Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 3
Principles and Components of Combining Investment Activities with Strategic Management of a Company
Olga Sukhorukova, National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"
Zoya Grygorova, National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"
Alla Kvasko, National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"
Maksym Siryk, National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute"
Yevgeniy Bobrov, KROK University of Economy and Law
Abstract
The article forms a comprehensive understanding of the options for combining investment activity and strategic management within a company. System-forming factors for providing investment activity of companies are identified and typical principles are identified for building new systems of investment processes strategic management. A company investment strategy development model is designed and filled with tools. Indicators for determining investment potential of a company within the strategy of its operation are highlighted and analytically substantiated.
Keywords
Investment Activity, Investment Strategy, Investment Liquidity, Strategic Management of Investment Processes, Investment Potential.
Introduction
In today's economic environment, companies' activities are mostly about finding ways to survive. Issues related to strategic development and investment activity have come to the background. But even under such conditions it is necessary to conduct activity of the company on the principles of strategic management, implement investment strategies, and ensure development of innovations. Many business owners are concerned about implementation of development strategies. Development strategy, in turn, is almost always based on an investment strategy. Many companies lack a development strategy in the process of conducting business activities, and no investment strategies are implemented, which leads to decreased efficiency in future.
Literature Review
The researcher Nofsinger (2017) determined that the investment strategy is the master plan of the company in the sphere of its investment activity, which determines the priorities of its directions and forms, the nature of formation of investment resources and the sequence of stages of realization of long-term investment goals that ensure effective development of the company. The papers Arnold (2010); Gitman (2008) state that complex investment systems have a greater uncertainty in behavior, and their development is focused on future opportunities for improving the company's performance. Scientists such as Jones (2013); Wit & Meyer (2005) point out that the potential for development of a company is not so much laid by the past or initial conditions of investment activity, as by future state of the system – by a set of processes determined by factors of influence of both internal and external environment.
Methodology
In terms of methodological support of scientific work, we distinguish a number of scientific approaches. 1). Orientation approach, according to which among the tasks of managing investment activity of the company are: a) matching the investment needs and capabilities of the company; b) strategic and ongoing maximization of the investment profit of the company; c) minimizing the investment risk of the company in the current and long-term periods; d) maintaining an optimal level of investment liquidity. 2). A pragmatic approach - as a set of practical actions and measures, methods and techniques related to the purposeful regulation of capital movement invested in objects for profit (income) or other beneficial effects. 3). Strategic approach according to which the investment strategy is defined as a system of long-term investment goals and a set of the most effective ways to achieve them.
Results and Discussion
Achieving high performance indicators by a company is possible only if the investment activities are aimed at a strategic growth. The company's investment management system should ensure realization of strategic potential, solving problems and shaping principles of investment activity. The results of grouping these principles are shown in the Table 1.
| Table 1 Typical Principles Used in the Process of Creating new Systems for Strategic Management of Investment Processes | ||
| No. | Basic principle | Principle description |
| 1 | Necessity → ability | Overcoming problems that arise in the process of building a management system (lack of financial resources, incompleteness of information, etc.) limit the ability to build this system |
| 2 | Anticipation → uncertainty | Natural limitation of abilities to anticipate all possible consequences of decisions and created management technologies (decisions concerning structure of management, functional filling, efficiency of activity, etc.) |
| 3 | Building time → rate of obsolescence | Building a new, more sophisticated management system takes considerable time, but significant rate of changes in the environment and the system itself cause its obsolescence. |
| 4 | Self-development and self-complication rates → development rates of analysis methods | Dynamics of changes in the qualitative and quantitative parameters of the management system leaves behind development of analysis methods. |
| 5 | Uniqueness of management system → necessity of a synergistic approach | Uniqueness of management systems complicates the process of maintaining their reliability, which necessitates application of a synergistic approach to their development. |
We see definition of the investment strategy as follows: the investment strategy is the only highly integrated system that ensures the strategic development of a company through comprehensive and consistent implementation of investment projects. This definition focuses on the following aspects of the investment strategy (Ireland et al., 2013):
• Integration of investment strategy and strategic management;
• Complexity of both the strategy itself and the process of implementing the investment strategy;
• Orientation on strategic development in implementation of investment strategy;
• Development and consistent implementation of investment projects.
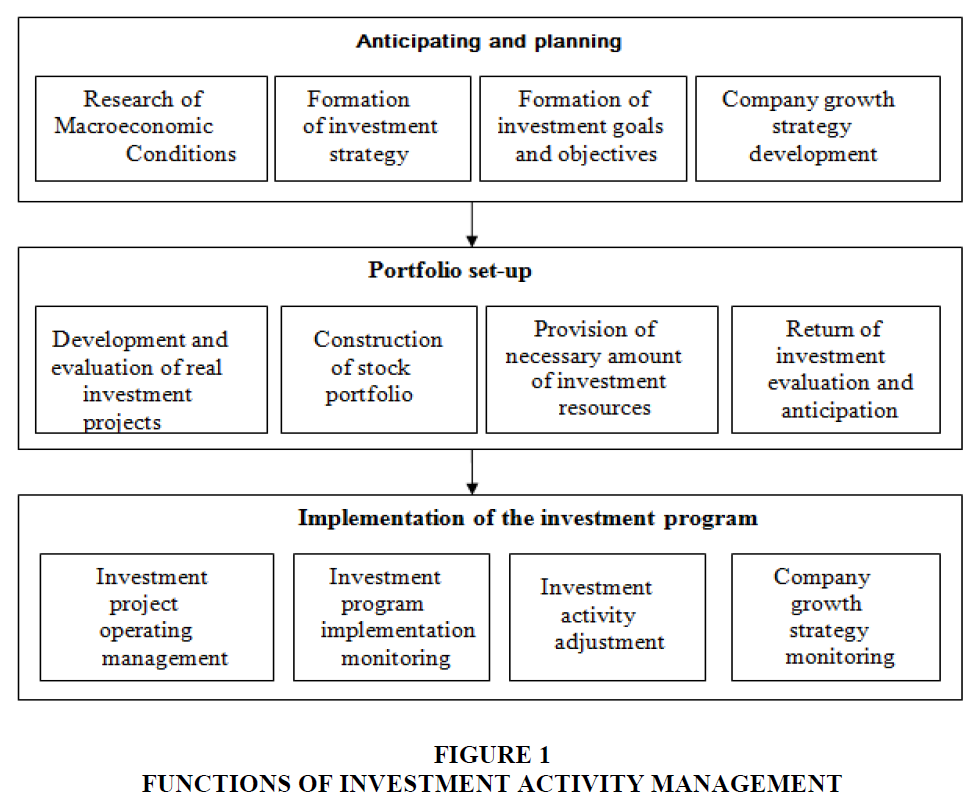
In the process of investment strategy issues elaboration, it is necessary to define a comprehensive approach to its development and implementation. The list and sequence of necessary functions is shown in Figure 1.
Investment strategy itself already bears a sign of complexity. Its complexity lies, first, in defining investment strategy as a system of interrelated elements, and second, in the complexity of the process of forming and implementing the strategy as a set of successive stages. Methodological aspect of the strategy lies in the fact that when formulating an investment strategy, it is necessary to determine the types of investments that will set up the investment portfolio, the main groups of risks of investment activity, the method of calculating economic efficiency, etc. (Wilmott, 2010).
The analytical aspect consists in creation and processing of the information support system of the investment strategy, which should include collection, structuring, processing of information about external and internal environment of the company.
The economic aspect of the investment strategy lies in the fact that it is necessary to work out a system of economic indicators of the investment strategy implementation process from assessment of attractiveness of the investment sources to assessment of the final economic efficiency.
The process approach means creating a company investment strategy management system that would meet basic principles of strategic management (Kleffner et al., 2003).
The principles of a new management paradigm, strategic management, are at the heart of the company's investment strategy development. The basic principles that ensure preparation and adoption of strategic investment decisions include:
1. Considering the company as an open socio-economic system capable of self-organization. This principle of strategic management means that when developing an investment strategy, the company is considered as a certain system, fully open to active interaction with factors of external investment environment.
2. Considering basic strategies of business activity of the company. Being part of the overall economic growth strategy of the company, which provides primarily growth of business activities, the investment strategy is subordinate to it.
3. Predominant orientation to the entrepreneurial style of strategic investment management. Standard approaches to managing a company's investment activity are gradually losing their effectiveness (Severinson & Yermo, 2012).
4. Ensuring a combination of prospective, ongoing and operational management of investment activities.
5. Ensuring adaptability of the investment strategy to changes of the external investment environment factors. This adaptability is realized in the system of general situational approach to the future activity of the company.
6. Provision of alternative strategic investment choices. Strategic investment decisions should be based on an active search for alternative options, directions, forms and methods of investment activity.
7. Provision of an innovative basis for implementation of investment strategy.
8. Considering the level of investment risks in the process of making strategic investment decisions.
9. Orientation on professionalism of the personnel in the process of implementing investment strategy.
10. Provision of support system for development and implementation of investment strategy.
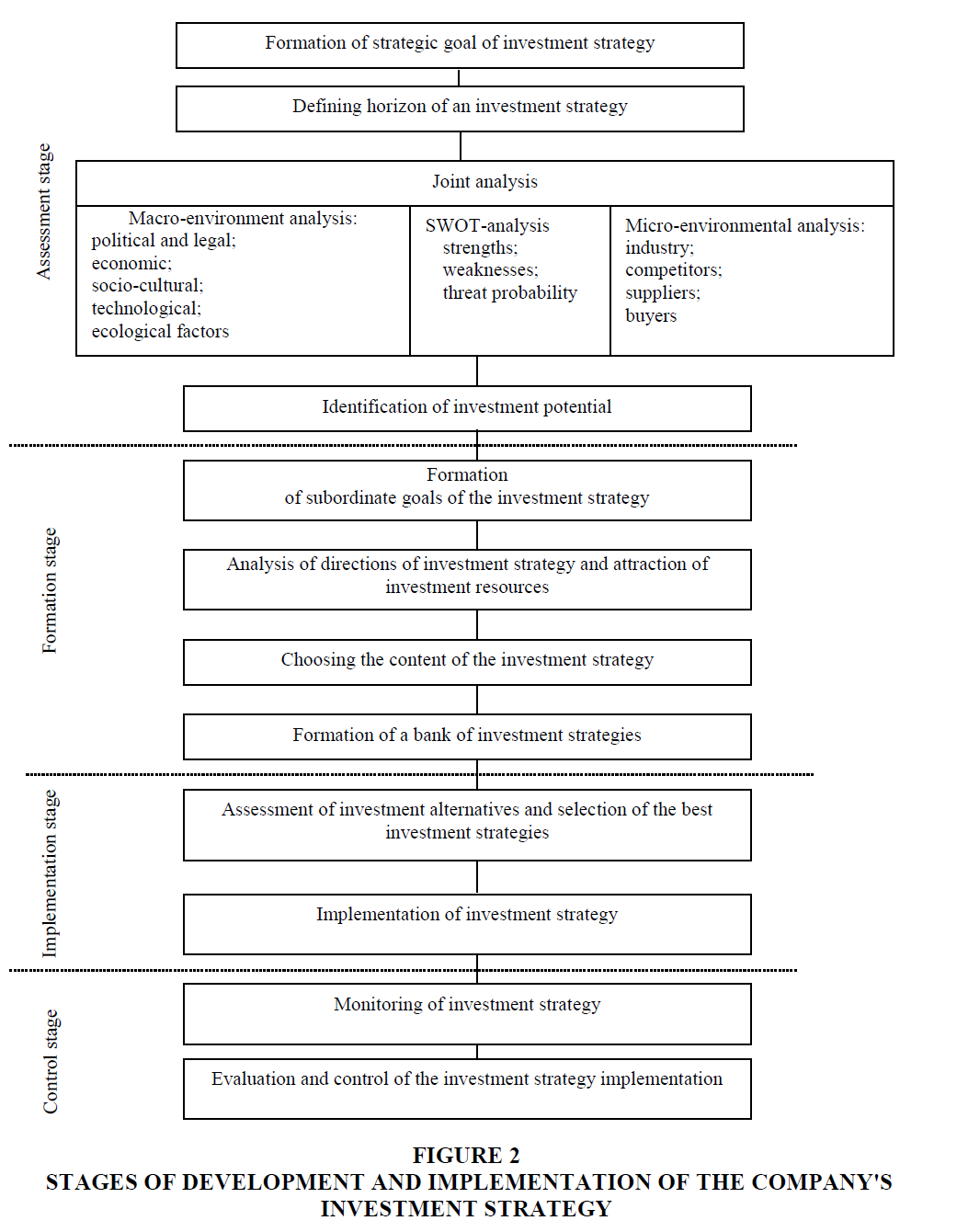
For building a generalized model of the company investment strategy it is proposed to use the scheme of the company investment strategy suggested by us, distinguishing certain stages, namely: assessment, formation, implementation and control (Figure 2).
If taking the general objective as a target function below, then we should point out that the general goal in implementing the company's investment strategy is to increase the S - value of the company, type of business (Hirdinis, 2019). This is a long-term goal.
S = f (k1, k2 .. ?n) → max (1)
where, S – value of the company, type of business (in some cases it may be replaced by the market value of the stock (for joint stock companies) or the value of capitalization of the assets; k1 - kn – resulting indicators for individual stages of the investment strategy, selected depending on the specific project, type of activity and the industry in which the company operates.
The next key stage is identification of the investment potential. It is proposed to use the following set of indicators to define investment potential of the company (Table 2).
| Table 2 Indicators of Investment Potential of the Company | |||
| Detailing the key indicator into groups | Indicator description | Symbols | Recommended value |
| 1. Indicators of internal business processes | 1.1. Power factor 1.2. Materials consumption 1.3. Energy consumption 1.4. Share of emergency repairs in working time balance 1.5. Yield of capital investment 1.6. Core personnel productivity |
?p ?e ?e Dfix Fr Lprod |
0.8-1 opt min opt min < 5% max max |
| 2. Finance indicators | 2.1. Company profit 2.2. Equity Ratio 2.3. Absolute liquidity |
P ?? ??.l. |
max ≥ 0.5 > 0.2 |
| 3. Business activity indicators | 3.1. Stability of the order portfolio (contract coverage) 3.2. Working capital turnover 3.3. Receivable turnover |
?cont. WCt RAt |
0.75-0.8 max max |
| 4. Indicators of training and development | 4.1. The share of strategic investments in the total share of expenses 4.2. Indicators of production processes automation 4.3 Level of production system technical flexibility 4.4. Number of personnel training hours |
Ds.i ?auto ?flex ?tr |
opt opt max max |
Depending on the possible values of these indicators, it is proposed to distinguish five major groups by the level of investment potential development of companies (Robin & Stephen, 2006):
1) Strategic investor (a stable, profitable company with high attractiveness for investors, makes long-term investments in various business areas - both in real and portfolio form);
2) Investor (a profitable company, attractive for investors that makes short-term small investments of idle cash in order to increase economic efficiency of business);
3) Ego investor (a company with undefined attractiveness that is undergoing development stage and invests only in its own development);
4) Re-investor (a company with a medium attractiveness for investors that invests mainly in one type of business with a view to further diversifying it);
5) De-investor (a company unattractive for investors that is in dire need of financial investments to keep it alive or to restructure its business).
The stage of formation and implementation of the investment strategy should be subordinated to the vector of strategic development of the company.
Conclusion
Development of an effective company investment management system based on a focused management requires inclusion in the list of principles that are in line with the overall purpose of the company - to increase its value in the long run. On the basis of generalization of different approaches to defining principles of investment activity management, it is proposed to form the following list: priority of value creation; value coordination; succession of investment decisions; continuity; flexibility; compliance; optionality; efficiency. In course of research, aspects of complexity of the investment strategy, complexity of definition and complexity of the process of its development and implementation, were analyzed. In the process of researching investment strategy, it was suggested to use the scheme of the investment strategy of the company distinguishing the determining stages: 1) assessment, 2) formation, 3) implementation and 4) control.
Recommendations
Further development of research on investment strategy issues will be in the context of exploring the relationship between development strategy and investment strategy. There is also a need for further improvement in the methods of efficiency evaluation and risk mitigation when implementing an investment strategy. Management procedures are recommended based on the principle of cost coordination, which is considered as the consistency of management actions based on the system of cost criteria for evaluating and ranking investment decisions made in the process of investment planning, project implementation, management motivation, and during monitoring and control of investments implementation.
References
- Arnold, G. (2010). Investing: The definitive companion to investment and the financial markets. Financial Times/ Prentice Hall.
- De Wit, B., & Meyer, R. (2005). Resolving strategy paradoxes to create competitive advantage. London. Thomson Learning.
- Gitman, L.J. (2008). Michael D. Joehnk fundamentals of investing.
- Hirdinis, M. (2019). Capital structure and firm size on firm value moderated by profitability. International Journal of Economics & Business Administration, 7(1), 174-191.
- Ireland, R.D., Hoskisson, R.E., & Hitt, M.A. (2013). Strategic management: Competitiveness and globalization (Tenth Edition). Cincinnati: Cengage Learning.
- Jones, C.P. (2013). Investments: principles and concepts. Language, 18(638p), 25c
- Kleffner, A.E., Lee, R.B., & McGannon, B. (2003). The effect of corporate governance on the use of enterprise risk management: Evidence from Canada. Risk Management and Insurance Review, 6(1), 53-73.
- Nofsinger, J.R. (2017). The psychology of investing. Routledge.
- Robin, C.P., & Stephen, L.A. (2006). Company director manual. Sydney: Thomson Reuters, 10001-10129.
- Severinson, C., & Yermo, J. (2012). The effect of solvency regulations and accounting standards on long-term investing: Implications for insurers and pension funds.
- Wilmott, P. (2010). Frequently asked questions in quantitative finance. John Wiley & Sons.