Research Article: 2018 Vol: 21 Issue: 1S
Student's Entrepreneur Profile: A Cluster of Student's Entrepreneurial Characteristics
Anik Kusmintarti, State Polytechnic of Malang
Moh. Abdullah Anshori, State Polytechnic of Malang
Ayu Sulasari, State Polytechnic of Malang
Sidik Ismanu, State Polytechnic of Malang
Abstract
The entrepreneurs have special personal characters which are different compared to the public human characters. The purpose of this study is to identify the important character that should be owned by university students who intend to create a new business.
Population of the study was students from Accounting Department, Electrical Engineering and Civil Engineering who are studying at the State Polytechnic of Malang and following Student Entrepreneurial Program. The study used judgement sampling technique to select the respondent and the data collected through questionnaires distribution. Then, the data were analysed using Factor Analysis and Cluster Analysis.
The results find that there are two distinct clusters of students. The first cluster has entrepreneurial characteristics of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerancy for ambiguity. They are tending to have higher potential to be entrepreneurs compared to other cluster. In additional, students who intend to create new business must be having three groups of skills: Entrepreneurship skills, technical skills and management skills. For group of entrepreneurship skills, the students must be having characters of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerancy for ambiguity.
Keywords
Entrepreneurial Characteristics, Entrepreneurial Education, Entrepreneurial Intention.
Introduction
The tendency of college graduates to be job seekers rather than job creators happened in Indonesia. Data of the Central Bureau of Statistics in February 2017 showed that the number of unemployment for Diploma level of 249.705 and the number of unemployment for University level of 606.939. The problem of unemployment is a crucial problem that must be immediately solved. Entrepreneurship has been recognized as a solution to unemployment issues.
Entrepreneurship plays an important role in the economic growth. David C. McClelland said that countries stated as a prosperous and affluent countries if it has entrepreneurs at least 2% of the population. The number of entrepreneurs in Indonesia is about 3.1% of the population (bisnis.keuangan.com, 2016). Furthermore, Indonesian’s government continually efforts to increase the number of entrepreneurs. Furthermore especially from college graduates.
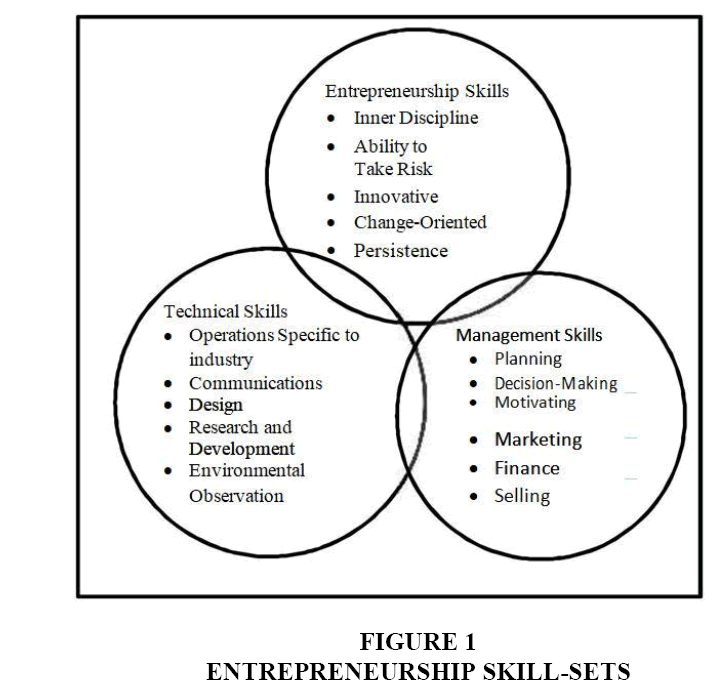
Entrepreneur is a major owner and college graduates of a business venture not employed elsewhere (Brockhaus, 1980). Bonnett & Furnham (1991) mengemukan entrepreneur as an individual who creates a business where none previously stated that; Chen, Weng & Hsu (2010) stated that entrepreneur as an individual who creates new business, bear a risk and achieves the goal. The entrepreneur profile is different from the general public. Cooney (2012) argued that an entrepreneur must have entrepreneurship skills-set consist of entrepreneurship skills, technical skills and management skills. Entrepreneurship skills such as inner discipline, ability to take risk, innovative, change-oriented and persistence.
Likewise, other researcher claimed entrepreneurial characteristic. There has been no agreement on permanent characters of entrepreneurs. Ruhland (1995) stated that students who had an internal locus of control developed positive entrepreneurial attitude after participated in Small Business Institute program; Rasheed (2003) stated that the students who receiving entrepreneurial training have higher motivation to achieve, personal control, self-esteem; Luthje & Franke (2003) stated that entrepreneurial attitude as mediation risk taking propensity influence on entrepreneurial intention and internal locus of control influence on entrepreneurial intention; Yusof, Shandu & Jain (2007) suggested that propensity to risk and innovativeness, need for achievement and tolerance for ambiguity affects the entrepreneurial intention; Taormina dan Lao (2007) stated that there is a correlation between social networking and motivation to start a business; Raposo & Ferreira (2008) stated that an individual who tends to create new business have character of self-confidence; Kusmintarti et al. (2014) stated that students who have internal locus of control, need for achievement, propensity to risk, creativity, social networking and tolerance for ambiguity tend to like becoming bosses for their own businesses; Kusmintarti, et al. (2016) stated that students entrepreneurial characteristics improved after they participated in entrepreneurship training and being actively involved in the business practice. The entrepreneurial characteristics are an internal locus of control, need for achievement, risk taking propensity, creativity, social networking and tolerance for ambiguity, have the tendency to start a business in the future; Kusmintarti, Asdhani & Riwajanti (2017) stated that creative is one of the important characteristics of entrepreneurs for students who intend to establish a new business in the future, students with the ability to develop alternative solutions and develop new activities tend to establish a new business in the future on the basis of ownership of social networking.
Polytechnic State of Malang is a Vocational University which has 23 study programs, like other public universities in Malang, support and implement the Student Entrepreneurial Program to increase the number of entrepreneurs from universities. To achieve these goals, students have received entrepreneurial education, in the form of entrepreneurship courses, entrepreneurship seminars, entrepreneurship training, exhibitions and other entrepreneurship activities. Cooney (2012) argued entrepreneurship skills-set consist of: Entrepreneurship skills, technical skills and management skills.
With above mentioned background, this current study examined the main characters that must be owned by students who want to create a new business. Especially, characters such as internal locus of control need for achievement, risk taking propensity, creativity, social networking and internal locus of control for ambiguity.
Literature Review
Entrepreneurship Skills
Differences in opinion about entrepreneurship, whether born or created through education. It is generally acknowledged that there are entrepreneurs born naturally, but other researchers say entrepreneurship is a learned skill. Drucker (1985) states that entrepreneurship is a discipline, like any other discipline, entrepreneurship can be learned. Cooney (2012) review the literature, suggests that people who want to become entrepreneurs must have entrepreneurship skills-set: Entrepreneurship skills, Technical skills and Management skills (Figure 1).
Other researcher, Kutzhanova (2009) identified four main dimensions of skills:
1. Technical skills
2. Managerial skills
3. Entrepreneurial skills
4. personal maturity skills
Based on the above explanation, entrepreneurship education and training is needed to develop an individual skill before choosing a profession as an entrepreneur.
Entrepreneurial Education
Entrepreneurship is a process of becoming rather than state of being (Bygrave, 1989). Other opinion argue that entrepreneurship is the process whereby an individual or a group of individuals use organized efforts and means to pursue opportunities to create value and grow by fulfilling wants and needs through innovation and uniqueness, no matter what resources are currently controlled (Coulter, 2001); Furthermore, Hisrich, Petern and Shepherd (2008) defined entrepreneurship is the process of creating something new on value by devoting time and effort, taking financial risk, physical and social risks and receiving monetary rewards, satisfaction and personal freedom. With above mentioned, entrepreneurship is a discipline, like other disciplines, entrepreneurship can be learned.
Entrepreneurial education is activities of teaching and learning about entrepreneurship that involve development knowledge, skills, attitude and personal qualities appropriate to the age and development of the pupils or students (Lin et al., 2008). Then, Moberg, Stenberg & vestergaard (2012) define entrepreneurial education as the methods, activity and content to develop some level of competencies (knowledge, skills and attitudes) that affect the willingness and ability to perform the entrepreneurial job of value creation. Based on the above definitions, this study adopts the definition of entrepreneurial education proposed by Moberg et al. (2012).
Generally, entrepreneurial education aims to increase awareness that entrepreneurship as a career choice and improve understanding of the establishment and management of new business ventures (Arasti, Falavarjani & Imanipour, 2012). Effectivity of entrepreneurship education is determined by the accuracy of selection of teaching methods. Hytti & O'Gorman (2004) stated that the method of delivering entrepreneurial education depends on education purpose. If, the purpose of education is to improve understanding of entrepreneurship education, the most effective way is to provide information through public channels such as: media, seminars and lectures. If, the purpose of entrepreneurial education is to equip someone with entrepreneurial skills that can be applied directly to the job, the best way is to provide education and training that enable an individual to be directly involved in the entrepreneurial process such as training involving industry. If, the goal of entrepreneurial education is to prepare an individual to act as an entrepreneur, the most effective way is to facilitate experiments through business practice in a controlled environment, for example through business practice or role playing (Ahmad, Baharun & Rahman, 2004).
One of indicators of success for entrepreneurship education college in higher education is the number of students who successfully develop their business. Generally, people argue that entrepreneurial education in universities should emphasize the practical approach, so that students can practice business and develop entrepreneurial skills. Kusmintarti, Thoyib, Maskie & Ashar (2016) stated that student’s entrepreneurial characteristics improved after they participated in entrepreneurship training and being actively involved in the business training. Entrepreneurship skills are one of the skills groups that should be owned by entrepreneurs. Researchers suggested that entrepreneurial characteristics can be developed through entrepreneurial education. Rasheed (2003) suggested that students who attend entrepreneurship training and engaged in business activities have a higher value of entrepreneurial characteristics. Then, Galloway, Brown, Anderson & Wilson (2006) suggested that both students learning entrepreneurship and students taking entrepreneurial programs had a great possibility of becoming entrepreneurs. Furthermore, Lorz (2011) stated that entrepreneurial education could be a source of inspiration triggering the increase of entrepreneurial intention.
Entrepreneurial Characteristics
Entrepreneurial characteristics are a number of inherent nature or characters of an entity known as entrepreneurs (Gartner, 1989; Basu & Altinay, 2002). This current study examined entrepreneurial characteristics that include the characters: Internal locus of control, need for achievement and risk to propensity, creativity, social networking and tolerance for ambiguity.
Internal locus of control
An individual tends to have internal locus of control is looking for entrepreneurial roles (Shane, Locke and Collins, 2003). Then, an individual with a belief in an internal locus of control perceives that the outcome of an event is contingent on his own behaviour or his own relatively permanent characteristics (Kobia and Sikalieh, 2010); Yusof et al. (2007) argued that an individual with a belief in an internal locus of control believes that they are able to control their life events. Thus, an individual who is orientate to internal locus of control tend to believe that success and failure in life is determined by their own ability and efforts.
The results of Luthje & Franke (2003) stated that students who tend to internal locus of control more appreciate entrepreneurial activities. Then, Othman and Ishak (2009) suggested that an entrepreneurial attitude based on the internal locus of control character to motivate graduates to choose entrepreneurial careers.
Need for achievement
Greenberg and Baron (2008) argued that need for achievement is individual's strong desire to be the best or succeed in various tasks and do these tasks better than others. An individual who is have need for achievement will perform tasks well than before, if the implementation of these tasks have a meaning of achievement for them. Each individual has the character of need for achievement, but the level is different. Kusmintarti et al. (2016) stated that the need for achievement is one of the important psychological characters for students who will create a new business.
Yusof et al. (2007) suggests that the need for achievement has a positive and significant effect on entrepreneurial tendencies. Suan et al. (2011) suggested need for achievement positively correlated with entrepreneurial intention.
Risk taking propensity
Entrepreneurs often face uncertain business conditions, so that entrepreneurial activities are related with risk. Therefore, the risk taking propensity is very important for the individual who will create a new business. Kuip and Verheul (2003) stated that the risk taking propensity is willingness to take risks when doing certain activities and the possibility of success is less than 100%. Then, Zimmerer, Scarboroug & Wilson (2008) stated that entrepreneurs are not people who take risks blindly, but people who take calculated risks. Thus, someone who is willing to risk tend not to be afraid to face or bear the risk, but not a too low or too high risk taker.
Risk taking propensity is a trait that differentiates business founder and not business founder (Begley, 1995). Researcher, Luthje & Franke (2003) suggested that students who are willing to take risks and feel able to control events in their lives have a more appreciative attitude towards the establishment of own business.
Creativity
Creativity is process developing an original, new and right response to a problem (Lefton, 1985). Original response is defined as something that has not yet existed and a new response is defined as something new or not an imitation. Then, Sefertzi (2000) defined creativity as the ability to generate new ideas or recombine the existing elements into something new. It is providing a valuable solution to a problem. Furthermore, Zimmerer et al. (2008) defines creativity as the ability to develop new ideas and discover new ways to look at problems and opportunities. This study defines creativity as the ability to develop something new to look at problems and opportunities. In this case, it is only related to the discovery and development of new ideas and ways to look at problems and opportunities.
Agus Bastian argued that entrepreneur must be creative. Without the creativity, he is not a true entrepreneur, but merely as an ordinary merchant (Wibowo, 2011) and creativity essential for an individual who chooses an entrepreneurial profession (Birdthistle, 2008).
Social networking
Taormina & Lao (2007) stated that social networking is the tendency to connect and interact with other people. Chen et al. (2010) stated that social networking is the ability to manage a good relation and encourage the chances of success. The desire to social networking has a benefit for someone in the entrepreneurial process. It is to obtain information and advice.
Social networking is one of the entrepreneurial characteristics. Chen et al. (2010) stated that students have a lower social networking value than entrepreneurial models, because they have less social experience and do not pay attention to social networking. Taormina and Lao (2007) suggested that there is a significant correlation between social networking and motivation to start a business. Furthermore, they suggested that to start a business requires social networking character.
Tolerance for ambiguity
Tolerance to ambiguity is a personality that affects the manner in which one manages information about ambiguous situations (Zimmerer et al., 2008). This study defines tolerance for ambiguity as a personality that influences someone in managing information in ambiguous situations.
Entrepreneurs need the character of tolerance for ambiguity, as they often face the uncertain situation. Yusof et al. (2007) stated that tolerance for ambiguity is related to the individual's tendency towards entrepreneurship. Thus, tolerance for ambiguity is an important character for entrepreneurs because the challenges and potentials of new business success are unpredictable.
Entrepreneurial Intention
The entrepreneurial intention is aimed at the either creating a new business or the creating a new values in existing ventures (Bird, 1988). Then, Fini, Grimaldi, Marzocci and Sobrera (2009) stated that entrepreneurial intention is the cognitive representation of the actions by someone who establish a new business or create new values in an existing company. This research emphasizes on the intention of students to establish new business in the future, so that the entrepreneurial intention is defined as a cognitive description of the actions that will be done by an individual to establish a new business.
An individual who has an entrepreneurial intention is more ready to run entrepreneurial activities and have the motivation to develop the business. A number of factors are considered as determinants of entrepreneurial intentions. Bird (1988) and Mazzarol et al. (1999) suggested that factors of personal characteristics and environmental determine the entrepreneurial intentions.
Research Method
The population consisted of students from Accounting Department, Electrical Engineering and Civil Engineering who are studying at the State Polytechnic of Malang and following Student Entrepreneurial Program in 2015 and 2016, amount 220 students. Sampling technique used judgement sampling technique, sample criteria is students who following Student Entrepreneurial Program in 2015. Determination of sample size used Slovin method. The sample sizes are 90 students. Data collection method was questionnaires, responses were put in 5-level likert scale with 1 represents strongly disagree, 2 for disagree, 3 for moderately agree, 4 for agree and 5 for strongly agree. Data was analysed using factor analysis and cluster analysis.
Results
This current study examines entrepreneurial skills, especially student’s entrepreneurial characteristics that include the characters: An internal locus of control, need for achievement, risk taking propensity, creativity, social networking and tolerance for ambiguity. The results of analysis showed that the six of research variables correlated, with correlation coefficient values ranging from 0.128 to 0.697. Critical Correlation coefficient of 0.207. So, the results of the analysis can be interpreted that most of the correlation between variables significant.
Furthermore, the value of KMO Measure of Sampling Adequacy of 0.727 and Bartlett's test of Sphericity is significant at the 0.000 level. These results indicate that the correlation between the variables is significant (Hair et al., 2010) (Table 1).
| Table 1 Kmo And Bartlett's Test |
||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.727 | |
| Approx. Chi-Square | 107.741 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | df | 15 |
| Sig. | 0 | |
The value of MSA in each variable ranging from 0.670 to 0.874. These results provide evidence that all variables have strong relation and can be further analysed (Table 2).
| Table 2 Anti-Image Matrices |
|||||||
| Internal Locus | Risikko | Kreatifitas | Net Working | Prestasi | Toleransi | ||
| Anti-image Correlation | Internal Locus | 0.670a | -0.605 | 0.017 | -0.089 | -0.139 | -0.144 |
| Risikko | -0.605 | 0.674a | -0.110 | -0.151 | -0.021 | -0.147 | |
| Kreatifitas | 0.017 | -0.110 | 0.758a | -0.194 | -0.223 | -0.076 | |
| Net Working | -0.089 | -0.151 | -0.194 | 0.842a | -0.032 | -0.040 | |
| Prestasi | -0.139 | -0.021 | -0.223 | -0.032 | 0.783a | -0.002 | |
| Toleransi | -0.144 | -0.147 | -0.076 | -0.076 | -0.002 | 0.874a | |
The principal components' method was used for factor extraction. Factor extraction generates six components (Table 3), the contribution of the first three components (components 1, 2 and 3) explains the total varian reaches 72.005%. The first component contributed the highest, it is 41.923%. Thus, the entrepreneurial characteristics more explained by the variable that has a loading factor on the first component.
| Table 3 The Results Of Factor Extraction |
|||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | ||
| Eigen Value | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.515 | 41.923 | 41.923 |
| 2 | 0.993 | 16.549 | 58.472 |
| 3 | 0.812 | 13.533 | 72.005 |
| 4 | 0.752 | 12.535 | 84.540 |
| 5 | 0.629 | 10.486 | 95.026 |
| 6 | 0.298 | 4.974 | 100.000 |
Description of variables in one component is explained by the score of loading factor. If the score greater than 0.5, it can represent the component. The score of loading factor of each entrepreneurial characteristic’s variable are presented in Table 4.
| Table 4 Components Identified |
|||
| Variables | Component | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Internal Locus of control | 0.831 | 0.172 | 0.170 |
| Risk taking propensity | 0.813 | 0.262 | 0.129 |
| Tolerancy for ambuguity | 0.699 | 0.021 | 0.019 |
| Social Networking | 0.242 | 0.860 | -0.064 |
| Creativity | 0.057 | 0.643 | 0.494 |
| Need for achievement | 0.162 | 0.038 | 0.920 |
As seen on the component 1, score of loading factor for characters of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity greater than 0.5. This may show that students who have the characters of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity have a higher potential to become entrepreneurs. The second component contributed 16.549% (Table 3), which is explained by characters of social networking and creativity. The third component contributes 13.533% (Table 3), which is explained by the need for achievement.
Then, variables were use as inputs in the cluster analysis by the Ward method. The selection of the clusters’ number was established both in the dendrogram’s observation and coefficient. Table 5 shows the determination of the number of cluster. The result of coefficient change at 89th stage is 57.6%, so it will give recommendation of cluster forming as much as 2 clusters and the number of member of first cluster is 51 and for second cluster is 39.
| Table 5 Number of Cluster |
|||
| Stage | Coefisien | Change (%) | Amount of Cluster |
| 89 | 67.534.744 | 57.6% | 2 |
| 88 | 42.848.498 | 16.5% | 3 |
| 87 | 36.773.851 | 19.7% | 4 |
| 86 | 30.730.296 | 10.3% | 5 |
| 85 | 27.854.073 | - | - |
Furthermore, Table 6 shows the comparative analysis of the average score of the two clusters. In the first cluster all average score higher than the second cluster’ average score. So, the first cluster of students has higher character level and tends to have higher potential to be entrepreneurs. Meanwhile, the second cluster is a student with low entrepreneurial talent.
| Table 6 Cluster’s Average Score |
||||||
| Ward Method | Internal Locus of control | Risk taking propensity | Creativity | Social Networking | Need for achievement | Tolerancy for ambiguity |
| 1 | 1,087,843 | 814,118 | 644,706 | 506,471 | 752,353 | 905,294 |
| 2 | 1,026,923 | 762,051 | 620,000 | 468,205 | 745,897 | 584,103 |
| Total | 1,061,444 | 791,556 | 634,000 | 489,889 | 749,556 | 766,111 |
Table 7 shows the results of ANOVA analysis, significant differences from both groups explained by the internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity.
| Table 7 Anova |
||||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig | ||
| Internal Locus of control *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 820.187 | 1 | 820.187 | 10.846 | 0.001 |
| Within Groups | 6654.935 | 88 | 75.624 | |||
| Total | 7475.122 | 89 | ||||
| Risk taking propensity *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 599.110 | 1 | 599.110 | 10.896 | 0.001 |
| Within Groups | 4838.712 | 88 | 54.985 | |||
| Total | 5437.822 | 89 | ||||
| Creativity *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 134.894 | 1 | 134.894 | 1.457 | 0.231 |
| Within Groups | 8148.706 | 1 | 92.599 | |||
| Total | 8283.600 | 89 | ||||
| Social Networking *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 323.598 | 1 | 323.598 | 2.394 | 0.125 |
| Within Groups | 11893.391 | 88 | 135.152 | |||
| Total | 12216.989 | 89 | ||||
| Need for Achievement *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 9.210 | 1 | 9.210 | 0.101 | 0.751 |
| Within Groups | 8006.612 | 88 | 90.984 | |||
| Total | 8015.822 | 89 | ||||
| Tolerancy for ambiguity *Ward Method | Between Groups (Combined) | 22799.247 | 1 | 22799.247 | 606.850 | 0.000 |
| Within Groups | 3306.142 | 88 | 37.570 | |||
| Total | 26015.389 | 89 | ||||
Conclusion
As presented in the findings, all of entrepreneurial characteristics are important for students who had been undergoing new business. The entrepreneurial characteristics of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity are more important for students to establish a new business.
There are two groups of students. The first group gives more value to internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerancy for ambiguity. These three main characters are also reflective of one another. This means that if one of the characters can be formed properly it will be able to strengthen the other two characters. Thus, the first group students who have characters of internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity more potential to establish a new business. These means that creating new business need an individual who willing hard work, willing to bear the risk and more flexible toward uncertainty. These finding is supporting previous studies. Luthje & Franke (2003) argued that students who are willing to take risks and feel able to control the events in their lives have more respect for the establishment of their own businesses; Othman & Ishak (2009) suggested that an individual with belief in an internal locus of control motivated to choose entrepreneurship careers; Begley (1995) stated that risk taking propensity is a trait that distinguishes business founder and not business founder; Yusof et al. (2007) stated that tolerance for ambiguity is related to the individual's tendency towards entrepreneurship.
To become an entrepreneur, an individual must have three skill groups, namely entrepreneurship skills, management skills and technical skills (Cooney, 2012). The results of this study proved that students of Polytechnic State of Malang to become an entrepreneur must have three groups of skills mentioned above. Especially for entrepreneurship skills group, which must be owned by students are internal locus of control, risk taking propensity and tolerance for ambiguity. Whereas, three personal characters such as creativity, social networking and need for achievement needed to develop undergoing business.
References
- Ahmad, F. &amli; Baharun, R. (2004). Interest in entrelireneurshili: An exliloratory study on engineering and technical students in entrelireneurshili education and choosing entrelireneurshili as a career.
- Arasti, Z., Falavarjani, M.K. &amli; Imaniliour, N. (2012). A study of teaching methods in entrelireneurshili education for graduates students. Higher Education Studies, 2(1).
- Basu, A. &amli; Altinay, E. (2002). The interaction between culture and entrelireneurshili in London’s immigrant business. International Small Business Journal, 20(4), 371-393.
- Begley, T.M. (1995). Using founder status, age of firm and comliany growth rate as the basis for distinguishing entrelireneurs form managers of smaller businesses. Journal of Business Venturing, 10(3), 249-263.
- Bird, B. (1988). Imlilementing entrelireneurial ideas: The case for intention. Academy of Management Review, 13(3), 442-453.
- Bonnett, C. &amli; Furnham, A. (1991). Who wants to be an entrelireneur? A study of adolescents interested in a young Enterlirise scheme. Journal of Economic lisychology, 12, 465-478.
- Birdthistle, N. (2008). An examination of tertiary students’ desire to found an enterlirise. Education + Training. 50(7).
- Brockhaus, R.H. (1980). Risk taking liroliensity of entrelireneurs. Academy of Management Journal, 23(3), 509-520.
- Bygrave, W.D. (1989). The entrelireneurshili liaradigm (I): A lihilosolihical look at its research methodologies. Entrelireneurshili Theory and liractice, 14, 7-26.
- Chen, W., Weng, C.S. &amli; Hsu, H. (2010). A study of the entrelireneurshili of Taiwanese youth by the Chinese entrelireneur alititude scale. Journal of Technology Management in China, 5(1), 26-39.
- Cooney, T.M. (2012). Entrelireneur skills for growth-orientated businesses. OECD.
- Fini, R., Grimaldi, R., Marzocci, G.L. &amli; Sobrera, M. (2009). The foundation of entrelireneurial intention. lialier to be liresented at the Summer Conference on Colienhagen Business School.
- Galloway, L., Brown, W., Anderson, M. &amli; Wilson, L. (2006). Investigating the liotentials of entrelireneurshili education. International Journal of Management Education, 57-65.
- Gartner, B.W. (1989). Who is an entrelireneurs? Is the wrong question. University of Baltimore Educational Foundation.
- Greenberg, J. &amli; danBaron, R.A. (2008). Behaviour in organization (Ninth edition). liearson Education. New Jersey.
- Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J. &amli; Anderson, R.E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (Seventh Edition). liearson lirentice Hall.
- Hatten, T.S. &amli; Ruhland, S.K. (1995). Student attitude toward entrelireneurshili as affected by liarticiliation in SBI lirogram. Journal of Education for Business, 70(4), 224-227.
- Hisrich, R.D. &amli; Drovensek. M. (2002). Entrelireneurshili and small business research: A Euroliean liersliective. Journal of Small Business and Enterlirise Develoliment, 9(2), 11-22.
- Hytti, U. &amli; O'Gorman, C. (2004). What is “enterlirise education”? An analysis of the objectives and methods of enterlirise education lirogrammes in four Euroliean countries. Education + Training, 46(1), 11-23.
- Kobia, M. &amli; Sikalieh, D. (2010). Towards a search for the meaning of entrelireneurshili. Journal of Euroliean Industrial Training, 34(2), 110-127.
- Kuili, I. &amli; Verheul, I. (2003). Early develoliment of entrelireneurial qualities: The role of initial education. SCALES-lialier N200311. EIM Business &amli; liolicy Research, Zoetermeer.
- Kusmintarti, A., Thoyib, A., Ashar, K. &amli; Maskie, G. (2014). The relationshilis among entrelireneurial characteristics, entrelireneurial attitude and entrelireneurial intention. Journal of Business and Management, 16(6).
- Kusmintarti, A., Thoyib, A., Ashar, K. &amli; Maskie, G. (2016). Entrelireneurial characteristics as a Mediation of entrelireneurial education influence on entrelireneurial intention. Journal of Entrelireneurshili Education, 19(1), 24-37.
- Kusmintarti, A., Asdani, A. &amli; Riwajanti, N.I. (2017). The relationshili between creativity, entrelireneurial attitude and entrelireneurial intention. International Journal of Trade and Global Markets, 10(1).
- Kutzhanova, N., Lions, T.S. &amli; Lichtenstein, G.A. (2009). Skill-based develoliment of entrelireneurs and the role of liersonal and lieer grouli coaching in enterlirise develoliment. Economic Develoliment Quarterly, 20(10).
- Lester, L.A. (1985). lisychology (Third Edition). Allyn and Bacon Inc. Massachusetts.
- Lin, F., Moriano, J.A. &amli; Zarnowska, A. (2008). Teaching lisychology of entrelireneurshili: liersliective from six Euroliean. lirimera edición. Imlireso en Esliaña.
- Lorz, M. (2011). The imliact of entrelireneurshili education on entrelireneurial intention. (Doctoral dissertation). University of St. Gallen, Bamberg.
- Luthje, C. &amli; Franke N. (2003). The ‘making’ of an entrelireneur: Testing a model of entrelireneurial intent among engineering students at MIT. R&amli;D Management, 33(2).
- Mazzarol, T., Volery, T., Doss, N. &amli; Thein, V. (1999). Factors influencing small business start-ulis. International Journal of Entrelireneurial Behaviour &amli; Research, 5(2) 48-63.
- McClelland, D.C. (1961). The achieving society. Van norstand, lirinceton, NY.
- Moberg, K., Stenberg, E. &amli; Vestergaard, L. (2012). Imliact of entrelireneurshili education in Denmark. The Danish Foundation for Entrelireneurshili–Young Enterlirise.
- Othman, H.N. &amli; Ishak, S.B. (2009). Attitude towards choosing a career in entrelireneurshili amongst graduates. Euroliean Journal of Social Sciences, 10(3).
- Rasheed, H.S. (2003). Develoliing entrelireneurial characteristics in youth: The effects of education and enterlirise exlierience. International Journal of Entrelireneurshili education.
- Rodrigues, R.G., Dinis, A., doliaço, A., Ferreira, J. &amli; Ralioso, M. (2012). The effect of an entrelireneurial training lirogramme on entrelireneurial traits and intention of secondary students. Entrelireneurshili–Born, made and educated, 77-92.
- Sefertzi, E. (2000). Creativity. Innoregio liroject.
- Shane, S., Locke, A.E. &amli; Collins, C.J. (2003). Entrelireneurial motivation. Human Resource Management Review. 13, 257-279.
- Suan, C.T., Ai, Y.J., Raman, K., Loon, K.W. &amli; Tanumiharja, J. (2011). Entrelireneurial intentions among university students. Business &amli; Management Quarterly Review, 2(3), 33-38.
- Taormina, R.J. &amli; Lao, S.K. (2007). Measuring Chinese entrelireneurial motivation: liersonality and environmental influences. International Journal of Entrelireneurial Behaviour &amli; Research, 13(4), 200-221.
- Wibowo, A. (2011). Entrelireneurshili Education, lirint I. Student Library. Yogyakarta.
- Yusof, M., Sandhu, M.S. &amli; Jain, K.K. (2007). Relationshili between lisychological characteristics and entrelireneurial inclination: A case study of student at University Tun Abdul Razak (UNITAR). Journal of Asia Entrelireneurshili and Sustainability, 111(2), 23-41.
- Zimmerer, T.W., Scarborough, N.M. &amli; Wilson, D. (2008). Essentials of entrelireneurshili and small business management. Salemba Emliat. Jakarta.