Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 1
Strategy of Socially Responsible Enterprise Personnel Management
Olha Kuzmenko, International European University
Dmytro Kilderov, Dragomanov National Pedagogical University
Tetyana Babych, Kyiv National Economic University named after Vadym Hetman
Svitlana Breus, Kyiv National University of Technologies and Design
Philip Stoyanov, University of National and World Economy
Abstract
According to the results of the analysis of the strategic personnel development management, it was determined that the development of socially responsible personnel is a top priority of a company, which wants to increase its position in the market and gain the reputation of a responsible employer. High loyalty of the personnel will ensure the growth of a company, so two directions of personnel development on social and environmental basis were proposed. The directions of education of socially responsible personnel were selected, which include many components which can be attributed to health insurance, sorting of garbage in the office, creation of green groups, organization of volunteer initiatives from company employees, balance between work and family, reduction of paper usage, issuance of non-disposable dishware, new standards of socially conscious management, a corporate university and an online learning portal. A strategy of socially responsible enterprise personnel development management is formed, which is aimed at educating the environmental consciousness of the company employees, which, as it was found, will contribute to the growth of employee loyalty, reputation, will shape the image of the green company, reduce the environmental impact, which in turn will ensure the development of environmental innovations, international cooperation, economic efficiency and increased government subsidies.
Keywords
Personnel Management Strategy, Development, Environmental Innovations, Economic Efficiency, Employee Loyalty.
JEL Classifications
M5, Q2
Introduction
Taking into account the turbulent conditions of the modern environment, there are changes in the content and nature of the work, its intellectualization is increasing, the mobility of workers is increasing, and other tendencies cause the constant growth of the human factor as a key aspect of the efficiency and competitiveness of an organization. It is a well-known fact that human capital is a strategically important resource of every company in the modern market, and its development is the main prerequisite for its competitiveness.
Currently, the planning and organization of the personnel development process is a leading task for achieving the current and long-term goals of a company in order to develop a highly skilled, competitive and knowledgeable employee. According to the traditional approaches to understanding social responsibility, the enterprise is obliged to be socially responsible not only to the society, but also to its own employees. Thus, it is necessary to introduce innovation methods of personnel development management, among which the leading position is taken by corporate social responsibility. Thus, social responsibility is gradually gaining the status of a new management philosophy, based on which companies define as their main goal not only increasing profits but also creating public goods and maintaining environmental sustainability.
Literature Review
The set of actions of managers of a certain organization regarding the development of personnel can be characterized in the form of a model that meets the strategic goals using the human potential for obtaining a certain economic effect (Aguinis & Glavas, 2019).
The personnel development management model can be understood as a set of features and elements that differentiate a company in its behavior regarding the development of its personnel (Mula, I., et al., 2017; Eyasu & Endale, 2020).
Currently, there are four models used in the practice of companies. The model of competitive advantages implies the creation of conditions for competition of employees in the enterprise, and according to it, individual abilities, skills, knowledge of employees should be used most effectively for ensuring and increasing the level of competitiveness of the enterprise itself (Barrena?Martinez et al., 2019; Carollo & Guerci, 2018). The use of this model implies constant audit of the personnel in order to identify the real needs of the enterprise in both its quantity and quality level. Continuous monitoring of employees, assessment of their abilities and level of knowledge, establishment of correspondences between the present needs of the enterprise and compliance with these needs of each employee are envisaged. Establishing the type of organizational culture according to which each employee is on his/her own and is not focused on teamwork.
The model of employee support envisages improving the quality of working life of the company personnel (Herrera et al., 2020; Freitas et al., 2020). The main steps to implement this model are as follows: elimination of heavy physical labor, automation and mechanization of labor; organization and implementation of social support programs for employees of an enterprise; creation of optimal working conditions at an enterprise, organization and implementation of programs for occupational health and safety; formation and implementation of appropriate organizational culture, etc.
The implementation of this model of personnel development is aimed at creating a strong internal motivation for employees to self-development and a strong degree of loyalty to the enterprise. Low level of employee turnover and developed organizational culture are additional advantages for the enterprise. However, the implementation of the above steps will not 100% lead to a real increase in the level of knowledge of employees, that is, the employee is not always ready to “give” to the enterprise (in the form of improving his/her skills and level of knowledge) as much as he received from it. This is the main drawback and risk of implementation of this model of personnel development.
The model of social support is implemented through the mechanism of becoming a socially responsible enterprise, which is declared as an element of corporate culture and overall strategy of doing business (Kaye & Humphreys, 2018; Voegtlin & Greenwood, 2016). The company, which adheres to the principles of socially responsible business, commits itself to conduct activities in accordance with ethical norms and to contribute to economic development by improving the quality of life of both its employees and their families, and the entire local population and society as a whole. In other words, socially responsible companies carry out their activities in such a way as to meet, or even exceed, the expectations of society related to the observance of ethical, legal, charitable, environmental, commercial and public principles. Unfortunately, this model of activity is not typical for most domestic enterprises and does not meet the principles on which business is conducted today.
The model concept of human development includes the following elements: providing the employee with continuing education and training opportunities; support for employee health; maintaining an adequate level of financial support for the decent life of the employee and his or her family (Morsiani et al., 2017; Mun & Jung, 2018). To unlock and realize the potential of the employee is the main purpose of such a model, which focuses on various aspects of the potential: intellectual, cultural, educational, creative, physical and labor. That is, the implementation of such a model of personnel development includes all the best features of the above models, aimed at multifaceted development of employees, convergence of coalition goals at the enterprise, which naturally leads to an increase in the level of competitiveness of the enterprise itself. However, this model is the most difficult to implement because of the large financial, managerial and organizational investments for its implementation.
Methodology
In the course of the study, a set of general and specific scientific methods was used. The theoretical basis of the study is the works of leading scientists on the issues of personnel development and social responsibility. The following study methods were used in the article: scientific abstraction, analysis and synthesis, systematic approach, logical, monographic method for substantiation of theoretical and practical recommendations on personnel development management on the basis of social responsibility; grouping, graphs for visual presentation of the results of theoretical and practical studies; scientific generalization for analysis of the proposed measures.
Results and Discussion
Innovations and inventors are one of the main drivers of the modern economy. The social responsibility of an innovator is an integral category aimed at solving social problems. The importance of innovations is increasing due to the need to address acute global problems of ecology, diseases, providing the growing population with food and water, social stability, etc. The social focus of innovations on improving the quality of life and empowering citizens sets new priorities for business.
The social responsibility of an innovator can be understood as honest, but not transparent, due to the trade secret of innovations, behavior of participants of innovation activities, which has a beneficial effect on the quality of life of both contemporaries and descendants.
The content of innovations affects the results of production activity of the personnel of enterprises. It is about developing and introducing innovative products to give it more originality; decommissioning of outdated products, involvement of new resources and technologies in production activities; mastering of new methods of organization of production and labor of the personnel of enterprises, etc. This, in turn, requires the creation of highly productive jobs and, accordingly, the provision of skilled employees capable of working in a constantly improving technology environment, demonstrating key and professional competencies, taking into account the requirements and specifics of innovation and production processes.
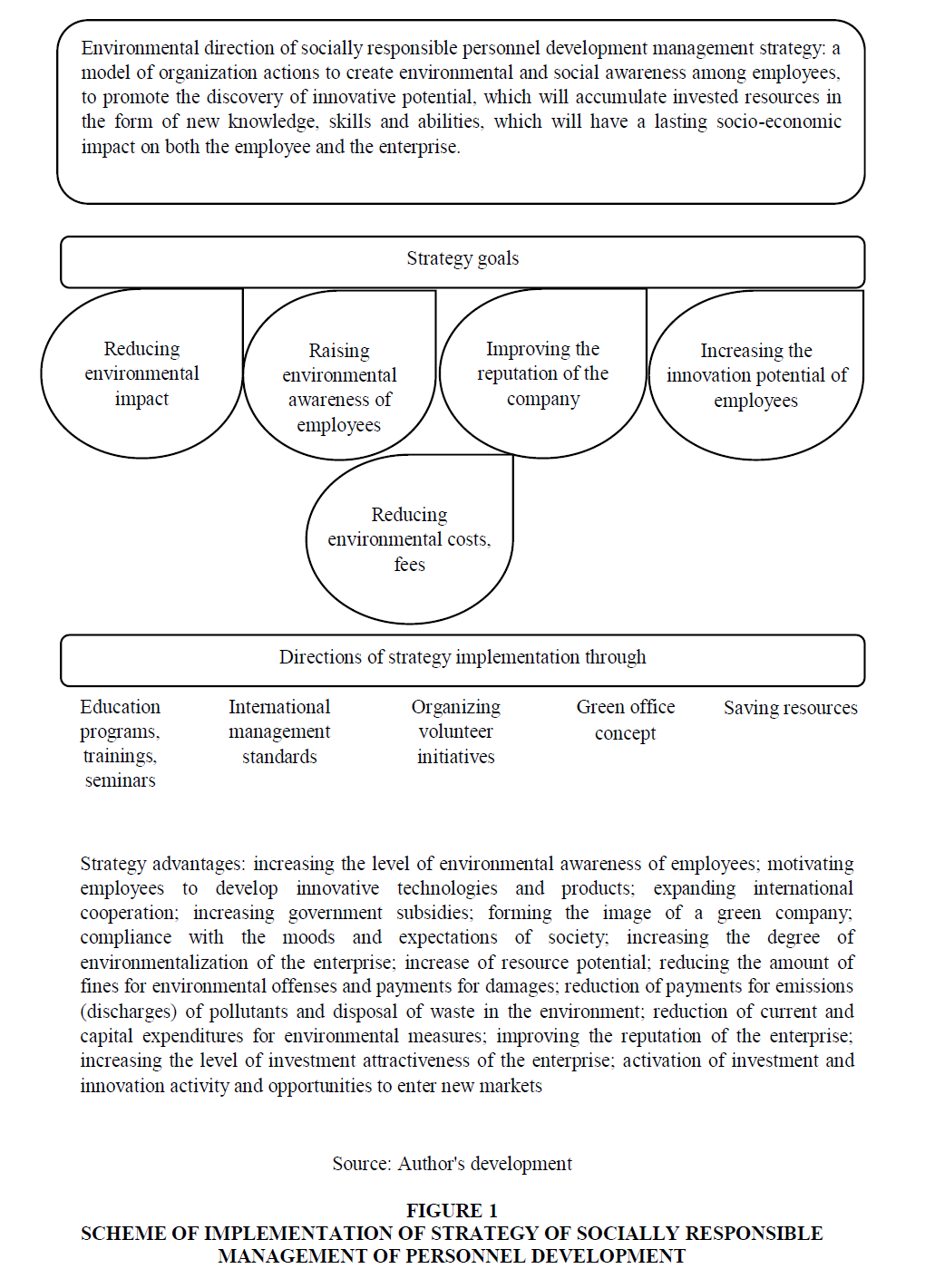
The personnel of the company is the bearer of social and environmental culture. The principles of responsible attitude to the environment, readiness to solve certain social and economic problems are established in its behavior. To be a successful and sustainable organization, reduce costs and impact on the environment, motivate personnel to take everyday care of nature, educate socially responsible employees, it is necessary to select a strategy of socially responsible personnel development management (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Scheme of Implementation of Strategy of Socially Responsible Management of Personnel Development
The main goals of the strategy are: reducing environmental impact; personnel motivation for daily care of nature; education of socially responsible and environmentally conscious employees; reducing environmental fees and payments; the possibility of expanding and conquering markets; ensuring the health of employees; increase of profit; cost reduction and production safety; raising the status of the enterprise, etc.
The implementation of the personnel development strategy includes the following areas: health insurance; sorting garbage in the office; formation of green groups; organizing volunteer initiatives from company employees; balance between work and family; new standards of socially responsible management; reduction of paper usage, corporate university; issuance of non-disposable dishware to employees, online learning portal.
The adoption of the principle of the concept of “Green Company”, namely sorting garbage at an industrial enterprise, will be a priority decision in the implementation of the strategy of environmental development of personnel.
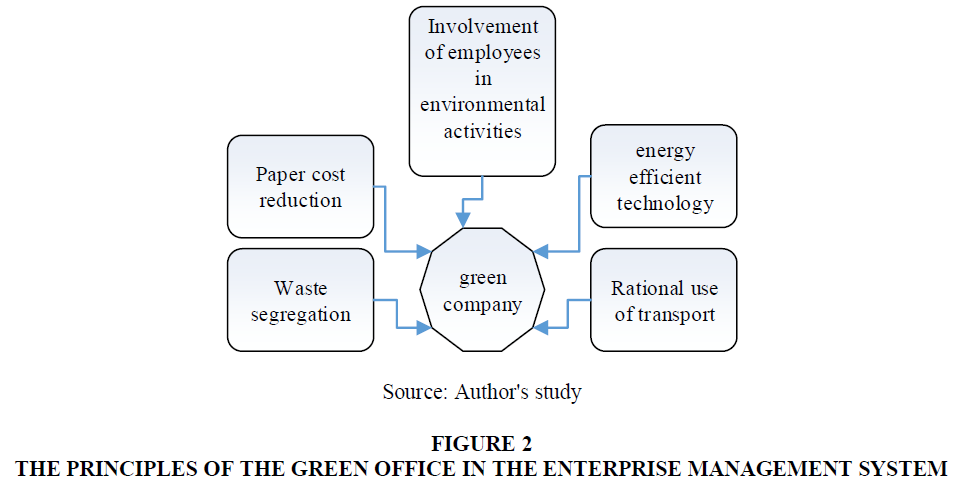
The green office is a company management concept that aims to reduce the environmental impact of organization activities and promote resource management while adhering to the principles in the Figure 2.
Taking care of future generations enhances the productivity and competitiveness of the company.
Firstly, according to certain studies, a corporate culture focused on taking care of environment attracts new clients and buyers, and improves the company competitiveness in the market. Introducing environmentally friendly principles of office operation is one of the manifestations of corporate social responsibility. And as numerous foreign studies show, social responsibility is exactly one of the factors that shape the opinions of buyers and often influences the choice of a product among a variety of products with approximately the same price and quality.
Secondly, companies with strong corporate values are more attractive to the most progressive part of the labor market participants. As for highly skilled workers with extensive experience, not only material remuneration but also the opportunity to work in a dynamic, innovative and responsible team is an important factor in choosing a place of work. Finally, a review of traditional office organization helps eliminate sources of hazards for employee health, which will help reduce respiratory illnesses, allergy and asthma cases, and reduce symptoms such as headache, eye irritation, apathy inherent in employees working in offices with limited ventilation.
Recommendations
An important step in the introduction of garbage sorting and the “Green Company” is to increase employee awareness in these matters. To inform your employees that the company will now implement the principles of garbage sorting. To tell them how important it is for the company to participate in this program and what help each of them will need. To explain to employees what benefits they will bring to the environment, to themselves, and to the budget of the organization. For clarity, it is necessary to give real savings figures.
It is necessary to be prepared to repeat the information to employees several times in order to consolidate the company values. The company should use information posters about saving paper, near office equipment, electricity, near desktop computers, water, and the need to dispose of garbage separately – in restrooms and in kitchens.
The stories on success of the “Green Office” can and should be emailed to employees, and a separate project page can be created on the corporate website. Participants of the project will be interested in thematic educational lectures, personal meetings with experts in the field of environmental protection and resource conservation. It is possible that, having learned from colleagues about a new energy-saving technology, some of the employees will engage in “greening” not only their workplace but also their own home.
Conclusions
A socially responsible personnel development management strategy was developed, which will be based on educating environmentally and socially aware personnel, pursuing green company practices, and skills in the given field gained by employees will provide the company with economic benefits. The introduction of the “Green Office” practices, namely separate sorting of garbage in the company offices, was a priority area for starting the implementation of the strategy. It is well known that garbage sorting is one of the main principles of a green company. Therefore, this project will change the attitude of employees to waste showing that carefully sorted waste is not waste but a valuable resource that can be reused without harming the environment.
It was studied that regarding social responsibility special attention is paid to company employees. The company tries its best to provide comfortable and safe working conditions with decent pay, cares about the health of employees, provides constant training and development of professional skills and observance of their rights, but have no focus on the moments of environmental consciousness and awareness of employees, discipline (regarding health and nutrition) and innovation.
However, it will not be possible to implement this project without reinforcing in the minds of employees of the importance of the project and the necessity of their involvement for ensuring the result. That is, it was determined that the project should be supported by various trainings, seminars and mass actions among employees.
References
- Aguinis, H., & Glavas, A. (2019). On corporate social responsibility, sensemaking, and the search for meaningfulness through work. Journal of Management, 45(3), 1057-1086.
- Barrena?Martinez, J., López?Fernández, M., & Romero?Fernández, P.M. (2019). The link between socially responsible human resource management and intellectual capital. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 26(1), 71-81.
- Carollo, L., & Guerci, M. (2018). ‘Activists in a suit’: Paradoxes and metaphors in sustainability managers’ identity work. Journal of Business Ethics, 148(2), 249-268.
- Eyasu, A.M., & Endale, M. (2020). Corporate social responsibility in agro-processing and garment industry: Evidence from Ethiopia. Cogent Business & Management, 7(1), 1720945.
- Freitas, W.R.D.S., Caldeira-Oliveira, J.H., Teixeira, A.A., Stefanelli, N.O., & Teixeira, T.B. (2020). Green human resource management and corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Brazilian firms. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 27(4), 1551-1569.
- Herrera, J., & de las Heras-Rosas, C. (2020). Corporate social responsibility and human resource management: Towards sustainable business organizations. Sustainability, 12(3), 841.
- Kaye, J., & Humphreys, K. (2018). A consortium approach to staff development. The Education of Dual Sensory Impaired Children: Recognising and Developing Ability, 17.
- Morsiani, G., Bagnasco, A., & Sasso, L. (2017). How staff nurses perceive the impact of nurse managers’ leadership style in terms of job satisfaction: a mixed method study. Journal of Nursing Management, 25(2), 119-128.
- Mula, I., Tilbury, D., Ryan, A., Mader, M., Dlouha, J., Mader, C., Benayas, J., Dlouhý, J., & Alba, D. (2017). Catalysing change in higher education for sustainable development. International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education, 18(5), 798-820.
- Mun, E., & Jung, J. (2018). Change above the glass ceiling: Corporate social responsibility and gender diversity in Japanese firms. Administrative Science Quarterly, 63(2), 409-440.
- Voegtlin, C., & Greenwood, M. (2016). Corporate social responsibility and human resource management: A systematic review and conceptual analysis. Human Resource Management Review, 26(3), 181-197.