Research Article: 2022 Vol: 25 Issue: 6
Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians within Thailand s Industry for Sustainable Success
Bundit Lamesawan, Industrial Business Administration, King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok
Nathasa Theanruechai, Industrial Business Administration, King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok
Sunee Wantanakomol, Industrial Business Administration, King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok
Citation Information: Lamesawan, B., Theanruechai, N., & Wantanakomol, S. (2022). Strategic management of migrant technicians within Thailand’s industry for sustainable success. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 25(S6), 1-12.
Keywords
Labour Management Strategy, Expat Employees, Migrant Technicians, Industrial Businesses
Abstract
Labor is a factor of production and human capital that is of great importance to economic development and national development. This research aims to study strategies for the management of migrant operating mechanics in Thailand’s industrial sector to achieve sustainable success. Qualitative and qualitative research methods were employed in this study. The quantitative data were obtained from interviewing 500 manufacturing entrepreneurs hiring labour migrants. As results, 5 strategic aspects for the predetemined objective were revealed, namely Planning, Selection, Knowledge, Performance and Relationship. Strategic recommendations are as follows: presenting the work structure diagram with roles and accountable person; making sure the visas of immigrant workforce are not expired; exploring successful performance coupled with the practice of knowledge exchange for rapid understanding; creating written assessment reports while employees are asked to sign to indicate that they are aware of the expectations; and providing opportunities for migrant workers to practise their professional knowledge and skills. The results of hypothesis testing showed that when classified by business organization size, it was found that there was Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians within Thailand’s Industry for Sustainable Success. Different measures for entrepreneurial success are found among small, medium-sized and large businesses (p<.05)
Introduction
The development of a country in a liberal economy focuses on promoting its adaptability as a competitive global player. Nowadays, it is found that most people are more interested in social, economic and political development, technology and the environment by using the fundamentals and resources available within the country. The result of development has had a huge impact on labor structures around the world as countries with no potential and lack of natural resources tend to suffer from increased poverty. For countries with the ability to develop, they will have rapid economic growth. The key factor is the ability to innovate and develop production technology and the ability to allocate resources and control production costs to a level that is superior to competitors. This is the reason for the migration of workers from underdeveloped countries where there is a lot of labor to developed countries but still has labor shortages. The development of labor immigration as a migrant worker stems from the continued economic growth of Thailand amid globalization to lead the country to the industrial age. Nowadays, each organization faces intense competition and ever-changing economic conditions.
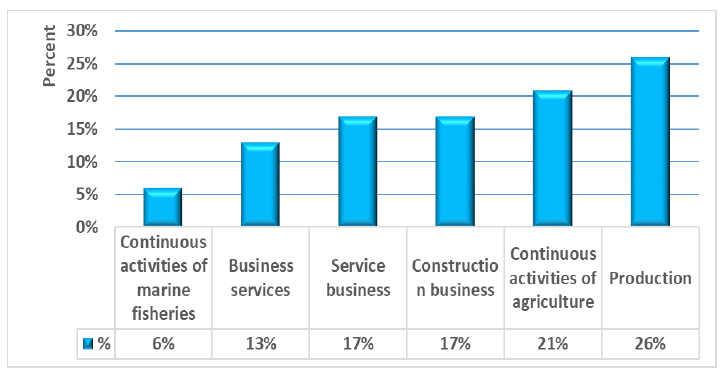
Human resource management, which is an intellectual asset, is considered a key strategy to develop the organization towards competitive advantages. Labor is a factor of production and human capital that is very important to the development of the economy and the country. If workers have the potential, it will affect the efficiency and effectiveness of the country's development. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the proper compensation of workers because it will enable the organization to attract the most talented people to the organization as well as being able to retain highly competent personnel with the organization at the same time, it can fairly deal with personnel whose performance does not meet the organization's requirements. Entrepreneurs have to adapt to this change so they hire expat employees from these 3 nationalities to work: Laos, Cambodia and Myanmar (Foreign Workers Administration Office, 2019). Such expat employees are classified into types of businesses in the manufacturing sector and the service sector in each business as shown in Figure 1 as follows.
Figure 1: Statistics on the Expat Employees of Laos, Combodis And Myanmar by Type of Business in 2019
From Figure 1, statistical data on the employment of expat employees in Laos, Cambodia and Myanmar were classified by type of business. The year 2019 can be seen that there would be sustainability of expat employees who came to work in each business group under the management of entrepreneurs, it was essential that there was a continuous workforce. However, according to the Ministry of Labor's data on labor protection, there had been ongoing complaints against employers of expat employees. Various causes of complaints such as employment conditions, working days and hours, wages, benefits, layoffs, complaints, etc., were increasing every year.
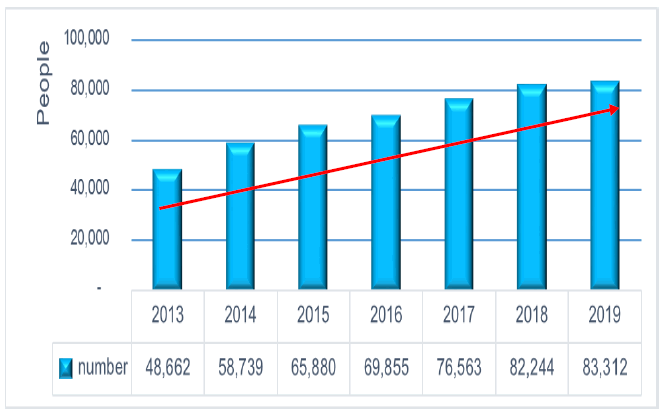
If we continued to look at the additional problems arising from the labor conflict, the consequences were resignation from work. There were 485,255 workers who resigned from 2013- 2019. There was information on the resignation of expat employees as shown in the graph in Figure 2 as follows:
From Figure 2, the number of expat employee’s resignation in 2013-2019 found that the resignation of expat employees from these three nationalities had increased continuously. There may be many reasons such as compensation, unfairness of supervisors, entering a new job but unable to adapt to the people in the team, systems that were not conducive to success and efficiency, etc. The high impact of resignation was the cost of recruiting new employees such as training, recruiting, and lower productivity. All of these things affected customer retention.
Therefore, if the organization would like to achieve its goals, the organization must adapt to the changing environment all the time such as selection, recruitment, performance appraisal, personnel development (training), salary, bonuses and benefits, as well as retirement from work, including taking care of life responsibilities. Organizing the working environment was an important human resource management process. If personnel management was ineffective, the organization's operations would encounter many obstacles such as resignation. Employee resignation was an organizational cost because the organization had invested in human development and work for some time. Resignation would cost more than the person's reward. Employee turnover rate was an indicator of investment wastage. On the other hand, it was a loss of corporate image (Pati Mo and Aziyah Awe, 2015). Entrepreneurs using migrant workers must have appropriate strategies and organizations should be ready to change themselves to develop and cope with the external environment. In order to add new channels, the researcher was interested in studying and creating a body of knowledge in creating strategies for managing migrant workers at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector as a strategy for the management of expat employees for entrepreneurs.
Literature Review
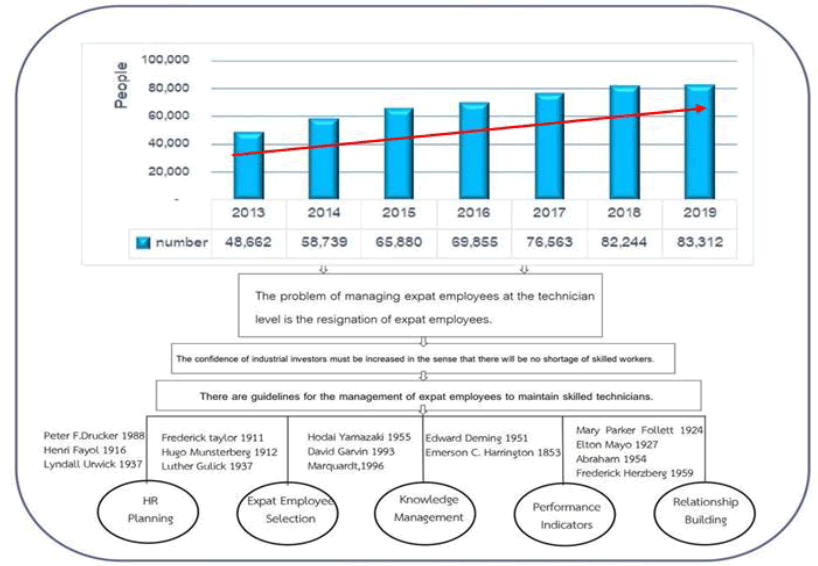
For the past concepts and theories, the researcher could summarize the strategies for managing expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector into 5 components: HR planning, expat employee selection, knowledge management, performance indicators and relationship building.
Figure 3:The Origin of the Research Component on the Strategic Management of Migrant Techinicians within Thailand’s Industry
Methodology
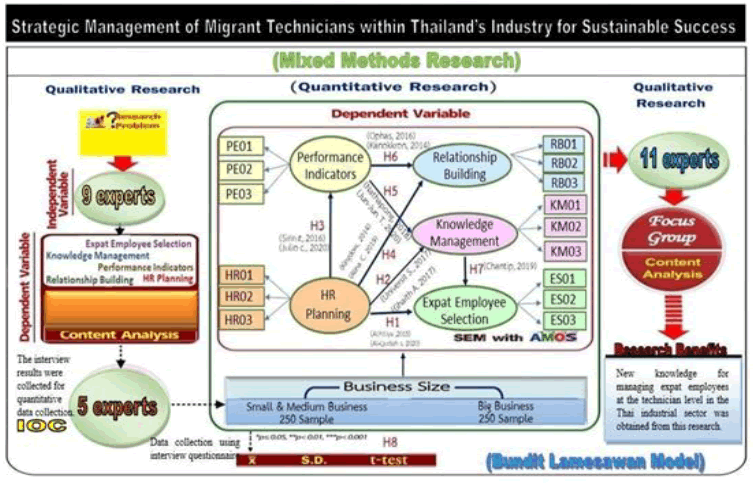
This research was a new knowledge creation using mixed method research consisting of 3 parts: qualitative research using interview techniques, quantitative research by survey data collection and qualitative research using group discussion techniques to verify the validity of the research model. The research process was as follows:
1. The qualitative research population was 9 quality system professionals for in-depth interviews and 11 for group discussions. The population used in the quantitative research was 1,100 industrial executives who received the Labor Relations Award. 500 samples were set according to the Comrey & Lee criteria referred to in Thanin's concept. The research tools were the Check-list and the Rating Scale questions. The weighting criteria were divided into 5 levels according to the Likert method. The Concordance Index between the question and objectives of this study found that the 100 observed variables had IOC values ranging from 0.6-1.0 For check-list questions, the standard deviation analysis was between 0.34-2.40 The Rating Scale questions, Corrected Item-total Correlation value was between 0.31-0.85. The confidence interval analysis of the questionnaire was performed using Cronbach's alpha coefficient and 0.98 was obtained. The data collection was conducted using multi-stage sampling method.
2. Data analysis was performed using both descriptive statistics, reference statistics, and multiple statistics to develop a structural equation model (SEM) using SPSS and AMOS software packages. The 4 criteria for evaluating the Data-model Fit to be considered were as follows: (1) The chi-square probability was greater than 0.05 (2) The relative chi-square value (CMIN/DF) was less than 2. (3) The Level of Compliance Index (GFI) was greater than 0.90 (4) The Root-Mean- Square Error (RMSEA) was less than 0.08. The research conceptual framework was shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: The Origin of the Elements of the Research Topic Strategic Management of Migrant Technician within Thailand’s Industry
The researcher presented an overview of Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians within Thailand’s Industry for Sustainable Success. The results of the research were summarized as follows.
1. The results of the analysis of strategies for managing expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector by qualitative research from in-depth interview techniques found that five elements could be identified: HR planning, expat employee selection, knowledge management, performance indicators and relationship building.
2. Strategies for managing expat employees at the technician level to achieve sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector as a whole were important at the highest level with an average score of 4.71 Expat employee selection and relationship building was at the highest level of importance with a mean score of 4.66 Knowledge management was at the highest level with an average score of 4.64 The performance indicators were of the highest importance, with an average score of 4.62 When classified individually in each aspect of the top three highest priority levels, it was found that:
2.1 The human resource planning component consisted of a structured diagram of the clearly responsible operations with an average value of 4.77(SD=0.44) followed by the system to clarify the basic workload and behavior of migrant workers with an average value of 4.77 (SD=0.45) and the foreign labor force planning in accordance with the nature of the work was averaged at 4.77 (SD = 0.46) respectively.
2.2 The recruitment and selection component of migrant workers consisted of non-expiring migrant visas with an average value of 4.74 followed by migrant workers who had to have a valid work permit with an average value of 4.72 and consulting on recruiting expat employees at the level of outsourced technicians averaged 4.71 respectively.
2.3 The knowledge management component consisted of the study of results achieved through the exchange of knowledge with each other for quick understanding with an average value of 4.75 followed by the campaign and promotion of migrant workers to recognize the importance of knowledge exchange with an average value of 4.75 the learning between operators with an average value of 4.71 and brainstorming sessions to formulate solutions or make operational decisions through experience and perspectives from stakeholders averaged 4.70 respectively.
2.4 In summarizing the results about the importance of the strategy for managing expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector as a whole, it could be classified by business size. It was found that SMEs gave priority to human resource planning with an average value of 4.73 followed by the recruitment and selection of expat employees with an average value of 4.70 and relationship building with an average value of 4.69 respectively. For large businesses, the highest priority was human resource planning with an average value of 4.68 followed by relationship building with an average value of 4.64 and the recruitment and selection of expat employees averaged 4.63 respectively.
2.5 Comparison of importance of strategies for managing expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector could be classified by business size. The difference between the mean of the two independent population groups was tested by t-test. Overall, when classified by business size, there was a statistically significant difference at the 0.05 level. SMEs were more important than large businesses as shown in Table 1.
| Table 1 Comparison of the Importance of Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians within Thailand's Industry of Sustainable Success |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians within Thailand’s Industry for Sustainable Success |
Small and medium-sized enterprises | Large scale enterprise | t-Value | P-Value | ||
| S.D. | S.D. | |||||
| Overall | 4.68 | 0.32 | 4.63 | 0.35 | 1.68 | 0.01* |
| 1. HR Planning | 4.73 | 0.29 | 4.68 | 0.32 | 1.68 | 0.03* |
| 2. Expat Employee Selections | 4.70 | 0.33 | 4.63 | 0.37 | 2.14 | 0.01* |
| 3. Knowledge Management | 4.66 | 0.37 | 4.62 | 0.39 | 1.36 | 0.04* |
| 4. Performance Indicators | 4.64 | 0.37 | 4.6 | 0.38 | 1.11 | 0.33 |
| 5. Relationship Building | 4.69 | 0.34 | 4.64 | 0.38 | 1.63 | 0.00* |
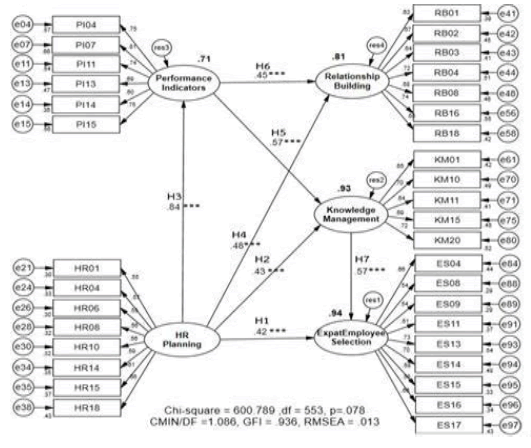
Structural equation modeling of foreign labor management strategies at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector, the researcher analyzed and adjusted the model by considering Modification Indices according to Arbuckle's recommendation. The values of the results were determined using a program with theoretical theory to exclude some inappropriate observational variables one by one. Then the new model would be processed and this would be done until the model had all four statistical values and was fit with the empirical data (Thanin, 2020) as shown in Table 2 that represents the structural equation model in Figure 5 and the meaning of the variables in Table 3.
| Table 2 Strtistics that Assessed the Fit of the Structural Equation Model Before and After the Model Improvement |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Criteria for consideration | Result before improvement | Result after improvement |
| p value of Chi-square | greater than 0.05 | 0.000 | 0.078 |
| CMIN/DF | less than 2 | 2.147 | 1.086 |
| GFI | greater than 0.90 | 0.674 | 0.936 |
| RMSEA | less than 0.08 | 0.048 | 0.013 |
Figure 5: Structural Equation Modelling Strategy for Strategic Management of Migrant Technicians Within Thailand’s Industry for Sustainable Success Sector in Standardized Estimates Mode after Model Improvement
| Table 3 Variable of Definition |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Meaning | Variable | Meaning |
| HR01 | The expat workforce is planned in accordance with the nature of the work. | KM01 | Expat workerforces must be given the opportunity to learn about how to use the modern machinery and equipment of the organization. |
| HR04 | There is a clear diagram of the operational structure with the responsible person. | KM10 | Expat employees must be trained to participate in decision-making and problem solving. |
| HR06 | Welfare plans have been adjusted such as bonuses, diligence and welfare benefits that are appropriate for the cost of living. | KM11 | Information and work practices of expat employees are always updated to be up-to-date. |
| HR08 | Overtime planning is provided in accordance with production. | KM15 | The results of learning from the skills and experiences of expat employees in various fields are systematically compiled. |
| HR10 | There are internal agencies that support and assist in the registration of expat employees. | KM20 | A working atmosphere is created in the department so that knowledge can be used to solve operational problems quickly. |
| HR14 | If it is found that expat employees have things that need to be developed, the organization is planned to increase their knowledge. | PI04 | The criteria for evaluating the performance of expat employees are set to the same standard. |
| HR15 | There is a plan to promote and develop opportunities for collaboration between expat employees and Thai workers. | PI07 | Moral and ethics have been defined as one of the criteria for evaluating the performance of expat employees. |
| HR18 | There is a hearing from the supervisor in order to plan for recruiting expat employees at the technician level in accordance with the work done. | PI11 | There is a strengthening and maintaining good relations between supervisors and expat employees. |
| ES04 | Outsourced services are used to provide advice on recruiting expat employees. | PI13 | Performance appraisals must be in accordance with standards and accepted by workers. |
| ES08 | Nationality is taken into account and jobs are assigned to suit the selected expat employees. | PI14 | Performance evaluations are monitored periodically, for example quarterly. |
| ES09 | In the recruitment of the organization, the working environment should be clearly identified, such as light, sound and heat. | PI15 | The results of the work assessment of expat employees will be reviewed to improve in the shortcomings. |
| ES11 | Characteristics/personality of expat employees in each job are clearly defined. | RB01 | There should be personnel officers in the organization who can communicate in foreign languages. |
| ES13 | Expat employees are hired as technicians to work on a daily basis before being considered for recruitment as monthly employees. | RB02 | Expat employees are given the opportunity to express their opinions through various channels such as comment boxes. |
| ES14 | The suitability of the age range and the work done is considered. | RB03 | There are activities to promote good relations between the organization and expat employees, such as New Year's Day. |
| ES15 | Expat employees must have skills in hand before working, which is an important factor in deciding to work. | RB04 | Annual awards are given to migrant workers for outstanding performance in order to improve their morale. |
| ES16 | Expat employees must have a health check before accepting work to ensure that they are physically ready to work. | RB08 | There is a channel for advice to help expat employees who have problems at work. |
| ES17 | There is a drug test result attached to the job application. | RB16 | There is an opportunity for promotion to foreign workers at the technician level, equally to Thai workers. |
| RB18 | Expat employees are commended for their good performance and role models. | ||
The results of hypothesis testing to analyze the causal influence between the latent variables in the structural equation model of the expat employee’s management strategy at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector consisted of 7 hypotheses: (1) The human resource planning directly influenced the recruitment and selection of expat employees. (2) The human resource planning directly influenced the knowledge management at a statistically significant level of 0.001 (3) The human resource planning directly influenced the performance indicator at a statistically significant level of 0.001 (4) The human resource planning directly influenced the relationship building at a statistically significant level of 0.001 (5) The performance indicator directly influenced the knowledge management at a statistically significant level of 0.001 (6) The direct influence component on the relationship building was statistically significant at the 0.001 level. (7) The knowledge management assessment directly influenced the migrant recruiting and selection at a statistically significant level of 0.001
Limitations and Future Studies
Different industries and sizes had different operating patterns. Therefore, if the causal influence of the structural equation model was studied in this regard by type and size of the business, it was found that SMEs businesses were more in demand for expat employees because labor costs were low and they were able to work hard, dirty and dangerous jobs without demanding more wages than Thai people. Thai workers would like to work in larger organizations, causing SMEs to have a shortage of Thai workers. Therefore, the management of expat employees at the technician level must be maintained because if the skilled staff resigns, it may affect the business. Therefore, it was imperative to maintain capable migrant workers.
Conclusion
This research was to create a new body of knowledge using mixed research which consisted of qualitative research using in-depth interview techniques, quantitative research using questionnaires and qualitative research using focus group techniques. There were 3 research objectives as follows: ( 1) To study the nature of general operations in the field of expat employee’s management at the level of technicians working in the Thai industrial business sector. (2) To study the composition of the guidelines for the management of expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial business sector. ( 3) To develop a structural equation model of the expat employee’ s management strategy at the level of technicians working in the business sector of the Thai industry.
Research on strategies for managing migrant workers at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector was an inductive research using a mixed research approach consisting of qualitative research and quantitative research. There were 3 steps as follows:
Step 1: The population used in qualitative research with in-depth interview techniques was recognized experts for which specialist eligibility criteria were clearly defined. The accepted experts were assigned a total of 9 people.
Step 2: The population used in quantitative research was responsible for creating shared value for industrial business organizations. The researcher therefore determined the sample size by using the research criteria in the type of component analysis or structural equation modeling. A sample size of 500 very good samples was determined (Comrey and Lee, 1992 cited in Thanin, 2020). A Multi-Stage Sampling ( Babbie, 2015) method, consisting of stratified sampling and simple random sampling, was used. The instrument used in this research was a questionnaire created which was divided into 5 parts as follows:
Part 1: It was a questionnaire about the general status of an industrial business organization. The questionnaire was a check-list of 3 items and an open-end questionnaire of 2 items.
Part 2: It was a questionnaire about the characteristics of labor management in the industrial business sector. The questionnaire was a checklist of 20 items.
Part 3: It was a questionnaire on strategies for managing expat employees at the technician level for sustainable success in the Thai industrial sector. The questionnaire was a rating scale with 100 questions.
Part 4: It was a questionnaire on opinions and recommendations towards the management of expat employees at the technician level in the Thai industrial business sector in addition to the questionnaire in Part 3. The questionnaire was open-ended which consisted of 5 questions.
Step 5: The population used in the qualitative research using focus group technique consisted of 11 experts. Purposive sampling was used in the study.
The researchers analyzed the quality of the tools using the IBM SPSS Statistics package. The results of the power factor analysis could be classified by item. For this research, the discriminant powers were between 0.30–1.90 Questions with a rating scale using Corrected Item- Total Correlation analysis ranged from 0.31 - 0.81 The reliability of the questionnaire was 0.97.
For the quantitative data collection, the researcher distributed the questionnaire to 500 people as required. Then, general fundamental data were analyzed including descriptive statistics, reference statistics and structural equation model analysis, which consisted of frequency, percentage, significance, standard deviation and bivariate correlations analysis. The difference between the significance of the two independent populations was tested by t-test, which was statistically significant at the 0.05 level with the Pearson Chi–square value. Structural equation models were also developed and statistical data analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics and IBM SPSS AMOS software packages.
Acknowledgement
Recommendations obtained from research on strategic management of migrant technicians within Thailand’s Industry for sustainable success were guidelines for executives in corporate strategic planning for resolving employee resignation issues. If an employee resigned, it would affect the work processes of the company. Therefore, knowing the reasons that influenced the employee's decision to leave and how to resolve them would be of great benefit to the improvement and development of the company's human resource management system to the maximum efficiency to maintain effective employees of the organization for sustainable success of Thai industrial business. In this research, the researcher had suggested the strategic guidelines for the management of expat employees at the technician level in the industrial business sector as follows:
Policy Level, Government Sector
(1) The government should support the training of expat employees at the technician level to enhance their working skills. (2) States should take strict measures for law enforcement, tackle illegal immigrant workers and seriously punish offenders. (3) The government sector should have a policy to focus on migrant workers in matters of human rights in order to comply with international principles. (4) The State should consider revising some occupations to enable expat employees to enter occupations due to labor shortages in the industrial sector.
Policy Level, Education Sector
(1) People who study personnel management can use information to develop knowledge to the practical level in view of problems and obstacles in order to understand how to use it for the most benefit and lead to strong development in the development of the country. (2) There is promotion and support to bring the body of knowledge from higher education institutions for further research and development. (3) The results of research and various body of knowledge from research of higher education institutions are brought to practical use.
Operational Level, Industrial Operators
(1) There is continuous development of skilled labor shortages to increase competitiveness. (2) The labor is properly hired according to the labor law. (3) There is equal treatment of expat employees in accordance with human rights principles.
References
Alina, C., & Armenia, A. (2019). An integrated psycho-sociological perspective on public employee’s motivation and performance. Management Development Institute, India.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Al-Q, S., & Abdallah M.O. (2020). The impact of strategic human resources planning on the organizational performance of public shareholding companies in Jordan. Department of Business Administration, Faculty of Business, Applied Science Private University, Amman Jordan.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Cronbach, L.J. (1970). “Essentials of psychological testing”, (3rd Edition). New York: Harper.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Deming, E.W. (1995). PDCA. Out of The Crisis. USA: The Massadhusetts of Technology Center for Advanced Engineering Study.
Drucker, P.F. (1988). The coming of the new organization. Harvard Business School Press.
Department of Labor Protection and Welfare Ministry of Labor. (2019). Information on claims and disputes and conflicts of foreign workers in Thailand.
Frederick, T. (1911). The principles of scientific management. New York : McMillan.
Fred, L., & Bruce, J.A. (2005). The psychological capital of Chinese workers: Exploring the relationship with performance. Department of Management University of Nebraska at Lincoln.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Garvin, D.A. (1993). Building a learning organization. Harward Business Review.
Ghaith, A. (2017). The impact of human resource management practices, organizational culture, motivation and knowledge management on job performance with leadership style as moderating variable in the Jordanian commercial banks sector. Faculty of Economics & Management Sciences, Malaysia.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Harrington, E.C. (1853). The twelve principles of efficiency. New York :The Engineering Magazine.
Herzberg, F. (1959). The motivation to work. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Henri, F. (1916). General and industrial management. London: Sir Isaac Pitman and Son.
Hue, J.B. (2021). A study on human resource function: recruitment, training and development, performance, appraisal and compensation. New Era University College, Malaysia.
Hugo, M. (1912). Organization Theory. Boston : Allyn and Bacon.
Jalil, B. (2016). Overlaps between human resources strategic planning and strategic management tools in public organizations. Department of Management, Ardabil Branch, Islamic Azad University.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Julia, E.H. (2013). Shared leadership in enterprise resource planning and human resource management system implementation. Michigan State University.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Lyndall, U. (1937). Paper on the science of administration. Clifton : Augustus M. Kelley.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Mary, P.F. (1924). Dynamic Administration: The collected papers of Mary Parker Follett. New York: Hippocrene Books.
Mayo, E. (1973). The human problems on industrial civilization. New York : Macmillan.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Marquardt, M. J., & Reynolds, A. (1996). The global learning organization. New York. Maslow, A. (1954). Hierarchy of Needs. (online).Available: http://en.wikipedia.org.
Siriyasap, Y. (2017). Human Resource Planning. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Press.
Tri Nguyen-Khac. (2021). Knowledge management: Perspectives and implications for HR Practices in Vietnam. East Asia University of Technology Hanoi Vietnam.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Thang Quyet, N.H., & Tan, T.N. (2021). Importance of human resources in building sustainable enterprises: Cases of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam. University of Technology (Hutech), Ho Chi Minh City Vietnam.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Yongzhan, L., & Gloria, C. (2018). Linking leadership styles to work engagement the role of psychological capital among Chinese knowledge worker.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed
Wantanakomol, S., & Silpcharu, T. (2020). Strategy for preventing corruptions in industrial business organizations with Delphi technique. Academy of Strategic Management Journal.
Received: 08-Mar-2021, Manuscript No. jmids-22-11552; Editor assigned: 10-Mar-2021, PreQC No. jmids-22-11552 (PQ); Reviewed: 15- Mar-2021, QC No. jmids-22-11552; Revised: 20-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. jmids-22-11552 (R); Published: 13-Apr-2022