Review Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 1
Talent Acquisition Strategies in the Digital Age Leveraging Technology for Recruitment Success
Balagouda Patil, Dayananda Sagar Business School, Bangalore
Parag Kalkar, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, Maharashtra
Sanjay Pareek, IIM Sirmaur, Himachal Pradesh
Anindita Das, Astha School of Management, Bhubaneswar, Odisha
Shikha Tewari, Graphic Era Hill University, Haldwani Campus
Pramila S., Christ University, Bangalore, Karnataka
Citation Information: Patil, B., Kalkar, P., Pareek, S., Das, A., Tewari, S., & Pramila, S. (2024). Talent acquisition strategies in the digital age leveraging technology for recruitment success. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(1), 1-12.
Abstract
Talent acquisition in today's fast-paced digital world has changed drastically due to new technologies and different expectations from candidates. Innovative digital tactics are becoming more and more important for organizations throughout the world when it comes to attracting, evaluating, and retaining top people. This change is more than just implementing new software; it signifies a complete overhaul of how recruitment may make use of technology for optimal results. Talent acquisition in the modern digital era makes use of data analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence (AI) to simplify tasks that used to require a lot of human effort. These days, AI algorithms find the best applicants by combing through mountains of application data, while automated systems take care of mundane but necessary jobs like setting up interviews and communicating with prospects afterward. Not only can these technologies shorten the hiring process, but they also make it more accurate and fair by reducing the impact of human prejudice. In order to improve recruitment results in the modern day, this study investigates how companies use technology. Automated and AI-powered applicant screening and process automation drastically cuts down on time-to-hire while simultaneously raising the bar for quality candidates, according to the study's findings. More accurate assessments and an improved applicant experience are the results of digital technology, which in turn increases engagement and retention. Recruiting in the digital era allows for easy communication and application processes, appealing to a pool of candidates that are comfortable using mobile devices. In order to gain a competitive edge in talent acquisition and bring recruitment processes up to date, this study examined the revolutionary power of digital technology. The main aim of the study is to explore & analyze talent acquisition strategies in the digital age leveraging technology for recruitment success & to check hypothesis - significant relationship between digital age leveraging technology based talent acquisition strategies & recruitment success. The chi-square test & likert scale analysis has been used for results.
Keywords
Talent Acquisition, Digital Age, Technology, Recruitment, Success.
Introduction
The field of talent acquisition has experienced a significant transition due to developments in technology and growing applicant expectations in today's fast-changing digital environment. Organizations globally are progressively utilizing inventive digital approaches to efficiently attract, evaluate, and retain highly skilled individuals. This transformation is not only about incorporating new technologies, but rather signifies a profound reconsideration of how recruitment might utilize technology to attain success.
Talent acquisition in the digital era utilizes artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and data analytics to simplify processes that were previously demanding and time-consuming. Currently, artificial intelligence algorithms are used to analyze large amounts of applicant data in order to select the most highly skilled individuals (Wildan, 2023). In addition, automated systems are responsible for handling repetitive chores like organizing interviews and sending follow-up emails. These technologies not only speed up the recruitment process but also improve its precision and impartiality by reducing human prejudice. In addition, the introduction of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) has completely transformed the way candidate assessments are conducted and how candidates are engaged. Virtual reality simulations enable recruiters to replicate authentic job situations, providing candidates with a direct encounter of the position and organizational environment. Augmented reality (AR), in contrast, superimposes digital information onto the physical environment, so altering the way candidates engage with job descriptions and corporate information.
Digital recruitment has become essential due to the widespread use of cellphones. Modern job seekers anticipate smooth application procedures and prompt communication via mobile platforms. Recruiters utilize mobile applications to advertise job openings, conduct virtual interviews, and maintain continuous communication with candidates, ensuring that the hiring process is easily accessible and convenient. Significantly, the use of data to inform decision-making has become a fundamental aspect of contemporary recruitment methods. Organizations examine extensive quantities of recruiting data to detect patterns, forecast future hiring requirements, and optimize their talent acquisition efforts. These insights empower recruiters to make well-informed decisions, customize recruitment efforts to target specific candidate categories, and constantly improve their strategy using real-time feedback and performance indicators. Social media has revolutionized the way companies present their image as employers and interact with potential job applicants. Social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram allow firms to display their company culture, values, and employee testimonies to a worldwide audience of potential applicants. Social media enables direct engagement with candidates, offering a platform for customized communication and fostering community development (Wan et al., 2024).
In the digital age, talent acquisition is distinguished by its capacity to combine advanced technologies with strategic human resource methods. By adopting digital transformation, firms not only streamline their recruiting procedures but also gain a competitive advantage in attracting top people in a fiercely competitive global market. As technology advances, the methods and instruments employed to recognize, evaluate, and include the workforce of the future will also progress.
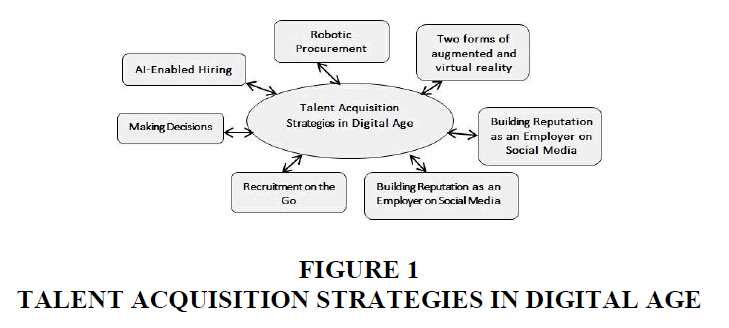
Talent Acquisition Strategies in Digital Age
In the era of digitalization, the process of acquiring talented individuals has experienced a substantial change, utilizing sophisticated technologies to improve the effectiveness of recruitment (Figure 1). Presented below are many significant strategies and technology that are now influencing the process of talent acquisition:
1. Employing automated technologies to retrieve applicants from many web platforms and databases according to predetermined criteria, hence reducing the need for manual sourcing and saving time and effort.
2. Utilizing digital technologies for conducting virtual interviews, creating immersive applicant assessments, and exhibiting company culture in order to improve the overall candidate experience and increase candidate engagement.
3. Employing artificial intelligence to screen resumes, match candidates, and use predictive analytics to streamline the hiring process and identify the most suitable individuals.
4. Examining recruiting data to enhance processes, enhance hiring results, and predict future talent requirements based on trends and patterns.
5. Utilizing mobile platforms and applications to advertise job openings, receive job applications, and communicate with prospects who are proficient in using mobile devices.
6. Utilizing social media platforms to establish and enhance a robust employer brand, interact with prospective recruits, and exhibit business culture and values.
7. Deploying CRM tools to cultivate relationships with candidates, sustain communication, and establish talent pipelines for future positions.
These tactics collectively optimize the effectiveness of recruiting, enhance the experience of candidates, and integrate talent acquisition activities with organizational goals in the digital era.
Review Literature
Andrade & Gonçalo (2021) investigated in the context of BRICS, with a specific emphasis on developing strategic skills. Andrade & Gonçalo (2021) investigated the impact of digital technologies on the strategic activities and capacities of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. Andrade & Gonçalo (2021) stressed the dynamic nature of digital transformation, emphasizing its impact on organizational strategy and competitiveness in emerging economies. The study conducted by Chauhan et al., (2022) examined the process of talent acquisition in the era of digitalization, with a specific emphasis on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation to improve the effectiveness of recruiting. (Chauhan, et al., 2022) investigated the utilization of these technologies to simplify recruitment processes, enhance decision-making, and maximize applicant sourcing. The study conducted by Chauhan et al., (2022) investigated the profound influence of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation on contemporary recruitment techniques, with a particular focus on how they improve the efficiency and efficacy of talent acquisition practices. In Hatum's (2013) article, the author explores the strategies employed by leading corporations in adapting to changing worker dynamics. The book, published by Springer, examines the methods and adaptations employed by prominent firms to successfully navigate and prosper in a swiftly evolving business environment. In Hatum's (2013) study, the author explores the difficulties brought about by technological progress, globalization, and changes in population demographics. The study provides valuable insights into how firms are adapting their strategies in people management, leadership development, and organizational culture to stay competitive and prepared for the future.
In his study, Kumar (2023) examined the principles and procedures of green accounting. The study examines the function of green accounting in evaluating environmental effects and incorporating sustainability factors into financial disclosure. In his study, Kumar (2023) analyzed the approaches and frameworks employed in green accounting, highlighting its significance in fostering corporate responsibility and environmental stewardship in business operations. The study conducted by Li, et.al. (2019) investigated the strategies employed by multinational corporations (MNCs) to oversee its research and development (R&D) workforce in China. The study conducted by Li et al. (2019) examined the correlation between people management strategies and strategic objectives. The authors explore the specific difficulties and approaches multinational corporations (MNCs) use to attract, nurture, and retain research and development (R&D) professionals in the Chinese market. They emphasize the significance of adjusting global talent management methods to fit the local environment in order to achieve organizational success. Leo conducted an investigation into talent management in the digital era, with a specific focus on the difficulties and advantages brought about by digital transformation. Leo explored how firms adapt to the changing landscape of talent acquisition, development, and retention in the face of technology innovations. Leo probably discussed methods for utilizing digital technologies and data-driven approaches to improve talent management procedures and stay competitive in the digital age. Mandia (2024) examined the influence of environmentally friendly packaging on consumer intentions during the current era of rapid change. The study investigated the impact of eco-friendly packaging on consumer behavior and purchase choices. In Mandia's (2024) study, the author examined the consequences of adopting sustainable packaging techniques for organizations that aim to meet customer preferences and sustainability objectives in a dynamic market environment.
The study conducted by Mukul et al., (2021) examined the impact of social capital on talent acquisition tactics in the Indian startup ecosystem. The study conducted by Mukul et al. (2021) examines the strategies employed by startups to utilize social networks, relationships, and connections in order to attract and retain talented individuals. The study conducted by Mukul et al. (2021) examined the importance of social capital in addressing resource limitations and promoting the development and creativity of organizations in India's dynamic and competitive startup ecosystem. The study conducted by Saadatmand et al. (2022) investigated the adoption of digital talent management strategies in Iran's mobile telecommunications industry. The study by Saadatmand et al. (2022) certainly gives a comprehensive framework or model that combines digital technology with talent acquisition, development, and retention tactics. (Saadatmand, et al., 2022) presumably examined the ways in which these digital changes improve efficiency, decision-making, and overall effectiveness of organizations in Iran's telecoms sector. Sen (2020) examined the strategic consequences of digital transformation in the field of human resources (HR). In Sen's (2020) study, the author examined the ways in which firms might utilize digital technology to transform their HR operations. The study specifically concentrated on key areas including recruitment, performance management, employee engagement, and learning and development. The book explored methods for incorporating digital technologies and data analytics to enhance HR procedures, enhance organizational flexibility, and facilitate lasting change in the ever-changing digital environment.
Thamage et al., (2021) examined the interplay between talent management practices, professional experience, promotional policies as well as competitive advantage. Thamage et al., (2021) investigated the impact of personnel management strategies and career progression regulations on the competitive advantage of mines in the mining industry. The study provided valuable information on how to improve personnel management procedures in order to boost the performance and strategic positioning of organizations in Botswana's mining sector. Teresa et al. (2024) investigated the impact of digital innovation on the development of learning organizations and the successful management of talent. The study conducted by Teresa et al. (2024) focused on highlighting methods to include digital advancements, such as e-learning platforms, AI-based learning analytics, and virtual reality technologies, in order to adjust to changing workforce requirements and enhance talent management strategies. The study conducted by Teresa et al. in 2024 emphasized the significance of ongoing learning and digital transformation in equipping firms to tackle future challenges and capitalize on opportunities in personnel management. Wan et al. (2024) investigated how cities modify their branding strategies in response to the widespread use of social media and the process of digital transformation. Presumably, they deliberated on tactics to utilize digital resources in order to improve the reputation of the city, draw in investments, boost tourism, and interact with both inhabitants and visitors. The study conducted by Wan et al. (2024) investigated the changing influence of digital platforms on the formation of urban identities and competitiveness in the contemporary era. Wiryanata et al., (2024) examined the utilization of strategic management and forecasting methodologies in the nickel sector of Indonesia. Their study probably analyzed strategic methodologies for industry participants to traverse the fluctuations in market conditions, developments in technology, and changes in regulations that impact the nickel market. The research conducted by Wiryanata, et al., in 2024 focuses on business management techniques and forecasting methodologies that are essential for maintaining and improving competitiveness in Indonesia's changing nickel industry. Wildan, (2023) investigated the effects of Information Technology 4.0 on employee performance. The author presumably analyzed the influence of IT 4.0 breakthroughs, such as AI, automation, and big data, on workplace dynamics and employee productivity. Wildan (2023) is doing a study on the ways that firms use to adjust to fast technological changes and enhance employee performance in the digital era. The research is expected to contribute to the understanding of how technology is influencing workforce capabilities and organizational success.
Objective of Research
• To study talent acquisition strategies in the digital age leveraging technology for recruitment success
• To explore & analyze talent acquisition strategies in the digital age leveraging technology for recruitment success.
• To suggest findings in tabular form & conclusion.
Main Hypothesis of the study
H1: There is no significant relationship between digital age leveraging technology based talent acquisition strategies & recruitment success.
H2: There is significant relationship between digital ages leveraging technology based talent acquisition strategies & recruitment success.
Sub – Hypothesis on the basis of Research Questions
H1: There is no significant relationship between influence of predictive analytics & decision-making in talent acquisition.
H2: There is no significant relationship between candidate experience and the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies.
H3: There is no significant relationship between the perception of risks associated with over-reliance on technology in recruitment.
H4: There is no significant relationship between the influence of mobile applications on candidate behavior and engagement and the responses given.
H5: There is no significant relationship between the perception that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated.
H6: There is no significant relationship between the perception that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics.
Research Methodology
The researcher utilized a descriptive research design in the present study. The researcher utilized a convenience sample design in the present study. Information was gathered from a total of 125 participants who were selected from 05 specific business establishments in India. The present study utilizes percentage analysis and Chi Square test to investigate the hypothesis. The secondary data has been gathered from a diverse range of published publications, theses, and notes. In order to accurately apply a statistical test, such as the Chi-Square Test, and ascertain if the distribution of responses on the Likert scale for all the research-based hypothetical questions differs significantly from what would be expected by chance, we will utilize the Chi-Square Goodness-of-Fit Test. This test examines the discrepancy between the observed frequencies and the anticipated frequencies in the absence of any preference.
Results and Discussion
To justify hypothesis, the following below hypothesis based research questions framed (Table 1).
| Table 1 Likert scale for Q1 | |||
| S. No. | Likert Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 47 | 37.6% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 36 | 28.8% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 15 | 12.00% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 08 | 6.4% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 19 | 15.2% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
Q1: Hypothetical Research Question #1
“Do you somewhat agreed that predictive analytics influence decision-making in talent acquisition?”
Since there are 5 categories and a total of 125 responses, if there were no preference, each category would be equally likely. E=Total Responses=125 / Number of Categories=5 = 125 Applied Chi-Square Test Calculation Formula:
The value of degrees of freedom (df) calculating =Number of Categories−1=5−1=4. Using a Chi-Square distribution table, find the critical value for df=4 at a significance level (α) of 0.05. The critical value is approximately 9.488 (Table 2).
| Table 2 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 47 | 25 | 22 | 484 | 19.36 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 36 | 25 | 11 | 121 | 4.84 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 15 | 25 | -10 | 100 | 4.00 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 8 | 25 | -17 | 289 | 11.56 |
| No Response/Neutral | 19 | 25 | -6 | 36 | 1.44 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 41.20 | ||
Discussion: The results suggest that the use of predictive analytics in talent acquisition significantly influences decision-making. A substantial proportion of respondents (47 out of 125) somewhat agree that predictive analytics play a role; while a notable number (36 out of 125) strongly agree. This finding highlights the importance of integrating advanced technology into recruitment processes to enhance their effectiveness and success. Since the calculated Chi-Square value (41.20) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between influence of predictive analytics & decision-making in talent acquisition”. The results indicate that predictive analytics influence decision-making in talent acquisition.
Q2: Hypothetical Research Question #2
“Do you somewhat agreed that what role does candidate experience play in the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies?”
Discussion: Since the calculated Chi-Square value (25.68) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between candidate experience and the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies”. The results indicate that candidate experience plays a significant role in the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies. A substantial proportion of respondents (32 out of 125) somewhat agree, while 43 out of 125 strongly agree. This finding underscores the importance of ensuring a positive candidate experience in the context of leveraging technology for recruitment (Tables 3 & 4).
| Table 3 Likert Scale for Q2 | |||
| S. No. | Likert_Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 32 | 25.6% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 43 | 34.4% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 17 | 13.6% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 11 | 8.8% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 22 | 17.6% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
| Table 4 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 32 | 25 | 7 | 49 | 1.96 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 43 | 25 | 18 | 324 | 12.96 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 17 | 25 | -8 | 64 | 2.56 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 11 | 25 | -14 | 196 | 7.84 |
| No Response/Neutral | 22 | 25 | -3 | 9 | 0.36 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 25.68 | ||
Q3: Hypothetical Research Question #3
“Do you somewhat agreed - Are the potential risks of over-reliance on technology in recruitment?
Discussion: Since the calculated Chi-Square value (36.16) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between the perception of risks associated with over-reliance on technology in recruitment and the responses given”. The results suggest that respondents perceive significant risks associated with over-reliance on technology in recruitment. A notable proportion of respondents (47 out of 125) somewhat agree, while 33 out of 125 strongly agree. This finding highlights the importance of balancing technology use with human oversight in recruitment processes (Tables 5 & 6).
| Table 5 Likert Scale for Q3 | |||
| S. No. | Likert_Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 47 | 37.60% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 33 | 26.40% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 17 | 13.60% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 9 | 7.20% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 19 | 15.20% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
| Table 6 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 47 | 25 | 22 | 484 | 19.36 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 33 | 25 | 8 | 64 | 2.56 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 17 | 25 | -8 | 64 | 2.56 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 9 | 25 | -16 | 256 | 10.24 |
| No Response/Neutral | 19 | 25 | -6 | 36 | 1.44 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 36.16 | ||
Q4: Hypothetical Research Question #4
“Do you somewhat agreed that mobile applications influence candidate behavior and engagement?
Discussion: Since the calculated Chi-Square value (50.32) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between the influence of mobile applications on candidate behavior and engagement and the responses given”. The results indicate that respondents perceive a significant influence of mobile applications on candidate behavior and engagement. A substantial proportion of respondents (51 out of 125) somewhat agree, while 35 out of 125 strongly agree. This finding emphasizes the importance of mobile applications in modern recruitment strategies, suggesting that they play a crucial role in engaging candidates and shaping their behavior during the recruitment process (Tables 7 & 8).
| Table 7 Likert Scale for Q4 | |||
| S. No. | Likert_Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 51 | 40.8% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 35 | 28.00% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 13 | 10.4% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 08 | 6.4% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 18 | 14.4% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
| Table 8 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 51 | 25 | 26 | 676 | 27.04 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 35 | 25 | 10 | 100 | 4.00 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 13 | 25 | -12 | 144 | 5.76 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 8 | 25 | -17 | 289 | 11.56 |
| No Response/Neutral | 18 | 25 | -7 | 49 | 1.96 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 50.32 | ||
Q5: Hypothetical Research Question #5
“Do you somewhat agreed that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated?
Discussion: Since the calculated Chi-Square value (100.00) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between the perception that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated and the responses given”. The results indicate that respondents significantly agree that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated. A large proportion of respondents (62 out of 125) somewhat agree, while 40 out of 125 strongly agree. This finding highlights the belief among respondents that trends in recruitment technology are predictable and that organizations can prepare for and adapt to these trends effectively (Table 9 & Table 10).
| Table 9 Likert Scale for Q5 | |||
| S. No. | Likert_Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 62 | 49.6% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 40 | 32.0% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 09 | 7.20% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 06 | 4.80% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 08 | 6.4% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
| Table 10 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 62 | 25 | 37 | 1369 | 54.76 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 40 | 25 | 15 | 225 | 9.00 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 9 | 25 | -16 | 256 | 10.24 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 6 | 25 | -19 | 361 | 14.44 |
| No Response/Neutral | 8 | 25 | -17 | 289 | 11.56 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 100.00 | ||
Q6: Hypothetical Research Question #6
“Do you somewhat agreed that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics?
Discussion: Since the calculated Chi-Square value (72.00) is greater than the critical value (9.488), we reject “the null hypothesis (H0). This means there is a significant relationship between the perception that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics and the responses given”. The results indicate that respondents have a significant belief that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics. A substantial proportion of respondents (56 out of 125) somewhat agree, while 38 out of 125 strongly agree. This finding underscores the importance of maintaining trust and transparency in handling candidate data, especially in the context of utilizing advanced analytics techniques like big data in recruitment processes (Tables 11& 12).
| Table 11 Likert Scale for Q6 | |||
| S. No. | Likert_Scale | Freq. (F) | Percentage (%) |
| 1 | Somewhat Agreed | 56 | 44.8% |
| 2 | All Strongly Agreed | 38 | 30.4% |
| 3 | Somewhat Disagreed | 14 | 11.2% |
| 4 | All Strongly Disagreed | 10 | 08.0% |
| 5 | No Response/Neutral | 07 | 5.60% |
| Total | 125 | 100% | |
| Table 12 Chi-Square Value | |||||
| Likert_Scale | (O)_ Observed | (E)_Expected | (O-E) | (O-E)^2 | (O-E)^2 / E |
| Somewhat Agreed | 56 | 25 | 31 | 961 | 38.44 |
| All Strongly Agreed | 38 | 25 | 13 | 169 | 6.76 |
| Somewhat Disagreed | 14 | 25 | -11 | 121 | 4.84 |
| All Strongly Disagreed | 10 | 25 | -15 | 225 | 9.00 |
| No Response/Neutral | 7 | 25 | -18 | 324 | 12.96 |
| Total | 125 | 125 | 72.00 | ||
Findings of the Study
Based on the findings from each research question and hypothesis, here is an overall summary of the study (Table 13).
| Table 13 Hypothesis Results in Tabular form | ||
| Hypothesis | Findings | Result |
| Main-Hypotheses | ||
| H1: “There is no significant relationship between digital age leveraging technology-based talent acquisition strategies and recruitment success”. | The study found a significant relationship between digital age leveraging technology-based talent acquisition strategies and recruitment success. This relationship was supported by evidence from various aspects of recruitment technology and its impact on candidate engagement, decision-making, risk perception, and data privacy. | Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis (H0) and accept the alternative hypothesis (H1). This implies that organizations leveraging digital age technologies in their talent acquisition strategies are likely to experience improved recruitment success. |
| Sub-Hypotheses Based on Research Questions | ||
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between the influence of predictive analytics and decision-making in talent acquisition”. | The study revealed a significant relationship between the influence of predictive analytics and decision-making in talent acquisition. Respondents indicated that predictive analytics play a crucial role in informing decision-making processes. | Thus, we reject H0 in favor of the alternative hypothesis, suggesting that predictive analytics positively impact decision-making in talent acquisition. |
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between candidate experience and the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies”. | The study found a significant relationship between candidate experience and the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies. Positive candidate experiences were associated with better outcomes in recruitment. | Therefore, we reject H0, indicating that candidate experience significantly contributes to the success of technology-driven recruitment strategies. |
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between the perception of risks associated with over-reliance on technology in recruitment”. | The study identified a significant relationship between the perception of risks associated with over-reliance on technology in recruitment. Respondents expressed concerns that excessive reliance on technology could pose risks. | Hence, we reject H0, suggesting that perceptions of risks impact recruitment strategies and decisions. |
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between the influence of mobile applications on candidate behavior and engagement”. | The study indicated a significant relationship between the influence of mobile applications on candidate behavior and engagement. Mobile applications were found to positively influence candidate interaction and engagement. | Therefore, we reject H0, indicating that mobile applications play a significant role in shaping candidate behavior and engagement during recruitment. |
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between the perception that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated”. | The study revealed a significant relationship between the perception that future trends in recruitment technology can be anticipated. Respondents believed that trends in recruitment technology are predictable and can be prepared for. | Thus, we reject H0, indicating that there is a perceived ability to anticipate and prepare for future trends in recruitment technology. |
| Null hypothesis (H0): “There is no significant relationship between the perception that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics”. | The study found a significant relationship between the perception that organizations ensure the privacy and security of candidate data when using big data analytics. Respondents believed that ensuring data privacy and security is crucial in leveraging big data analytics for recruitment. | Therefore, we reject H0, suggesting that perceptions of data privacy and security practices impact the adoption and effectiveness of big data analytics in recruitment. |
Conclusion
Integrating state-of-the-art technology with strategic human resource techniques is a hallmark of talent acquisition in the digital era. To stay ahead of the competition in today's global talent market, companies are optimizing their recruitment procedures and embracing digital transformation. The methods and resources used to find, evaluate, and involve tomorrow's workers will also change as technology develops further. The study finds that utilizing technology-based talent acquisition tactics in the digital age has a substantial impact on the success of recruitment. This conclusion is substantiated by evidence demonstrating the beneficial effects of predictive analytics, applicant experience, mobile applications, and anticipation of future trends in recruiting technology. Furthermore, apprehensions and perspectives regarding dangers and the protection of data privacy and security can have a substantial impact on the formation of recruitment tactics. Organizations that successfully incorporate these insights into their recruitment procedures are likely to achieve superior results in talent acquisition.
References
Andrade, C. R. D. O., & Gonçalo, C. R. (2021). Digital transformation by enabling strategic capabilities in the context of “BRICS”. Revista de Gestão, 28(4), 297-315.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chauhan, D. S., Singh, P., & Chawla, T. (2022). Talent Acquisition in the Digital Age: Leveraging AI and Automation for Recruitment Success. RES MILITARIS, 12(6), 3112-3113.
Hatum, A. (2013). The New Workforce Challenge: How Today's Leading Companies are Adapting for the Future. Springer.
Kumar, S. (2023). A Study on Green Accounting: Role and its Process. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 10(2), 21-24.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Li, L. Q., Xin, K., Pucik, V., & Wei, W. X. (2019). MNCs’ R&D talent management in China: aligning practices with strategies. Chinese Management Studies, 13(4), 1086-1106.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Leo, O. O. Talent management in the digital age: Challenges and opportunities. Journal of The Management Sciences, 213.
Mandia, U. (2024). From Screen to Store: Green Packaging's Effect on Consumer Intentions in New age Disruptive Era. Kaav International Journal of Economics , Commerce & Business Management, 11(2), 7-14.
Mukul, K., & Saini, G. K. (2021). Talent acquisition in startups in India: the role of social capital. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 13(5), 1235-1261.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Saadatmand, M. R., Safaie, N., & Dastjerdi, M. (2022). Presenting a structural model of digitalised talent management in a new age: A case study on the mobile telecommunication industry in Iran. SA Journal of Human Resource Management, 20, 10.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sen, S. (2020). Digital HR strategy: Achieving sustainable transformation in the digital age. Kogan Page Publishers.
Thamage, M. A., & Motshegwa, B. (2021). The Relationships of Organisational Talent Management, Professional Experience, Promotion Policy and Competitive Advantage in the Debswana Jwaneng Mine, Botswana. Journal of Public Administration and Development Alternatives (JPADA), 6(2), 32-47.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Teresa, G., & Fantinelli, S. (2024). Managing the future of talents: Digital innovation in learning organizations. The Learning Organization.
Wan, F., & Li, J. (2024). Navigating the digital age: City branding in the era of social media and digital transformation. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1-34.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Wiryanata, M. A., Abdan, & Imron, M. A. (2024). Business Management and Strategic Forecasting Lens: Navigating the Future of Indonesia's Nickel Industry. Kaav International Journal of Economics , Commerce & Business Management, 11(1), 1-7.
Wildan, M. A. (2023). Employee Performance Lens on Rapid Changing in Information Technology 4.0. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 10(2), 9-16.
Received: 15-Jul-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-15032; Editor assigned: 16-Jul-2024, PreQC No. AMSJ-24-15032(PQ); Reviewed: 26- Aug-2024, QC No. AMSJ-24-15032; Revised: 06-Sep-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-15032(R); Published: 02-Nov-2024