Research Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 5
Studying Trends in E-banking: A Bibliometric Analysis
Poonam Painuly, Gurukula Kangri (Deemed to be University)
Sandeep Rohal, Gurukula Kangri (Deemed to be University)
Citation Information: Painuly, P., & Rohal, S. (2024). Studying trends in e-banking: a bibliometric analysis. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(5), 1-19.
Abstract
Background: E-banking, or electronic banking, has become an integral part of the modern banking industry, transforming the way individuals and businesses conduct financial transactions. Understanding the evolving trends in e-banking research is crucial for practitioners and researchers to stay informed and identify emerging areas of study. Objective: This paper aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis of e-banking literature to identify trends and patterns in research. By analyzing citation networks, co-authorship networks, and keyword co-occurrence, this study seeks to gain insights into the growth of research, influential authors and institutions, emerging topics, and collaboration patterns. Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in the two major academic databases, Scopus and Web of Science. Articles published within the last 15 years were included in the analysis. Bibliometric software tools, such as Bibliometric Biblioshiny, were utilized to visualize and analyze the collected data. Findings: The analysis revealed a steady growth in e-banking research over the past decade. Key findings include the various types of reports including most relevant words, authors, affiliations etc. The findings provide valuable insights into the existing knowledge base and serve as a foundation for future research. Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive overview of trends in e-banking research. The findings highlight the various reports and the increase in number of studies on per year basis. These insights can guide practitioners and researchers in identifying future research directions and areas for collaboration, ultimately contributing to the advancement of e-banking and its related disciplines.
Keywords
E-banking, Trends, online banking, Bibliometric Analysis, R-Studio, PRISMA, Biblioshiny.
Introduction
The advent of the digital era has revolutionized numerous aspects of our lives, including the way we conduct financial transactions. E-banking, also known as electronic banking, has emerged as a significant component of the modern banking industry, offering individuals and businesses the convenience and flexibility to engage in financial activities through electronic channels. Customers may manage their accounts, move money between accounts, pay bills, and shop online with only a few clicks or taps on their smartphones. The purpose of this work is to undertake a bibliometric analysis of the literature on electronic banking in order to reveal patterns and trends that have emerged through time and provide light on the development of this area of study.
The objective of this study is to explore the body of e-banking literature using bibliometric analysis, a quantitative research method that examines patterns and trends within scholarly publications. By employing bibliometric techniques, such as citation analysis, co-citation analysis, and keyword analysis, we seek to unravel the growth, impact, and interconnections among research articles in the field of e-banking. This analysis will shed light on key research areas, influential authors and institutions, emerging topics, and collaboration patterns, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the evolution of e-banking research.
Bibliometric analysis plays a crucial role in understanding the progress and development of research in a specific field. By examining the citation patterns of articles, researchers can discern the influence and impact of specific works, identifying seminal contributions that have shaped the field. Co-citation analysis provides insights into the intellectual structure of the field, revealing clusters of related works and influential authors. Keyword analysis helps uncover prevalent themes and topics that researchers have explored in their studies. Overall, bibliometric analysis provides a systematic and quantitative approach to examine the literature, enabling researchers to make informed observations about the evolution and trends within a particular domain.
In the context of e-banking, conducting a bibliometric analysis is of utmost importance. E-banking has transformed the banking landscape, providing customers with anytime, anywhere access to financial services. As this field continues to evolve rapidly, it is crucial to understand the trends and patterns of research in order to keep pace with emerging developments and challenges. By conducting a bibliometric analysis, we can identify the most influential works and authors, explore collaboration patterns, and gain insights into emerging research topics.
Moreover, the findings of this study have practical implications for practitioners and policymakers in the banking industry. Understanding the research trends in e-banking can help financial institutions align their strategies, adopt best practices, and cater to the evolving needs of their customers. Policymakers can benefit from this analysis by identifying regulatory gaps and shaping policies that support the growth and security of e-banking services. Additionally, researchers and academicians can use the findings to identify research gaps, inspire new studies, and foster interdisciplinary collaboration within the field.
In the following sections, we will explain the methodology used for the bibliometric analysis, the steps taken to acquire the data, the analysis itself, the results, and our interpretation of those results. Our research aims to add to the current body of knowledge on e-banking, provide useful insights for stakeholders, and pave the way for further study in this exciting and quickly developing sector.
In short, e-banking has emerged as a transformative force in the digital era, reshaping the way individuals and businesses engage in financial activities. Conducting a bibliometric analysis of e-banking literature allows us to examine the research landscape, identify trends and patterns, and understand the evolution of the field. By applying bibliometric methods, we can uncover influential works, discern collaboration networks, and explore emerging research areas. The insights gained from this analysis have implications for practitioners, policymakers, and researchers, enabling them to make informed decisions, shape policies, and advance knowledge in the realm of e-banking.
Method and Strategy
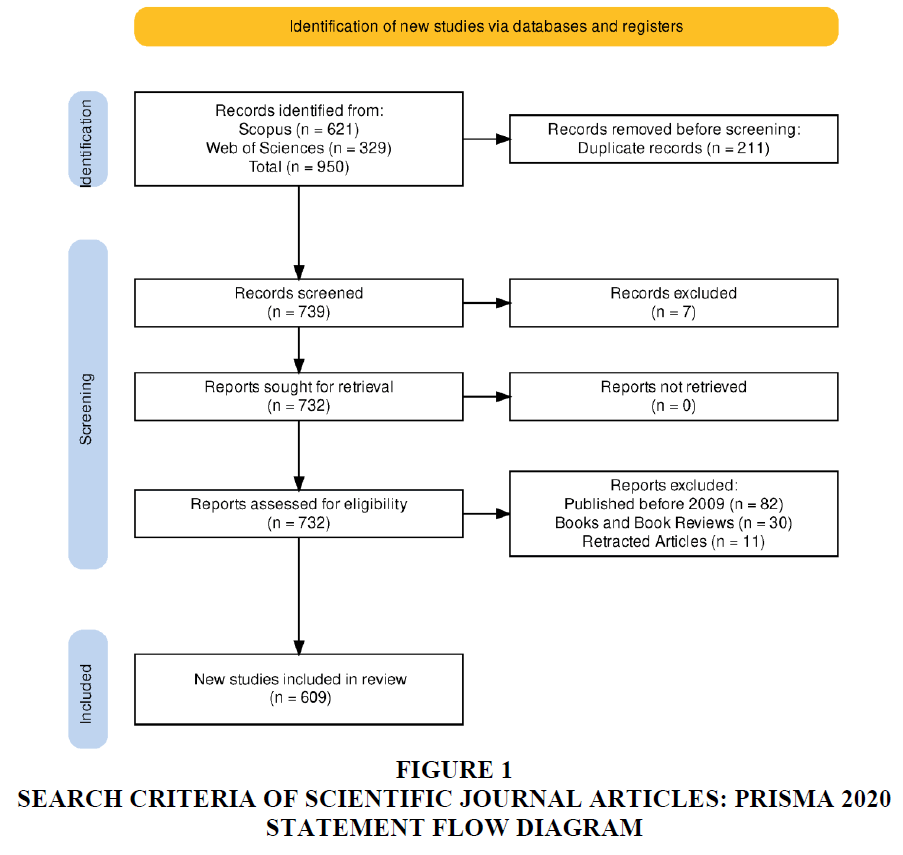
The “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)” statement 2020 acts as a roadmap for this study. The terms “E-banking, customer experience, internet banking trends etc.” were searched on many prominent online libraries. But only the data from Scopus and Web of Science has been taken for analysis as these two are the major databases and both acts as friendly search engines and provide the citation analysis. Their inconsistency is also lower than other databases such as Google Scholar. Only papers written in English were considered for this review. On July 18, 2023, searches were performed in all available databases. Publications between 2009 and 2023 had their titles and abstracts read, with the complete text being acquired if there was any doubt as to their eligibility when written in English. There was a total of 950 publications included, and they were all scientific studies of some aspect of topic’ introduction or implementation. The current strategy is broken down into its three main sections which are shown below.
Step I. Study eligibility requirements are as follows: Specifying the eligibility criterion.
Step II. Extraction of Data: Using a Multi-Tiered Screening Process to Find Relevant Studies.
Step III. Execution of data: providing an overview of the papers that were determined to have similar results using content analysis, as well as the research profile and topic emphasis of those studies.
Study Eligibility Requirements: Inclusion Criteria
1. Articles in Scopus/WOS journals that report the results of rigorous qualitative and quantitative research.
2. English-language articles that have been published in a journal after extensive evaluation and reviewed by academic experts before July, 2023.
3. Articles explicitly focusing on E-banking, customer experience about e-banking and its trends.
Exclusion Criteria
1. Articles at odds with the topic of e-banking, customer experience of e-banking and its trends.
2. Articles not directly connected with topic.
3. Matching authors, titles, volumes, issues, and DOIs in duplicate articles.
4. Editorials, Book Chapters and others except journal papers and articles.
Extraction of Data
After compiling a comprehensive set of terms, we converted them into query strings. The following keywords were searched on Scopus database: E-banking, customer experience and trends of e-banking and same for the WOS database. We then made it such that these keywords were used to search the database's title, abstract, or authors. In July of 2023, we conducted a search and found 950 articles. Scopus alone yielded 621 articles, while Web of Sciences yielded 329 articles. In this case, relevant studies were chosen by using predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Duplicate articles were checked for first with the help of R-Studio. There were 211 duplicate studies deleted because they had the same authors, titles, volume numbers, issue numbers, and digital object identifiers (DOIs). The duplicate articles were found using R-Studio 2023.03.0. Then the remaining 739 articles were screened.
At this stage of screening the articles, 7 articles were excluded as they were of other language than that of English, as we have mentioned in our criteria that only English language documents will be studied. Then the screened articles (remaining 732 articles) were sought for report retrieval and the report was yielded for all the articles, hence no articles were removed at this stage of the PRISMA. The reports now accessed for eligibility. 82 studies were disregarded because their content was published before the year 2009. 30 papers were thrown out due to their document type as many of them were editorials or book chapters or working papers, where the criteria includes only journal articles. A number of 11 articles was removed from the study as they had been regarded as Retracted articles by the automation tool used. The tool used in this case was R-Studio Bibliometric Shiny Package. Only 609 studies were included in the final collection. Research profiling and content analysis, which together constituted the data execution technique, will be discussed in the next section. The whole data extraction procedure is also detailed in a PRISMA statement 2020 for easy reference (Figures 1-5).
The downloaded articles were uploaded to R-Studio software having version 2023.03.0 for bibliometric analysis of the data. There were two choices, Vos-Viewer and R-Studio Bibliometrix Biblioshiny. We have chosen Biblioshiny R-tool as it is more flexible open source software for the bibliometric analysis of data of two separate databases.
Results
This study of bibliometric analysis includes the main information about the combined data retrieved from both the databases; knowledge about the most cited journals, authors, documents; most frequent sources, affiliations; most production by country; conceptual mapping and keywords cluster; co-occurrence network and publication on per year basis.
The table 1 represents the descriptive analysis of bibliometric data. From the table it can be observed that the data covers the period from 2009 to 2023 and it was retrieved from 387 different sources having a total of 609 journal articles published by 1437 authors. Out Of 69 articles, 101 work single author and the rest work the work of multiple authors. The average age of every document is 6.42 years and citation being 9.368 on average for the included studies. The included studies had total number of references as 3837, 1346 keywords Plus and 1490 author keywords. The annual growth rate is -3.96. The document type consists of 413 articles, 5 early access, 140 conference papers, 42 for proceeding papers and the rest being others.
| Table 1 Descriptive Analysis | |
| Description | Results |
| Main Information About Data | |
| Timespan | 2009:2023 |
| Sources (Journals, Books, etc.) | 387 |
| Documents | 609 |
| Annual Growth Rate % | -3.96 |
| Document Average Age | 6.42 |
| Average citations per doc | 9.368 |
| References | 3837 |
| DOCUMENT CONTENTS | |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 1346 |
| Author's Keywords (DE) | 1490 |
| , AUTHORS | |
| Authors | 1437 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 101 |
| AUTHORS COLLABORATION | |
| Single-authored docs | 110 |
| Co-Authors per Doc | 2.73 |
| International co-authorships % | 2.135 |
| DOCUMENT TYPES | |
| article | 413 |
| article; early access | 5 |
| conference paper | 140 |
| conference paper article | 3 |
| conference review | 5 |
| proceedings paper | 42 |
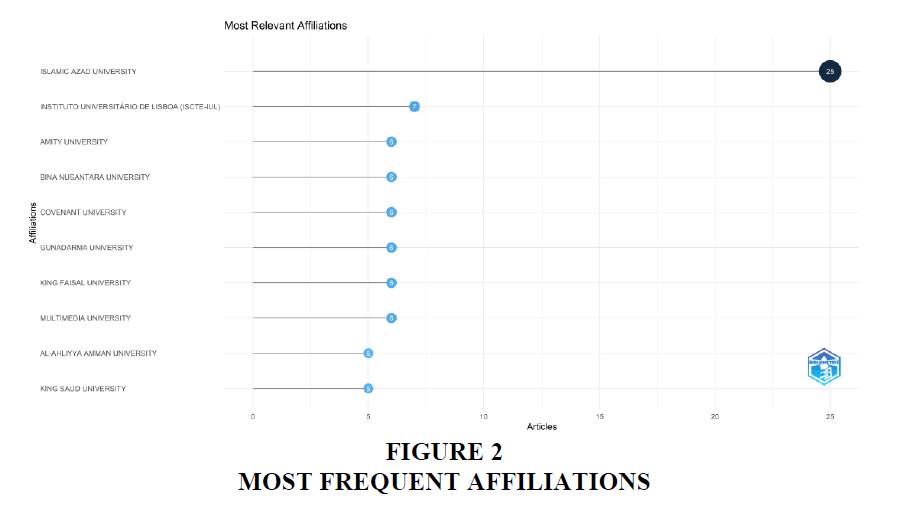
The table 2 describes the most frequent affiliations of the included studies from the year 2009 to 2023 which is based upon the first author’s affiliation. The Islamic Azad University which is a private university situated in Tehran, Iran, also being one of the biggest communities’ colleges in the World had the highest number of affiliations numbering to 25 articles. It is world’s 6th largest University. The list includes universities across the world including the Amity University of India being ranked 3rd in the list with 6 affiliations.
| Table 2 Most Relevant Affiliations | |
| Affiliation | Articles |
| Islamic Azad University | 25 |
| Instituto Universitário De Lisboa (Iscte-Iul) | 7 |
| Amity University | 6 |
| Bina Nusantara University | 6 |
| Covenant University | 6 |
| Gunadarma University | 6 |
| King Faisal University | 6 |
| Multimedia University | 6 |
| Al-Ahliyya Amman University | 5 |
| King Saud University | 5 |
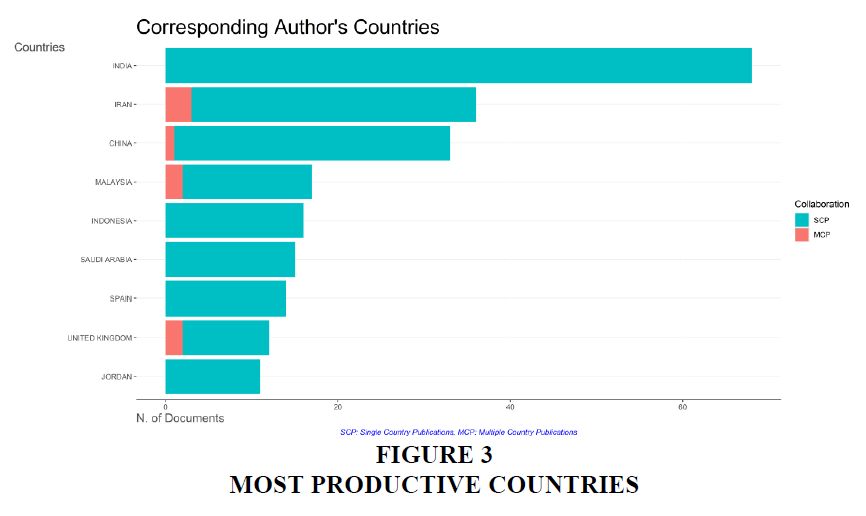
The table 3 yielded the knowledge about 10 most productive countries which is based upon the first author’s affiliation. The India has topped the list with a number of 68 articles followed by 36 articles from Iran and 33 from China. “It shows that the authors across the globe has taken participation in the study and research.
| Table 3 Most Productive Countries | |
| Country | Articles |
| India | 68 |
| Iran | 36 |
| China | 33 |
| Malaysia | 17 |
| Indonesia | 16 |
| Saudi Arabia | 15 |
| Spain | 14 |
| United Kingdom | 12 |
| Jordan | 11 |
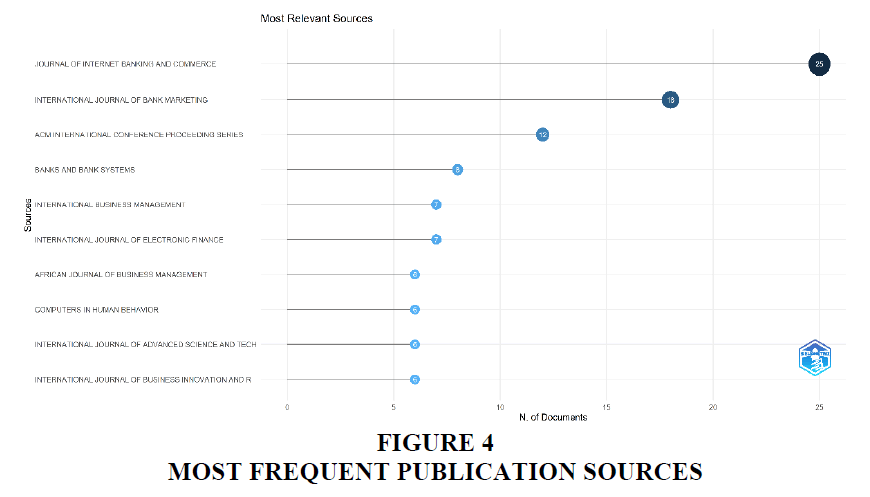
The table 4 provides information about the top 10 most frequent journals for publishing the research on the topic related to e-banking, customer satisfaction relating to e-banking and its trends.” Only 3 journals have published more than 10 articles during the tenure of 2009 to 2023, and it was topped by Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce with a number of 25 articles followed by other International Journals like International Journal of Bank Marketing and ACM International Conference Proceeding Series with a number of 18 and 12 publications respectively. It also provides the insight that the journals from all across the world are included in the list standing that e-banking is the rising topic across the globe and it is in trend in the world.
| Table 4 Most Frequent Publication Sources | |
| Sources | Articles |
| Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce | 25 |
| International Journal of Bank Marketing | 18 |
| ACM International Conference Proceeding Series | 12 |
| Banks and Bank Systems | 8 |
| International Business Management | 7 |
| International Journal of Electronic Finance | 7 |
| African Journal of Business Management | 6 |
| Computers in Human Behavior | 6 |
| International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology | 6 |
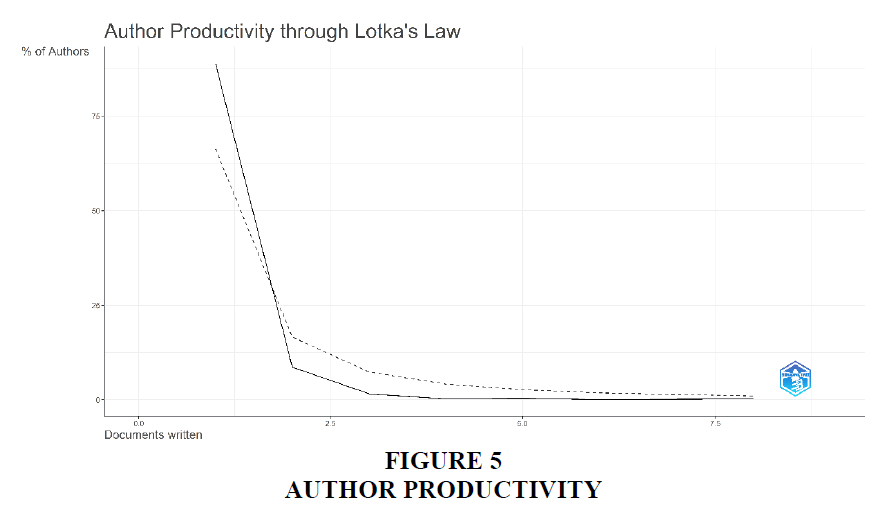
The table 5 shows the Author Productivity as per the Lotka’s Law (Figure 5). Lotka's Law, also known as the inverse square law of scientific productivity, is a principle that describes the distribution of productivity among authors in a given field. It is based on the observation that a small number of authors tend to be responsible for the majority of publications, while a large number of authors have relatively few publications.
| Table 5 Author Productivity | ||
| No of Articles | No of Authors | Freq |
| 1 | 1278 | 0.889 |
| 2 | 124 | 0.086 |
| 3 | 23 | 0.016 |
| 4 | 3 | 0.002 |
| 5 | 5 | 0.003 |
| 6 | 1 | 0.000 |
| 8 | 3 | 0.002 |
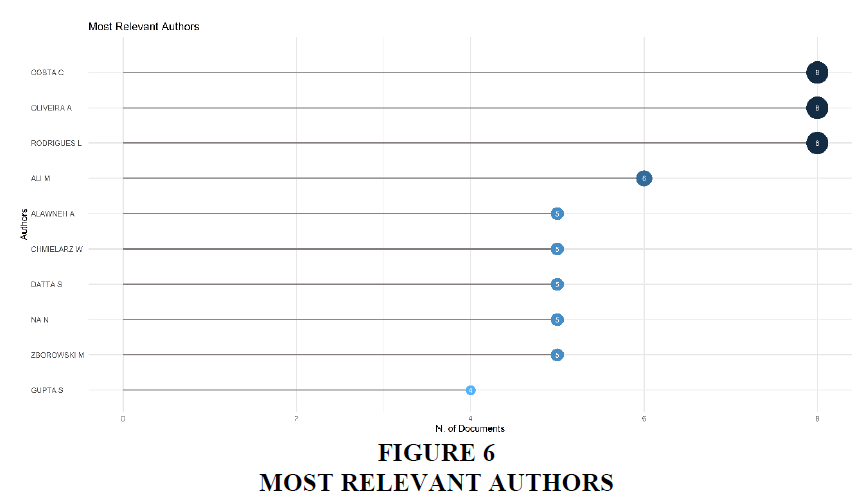
Table 6 illustrates the names of top 10 most productive authors during the period selected for the research. Costa C tops the list along with Oliveira A and Rodrigues L, all having a number of articles of 8, with a fractionalized number of 2.67. Other authors having multiple publications under their names are also mentioned in the list of the most productive authors during the period.
| Table 6 Most Productive Authors | ||
| Authors | Articles | Articles Fractionalized |
| Costa C | 8 | 2.67 |
| Oliveira A | 8 | 2.67 |
| Rodrigues L | 8 | 2.67 |
| Ali M | 6 | 2.2 |
| Alawneh A | 5 | 2.5 |
| Chmielarz W | 5 | 2.5 |
| Datta S | 5 | 2.5 |
| Na N | 5 | 5 |
| Zborowski M | 5 | 2.5 |
| Gupta S | 4 | 2.16 |
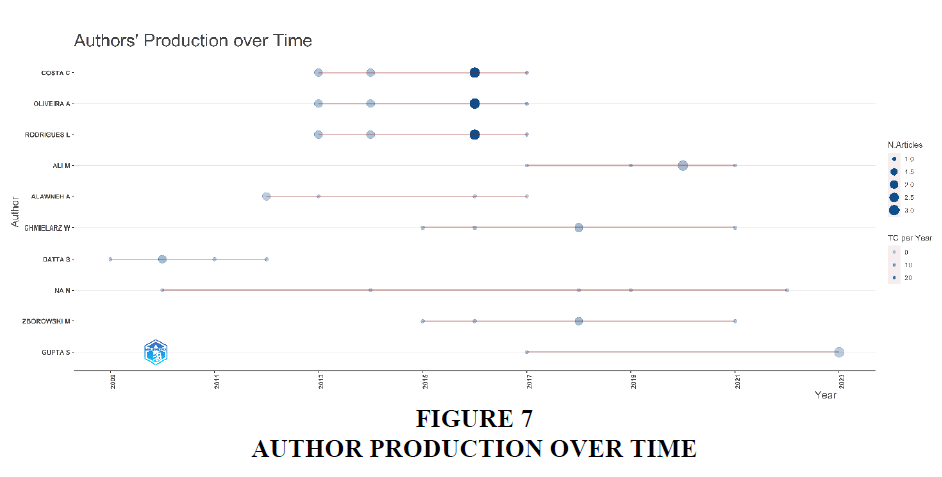
The Figures 6-9 (Authors’ Production over time) shows that in which year, the most relevant authors mentioned in the table 6 have got their research published. It gives the valuable insight showing which author has been actively involved in the research related to e-banking and who is the emerging author among all. As the figure illustrates, the top 3 authors have their articles published within the year 2013 to 2016 only, where the author NA N has been active since 2010 having his recent publication in the year 2022. Also, Gupta S is the only author having publication in the year 2023.
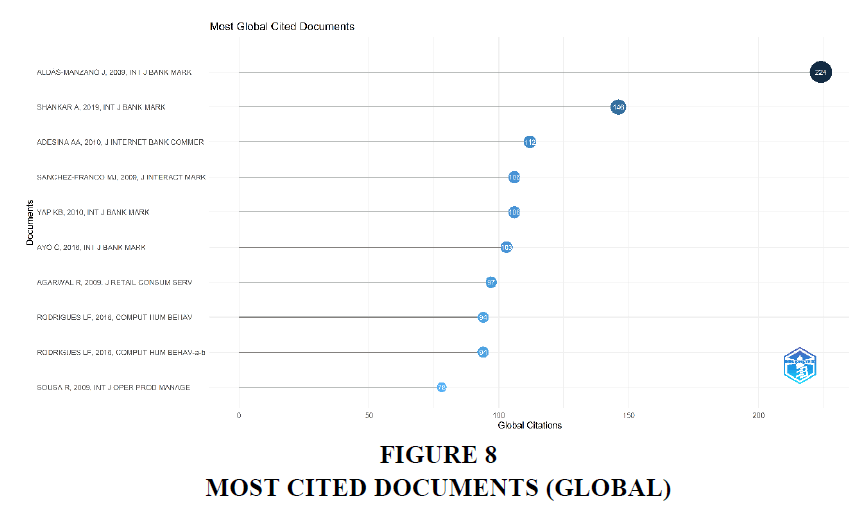
The table 7 shows the top 10 most globally cited documents during the period, its total citations and total citations per year over the period from 2009 to 2023. The research shows that the Aldas Manzano J, published in the year 2009 in the international journal of banking and marketing was the most cited document with a citation score of 224 and a per year average citation of 14.993. Whereas we can clearly see the 2nd most cited paper in the list, who has total citation of 146, and a clear winner in the case of total citation per year with a score more than 29.2. It was published in the year 2019. It is the only article in the list published within the last 5 years. It was an Indian article written by Shankar A, which was also published in the international journal of bank marketing.
| Table 7 Most Cited Documents (Global) | ||
| Paper | Total Citations | TC per Year |
| Aldás-Manzano J, 2009, Int J Bank Mark | 224 | 14.933 |
| Shankar A, 2019, Int J Bank Mark | 146 | 29.2 |
| Adesina Aa, 2010, J Internet Bank Commer | 112 | 8 |
| Sanchez-Franco Mj, 2009, J Interact Mark | 106 | 7.067 |
| Yap Kb, 2010, Int J Bank Mark | 106 | 7.571 |
| Ayo C, 2016, Int J Bank Mark | 103 | 12.875 |
| Agarwal R, 2009, J Retail Consum Serv | 97 | 6.467 |
| Rodrigues Lf, 2016, Comput Hum Behav | 94 | 11.75 |
| Sousa R, 2009, Int J Oper Prod Manage | 78 | 5.2 |
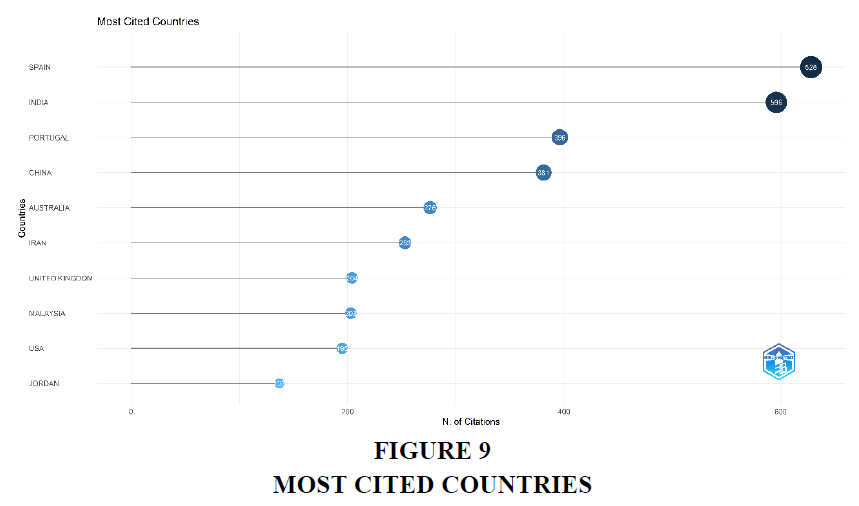
Table 8 illustrates Top 10 most cited countries. Along with the name of the country, it shows the total citations and Average citation, which is calculated by diving the total number of citations by total number of articles published. Spain has the greatest number of total citations with a score of 628, closely followed by India with a score of 596. But there is a significant difference in the average article citation of both the countries. They have 44.9 and 8.8 as the score of average article citation respectively. Australia tops the list of average article citation with a score of more than 55, which suggests that its each article is cited around 55 times in average.
| Table 8 Most Cited Countries | ||
| Country | TC | Average Article Citations |
| Spain | 628 | 44.9 |
| India | 596 | 8.8 |
| Portugal | 396 | 44 |
| China | 381 | 11.5 |
| Australia | 276 | 55.2 |
| Iran | 253 | 7 |
| United Kingdom | 204 | 17 |
| Malaysia | 203 | 11.9 |
| USA | 195 | 27.9 |
| Jordan | 137 | 12.5 |
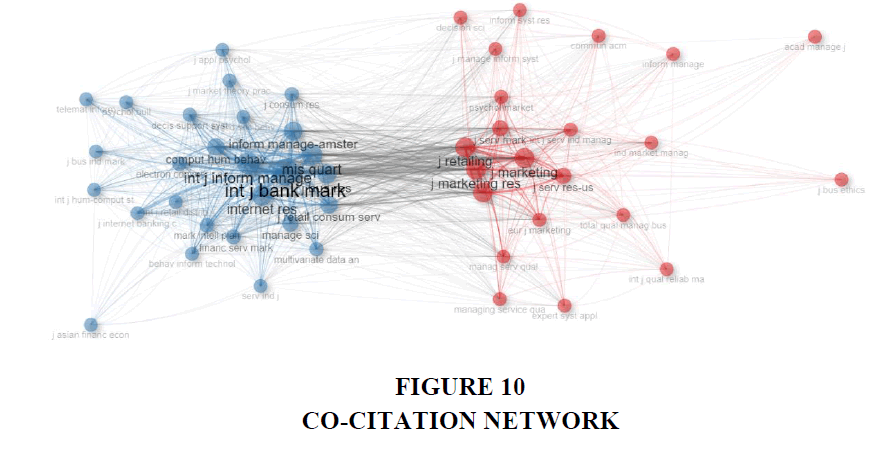
Figure 10, illustrates the co-citation network between the different publication sources during the selected tenure of the study. A co-citation network among publication sources is a visual representation of the relationships between different academic sources based on their co-citation patterns. Co-citation occurs when two or more sources are cited together in the reference lists of other publications, indicating a connection or similarity between them. The network is constructed by analyzing a corpus of academic literature and creating a graph where each publication source is represented as a node, and co-citation relationships are represented as edges connecting the nodes. Co-citation networks offer valuable insights into the intellectual structure of a research field, identifying influential sources, seminal articles, and clusters of related research. They aid researchers in understanding knowledge flow, identifying emerging trends, and assessing the impact of publications within a specific domain, making them powerful tools in bibliometric analysis.
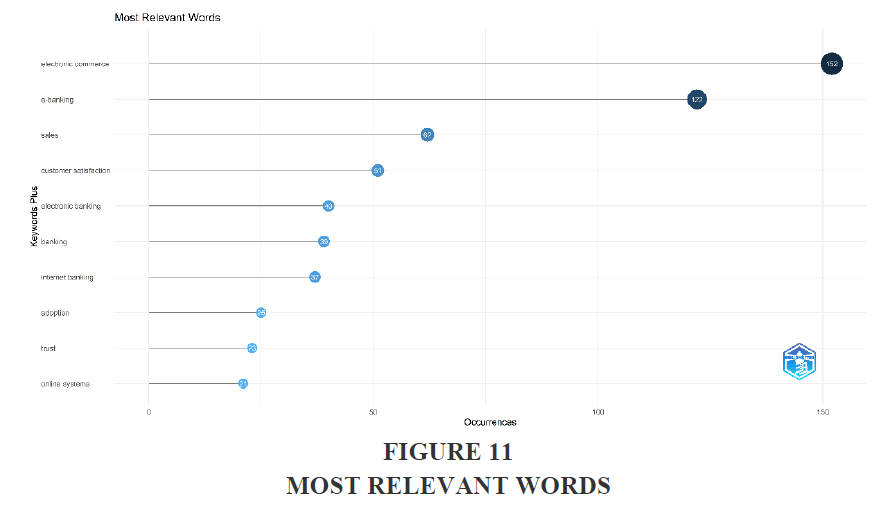
The table 9 shows the occurrence of words on the basis of keywords plus used in the study. The word electronic commerce has been used 152 times in the keywords, e-banking has been used 122 times. Other keywords like customer satisfaction, electronic banking, banking, internet banking and online systems has also been used frequently. Figure 11 represents the graphical representation of the same.
| Table 9 Most Relevant Words | |
| Words | Occurrences |
| electronic commerce | 152 |
| e-banking | 122 |
| sales | 62 |
| customer satisfaction | 51 |
| electronic banking | 40 |
| banking | 39 |
| internet banking | 37 |
| adoption | 25 |
| trust | 23 |
| online systems | 21 |
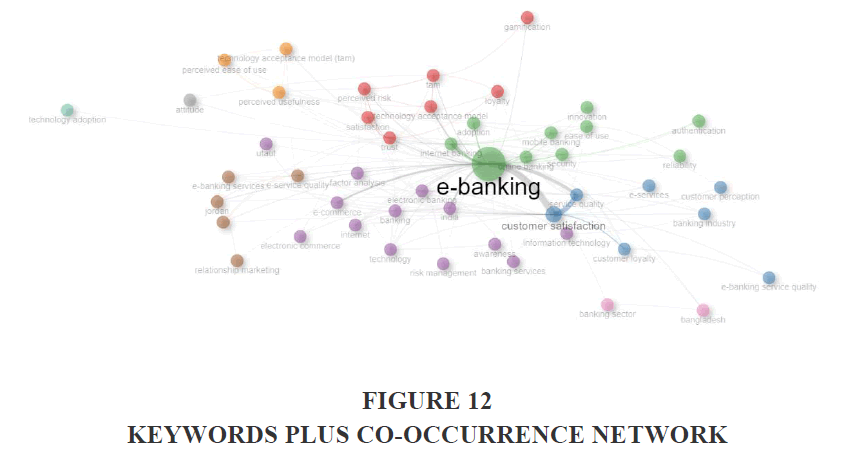
Figure 12 shows the keyword plus co-occurrence network, which shows that which keywords are used together in the same study. In a study more than 1 keyword is used and the network developed after studying the pattern of occurrence of 2 or more keywords together is known as keywords plus co-occurrence network. From the figure we can see that e-banking is the most used keyword along with any other keyword used in the study.
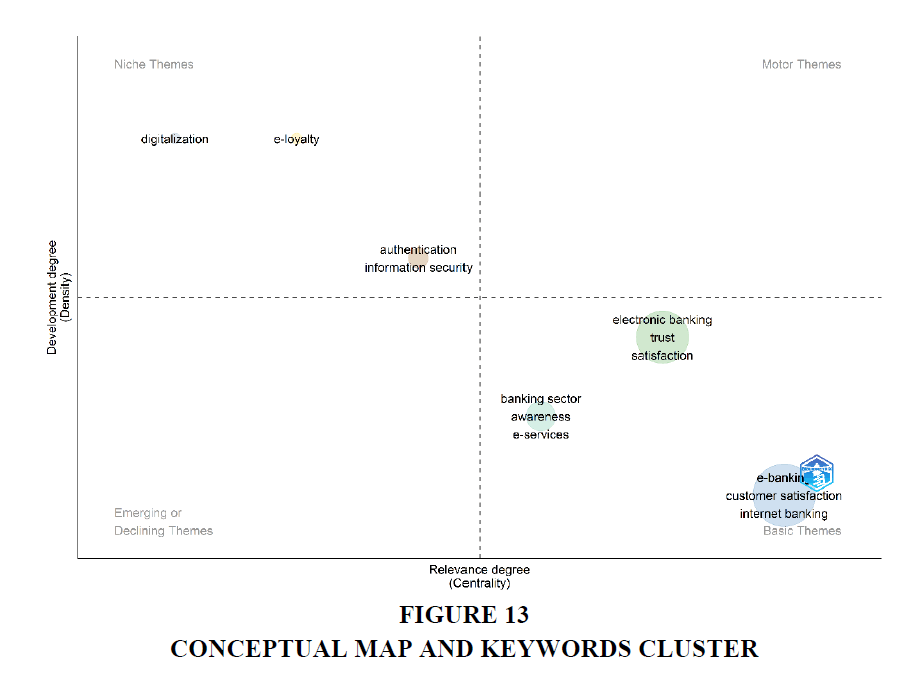
Figures 13-15 presents the conceptual map and keywords cluster based upon authors keywords. The figure demonstrates four themes that contains keywords. The Q1 which is the upper right quadrant shows the main/motor themes of the research topic. The 2nd quadrant describes the highly specialized themes which are also called as Niche Themes. This contains the keywords like digitalization, e-loyalty, authentication and information technology. The emerging and declining themes are represented by the 3rd quadrant which is the lower left quadrant in the figure. The Q4, which represents the basic themes of the study which can be found as a base in most of the studies included in this research, shows the keywords like electronic banking, trust, satisfaction, banking sector, awareness, e-services, e-banking, customer satisfaction and internet banking. These keywords serve as a base of the study. These keywords are highly important for developing the concept of e-banking and customer satisfaction through e-banking.
Discussion
The results of this bibliometric analysis are based upon the available data of publication on e-banking and customer satisfaction related to it. This study included the period of 2009 to 2023 using both Scopus and WOS databases combined. The finally included number of studies were 609 journal articles which were included after the specified inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned. The study had the aim to assess publication trends over the year related to the e-banking, customer satisfaction and its trends towards it.
Table 10 shows the number of publications on per year basis. The table shows only 609 finally included articles in this bibliometric analysis. It shows that the trend does not have a specific pattern as the number of publications is similar from 2009 to 2014. After that we can observe that there is a wave motion for the next couple of years and after that we can observe a gradual growth in the publication for the next few years. Year 2022 has the greatest number of publications as 77.
| Table 10 No. of publications per year | |
| Year | Articles |
| 2009 | 37 |
| 2010 | 37 |
| 2011 | 37 |
| 2012 | 33 |
| 2013 | 34 |
| 2014 | 36 |
| 2015 | 29 |
| 2016 | 43 |
| 2017 | 27 |
| 2018 | 39 |
| 2019 | 44 |
| 2020 | 66 |
| 2021 | 49 |
| 2022 | 77 |
| 2023 | 21 |
Table 11, illustrating the average citation per year. The table has multiple columns, showing year, mean of total citation per article, number of articles published in the year, Mean total citation per year and its citable years. The citable years are on declining with every year as the article published in the year can have 15 citable years whereas the article published in 2023 will have only 1 citable year. The mean total citation per article of the year 2009 is the highest among all having 20.81 and whereas the mean total citation per year of the year 2019 is highest being 2.16 closely followed by 2017 having a score of 2.06.
| Table 11 Average Citations Per Year | ||||
| Year | Mean TC per Art | N | Mean TC per Year | Citable Years |
| 2009 | 20.81 | 37 | 1.39 | 15 |
| 2010 | 18.14 | 37 | 1.3 | 14 |
| 2011 | 8.14 | 37 | 0.63 | 13 |
| 2012 | 10.15 | 33 | 0.85 | 12 |
| 2013 | 12.15 | 34 | 1.1 | 11 |
| 2014 | 6.31 | 36 | 0.63 | 10 |
| 2015 | 8.66 | 29 | 0.96 | 9 |
| 2016 | 14.79 | 43 | 1.85 | 8 |
| 2017 | 14.44 | 27 | 2.06 | 7 |
| 2018 | 8.18 | 39 | 1.36 | 6 |
| 2019 | 10.82 | 44 | 2.16 | 5 |
| 2020 | 7.94 | 66 | 1.99 | 4 |
| 2021 | 5.1 | 49 | 1.7 | 3 |
| 2022 | 1.77 | 77 | 0.88 | 2 |
Figure 16 illustrating the Trending Topics of the research, shows that in the research period selected of 15 years, which topic was trending in every year. The figure also illustrates the term frequency, as how many times the specific term has been used in the study during the year. In the year 2009, the most trending topic was virtual banking, followed by electronic commerce in the year 2010, customer relationship management in 2011, risk management in the year 2012, internet in 2013, electronic banking in 2013, gamification in the year 2014, e-banking in 2015, trust in 2016, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and service quality in the next years. In the year 2021, e-banking service, digitalizing in 2022 and quality function deployment in the year 2023 was the most trending topics. The figures guides that in which year, which term was most frequently used and remained as a trending topic. This analysis will help the policymakers, researchers and other persons to know the trending topics, analyzing trends in the banking industry, e-banking and customer satisfaction with e-banking.
Conclusion
The bibliometric analysis conducted in this study has provided valuable insights into the trends and patterns of e-banking research, shedding light on the evolution and significance of this dynamic field. Through quantitative analysis of citation networks, co-citation patterns, and keyword co-occurrence, we have gained a comprehensive understanding of the e-banking literature landscape, identifying key areas of focus, influential authors and institutions, emerging topics, and collaboration patterns.
The analysis revealed a steady growth in e-banking research over the past decade, reflecting the increasing importance of this field in the digital era. Additionally, the analysis highlighted the influential role of certain authors and institutions in shaping the discourse of e-banking research. These key contributors have significantly impacted the field, guiding and influencing the direction of studies and setting the stage for future developments. Recognizing their contributions can inspire new researchers to build upon existing work and contribute to the ongoing advancement of e-banking knowledge.
Furthermore, the identification of emerging topics such as digitalization and customer behavior demonstrate the shifting priorities and challenges faced by the e-banking industry. Understanding customer behavior is essential for tailoring personalized banking experiences and meeting the evolving needs of tech-savvy customers. Collaboration patterns among researchers from different disciplines and institutions indicate the interdisciplinary nature of e-banking research. Collaboration fosters the exchange of knowledge and ideas, encouraging innovative approaches to address complex challenges in the e-banking domain. Encouraging more collaborative research initiatives can accelerate advancements in e-banking and facilitate the exchange of best practices among experts from diverse backgrounds.
In summary, the bibliometric analysis has provided a comprehensive overview of trends and patterns within the e-banking literature. The findings of this study offer valuable insights for practitioners, policymakers, and researchers in the banking industry. Understanding the growth areas, influential contributions, and emerging topics in e-banking research can guide strategic decision-making, policy formulation, and future research directions.
Limitations
It is important to acknowledge some limitations of this study. The analysis was confined to a specific time frame and might not capture developments in e-banking research beyond the defined period. Additionally, the selection of databases and inclusion/exclusion criteria may have influenced the composition of the dataset, potentially introducing bias. Future studies could consider expanding the time frame and incorporating additional data sources to enhance the comprehensiveness of the analysis.
References
Agarwal, R., Rastogi, S., & Mehrotra, A. (2009). Customers’ perspectives regarding e-banking in an emerging economy. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 16(5), 340–351.
Aldás-Manzano, J., Lassala-Navarré, C., Ruiz-Mafé, C., & Sanz-Blas, S. (2009). The role of consumer innovativeness and perceived risk in online banking usage. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 27(1), 53–75.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ayo, C.K., Oni, A. A., Adewoye, O.J., & Eweoya, I.O. (2016). E-banking users’ behaviour: E-service quality, attitude, and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 34(3), 347–367.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Caputo, A., & Kargina, M. (2022). A user-friendly method to merge Scopus and Web of Science data during bibliometric analysis. Journal of Marketing Analytics, 10(1), 82–88.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Haddaway, N.R., Page, M.J., Pritchard, C.C., & McGuinness, L. A. (2022). PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 18, e1230.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rodrigues, L. F., Costa, C. J., & Oliveira, A. (2016). Gamification: A framework for designing software in e-banking. Computers in Human Behavior, 62, 620–634.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rodrigues, L. F., Costa, C. J., & Oliveira, A. (2017). How does the web game design influence the behavior of e-banking users? Computers in Human Behavior, 74, 163–174.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rodrigues, L. F., Oliveira, A., & Costa, C. J. (2016a). Does ease-of-use contributes to the perception of enjoyment? A case of gamification in e-banking. Computers in Human Behavior, 61, 114–126.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rodrigues, L. F., Oliveira, A., & Costa, C. J. (2016b). Playing seriously – How gamification and social cues influence bank customers to use gamified e-business applications. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 392–407.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sanchez-Franco, M. J. (2009). The Moderating Effects of Involvement on the Relationships between Satisfaction, Trust and Commitment in e-Banking. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 23(3), 247–258.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Shankar, A., & Jebarajakirthy, C. (2019). The influence of e-banking service quality on customer loyalty: A moderated mediation approach. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 37(5), 1119–1142.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Sousa, R., & Voss, C. A. (2009). The effects of service failures and recovery on customer loyalty in e-services: An empirical investigation. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 29(8), 834–864.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Yap, K. B., Wong, D. H., Loh, C., & Bak, R. (2010). Offline and online banking – where to draw the line when building trust in e-banking? International Journal of Bank Marketing, 28(1), 27–46.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 19-Feb-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14521; Editor assigned: 20-Feb-2024, PreQC No. AMSJ-24-14521(PQ); Reviewed: 30-Mar-2024, QC No. AMSJ-24-14521; Revised: 29-Apr-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14521(R); Published: 05-Jul-2024