Research Article: 2023 Vol: 26 Issue: 6S
Organizational &Customer Factors Influencing Adoption of Electronic Banking
Mohamed Mohamed AbdElaziz Youssef, AIN Shams University
Citation Information: AbdElaziz Youssef, M.M. (2023). Organizational & Customer factors influencing adoption of electronic banking: proposed strategies for Egyptian banking sector. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 26 (S6),1-15.
Abstract
Electronic Banking is somewhat an innovation that empowers clients to perform numerous monetary administrations with compelling reason need to visit bank offices. It is an internet-based innovation that can be gotten to through a PC (Web banking) or a remote organization and cell phone (Portable banking). This innovation is taken on by practically every one of the banks overall for the majority years now yet there is high potential for development. Many past examinations have analysed the advantages of dissemination and reception of this financial elective channel to the two clients and banks. Nonetheless, the take-up of this innovation in Egypt is still sluggish regardless numerous Egyptian clients are depending on bank offices to perform monetary exchanges. This paper investigates some hierarchical and client factors that impact the dissemination and reception of electronic banking in Egypt towards expanding the pace of utilization by both Egyptian banks and clients. The concentrate likewise proposes a few directing techniques for Egyptian financial area in view of the investigated factors. These procedures are change the executives, building bank-client relationship (trust), making mindfulness, and eliminating the gamble and security client worries of innovation. The concentrate additionally suggests that the Egyptian banks ought to think about the socioeconomic factors, uncommonly age, schooling and pay level while setting methodologies for electronic banking as an elective channel to conventional banking. The significance of client and representatives’ previous involvement with utilizing innovation likewise was featured in this research
Keywords
Egypt, Electronic Banking, Adoption, Organizational Factors, Change Management, Customer Factors, Banks Strategies.
Introduction
Overview
Electronic Banking is somewhat an innovation that empowers clients to perform numerous monetary administrations with compelling reason need to visit bank offices (Anderson et al.,1997). It is web-based innovation that can be gotten to through a PC (Web banking) or a remote organization and cell phone (Portable banking). This innovation is taken on by practically every one of the banks overall for the majority years now yet there is high potential for development Mols (2000). Auditing the previous writing on this issue, it was found that these new conveyance banking channels, for example, Web banking and Portable banking are intended to supplant slowly the conventional physical banks. Likewise, it was seen through the survey that there are a few benefits for taking on and tolerating these channels by clients. Furthermore, different partners would profit from the effective reception of this framework, for example, banks, advertisers, charge cards organizations and others (Ayo & Adewoye, 2010).
Nonetheless, In Egypt the case is different however many banks have put vigorously in the data innovation frameworks and were approved by the National Bank of Egypt to utilize the electronic banking beginning around 2002 (The National bank of Egypt 2014), notwithstanding, a few banks are as yet depending on conventional banking through branches and, surprisingly, in the banks that have executed the new electronic channels the pace of reception for these channels by clients isn't as wanted.
Purpose and Scope
This exploration paper targets investigating the authoritative and client factors that impact effective reception to electronic banking in the financial area in Egypt. As per past explores, such effective reception is supposed to be converted into a few advantages for different partners (Central bank of Egypt, 2014). After investigating and examining these variables, the analyst would propose a few systems for the Egyptian financial area towards fruitful reception for electronic banking.
Importance of the Study
However numerous past examinations have handled the reception and acknowledgment of electronic banking by client, yet to the information on the scientist few examinations have accumulated both hierarchical and client factors particularly with regards to a non-industrial nation like Egypt. Thus, the motivation behind this examination paper is to investigate the hierarchical and client factors that impact the fruitful reception of the electronic banking in Egyptian financial area (Central Bank of Egypt, 2008).
Decrease of expenses, incomes increment, efficient, accommodation, future promoting and deals apparatus, presenting new monetary items and administrations are a portion of the normal benefits of embracing these new banking electronic conveyance channels for some partners as follows.
Electronic Banking Benefits for Customers
There are many advantages for the clients who are utilizing electronic banking like comfort, saving time and exertion. In this way, rather than visiting the bank office and stand in lengthy lines, the client can get to and deal with his record 24 hours/7 days from home or office or some other spot. A portion of the monetary exchanges that can be made through utilizing the electronic banking are as per the following:
• Check account balance, get Visa data and get different alarms.
• Pay Mastercard obligations.
• Take care of utilities bills
• Move subsidizes between inside accounts.
• Figure out the area of ATMs
•Stop installment on checks and block lost or taken cards.
• Remain refreshed on unfamiliar trade rates and financial exchange news
Appropriately, by taking on the electronic banking the client saves his time, exertion and cash, notwithstanding his genuine serenity through keeping away from the dangers of conveying cash.
Electronic Banking Benefits for Banks
There are many advantages for banks taking on the electronic banking, for example, coming to the clients in the far geological regions where the bank doesn't have an actual branch. In this way, it saves the expenses of laying out new branches with the relative foundation, faculty, and gear. Likewise, the bank that utilizes these electronic conveyance channels next to the conventional banking through branches upgrade its picture before its clients since it shows that bank is quick to work on its administrations to fulfill clients utilizing the most recent mechanical developments which are considered as an upper hand.
Banks can involve electronic banking for some reasons: educational and value-based. Enlightening purposes incorporates illuminating the clients about the new items and administrations, ATMs areas, illuminate client about any new security and security measures for safeguarding his monetary information.
Benefits for other Stakeholders
Different partners would profit from reception of electronic banking in banks and clients, for example, Mastercards organizations that can involve the electronic channel as a showcasing device for its offers and motivations to the clients. Additionally, Network access suppliers and portable organizations who might profit from the development of the quantities of clients of web and versatile sets.
Electronic Banking in Egypt
As per the Service of Correspondence and Data Innovation (MCIT) in its ICT pointers distributed January 2014 ( MCIT,2014) , the quantity of web clients in Egypt came to 38.75 million in December 2013. Additionally The MCIT markers showed that the quantity of Versatile Supporters came to 99.7 in December 2013.
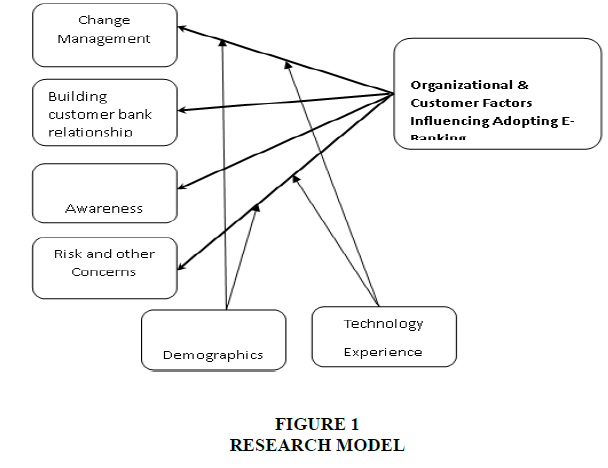
The Above figure 1 show that Egyptian banks can possibly involve the Electronic banking as an option viable conveyance banking channel. Be that as it may, as per the National bank of Egypt (NBE) (2014), in spite of the fact that there are presently 40 banks in Egypt, 5 banks are public and the leftover are private banks and parts of unfamiliar banks ,just 19 banks who were approved by NBE to do the E-banking ( National bank of Egypt 2008).
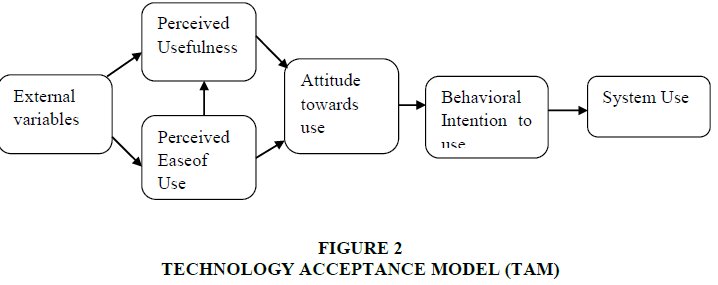
However there are no precise insights to show the specific number of Egyptian banks who are utilizing presently the Electronic banking, yet the pace of reception by banks and clients isn't true to form. Additionally it has been seen through going through the E-banking sites of a few public Egyptian banks that the administrations presented by these banks are restricted to instructive purposes, for example, illuminating the clients about their record adjusts or to send them SMS cautions for the most recent exchanges, while they don't utilize the E banking in value-based purposes, for example, move assets between accounts or taking care of bills Figure 2.
Problem Statement
However, a few Egyptian banks have carried out the Electronic banking beginning around 2003, yet at the same time the take-up pace of the Electronic banking by both Egyptian banks and clients is slow. Thus, we might observe that a few banks are involving electronic banking for just educational and informative purposes yet depending on offering their monetary types of assistance through its branches, while others are as yet depending totally on bank offices as it were. The utilization rate likewise by clients is extremely sluggish, however the Egyptian banks are as yet furnishing electronic banking to its clients with no membership charges. In this way, the exploration objective is to investigate the authoritative and client factors that impact the reception of electronic banking in the financial area in Egypt (Chawla & Sehgal, 2012).
Research Question
What are the authoritative and client factors impacting the effective reception of Electronic banking by banks and client in Egypt?
Research Model and Variables
Research Variables
Dependent variable: Authoritative and client factors affecting reception of electronic banking.
Independent Variables
1. Change Management: Vision and techniques took on by pioneers. Delegating Egyptian Top Administration with Worldwide and global Experience. ( Particularly in Boss data official and Showcasing Positions).
2. Building customer-bank relationship (trust): Understanding the client through powerful correspondence to check which Electronic financial channel fit the client, through recognizing client inclinations, conduct, accepted practices and needs. Offering help and certifiable counsel through the bank client support and IT staff.
3. Creating awareness for customers (the upsides of utilizing Electronic channels, utilizing powerful promoting instruments, client care, Bank site and so on).
4. Risk and other concerns of the customers (security, protection, administration dependability, usability &giving the client the opportunity to attempt the assistance. Giving nonstop preparation to both the bank staff and clients to recognize misrepresentation and cybercrimes.
Moderating Variable
1. User Involvement in innovation (Do the client have a pc and web association - Is he a web banking client ... and so on?)
2. Demographics: Age, Orientation, Level of Training, Calling &Income Level...etc
Literature Review
Concept of Electronic Banking
In this exploration electronic banking is characterized as admittance to the financial cycle by means of a Web gateway set up by an actual bank (through a PC or a cell phone) and through which clients can do numerous monetary exchanges (Chiou & Shen, 2012). As indicated by Salehi and Alipour Electronic banking can be characterized additionally as follows: Web banking (or internet banking), phone banking, television-based banking, cell phone banking, and e-banking (or disconnected banking).
Organizational Factors
Organization strategy
Authoritative key course and desires influences its inclination to embrace new advancements. Along these lines, by carrying out new innovation associations might try to lessen costs, to accomplish advantage over its rivals or to safeguard its piece of the pie (Bradley & Stewart, 2003). As per Jalal et al. ( 2011), propels in innovation and the far reaching of web use urged many banks to remember the web for their brilliant courses of action to give its clients different monetary administrations. Different scientists have distinguished more drivers that encourage the banks to embrace web banking.
Munusamy et al. (2012) affirmed that Web banking methodology is more successful contrasted with conventional banking regarding more benefits, faithful and serious clients, while different examinations have additionally shown that the additional financial channels the bank give the more noteworthy the probability of purchaser fulfillment as certain clients like to depend on blend of banking conveyance channels as opposed to one restrictive channel (Chiou & Shen, 2012).
Organization’s characteristics
Bradley & Stewart (2003) found that the hierarchical qualities significantly affect its course to embrace new developments. Thus, inventive associations would take on the new developments quicker and simpler. The creators further expressed that the design of an association whether it was a regulatory or adaptable would block or support new developments. Trader?Leigh (2002) noted likewise that reception of innovation would include changes in hierarchical culture, approaches, standards and obligations and that might struggle with regulatory designs and can be met with obstruction.
Top management support
Kotter (1996) expressed that any adjustment of associations would be conceivable provided that it was started and upheld by the association top administration. Drew likewise tracked down that one of the boundaries to foster new monetary items is absence of help from top administration and that serious administration contribute in the achievement and speed in presenting new monetary items and administrations. Gupta (2008) had additionally a similar view expressing that the banks who might want to roll out an improvement through the reception of innovation need to depend on its center capabilities and such change ought to be leaded by the top administration who ought to have a dream towards making worth to different client sections.
Employee resistance to change
There are many explanations behind workers' protection from change, for example, feeling of dread toward the obscure, losing positions or changing business as usual so for them change addresses a genuine danger. The apparent dangers by workers might result from not monitoring the principal objectives for change or their trepidation that they could lose a few advantages assuming that that change was executed (Muthoni, 2012).
Change management
The change the board, as indicated by Muthoni (2012), is the utilization of certain devices, cycles and standards for addressing individuals worries towards any change to accomplish the imminent outcomes for a specific change project. Von Urff Kaufeld et al. (2009) characterized the change the executives as an interaction and system to deal with individuals’ side of hierarchical changes to accomplish the business wanted results; a capability of directors and managers to assist representatives with tolerating changes and thus speed up the change cycle inside the association (Mann & Sahni, 2008). Change the board has become one of the center skills of authoritative forerunners in numerous associations. Banan (2010) referenced in his exploration on E banking and administrative difficulties that administration of progress previously and during the execution of data and correspondence innovation (ICT) stand out by associations. In this way, effective associations are the people who can arrangement and mange change.
Kotter (1996) has tracked down that choosing the perfect individuals to configuration, create and execute the authoritative change process is viewed as one of the principal factors for progress. Likewise, the precise choice of viable IT pioneers who might lead the innovative change process is fundamental for the progress of this cycle. Von Urff Kaufeld et al. (2009) expressed that compelling IT pioneers shouldn't just have specialized abilities yet additionally the business information to have the option to adjust the IT systems to that of the association. Von Urff Kaufeld et al. (2009) introduced in their review a lengthy authority development model proposed by Chari (2006) which incorporate four essential jobs for viable IT pioneer specifically: technologist, empowering influence, trend-setter and specialist. Every one of these jobs requires set of skills as follows:
1. Mechanical job: This job requires having expanded innovative experience.
2. Empowering agent: IT pioneer ought to have business information, successful correspondence, preparing abilities, reliability, errand and assets distribution and viable control.
3. Pioneer: Vision, moderate reasoning, group administration and motivation.
4. Specialist: Impact, business opportunity locater, client understanding, individual responsibility,
In their finishing up comments, Von Urff Kaufeld et al. (2009) expressed that compelling IT pioneers ought to have mindfulness and information on the business climate and their association construction to have the option to utilize the above skills (Metwally et al., 2012).
Customer Factors
Numerous different methodologies were utilized to dissect client's reception to new data framework advancements. In this segment, a portion of the significant acknowledgment speculations and models will be introduced to clear up factors influencing client's reception for innovation notwithstanding different factors that were broadened or created by different specialists.
Theory of innovation diffusion
As indicated by Rogers (1995) , the development reception process is the cycle through which an individual or a chief passes from information on an advancement to framing a demeanor towards it then to a choice to take on it or to dismiss it , to execution of the groundbreaking plan to affirmation of this thought.
Rogers introduced five advancement credits that influence reception rates by clients to be specific: relative benefit, similarity (the degree that the new development is reliable with the client needs, values and experience), intricacy, trialability (administration analysis would influence the client choice to embrace) and recognizability (degree to which the help can be seen to find lasting success in genuine use).
Technological Acceptance Model (TAM)
Hat is one of the principal models that were utilized broadly to foresee how much the client can acknowledge and take on innovation. This Model was created by Davis (1989) numerous past investigations have involved the Hat model to quantify client acknowledgment for data frameworks. The super two variables in this model as displayed in Figure 2 are Seen Value (PU) and Saw Convenience (PEOU). Seen Convenience implies how much the client feels that his use of specific PC framework would work on his exhibition. Seen Usability implies how much the client accepts that utilizing a specific framework will be simple and with no work for him.
A study conducted in Egypt on the aim of proceeding with use of web banking by clients, utilizing the Hat model, showed that apparent usability was the principal factor for proceeded with utilization of web banking. El-Kasheir et al.(2009); Izogo, et al. ( 2012) have refered to a review directed in Thailand on portable financial reception showing that clients might embrace the versatile financial innovation provided that they see the innovation as being valuable.
Other Factors Influencing Customer Adoption
Customer relationship and trust of the physical bank
As indicated by Chiou & Shen (2012) clients setting their ventures with a specific bank will build their dependence on that specialist organization, permitting the supplier some command over the client; in this way, clients won't consider changing to different banks, assuming they are happy with the help quality given by their bank and since they put away time and cash with the bank, they might lose the honors and rewards gave by their bank to being steadfast. Client likewise may lay out private associations with specific bank representatives assuming they track down them, recognizable, agreeable and responsive (Cho, 2004). Thus, there is extraordinary probability, in view of the trust and long client relationship with the bank, that clients attempt and take on other new administrations given by the bank and that was upheld by the exploration discoveries of Chiou & Shen (2012) who further expressed that without entrust in and generally speaking fulfillment with the bank, clients will be hesitant to put more in the bank and their inspiration to utilize its Internet providers will diminish. Similar discoveries were found in a review led by Flavián et al. (2006) who showed that that there is a reasonable connection between purchaser trust in the conventional channel and the probability of utilizing administrations given by a similar bank on the web.
Demographics
The socio economics factors incorporate age, orientation, pay, occupation and schooling. Numerous scientists have found that socioeconomics may impact the reception of electronic banking. As to, Lichtenstein & Williamson (2006) showed in their review that the ladies number embracing web banking in certain nations like UK is equivalent to men. Izogo et al. (2012) found in their review in regards to the effect of the socioeconomic factors on customer reception of web banking in Nigeria that guys in their examination test are utilizing the electronic financial more than females (Clemes et al., 2012).
In a review led by Munusamy et al. ( 2012) analyzing the impact of segment factors on the reception of Web retail banking in Malaysian climate , it was observed that age is adversely connected with the reception of web banking . The more youthful purchasers are bound to take on Web banking as they are having more mechanical information than the more seasoned customers. Similar discoveries were expressed in different examinations as follows:
(Lichtenstein & Williamson, 2006; Bucevska & Bucevska, 2013). It was noted additionally that more seasoned clients may not embrace the electronic banking on account of the web apparent dangers, while the more youthful clients are bound to take on the electronic financial administrations as they will endure high dangers ( Muzividzi et al., 2013).
In inconsistency to above explores discoveries, different examinations showed that the segment factor significantly affects the reception of web banking (Gan et al., 2006 ). El-Kasheir et al. (2009) found that the socioeconomics factor affected the aim of proceeded with use to web banking (Mattila, 2003).
Awareness
Creating awareness among clients is one of the central point that contribute in the progress of taking on imaginative monetary items or administrations by clients. Suganthi who have directed an observational concentrate on E-banking in Malaysia suggested that Malaysian banks ought to build the special missions to increment client mindfulness on the electronic financial innovation. Lichtenstein &Williamson (2006) Showed that numerous Australians that don't utilize the web referenced not having known or pondered Web banking, nor have they seen the innovation promoted in Australia. Al-Sukkar and Hasan credited the sluggish pace of reception of web banking by clients in the Center East to absence of mindfulness (Hiatt, 2006).
A few investigations have exhibited different sources to make mindfulness among clients seeing electronic banking, for example, bank representatives and authorities, companions and family members, print media, TV and radio and online promotion (Mols, 2002).
User Experience with Information Technology and Internet
In a review directed by Muzividzi et al. (2013), it was referenced that past PC experience earlier innovation and individual financial experience is decidedly connected with client disposition and conduct towards web banking ; anyway a few buyers don't have even the necessary PC abilities and offices expected to do Web banking. They further demonstrated that the more experience the client have in web and online administration, the more certain his disposition would be towards the reception of web based financial administrations.
Security, Privacy and Risk Concerns
As per Altintas &Gürsakal (2007), they noticed that the web banking depends chiefly on security and trust thus, the burglary of client data brings about client losing his certainty and confidence in the framework and his bank too. Security relates to the apprehension about monetary misfortune, in this way, Web misrepresentation or duplicity can adversely influence client propensity towards electronic financial security given by banks (Muzividzi et al., 2013).
A review which zeroed in on obstruction as fundamental element of Versatile banking in Egypt has uncovered that the best worry for all the examination respondents had, was connected with the gamble to send or save bank exchange information or the unfortunate unwavering quality of association (Elbadrawy & Aziz, 2011).
Resistance to Change
As per Elbadrawy & Aziz (2011) that many examinations zeroed in basically on the variables prompting the reception of advancement nonetheless, scarcely any investigations have considered the elements that possess or the defer the dissemination of advancement, for example, opposition and particularly with regards to a non-industrial nation like Egypt. They further showed that the client obstruction can take three structures total direct dismissal, defer in reception or resistance. The first from is the radical of the three, the second is a sort of deferment and the third is viewed as kind of dismissal anyway the client is willing attempt the development prior to taking the choice of dismissal.
Hypothesis Development
The exploration speculations are as per the following:
H1: Change The executives is decidedly connected with fruitful reception of electronic banking in Egyptian banks.
H2: Building Client bank relationship (trust) is decidedly connected with the reception of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H3: Client inclination to utilize customary banking to innovative electronic channels is adversely connected with client reception of Electronic banking.
H4: Making Mindfulness by banks is emphatically connected with the reception of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H5: Beating the security, risk and different worries of the clients will build the reception pace of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H6: Socioeconomics factors (age, training, position and pay level) can influence the reception pace of Electronic banking by both Egyptian banks and Egyptian clients.
H7: Client past involvement in innovation decidedly influences the reception of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients also banks workers.
Most banks are quick to lay out an enduring business relationship with their clients. In this way, they endeavor to upgrade the assistance quality and deal client motivations to fulfill their client to remain faithful to their bank. For this reason, we find that numerous unfamiliar and confidential banks in Egypt have Sent off numerous client relationship the board Projects (CRM) to reinforce this relationship and gain client's trust. So, the additional time the client stay with his bank, the more honors the client will get as far as credit offices, extraordinary loan costs ,...etc.
Concerning Egyptian clients, however they have numerous elective banks to go for, but much of the time we see that as assuming clients are happy with the nature of administrations given by their bank and trust bank representatives, frameworks, and notoriety, almost certainly, they embrace new electronic financial channels, for example, web and portable banking given by their banks. This is predictable with other specialists' examinations like (Cho, 2004; Flavián, et al., 2006 & Chiou & Shen, 2012).
H1: Change The executives is emphatically connected with effective reception of electronic banking in Egyptian banks
H2: Building Client bank relationship (trust) is decidedly connected with the reception of electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H3: Client inclination to utilize customary banking to innovative electronic channels is adversely connected with client reception of Electronic banking.
H4: Creating Awareness by banks is decidedly connected with the reception of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H5: Beating the security, risk and different worries of the clients will build the reception pace of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients.
H6 Demographics factors (age, training, position and pay level) can influence the reception pace of Electronic banking by both Egyptian banks and Egyptian clients.
H7: Client past involvement in innovation decidedly influences the reception of Electronic banking by Egyptian clients also banks workers.
Individuals who have past involvement with utilizing computers, Web and PDAs are bound to embrace electronic banking. It is additionally noted through writing that there is high chance that individuals who utilized the web banking would utilize likewise the portable banking. Along these lines, Egyptian banks ought to consider this component on their promoting plans. They ought to likewise consider ceaseless preparation to IT staff, client care staff and clients on new data frameworks (Gan et al., 2006).
Discussions and Conclusion
Discussions
This paper has investigated the authoritative and client factors impacting reception of electronic banking inside the financial area in Egypt.
With respect to hierarchical variables, it was found that addressing individuals worries over change prompts fruitful reception of progress projects. Thus, top administration in the Egyptian banks ought to lay out powerful techniques to assist their representatives with tolerating change to accomplish the ideal business results. Likewise, a survey of association structure, cycles, frameworks and polices ought to be finished to study in the event that any adjustment is expected prior to beginning any change undertaking like electronic banking.
With respect to client factors, Egyptian banks ought to think about these elements on planning their methodologies. A few proposed techniques are summed up as follows:
Banks ought to fabricate an enduring relationship with their client in light of trust. Faithful clients ought to be conceded unique financing costs and credit offices. Utilizing CRM programs is viewed as one of the compelling instruments of building a drawn-out relationship. Through this program banks can see client profile; client assistance would have the option to alter client information. What's more, dividing and focusing on clients for new financial administrations or electronic channels would be simpler through utilizing such projects.
Security and other gamble worries of the clients towards utilizing electronic banking ought to be tended to by Egyptian banks. All banks frameworks, organizations and electronic channels ought to be exceptionally gotten and conform to the worldwide security norms. Banks additionally ought to constantly guarantee clients that their secret information are gotten and their monetary exchanges through electronic channels are protected. Persistent schooling and preparing to both IT and client assistance staff is fundamental for recognizing any programmers' assaults or cheats. Banks likewise ought to give assistance in the event that clients face any hardships in utilizing the online banking.
Banks ought to target youthful salaried faculty, who are profoundly taught and PC proficient, in their special exercises for electronic Banking. Additionally, finance managers and experts, for example, specialists, architects, teachers and legal counselors are bound to embrace electronic banking.
Egyptian banks ought to utilize both customary banking and electronic channels since certain clients are hesitant to utilize innovation and really like to utilize bank offices and eye to eye correspondence.
Conclusion
This examination has investigated both authoritative and client factors and proposed a few systems towards expanding the reception pace of electronic banking by Egyptian clients. The impediment of this examination is that it depended exclusively on writing audit and a few perspectives on bank authorities. Thus, further experimental explores ought to be directed to demonstrate legitimacy of the speculations remembered for this exploration.
References
Altintas, M. H., & Gürsakal, N. (2007). Phishing Attacks and Perceptions of Service Quality: A Content Analysis of Internet Banking in Turkey.Journal of Internet Banking & Commerce,12(2).
Anderson, J., Fears, R., & Taylor, B. (1997). Managing technology for competitive advantage.
Ayo, C.K., & Adewoye, J. O. (2010). The state of e-banking implementation in Nigeria: A post-consolidation review.Journal of emerging trends in economics and management sciences,1(1), 37-45.
Banan, M.R. (2010). E-banking and managerial challenges.Computer Science & Telecommunications,24(1).
Bradley.L, Stewart K. (2003). The diffusion of online Banking. Journal of Marketing Management, 19, 1087-1109.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bucevska, V., & Bucevska, J. (2013). An empirical analysis of factors affecting the adoption of electronic banking in macedonia: a logit model.Advances in Business-Related Scientific Research Journal,4(1).
Central bank of Egypt (2014). http://www.cbe.org.eg.
Central Bank of Egypt.(2008). http://www.cbe.org.eg/NR/exeres/60E91010-E5F6-4C27-A087-B5648051E597.html.
Chari, V. (2006). Model of CSFs for effective IS leadership.Unpublished Information Systems Honours Research Project. Grahamstown: Rhodes University.
Chawla, S., & Sehgal, R. (2012). An empirical analysis of the awareness and satisfaction level of internet banking users with respect to demographic profile.Iup Journal of Marketing Management,11(1).
Chiou, J.S., & Shen, C.C. (2012). The antecedents of online financial service adoption: the impact of physical banking services on Internet banking acceptance.Behaviour & Information Technology,31(9), 859-871.
Cho, J., (2004). Likelihood to abort an online transaction: influences from cognitive evaluations, attitudes, and behavioral variables. Information & Management 41 (7), 827–838.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Clemes, M.D., Gan, C., & Du, J. (2012). The factors impacting on customers' decisions to adopt Internet banking.Banks & bank systems, (7, I. 3), 33-50.
Davis, F.D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology.MIS quarterly, 319-340.
Elbadrawy, R., & Aziz, R.A. (2011). Resistance to mobile banking adoption in Egypt: A cultural perspective.International Journal of Managing Information Technology (IJMIT) Vol,3.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
El-Kasheir, D., Ashour, A.S., & Yacout, O.M. (2009). Factors affecting continued usage of internet banking among Egyptian customers.Communications of the IBIMA,9, 252-263.
Flavián, C., Guinalìu, M., & Torres, E. (2006). How bricks-and-mortar attributes affect online banking adoption.International Journal of Bank Marketing,24(6), 406-423.
Gan, C., Clemes, M., Limsombunchai, V., & Weng, A. (2006). A logit analysis of electronic banking in New Zealand.International Journal of Bank Marketing,24(6), 360-383.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gupta, P.K. (2008). Internet banking in India–Consumer concerns and bank strategies.Global journal of business research,2(1), 43-51.
Hiatt, J. (2006).ADKAR: a model for change in business, government, and our community. Prosci.
Izogo, E.E., Nnaemeka, O.C., Onuoha, A.O., & Ezema, K.S. (2012). Impact of demographic variables on consumers’ adoption of e-banking in Nigeria: An empirical investigation.European Journal of Business and Management,4(17), 27-39.
Jalal, A., Marzooq, J., & Nabi, H. A. (2011). Evaluating the impacts of online banking factors on motivating the process of e-banking.J. Mgmt. & Sustainability,1, 32.
Kotter, J.P. (1996). Leadership change.Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA.
Lichtenstein, S., & Williamson, K. (2006). Understanding consumer adoption of internet banking: an interpretive study in the Australian banking context.Journal of electronic commerce research,7(2), 50.
Mann B.S & Sahni S (2008). Understanding customer service quality and customer loyalty of internet banking in private and public sector banks. Gyan Management, 2, 1, 129-140.
Mattila, M. (2003). Factors affecting the adoption of mobile banking services.Journal of internet Banking and Commerce,8(1), 101-119.
Metwally, E.L.H.A.M., Hatem, T.A.R.E.K., & Flood, R.O.B.E.R.T. (2012). Leadership actions facilitating successful implementation of atms and internet banking in Egyptian private sector banking.Journal of Information Technology Management,23(1), 62.
Mols, N.P. (2000). The Internet and services marketing–the case of Danish retail banking.Internet Research,10(1), 7-18.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mols, N.P. (2002). The impact of organizational and environmental factors on the implementation of internet-based marketing channels.Journal of Marketing Channels,9(3-4), 103-131.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Munusamy, J., De Run, E., Chelliah, S., & Annamalah, S. (2012). Adoption of retail internet banking: A study of demographic factors.Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce,17(3).
Muthoni, M. A. (2012).Managing change at national bank of Kenya ltd(Doctoral dissertation).
Muzividzi, D.K., Mbizi, R., & Mukwazhe, T. (2013). An analysis of factors that influence internet banking adoption among intellectuals: case of chinhoyi university of technology.Interdisciplinary journal of contemporary research in business,4(11), 350-369.
Trader-Leigh, K.E. (2002). Case study: Identifying resistance in managing change.Journal of organizational change management,15(2), 138-155.
Von Urff Kaufeld, N., Chari, V., & Freeme, D. (2009). Critical success factors for effective it leadership.Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation,12(1).
Received: 04-Aug-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13903; Editor assigned: 05-Aug-2023, Pre QC No. JMIDS-23-13903(PQ); Reviewed: 19-Aug-2023, QC No. JMIDS-23-13903; Revised: 21-Aug-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-13903(R); Published: 28-Aug-2023