Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 2
Testing the Reliability of the Banking Service Quality: A Case Study of Commercial Banks in Vietnam
Phan Dien Vy, Banking University of Ho Chi Minh City
Phan Thanh Tam, Lac Hong University
Abstract
Nowadays, commercial banks have become an indispensable financial institution to operate the economy. Still, the state-owned commercial banking system is also considered an effective arm of the Government in implementing monetary policy to stabilize the macro-economy, curb inflation, and ensure its social security. Besides, the quality of banking services plays a significant role. It is understood as banking operations in terms of capital, currency, the bank’s payment to customers to meet business needs, profit, living life, and storing property. Therefore, this study objective testing the reliability of the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam. The study surveyed 900 customers related to commercial banks, but 765 samples processed and answered 39 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to November 2020. The authors tested Cronbach’s Alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) for the banking service quality.
Keywords
Banking, Service, Quality, Commercial, Bank, BUH, and LHU.
Introduction
According to Anouze & Alamro (2019), most banks thought the bank was a financial industry, not a service industry. Therefore, their competitive tendencies are based on financial ability rather than service quality. They devote human, material, time, and system resources to financial management rather than customer and service management. According to Aldaibat & Irtaimeh (2012), research on challenges for the Banking and Finance sector of Vietnam in the integration framework, experts have concluded: “one of the two challenges is the fierce competition in service quality.” Besides, the development strategies of Vietnamese commercial banks are in the coming years. Industry leaders have commented that improving service quality is a vital issue in the competition of the financial services industry. And Therefore, service quality with the banking industry has been and is being focused on customers. In the future, it will also be an essential highlight for banks to focus on investing resources to build customer relationships. Sustainable attracting potential customers and developing stably by Aneesh et al. (2014).
In recent years, besides the results achieved, the provision of banking services is still limited. Each service and the commercial bank even has not built many separate brands, the scale of each service is small, the service quality is low, the competitiveness is weak, especially the utility of some services (Baker et al., 2020). Customers are not high, while the bank’s marketing activities are still limited, so the percentage of customers accessing and using banking services is still low. For a modern and developed bank like a foreign country, service activities have developed very strongly. Revenue from service activities accounts for a large proportion and has a particular impact on the bank. Stemming from this fact, the study of factors affecting the quality of banking services of commercial banks in Vietnam will have high practical significance as a scientific basis for the implications.
Literature Review
Banking Service Quality (DNCS)
According to Cheserek et al. (2015), Banking service is a process of back-end and front-end activities where customers service providers interact with each other. The purpose of this interaction is to satisfy the customer’s needs and wants in the way the customer expects and create value for the customer (Cronin & Taylor, 1992).
According to Prasad & Bhavani (2015), Service quality is synonymous with meeting customers’ expectations, satisfying customers’ needs. Therefore, the customer’s service quality is determined by the customer and is a subjective category because it depends on the customer’s needs and expectations (Gronroos, 1984). The same level of service quality, but different customers will feel differently, and even the same customer sometimes feels different at other times, different stages by Igaz & Ali (2013).
According to Islam & Ali (2011), Banking service quality is a concept that refers to the level of characteristics of banking products and services to satisfy the different needs of customers. Each type of banking service feature needs to meet customers’ requirements and provide timely and secure banks and customers (Fragoso & Espinoza, 2017). Customer requirements depend on the service consumer’s purpose, income, the level of awareness, and the customer’s knowledge (Kotler & Keller, 2006; Kotler, 2000). Banking products and services are considered an intangible commodity, requiring a certain level of understanding of both the supplier and the customer. Moreover, to provide banking services, it is necessary to have the application of technology. The quality of banking services should always be maintained and improved by Lau et al. (2013).
Reliability (Rel)
According to Islam & Ali (2011), reliability speaks volumes about providing accurate, punctual, and reputable services. This factor requires consistency in delivery and respect for commitments and promises to customers. Besides, reliability can perform services as committed to customers, keep the information confidential, and specific customers’ assets. According to Cheserek et al. (2015), that commercial banks have a high degree of credit, always doing what commercial banks have committed, all questions. Making customers’ complaints are cared for and solved satisfactorily by commercial banks and customers’ information is kept confidential will increase banking services quality (Lau et al., 2013). With those as mentioned above, the researchers have hypothesis following:
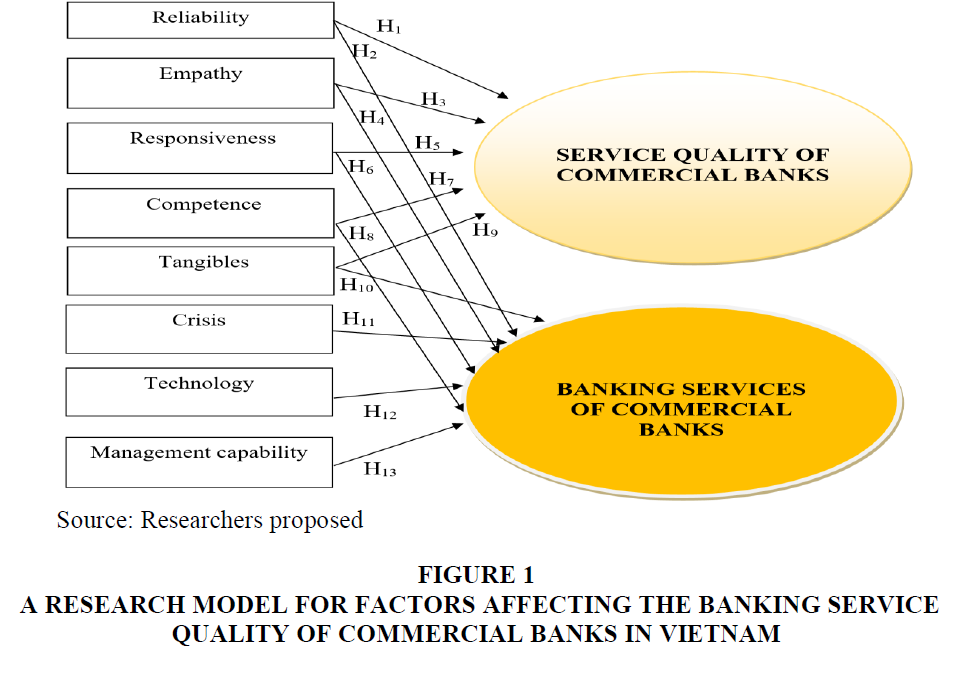
H1 Reliability has a positive relationship with the service quality of commercial banks
H2 Reliability has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Empathy (Emp)
According to Amin & Isa (2008), empathy is caring and caring for customers, giving customers the best thoughtful treatment that can help customers feel like “high customers. “from the bank and always warmly welcomed any time anywhere. The people factor is the core of this success, and the more a bank’s interest in customers and the more sympathy will increase (Parasuraman et al., 1985). According to Ahmed (2017), empathy is the employee’s attention and care to customers, the friendly, enthusiastic, and fair treatment of all customers. Customers want commercial banks to take care of themselves, their families, and understand their particular needs and interests. Employees care about customers. Employees understand the unique needs and benefits that customers want to promptly meet customers’ needs (Parasuraman et al., 1988). For the things mentioned earlier, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H3 Empathy has a positive relationship with the service quality of commercial banks
H4 Empathy (Empathy) has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Responsiveness (Res)
According to Rakesh (2012), the response level: this is the criterion that measures the ability to solve problems quickly, effectively handle complaints, ready to help customers and respond to customer’s request. In other words, responsiveness is the service provider’s level of response to what the customer wants (Tsoukatos & Evmorfia, 2010). The response level is the desire and willingness to help of the staff providing timely service to customers. According to Islam & Ali (2011), do commercial banks offer customers complete, convenient, and accurate information, can solve problems quickly, handle complaints effectively, and respond to meet customer requirements or not. In the course of a transaction, when there is any change of information, commercial banks promptly notify customers (Yaseen & El Qirem, 2018). The researchers have hypothesis following:
H5 Responsiveness has a positive relationship with the service quality of commercial banks
H6 Responsiveness has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Competence (Com)
This factor is the factor that creates the trust and trust of customers through professional service, sound professional knowledge, polite demeanor, and ability. Good communication, so customers feel secure every time they use the bank’s services (Payne et al., 2018). Service capacity is expressed through professional qualifications to perform the service. Serviceability manifests itself when employees interact with customers; employees directly perform the service and research to capture relevant customer service information (Ahmed, 2017). The mentioned above, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H7 Competence has a positive relationship with the service quality of commercial banks
H8 Competence has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Tangibles (Tan)
According to Prasad & Bhavani (2015), those tangible means are the facilities’ external image, the attitude of staff, documents, manuals, and information systems. Bank contact. Generally speaking, everything that customers see directly with the eyes and senses can affect this factor (Moyo, 2018). Tangible means are shown through the service staff’s appearance, costumes and facilities, and equipment for the service. The mentioned above thing, the researchers, have hypothesis following:
H9 Tangibles have a positive relationship with the service quality of commercial banks
H10 Tangibles have a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Crisis (Cri)
According to Amin & Isa (2008), the crisis factor is an intact lesson from the 2008-2009 global economic crisis is the historical crisis, a prolonged economic recession. The worst and most serious since the Great Depression of the 1930s. The collapse of investment bank Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, was the largest bankruptcy in the world’s history by Ngwu et al. (2019). This factor is also a fairly significant factor related to service quality included in the research model. The mentioned above thing, the researchers, have hypothesis following:
H11 Crisis has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Technology (Tec)
According to Devesh (2019), the technological factor representing the industrial revolution 4.0 has been happening fast, affecting all aspects of the globe, including Vietnam. Banking is one of the sectors considered to be the most strongly influenced by the industrial revolution of 4.0. Still, this new wave of technology is creating remarkable changes in the financial and banking sectors, significantly changing the distribution channel and traditional banking products and services (Yaseen & El Qirem, 2018). The mentioned above thing, the researchers have hypothesis following:
H12 Technology factor has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
Management Capacity (Man)
Governance capacity is a crucial factor in the banking sector. If banks want to keep up with the industrial revolution 4.0, banks must change their operation by applying banking management software. Banks need to create added value by quality, performance, process. According to Yaseen & El Qirem (2018), banking governance in the era of technology 4.0 requires management levels to improve. Improve management capacity in strategic management, finance, human resources, services, and marketing (Ngwu et al., 2019). The mentioned above thing, the researchers, have hypothesis following:
H13 Management capacity has a positive relationship with the banking services of commercial banks
A research model for factors affecting the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam following (Figure 1):
Figure 1 A Research Model for Factors Affecting the Banking Service Quality of Commercial Banks in Vietnam
Methods of Research
The research process is done through steps: The authors researched and synthesized the theoretical bases and related studies at home and abroad, thereby building the research model. After having a research model, the authors formed an expected scale, examined the model and scale, and collected preliminary data to assess the scale’s reliability and value preliminarily. After primary completion, the authors collected official data to test the research model and hypothesis. Finally, the authors give conclusions and suggest policy implications to improve the quality of commercial banking services (Hair et al., 2010).
By synthesizing references, authors are researching at the table to find out the concept related to banking services quality. The criteria measured the quality of banking services and the factors affecting the quality of commercial banking services. The author examined and screened the variables in the evaluation model for the quality of banking services. Qualitative research is conducted to check the appropriateness of the theoretical model, and at the same time, help discover, adjust, and supplement the questions used to measure research concepts to ensure an appropriate building scale consistent with research theory.
The research model’s original scale is based on the theory outlined in the above-mentioned studies as a basis for qualitative research. This method is used to adjust the scales, forming questionnaires to interview customers using banking services. Qualitative research is used in the discovery phase, in which data is collected in qualitative form through discussion and interpretation techniques (Hair et al., 2010). Exploratory research to clarify the problem of preliminary research unknowns is a common way to reduce data collection errors and scale errors and increase the answer sheets’ validity.
The authors conducted a group discussion with 30 managers, and during the debate, the authors gave his original scale design to survey the opinions of 30 managers. For this thesis topic, qualitative research is done through interviews to get views on the scales through in-depth interviews with 30 managers. In this study, the authors used a qualitative research method to evaluate factors affecting commercial banking services quality through group discussion of 30 managers of commercial banks’ branches in Dong Nai province. The group discussion results showed that eight factors affect the quality of commercial banking services in Dong Nai. Effects of group discussion of 30 managers agreed and added some details with the scales.
The study surveyed 900 customers related to commercial banks, but 765 samples processed and answered 39 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to November 2020. The authors applied simple random sampling, tested Cronbach’s Alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and experimented with Structural Equation Model (SEM) by Hair et al. (2010).
Finally, the purpose of confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) helps the authors to clarify. Authors tested Chi-square testing is P-value > 5%; CMIN/df ≤ 2.0, some cases CMIN/df maybe ≤ 3.0 or < 5.0; GFI, TLI, CFI ≥ 0.9. GFI is still acceptable when it is greater than 0.8; RMSEA ≤ 0.08.
Research Results
Testing Cronbach’s alpha for factors affecting the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam following:
Table 1 showed that all of Cronbach’s Alpha is greater than 0.7. Besides, the research results are very consistent with the data set and eligible for the next steps.
| Table 1 Cronbach’s Alpha for Factors Affecting the Banking Service Quality of Commercial Banks in Vietnam | |
| Reliability (Rel), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.959 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Rel1: You feel secure when using the services at the bank | 0.941 |
| Rel2: The bank’s employees made the transactions accurately and without errors | 0.958 |
| Rel3: The bank always delivers service at the right time when it commits itself to the customer | 0.950 |
| Rel4: The bank has a high reputation in the heart of customers | 0.935 |
| Empathy (Emp), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.871 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Emp1: Bank employees always build good relationships and meet customers’ needs | 0.845 |
| Emp2: Bank staff are always enthusiastic and friendly to customers | 0.807 |
| Emp3: Bank staff always serve fairly and conscientiously to all customers | 0.861 |
| Emp4: The bank always asks, congratulates, gives gifts to customers on major holidays of the year | 0.825 |
| Responsiveness (Res), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.964 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Res1: The Bank always satisfies all difficulties, questions, and complaints of customers | 0.940 |
| Res2: Time for customers to wait for their transactions is less than 5 minutes at the Bank | 0.964 |
| Res3: Simple, fast, and effective transaction execution procedures and processes at the Bank | 0.960 |
| Res4: The bank always has a hotline to serve customers | 0.944 |
| Competence (Com), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.951 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Com1: Employees handle transactions properly, quickly, and effectively at the bank | 0.929 |
| Com2: Bank staff have full knowledge and professional capacity to advise and answer customers’ questions |
0.942 |
| Com3: Bank staff are always polite, considerate, and warm to all customers | 0.940 |
| Com4: Bank staff always keep customers’ information confidential and professional ethics | 0.930 |
| Tangibles (Tan), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.957 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Tan1: The Bank has a spacious head office, convenient for customers to transact | 0.806 |
| Tan2: The Bank has a system of modern equipment and machines | 0.816 |
| Tan3: Papers, forms, vouchers used in banking transactions are designed to be simple, straightforward, and easy to implement |
0.847 |
| Tan4: Bank staff have a very professional manner and dress neatly and politely when communicating with customers |
0.803 |
| Crisis (Cri), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.945 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Cri1: The Covid-19 pandemic has changed the perception of customers when using banking services | 0.932 |
| Cri2: The Covid-19 pandemic changed the behavior of technology use | 0.887 |
| Cri3: The Covid-19 pandemic created many difficulties and challenges for banks and increased terrible debt |
0.939 |
| Technology (Tec), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.910 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Tec1: Industry 4.0 has far-reaching effects on banking services | 0.908 |
| Tec2: The bank changes in digital banking products and services to meet customer needs | 0.884 |
| Tec3: Banks invest in modern infrastructure and technology systems | 0.910 |
| Tec4: The bank has a risk management system in digital banking | 0.868 |
| Tec5: The bank has a Big Data application in the banking | 0.872 |
| Management capability (Man), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.952 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Man1: The bank has the policy to attract high-quality human resources in the technology sector | 0.929 |
| Man2: The bank has a professional staff training and development policy | 0.942 |
| Man3: The Bank has a policy of maintaining human resources in the 4.0 era | 0.944 |
| Man4: The Bank always pays attention to the knowledge, skills, and attitudes of its employees and employees when dealing with customers |
0.931 |
Table 2 showed that all of Cronbach’s Alpha is greater than 0.7. Banking services (BS) has Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.946, and Service Quality (SQ) has Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.873.
| Table 2 Cronbach’s Alpha for the Banking Service Quality of Commercial Banks | |
| Banking services (BS), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.946 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| BS1: The crisis factor ultimately affects banking services | 0.937 |
| BS2: Technology factors ultimately affect banking services | 0.890 |
| BS3: Management capacity factor ultimately affects banking services | 0.938 |
| Service quality (SQ), Cronbach’s Alpha: 0.873 | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| SQ1: In general, you highly appreciated the service quality at the bank | 0.857 |
| SQ2: You will introduce to friends and relatives about banking services in the future | 0.808 |
| SQ3: You will continue to use banking services in the future | 0.860 |
| QS4: In general, you highly appreciated the banking services | 0.822 |
Table 3 showed that column “P” <0.01 with significance level 0.01. This result indicated that eight factors affected commercial banks’ banking service quality in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01. Testing Bootstrap of 10.000 samples for (Mean, Bias) factors affecting the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam. Testing Bootstrap of 10.000 showed that the value of “SE-Bias” <0.01. This result indicated that eight factors affected commercial banks’ banking service quality in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01.
| Table 3 Factors Affecting the Banking Service Quality of Commercial Banks | |||||||
| Relationships | Coe. | Standardized Coefficient | SE. | CR. | P | ||
| QS | <--- | Emp | 0.165 | 0.159 | 0.034 | 4.779 | *** |
| QS | <--- | Res | 0.078 | 0.169 | 0.015 | 5.087 | *** |
| QS | <--- | Tan | 0.096 | 0.178 | 0.019 | 5.122 | *** |
| QS | <--- | Com | 0.060 | 0.125 | 0.016 | 3.775 | *** |
| QS | <--- | Rel | 0.239 | 0.477 | 0.019 | 12.729 | *** |
| BS | <--- | Emp | 0.187 | 0.097 | 0.057 | 3.267 | 0.001 |
| BS | <--- | Tec | 0.139 | 0.089 | 0.049 | 2.857 | 0.004 |
| BS | <--- | Cri | 0.096 | 0.080 | 0.033 | 2.936 | 0.003 |
| BS | <--- | Tan | 0.171 | 0.172 | 0.032 | 5.384 | *** |
| BS | <--- | Com | 0.076 | 0.085 | 0.027 | 2.829 | 0.005 |
| BS | <--- | Rel | 0.489 | 0.528 | 0.030 | 16.429 | *** |
| BS | <--- | Man | 0.080 | 0.085 | 0.030 | 2.644 | 0.008 |
| BS | <--- | Res | 0.080 | 0.093 | 0.025 | 3.191 | 0.001 |
Conclusions
In the current fierce competition between banks, increasing service quality is considered the foundation of the banks’ competitive strategy to attract and retain customers. Therefore, the research and analysis of the factors affecting banking service quality. The study surveyed 900 customers related to commercial banks, but 765 samples processed and answered 39 questions. The data collected from July 2020 to November 2020. The authors tested Cronbach’s Alpha, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) for the banking service quality. Finally, eight factors affect the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam with a significance level of 0.01. Besides, research results are an essential scientific basis for commercial banks to increase commercial banks’ service quality in Vietnam. Commercial banks should pay attention to factors in the following: Reliability (Rel), Empathy (Emp), Responsiveness (Res), Competence (Com), Tangibles (Tan), Crisis (Cri), Technology (Tec), and Management capability (Man).
Policy Implications
Based on the results mentioned above, to enhance the banking service quality of commercial banks in Vietnam.
(1) Policy implication for reliability. Commercial banks should improve human resources quality and have a long-term strategy for developing high-quality human resources. Because according to the principle of man is the decisive factor. Banks need to improve service quality before integration requirements. It is necessary to improve the quality of human resources and improve the bank’s professional qualifications in the bank, in all branches. To adopt policies to attract talented people, talented people, and capable people in banking services from other banks, other components, and domestic and foreign universities. The central attraction policy is the remuneration policy, the arrangement and use, the promotion of the expertise and working atmosphere in the branch. Boldly apply the model of hiring foreign experts in the banking service sector to work at the bank.
(2) Policy implication for empathy. Commercial banks should improve the level of banking technology modernization. On the one hand, it is suitable for the bank’s financial potential, consistent with its technology’s common ground, but must ensure the region’s general trend and the world. Be aware that service quality depends on this second most crucial factor: the level of technology. There is a qualified and qualified staff, but the machinery and equipment system are not modern. The technological level is not advanced. It is impossible to make a system of high quality and prestigious banking services to provide to customers.
(3) Policy implication for responsiveness. Commercial banks should improve the quality of governance and internal inspection and control. This work must be regularly raised to a level of modern technology. At the same time, it is necessary to periodically review the processes and internal regulations in the branch to complete, supplement, upgrade, and avoid loopholes that are easily exploited.
(4) Policy implication for competence. Commercial banks should improve to collect feedback from customers. Timely assess the opposite information. Customer opinions should be respected by the bank, preferably a letter of thanks, and a policy of encouraging customers. The comments are valuable and have practical meaning that should reward customers.
(5) Policy implication for tangibles. Commercial banks should improve personnel allocation appropriately, and creating motivation for employees is also a measure to improve bank employees’ working efficiency. For employees performing non-credit services, it is necessary to have a selection process according to the employee’s wishes, the requirements of the job, and there is a regular assessment of job suitability. doing with that employee. To motivate employees to work, the bank may be interested in staff remuneration with salaries, bonuses, and welfare regimes - additional health care benefits for relatives of employees, such as husbands or children.
(6) Policy implication for a crisis. Commercial banks should look directly at the fact that even if they offer many programs to improve their services’ quality, it is not wholly ineffective, somewhat uncontrollable. All changes in reality. Although service quality is something that is not easy to raise, taking responsibility is something that should be made more substantial. Commercial banks should plan the mission, core values , and culture that have not been placed in each employee’s heart. Saying this may seem forced and forced, but the fact that he was an employee of an organization and did not consider himself there without the determination to contribute his best to the organization is not worthy to stand in that line. Customers who see a bank that values brand and image will feel more secure.
(7) Policy implication for technology. Commercial banks should improve to invest deeply in technology and information technology (IT) systems. A bank with the right technology, good management, and security systems for both customers and employees will always operate smoothly and promptly to meet customers’ changing needs. Along with that, a good design will help the bank minimize the risks that may be encountered.
(8) Policy implication for management capability. Commercial banks should enhance retraining, and monitoring the training quality is the key. The bank gives its employees a one-course training session, the employees themselves complete the tests, but then they go back to it. Employees themselves just want to pass the course, pass the test, and then do the coping, then the training is just like not. Must strictly control after training, find it not okay to retrain to improve the quality of staff. Improving the service quality for customer care of each bank is an indispensable development strategy to help customers become more engaged, make more transactions, and introduce the bank to many other customers who make an essential contribution to banks’ sustainable development.
References
- Ahmed, M. (2017). Service quality measurement regarding banking sector. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 8(6), 116-127.
- Aldaibat, B.F., & Irtaimeh, H. (2012). The role of strategic human resource management at Jordanian banking sector through implementation total quality management (TQM). European Scientific Journal, 8(25), 1-14.
- Amin, M., & Isa, Z. (2008). An examination of the relationship between service quality perception and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 1(3), 191-209.
- Aneesh A., Dileeplal J., & Abraham M. (2014). An integrated fuzzy weighted Servqual-QFD approach for service quality improvement. International Journal of Engineering Research, 3(12), 774-776.
- Anouze, A.L.M., & Alamro, A.S. (2019). Factors affecting intention to use e-banking in Jordan. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 38(1), 86-112.
- Baker, S., Bloom, N., Davis, S., & Terry, S. (2020). Covid-induced economic uncertainty. National Bureau of Economic Research, 3(2), 13-23.
- Cheserek, L.K., Kimwolo, A.K., & Cherop, F. (2015). Effect of quality financial services on customer satisfaction by commercial banks in Kenya. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 5(7), 102-112.
- Cronin, J.J., & Taylor, S.A. (1992). Measuring service quality: A reexamination and extension. Journal of Marketing, 56(3), 55-68.
- Devesh, S. (2019). Service quality dimensions and customer satisfaction: empirical evidence from retail banking sector in Oman. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 30(15-16), 1616-1629.
- Fragoso, J.T., & Espinoza, I.L. (2017). Assessment of banking service quality perception using the SERVPERF model. Contadur