive of UDS's Management Information System (Wa campus) were still incredibly slow and compromised. Furthermore, the study revealed that UDS (Wa-campus) does not have a student management information system manager and instead depends on the manager at central administration in Tamale. Furthermore, the study discovered that the Management Information System at UDS (Wa campus) is managed by less specialists than at other public universities in the country. According to the report, UDS (Wa campus) management can employ information and communication technology experts with expertise in management information systems (MIS) and computer engineering to ensure that the management information system at UDS (Wa campus) works properly. Alshamsi et al. (2019) stressed the significance of understanding the principles of (IS), (IT), and strategic management information system (SMIS), as well as the need for SMIS, implementation issues associated with SMIS, and similar models. As a result, this article provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the success and problems of the Ministry of Interior's strategic management information system. Without a question, as a result of the advancement of digital technology, businesses depend heavily on information systems these days. While public organizations should adhere to policy in order to achieve their objectives, in the long run, they face a slew of challenges that jeopardize mission accomplishment or the implementation of successful plans to achieve the mission. The UAE is now making strides toward Vision 2021. Implementing strategic knowledge processing is crucial to achieving these goals. According to the report, incorporating a strategic planning system does not guarantee that an organization will be able to meet its strategic goals and objectives. It is critical to evaluate the strategic planning process and its relationship to other management processes within a company. Via the use of secondary data sources, this paper analyzes recent literature and offers a detailed understanding of concepts, mechanisms, and models. The expected results of the study would favor professionals, academia, researchers, government departments, and regulators.
Almalki et al. (2017) described the challenges of applying an Information System Strategy in a Saudi-based market environment in general and in a bank in particular. This research examines the types of issues that can occur in a bank using a case study and a survey to illustrate these difficulties. The survey findings are then analyzed and discussed in the report. It makes several suggestions based on the feedback that may help in solving these difficulties. The results clearly indicate that management problems between IT and industry could be eliminated if there was a proper link between IT and business. According to Babaei & Beikzad (2013), today's the growth of IT and its major impact on the productivity of public and private organisations worldwide, as well as the global trend to use various forms of information systems, including Management Information System (MIS), has led Iran to follow suit. This trend was faced with successes, setbacks, and roadblocks. An analysis of issues encountered during the planning process, implementation, operation, and advancement of management information systems in a country may be very useful in the decision-making of public and private sector organizations. In Iran, the wise implementation of new IT, especially MIS, will pave the way for growth while also increasing its quality and effectiveness.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Attempts have been made in this essay to discuss MIS, its challenges, and its significance in an organizational context. It is reasonable to believe that MIS is the lifeblood of every organisation. Both the public and private sectors must work together committed to obtaining systematic or structured facts prior to making decisions Via computer simulations and gaming strategies, precise solutions to management challenges will be presented. Managers today must exercise caution because they will become inundated with statistics that are only slightly important rather than faced with concrete and absolutely valuable evidence. This condition can be prevented by establishing a robust and usable MIS unit.
Finally, in delivering a large range of streamlined alternatives, MIS plays a vital role for policymakers to select their preferred choices. This is important because it means that whatever decisions decision-makers produce, the result is more often than not optimistic. In fact, this is why many decision-makers opt for MIS tools for tough business decisions. And as a recognized concept it guarantees viable decisions in our industries to have good decision-making opportunities. Organizational management does not often know the information required, and database experts often do not understand or are aware of management in order to provide appropriate information for the managers they represent. An MIS should be planned and run in relation to organisations in order to be competitive.
The study encourages top management of organizations to participate in developing MIS and make a significant contribution to machine architecture. Knowledge experts (including systems analysts, planners, ITC personnel, accountants, and operations researchers) can work together to become more knowledgeable of administrative task criteria in order to produce more effective MIS.
References
- Ali, B.J., & Oudat, M.S. (2020). Financial risk and the financial performance in listed commercial and investment banks in bahrain bourse. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 13(12), 160-180.
- Ali, B.J., Bakar, R., & Omar, W.A.W. (2016a). The critical success factors of accounting information system (ais) and its impact on organisational performance of Jordanian commercial banks. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, 4(4), 658-677.
- Ali, B.J., Omar, W.A.W., & Bakar, R. (2016b). Accounting information system (AIS) and organizational performance: Moderating effect of organizational culture. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, 4(4), 138-158.
- Almalki, M., Al-fleit, S., & Zafar, A. (2017). Challenges in implementation of information system strategies in saudi business environment: A case study of a bank. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology, 43(1), 56-64.
- Al-Mamary, Y.H., Shamsuddin, A., & Abdul Hamid, N.A. (2014). The role of different types of information systems in business organizations: A review. International Journal of Research, 1(7).
- Alshamsi, Y.A.A.B., Hock, O.Y., Karim, A.M., & Hossain, M.I. (2019). Developing a framework on performance and challenges of strategic management information system: A case study on ministry of interior, UAE. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 9(5), 633-646.
- Ampofo, J.A. (2020). Challenges of student management information system (MIS) in Ghana: A case study of University for Development Studies, Wa Campus. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research, 2(5), 332-343.
- Babaei, M., & Beikzad, J. (2013). Management information system, challenges and solutions. European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences: Proceedings, 2(3 (s)), 374.
- Boell, S.K., & Cecez-Kecmanovic, D. (2015). What is an information system?. In 2015 48th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 4959-4968). IEEE.
- Karim, A.J. (2011). The significance of management information systems for enhancing strategic and tactical planning. JISTEM-Journal of Information Systems and Technology Management, 8(2), 459-470.
- Meiryani, P.S., & RA Aryanti Wardaya Puspokusumo, L. (2020). Decision making and management information systems. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(7), 320-325.
- Mishra, L., Kendhe, R., & Bhalerao, J. (2015). Review on management information systems (MIS) and its role in decision making.
- Nayak, G., Sequeira, A.H., & Senapati, S. (2012). Management information system for effective and efficient decision making: A case study.
- Oudat, M.S., & Ali, B.J. (2021). The underlying effect of risk management on banks' financial performance: An analytical study on commercial and investment banking in Bahrain. Elementary Education Online, 20(5), 404-414.
- Oudat, M.S., Ali, B.J., & Qeshta, M. H. (2021). Financial performance and audit committee characteristics: An empirical study on bahrain services sector. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(2), 4279.
- Romney, M., Steinbart, P., Mula, J., McNamara, R., & Tonkin, T. (2012). Accounting Information Systems Australasian Edition. Pearson Higher Education AU.
- Salameh, A.A., Abu-AlSondos, I.A., Ali, B.J., & Alsahali, A.F. (2020). From citizens overview: Which antecedents' can assist to increase their satisfaction towards the ubiquity of mobile commerce applications?. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 14(17).