Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 3
Stability Strategy and its Direct Role in Achieving Competitive Advantage at Jordanian Communication Companies
Ziad Ali Eid Alshawabkeh, Al-Balqa Applied University
Bassam Fathi Aldiabat, Al-Balqa Applied University
Mohammad A. Al-Zubeidi, Al-Balqa Applied University
Belal Hashem Nsour, Al-Balqa Applied University
Feras Suliman Al-Shalabi, Al-Balqa Applied University
Reham Zuheir Al-Momani, Amman Arab University
Khaled Banyhamdan, Amman Arab University
Lina Hamdan Mahmoud Al-Abbadi, Al-Ahliyya Amman University
Abstract
The study aimed to identify the direct effect of the Stability Strategy in achieving the competitive advantage of Jordan Telecom Companies by surveying the opinions of the executives and middle level managers in these companies. The researchers conducted an exploratory survey of all companies operating in the Jordanian telecom sector (34). The researchers also distributed the questionnaires the study community which totaled 160 members. Questionnaires were distributed, of which, 130 were retrieved and were valid for analysis. There was a statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of the stability strategy in achieving competitive advantage of cost reduction, quality improvement, flexibility and innovation combined. The study showed an absence of significant statistical effect at 0.05 level of significance in achieving the competitive edge of innovation and quality. The study recommends that companies working in the telecommunications sector reduce direct production costs to provide a competitive advantage, and recommends that researchers undertake further studies of stability strategy in different industry sectors.
Keywords
Stability Strategy, Competitive Advantage, Jordanian Communication Companies.
Introduction
The origin of the word strategy goes back to the Greek word of “Strategos” that had been used during the war between the Greeks and the Persians in 506 AD (Rashid & Julab, 2015). That means the art of war and battle management. Webster New World dictionary defined strategy as the science of planning and directing military operations (Almagraby, 2007). Oxford dictionary defined strategy as the art of buildup and movement of military equipment’s in order to totally control the enemy (Jawad, 2010).
The task of forming a business strategy is the soul and center of business management and marketing. Business strategy is the managing of a plan to acquire a share of the market, to attract customers, and to accomplish organization goals. As a result, business strategies are the choices made by managers to enter, operate, and compete in markets (Thompson et al., 2004).
Study Theoretical Frame
According to Idris & Al-Ghalebi (2016), in his famous article (The Strategy Concept: Five Ps for Strategy) Mintzberg was able to form a comprehensive strategy concept that include the opinion of several researchers and created the five Ps of strategy:
1. Plan: To determine behavior and dealing with specific situation and designed to achieve goals and how management determines business direction.
2. Ploy: Entering competition world and concerned with deceiving and circling competition.
3. Pattern: Integration of parts through intended and unintended behavior to reach the center.
4. Position: Stable situation in environment and business location that is dynamic and effective.
5. Perspective: The ability to visualize things in their correct relations.
Wheelen & Hunger (2010) defined organization strategy as a designed comprehensive plan that explains how organizations accomplish their mission and goals. It also emphasizes competitive advantage and deemphasizes competitive weakness. In general ideal business organizations depend on three levels of strategies; organization strategy, business strategy, and operational strategy (Idris & Morsi, 2006).
Strategy Levels
As mentioned earlier, Wheelen & Hunger (2010) explains strategy levels in companies as follows:
Organization level strategies: concerned with determining competition as what business type the organization is in, what new business the organization will enter, what business the organization with withdraw from, and how to concentrate resources on businesses the organization competes in and accomplishing its goals (Al-Issawi et al., 2012). The most important strategies at organization level according to ALDahan et al. (2011) are growth, stability, decline, and mix strategies.
1. Growth strategy: the strategy an organization follows in order to accomplish new goals at higher levels from previous goals. This can be done by internal growth to expand operation locally or internationally and external growth by merging, acquiring, or strategic alliance. According to David (2011), merging between two companies, acquiring is to buy other businesses, and strategic alliance is partnership with other business to accomplish strategic goals of mutual benefit. Growth strategies are either focus or diversity strategies.
2. Stability strategy: it is the strategy that an organization follows to remain at current position that includes according to Al-Durra & Jaradat (2014), Alghalbi & Idris (2007) alternatives such as stop and proceed with caution, slow growth, avoid change, profit and harvest.
3. Decline Strategy: the strategy that organization follows when it needs to downsize and can choose one of the following alternatives such as circle, merge, sell and consolidate or bankruptcy.
Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage is a concept that had been used to describe the performance of a company compared to the competition in the market. Such advantage is based on the difference between different organizations that allows them to compete and for that to happen, companies must create more value for their customers than competition (Navarro-Garcia et al., 2018). Dimensions of competitive advantage:
Quality
David (2011) defined quality as the method used by organizations to actually accomplish a competitive advantage and a path to fast growth and profit. Hill & Jones (2008) defined quality as everything related to product such as design, form, trust, performance, and features where the product add value more than competition. Further, Evans & Collier (2007) said that products with higher qualities improve business reputation and customer satisfaction which allows companies to charge higher prices for better qualities.
Quality was defined by AlSabbagh (2002) as a philosophy of culture, organizing, and managing that depend on continuous improvement of products and participation of all workers in organization. Also the concentration on servicing customer needs and wants in order to accomplish goals of growth, survival, and stability.
Other researchers indicated that quality means the ability to offer products that meet customer needs and wants (Zolghadar, 2007), quality is the different view of customers or organization that meets different customer expectations which mean products are trusted and efficient to meet customer needs (Atem & Yella, 2007). As a result, the researchers believe that quality is a cornerstone of business success where products meet or exceed customer wants and needs. Such a notion is the soul of competitive advantage.
Flexibility
It is considered a major dimension in competitive advantage in today and future markets as customer needs and wants are changing and diversified where flexibility means the fast response to changing customer demand and minimizing response time (ALShawabkeh, 2016). Evans & Collier (2007) in Taleb & Zainab (2012) suggested that many organizations use flexibility as a competition tool that explain the capacity and ability to adapt successfully with the changing market environments and operations.
Furthermore, strategic ability of organizations and building a competitive position depends on the knowledge of customers and maintaining long term relation. In addition, retaining current customers and satisfy their needs with fast and quality service. According to Hill & Jones (2008), competitive advantage results in profit. At the same time, profit depends on product value, price, and production cost.
The researchers agree that flexibility is one of the major dimension of competitive advantage and any organization that wants to succeed, survive, and grow must respond to customer wants and needs in minimum time and cost.
Cost leadership
It is considered the oldest dimension of competitive advantage that means the ability of organizations to produce and distribute products with minimum cost compared to competition. Cost plays a major role in product pricing where minimizing cost allows companies to charge lower prices and create a competitive advantage and control markets. Such strategy holds true in markets where customers are sensitive to prices (Idris & Al-Ghalebi, 2016). The researchers suggest that reducing cost related to human resources especially indirect cost (transportation and driving compensation) is possible by hiring local employees. Such close distance labor will help organization save on transportation and driving costs and support the reduction in production cost.
Innovation
Innovation is considered the base of success for organizations. Innovation wins customers and satisfies their needs and future wants. Innovation is defined as the application of an idea developed inside or outside the organization, and related to product, system, operation, policy, program, or service (Hareem, 2010).
There are some researchers who differentiate between innovation and creativity. They believe that innovation proceed creation and its role to deliver the idea, where creation apply the idea. Others see innovation as part of creativity, where innovation is global, and creativity is local (Hareem, 2010). In addition, some researchers call for the separation between innovation and creativity. They suggested that innovation relates to distinguished new idea, where creativity applies the new idea in a form of operation, product or service (Belmahdi & Broush, 2005).
In general, it is for certain to say that innovation proceed creativity and a condition for its success. As a result, organizations are competing in being creative and consider creativity as a competitive advantage.
Literature Review
The literature demonstrated several studies that discussed the importance of employing stability strategy in order accomplish a competitive advantage or to maintain competitive position in markets.
In their study of the auto industry Navarro-Garcia et al. (2018), examined the role of the mediator that is played by competitive advantage in relations between strategic resources and the dynamic abilities and performance. The study was conducted in a dynamic and changing sector (sale of new cars in Portugal). The researchers used structural equation modeling in analyzing the data collected from 89 new car sale companies. The study showed that accomplishing competitive advantage depends on strategic resources and its ability to develop dynamic abilities. The study also showed that companies must not concentrate on just results, but concentrate on developing sustainable competitive advantages. In this study, competitive advantage is a mediator variable of the effect of strategic resources and dynamic abilities on performance.
Soosay et al., 2018 study titled “Strategies for Sustaining Manufacturing Competitiveness: Comparative case studies in Sweden and Australia”. Provided a report of sustainable domestic production investigation in Australia and Sweden in order to discover the factors that help industrial companies survive and ability to compete. The study was conducted on six companies in 2010 and compared three of them with previous projects in Australia. In Sweden, eight companies were studies in two separate periods with 30 years intervals.
The study showed that a change has happened in the nature of competition in both countries due to the increasing complexities of business environments and changes in technology and customer expectations. Despite the difference between both countries, the study indicated that all industrial companies were aware of business environment and its relation to competitive advantages. In general, the study showed that Sweden companies are more experienced in crises management and the benefit of operating internationally.
A study of “The Impact of the Integration of Stability Strategy and Human Resources Strategy in Accomplishing Competitive Advantage” by Alshawabkeh et al. (2018) tried to verify the role of integration between stability strategy and strategic human resources strategy in accomplishing competitive advantage. The study surveyed the executives and middle managers, human resource managers.
The study results showed that there was no effect between stability strategy and human resources strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage whereas, the study showed an effect of the integration of both strategies as explained by quality, flexibility, and innovation. The study also showed that no effect was shown as the integration was explained by cost reduction.
Another study by Zubaidi & Mahmoud (2010), titled “The Impact of Knowledge Management Dimensions for Competitive Advantage in Banks” was aimed to verify the range of knowledge management dimensions effect for competitive advantage for banks operating in the north part of the West Bank. The sample was bank employees and consisted of 240 participants.
The study showed that the knowledge management and competitive advantage do exist in banks. There was an effect of knowledge management in acquiring a competitive advantage by banks. There was also a positive and statistically significant between knowledge management (creating, storing, sharing, and applying) and competitive advantage dimensions (quality, response, operation efficiency, innovation, and creativity).
Also study by Alshawabkeh et al. (2018), study titled
“The Effect of Applying Human Resources Strategy in Accomplishing Competitive Advantage in Communication Sector in Jordan: An Applied Study”
was to verify the effect of human resources management strategy in accomplishing competitive advantage. The researcher conducted an exploratory study of all telecom companies in the communication sector in Jordan. The sample consisted of 34 telecom companies and 160 surveys were distributed. A total of 130 surveys were retrieved and all were useable to analyze.
The study showed that human resources strategy had a statistically significant effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage explained by cost reduction, quality improvement, increased flexibility, and increased innovation.
A study of reducing cost as a factor to accomplish a competitive advantage in the Algerian industrial sector, by BuDahoush (2008) the study was aimed to clarify the importance of reducing cost in achieving a competitive advantage internationally but not in the Algerian industrial sector.
The results of the study showed that organizations are able to accomplish a competitive advantage by introducing a new product, or reducing cost through the efficient use of financial, human and organizational resources. BuDahoush also added that cost reduction strategy is the best choices in competitive markets were companies improve performance and quality of products. Such strategy adds value to the products and reduces production cost.
Mahel et al. (2007), study titled
“The Effect of Stability Strategy on Customer Satisfaction: An Analytical Study on Takreet Yougart Company”
showed the relation and effect between stability strategy and customer satisfaction through the role of the organization in analyzing stability strategy and its relation to customer satisfaction. The study investigated the possibility of using stability strategy to satisfy customer wants and then accomplish customer satisfaction.
The results of the study showed a weak awareness of the company of the importance of strategic choices and not adopting the strategy that suit business and market environment. The study also showed a weak relation between stability strategy and customer satisfaction.
Relationship between Stability Strategy and Competitive Advantage
The importance of selecting the stability strategy by business organizations is due to the organization focus on funneling all resources in current business activities and to avoid risks associated with the expansion and growth of products and markets. It also helps in minimizing the effect of changing environment, consumer needs and the difficulty in obtaining the necessary resources or technology. Stability strategy is appropriate for successful organizations operating in a predictable environment.
The previous arguments indicate a strong relationship between stability strategy and competitive advantage. Organizations that is able to survive and maintain a consistent mission, objectives and values can maintain a competitive advantage and deliver their products to their customers at the right time, right place. As a result, organization accomplishes reasonable profit rates, improve quality and lower operating costs (Masaadah, 2015; Al-Durra & Jaradat, 2014).
In summary, the literature showed positive indicators between stability strategy and competitive advantage in markets. The previous studies in several business environments such as the auto industry, the banking sector, human resources, communication sector indicated a positive relation between adopting a stability strategy and maintaining a competitive position.
Importance of the Study
1. Field importance: The importance of communication sector in Jordan where it is considered a major contributor with 16.3% of Jordan GDP in 2012 and provided 82 thousand accumulated jobs. The mobile coverage is 120% for every 100 people and internet access is around 60 % for the population. Such numbers indicate the important role of communication sector in economic and social development, create jobs, and provide highly qualified labor which reflects the dynamic role of the telecom sector (Ministry of Planning & International Cooperation).
2. Scientific importance: Due to its important role, organizations adopt stability strategy to manage business in such environments of economic certainty and clear market conditions. Such strategies maintain the business mission, goals and strengthen the organization position to compete in markets. In addition, stability strategy increases profitability, reduces cost, and increases quality of work.
Study Objectives
The objectives of the study are as follow:
1. To identify the effect of organization strategy in achieving a competitive advantage.
2. To identify the effect of organization strategy in achieving quality.
3. To identify the effect of organization strategy in achieving cost reduction.
4. To identify the effect of organization strategy in achieving flexibility.
5. To identify the effect of organization strategy in achieving innovation.
6. Provide some suggestions and recommendations to improve organizations strategies and achieving competitive advantage.
Study Problem
The problem of this study is to explain the effect of stability strategy in achieving competitive advantage in the communication sector in Jordan. The main question of this study is
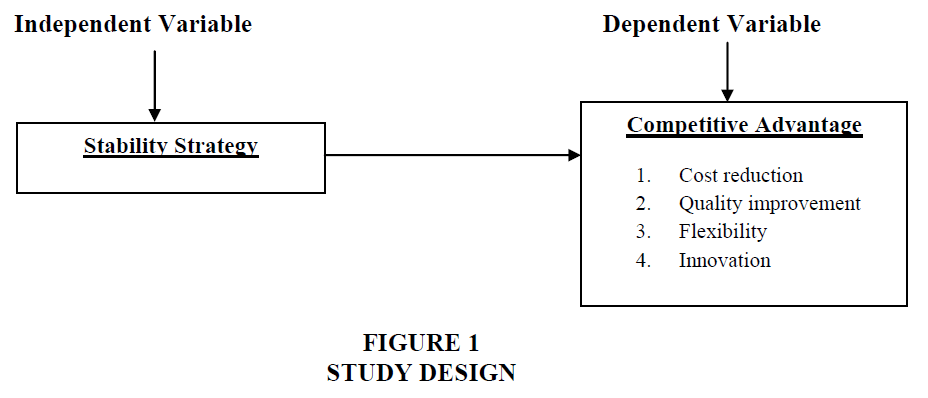
“Does stability strategy affect the accomplishment of a competitive advantage (explained by cost reduction, quality improvement, flexibility, and innovation)” (Figure 1).
Study Design
Study Hypothesis
The main hypothesis:
H0: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage at Jordan telecom companies.
H0.1: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing cost reduction at Jordan telecom companies.
H0.2: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing quality improvement at Jordan telecom companies.
H0.3: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing flexibility at Jordan telecom companies.
H0.4: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing innovation at Jordan telecom companies.
Research Methodology
Study Society and Sample
The sample of this study consisted of communication companies registered at the Bearu of Jordanian communication sector for the year 2016 and totaled 34 companies. Such companies offer local communication fixed and mobile services, international communication, internet service. The researcher conducted an exploratory study and collected data by distributing surveys to population members. A total of 160 surveys were distributed and 130 surveys were retrieved that were useable for analysis.
Study Instrument
A survey was used to collect primary data. Stability strategy and competition advantage dimensions were measured as explained by Alshawabkeh et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2012; Suhong et al., 2006.
The researchers evaluated the survey by showing it to several academics in Jordanian public and private universities. Notes were taken and the survey was modifies according to such notes. The survey was also evaluated by a sample from the study population in order to validate the instrument. The test of reliability Cronbach’s Alpha was used to measure the instrument reliability as shown in the following Table 1.
| Table 1 : Stability Coefficients Of Study Instrument And Its Dimensions According To Cronbach's Alpha Coefficient Equation | ||
| Variable | Dimension | Reliability factor |
| Stability Strategy | Stability strategy | 0.687 |
| Competitive advantage | Cost reduction | 0.734 |
| Quality improvement | 0.8 | |
| Flexibility | 0.883 | |
| Innovation | 0.84 | |
| Total reliability of competitive Adv. | 0.899 | |
| Total reliability | All | 0.811 |
The value of Cronbach’s Alpha is 0.811 as shown in Table 1. When the value exceeds 0.60 according to Sekaran & Bougie (2013), the instrument is considered reliable and the data is suitable to Table 2.
| Table 2 : The Arithmetical Averages And Standard Deviations Of Respondents’ Sample | |||
| Number | Subject | Standard deviation | Average |
| 1 | Stability | 0.89 | 3.87 |
| 2 | Competitive Advantages | ||
| 2a | Cost reduction | 0.61 | 3.81 |
| 2b | Quality | 0.75 | 4.05 |
| 2c | Flexibility | 0.56 | 4.22 |
| 2d | Innovation | 0.74 | 3.99 |
The results in Table 2 showed that stability strategy scored high among the executives and middle level managers at Jordan Telecom Companies with a mean of (3.87) and a standard deviation of (0.89).
The results in Table 2 also showed that the level of competitive advantage dimensions of cost reduction among the executives and middle level managers at Jordan Telecom Companies was high, with means of (3.81) and a standard deviation of (0.61). As well the results also showed that the level of competitive advantage dimensions of quality among the executives and middle level managers at Jordan Telecom Companies was high, with means of (4.05) and a standard deviation of (0.75), and the results also showed that the level of competitive advantage dimensions of flexibility among the executives and middle level managers at Jordan Telecom Companies was high, with means of (4.22) and a standard deviation of (0.56). Furthermore the results showed that the level of competitive advantage dimensions of innovation among the executives and middle level managers at Jordan Telecom Companies were high, with means of (3.99) and a standard deviation of (0.74).
Hypothesis Testing
After analyzing the data using the simple regression to determine the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, the following are the results related to the hypothesis of the study:
The main hypothesis: There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage (cost reduction, quality improvement, flexibility, & innovation).
As shown in Table 3, the results indicate that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage. The value of calculated F is equal 5.4 which are higher than the value of F at 0.05 level of significance and 128 degrees of freedom, an indication of significant effect.
| Table 3 : Simple Regression Results Of The Effect Of Stability Strategy In Accomplishing Competitive Advantage | |||
| Variable | Sig | T | Beta |
| Stability strategy | 0.022* | 2.325 | 0.201 |
Table 3 showed that the value of R2 is equal 0.041 percent which means that 4 percent of changes in competitive advantage are explained by stability strategy and 96 percent of changes are explained by other variables. The analyses also showed that stability strategy affect competitive advantage where T equal 2.325, and Beta equal 0.201 at 0.05 level of significance. Such results suggest the rejection of the null hypothesis that there was no significant effect between stability strategy and accomplishing competitive advantage and accept the alternative hypothesis.
The main hypothesis is divided into four minor hypotheses as follows:
There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance between stability strategy and accomplishing a competitive advantage of cost reduction.
The results are shown in Table 4.
| Table 4: Simple Regression Results Of The Effect Of Stability Strategy In Cost Reduction | |||
| Variable | Sig | T | Beta |
| Stability strategy (cost reduction) | 0.001* | 3.289 | 0.279 |
Note: R= 0.279, R2=0.078, F= 10.817, F/Sig=0.001*
As shown in Table 4, the results indicate that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage of cost reduction. The value of calculated F is equal 10.8 which are higher than the value of F at 0.05 level of significance and 128 degrees of freedom, an indication of significant effect.
Table 4 showed that the value of R2 is equal 0.078 percent which means that 8 percent of changes in competitive advantage are explained by stability strategy and 92 percent of changes are explained by other variables. The analyses also showed that stability strategy affect competitive advantage of cost reduction where T equal 3.289, and Beta equal 0.279 at 0.05 level of significance. Such results suggest the rejection of the null hypothesis that there was no significant effect between stability strategy and accomplishing competitive advantage of cost reduction and accept the alternative hypothesis.
There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage of quality improvement.
The results are shown in Table 5.
| Table 5: Simple Regression Results Of The Effect Of Stability Strategy In Quality Improvement | |||
| Variable | Sig | T | Beta |
| Stability strategy (quality improvement) | 0.545 | 0.607 | 0.054 |
Note: R=0.054, R2=0.003, F=0.369, F/Sig=0.545.
As shown in Table 5, the results indicate that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage of cost reduction. The value of calculated F is equal 0.369 which is lower than the value of F at 0.05 level of significance and 128 degrees of freedom, an indication of non-significant effect.
Table 5 also showed the value of R2 is equal 0.003 percent which means that less than 1 percent of changes in competitive advantage of quality improvement are explained by stability strategy and 99 percent of changes are explained by other variables. The analysis also showed that stability strategy did not affect competitive advantage of quality improvement where T equal 0.607 and Beta equal 0.054 at 0.05 level of significance. Such results suggest the acceptance of the null hypothesis that there was no significant effect between stability strategy and accomplishing competitive advantage of quality improvement and reject the alternative hypothesis.
There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage of flexibility.
The results are shown in Table 6.
| Table 6: Simple Regression Results Of The Effect Of Stability Strategy In Flexibility | |||
| Variable | Sig | T | Beta |
| stability strategy and flexibility | 0.001* | 3.303 | 0.28 |
Note: R=0.280, R2=0.079, F=10.911, F/Sig =0.001*
As shown in Table 6, the results indicate that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage of cost reduction. The value of calculated F is equal 10.911 which are higher than the value of F at 0.05 level of significance and 128 degrees of freedom, an indication of significant effect. Table 6 also showed the value of R2 is equal 0.079 percent which means that less than 1 percent of changes in competitive advantage of quality improvement are explained by stability strategy and 92 percent of changes are explained by other variables. The analysis also showed that stability strategy did affect competitive advantage of flexibility where T equal 3.303 and Beta equal 0.280 at 0.05 level of significance. Such results suggest the rejection of the null hypothesis that there was no significant effect between stability strategy and accomplishing competitive advantage of flexibility and accept the alternative hypothesis.
There is no statistically significant effect at 0.05 level of significance of stability strategy in accomplishing a competitive advantage of innovation.
The results are shown in Table 7.
| Table 7: Simple Regression Results Of The Effect Of Stability Strategy In Innovation | |||
| Variable | Sig | T | Beta |
| Stability strategy and Innovation | 0.114 | 1.592 | 0.139 |
Note: R=0.139, R2=0.019, F=2.533, F/Sig=0.114
As shown in Table 7, the results indicate that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing a competitive advantage of cost reduction. The value of calculated F is equal 2.533 which are lower than the value of F at 0.05 level of significance and 128 degrees of freedom, an indication of non-significant effect.
Table 7 also showed the value of R2 is equal 0.019 percent which means that less than 2 percent of changes in competitive advantage of innovation are explained by stability strategy and 98 percent of changes are explained by other variables. The analysis also showed that stability strategy did not affect competitive advantage of innovation where T equal 1.592 and Beta equal 0.139 at 0.05 level of significance. Such results suggest the acceptance of the null hypothesis that there was no significant effect between stability strategy and accomplishing competitive advantage of flexibility and reject the alternative hypothesis.
Results
The major results of the study showed that stability strategy has an effect in accomplishing competitive advantage of cost reduction, quality improvement, flexibility, and innovation combined together. It also showed that stability strategy have an effect in accomplishing competitive advantage of cost reduction and flexibility. Meanwhile, the results showed that stability strategy have no effect on accomplishing competitive advantage of quality improvement and innovation.
Conclusion
It is clear from the results that there is an impact for stability strategy in competitive advantage in achieving both cost and flexibility. Which is confirms with the study literature. The organizations seek to maintain the current situation through the stability strategies, in order to maintain their market share in light of the economic conditions and markets. Furthermore, organizations reduce their direct and indirect costs in order to maintain its competitive advantage and protect itself from decline.
Regarding flexibility dimension, the circumstances experienced by the organizations when adopting the strategy of stability, it must adapt to these circumstances and has the legitimacy to respond to changes in the market as well as customers and this is consistent with the theoretical literature in strategic management science.
It is clear from the results that there is no effect of the stability strategy in achieving competitive advantage in both qualitative and innovative dimensions. This result is logical because when organizations adopt a stability strategy they reduce the quality in order to reduce the cost. The organizations conditions or the markets situation does not allow this especially when organization is looking for reducing the cost, therefore this result is logical and stability strategy does not affect the quality. Moreover, this conclusion also applies to innovation, where innovation is expensive in terms of testing or attracting qualified personnel to innovation process. When the company adopts a stabilization strategy, it is natural to minimize innovation processes, and this conclusion matches with theoretical literate.
Recommendations
Upon the analyses of the data and the obtained study results, several recommendations were drawn. First, companies must use distribution channels for new services similar to current distribution channels. Second, companies must work at reducing direct cost of labor that affect production operations and select employees who are within close distance from the location of the company. Third, companies must study, analyze and evaluate training programs to assess the currents and future needs of the company. And fourth, companies must train employees continuously to enable them to skillfully adapt to the changing strategies by establishing training centers or cooperation with local universities in order to reduce cost, improve quality, increase creativity and innovation of products and services.
In addition, the researchers recommend conducting future studies of stability strategy effect on accomplishing competitive advantage in different sectors of the economy.
References
- Abraham, S.E., Karns, L.A., Shaw, K., & Mena, M.A. (2001). Managerial competencies and the managerial performance appraisal process. Journal of Management Development, 20(10), 842-852.
- Ambler, S.W. (2002b). Know the user before implementing a system. Computing Canada, 28(3), 13.
- Boynton, A.C., Zmud, R.W., & Jacobs, G.C. (1994). The influence of it management practice on IT use in large organizations. MIS Quarterly, 29, 299-324.
- Chong, V.K. (2004). Job?relevant information and its role with task uncertainty and management accounting systems on managerial performance. Pacific Accounting Review, 16(2), 1-22.
- Cui, T.J., Liu, S., & Li, L.L. (2016). Information entropy of coding metasurface. Light: Science & Applications, 5(11), e16172.
- Cummings, M., & Dawkins, J. (2000). Management information systems for the information age. Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
- Davis, S., & Albright, T. (2000). The changing organizational structure and individual responsibilities of managerial accountants: A case study. Journal of Managerial Issues, 12(4), 446-467.
- Ghasemi, R., Mohamad, N.A., Karami, M., Bajuri, N.H., & Asgharizade, H. (2016). The mediating effect of management accounting system on the relationship between competition and managerial performance. International Journal of Accounting and Information Management, 24(3), 272-295.
- Guimaraes, T., Staples, S.D., & Mckeen, J.D. (2003). Empirically testing some main user-related factors for system development quality. The Quality Management Journal, 10(4), 39-50.
- Hansen, D.R., & Mowen, M.M. (2005). Environmental cost management. Management Accounting, 7, 490-526.
- Kertajaya, H. (2009). Welcome to the new order of the marketing world.
- Laudon, K.C., & Laudon, J.P. (2013). Management information system. Pearson Education Limited, London.
- Martin, E.W., Brown, C.V., Hoffer, J.A., Perkins, W.C., & DeHayes, D.W. (1998). Managing information technology: What managers need to know. Prentice Hall PTR.
- McLeod, R., & Schell, G.P. (2007). Management information systems. Pearson Prentice Hall. India.
- Moturi, C., & Mbiwa, P. (2015). An evaluation of the quality of management information systems used by SACCOS in Kenya. The TQM Journal, 27(6), 798-813.
- Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, West Sussex, United Kingdom.