Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 1
Role of Knowledge Processes as a Mediator Variable in Relationship between Strategic Management of Human Resources and Achieving Competitive Advantage in Banks Operating in Jordan
Hazem Khaled Shehadeh, Zarqa University
Maan Hussein Mansour, Zarqa University
Abstract
This research is concerned with studying direct and indirect relationship between strategic management of human resources and achieving competitive advantage through knowledge processes as a mediator variable in banks operating in Jordan. To achieve this, a sample of 348 managers, assistant managers, heads of departments and their assistants in significant departments, which have direct relation with this study. Study results showed that there is a significant relationship between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan and achieving competitive advantage (lowest cost, quality, creativity). In addition, the existence of a significant relationship between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan in question and knowledge processes (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application). The existence of a significant relationship between practicing knowledge processes and achieving competitive advantage (lowest cost, quality, creativity)as well as the existence of a significant indirect relationship between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan in question and achieving competitive advantage through knowledge processes as a mediator variable
Keywords
Strategic Management of Human Resources, Knowledge Processes, Competitive Advantage.
Introduction
Human resources management in modern times is considered one of the most important and most sensitive organizational functions in the organization. As it deals with human element, in which organizations can achieve competitive advantages. It is the most expensive resource needed by leadership and management in all its fields and work stages. Furthermore, anyone is concerned about the success of business organizations find that their success lies neither in their use of advanced technology nor in diversifying their funding sources. Business organizations are not just a set of buildings or policies and laws rather they are a group of individuals who share common relationships and interact with each other to perform main tasks and functions aid them in achieving the organization's goals and their objectives. Thus, the human element is the basic basis on which organizational structure is based, and affects and is influenced by a variety of variables in organization's environment (Daft, 2010).
The difference among business organizations must be attributed to different performance among individuals. Technology, markets and products can bring competitiveness to organizations, but human resources sustain them (Caliskan, 2010).
Strategic management of human resources represents an extension of concepts and principles of human capital theory, which emphasizes that individuals are an asset of the organization's assets and that individual differences among them require the organization to formulate a strategy for human resources with clear goals and policies that raise human's element efficiency, improving productivity and supporting the organization's capability to achieve competitive advantage through continuous alignment between human resources strategy, organization's overall strategy and its competitive strategies as well as coordination and internal integration of human resources management practices (Gilani et al., 2012).
In addition, numerous studies have also confirmed that human resources are the most important elements of knowledge creation, its participation and application, whereas knowledge is established and practiced through human resources in the organization and it appears in the production and distinguished performance of the organization. The human resource is the basic generator of knowledge and the main part through which the organization moves from individual knowledge to organizational knowledge, thus individuals are knowledge-makers who generate knowledge as part of their work; they are the strength of intangible assets, which are a source of success and competitive growth of organization.
The practices of the strategy of recruiting human resources with knowledge, expertise and abilities to the necessary level, this leads to creating new knowledge for the organization. These individuals are easily integrated into the organization, have the ability to use and apply knowledge quickly and efficiently. Additionally the strategy of training and learning is the most important tools of change behaviors of individuals, and then generating knowledge and sharing it as well as performance appraisal, reward and compensation strategies represent an incentive for increased interest in creating, sharing and applying knowledge (Chen & Huang, 2009)
Based on above, the research aims at confirming nature of the relationship between strategic management of human resources and achieving competitive advantage. In addition, examining the nature of the relationship between strategic management of human resources and knowledge management processes and studying role of knowledge processes as a mediator variable in relationship between strategic management of human resources as well as achieving competitive advantage in banks operating in Jordan.
Theoretical Framework
Strategic Management of Human Resources
Strategic management serves as an input to strategic thinking at the organization level, not limited to senior management. Strategic direction should extend to include all axes of each of entity of organization's entities. One of these axes is human resources, which focuses on finding the best ways to prepare, create and develop workforce structure and integrating it into the appropriate career tracks for them. In addition to managing human resources within these tracks in a way that ultimately achieves raising performance level of human element, increasing organization's competitive performance.
Strategic management is defined as the process by which human resources management practices are connected to organization's strategic objectives for the purposes of enhancing performance level and developing organizational culture supporting innovation and creativity. (Dessler, 2005) and it is described by (Mathis & Jackson, 2011) as the best use of human resources that helps organization to gain and maintain competitive advantage.
Strategic management of human resources includes an active study of human resources, analyzing and linking it to organization's goals and strategies, so that human element becomes one of the weapons to achieve competitive advantage and improving organization's market conditions and its business results.
It should be noted that the process of preparing general strategy of organization is carried out at the level of organization's senior management or through a specialized team under supervision of senior management.
Moreover, with participation of relevant parties at each stage of strategy preparation, which means that the human resources management is present at each stage of general strategy preparation (Wheelen & Hunger, 2012).
(Sani, 2012) emphasized that we should view at human resource management on a strategic basis and on the basis of systemic concept of human resource management functions, which consider human resource management functions as interactive and related elements that influence and are influenced by surrounding contexts around them. This happens through two levels of compatibility: horizontal compatibility achieving integration among special strategies of human resources management and vertical compatibility that requires achieving integration of human resource strategies and organization's overall strategy.
Functional Strategies of Human Resources Management
Human resources strategies include designing and implementing a set of administrative activities that are linked specifically to organization's needs of human resources, developing its abilities and promoting its efficiency. Furthermore, with a view of maximum benefiting from its efforts and thoughts to achieve organization's strategic objectives and in line with study objectives things that have the most influence in achieving competitive advantage will be presented, they are:
Strategy of Human Resources Formation
It is considered the first step in forming human resources structure and it includes:
Strategy of analyzing and designing functions
It is a process under which, there is information collection and factual facts about the nature of organization's functions. In addition, analyzing, summarizing and presenting them in a form of written lists, showing their tasks, responsibilities and powers. Through psychological, physical and social environment in which they are performed as well as potential risks accompanying their performance and then knowing and identifying necessary human skills and abilities required to perform them (Akeely et al., 2005).
Functions design method has to be linked to the organization's strategy, as it may require new or different tasks or different approaches to carry out same tasks. Organization's strategy effects on designing and determining tasks of various functions/jobs within organization. Additionally, the way in which functions are designed can affect organization's ability to accomplish competitive advantage. If the organization wants to follow a cost-effective strategy, it has to organize its functions in a simple and repetitive manner. This allows organization to hire employees do not have highly skills and easily train them. On the other hand, if the organization wants to compete through price, it may resort to regulate its production operations according to work teams (El-Morsi & Al-Sabbagh, 2011).
Human resources planning strategy
It is considered of the important strategic functions as it is based on other functions of human resources management. It is related to identifying actual human resource needs of organization in terms of quantity, quality and in a manner in agreement with the mission and organization's strategic objectives (DeCenzo & Robbins, 2010).
In addition, human resources planning at organizational level needs (Abu Sheikha, 2018):
1. Special data on the current situation that provide sufficient information on organization's employees, such as age, family status, scientific qualifications, practical experiences and special abilities and skills.
2. Performance rates for various functions in the organization.
3. Objective and fair measure of total productivity and partial productivity of production elements.
4. Dynamic system for function/job classification on objective basis.
Employment Strategy
Recruitment/employment process is considered a natural extension for human resources planning and a basic tool by which people can be used, chosen and differentiation is made among them, as they can be the most suited to current and future employment requirements. In addition, it is way that enables the organization to achieve competitive advantage exemplified by the quality of human resources that are difficult to be imitated by competitors (Al-Dmour, 2008).
The source of individuals is internally, which means to looking for people who already work in the organization (internal channels), or it may be externally through external labor market (external channels) (Davies et al., 2007).
Training and Development Strategy
Training strategy is regarded as a complementary function to the recruitment function. It is not enough for an organization to attract individuals, but it is essential to this function to be followed by preparing training programs that assist in developing employees' knowledge and skills as well as improving their abilities to perform the tasks assigned to them (Abbas, 2007) .
Training process is a continuous and integrated process where success at any stage depends on correct performance of previous stages. (Armstrong, 2012) adds that organizations in business environment face numerous challenges such as quality, technology and demographic shifts. In order for the organization to meet these challenges, it has to provide keys to dealing with them; the most important of these is the strategy of training and continuous development and in a way that is in harmony with organization's strategy (Al-Zahrani, 2012).
Strategy of Appraising Human Resources Performance
Performance is one of the important outcomes that connect individuals, jobs, organization and environment. Performance appraisal is a tool through which business quality is measured and how it is developed. In addition, performance appraisal strategy is considered one of the basic steps in production and operations system derived from organization’s strategic plans and objectives to ensure that their productivity meets acceptable standards (Poister & Streib, 2005).
Compensations and Rewards Strategy
Economic nature of the contract between the employee and the organization is that the worker commits to work and production in accordance with terms of agreed upon contract. At the same time, the organization is obliged to compensate individual for the work he provides, whether this compensation is in the form of wages, salaries and incentives. This is called direct compensation as it is connected with work and is paid on individual’s performance for his work, or it is in direct such as moral rewards of the individual, like social, health benefits and participation in decision-making. Thus, this leads to increased motivation of the individual, so this is reflected on improving his performance and increasing his productivity. In addition, it represents a major source for achieving organization’s competitive advantage (Shammot, 2014).
Competitive Advantage
The topic of competitive advantage has taken space and place in domains, strategic management and business economics, as competitive advantage is an important strategic element that helps in capturing opportunities. It offers a substantial and real opportunity for the organization to achieve sustained profitability compared to its competitors (Al-Yousfi, 2013). There is no specific concept of competitive advantage due to large number of elements associated with this concept. Thus, competitive advantage is defined as a situation that brings organizations more than a competitive position, that is, the organization's access to an advanced competitive position in business environment (Liu, 2008). Otherwise, the ability of the organization to perform its work in a way that is difficult for its competitors to imitate (Kotler & Armstrong, 2012).
Elements of competitive advantage are represented in translating customers’ needs and desires into specific indications in product or service, which contribute to satisfying their needs and desires in better manner than what competitors offer. Researchers' views differed about classification of competitive advantage’s elements, as illustrated in the following Table 1.
| Table 1 Views Of Researchers On Competitive Advantage |
|||||||||
| Researcher | Organization Reputation | Alliances | Growth | Creativity | Flexibility | Reliability | Focus | Quality | Low Cost |
| Porter,1979 | * | * | * | ||||||
| Hayes&Nheel Wright,1984 |
* | * | * | * | * | ||||
| Schuler et al,1987 | * | * | * | ||||||
| Wisemman,1989 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| Hicks,1993 | * | * | * | * | |||||
| Mintzberg,1998 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| Lynch,2000 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| Total | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
| Percentage | 28% | 14% | 28% | 86% | 14% | 28% | 42% | 100% | 86% |
Note: *indicates the researcher examined the dimensions of competitive advantage.
Results show that there are three elements have received the highest percentage of researchers’ interest: quality advantage 100% and lowest cost advantage 86% creativity advantage 86%, where they are the elements adopted in current study.
Example: Porter, 1979 examined Low Cost, quality, and focus as competitive advantages dimensions. Source: Alsakarnah, 2005.
Knowledge Processes
Through reviewing literature related to knowledge management and its processes, it is evident that there is diversity of researchers' views on identifying knowledge processes and their names. Some researchers identified knowledge processes in knowledge generation, knowledge transfer, sharing in it and organizational learning (Hijazi, 2005). (Marquardt, 2002) proposed knowledge processes by acquisition, generation, storage and extracting information, analyzing and transferring it. (Chen, 2007) defined it as response to knowledge, knowledge acquisition and disseminating, using it. For research purposes, the researchers agreed on the dimensions cited by Hijazi (2005) and Chen (2007) which is knowledge generation, knowledge sharing and knowledge application.
Knowledge generation
It means creating knowledge, which refers to the organization's ability to develop new, creative and useful ideas. Moreover, to make these ideas reach to creativity level, it must be able to solve problems facing the organization more efficiently and lead to innovations in the market as well as it to enable the organization to translate new ideas into goods, services and working methods (Bhatt, 2001).
Knowledge sharing
It requires existence of context, field and environment that provide possibility of interaction among individuals within organization, whether they are areas that allow direct and personal contact among individuals face-to-face or virtual. This enables individuals to interact and exchange knowledge using technology of communications such as e-mail and electronic meetings or building common mindset areas that facilitates and stimulates knowledge exchanging process among organization's members (Bhatt, 2001).
Knowledge application
It refers to actual use of knowledge, which is generated or acquired in an effective method that ensures achieving organizational objectives efficiently and effectively. This is by making use of them in problem solving, capturing opportunity and decision-making. After that translating them into new goods, services and new processes (Emadzade et al., 2012).
Literature Review
Inkinen et al. (2015) study concentrate on the conscious and systematic managerial activities for dealing with knowledge in firms (i.e. Knowledge Management (KM) practices), which aim at innovation performance improvements through proactive management of knowledge assets. The study explores the impact that KM practices have on innovation performance.
Also the authors provide empirical evidence on how various KM practices influence innovation performance in Finland. The authors find that firms are capable of supporting innovation performance through strategic management of knowledge and competence, knowledge-based compensation practices, and information technology practices. The authors also point out that some of the studied KM practices are not directly associated with innovation performance.
Sáenz et al., 2017 study analyzes the mediating role of Organizational Learning (OL) in the relationship between knowledge-based HRM practices and innovation in a set of Spanish firms with more than 100 employees. A structured questionnaire was used to gather information about the relevant variables under study and Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) based on Partial Least Squares (PLS) was then used to test the hypotheses put forward by the research .the findings demonstrate the relevance of knowledge-based HRM practices as predictors of innovation performance, and the role of organizational learning as a mediating factor between HRM and innovation. In particular, OL mediates this relationship in the case of training and development practices (partial mediation) and performance assessment (total mediation). Overall, the results extend existing understanding of the interrelationships between HRM, learning, and innovation in organizations and thereby contribute to the knowledge-based view of the firm as well as discussions on strategic HRM and innovation management
Al-lafi, 2018 study aimed at identifying strategic role of human resources and its impact on creativity among employees of Zain Telecommunications Company in Jordan and identifying differences in innovation levels among these employees. It showed there is an average level of exercising strategic role of human resources. In addition, it showed that there is an average level creativity among employees of Zain Telecommunications Company. Additionally, the study also found that there is a statistically significant impact of the strategic role of human resources (planning, recruitment, selection and employing) on creativity of employees of Zain Company operating in Jordan. The study recommended focusing on the role of strategic human resources in the following areas: (human resources planning, recruiting human resources, selection and appointment of human resources). Due to its clear impact in promoting creativity among employees, besides to the necessity of involving employees at all management levels in necessary improvements to be made as well as introducing them to human resources management systems.
Al-Awlaki, 2018 sought to analyze relationship between human resources management strategies and developing organizational creativity through knowledge processes as a mediator variable in Yemeni Banks. The results of the study showed a significant relationship between practicing strategic management of human resources and developing organizational creativity as a goal to reach competitive advantage of commercial banks. Besides, there is existence of significant relationship between practicing strategic management of human resources and developing organizational innovation through generating, acquiring, sharing and applying processes of knowledge. Al-Shawbkeh, 2016 showed impact of applying human resources strategy in achieving competitive advantage through a survey of the executive directors’ views, middle management managers and heads of human resources departments in Jordanian telecommunications sector. It concluded that strategic management practice a significant impact in achieving competitive advantage (cost reduction, quality and increasing flexibility and innovation) for telecommunications companies in Jordan. Al-Kader’s study (Al-Kader, 2014) concluded that applying strategic management of human resources contributes to increasing quality ratios of performance, organizational effectiveness and to facing sharp competition, in addition to its contribution in reducing productivity operations’ costs in cable’s industry establishment by allocating budgets for training and development consistent with organization’s overall strategy.
On the same topic, (Al-Maqadma, 2013) studied the role of recruiting human competencies and enhancing knowledge processes in work environment as a strategic dimension to human resources management and its impact on competitive advantage. It concluded that there is a strong correlation between availability of human competencies, achieving competitive advantage and knowledge processes and achieving competitive advantage. It recommended the need to adopt strategic method in human resources management for the purposes of that the organization to maintain its competitive advantage.
While (Haque and Shamyla, 2012) concluded that knowledge processes (knowledge generation and knowledge sharing) have a positive impact on improving performance of Pakistani Banks in terms of raising their creativity averages and reducing costs associated with operating operations in banks in question. (Bhandari, 2016) study aimed at clarifying role of linking human resources strategy to organization’s general strategy. It concluded that integration process leads to increasing organization’s competitiveness ability and avoiding competitors' threats in terms of increasing quality levels, innovation and creativity averages and reducing costs, which achieves sustainable compitive advantage.
(Mainali et al., 2017) study sought to identify the role of knowledge processes as a source of competitive advantage in business organizations and concluded that processes of knowledge generation, acquisition and application significantly contribute in enhancing comparative advantage through organization’s adoption of strategic method in knowledge management continuously and in regular basis. Al-Maaitah et al., 2013 study showed that human resources management according to strategic method, which focuses on recruiting, developing and maintaining gifted individuals, contributes significantly in achieving competitive advantage for the (15) companies that have been studied, which are listed in Amman Stock Exchange. It also concluded that knowledge processes contributes significantly in achieving competitive advantage for companies in question. (Ramadan, 2012) study also emphasized that organizations' focus on training and recruitment individuals with high capabilities and potentials and enhancing knowledge processes contribute to increasing organization's competitive advantage in terms of improving its productivity and rising innovation and creativity rates.
Research Methodology
Research Problem
Globalization and Jordan's application of correction programs and economic transformation have a clear impact on banking sector. Removing all restrictions on foreign remittances and foreign investments led to creating new challenges involved in raising competitive level among local banks themselves and between them and foreign banks. Furthermore, Jordanian Competiveness Report (2007) pointed to the limitation of banks management's dealing with human resources as a strategic resource and the weakness experienced by banks in retaining knowledge assets represented by expertise and weakness of knowledge sharing processes among employees and benefiting from them. This is reflected in poor ability of banks to provide competitive services characterized by innovation, low price and high quality. Hence, this study aims at identifying role of knowledge processes as a mediator variable in relationship between strategic management of human resources and achieving competitive advantage in Jordanian commercial banks.
Research Significance
Theoretical significance of this study arises in dealing with strategic management of human resources as one of significance subjects in administrative field. Furthermore, it is a key factor in the success of organizations and their achievement of competitive advantage also its attempt to bring to light the compound relationship between strategic management of human resources and competitive advantage by mediating knowledge processes as a mediator variable. Thus, this contributes to the formulation of new strategies for Jordanian banks to support their abilities to achieve competitive advantage.
Research Hypotheses
H1: There is no statistically significant impact between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan in question and achieving competitive advantage taken in a comprehensive manner, with each dimension of competitive advantage dimensions (lowest cost advantage, quality advantage and creativity advantage) alone.
H2: There is no statistically significant impact between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan in question and knowledge management processes taken in a comprehensive manner, with each dimension of knowledge processes (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) alone.
H3: There is no statistically significant impact between knowledge processes in banks operating in Jordan in question and achieving competitive advantage taken in a comprehensive manner, with each dimension of competitive advantage dimensions (lowest cost advantage, quality advantage and creativity advantage) alone (lowest cost advantage, quality advantage, creativity advantage) alone.
H4: There is no statistically significant indirect impact between applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan in question and achieving competitive advantage taken in a comprehensive manner, with each dimension of competitive advantage dimensions (lowest cost advantage, quality advantage and creativity advantage) alone through knowledge processes as a mediator variable.
Population and Study Sample
There are 24 banks in Jordan, divided into commercial and Islamic banks. Banks vary in their investments' volume, number of employees and it branches in all over Jordan. The researchers targeted administrative staff of decision-makers in banks as they have ability, knowledge and access of bank's policies of strategies and other policies that represent bank leadership. The researchers targeted managers, assistant managers and heads of departments and their assistants in departments of interest and which are related directly to this study. Therefore, the study sample is a purposive sample. In order to ensure collecting information that represents banks operating in Jordan. The total of distributed questionnaires was (390). The number of questionnaires that the researcher was unable to retrieve was (23) and (19) were excluded after being proved invalid. The number of valid questionnaires for analysis reached (348) with a percentage (89%) of total questionnaires, so this represents the study sample.
Study Instrument
The study was based on a questionnaire as an instrument for collecting preliminary study data from individuals. Strategic management variables of human resources were measured and developed based on relevant studies such as (Chen & Huang, 2009), and (Abu Doleh & Al- Obaidat, 2007). This instrument has (32) variables to measure five dimensions of strategic management of human resources: strategic planning of human resources (7) variables, strategy of human resources formation (7), training and development strategy (6) compensations and rewards strategy (6) performance appraisal strategy (6). Concerning knowledge processes, they were measured based on an instrument developed by (Al-Turk, 2011). The instrument consisted of (18) variables for measuring dimensions of knowledge processes, namely knowledge generation (6) variables, knowledge sharing (6) variables and knowledge application (6) variables. Furthermore, dimensions of competitive advantage were measured by the instrument developed by (Ramadan, 2012) (Alma'aitah et al., 2013).
The researchers used a multi-item scale, based on five-point Likert scale, where 5 is strongly agree, while 1 is strongly disagree with a neutral score in the middle.
Results Of Statistical Analysis
This study dealt with the role of knowledge processes as a mediator variable in relationship between strategic management of human resources and achieving competitive advantage in Jordanian banks. A set of objectives were formulated to identify the relationship strength and its significance.
Therefore, the researchers used statistical analytical descriptive method, which was defined by Thoukan (2002) as a method that studies phenomenon in its dimensions as it exists in reality and it is expressed in qualitative and quantitative terms. Qualitative expression: It describes phenomenon and describes its properties, as mentioned in theoretical framework, where quantitative expression gives us a precise description of amount and size of phenomenon. Statistical analytical descriptive method also depends on information emanating from society in different ways, which is collected through a representative sample of study population. This method is considered the most appropriate one to achieve objectives of the current study with its dimensions, and describing its characteristics.
Instrument Validity
The researchers examined the face validity of study instrument by submitting the list to arbitration by academic professors and in business administration specialists in Jordanian universities. In addition, the list was reviewed by some officials in banks operating in Jordan for comment and reviewing. In light of comments of arbitrators and their proposals, the language wording of some items were modified, a number of items were deleted for their replication and their irrelevance, other items were added and similar items were integrated.
Reliability of Study Instrument
It is a degree, in which the measure is given approximate readings when applied each time. A fluctuating instrument that gives varied results when applied more than once is cause for concern and distrust in its results (Qahtani, 2015). If the questionnaire is applied several times to the same sample, to what extent the same results will be obtained. Internal reliability of the questionnaire was measured by using Cronbach's alpha coefficient. Cronbach's alpha coefficient is between (1) and (0). In general, if alpha is less than (0.4), reliability will be in low value. Items is considered with average stability if its value is (0.4-0.7), whereas reliability is considered high if its value is higher than 0.7 (Al-Qahtani, 2015). Table 2 shows the Cronbach's alpha coefficients for study variables.
| Table 2 shows Cronbach's alpha coefficients for study variables |
|
| Paragraphs | Cronbach’s alpha coefficient |
| Strategic Planning | 0.761 |
| Human Resources Formation | 0.849 |
| Strategy of training and development | 0.876 |
| Compensation and rewards strategy | 0.776 |
| Evaluation of human resources performance | 0.828 |
| Generating knowledge | 0.833 |
| Knowledge sharing | 0.872 |
| Application of knowledge | 0.781 |
| the quality | 0.773 |
| Creativity | 0.745 |
| Lower cost | 0.732 |
| Overall performance | 0.953 |
Questionnaire items have high reliability and this is deduced from Cronbach's alpha coefficients shown in Table 2, all of which exceeded minimum value of alpha Cronbach's coefficient (0.7). Items of training and development strategy achieved the highest reliability at (0.876). At the same time, items of lowest cost variable achieved the least reliability among items with a value of (0.732). As for the reliability of all questionnaire items, they have a high reliability with a value of (0.953).
Testing Study Hypotheses
H1: There is no statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among applying dimensions of strategic management of human resources (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) in banks operating in Jordan under study and achieving competitive advantage. To test the hypothesis, the researchers used multiple linear regression analysis and Table 3 shows regression test results.
The major hypothesis was tested at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) and the results were as follows:
Tabulated f-value was calculated to compare it with calculated f-value. It was found that calculated f-value was (236.181) was greater than its tabulated value (2.42). This was clear from that there was a statistically significant relationship among variables. Therefore, to check that there was statistically significant impact at the significance level adopted in this study, Table 3 shows that significance level of F was (0.000),which was less than the significance level adopted in this study and its value (0.05), so we reject the first null hypothesis and accept the alternative “There is statistically significant relationship at significance level of (α ≤ 0.05) among applying dimensions of strategic management of human resources (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) in banks operating in Jordan under study and achieving competitive advantage”. In order to confirm that there is a correlation relationship and its strength among independent variables and dependent variable, R-value was used. Table 3 showed that the value of correlation coefficient was=0.881, which indicates a strong positive relationship among independent variables combined (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) and dependent variable (competitive advantage) because it was more than (0.5).
| Table 3 Results of multiple linear regression analysis to test the first hypothesis |
||||||||
| Dependent Variable | Coefficient of Correlation R | R2 | F Calculated | Level of Significance | IV (Strategic Management) | B Value | T Value | Sig |
| Competitive Advantage | 0.881 | 0.775 | 236.181 | 0.000 | Strategic Planning | 0.127 | 4.251 | 0.000 |
| Human Resources formation | 0.074 | 2.015 | 0.045 | |||||
| Strategy of training and development | 0.208 | 6.443 | 0.000 | |||||
| Compensation and Rewards | 0.097 | 3.071 | 0.002 | |||||
| Evaluation of human resources performance | 0.383 | 11.432 | 0.000 | |||||
The results also showed an explanatory capacity of the independent variables combined (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) and their value was (77.5%). It was deducted from coefficient of determination value R2=0.746. And the Size effect of independent variables on the dependent variable is (2.94), which is classified as a significant effect; therefore independent variables have a significant impact on the dependent variable.
The table also showed that calculated t-value of independent variables (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) was respectively (3.071, 11.432, 6.443, 4.251, 2.015) with a statistically significant relationship at significance level (0.5) and calculated t-value was higher than its tabulated value (1.96). In addition, significance level of these variables was less than significance level adopted in this study, which is (0.05).
H2: There is no statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among applying dimensions of strategic management of human resources (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) in banks operating in Jordan under study and knowledge management processes in all and for every dimension of knowledge processes. To test the hypothesis, the researchers used multiple linear regression analysis and Table 4 shows regression test results..
The major hypothesis was tested at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) and the results were as follows:
Tabulated f-value was calculated to compare it with calculated f-value. It was found that calculated f-value was (165.381) which were greater than its tabulated value (2.42). This was clear from that there is a statistically significant relationship among variables.
Therefore, to check that there was statistically significant relationship at the significance level adopted in this study, Table 4 shows that significance level of F was (0.000), which was less than the significance level adopted in this study and its value (0.05), so we reject the second null hypothesis and accept the alternative “There is statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among applying dimensions of strategic management of human resources (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) in banks operating in Jordan under study and knowledge processes. In order to confirm that there is a correlation relationship and its strength among independent variables and dependent variable, R-value was used”. Table 4 showed that the value of correlation coefficient was=0.841, which indicates a strong positive relationship among independent variables combined (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) and dependent variable ( knowledge processes) because it was more than (0.5).
| Table 4 Results Of Multiple Linear Regression Analysis To Test The Second Hypothesis |
||||||||
| Dependent Variable | Coefficient of Correlation R | R2 | F Calculated | Level of Significance | IV (Strategic Management) | B Value | T Value | Sig |
| Knowledge Operations | 0.841 | 0.707 | 165.381 | 0.000 | Strategic Planning | 0.175 | 4.591 | 0.000 |
| Human Resources formation | 0.034 | 0.725 | 0.469 | |||||
| Strategy of training and development | 0.322 | 7.836 | 0.000 | |||||
| Compensation and Rewards | 0.114 | 2.844 | 0.005 | |||||
| Evaluation of human resources performance | 0.270 | 6.334 | 0.000 | |||||
The results also showed an explanatory capacity of the independent variables combined (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) and their value was (70.7%), which was deducted from coefficient of determination value R2=0.707. And the Size effect of independent variables on the mediator variable is (2.42), which is classified as a significant effect; therefore independent variables have a significant impact on the mediator variable.
The table also showed that calculated t-value of independent variables (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards, performance appraisal of human resources) was respectively (6.334, 2.844, 7.836, 4.951,) with a statistically significant relationship at significance level (0.5) and calculated tvalue was higher than its tabulated value (1.96). In addition, significance level of the variable (0.469) was more than the significance level adopted in this study, which was (0.05).
H3: There is no statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) in banks operating in Jordan under study and achieving competitive advantage. To test the hypothesis, the researchers used multiple linear regression analysis and Table 5 shows regression test results.
The major hypothesis was tested at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) and the results were as follows:
Tabulated f-value was calculated to compare it with calculated f-value. It was found that calculated f-value was (132.763), which was greater than its tabulated value (3.13). This was clear from that there is a statistically significant relationship among variables. Therefore, to check that there was statistically significant relationship at the significance level adopted in this study, Table 5 shows that significance level of F was (0.000), which was less than the significance level adopted in this study and its value was (0.05). Therefore, we reject the second null hypothesis and accept the alternative “There is statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among knowledge management processes in all in every dimension of knowledge processes (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) in banks operating in Jordan under study and achieving competitive advantage”. In order to confirm that there is a correlation relationship and its strength among independent variables and dependent variable, Rvalue was used. Table 5 showed that the value of correlation coefficient was=0.733, which indicates a strong positive relationship among independent variables combined (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, knowledge application) and dependent variable (competitive advantage) because it was more than (0.5).
| Table 5 Results of multiple linear regression analysis to test the Third hypothesis |
|||||||||
| Dependent Variable | Coefficient of Correlation R | R2 | F Calculated | Degree of Freedom | Sig | IV (Knowledge Operations) | B Value | T Value | Sig |
| Competitive advantage | 0.733 | 0.537 | 132.763 | 3 | 0.000 | Generating knowledge | 0.262 | 5.264 | 0.000 |
| 344 | Knowledge sharing | 0.276 | 4.712 | 0.000 | |||||
| 347 | Application of knowledge | 0.266 | 3.888 | 0.000 | |||||
The results also showed an explanatory capacity of the independent variables combined (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, knowledge application) of the dependent variable (competitive advantage) its value was (53.7%), which was deducted from coefficient of determination value R2=0.537.And the Size effect of mediator variables on the dependent variable is (1.16), which is classified as a medium effect, therefore mediator variables have a significant impact on the dependent variable.
The table also showed that calculated t-value of independent variables (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) was respectively (3.888, 4.712, 5.264) with a statistically significant relationship at significance level (0.5) and calculated t-value was higher than its tabulated vale (1.96). In addition, significance level of the variables above was less than the significance level adopted in this study, which was (0.05).
H4: There is no statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among applying strategic management of human resources in banks operating in Jordan under study and achieving competitive advantage in, through knowledge processes as a mediator variable to test the hypothesis. Path analysis was used to examine the role of mediator variable between dependent variable and independent variable. To test the hypothesis, the researchers used multiple linear regression analysis and Table 6 shows regression test results.
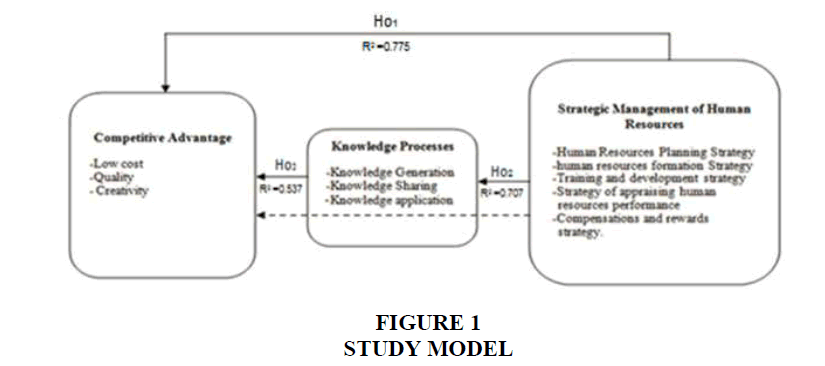
Table 6 shows the study structural model by using (Amos v23), which consists of three variables: independent variable: strategic Human resources management, mediator variable: knowledge processes, dependent variable: competitive advantage. It is noted from arrows with one direction, which show that direct relationship between competitive advantages and applying strategic human resources management (0.137) is less than indirect relationship, which is (0.157) if knowledge processes variable enters as a mediator variable between competitive advantage and applying strategic human resources management. Thus, we reject fourth null hypothesis and accept the alternative. “There is indirect statistically significant impact at significance level (α ≤ 0.05) among applying strategic management of human resources in Jordan and achieving competitive advantage in all, through knowledge processes as a mediator variable”.
Based on matching indicators in Table 6, the current structural model is characterized by a good match because P-value for all variables is less than (0.001) for significance level. In addition, its value plus CR for relationship model in all is more than (1.964) and CFI value equals (1.00) (Table 7).
| Table 6 path Analysis to detect the existence of the role of the intermediate variable (knowledge processes) between the dependent variable (competitive advantage) and the independent (strategic management of human resources) |
||||||
| Variables | Direct effect | Indirect effect | Total effect | |||
| Strategic human resources management | Knowledge processes | Strategic human resources management | Knowledge processes | Competitive advantage | Knowledge processes | |
| Knowledge Processes | 0.183 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.183 | 0.000 |
| Competitive Advantage | 0.137 | 0.856 | 0.157 | 0.000 | 0.294 | 0.856 |
| Table 7 indirect relationship between strategic management and competitive advantage through knowledge processes as an intermediate variable |
||||
| CIMIN | CFI | P value |
value CR | Relationship |
| 0.000 | 1 | 0.000 | 6.296 | Strategic Human Resources Management and Competitive Advantage. |
| 0.000 | 6.897 | Strategic Human Resources Management and Knowledge Processes. | ||
| 0.000 | 13.296 | Knowledge Processes and Competitive Advantage. | ||
Discussion
Strategic management of human resources with its dimensions (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards strategy, performance appraisal of human resources) is linked to achieving competitive advantage of banks operating in Jordan with a statistically significant relationship and it is classified within strong relationships (0.881). Strategic management dimensions of human resources have a high explanatory capacity of approximately (78%). The results showed that all dimensions of strategic management have a statistical significance relationship with competitive advantage. This result is consistent with the results of the previous studies (Al-Lafi, 2018) and (Al-Shawabkeh, 2016) as these studies suggested concluded that strategic management plays a role in achieving competitive advantage (cost reduction, quality, increasing flexibility and innovation) for telecommunications companies in Jordan.
Strategic management of human resources has a statistically significant relationship with knowledge processes. Dimensions of strategic management of human resources (strategic planning, human resources formation, training and development strategy, compensations and rewards strategy, performance appraisal of human resources) are linked with strong relationships (0.841). In addition, dimensions of strategic management of human resources have explanatory capacity (71%). The results showed that human resources formation as one of dimensions of strategic management of human resources has no statistically significant relationship with knowledge processes at significance level (0.05). Whereas, the other dimensions of strategic management have a statistically significant relationship with knowledge processes. This result is corresponding to the results of previous studies (Al-Maqadma, 2013) and (Bhandari, 2016), which recommended of adopting strategic method of human resources management as it relates to knowledge generation, sharing and applying it.
The strength of relationship between strategic management of human resources and competitive advantage is strong and has greater explanatory capacity when compared to the relationship of strategic management with knowledge processes and both are statistically significant at significance level (0.05).
There is a statistically significant relationship between dimensions of knowledge processes (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) and competitive advantage. The relationship between knowledge processes and competitive advantage is classified as a strong relationship (0.733) and the dimensions of knowledge processes have an explanatory capacity over competitive advantage (54%). In addition to all dimensions of knowledge processes (knowledge generation, knowledge sharing, and knowledge application) are linked to competitive advantage with a statistically significant relationship. This result is in consistence with the study results of (Haque & Shamyla, 2012) and (Raguz et al., 2017), which showed that knowledge generation, acquiring and applying it contribute significantly to enhancing competitive advantage through the adoption of the strategic method of human resources continuously and on regular basis.
The explanatory capacity of strategic management on human resources (78%) which is more than the explanatory capacity of knowledge processes on competitive advantage (54%).
The variable of knowledge processes has a mediator role between the relationship of the two variables: strategic management of human resources and competitive advantage, whereas the existence of knowledge processes variable as a mediator variable increases the value of the relationship with the competitive advantage. Whereas, the value of indirect relationship between strategic management and competitive advantage with the existence of knowledge processes variable was (0.157). At the same time, when comparing value of direct relationship between strategic management of human resources and competitive advantage without the existence of knowledge processes variable (0.137), which is less than indirect relationship. It is in consistence with study results of (Al-Maitah et al., 2013) and (Ramadan, 2012), where they concluded that strategic management of human resources through knowledge processes as an mediator variable contributes to competitive advantage, improving its productivity and increasing its innovation and creativity rates through its focusing on recruiting individuals with high capabilities and linking human resources planning to general strategic planning of the organization.
Conclusion
The issue of the weakness of banks operating in Jordan to achieve competitive advantage is currently a very important and critical issue, especially in light of the economic, social, political and technological changes and the liberalization of trade in banking services in the world's banking sector organizations in general, and in Jordan In particular, working on the ability of banks operating in Jordan to achieve competitive advantage by identifying the factors influencing them will contribute to improving the performance of these banks and support their ability to compete, survive and grow. Thus, the scientific significance comes through the importance and vitality of the environment in which the research will be applied and the results of the research is expected to increase the ability of banks operating in Jordan to operate in a competitive framework and to solve the problems they face in human resources through the strategic management of the human resource and the development Human resource strategies make them a source of competitive advantages, and enable banks to identify opportunities and threats and identify the strengths and weaknesses associated with human resources and thus develop appropriate strategies to exploit opportunities and confront threats.
Although there have been previous studies on the nature of the relationship between strategic human resources management and the achievement of competitive advantage, this research is scarce in its subject area where the researcher has not monitored any study on the impact of knowledge management processes as an intermediary variable on the relationship between the two variables, Hence the scientific importance, especially in the light of the lack of the Arab library for this type of studies and thus bridging the research gap, and this study can be a scientific addition through open the field for researchers to further study and analysis in the field of human resources strategy and management of knowledge.
The results of the research are expected to increase official’s awareness in banks operating in Jordan to the importance of creating, developing, sharing and using knowledge to improve employee productivity, reduce costs, improve the quality of banking service, enhance creativity and achieve customer satisfaction and preservation.
Study Recommendations
Based on the study results, this study recommends the following:
1. The need for Jordanian banks to increase their focusing on exploring and recruiting individuals with knowledge and competence. In addition, promoting and spreading organizational learning culture for its necessity in exploring and strengthening employees' knowledge and enhancing their skills as well as increasing communication and cooperation processes with scientific, research and academic centers such as universities.
2. Increasing awareness level among officials in Jordanian commercial banks of the importance of linking dimensions of strategic management of human resources to the general strategy of the organization, which enables it to achieve competitive advantage through influence by knowledge.
3. Reviewing performance appraisal strategy and participation of all employees and managers in planning and developing their career path in order to give an opportunity to employees for creativity and excellence in performance, in addition to achieving balance between employee's objectives and company's general objectives.
References
- Abu Sheikha, N. (2018). Human resources department. Dar Wael for Publishing and Distribution.
- Al Hazaymeh, A.H. (2011). The impact of information technology in achieving competitive advantage in the joint stock companies. Unpublished Master thesis, Amman Arab University .
- Al-Akeely, M.H., Alam, M.K., Bismar, H.A., Khalid, K., Al-Teimi, I., & Al-Dossary, N.F. (2005). Mirizzi syndrome: ten years’ experience from a teaching hospital in Riyadh. World Journal of Surgery, 29(12), 1687-1692.
- Al-Damour, M.M. (2008). The reality of strategic planning for human resources in the public sector in Jordan. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Arab Academy for Banking and Financial Sciences .
- Al-Lafi, K.K. (2018). The strategic role of human resources management and its impact on creativity among the employees of the telecommunications company Zain operating in Jordan. IUJ Journal of Economic and Administrative Studies, 26(2), 112-136.
- Alma, M.A., Al-Shalabi, F.S., & Aljamal, W.H. (2013). Talent management and competitive advantage: The moderating effect of knowledge integration. International Journal of Computer Applications, 66(11), 19-27.
- Al-Maqadma, A. (2013). Role of human competencies in achieving competitive advantage: A case study of the Islamic University of Gaza. Master Thesis, Islamic University of Gaza.
- Al-Qahtani, S. (2015). Applied statistics: Basic concepts and statistical analysis tools. General Directorate of Printing and Publishing, Riyadh .
- Al-Sakarna, B. (2005). Leadership strategies and their role in achieving competitive advantage and performance improvement for telecommunications companies in Jordan. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Amman Arab University for Postgraduate Studies .
- Al-Shawabka, Z. (2016). The effect of human resource strategy on achieving competitive advantage in the Jordanian telecommunications sector. Derasat Journal-Administrative Sciences, 43(1), 431-451.
- Al-Youssafi, M. (2013).The relationship of using electronic banking services to the competitiveness of Yemeni Banks. Master Thesis, Faculty of Commerce, Menoufia University.
- Aqili, O. (2005). Management of contemporary human resources after a strategic. Dar Wael for Printing, Publishing and Distribution .
- Armstrong, M. (2012 ( . Human resource management practice. London: Kogan.
- Awlaki, A. (2018). The effect of human resources management strategies and the development of organizational creativity through knowledge processes as an intermediate variator a field study in Yemeni Commercial Banks. Journal of Aljazira University .
- Bhandari, S. (2016). Strategic human resource management: Competitive edge provider. Imperial Journal of Interdisciplinary Research, 2(9), 383-389.
- Bhatt, G., Gupta, J.N., & Kitchens, F. (2005). An exploratory study of groupware use in the knowledge management process. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 18(1), 28-46.
- Bhatt, G.D. (2001). Knowledge management in organizations: Examining the interaction between technologies, techniques, and people. Journal of Knowledge Management, 5(1), 68-75.
- Caliskan, E.N. (2010). The impact of strategic human resource management on organizational performance. Journal of Naval Science Engineering, 6(2), 100-116.
- Chen, C.J., & Huang, J.W. (2009). Strategic human resource practices and innovation performance-The mediating role of knowledge management capacity. Journal of Business Research, 62(1), 104-114.
- Chen, L.E. (2007). Linking knowledge management to organisational business performance in construction. Unpublished PhD Thesis. Griffith University, Australia.
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, (2nd edition).
- Daft, R. (2010).Organization theory and design. South Western Cengage Learning Caliskan.
- Dalkir, K. (2005). Knowledge management in theory and practice. Elsevier Butterworth–Heinemann.
- David, F.R. (2011). Strategic management: Concepts and cases, (13th edition). Boston: PearsonPrentice Hall.
- Davis, T., Cutt, M., Flynn, N., & Mowl, P. (2016). Talent assessment: A new strategy for talent management. Routledge.
- DeCenzo, D.A., & Robbins, S.P. (2010). Fundamentals of human resource management. John Wiley and Sons.
- Dessler, G. (2005). Human resource management, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- El-Morsi, J., & El-Sabbagh, S.M. (2011). Contemporary trends in human resources management. Dar El-Kholy for Printing, Tanta,Egypt.
- Emadzade, M.K., Mashayekhi, B., & Abdar, E. (2012). Knowledge management capabilities and organizational performance. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(11).
- Findikli, M.A, Yozgat, V., & Rofcanin, Y. (2015). Examining organizational innovation and knowledge management capacity the central role of strategic human resources. Practices Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 181(2015), 377-387.
- Gay, L.R. &Airasian, P. (2000). Educational research: Competences for analysis and experiences. Prentice-Hall: USA, N.J.
- Gilani, M.H., Zadeh, M.S., & Saderi, H.R. (2012).The role of strategic human resource management in creation of competitive advantage (Case study: A commercial organization in Malaysia). International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(16), 225-238.
- Haque, A., & Anwar, S. (2012). Mediating role of knowledge creation and sharing between organizational culture and performance: An empirical analysis of Pakistan’s banking sector. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 2(4), 3276-3284.
- Inkinen, H.T., Kianto, A., & Vanhala, M. (2015). Knowledge management practices and innovation performance in Finland. Baltic Journal of Management, 10(4), 432-455.
- Kazim, A. (2008). The impact of intellectual capital in organizational innovation, a field study in a sample of the mixed industrial sector companies. Qadisiyah Journal of Administrative and Economic Sciences, 10(3), 65-80.
- Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2012). Principles of marketing. Boston: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Liu, T. (2008).Organization learning and social network market orientation: The role of resource-based view strategy in gaining dynamic capabilities advantages. Retrieved from www.hicbusiness.org
- lkhadr, H.A. (2014) .The role of the modern strategy for human resources management in facing the challenges of the organizational environment: A case study of the cable industry corporation. Mohammed Khiedr University.
- Lynch, R.L., & Smith, J.R. (2006). Corporate strategy. Harlow, England: FT/Prentice Hall.
- Mainali, L., Raguz, M., O’Brien, W.J., & Subczynski, W.K. (2017). Changes in the properties and organization of human lens lipid membranes occurring with age. Current Eye Research, 42(5), 721-731.
- Marquardt, M.J. (2002). Building the learning organization. Davies-Black Publishing, an imprint of Consulting Psychologists Press, Inc
- Mathis, R.L., & Jackson, J.H. (2011). Human resource management: Essential perspectives. Cengage Learning.
- Obeidat, T. (2002). Scientific research concept, tools and methods. Al-Fikr Publishing House, Jordan .
- Poister, T. H., & Streib, G. (2005). Elements of strategic planning and management in municipal government: Status after two decades. Public Administration Review, 65(1), 45-56.
- Ramadan, W. (2012). The influence of talent management on sustainable competitive advantage of small and medium sized establishments. E-Leader Berlin ,Oakville, Canada.
- Sáenz, J., Aramburu, N., & Kianto, A. (2017). Knowledge-based HRM practices, organizational learning and innovation performance. In European Conference on Knowledge Management. Academic Conferences International Limited.
- Sani, A.D. (2012). Strategic human resource management and organizational performance in the Nigerian insurance industry: The impact of organizational climate. Business Intelligence Journal, 5(1), 8-20.
- Sawitri, D., & Muis, M. (2014). Human resource management: A strategic theoretical perspective. International Journal of Organizational Innovation (Online), 6(3), 6-20.
- Shammot, M.M. (2014).The role of human resources management practices represented by employee’s recruitment and training and motivating in realization competitive advantage. International Business Research, 7(4).
- Slack, N., Chambers, S., Harland, C., Harrston, A., & Johnston, M. (2009).Operations management.
- Vrdoljak Ragu?, I., Borovac Zekan, S., & Peronja, I. (2017). Knowledge as a source of competitive advantage in knowledge based companies. In DIEM: Dubrovnik International Economic Meeting, 3(1), 533-544.
- Wheelen, T.L., & Hunger, J.D. (2012). Strategic management and business policy: Concepts and cases. New Jersey: Person, Prentice Hall.
- Zahrani, A. (2012). The reality of human resources management information systems and their impact on the competitive advantage: A field study on the Saudi public shareholding companies. The Scientific Journal of the Faculty of Commerce.