Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 4S
Social Media Communication and Behavioral Intention of Customers in Hospitality Industry: The Mediating Role Customer Satisfaction
Anam Yasir, National College of Business Administration & Economics
Ghulam Abid, Kinnaird College for Women
Jawad Rahim Afridi, Sarhad University of Science and IT
Natasha Saman Elahi, National College of Business Administration & Economics
Natasha Saman Elahi, National College of Business Administration & Economics
Keywords
Restaurant Generated Communication, Customer Generated Communication, Customer Satisfaction, Behavioral Intention.
Abstract
Social media communication is considered to be an important predictor of the behavioral intention of customers in the hospitality industry. Despite the importance of this, our study examined indirect of the effect of restaurant generated and customers’ generated communication on social media on behavioral intention to visit restaurants through customer satisfaction towards restaurants in the hospitality industry of Pakistan. Data were analyzed by using PROCESS macro by Hayes on a sample of customers from various restaurants. Results show restaurant and customer generated communication on social media is positively associated with customer satisfaction and behavioral intention. Furthermore, customer satisfaction mediates restaurant-generated communication on social media and behavioral intention relationship as well as customer generated communication on social media and behavioral intention. The findings of this study strongly contribute towards a better understanding of social media communications in this modern world of web 2.0 and how this communication induces customer satisfaction to visit restaurants.
Introduction
In the hospitality industry, it is essential for restaurants to build a strong image based on the provision of quality services (Martínez & Nishiyama, 2017). As part of quality service, effective communication by restaurants is important for building a strong restaurant image in customer’s mind (Kharouf et al., 2018). There are two kinds of communication that improve the relationship with customers (Herzberg, 1966). One type of communication is satisfies the beneficiary’s needs and other one makes the beneficiary feels comfortable in a relationship. Restaurant’s communication induces a sense of comfort among customers. With changing of times, traditional forms of communication are replaced by innovative networks (Llopis-Amorós et al., 2019). These days, customers are using social media i.e., Face book/ LinkedIn, micro blogs like Twitter and content-sharing communities like YouTube/Instagram (Yoong & Lian, 2019) to explore the information related to their eating times (Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). Therefore, now a day’s restaurants are more interested in taking part at social media to provide product and service related information to their customers.
It is claimed that electronic word of mouth has become a powerful source of communication in the tourism and hospitality industry (Bilro et al., 2018). Likewise, the usage of online reviews in the process of decision making about restaurants and events has become much popular in the hospitality industry (Smith & Anderson, 2016) as customers exchange their information and make comments on products and services on social media. Customer’s reviews on social media have a direct impact on peer behavior (Roozen & Raedts, 2018). In the hospitality industry, this is more important for customers to visit social media sites before making their decisions, (Bilro et al., 2018). They look for advertisement about restaurants and analyze reviews of other customers about specific event or restaurant how contextual as well as individual characteristics are relate to thriving at work” (Abid et al., 2019). Customers engaged in disseminating their reviews for helping others in their decision-making process (Romero, 2017). Recent researches have shown that online reviews of customers determine attitude of people for a product or service (Lee & Jeong, 2018). Other studies endeavored to anticipate attitudes of customers i.e., customer satisfaction from user generated communication on social media and its effect on customer purchases (Rafique et al., 2020; Bilro et al., 2018; Filieri et al., 2015). Customer satisfaction is considered as a good predictor of behavioral intention and has been extensively examined in many studies. For example, Byun & Soocheong (2019) examined the effect of signaling on customer satisfaction and behavioral intention. Despite the significance of social media communication in the hospitality industry, the influence of customer satisfaction generated from social media communication on behavioral intention has not been explored. Although previous studies have analyzed the effect of social media communication on attitudes of customers, but according to our best knowledge, no study has been found to analyze the role of customer satisfaction in this process. Therefore, this study fills this gap by analyzing the role of customer’s satisfaction in predicting behavioral intention of customer through communication on social media. In particular, this study analyzes the mediating role of customer satisfaction between restaurant generated and customer generated communication on social media and behavioral intention of customer.
Thus, the core objective of the study is 1) to explore the effects of restaurant generated and customer generated communication of social media on behavioral intention and customer satisfaction,) to study the indirect effect of effects of restaurant generated and customer generated communication of social media on behavioral intention through customer satisfaction. This research paper is organized as follows. After the introduction of topic, literature review builds up conceptual framework and develops hypotheses. Third section presents methodology. Discussion of results is in part four. Last section explains findings, implications and future directions.
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Restaurant Generated Communication on Social Media and Customer Satisfaction
Social media has provided people a vast online exposure, especially through social networking. Social networking is composed of digital sources providing information (Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). These sources are originated, circulated, and used by internet users that educate others about a specific product, service or brand (Chauhan & Pillai, 2013). Firms are now responsive to two-way interactions with customers (Li & Bernoff, 2011). Social media provides innovative ideas to interact with companies and firms. Therefore, firm-created communication on social media is referred to as an important factor in promotion mix (Bambauer-Sachse & Mangold, 2011). Social media communication is used as a powerful source for providing information and engaging and listening from customers about products and services (Brodie et al., 2013).
Social media communication, in comparison to other traditional sources of communication, appeals more extensive population (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2010; Keller, 2009). This type of advertisement through social media is a new practice (Nielsen, 2013). Social media communication among firms gains more importance as information is readily disseminated over the internet (Li & Bernoff, 2011). In the hospitality industry, social media communications by restaurants are considered as an influential source for dissemination of information (Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). It is defined as “A form of advertising fully controlled by the company and guided by a marketing strategy agenda” (Qaiser et al., 2021; Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). The availability of information attracts consumers as they become more aware of the restaurant, they choose. This leads towards the satisfaction of customers as they are more willing to visit a restaurant for which they communicated with social media (Llopis-Amorós et al., 2019). Considering the importance of restaurant generated communication on social media, this study proposes:
H1: Restaurant generated communication on social media is positively related to customer satisfaction.
Customer Generated Communication on Social Media and Customer Satisfaction
Customer/users generated communication on social media is defined as “content made publicly available over the internet created outside of professional routines and practice” (OECD, 2007). Users of a product, brand, or restaurant edit information on social media in this way; it becomes an interesting mode of communication. In modern era of web 2.0, people with similar thoughts and interests make communities over the internet, making customer to customer communications (Mangold & Faulds, 2009; Winer, 2009). This becomes a source of information among consumers about specific brands or products (Mangold & Faulds, 2009). Past researchers have shown that consumers consider information generated by other customers as a more reliable source rather than information created by the manufacturer or firm itself (Cheong and Morrison, 2008). In the context of hospitality and tourism management, customers rely on information generated by other customers on social media about restaurants or festivals (Llopis-Amorós et al., 2019). Customers feel more satisfied with those restaurants for which other people communicate and show their loyalty (Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). Based on the above-mentioned discussion, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H2: Customer generated communication on social media is positively related to customer satisfaction.
Behavioral Intention
Behavioral intention refers to the degree of planning of a person to perform an action in near future (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1980) Behavioral intention can be both favorable and unfavorable (Ali & Amin, 2014). Favorable behavioral intention means positive word of mouth; a person spends more with a restaurant and shows loyalty. While the unfavorable behavioral intention is negative word of mouth, a person spends less with a restaurant. Behavioral intention is a representation of a customer’s conative loyalty for a restaurant. Customer loyalty is considered a significant objective in the hospitality industry as it is an important indicator for sustainability of a company and is the best measure for customer retention (Chen & Chen, 2010). Customer loyalty is classified into four stages. It starts with cognitive loyalty (from previous knowledge), moves to affective loyalty (emotional satisfaction) which derives conative loyalty (intention to behave), and ends at action loyalty (overcoming hurdles to behave) (Oliver, 1999). From a measurement point of view, action loyalty is a difficult concept to measure (Han et al., 2011). Therefore, instead of action loyalty, conative loyalty as a measure of behavioral intention is mostly used in research (Yang & Peterson, 2004). Some researchers also use the attitudinal aspect of loyalty (Varki & Colgate, 2001; Yi & La, 2004).
According to theory of planned behavior, behavioral intention is formed as a result of attitudes, subjective norms or perceptions (Pelaez et al., 2017). In the hospitality industry, intention to visit a restaurant again and recommending to others are widely used to measure the loyalty of customers (Bonn et al., 2007; Chen & Chen, 2010). Therefore, good services of restaurant induce customers to revisit and say positive things about the restaurant to others (Chen & Tsai, 2007; Lee et al., 2011). For potential customers, behavioral intention of other customers is the most reliable source of information (Williams & Soutar, 2009). Social mechanisms of companies help in shaping consumer behavior. Reviews of other people demonstration on social media are also important in this regard (Pütter, 2017). Therefore, when restaurants communicate their information or when customers get awareness from other people through social media, their intention to visit restaurant increases. Information quality communicated through social media is a strong predictor of behavioral intention of customers (Nath et al., 2019). Soliman (2019) has extended the theory of planned behavior by including electronic word of mouth as a predictor of revisit intention. Similarly, Harb, et al., (2019) also used theory of planned behavior to analyze factors that affect behavioral intention of customers using social media sites. From the above literature, this study proposes:
H3: Restaurant generated communication on social media is positively related to behavioral intention of customers.
H4: Customer generated communication on social media is positively related to behavioral intention of customers.
In services industry like hospitality, it is quite necessary to have a look on satisfaction of customers. If customers become dissatisfied due to inefficient services, then negative impact of dissatisfied customers is higher than positive effects of satisfied customers (Kim et al., 2017). This concept was also highlighted by Sürücü, et al., (2019) who argued that customer satisfaction is related to repeat purchases by customers. Literature on hospitality and tourism reports a positive and significant relationship between customer satisfaction and behavioral intention (Byun et al., 2019; Cheng et al., 2014; Gao, 2016; Mangold & Faulds, 2009; Shahzadi et al., 2018; Wu & Li, 2017). Thus, considering previous literature, we find it reasonable to assume positive relationship between customer satisfaction and behavioral intention.
H4: Customer satisfaction is positively related to behavioral intention of customers.
Customer perception of a restaurant is greatly influenced by the provision of services. Any issue regarding customer’s services can affect value of a restaurant (Palmer et al., 2000). Many researchers have pointed out factors and remedies of service failures because it can lead to dissatisfaction of customers and discontinued spending in restaurant (Ha & Jang, 2009; Kim & Jang, 2014). Full provision of services by restaurants leads to satisfaction of customers (Byun et al., 2019). Positive signals received from social media tend to be more appealing for customer satisfaction and behavioral intention.
Research on social media communication by users and company influencing behaviors of customer analyzed mediating role of customer’s attitude in this process (Bruno et al., 2019). When customers receive social media communications about the restaurant either by the restaurant itself or by other customers, they become more satisfied, and their intention to visit that restaurant increases. Customer’s behavioral intentions are shown by their favorable comments (Wang et al., 2004) about business or by their recommendations to others (Chen & Tsai, 2007). Customers post this kind of information on social media which appeals to other customers for a restaurant. Due to the increased popularity of the internet and social media, electronic word-of-mouth exerts a powerful impact on shaping behavior of customers in the hospitality and tourism industry (Chen & Law, 2016). Customer’s communications in this way also help firms to indicate their market conditions for knowing behavioral intentions of customers (Kruger & Saayman, 2017). Varkaris & Neuhofer (2017) analyzed the role of consumer decision making in technology-assisted context by using the qualitative approach. According to this study, customers decide about restaurant using social media communication. As according to theory of planned behavior, attitude of customers formed from exposure to different services makes behaviors and shows intentions of customers (Ajzen, 1991). Considering the literature and the underlying explanations, we assume that communication on social media affects satisfaction of customers, which in turn, determines behavioral intention of customers. Thus, following hypotheses are proposed:
H6: Customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between restaurant generated communication on social media and behavioral intention of customers.
H7: Customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between restaurant generated communication on social media and behavioral intention of customers.
Methods
Participants and Procedure
In this study target population was the people who visit restaurants for dine-in. through purposive sampling technique as this research aims to explore effects of social media communication in specific cultural context. Purposive sampling focus on respondents who share similar characteristics (Etikan, Musa & Rukayya, 2016). Survey research design was conducted in various restaurants of Lahore (Pakistan) for data collection. Data was collected in the months of October and November through self-administered questionnaires. A consent letter was obtained from university for data collection purpose. Firstly, permission was taken from front manager of restaurant. After that, customers were requested to fill in questionnaire when they got free from dine-in. Frequent visits to various restaurants were arranged for data collection. Most of the visits to restaurants were at lunch time. On average, a customer used to take 15-20 minutes for recording his/her responses. After collecting questionnaire, a small gift wrap was presented to customer as a good gesture for thanks. A total of 450 questionnaires were distributed. Of them, 370 responses were returned, capable of using in data analysis. In this way, actual response rate of study was 82% which was beyond average in this kind of study and suitable for organizational researches (Bordia, Restubog, Jimmieson & Irmer, 2011).
Measures
Questionnaire consisted of scales which have already been developed and validated in literature. A five-point Likert scale was used to measure items, where 1=strongly disagree to 5=strongly agree. Description of scale of studied variables is described below.
Restaurant Generated Communication on Social Media
Customer’s perception about social media communications generated by restaurant was measured using scale developed by Schivinski & Dabrowski (2014). There were 4 items in scale. A sample item from the scale is “The restaurant’s social media communications are very attractive.” Reliability of the scale was 0.74.
Customer Generated Communication on Social Media
Social media communication created by other customers of restaurant play a significant role in generating satisfaction of customers, as described in literature. In this regard, measurement scale developed by Schivinski & Dabrowski (2014) was used in questionnaire. There were 4 items in scale. A sample item from the scale is “The content generated on social media sites by other customers about restaurant performs well, when compared with other restaurants”. Reliability of the scale was 0.71.
Customer Satisfaction
Mediating role of customer satisfaction was measured using scale developed by Llopis-Amorós, et al., (2019). Sample item from scale is “I am satisfied with the overall restaurant experience.” Reliability of the scale was 0.80.
Behavioral Intention
Customer’s behavioral intention is dependent variable of this study. It was measured using scale by Llopis-Amorós, et al., (2019). Sample item of behavioral intention from questionnaire is “I recommend restaurant to someone who seeks my advice”. Reliability of the scale was 0.72.
Demographics
Due to the effects of these demographics on studied variables, gender, age, qualification, marital status and frequency to visit restaurants were included as controls.
Research Model
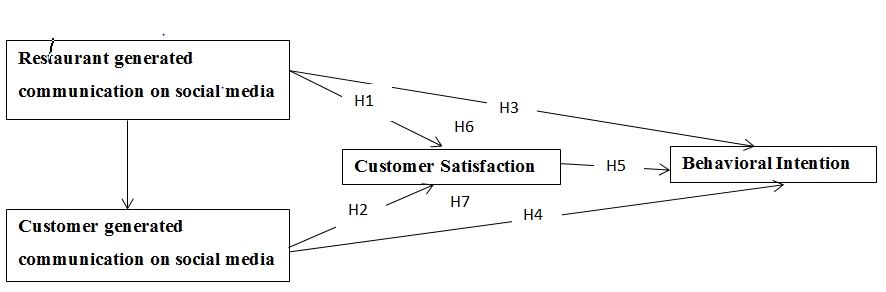
This research is intended to describe relationship between restaurant generated and customer generated communication on social media and behavioral intention with mediating effect of customer satisfaction. Figure 1 shows model of this research. Restaurant generated communication on social media and customer generated communication on social media are independent variables. Customer satisfaction is mediator. Behavioral intention of customers is the dependent variable of this research.
Data Analysis Approach
For the analysis of data, SPSS24 was used. Using this software, descriptive statistics were analyzed. In descriptive statistics, mean, standard deviation, reliability and correlation of variables were calculated. PROCESS macro model 4 (Hayes & Preacher, 2013) were used for hypotheses testing. There were two mediation models as theoretical framework includes two independent variables.
Results
Descriptive Statistics
Table 1 consists of descriptive statistics and correlations of variables. Demographics include gender, marital status, age, qualification, and frequency to visit restaurant in a month. Variables under study are restaurant generated and consumer generated communication on social media, customer satisfaction and behavioral intention. For descriptive statistics, mean and standard deviation are mentioned in table. Values of reliabilities of constructs are within range of 0.71 to 0.8. Correlation results show that restaurant generated communication on social media is positively and significantly related to customer generated communication (r=0.5, p<0.01), and to customer satisfaction (r=0.42, p<0.01), and to behavioral intention (r=0.39, p<0.01). There is positive and significant correlation between customer generated communication on social media and customer satisfaction (r=0.34, p<0.01), and behavioral intention (r=0.4, p<0.01). Same association is also observed between customer satisfaction and behavioral intention (r=0.51, p<0.01). Correlation results provide initial support to derived hypotheses in the study.
| Table 1 Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Matrix. **: P<0.01, *: P<0.05; a reliabilities (in parentheses) appear on the diagonal |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 1 | Gender | |||||||||||
| 2 | Marital status | -0.04 | ||||||||||
| 3 | Age | 21.00 | 4.57 | -0.02 | 0.58 | |||||||
| 4 | Qualification | 3.17 | 0.74 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.47** | ||||||
| 5 | Frequency to visit restaurant | 3.57 | 4.0 | -0.20 | -0.03 | 0.04 | -0.18 | |||||
| 6 | Restaurant generated communication | 3.54 | 0.80 | 0.17 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0.07 | -0.12 | (0.74) | |||
| 7 | Customer generated communication | 3.56 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | -0.17 | 0.50** | (0.71) | ||
| 8 | Customer satisfaction | 3.88 | 0.79 | 0.16 | 0.02 | -0.02 | 0.13 | -0.13 | 0.42** | 0.34** | (0.80) | |
| 9 | Behavioral intention | 3.79 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.12 | -0.13 | 0.39** | 0.40** | 0.51** | (0.72) |
Hypotheses Testing
Table 1 consists of descriptive statistics and correlations of variables. Demographics include gender, marital status, age, qualification, and frequency to visit restaurant in a month. Variables under study are restaurant generated and consumer generated communication on social media, customer satisfaction and behavioral intention. For descriptive statistics, mean and standard deviation are mentioned in table. Values of reliabilities of constructs are within range of 0.71 to 0.8. Correlation results show that restaurant generated communication on social media is positively and significantly related to customer generated communication (r=0.5, p<0.01), and to customer satisfaction (r=0.42, p<0.01), and to behavioral intention (r=0.39, p<0.01). There is positive and significant correlation between customer generated communication on social media and customer satisfaction (r=0.34, p<0.01), and behavioral intention (r=0.4, p<0.01). For the analysis of data, SPSS24 was used. Using this software, descriptive statistics were analyzed. In descriptive statistics, mean, standard deviation, reliability and correlation of variables were calculated. PROCESS macro model 4 (Hayes & Preacher, 2013) were used for hypotheses testing. There were two mediation models as theoretical framework includes two independent variables
Table 2 shows results for derived hypothesis. Finding of SPSS PROCESS macro show that restaurant generated communication on social media significantly influence customer satisfaction (β=0.42, t=8.83, p<0.001), supporting H1, and also positively impacts behavioral intention (β=0.21, t=4.21, p<0.001), supporting H3. Similarly customer satisfaction is also positively and significantly related to behavioral intention (β=0.42, t=8.46, p<0.001), supporting H5. Total effect model is also significant and positive. Mediating role of customer satisfaction is proved by indirect effects of restaurant generated communication on social media on behavioral intention of customers. Simple mediation model predicts that restaurant generated communication on social media has an indirect effect on behavioral intention via customer satisfaction. This indirect effect is positive (β=0.18) and formal two-tailed significance of normal distribution (Sobel test) shows that this indirect effect is significant (Sobel: z=6.09, p<0.001). Bootstrap results are also persistent with Sobel test, as 90%CI (0.12, 0.24) around indirect effect have a non-zero point. Thus, H6 is supported.
| Table 2 Results of Simple Mediation Model Regressing Customer Satisfaction as a Mediator |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct effect model | ||||
| Customer Satisfaction | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Restaurant generated communication on social media | 0.42 | 0.05 | 8.83 | 0.00 |
| Constant | 2.37 | 0.17 | 13.58 | 0.00 |
| Direct effect model | ||||
| Behavioral Intention | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Restaurant generated communication on social media | 0.21 | 0.05 | 4.21 | 0.00 |
| Customer satisfaction | 0.42 | 0.05 | 8.46 | 0.00 |
| Constant | 1.41 | 0.20 | 6.95 | 0.00 |
| Total effect model | ||||
| Behavioral Intention | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Restaurant generated communication on social media | 0.39 | 0.05 | 7.88 | 0.00 |
| constant | 2.41 | 0.18 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| Indirect effect and significance using the normal distribution | ||||
| Value | SE | z | P | |
| Sobel | 0.18 | 0.03 | 6.09 | 0.00 |
| Indirect effect of X on Y | ||||
| M | SE | LL90%CI | UL90%CI | |
| Effect | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.24 |
Further, results in Table 3 shows that customer generated communication on social media significantly influence customer satisfaction (β=0.35, t=6.88, p<0.001), supporting H2, and also positively impacts behavioral intention (β=0.26, t=5.33, p<0.001), supporting H4. Total effect model is also significant and positive. Mediating role of customer satisfaction is proved by indirect effects of customer generated communication on social media on behavioral intention of customers. Simple mediation model predicts that customer generated communication on social media has an indirect effect on behavioral intention via customer satisfaction. This indirect effect is positive (β=0.15) and formal two-tailed significance of normal distribution (sobel test) shows that this indirect effect is significant (Sobel: z=5.43, p<0.001). Bootstrap results are also persistent with Sobel test, as 90%CI (0.09, 0.22) around indirect effect have a non-zero point. Thus, H7 is supported.
| Table 3 Results of Simple Mediation Model Regressing Customer Satisfaction as a Mediation |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct effect model | ||||
| Customer Satisfaction | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Customer generated communication on social media | 0.35 | 0.05 | 6.88 | 0.00 |
| Constant | 2.63 | 0.19 | 14.10 | 0.00 |
| Direct effect model | ||||
| Behavioral Intention | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Customer generated communication on social media | 0.26 | 0.05 | 5.33 | 0.00 |
| Customer Satisfaction | 0.43 | 0.05 | 8.96 | 0.00 |
| Constant | 1.22 | 0.21 | 5.87 | 0.00 |
| Total effect model | ||||
| Behavioral Intention | ||||
| B | SE | T | P | |
| Restaurant generated communication on social media | 0.41 | 0.05 | 8.10 | 0.00 |
| Constant | 2.34 | 0.18 | 12.73 | 0.00 |
| Indirect effect and significance using the normal distribution | ||||
| Sobel | Value | SE | Z | P |
| 0.15 | 0.03 | 5.43 | 0.00 | |
| Indirect effect of X on Y | ||||
| M | SE | LL 90%CI | UL90%CI | |
| Effect | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.22 |
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of social media communication on customer satisfaction and behavioral intention of customers. This study also serves to analyze the indirect effects of customer satisfaction on behavioral intention of customers through social media communication. In line with our proposed model, the study findings showed that first, restaurant generated communication on social media is positively and significantly related to customer satisfaction. Customers get more attraction towards those restaurants which post about their products and services on social media. These finding are in line with the ideas of previous researchers (Zafar et al., 2021; Llopis-Amorós et al., 2019; Schivinski & Dabrowski, 2014). Similarly, customer generated communication on social media also influences customer satisfaction significantly. This form of communication on social media becomes a source of information for other customers. Thus, it also derives satisfaction level of customers. Our results are consistent with previous studies of Mangold & Faulds, 2009) as well as Cheong & Morrison (2008). As far as the results of communication on social media and behavioral intention are concerned, they are also positive and significant according to hypothesized relationships. Customers intend to visit those restaurants about which they receive information on social media, as mentioned by other researchers also (Bonn et al., 2007; Chen & Chen, 2010), whether this kind of information is generated by restaurant itself or by other customers.
Customer satisfaction has an important relationship with behavioral intention as the satisfaction of customers induces them to visit a specific restaurant. This relationship is also proved significantly in this study like many others (Wu & Li, 2017; Asif et al., 2017; Shahzadi, Malik, Ahmad & Shabbir, 2018; Byun & Soocheong (Shawn), 2019). Social media communications induce satisfaction of customers (Chen & Tsai, 2007), as they rely upon the knowledge received for visiting restaurants. This mediating role of customer satisfaction by restaurant generated and customer generated communication on social media on behavioral intention is also reported positive and significant in this study. Concluding, restaurants should pay attention towards what is communicated on social media. In this modern era of technology, advertisement through social media is a powerful source for inducing customers. After proper communication about products and services, next is the customer satisfaction which is important for restaurants. Only a satisfied customer will visit restaurant again, resulting in high business growth.
Theoretical and Practical Contributions
This study is an attempt to add knowledge in existing literature by empirically analyzing the predecessors and outcomes of customer satisfaction in hospitality industry. In the context of Pakistan, this study is an attempt to explain communication on social media as antecedents of customer satisfaction with behavioral intention as an outcome. According to our best knowledge, this is the only study which is examining customer satisfaction as a mediator of communication on social media and behavioral intention. In this way, this study is an addition to existing literature by analyzing indirect effects of customer satisfaction on behavioral intention of customers through social media communication. Results of this study are in favor of hypothesized relationships formulated in literature review. This study has important practical implications for managers of restaurants. Current study has observed social media communication and customer satisfaction as important predictors of behavioral intention. In today’s contemporary world, work environment is continuously changing. Therefore, restaurants should pay attention towards more advanced internet applications to induce satisfaction among their customers. In this way, this study assists restaurant managers to improve their business practices and to have market edge.
Limitations and Future Directions
This research also faced some limitations. Primary issue was in data collection. Data was collected through self-administered questionnaires from selected restaurants of Lahore. These restaurants may not be the representative of different cities and sectors of Pakistan. It may give rise to spurious results and common variances. Future researchers are encouraged to employ more restaurants for data collection. Secondly, this study is the first attempt to examine the role of social media communication on behavioral intention of customers through customer satisfaction. However, the study is conducted in specific cultural setting of Pakistani restaurants. Future research might consider other developed countries as the culture and working procedures of their restaurants are different from developing ones. Third, researchers of this study examine that other variables of hospitality industry should also be analyzed in model of this research. For example, value for money and brand engagement is powerful factors for revisit intention of customers (Mohsin & Lockyer, 2010; Llopis-Amorós et al., 2019). If customers are convinced by social media communication, then the role of these two variables can also be expected as strong predictor of behavioral intention. Future studies can try to explore overall value for money and brand engagement in their study.
Conclusion
The present study contributes to existing literature of behavioral intention by empirically analyzing its antecedents in the context of hospitality industry of Pakistan. Findings of the study confirm the presence of significant and positive relationship between hypothesized relationships. Concluding, restaurants should pay attention towards what is communicated on social media by restaurants themselves and by their customers. In this modern era of technology, advertisement through social media is a powerful source for inducing customers to visit restaurants. After proper communication about products and services, next is the customer satisfaction which is important for managers. Only a satisfied customer will visit restaurant again, resulting in high business growth.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, G.A. A.Y.; methodology, G.A & A.Y.; software, G.A,.; validation, N.S.E.; formal analysis, N.S.E..; investigation, G.A, A.Y., resources, G.A., data curation,A.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, G.A, A.Y. N.S.E; writing—review and editing, A.Y. N.S.E..; visualization, N.S.E.; supervision, G.A.; project administration, G.A.; funding acquisition, G.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
“This research received no external funding”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures performed in study ensured that human participants’ involvement in the research was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and/or national research committee and with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the National College of Business Administration & Economics, Lahore.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.”
Conflicts of Interest
Declare conflicts of interest or state “The authors declare no conflict of interest”.
References
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational behavior and human decision processes, 50,179-211.
- Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1980). Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs.
- Ali, F., & Amin, M. (2014). The influence of physical environment on emotions, customer satisfaction and behavioural intentions in Chinese resort hotel industry. Journal of global business advancement, 7(3), 249-266.
- Asif, M.F., Mirza, U.K., Khan, A.H., Asif, M.Z., Riaz, S., & Ahmed, S. (2017). Job satisfaction: Antecedent and consequences. Bulletin of Business and Economics, 6(4), 185-194.
- Bambauer Sachse, S., & Mangold, S. (2011). Brand equity dilution through negative online word-of-mouth communication. Journal of retailing and consumer services, 18(1), 38-45.
- Bilro, R. (2018). Exploring online customer engagement with hospitality products and its relatioship with involvement, emotional states, experience and brand advocacy. Journal of hospitality marketing and management, 10(2), 298-308.
- Bonn, M.A. (2007). Heritage/cultural attraction atmospherics: Creating the right environment for the heritage/cultural visitor. Journal of travel research, 45, 345-354.
- Brodie, R. (2013). Consumer engagement in a virtual brand community: An exploratory analysis. Journal of Business Research, 66(8), 105-114.
- Bruno, S., Daniela, L., & Christina, S. (2019). The influence of social media communication on consumer's attitudes and behavioral intentions concerning brand-Sponsored events. Event Management, 23(6), 835-853.
- Byun, J., & Soocheong J. (2019). Can signaling impact customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions in times of service failure? evidence from open versus closed kitchen restaurants. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 7(3), 1-10.
- Chauhan, K., & Pillai, A. (2013). Role of content strategy in social media brand communities: A case of higher education institutes in India. Journal of Product and Brand Management, 1(22), 40-51.
- Chen, C., & Chen, S. (2010). Experience quality, perceived value, satisfaction and behavioral intentions for heritage tourists. Tourism Management, 31, 29-35.
- Chen, C., & Tsai, D. (2007). How destination image and evaluative factors affect behavioral intentions? Tourism Management, 28, 1115- 1122.
- Chen, Y.F., & Law, R. (2016). A review of research on electronic word-of-mouth in hospitality and tourism management. International Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Administration, 17(4), 347–372.
- Cheng, C., Wu, H., & Wong, J. (2014). An empirical analysis of synthesizing the effects of festival quality, emotion, festival image and festival satisfaction on festival loyalty: A case study of Macaufood festival. International Journal of Tourism Research, 17(6), 521-536.
- Cheong, H., & Morrison, M. (2008). Consumer's reliance on product information recommendation found in UGC. Journal of interactive advertising, 8(2), 38-49.
- Filieri, R., Alguezauib, S., & McLeaya, F. (2015). Why do travellers trust TripAdvisor? Antecedents of trust towards consumer-generated media and its influence on recommendation adoption and word of mouth. Tourism management, 51(1), 174-185.
- Gao, Y. (2016). A meta-analysis of behavioral intentions for environmental-friendly initiatives in hospitality research. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 54, 107-115.
- Ha, J., & Jang, S. (2009). Perceived justice in service recovery and behavioral intentions: The role of relationship quality. International Journal of hospitality management, 28(3), 319-327.
- Harb, A., Fowler, D., Chang, C., Blum, S., & Alakaleek, W. (2019). Social media as a marketing tool for events. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 10(1), 28-44.
- Herzberg, F. (1966). Work and the nature of man. Cleveland, OH: World Publishing Company.
- Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media. Business Horizons, 53(1), 59-68.
- Keller, K. (2009). Building strong brands in a modern marketing communications environment. Journal of Marketing Communications, 15, 139-155.
- Kharouf, H., Sekhon, H., Fazal-e-Hasan, S.M., Hickman, E., & Mortimer, G. (2018). The role of effective communication and trustworthiness in determining guests’ loyalty. Journal of hospitality marketing and management.
- Kim, B., Kim, S., & Heo, C.Y. (2017). Consequences of customer dissatisfaction in upscale and budget hotels: Focusing on dissatisfied customers’ attitude toward a hotel. International journal of hospitality and tourism administration, 10(1), 234-246.
- Kim, J., & Jang, S. (2014). A scenario-based experiment and a field study: A comparative examination for service failure and recovery. International journal of hospitality management, 41,125-132.
- Kruger, M., & Saayman, M. (2017). Segmenting beyond behavioural intentions-fine tuning music festival visitors’ music appreciation. International journal of event and festival management, 8(2).
- Lee, J., Lee, C., & Choi, Y. (2011). Examining the role of emotional and functional values in festival evaluation. Journal of travel research, 50, 685-696.
- Lee, S., & Jeong, M. (2018). e-Social influence and customers’ behavioral intentions on a bed and breakfast website. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 27(3), 366–385.
- Li, C., & Bernoff, J. (2011). Groundswell: Winning in a world transformed by social technologies. Boston:MA: Harvard Business Review.
- Llopis-Amorós. (2019). Social media communications and festival brand equity: Millennials vs. Centennials. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 40, 134-144.
- Mangold, W., & Faulds, D. (2009). Social media: The new hybrid element of promotion mix. Business Horizons, 52(4), 357-365.
- Nath, A., Saha, P., & Salehi-Sangari, E. (2019). Blurring the borders between B2B and B2C: A model of antecedents behind usage of social media for travel planning. Journal of business and industrial marketing, 34(7), 1468-1481.
- Nielsen. (2013). Paid social media advertising: Industry update and best practices.
- OECD. (2007). Organisation for economic co-operation and development.
- Oliver, R. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of marketing, 63(4), 33-44.
- Palmer, A. (2000). Equity and repurchase intention following service failure. Journal of services marketing, 14(6), 513–528.
- Pelaez, A., Chen, C.W., & Chen, Y.Z. (2017). Effects of perceived risk on intention to purchase: A meta-analysis. Journal of computer information systems, 10(1), 1-10.
- Pietro, L., & Pantano, E. (2013). Social network influences on young tourists: An exploratory analysis of determinants of the purchasing intention. Journal of Direct, Data and Digital Marketing Practice, 15, 4-19.
- Pütter, M. (2017). The effect of social media on consumer buying intention. Journal of International Business Research and Marketing, 3(1).
- Qaiser, N., Sattar, N., Arshi, S., Asif, M.F., & Afridi, J.R. (2021). Impact of thriving on job performance, positive health and turnover intention: Consequences of thriving at workplace. International Journal of Information, Business and Management, 13(2), 97-107.
- Rafique, T., Asif, M.F., Afridi, J.R., Rehman, N.U., & Mahmood, K. (2020). Credibility of social networking sites: Impact on organizational attraction in recruitment filed. Sarhad Journal of Management Sciences, 6(2), 279-294.
- Romero, J. (2017). Customer engagement behaviors in hospitality: Customer-Based antecedents. Journal of hospitality marketing and management, 26(6), 565–584.
- Roozen, I., & Raedts, M. (2018). The effects of online customer reviews and managerial responses on travelers’ decision-making processes. Journal of hospitality marketing and management, 1(3), 26-33.
- Schivinski, B., & Dabrowski, D. (2014). The effect of social media communication on consumer perceptions of brands. Journal of Marketing Communications, 3(1).
- Shahzadi, M., Malik, S.A., Ahmad, M., & Shabbir, A. (2018). Perceptions of fine dining restaurants in Pakistan: What influences customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions? International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, 10(1).
- Soliman, M. (2019). Extending the theory of planned behavior to predict tourism destination revisit intention. International Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Administration, 3(10).
- Sürücü, Ö., Öztürk, Y., Okumus, F., & Bilgihan, A. (2019). Brand awareness, image, physical quality and employee behavior as building blocks of customer-based brand equity: Consequences in the hotel context. Journal of hospitality and tourism management, 40, 114-124.
- UNTWO. (2018). World Tourism Organization, UNWTO Tourism Highlights. Madrid: UNWTO.
- Varkaris, E., & Neuhofer, B. (2017). The influence of social media on the consumers’ hotel decision journey. Journal of hospitality and tourism technology, 8(1), 101-118.
- Varki, S., & Colgate, M. (2001). The role of price perceptions in an integrated model of behavioral intentions. Journal of service research, 3, 232-240.
- Wang, Y., Po, L.H., Chi, R., & Yang, Y. (2004). An integrated framework for customer value and customer-relationship-management performance: A customer-based perspective from China. Managing service quality, 14(2/3), 169-182.
- Williams, P., & Soutar, G. (2009). Value, satisfaction and behavioral intention in an adventure tourism context. Annals of tourism research, 36, 413-438.
- Winer, R. (2009). New communications approaches in marketing: Issues and research directions. Journal of interactive marketing, 23(2), 108-117.
- Wu, H.C., & Li, T. (2017). A study of experientiel quality, perceived value, heritage image, experientiall satisfaction, and behavioral intentions for heritage tourists. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, 41(8), 904-944.
- Yang, Z., & Peterson, R. (2004). Customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: The role of switching costs. Psychology and Marketing, 21(10), 799-822.
- Yi, Y., & La, S. (2004). What influences the relationship between customer satisfaction and repurchase intention? Investigating the effects of adjusted expectations and customer loyalty. Psychology and Marketing, 21, 351-373.
- Yoong, L., & Lian, S. (2019). Customer engagement in social media and purchase intentions in the hotel industry. International Journal of academic research in business and social sciences, 9(1), 54–68.
- Zafar, R., Abid, G., Rehmat, M., Ali, M., Hassan, Q., & Asif, M.F. (2021). So hard to say goodbye: Impact of punitive supervision on turnover intention. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 1-23.