Research Article: 2022 Vol: 25 Issue: 2S
The Approach of Digital Transformation to Standardization of Public Sector Services: Russian Case of Remote Work
Natalya Vladimirovna Yudina, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Svetlana Vasilievna Zemlyak, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Victor Mikhailovich Kondrashov, Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Citation Information: Natalya, V.Y., Svetlana, V.Z., & Victor, M.K. (2022). The approach of digital transformation to standardization of public sector services: Russian case of remote work. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 25(S2), 1-10.
Keywords
Budgetary Institutions, Performance-Based Contract of Employment, Labor Rate Setting, Distance Employment, Microelement Rationing
Abstract
The article is devoted to the problems of standardization of labor activity of employees of domestic budgetary institutions in the conditions of massive spread of remote work in the sphere of education, health care and culture. The purpose of the study is development of areas for optimization of the existing practice of labor rate setting on the example of a case of labor relations in the Russian public sector. Research methods are based on the principles of remuneration of public sector employees in compliance with the model of performance-based contract of employment. As the result of the study, modern problems of labor rate setting in the public sector have been revealed, and key aspects of modern practice of labor rate setting for budgetary institutions employees have been systematized using a Russian case as the example. The authors suggest the approach of microelement rate setting of labor activity of budgetary institution employees working remotely. Further research areas can be models of optimization of the domestic practice of labor rate setting in the public sector.
Introduction
In the context of the current situation, significant increase is observed in the interests of various participants in labor relations, both the employer, the state, and the employee, in such aspects of labor activity as labor costs, labor results and the level of labor quality. It occurs both within the frames of the real sector of domestic economy and within the sector of public and municipal services. The reason for this interest can lie in the growth of integration of state, employer’s and employee’s interests. This integration of interests is realized through scientifically based rate setting of employees’ labor activity in modern conditions.
On the one hand, one can say that the interest of labor activity participants in labor rate setting is currently conditioned by the necessity of scientific development and practical justification of regulated work time expenditures of employees of organizations and employees’ cost of labor. Such regulation of work time standards and working hour’s ads to development of long-term labor relations on the stable and transparent basis. At the same time, actual requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation suggest that each domestic employer is obliged to promptly ensure development of a set of scientifically based labor standards at his enterprise or organization. In addition, the employer is obliged to ensure regular updating of labor standards considered changes in any organizational and technical conditions as a part of labor process implementation.
Covid-19 pandemic acted as a driver for impetuous spread of remote labor activity, both in the Russian Federation and throughout the world (World Health Organization, 2020). Accordingly, it determined the interest of researchers towards the changes characterizing labor market in pandemic conditions.
Development of remote labor activity in the modern conditions of large-scale dissemination of information and communication technologies is one of the fundamental changes in many labor processes (https://www.doi.gov/telework). Accordingly, it determines the necessity of bringing of the existing labor standards in line with the realities of development of digital economy and mass digitalization of various types of labor activity.
The purpose of the study is development of areas for optimization of the existing practice of labor rate setting on the example of a case of labor relations in the Russian public sector. Research methods are based on the principles of remuneration of public sector employees in compliance with the model of performance-based contract of employment.
Methodology
Passage of many institutions and organizations of the social sphere to remote work in 2020 led to the necessity of examining of a number of problems. Researches performed in the sphere of remote work have repeatedly shown that employees tend to work longer in remote work mode than when they are in the employer's premises. The reason stays partly in the fact that the time for commuting is being replaced by labor activities, while daily routine changes, and the boundaries between paid work and personal life are washed out (Mayhew & Anand, 2020). Remote work may result in a longer business day, as well as to longer working hours in the evenings and on weekends. Accordingly, passage to remote work is accompanied by growth in the intensity of the performed works: only 12% of employees of educational institutions believe that remote mode has not made the work more laborious.
Handwerker, Meyer, Piacentini, Schultz & Sveikauskas (2020) study the particulars of the labor market in the context of COVID-19 pandemic.
Lee, Schmidt-Klau & Verick (2020) examine global perspectives of labor market transformations under the influence of the pandemic.
In pandemic conditions, active development of distance employment takes place in all countries sufficiently prepared for it, both in technical and infrastructural aspects.
Carillo, Cachat-Rosset, Marsan, Saba & Klarsfeld (2020) examine pandemic-induced development of remote work in France.
Deakin & Novitz (2020) analyze areas of labor legislation transformation under the influence of mass circulation of remote work as the result of Covid-19 pandemic.
Okubo, Inoue & Sekijima (2020) study explosive growth of distance work in Japan under the impact of Covid-19 pandemic.
Sankaran (2020) considers the prospects for development of distance employment regulation in the modern conditions.
A separate study of working hours of employees working remotely due to COVID-19 pandemic has also demonstrated that remote workers spend extra hours for work: 38% of respondents said they would more likely work longer at home (McCulley, 2020). One in four employees (27%) working remotely due to the pandemic said he was working in his spare time to meet the requirements applied to his work (https://www.eurofound.europa.eu/publications/report/2020/living-working-and-covid-19).
In the conditions of forced passage to remote work mode, various aspects of psychological well-being of employees acquire enhanced importance (TUC (Trades Union Congress). 2020). Breaking of usual life and work rhythms, as well as intension and uncertainty of the general information background may entail various psychological deformations (ILO, 2020).
Many employees faced significant challenges. For example, remote work mode leads to blurring of anyhow illusive boundaries between work and personal life. The problem of permeability of boundaries between work and privacy is especially acute for those who have families with children. Work rhythms overlap family ones, and it creates difficulties and discomfort both in professional activity and in personal life (Bruce-Hickman, Fan, Plaat & Sheth, 2020).
As of today, labor relations between employers and all employees in Russian budgetary sphere, that is, in every state or municipal domestic institution, are based on the terns of “performance-based contract of employment” as per legal requirements.
One should note that a performance-based contract of employment is a special system of measures aimed at ensuring decent level of wages for all employees of the domestic public sector. It is assumed that the level of well-being of employees in the domestic public sector will correspond to current living standards of the Russian middle class. Thus, a performance-based contract of employment is aimed at stimulation of high-quality, active and effective work, which will be performed by the employees within the interests of various groups of consumers.
Thus, the system of performance-based contract of employment purposed for stimulation of work of public sector employees foresees fulfillment of two key tasks.
Firstly, bringing of the size of the basic part of the wages paid to employees of the domestic public sector to the actual competitive level, that is, to the average wage in the region.
Secondly, formation is foreseen of mechanisms ensuring stimulation of active and high-quality labor, as well as of the necessary "recruitment package". These mechanisms are implemented through inclusion of various compensation payments and commercial incentives into the structure of wages charged to public sector employees.
Passage to performance-based contract of employment was initiated in the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation from May 7, 2012 No. 597 "On measures for implementation of state social policy."
Introduction of the model of public sector employee’s remuneration on the terms of a performance-based contract of employment is aimed at achievement of the following objectives presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Objectives of Implementation of the Remuneration Model on the Basis of a Performance-Based Contract of Employment
Results of the Research
The process of passage to the labor remuneration model on conditions of a performance-based contract of employment in the budgetary sphere was launched by the Program of phased perfection of labor remuneration system in state (municipal) institutions for 2012–2018 (Order of the Government of the Russian Federation from November 26, 2012 No. 2190-r “On approval of the Program of phased perfection of labor remuneration system in state (municipal) institutions for 2012–2018”). This Program legislates the main provisions of the performance-based contract of employment. Thus, an official definition of the performance-based contract of employment as “an employment contract, which specifies his job description, terms of remuneration, indicators and criteria for assessment of efficiency of his activity for assignment of incentive payments depending on the result of his deliverables and of the quality of rendered state (municipal) services provided, as well as forms of social assistance".
As the result of legislative recognition of such an understanding of the essence of the performance-based contract of employment, its idea was narrowed down up to two following processes: the process of increasing in employees’ wages and the process of signing of necessary labor agreements with all employees of the domestic budgetary sphere in a new form. Besides that, the Program formalizes the plans of perfection of the remuneration practice for all employees of the domestic budgetary sphere and the plans of increase in the current amount of remuneration.
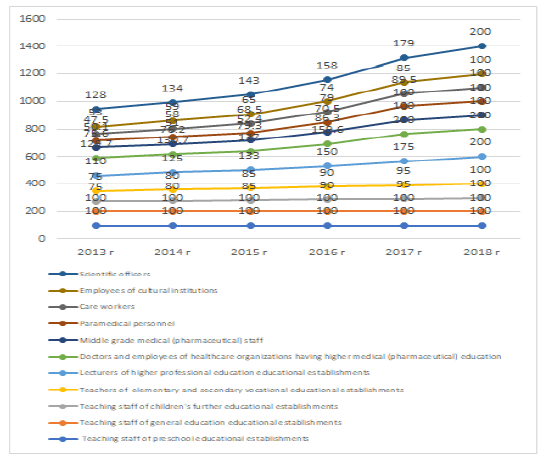
Figure 2 shows the dynamics of (indicative) values of the ratio between the average salary of employees of institutions and the average wages in the region.
Figure 2: Dynamics of Indicative Values of the Ratio Between the Average Salary of Employees of Institutions and the Average Wages in the Region
Source: compiled by the author based on [www.gks.ru]
Increase in the amount of budget financing can be called the main source of growth in the size of wages of all workers of the domestic public sector as the result of implementation of the performance-based contract of employment. In addition, funds received through reorganization of a number of inefficient institutions were used for employee compensation, as well as funds received by institutions from various income-generating activities.
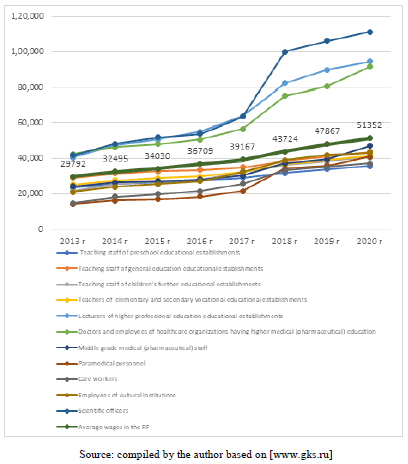
Figure 3 shows the dynamics of the average wages of employees of budgetary institutions and of the average wages in the Russian Federation.
Figure 3: Dynamics of the Average Wages of Employees of Budgetary Institutions and of the Average Wages in the Russian Federation
Source: compiled by the author based on [www.gks.ru]
One can note that, during the period under study, only three categories of public sector employees: magistral staff of universities, doctors and other medical workers with higher education and scientific workers has the average wages higher than the average wages in the Russian Federation. All other categories of public sector employees have wages still below the national average.
The wages charged to the employees of domestic budgetary organizations consists of two parts: the basic part and the incentive part. It should be kept in mind that the incentive part of the wages is a variable share of the wages and should depend on the results achieved by the employee in his labor activity.
Respectively, objective quantitative accounting of each employee’s deliverables is required. Therefore, specialization of the necessary indicators and quantitative criteria of efficiency of labor activity performed by the employee as of today is a mandatory prerequisite for conclusion of the employment contract between any employer and an employee admitted to the organization of the domestic budgetary sphere. These performance indicators and quantitative criteria are necessary for determination of the amount of incentive payments charged to each employee of the domestic budgetary sphere.
Using the rate setting system, it is necessary to ensure solution of a complex of social problems, implying formation of favorable opportunities to increase the level of satisfaction of all public sector employees with the contents of labor activity and labor conditions, as well as to activate employee's labor and intellectual potential.
Thus, one can say that well-developed labor rate setting is currently the basis for efficient and stable functioning of individual domestic budgetary sphere institutions. Also, rate setting system can have a significant impact in modern conditions on the process of institutionalization of social and labor relations, as well as of economic relations in the domestic budgetary sphere.
Various labor standards (time rate, production rate) are used for determination of the amount of work performed by each employee. In its turn, various labor standards in modern conditions are used for calculation of the level of labor intensity of the performed works, for determination of the required number of employees of the budgetary institution and formation of the manning table in the institution. Besides that, labor standards are used for calculation of the cost of employer's expenditures for various types of work performed, i.e., for calculation of the payroll budget required by the institution.
Establishment of labor rate setting system in the budgetary institution is aimed at achievement of the following objectives:
Achievement of the level of workload of the personnel of the institution optimal for it;
Perfection of the set of labor processes and algorithms in which employees of the institution are involved;
Increase of the quality level of various services rendered by public sector institutions due to optimal labor organization.
Each domestic state (municipal) institution should develop a "Regulation on labor rate setting system of the institution". Besides that, each of these institutions should implement the system of scientifically based labor activity rate setting. The main tasks of implementation of this system in domestic budgetary institutions are:
Creation of conditions necessary for improvement of labor management in domestic budgetary institutions;
Ensuring of normal level of labor intensity for employees in budgetary institutions when performing various works, as well as in course of provision of state and municipal services;
Increasing of quality level of rendered services;
Increase of satisfaction of services consumers (students, patients, and parents, legal representatives of students or patients) with the quality of these services;
Ensuring efficient use of budgetary funds and funds earned by the institutions.
Introduction of modern systems of labor activity rte setting in domestic budgetary institutions has become one of the key stages of works on reforming the previously existing remuneration plan. It’s indeed employee compensation that forms a significant share of costs of domestic budgetary institutions. At the same time, quality level of various services rendered by budgetary institutions largely depends just on the human factor. Accordingly, improvements of organization of labor activity of employees of domestic budgetary institutions, as well as matching of time spent by employees with the achieved deliverables and with the amount of labor remuneration in modern conditions are necessary for optimization of rendering services by budgetary institutions to the population.
Formation of systems of labor activity rate setting in domestic budgetary institutions should be carried out taking into account a set of labor standards established by federal branch ministries.
Organization of all types of works on labor activity rate setting of employees of budgetary institutions may be carried out by the head of the budgetary institution. Besides that, in accordance with the established procedure, the head of the budgetary institution may assign these activities and organizational and technical measures on labor rate setting to one of his deputies.
Development of the system of labor activity rate setting within the frameworks of a specific budgetary institution should be carried out by those specialists possessing a set package of necessary knowledge, skills and abilities in the sphere of organization of labor activities and personnel labor rate setting. These can be individual employees of the budgetary institution, a specialized structural unit of the budgetary institution or specialists from a third-party organization.
The plan was approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 509 from September 30, 2013 for development of standard branch and inter-branch work quotas. In accordance with the requirements of this plan, a wide list of standard labor guidelines was developed in 2014 for various categories of employees. The developed standard guidelines should be used for quantitative regulation of uniform works, execution of which involves use of standard technological processes and performance of standard labor operations. One should keep in mind that standard norms are used for rate setting of works performed in standard organizational and technical conditions, within the frames of the respective branch of the domestic economy.
Analytical method is the main method of rate setting of works performed in budgetary institutions. Within the framework of this method, such standardization tools are used as labor activity time schedule, labor activity photo chronometry and photographs of the working day. Besides that, various mathematical and statistical tools are used within the framework of the analytical method of rate setting.
In accordance with the legal requirements, labor relations between employers and all employees in the Russian budgetary sphere are based on the condition of signing of the “performance-based contract of employment”. Performance-based contract of employment is a special system of measures aimed at ensuring a decent level of wages to all engages in the domestic public sector.
The structure of wages in accordance with the model of a performance-based contract of employment involves taking into account each employee’s labor contribution to the activities of the budgetary institution, which necessitates introduction of a system of personnel labor rate setting labor in each institution. At the same time, large-scale spread of remote format of labor activity entails the gap between labor standards currently in force in budgetary institutions and actual labor costs of the employees.
Accordingly, it is necessary to improve the existing practice of labor rate setting in the budgetary sphere and to update the existing guidelines, taking into account possible use of the remote mode of performance of labor functions by the employees. It is expedient to use microelement rate setting for development of new work time standards in budgetary institutions.
In the context of large-scale introduction of remote work in state and municipal institutions, it is reasonable to carry out microelement rate setting of labor activity of various categories of specialists. The main advantage of the practice of labor activity microelement rate setting is the possibility of calculation the standards for performance of various operations without carrying out large-scale research. Microelement rate setting is performed using special computer programs, through which various labor processes are designed, as well as various labor standards are substantiated and calculated.
When performing microelement rate setting of labor activity, the specific labor process is decomposed or is divided into separate elements. Intrinsically, these elements of the labor process are labor movements of the employee isolated from each other or complexes of labor movements. Having divided the labor process into separate elements, it is necessary to consistently perform quantitative analysis and description of each selected element of the labor process.
After a certain technologically correct and optimal sequence of specific works performance is set, the optimal work pace for each process is established. After that, elimination of unnecessary operations and movements is carried out. Thus, rationalization of the investigated labor process takes place.
Within the frames of microelement rate setting, labor process is subdivided into such elements as single movement of certain limbs, their parts or of the entire body of the operator engaged in his work. Such operator’s actions can be called motions or labor movements.
Motions can be united into complexes of individual motions. Complexes of motions are continuously performed; these complexes have the same labor objective and are constant during the time used for achievement of this labor objective. The identified complex of certain motions is called labor action in the context of microelement rate setting.
Operator’s labor actions are grouped into certain working practices. After that, complexes of certain working practices are grouped into process operations.
It is most expedient to develop the description of a specific technological process in compliance with the following algorithm: process operation - working practice - labor action - motion.
Microelement rate setting of labor activity of budgetary institution employees working remotely will make it possible to decompose the performed working processes and calculate time-dependent rates of performance of specific process operations.
Discussion
The authors of the article try to simulate the consequences of the labor market "Covid" transformation. In authors’ opinion, as of today, the necessity is obvious of clarification, detailed elaboration and verification of the standards of performance of various state and municipal services, taking into account the quantitative indicators of their rendering established to his date.
Further areas of research may include models of optimization of domestic practice of labor rate setting in the budgetary sphere. The researchers could take into account the issues of the implementation of such specific definitions as both sustainability of digital management decisions (Barykin, Borisoglebskaya, Provotorov, Kapustina, Sergeev, De La Poza Plaza & Saychenko, 2021) and digital twins (Barykin, Bochkarev, Dobronravin & Sergeev, 2021; Barykin, Kapustina, Sergeev, Kalinina, Vilken, Putikhin & Volkova, 2021), as well as digital ecosystems development (Barykin, Kapustina, Kirillova, Yadykin & Konnikov, 2020; Barykin, Smirnova, Sharapaev & Mottaeva, 2021) regarding the standartization in the public service sector. Simulating a human capital management system with innovative characteristics in the digital economy considered in the works (Azarenko, Kazakov, Kulagina & Rodionov, 2020; Zemlyak, Sivakova & Nozdreva, 2021) is also important.
Conclusion
At present, a number of serious problems can be noted in the modern practice of rate setting for labor activity of employees of domestic public sector institutions. The authors suggest the approach of microelement rate setting of labor activity of budgetary institution employees working remotely.
A set of standardization activities in budgetary institutions is performed directly by these institutions. At the same time, the level of efficiency of standardization activities carried out by budgetary institutions is extremely low due to lack of competent personnel. Therefore, budgetary institutions hire various private organizations for performance of standardization activities. These organizations carry out works on labor rate setting in budgetary institutions based on requests announced by the customer (in particular, the budgetary institution). Thus, involving a private organization, each budgetary institution gets a real opportunity to influence the results of standardizing activities performed by a private organization. Such approach of budgetary institutions to performance of standardization activities results in the system of labor rate setting formed in the institution to become a tool, making possible to reduce or, on the contrary, to increase the number of individual full-time employees working in the institution.
Such problem should be noted as the level of quality of standardizing works services provided by various private organizations. So, individual private organizations do not calculate the indicators necessary to register actual working hours when performing standardizing works; rate setting of labor operations can be carried out without visiting specific budgetary institutions. As the result, distortion of current situation in budgetary institutions takes place in the reports of standardizing organizations. However, since labor rate setting today is not a type of commercial activity subject ti licensing, it is impossible to effectively control the quality of standardizing operations performed by private organizations.
Taking into account large scale introduction of remote work into the activities of employees of state and municipal institutions, the following aspects of labor rate setting activities need to be developed.
Firstly, to this date, there are no decisions on regulation and subsequent application of methods and specific methods of calculation and further establishment of the identified work time standards with regard to specific categories of employees in the context of remote work circulation.
Secondly, as of today, there are no decisions on establishment of certain procedures and conditions for consistent introduction of labor activity standards with regard to remote work of individual specialists, as well as in respect to individual workplaces.
Thirdly, as of today there are no decisions on establishment of certain procedures and conditions for replacement and revision of the existing work time standards, as far as the practice of remote work of specialists of budgetary institutions is being introduced.
Finally, to this date, there are no decisions determining specific measures aimed at maximum compliance with previously established work time standards for employees of domestic budgetary institutions.
Funding
The article has been prepared based on the results of studies supported by budgetary funds in accordance with the state order for the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation on the topic «Organization and methodology for the rationing of work (services) performed in the budgetary sphere of the education system, health care and culture, taking into account the digitalization of the economy and an increase in the share of remote (remote) work».
References
Azarenko, N., Kazakov, O., Kulagina, N., & Rodionov, D. (2020). The model of human capital development with innovative characteristics in digital economy. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 940(1), 0–16.
Barykin, S.Y., Kapustina, I.V., Kirillova, T.V., Yadykin, V.K., & Konnikov, Y.A. (2020). Economics of digital ecosystems. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(124), 16. .
Barykin, S.Y., Smirnova, E.A., Sharapaev, P.A., Mottaeva, A.B. (2021). Development of the Kazakhstan digital retail chains within the EAEU E-commerce. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20(2), 1–18.
Barykin, S.E., Borisoglebskaya, L.N., Provotorov, V.V., Kapustina, I.V., Sergeev, S.M., De La Poza Plaza, E., & Saychenko, L. (2021). Sustainability of management decisions in a digital logistics network. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(16), 9289. .
Barykin, S.Y., Bochkarev, A.A., Dobronravin, E., & Sergeev, S.M. (2021). The place and role of digital twin in supply chain management. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20, 1–19.
Barykin, S.Y., Kapustina, I.V., Sergeev, S.M., Kalinina, O.V., Vilken, V.V., Putikhin, Y.Y., & Volkova, L.V. (2021). Developing the physical distribution digital twin model within the trade network. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 20, 1–24.
Bruce-Hickman, K., Fan, K., Plaat, F., & Sheth, S. (2020). Decision-making on the labour ward during the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia, 45. .
Carillo K., Cachat-Rosset, G., Marsan, J., Saba, T., & Klarsfeld, A. (2020). Adjusting to epidemic-induced telework: Empirical insights from teleworkers in France. European Journal of Information Systems, 30. .
Deakin, S., & Novitz, T. (2020). Covid-19, labour law, and the renewal of the social state. Industrial Law Journal, 49, 493-496. .
Handwerker, E., Meyer, P., Piacentini, J., Schultz, M., & Sveikauskas, L. (2020). Employment recovery in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Monthly Labor Review.
ILO. (2020). Teleworking during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond: A practical guide.
Lee, S., Schmidt-Klau, D., & Verick, S. (2020). The labour market impacts of the COVID-19: A global perspective. The Indian Journal of Labour Economics, 63, 11-15. .
Crossref, Google scholar, Indexed at
Mayhew, K., & Anand, P. (2020). COVID-19 and the UK labour market. Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 36, 215-224.
McCulley, L. (2020). Lockdown: Homeworkers putting in extra hours -instant messaging up 1900 %..
Okubo, T., Inoue, A., & Sekijima, K. (2020). Teleworker performance in the COVID-19 era in Japan. Asian Economic Papers, 1-37. .
Sankaran, K. (2020). Emerging perspectives in labour regulation in the wake of COVID-19. The Indian journal of labour economics: The quarterly journal of the Indian Society of Labour Economics, 63, 1-5. .
Crossref, Google scholar, Indexed at
TUC. (Trades Union Congress). (2020). COVID-19 Coronavirus guidance to unions. London: TUC.
WHO (World Health Organization). (2020). WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19, 11.
Zemlyak, S.V., Sivakova, S.Y., & Nozdreva, I.E. (2021). Risk assessment model of government-backed venture project funding: The case of Russia. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24(1), 1–12.
Received: 16-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. JMIDS-21-8828; Editor assigned: 18-Dec-2021, PreQC No. JMIDS-21-8828 (PQ); Reviewed: 07-Jan-2021, QC No. JMIDS-21-8828; Revised: 27-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. JMIDS-21-8828 (R); Published: 16-Jan-2022