Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 1
Strategic Management of Innovation Implementation in the Company
Pavlo Hrynko, Kharkiv State University of Food Technology and Trade
Olena Kharlamova, International Academy of Certification of Accountants and Auditors
Svyatoslav Zavorotnij, Poltava University of Economics and Trade
Tokhir Turmanov, Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers, Uzbekistan
D?nys Martyshyn, Interregional Academy of Personnel Management
Abstract
The article is devoted to the issue of improving strategic management as the number of innovations in the company grows. The original division of stages of development of innovative strategy is proposed. The composition of strategy of introduction and support of innovations in the company is presented. The substantiation and analytical description of the developmental innovation strategies are conducted. Qualitatively and analytically sound strategy is the basis for increasing the competitiveness of the company, creating a strong position in the market and forming conditions for profitable activity in tough market conditions. The problem is that the ability of a company to innovate stems from a combination of tools in a single system: a consistent set of interdependent processes and structures that guide the search for new problems and their solutions, synthesize ideas into business concepts, and choose which projects receive funding, in other words, an innovative strategy. The proposed methodological recommendations allow not only to evaluate the attractiveness of the industry and the innovation potential, but also to see the problems in the field of innovation development, as well as to find solutions to these problems by choosing the right innovation strategy.
Keywords
Strategic Management, Innovations, Innovation Strategy, Innovation Portfolio, Innovation Project, Business System.
JEL Classifications
M21
Introduction
In the current conditions of globalization and changing economic conditions, there is an increasing trend that a number of successful companies are beginning to give market share to more competitive and modern companies. The response of the inferior companies is to use effective and rapid forms of organizational development, which are aimed at introducing advanced innovative technologies and developing the current model of strategic management. It is these factors that shape the relevance of the study.
Literature Review
Problems of innovation management are discussed in the studies of such scientists as (Hair et al., 2010; Dodgson et al., 2008; Oki, 2015). The focus of a number of scientists (Makedon et al., 2019; Pelser, 2014) is the latest approaches to strategic innovation management. However, despite considerable experience in developing a methodology for strategic innovation management, questions remain regarding the development of methodological tools for innovation management in modern companies (Drobyazko et al., 2019 a & b; Durmanov et al., 2019).
Methodology
The axiom that the effective functioning of the company is ensured by the proper management of its activity is methodologically justified. A rigid management approach is based on strategic management. Qualitatively and analytically sound strategy is the basis for increasing the competitiveness of the company, creating a strong position in the market and forming conditions for profitable activity in tough market conditions.
Findings and Discussions
Innovative management is one of the areas of strategic management at the highest level of the organization. The problem is that the ability of a company to innovate stems from a combination of tools in a single system: a consistent set of interdependent processes and structures that guide the search for new problems and their solutions, synthesize ideas into business concepts, and choose which projects receive funding, in other words, an innovative strategy (Song et al., 2013). Most often, researchers identify 4 stages of strategy development: development of goals, strategic analysis, choice of an innovation strategy, implementation of an innovation strategy (Pérez-Luñoa et al., 2011; Tarkhanova, 2018). However, having analyzed the modern scientific approaches and experience of leading companies in the world, we consider it necessary to focus on the stages of developing an innovation strategy. We shall describe the features of the implementation of each of these stages.
Stage 1: Innovative development vector
The first step in building an innovation strategy is to identify the direction of innovation development at the highest level of the company management (Katz, 2007). When defining the course of innovative development, we must take into account the following important conditions: 1) strategy, not cost, matters for innovation; 2) blind rates should be abandoned in favor of viable business models; 3) the need for innovation arises throughout the business system. Companies do not innovate on their own.
Stage 2: Company potential analysis
The analysis of the current state is an indicator of the “technical” possibility of company development in one or another format. It consists of the analysis of resources and the analysis of the capabilities of the company, based on which you can make the choice of the most appropriate model of activity (Gooderham, 2007; Svitlana et al., 2019).
We define the dynamic ability of a company, which is defined as the ability of an organization to purposefully create, expand or modify its resource base. For innovation the following company capabilities are most relevant: 1) search – assessing market opportunities and technologies and taking into account the threats posed by them; 2) choice – the process of choosing from future options based on the assessment of available resources, the likelihood of creating additional value; 3) adjustment – ensuring coordination and integration of innovation activities; 4) development – implementation of innovations developed internally and attracted from outside the companies on time and within the budget, protection and benefits from innovations.
Stage 3: Innovative project portfolio
One of the tools for determining the importance of innovation is the innovation ambition matrix, which demonstrates the level of novelty of offers and markets. The innovation ambition matrix should have three levels: 1) existing level – optimization of existing products for existing customers; 2) complementary level – expansion from existing business to new business for the company; 3) transformational level – development of products and markets that do not exist yet (Suárez, 2014).
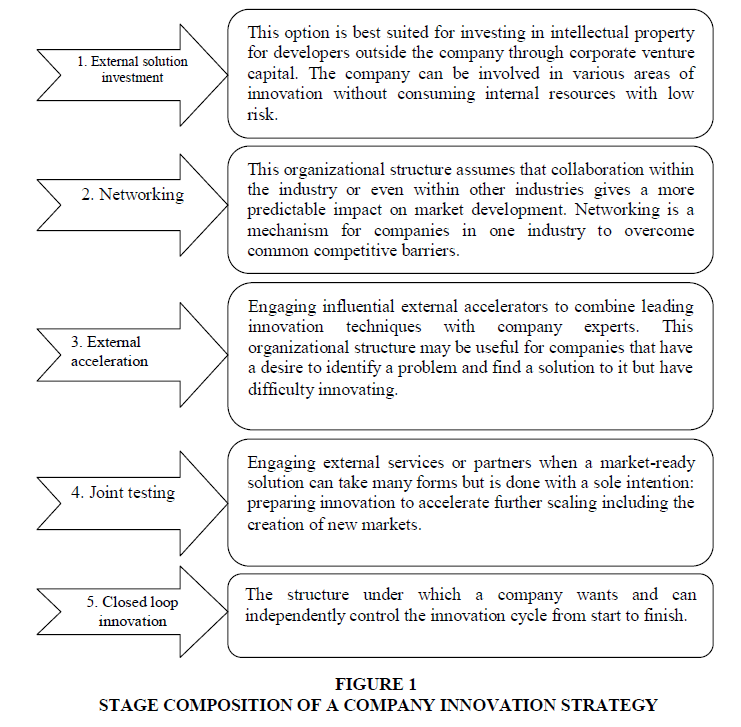
Stage 4: Functional strategy substantiation
The organizational composition of a strategy for innovation implementation is presented in Figure 1.
Stage 5: Innovative project team creation
Creation of an effective special team requires the destruction of existing working relationships and the creation of new ones.
Stage 6: Integration of innovative project team into company activities
A special team is responsible for generating and incubating ideas, while business units have the process of commercializing those ideas.
Stage 7: Choosing an innovative strategy for the base market
We propose to identify four major innovation strategies that a company can use to implement a particular innovation (Table 1).
| Table 1 Developmental Innovation Strategies Of A Company | ||||
| Strategy characteristic features | Proactive | Active | Reactive | Passive |
| Goals | Technology and market leadership | Be prepared for rapid imitation | Waiting and gradual adoption of innovations | Perform what the client needs |
| Technological innovation type | Radical and gradual | Mostly gradual | Only gradual | Gradual |
| Innovation costs | Fundamental and applied research, new products | Applied research, products, which are new for companies | Focus on operations | Formally, no costs |
| Risks | High risks | Medium risks | Low risks | No risks |
1. Proactive – investing heavily with the prospect of making big profits. Such a strategy is relevant in areas of rapid development, when there is a very high level of uncertainty or when an existing company has tangible technological leadership and may risk as a trailblazer.
2. Active – investing in a number of different options where reasonable returns are expected. This strategy is relevant for companies operating in relatively stable markets where they are able to reap the benefits of being an instant follower.
3. A reactive strategy in which further development options remain open, while others have greater risks taking the lead in developing new technologies. This strategy is typically adopted by companies that follow industry leaders and instant followers, but are able to reap the benefits while saving on the production of cheaper goods and services.
4. Passive – the least risky strategy in which a company implements innovation solely with market demand.
Recommendations
Recommendations based on the research results we formulate in the context that the choice of strategy for innovative development depends on various factors, such as market position and innovative potential of the company. The proposed methodological recommendations allow not only to evaluate the attractiveness of the industry and the innovation potential, but also to see the problems in the field of innovation development, as well as to find solutions to these problems by choosing the right innovation strategy.
Conclusion
Implementing an innovation strategy is a complex process that requires the appropriate qualification of the company management and the time to implement. It is determined that modern strategic management provides effective tools for implementation and further sustainable development of the company innovation activity. These tools represent a gradual rebuilding of the strategy through the basic adoption of a market model of innovation activity, the assessment of the current state of the company in the market, the creation of structure, team and portfolio of innovations and the choice of the optimal innovative strategy for entering the market.
References
- Dodgson, M., Gann, D.M., & Salter, A. (2008). The management of technological innovation: strategy and practice. Oxford University Press on Demand.
- Drobyazko, S., Alieksieienko, I., Kobets, M., Kiselyova, E., & Lohvynenko, M. (2019a). Transnationalisation and segment security of the international labor market. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues 9(2): XX.
- Drobyazko, S., Barwi?ska-Ma?ajowicz, A., ?lusarczyk, B., Zavidna, L., & Danylovych-Kropyvnytska, M. (2019b). Innovative entrepreneurship models in the management system of enterprise competitiveness. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education.
- Durmanov, A., Bartosova, V., Drobyazko, S., Melnyk, O., & Fillipov, V. (2019). Mechanism to ensure sustainable development of enterprises in the information space. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 7(2), 1377-1386.
- Gooderham, P.N. (2007). Enhancing knowledge transfer in multinational corporations: a dynamic capabilities driven model. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 5(1), 34-43.
- Hair, J.F.J., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., & Anderson, R.E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis upper saddle river: pearson prentice hall.
- Katz, B. (2007). The integration of project management processes with a methodology to manage a radical innovation project. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Stellenbosch: University of Stellenbosch.
- Makedon, V., Valikov, V., Kurinnaya, I., & Koshlyak, E. (2019). Strategic innovative development of the enterprises: theory and methodology. Scientific Journal Economics and Finance, (2), 52-62.
- Oki, K. (2015). Managing internal competition in multinational corporations: the role of home bases. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 15(2), 252-267.
- Pelser, T. (2014). The affect of innovation strategies and their connect to company performance. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 5(9), 60.
- Pérez-Luño, A., Wiklund, J., & Cabrera, R.V. (2011). The dual nature of innovative activity: How entrepreneurial orientation influences innovation generation and adoption. Journal of Business Venturing, 26(5), 555-571.
- Song, M., Zhao, Y.L., & Di Benedetto, C.A. (2013). Do perceived pioneering advantages lead to first-mover decisions?. Journal of Business Research, 66(8), 1143-1152.
- Suárez, D. (2014). Persistence of innovation in unstable environments: Continuity and change in the firm's innovative behavior. Research Policy, 43(4), 726-736.
- Svitlana, B., Liliya, B., Oksana, K., & Inna, G. (2019). Modelling instruments in risk management. Crisis, 6, 9.
- Tarkhanova, E.A. (2018). Innovations and sustainability in the financial and banking sectors. Terra Economicus, 16(2).