Original Articles: 2017 Vol: 16 Issue: 1
Social Management Systems' Modeling Based on the Synergetic Approach: Methods and Fundamentals of Implementation
Lyutsiya Mugtabarovna Gaisina, Ufa State Petroleum Technological University
Oleg Mikhailovich Barbakov, Industrial University of Tyumen
Yuliya Ivanovna Koltunova, Industrial University of Tyumen
Elvira Venerovna Shakirova, Irkutsk National Research Technical University
Elena Gennadyevna Kostyleva, Ufa State Petroleum Technological University University
Keywords
modeling, synergetic approach, concept, social environment, socially oriented management, bifurcation point, complicated open system, external environment factors.
Introduction
The analysis of the management systems of the enterprises of oil and gas industry conducted in this article showed that they were not ready to the conditions of the political, social and economic crisis which began in the second half of 2014. Not only the financial performance indices connected with the critical prices’ fall for the raw materials had been affected, but also the personnel potential.
The socially oriented management is urged to resolve many social problems in the industry, but it is required to take into account, in case of the management system development model, the specificity of the oil and gas complex enterprises, without destroying, but on the contrary, strengthening the social potential of the oil and gas complex. The use of the synergetic approach makes it possible to achieve the management models creation, while preserving the social features of the existing organizational structures at the enterprises.
The social research which had been done, showed that there was a high staff turnover at the enterprises of the industry, generally among the most competent and experienced specialists, a high coefficient of the personnel turnover, both recruited and dismissed, was traditionally noticed. The lack of the employees’ motivation to continue their careers in that industry, their orientation on a temporary employment (the main goal being to save up some money, rather than develop their own company) – these and other managerial problems considerably increase instability at the industrial enterprises in the times of crisis. (Gaisina, Bakhtizin, Mikhaylovskaya, Khairullina, Belonozhko, 2015; Gaisina, Gareev, Valitova, Khairullina, Ustinova, 2015).
Such operating conditions of the enterprises are also complicated by the fact that the oil and gas complex is presented by a number of organizations that differ in their structure. The systems managing so many social objects stand out as highly complex ones. Thus, if the implementation of the socially oriented management becomes a goal, it is necessary to develop a special synergetic model of the management system, which will allow every participant of the production process to meet his or her social needs and interests. (Belonozhko, Silin, 2014; Belonozhko, Scythian, 2011).
Let’s pay attention to the imminent relevance of such developments from the viewpoint of the practical management technologies. In the 70-s of the 20th century the theory of organizational development started spreading as a practical technology of the implementation of a socially oriented management model. Due to the fact that a number of consulting agencies were opened, and development departments began to appear in the structure of large industrial corporations. However, the technical revolution at the end of the 70 -s – the 80-s of the 20th century, followed by an intensive economic development, significantly shifted the focus from the humanistic concepts of long-term organizations’ development to seeking the optimum rapid solutions of the productivity improvement. A long systematic work of the consultants with the organizations’ staff was replaced for the work with the senior and mid-level management, and instead of working with the corporate culture, the focus was shifted to the quality improvement of interpersonal communications among the individuals.
Thus, the practical results and the results of implementation of the socially oriented management concept were arranged in three main directions: the organizational humanity theory, the open systems’ theory and the training through practice theory. The specified theories provide an available technology of the socially oriented management implementation, intercrossing with one another at a varying extent with the principles of the synergy modeling of the management systems.
But the use of the principles of the provided directions in the social conditions of the domestic oil and gas industry is impossible without a proper correction. However, it does not invalidate the practical value of the results already obtained in the foreign management practice.
According to the theory of the organizational humanism offered by D. Porras and R. Golembiewski when modeling is a socially oriented management system, in the center of attention should not be organizational processes, but the individuals and interpersonal relations. (Porras, 2007; Golembiewski, Munzenrieder, 1988). In this case, the organizational development achieves certain success irrespective of the surrounding situation (the developed or the developing countries) and the patterns of ownership (the state, private enterprises, and individual entrepreneurs). However, later R. Golembiewski expressed doubts concerning the independence of the organizational development on the external environment.
Methods
In this work the basis of modeling management systems was constituted by the value statements of the organizational humanism, which define interpersonal relations as a leading aspect of the management system impact on the interpersonal communication as the organizational environment components of the enterprise. However, it is necessary to consider the factor of a greater dependence of the entities on the external environment that is observed in the Russian society and can be minimized in western type societies. It is necessary to agree with the internal isolation of the social environment of the entities, but it is impossible to ignore the external relations, since historically domestic enterprises represented the most important part of the social and economic system of Russia and, if we are not speaking about a sufficient state support, then within the management system it is necessary to consider the human resources, first of all, as professional social groups. So, the increase in prestige of this or that professional status of a worker or the determination of the social value of the professional groups at the enterprise scale can play a key role in the processes of integration and management (Barbakov, Romanovsky,20014; Barbakov, Bar, 2015; Valitova, Gareyev, Grogulenko, Kostyleva, 2016). The attention should be paid to the professional identity forming, the social environment of oil and gas entities should reveal, increasing, rather than reducing the external relations. Apparently, when modeling management systems the attention is not focused on the separation from the external social environment, but on the contrary, on the enterprise integration in the social and economic system of the Russian society.
The open systems’ theory became at the same time both a continuation of the system approach and the organizational development method. The postulate that the organization as an independent social organism actively reacts to any external and internal impacts by changing its structure and functions is its cornerstone (Von Bertalanffy, 1973). At the same time, the organization as a system is not uniform and consists of separate elements – subsystems (technological, social, psychological, etc.).These subsystems closely interact between themselves; therefore any change in one part of the system inevitably leads to the changes of other parts. In this regard, the intervention of consultants should be complex anyway and should consider possible changes of the entire system in case of the impact on separate elements. Besides, the consultants should consider the direction of the environmental factors’ impact which can promote positive qualitative changes of the system as well as hinder them to a high extent.
The provided synergetic modeling of the entities’ management systems is based on the fundamental principles of the system approach; the basic statements of the open systems’ theory are used as well. But it is necessary to consider social properties of the professional domestic environment of the groups that are present in the industrial sphere, such as the conservatism and the lack of bright aspiration to innovations. It is not a shortcoming, but a feature, thus, it is not necessary to pay a lot of attention to the organization development impulses as the supporters of the theory of the dug-out systems imagine.
The third concept which can be used in case of the modeling management systems of il and gas entities based on the synergetic approach to the management possible to note is the theory of training through practice the basis of which was formed by Lippitt's work, Watson, Westley, White etc. (Mazur, Shapiro, 2000). This theory offers a complex technique of the impact on the organization, which is based on the laboratory methods of Lewin’s trainings and works on the activity psychology. As a result, the model of procedural consulting impact on the organization was created. The main source of the organization development, by this theory provisions, is the fixed training of the employees through the practical action (system of trainings). And the direction to it is set by the consultants for the organizational development together with the senior managers determining the main (desirable) strategy of the entity.
For the purpose of carrying out necessary transformations of the organization environment when modeling a management system, it is convenient to organize the implementation of such type of training, thus creating the managerial competences among the employees. However, we speak about a social environment of industrial enterprises which, as shown by statistics only in 10 – 15% of cases, use innovative technologies in the management, as well as in the production processes (Kozlova, 2012). At the same time, it is noted that the innovations are implemented not via the direct interactions’ system but they also concern information technologies. Here, the social features of professional social groups of the entity play a role, employees prefer not to change the system of direct social contacts, keeping the relative stability and direct the intervention assumed by the supporters of this theory that may cause a negative reaction. It is possible to realize the principles of the socially oriented management within the training through practice theory, using only the internal potential, gradually introducing the consulting technologies into the organization environment.
Thus, the basic provisions of the offered management systems’ modeling based on the synergetic approach are determined, firstly, by the results of the conducted complex of the social research which reflects the condition of various aspects of the management system of entities of oil and gas industry. The determination of many contradictions which are arising in the management process having the social nature was the result of the research. Therefore, the management model must be focused on a social environment of the entity – both the external and the internal ones for the elimination of the problems determined by the research.
It was proved by the expert poll as well, where the most accepted opinion about the necessity of applying the system of social relations has been expressed. Together with this the experts note the difficulties in the management of such large number of social objects and the need for the transformation of the existing management system of the industry in general.
Secondly, in case of conceptualization of the modeling, the static data have been taken into account, concerning the state of modern oil and gas industry of the Russian society; the Russian legislation and regulations on the management of oil and gas complex have been analysed, as well as the data of the official statistics of the management sphere state in oil and gas industry; the economic, the accounting, the financial reporting of some entities of the oil and gas industry. The analysis has shown the need for a change of the managerial paradigm for the entities that is connected with the unfavorable social and economic conditions in the country. Together with this, insufficiency of skilled workers in the management sphere has been noted. This insufficiency impedes the management reorganization and the adaptive approach is needed enabling to use the available managerial and professional resources.
Thirdly, the modeling reflects the current trends of the management theory transformations based on the system and synergetic approaches to the analysis of social management processes. Such approaches allow considering all the modern practices of management, on the one hand, and keeping the integrity of the social environment of the entity and introducing the necessary changes, ensuring a new quality of the system of social relations, on the other hand.
Results
But in the course of development of an adaptive application model of the identified provisions and the principles of the synergetic management, an important methodological problem came to light. Considering that their own methodology of the synergetic management theory has not been created yet, in a practical part of its application it is possible to use the closest related "method of the organizational development" (Pugacheva, Solovyenko, 1999).The method of the organizational development represents the scientific theory and methodology, which is based on the combination of behavioural approach and humanistic principles the ultimate goal of which is a systematic change of operation of an organization due to the directed external interference, for the solution of tasks on the performance improvement (Spivak, 2000). The part of the ideas of the organizational development method was taken from the theory of the human relations of D. McGregor who had suggested considering the organization as a component of two systems – technological and social ones. His " Theory X" and " Theory Y", and later "Theory Z" by W. Ouchi which reflected the Japanese management model showed the influence of the social communications between human relations and the management system on the labor productivity.
Outsourcing became the other key idea of that method for the creation of a steady organization. A big role was played by the works of K. Lewin, a social psychologist, one of the original authors who offered the laboratory training, polls, observation, feedback and the research through the action in relation to the creation (restructuring) of the industrial body in the development of HR management (Lewin, 2000).
All the specified aspects can be used when modeling a management system on the basis of the synergetics’ principles as the synergetic effects of the organizational environment can be provided as a complex training system of the organization from the outside directed to the management quality improvement in the conditions of a constantly changing environment (Bennis, 2000). For the development of the organization resistance to the changes of the external environment, the intervention shall affect, first of all, not the production structure and technology, but the culture of the organization as a system of ethical values, beliefs and standards of the employees’ behavior.
It corresponds to the methodological basis of this research and the developed system of the synergetic modeling where the entity is a management object of a complex open social system. The provision on the self-development of the organization is also advanced as a basis when a need of the intervention about which the organizational development method supporters speak, is minimal.
The model of the procedural consultation of organization managers on the purpose of forming the directions of the organization development worked out by E. Shein can be used in the implementation process of the synergetic management. The offered procedural consultation includes the diagnostics of a problem, the goal setting and the tasks, the picture of the "present" and "future" of the organization, the development of a number of methods, individual for each organization, and the methods of the goal achievement, the introduction and the tracing of the results. At the same time E. Shein differentiated between the process of consultation and a "purchased model of consultation" when the manager would buy information offered by the consultant (Shein, 2002).
The control of the external environment factors’ role specified by R. Beckhard needs to be performed by means of the outsourced consultants in the organization development (Beckhard, Pritchard, 1967).
In terms of foreshortening of the defined tasks of paragraph 13 the fundamental principles of the implementation of the organizational development advanced in F. Hughes’ work, who divided them into 4 major groups are of great interest (Mazur, Shapiro, 2000). Such principles are offered also for the use in the synergetic approach implementation with a small correction. For a comparison of the applicability of the postulates of the organizational development to the synergetic approach implementation within the approbation of the author's concept let us consider them in more detail.
Group I: principles of the organization employees’ development:
1) The organization staff has a need for a self-improvement and a personal growth. This requirement can be most effectively satisfied with two methods: the support from the organization management or the competition ("to challenge");
2) Abilities of the most part of the employees are used by the organization not to a full extent, they could have made more profit if they were entrusted with more responsibility and were given more opportunities to show themselves;
3) Every person possesses the emotional sphere influencing their likes and dislikes including their contacts with other employees. As a rule, in the formal organization these tendencies are not considered that reduces the satisfaction extent from the work and the quality of work;
4) Human feelings are important and open additional opportunities of managing people, forming a command spirit, setting and solving complex tasks, improving the labor life quality and the job satisfaction.
Group II: principles of the team development:
5) Initially the labor team itself is neutral. The neutrality is broken inside the informal groups depending on the nature and type, can bring both the profit to the organizations, increasing efficiency of work due to mutual cooperation, and harm;
6) The performance of the labor team can be significantly increased at the expense of the satisfaction of the individual needs of the team members and forming the favorable interpersonal relations on the basis of mutual cooperation;
7) The effectiveness of the team work can be increased due to the restriction of the formal leader’ managing function and granting more independence to the team.
Group III: principles of the organization development in general:
8) The organization represents a complex system in which the change of one of the elements (subsystems) inevitably attracts the change of the other elements;
9) Most of the organizations create an unfriendly environment for interpersonal interactions in which the level of mutual cooperation and support of the workers is much lower than a desired one;
10) The organizational structure isn’t static, it can be changed on the purpose of meeting of the individual, collective or production needs.
Group IV: principles of interaction.
11) A frequent application of a stressful strategy "victory or defeat" significantly reduces the quality and the effective performance of both the organizations in general, and the certain employees, it ceases being a significant incentive very quickly;
12) The majority of interpersonal conflicts between the employees is caused by the shortcomings of the organizational structure, but not by the qualities of direct participants of the conflict;
13) The resolution of interpersonal conflicts in the organization should not take the path of "punishment" or "concealment", but it should be an open discussion of the reasons and problems which caused them. It gives rise both to the personal growth of the employees, and to the efficiency growth of the organization.
Thus, so far it is possible to present the modeling of the management systems based on the synergetic principles, using the organizational development method provisions and the practice of the consultative impact. Such modeling includes the determination of the purposes, tasks, impact stages on the management objects and also the results’ tracing (feedback). The basis of the organizational development model through the procedural and consulting impact
(which is often called by the term "intervention"-invasion in literature) rests on three main postulates.
1. The choice of technology and methods of the consultants’ intervention into the organizational development fully depends on the search and diagnostics of the organizational problems determining the direction and the depth of the necessary correction.
2. Heads of the organizations who are involved both in diagnostics of the organizational problems and in planning of correcting impacts should be widely attracted. Openness, clearness, availability of the consultants’ actions of the organizational development should be attracted.
3. The consultation should include not only and not just the changes in the organization, but the training in these technologies among the staff members being able to maintain the development directions achieved and promote it actively in the future.
It is important that the method of the organization development should be aimed at the research of the problems of the organization by the consultants through a set of special practical methods and techniques (observation, poll, an experiment, a laboratory training), and should include participation in the diagnostics and the problem resolution, both on the part of the administration of the entity, and on the part of its employees.
Within the implementation of the socially oriented management it is especially important, as such technologies allow managing the social environment, obtaining the implementation of the main values of the concept.
As it is seen from the research, the method of the organizational development is really the closest to the synergetic approach of the creation of organizations, and has the expressed socially oriented focus. Therefore, in the solution of the problems of management systems’ transformation by the entities (on the example of oil and gas industry) the same methods of active problems’ identification and the innovations’ implementation can be utilized.
Nevertheless, we will focus our attention on the distinctions. The comparative analysis of the synergetic approach and the method of the organization development is given in table 1.
| No. | Index | Method of organizational development | Synergy approach | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 1. | Notion of the organization | Complicated open system | Complicated open dissipative spontaneous system | |||
| 2. | Structure of the organization | It consists of the social, technological individual and psychological subsystems which mutually influence each other | It consists of the social and technological subsystems which mutually influence each other | |||
| 3. | Attitude to the external factors | It affects the system, but has no decisive influence (the theory of organizational humanity as constituting theories the organizational development denies such an impact, believing that interpersonal interactions are the cornerstone of changes) | It is a source of self-development and self-organization of the system, forming the external conditions of the crisis leading to the points of the bifurcation development | |||
| 4. | Function of the management system | In contact with a facilitator (a consultant for the development) it is supposed to provide conditions for the formation of such interpersonal relations among the workers of the team that would provide high-quality organization development | It impacts on the organization which can enter as a resonance with the self- development direction strengthening it over and over again, and at the same time in a dissonance, becoming a source of instability of the system and a possible crisis | |||
| 5. | Interpersonal interaction role | The quality of interpersonal, group | Interpersonal interaction is a part of more complex structures (group, team), the effective interactions can give a synergetic effect (A multiple excess of the algebraic amount of the efforts), the inefficient interactions, on the contrary, are the reason of instability of the system | |||
| relations is a basis of organizational development and a source of the increasing efficiency of the organization | ||||||
| 6. | Development source | The impact of a consultant facilitator who can be both external and internal in relation to the organization. Out of the purposeful impact there is no development | It is inside the organization, it represents the amount of the individuals’ interactions of formal and informal structures in the organization, and also the organization and factors of the external environment | |||
The main link uniting these approaches is the social orientation of the management: the source of changes of the organization (including a directed change that is the development) is the employees who interact among themselves, with the administration of the entity and with the external environment. Nevertheless, there are also essential differences (table 1).
An essential advantage of the method of the organization development is well thought over and approved of by the methodology of the structurally functional changes of the organization. The method of the organization development had widely been adopted originally in the USA and then it spread around the world. Now it is applied not only in commercial enterprises, but also in state organizations, public and international structures, etc. At the same time the method of the organization development won the popularity in many industries, including chemical, oil and gas, automotive, defense industries. Theoretical developments of the theory of the organization development are actively applied in the health care, education, social sphere, at the level of state bodies and local self-government, etc.
In the course of modeling the majority of acceptances and methods of the organizational development were adapted for the use of the synergetic approach. The basic provisions of the management system modeling based on the synergy approach, are the following:
1. Organization is a complex open system.
2. Organization is capable of developing.
In modeling the implementation process the main attention is paid to the source of changes and development, the external factor or the external environment factors are not used here, here we speak about the forming of such a social environment which stimulates the development of the organization and the subsystems constituting it. Critical changes of the external and internal factors to the bifurcation points of the development are the main sources of the social environment development of the entity.
Having analysed the current state of the management system of the entities of oil and gas industry and the main problems concerning social conditions of their functioning we come to a conclusion that the solution of many contradictions is possible in case of a special modeling of management systems. The modeling of management systems within the considered synergetic approach and the socially oriented management requires the development of a special concept allowing to solve the specified problems of management of the industry, having realized the model of the synergetic management of the oil and gas entities.
Within such offer the adapted concept of the synergetic socially oriented management which represents the management of oil and gas industry entities as the system of interconnected ideas of this or that event (in the study it is about the purposes, tasks, principles, methods of management of oil and gas entities (Latin conception is a frame of reference, the main idea) has been developed (Social research: methods, technique and statistics: The dictionary reference, 1991), in the foreshortening of the principles of synergetics and socially directed values.
The concept presented is based on the principles and provisions of the socially oriented management, the developed assessment criteria of the synergetic effects, properties of the management system and organizational environment, methods and the synergetic management techniques of the social relations system.
The concept provided is necessary and urgent for modern entities of the industrial type, as represents, despite the difference in the professional specialization, a complete production cycle: from the geological exploration to the sale of oil products to the consumers.
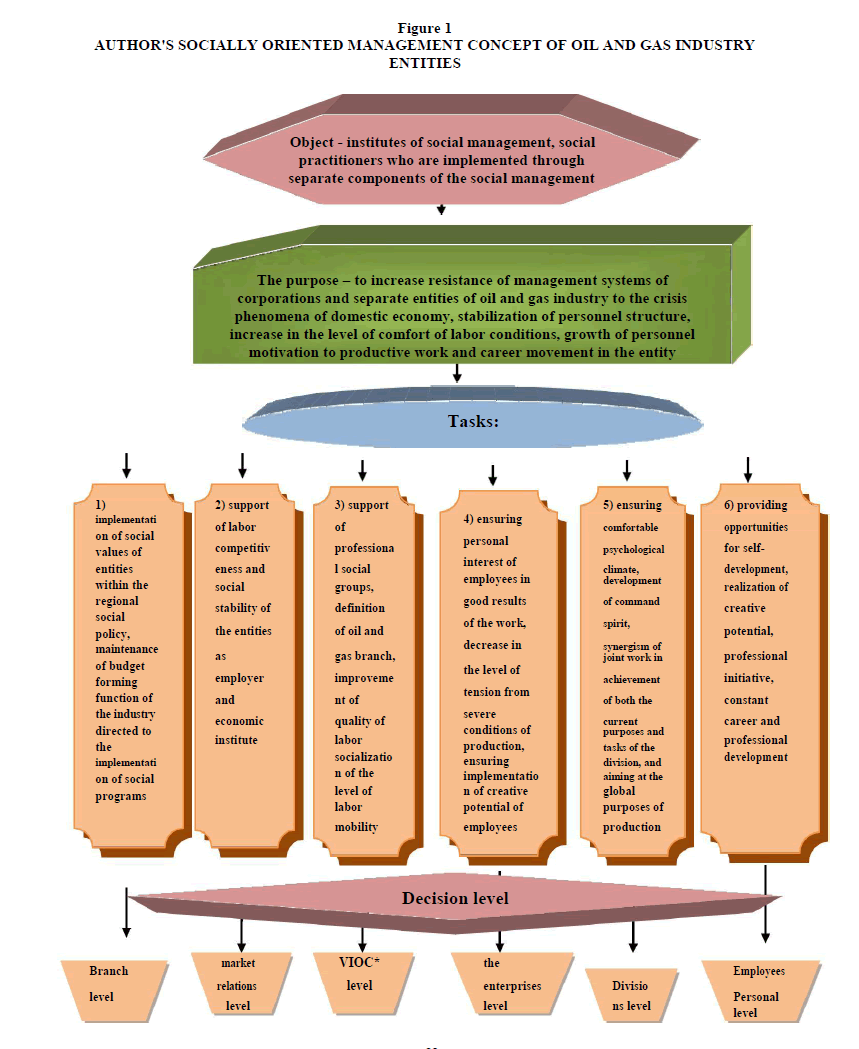
Within the provided socially oriented concept based on the synergetic approach, the object is the social management practice implemented through the separate components at the entities of oil and gas industry. The object was determined proceeding from the tasks and purpose of this research implemented by means of studying the organization environment of the entities of oil and gas complex in the conditions of transformation. The subject, action of the concept, is also determined in the framework of this study which consisted of social aspects of the implementation of the socially oriented management, and characterized by the following impact aspects:
1. The political, social and economic, administrative, legal, market relations which are formed among the public authorities, local administrations, market environment (competitors, suppliers, contractors, customers) and the systems of the social management at the entities of oil and gas industry;
2. The social and economic, administrative and legal, social and psychological relations developing among various levels of management systems of the studied group of companies;
3. The social and economic, administrative and legal, employment, disciplinary, social and psychological relations developing among the management systems of the entities and the non-management employees.
Discussion
The purpose of the study assumes the development of the sociological concept of the socially oriented management on the basis of the synergetic approach. The offered concept is designed to guarantee the practical results of the synergetic approach application, solving the contradictions existing at the moment in the socially managerial sphere, and proceeding from it, the main objective of the implementation of the author's concept is:
1. The increase of the management systems’ resistance of the entities of oil and gas industry to the crisis phenomena of the domestic social and economic sphere.
2. The stabilization of the professional structure of the entities.
3. The increase of the comfort level of labor conditions.
4. The comfort growth of the employees motivation of the productive work and the career promotion in the entity
The comfort growth of the employee’s motivation of the productive work and the career promotion in the entity.
The purpose of the concept determines the levels of the solvable tasks which are determined proceeding from the current state and the problems of the management sphere of oil and gas industry:
1. On the level of the industry it is the strengthening of the social value of the entities within the regional social policy, forming the special social programs of support and development of the industrial professional teams;
2. On the fuel and energy complex market level it is the creation of social conditions of the labor competitiveness support of the entities as that of the employer in the constantly changing market conditions.
3. On the level of the vertically integrated oil companies (VIOC) it is the support of professional social groups by means of the determination of oil and gas industry workers’ steady social status, the labor quality improvement, labor quality socialization and the professional competencies, monitoring of the labor mobility;
4. On the level of the entities it is ensuring personal interest of the employees in the positive results of the work, the level of tension decrease from severe production conditions, ensuring the implementation of the creative potential of the employees.
5. On the level of divisions it is ensuring a comfortable psychological climate, the development of the command spirit, synergism of the joint work in the achievement of both the current purposes and division tasks, and aiming at the global purposes of the production.
6. On the personal level of the employees it is providing opportunities for the self- development, implementation of the creative potential, professional initiative, fixed career and professional development.
The schematically offered management concept of the entities of oil and gas industry can be presented as follows (Fig. 1)
* VIOC-vertically-integrated oil company
The tasks of the urgent difficulties of the implementation of oil and gas industry management of the entities which arose in those conditions, contradictions of the entities’ functioning as the key social objects of the industrial sphere have been defined. The solution of these tasks is fully possible only within the socially oriented synergetic approach towards the creation of management systems.
The offered concept reflects multilevel management systems of oil and gas industry entities including not only a sample organizational structure of the domestic vertically integrated oil companies, but also the state regulation and market environment. At the same time the task of management systems on the market and state level is, first of all, the stability development of the organization in the external environment, and on the production level is the forming of self-developing and self-trained production mechanism.
Conclusion
Summing up the results, it is important to note that at this stage it is necessary to study the sales terms of the socially oriented management concept in oil and gas complex entities that is specified by the transformation of the modern Russian society. Within the sociological science the problem of the application possibility of the synergetic approach to the management as a methodological basis of modeling of a socially oriented management system becomes aggravated (Gaisina, Mikhaylovskaya, Khairullina, Ustinova, Shakirova, 2015; Gareyev, Kostyleva, 2016; Ustinova, Rudov, Kostyleva, Grogulenko, Kulishova, 2016). From the point of view of the synergy presentation of the organizational environment, the role of the management system changes. A lot of modern theories including a method of the organization development, present the manager as the assistant and colleague of the consultant keeping the organization development within the provided concept the role of the manager comes down to the directing impact of unstable fluctuations of the organization, ability of forecasting crises, and the directed point impact at the moments of bifurcations. Now, in the sociology of management there are no unambiguous relations and complex reasons for the synergetic methods’ use. The paradigm shift of the management determines the change of forms and managerial impact methods, on the one hand, strengthen the social orientation in the management, and on the other hand, the compliance to the existing organizational environment of industrial enterprises is required. The synergy approach which allows realizing the natural social potential of organizational teams meets such requirements, without breaking the integrity of the entity.
References
- Barbakov, O.M. & Bar, M.M. (2015). Marketing communication in an industrial environment. Problems of forming of a common economic space and social development of the CIS countries. Materials of the international scientific and practical conference, 45-53.
- Barbakov, O.M. & Romanovsky, D.V. (2014). Anti -recessionary policy on a small businesses. Problems of forming of a common economic space and social development of the CIS countries. Materials of the international scientific and practical conference, 266-269.
- Beckhard, R. & Pritchard, V. (1992). Change of essence: Art of creation and promotion of change of the environment in the organizations (Jossey-bass non-commercial sect). New York.
- Belonozhko, M.L. & Scythian, A.L. (2011). The organizational basis for functioning of the government at the regional level. Tyumen: TSOGU.
- Belonozhko, M.L. & Silin, A.N. (2014). Social research in the decision making mechanism. Tyumen: TSOGU.
- Bennis, W. (2000). Leadership of Change. Breaking the Code of Change. Harvard Business School Press, Boston.
- Gaisina, L.M., Gareyev, E.S., Valitova, N.E., Khairullina, N.G. & Ustinova, O.V. (2015). Corporate staff identity as a factor of increasing labor productivity. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(5), 274-285.
- Gaisina, L.M., Mikhaylovskaya, I.M., Khairullina, N.G., Ustinova, O.V. & Shakirova, E.V. (2015). The role of the media in the spiritual and moral evolution of the society. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences.6(5), 93-101.
- Gareyev, E.S. & Kostyleva, E.G. (2016). Middle class as an element of stability of social hierarchy of the Russian society. Economy and management: Scientifically - the practical magazine, 3(131), 73-77.
- Gaisina, L.M., Bakhtizin, R.N., Mikhaylovskaya, I.M., Khayrullina, N.G. & Belonozhko, M.L. (2015). Social technologies as an instrument for the modernization of the social space in the social and labor sphere.
- Golembiewski, R.?. & Munzenrieder R.F. (1988). Phases of Burnout: Developments in the Concepts and Applications. New York.
- Kozlova, E.V. (2012). Implementation of the innovative strategic policy in the industrial enterprises of Russia: Conditions and prospects. Bulletin of the Saratov state social and economic university, 2, 103-106.
- Lewin, K. (2000). The theory of the field in social sciences. SPb.: "Sensor".
- Mazur, I.I. & Shapiro V.D. (2000). Restructuring of the entities and companies. Moscow: The higher school.
- Porras, J. (2007). A Success constructed forever: How to give a sense to the existence. Moscow: CJSC Olympe business.
- Pugacheva, E.G. & Solovyenko, K.N. (1999). The higher school: Some problems of self-organization. Sotsis, 11, 99-101.
- Shein, E.H. (2002). Organization of the culture and leadership: the monograph. SPB: St. Petersburg.
- Spivak, V.A. (2000). Organizational behavior and personnel management. SPB: St. Petersburg.
- Ustinova, O.V., Rudov, S.V., Kostyleva, E.G., Grogulenko, N.V. & Kulishova, N.D. (2016). The processes of globalization in the Russian views. The Man in India, 96(7), 2165-2177.
- Valitova, N.E., Gareyev, E.S., Grogulenko, N.V. & Kostyleva, E.G. (2016). Management of the international relations in the polyethnic regions of Russia (on the example of the Republic of Bashkortostan). Materials of the international scientific conferences, 28-31.
- Von Bertalanffy, (1973). History and the status of the general theory of systems. In the book: System researches.Methodological problems: Annual. Moscow: Nauka.