Research Article: 2024 Vol: 27 Issue: 1
Organizational Culture and Its Impact on the Organizational Performance: An Analytical Study of a Number of Private Sector Banks in Thi- Qar Governorate
Rana Abdul Sattar Al- Hammadi, Nassiriya Technical Institute -Southern Technical University
Citation Information: Sattar Al- Hammadi, R.A. (2024). Organizational culture and its impact on the organizational performance: an analytical study of a number of private sector banks in thi- qar governorate. An overview. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 27(S1), 1-15.
Abstract
The research aims to investigate the impact of organizational culture on organizational performance and to analyze this impact on the level of work in surveyed organizations. To achieve this goal, the researcher built a model that explains the relationship and impact of the research variables (organizational culture and organizational performance). A sample of employees working in a number of private sector banks in the governorate was selected to test the research hypotheses. The researcher relied on a questionnaire prepared for this purpose, distributing 70 questionnaires, of which 67 were retrieved and adopted for statistical analysis. The data was analyzed using a number of statistical methods through the use of the SPSS V.24 program and the SmartPls3 program. Excel 2016 was also used for representing the results with charts. The following are some key findings from previous research on the impact of organizational culture on organizational performance, The results confirm the main research hypothesis, which is that there is a significant effect of organizational culture on organizational performance in a number of private sector banks in Thi - Qar Governorate
Keywords
Organizational culture, organizational performance, Power Distance.
Introduction
Organizations in general, and private sector organizations in particular, are witnessing many external developments and challenges, especially in contemporary environments and what is imposed by reality, which puts many organizations facing challenges in searching for means of survival and competition. Organizations have their personal characteristics and the style of work that presents their defining identity in the organizational environment. Extensive studies in this field have demonstrated the clear role of organizational culture on the level of performance, with the foundations it provides for encouraging and supporting teamwork and creating an environment that supports creativity in a way that is consistent with achieving the goals of the organization and the goals of the individuals working in it (Ambroz & Praprotnik, 2008).
Based on the above, the current research presents the impact that organizational culture has on organizational performance, as the research is interested in studying these two terms and knowing the extent of their presence in a number of private sector banks in Thi- Qar Governorate, due to the importance that the financial and banking sector in the governorate represents through broad services at the lending level. For people, companies, and savings, as these and other services represent a major pillar of the work, activity, and effectiveness of the banking sector, which supports economic activity and represents an effective contribution to financing many economic sectors in the governorate.
Based on the above, the concept of organizational culture will be discussed through 3 dimensions, which are (individualism versus collectivism - power distance - cultural compatibility), and the concept of organizational performance will be discussed through 3 dimensions as well, which are (market share - customer satisfaction - creativity) through a number of sector banks. The private sector in Thi-Qar Governorate is (Taif Islamic Bank, Baghdad Bank, Gulf Bank, International Development Bank, United Investment Bank)
In order to understand and clarify the nature of the relationship between organizational culture and organizational performance, the research was divided into four sections, as follows:
• The first section: research methodology
• The second section: The theoretical framework of the research
• The third section deals with the practical aspect of the research
• The fourth section: conclusions and recommendations of interest to the research.
Research Methodology
The Research Problem
The research problem can be summarized by asking the following questions:
What is the level of organizational culture and its dimensions in the private sector banks under discussion in Thi-Qar Governorate?
What is the level of organizational performance and its dimensions in the private sector banks subject to current research in Thi -Qar Governorate?
What is the impact of organizational culture on developing and enhancing the application of organizational performance in the banks under study?
The Importance of Research
The importance of the current research is highlighted in the following:
1. Focus on the importance of the two variables in the application field of the banking sector in light of the dynamic environment and its challenges
2. The lack of research that has dealt with the two concepts at the level of application in private sector banks, to the best of the researcher’s knowledge
3. Determine the extent of the research community’s awareness of the exclusion of both organizational culture and organizational performance in the organization.
Research Objectives
The current research seeks to achieve the following goals:
1. Determine the level of availability of organizational culture in the organizations under research
2. Knowing the extent of the spread of organizational performance and its dimensions in the organizations under research
3. Testing the extent to which organizational culture, with its combined dimensions, influences organizational performance, with its combined dimensions, in the organizations under research.
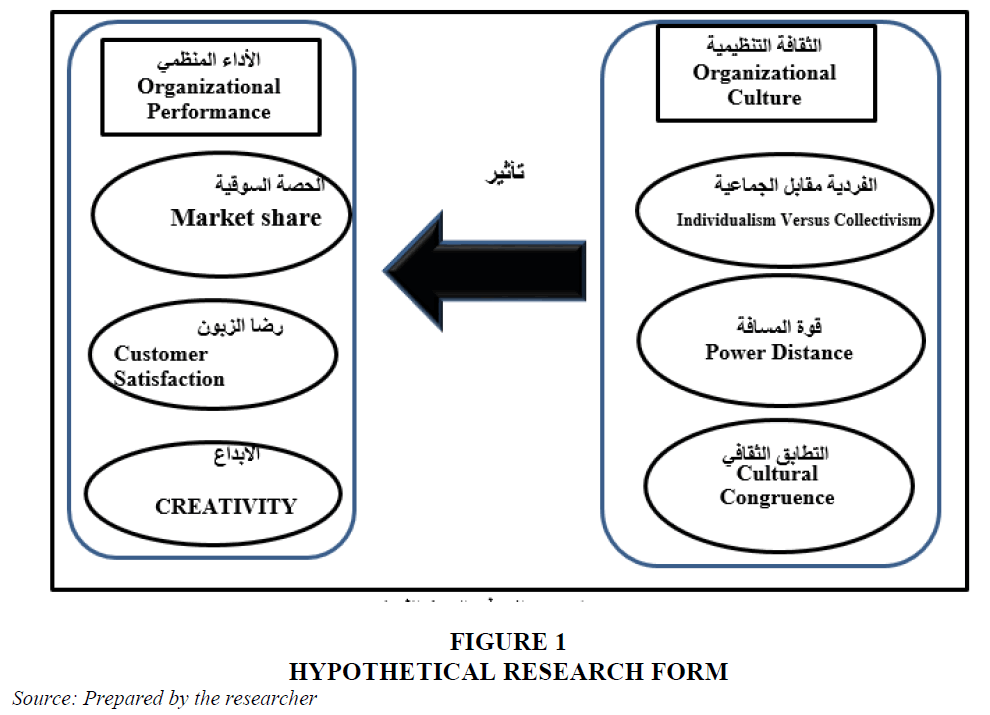
Hypothetical Research Model
• Figure 1 shows the hypothetical research model, which explains the relationships between the research variables, as the research consists of two variables: -
• The explanatory variable (independent): - Organizational culture, which is measured via (individualism versus collectivism - power distance - cultural congruence).
• Response variable (dependent): - Organizational performance, which is measured through (market share - customer satisfaction - creativity).
Research Hypotheses
In light of the proposed hypothetical research model for the research, the main research hypothesis was formulated (there is a significant effect of organizational culture on organizational performance), and the following sub-hypotheses emerged from it:
The first sub-hypothesis: There is a significant effect of the individualism versus collectivism dimension on organizational performance.
The second sub-hypothesis: - There is a significant effect of the power distance dimension on organizational performance.
The third sub-hypothesis: - There is a significant effect of the cultural congruence dimension on organizational performance.
Research Methodology
To achieve the best results in the current research, the descriptive analytical method was adopted
Search tools
1. The theoretical aspect: - For the purpose of completing the research requirements, a number of foreign researches related to the research variables were used.
2. The applied aspect of the research involved the use of a questionnaire form that was designed to meet the requirements of the study. The questionnaire consisted of three axes. The first axis focused on the personal characteristics of the research sample, while the second axis dealt with the sections related to organizational culture and was represented by 15 items as an independent variable. The third axis was allocated to the dependent variable, which was organizational performance, and was also represented by 15 items. A five-dimensional Likert scale was used to measure the response intensity of the sample members, which ranged between "completely disagree" and "completely agree Table 1 represents the research variables, the dimensions of each variable, and the scale adopted for each of them:
| Table 1 The Main Research Variables, Dimensions, and Sequence of Items Measured by the Questionnaire and the Adopted Scale | |||
| Main variables | Dimensions | Paragraph sequence | Approved standard |
| Organizational Culture (OC) | Individualism versus collectivism | 1-5 | Schuldt & Gomes (2020) |
| The power of distance | 6-10 | ||
| Cultural congruence | 11-15 | ||
| Organizational performance ( OP) |
market share | 16-20 | Kapla & Norton(1992) |
| Customer satisfaction | 21-25 | ||
| creativity | 26-30 | ||
The Theoretical Framing of the Research Variables
Organizational Culture (OC)
First: The concept of organizational culture: - Organizational culture is referred to in the literature according to different points of view as the collective programming of the mind that distinguishes the members of the organization from others. Others have argued that it is a polytheistic pattern of beliefs and values that help individuals understand the requirements of organizational performance and thus provide them with rules of behavior. In the organization (Olanipekun et al., 2014).
From Pettigrew's point of view, it represents cohesion and consistency as a form of collective agreement that helps others understand the nature of life in the organization, which appears clear in the nature of symbols and rituals, as well as management beliefs and prevailing ideologies, and their influence in understanding the legitimacy of authority seems to reflect the application of a type It is one of the types of social control that makes individuals in the organization conform to collective standards (Morrison et al., 2006). This seems consistent with the point of view of (Alvesson, 2012) as he believes that organizational culture is a model of assumptions, values, and beliefs that give way It helps individuals in the organization interpret experiences and expectations, and at the same time it helps them maintain the continuity of their membership in the organization and the departments to which they belong within the organizational structure.
That is, it can be said, according to the above concepts, that organizational culture is the framework that guides behaviors within the organization through what it defines in terms of organizational values, norms, standards, and assumptions that individuals share among themselves, which affect their behaviors in a tangible way by determining the appropriate way to perform job tasks, and it is the result of what leaders hold. Values and beliefs that are reflected through an application on the ground.
Dimensions of Organizational Culture
Individualism Versus Collectivism
Organizational culture allows individuals to maintain their independence through self-interest and the discovery of unique internal features and the opportunity to express them. It may seem that in individual cultures there is no reliance on harmony so that it may overlook the positive effects of diversity in the members within the organization. On the other hand, collective cultures have a strategy Others depend on diversity in the work environment, and attention is focused on mutual interchangeable goals according to the public interest. Collective culture leads to feelings of similarity between individuals and a common destiny (Hartung, 2000). Many scholars emphasized that in order to try to understand and classify cultures, it is necessary to track and monitor the principles used by groups that guide thoughts and actions in dealing with common problems (LeFebvre& Franke , 2013).
Power Distance
The power of distance gives managers unlimited power in dealing with subordinates, and through it older employees gain appreciation and respect from junior employees, which may not necessarily be linked to previous competence.
It is estimated to be related to expertise, experience, and age. Previous solutions are usually made at higher levels, and some believe that quality Decisions may seem poorer in some organizations due to the high power distance and lack of participation and communication, which is an excuse for not having to justify or defend the decisions of senior management to lower levels in the organization (Ghosh, 2011). The power of distance, the hierarchical structure, and the level of centralization affect decision-making mechanisms in organizations. The unlimited power of control gives employees limited discretionary power. In contrast, it is noted that in organizations where the power of distance is low, managers are interested in equality, empowerment, and allowing sub-units to make decisions on issues that concern them (Uzun, 2020).
Cultural Congruence
There are many questions that are still searching for an answer about the importance of cultural congruence and its impact on organizational effectiveness. Studies have focused on the effect of collective and individual values in managing diversity. People whose values match those of organizations are likely to have a faster level of performance and thus obtain rewards easily because cultural congruence affects the choice of individuals. For behaviors that achieve the greatest possible job satisfaction (Palthe, 2014).
The Importance of Organizational Culture
• Organizational culture occupies a wide importance for several reasons, the most important of which are:
• Contribute to motivating employees to innovate new products and support creative thinking
• Organizational culture occupies a wide place at the organizational level by responding sincerely to customer needs
• Help to face global competitiveness and change the pattern of technology in the work environment
• Contribute to teaching all members of the organization how to act through organizational behavior
• Organizational culture provides a fruitful point for any organization, for example, high employee ethics and creating competitiveness in the organizational environment
• Employee loyalty to the organization contributes to providing unparalleled services to all customers (Kumar, 2016).
Organizational Performance (OP)
The Concept of Organizational Performance
Organizational performance can be identified through results in various aspects of interest in the organization, starting from the variation in the areas of human resources, operations management, marketing, operations management, strategy and information systems. The ultimate goal of research in these areas is focused on explaining how organizational performance is enhanced, formed and sustained And help companies improve their profitability and long-term survival, as they can be defined as financial and non-financial indicators that are able to assess the degree of any of the organizational goals that the organization can achieve (Singh et al., 2016). It can be said that organizational performance appears through creating harmony. Between specific strategies and stakeholders (suppliers - suppliers - employees - customers) and seek to improve the organization's operations, for example, allocating all resources (financial - human - informational - operational) through effective management. The ability to invest its intellectual energies to enable the organization to perform (Kotler & Keller, 2000).
Dimensions of Organizational Performance
Market Share
The market share is positively related to the company's performance and is referred to as one of the broad determinants of business profitability. Some believe that the market share is able to reflect the current competitive position of the company. It is believed that organizations with high market shares better meet customer needs and enjoy a competitive advantage against competitor (Hsu, 2022). Modern analysis also supports the positive link between market share and organizational performance as a source of competitive advantage by employing understanding of customers, competitors, and distribution channels in a way that enhances performance results such as (sales) (growth), market share, and profits (Shah & Dubey, 2013).
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is related to the level of service or the commodity provided. It represents the customer’s sense of pleasure resulting from the comparison between the performance of the product and the individual’s expectations. From the point of view of Kotler & Keller (2000), customer satisfaction is important to the company, as it is what drives him to talk about us positively. In other words, satisfied customers represent assets For the company Chidozie & Anayochukwu.
On the other hand, customer satisfaction is considered the key to the organization's success and support for its competitiveness, as it challenges its ability to attract and retain customers. The organization can also take the required measures to meet needs in light of understanding customers' perceptions (Ambro & Praprotnik, 2008).
Creativity
In the field of organizational behavior, many researchers offer many definitions of creativity. From Farid's El-Sharkawy & Austin point of view, is the production of new and useful ideas. Brennan & Dooley (2005) emphasized that creativity is a combination of flexibility, originality, and sensitivity of thought that allows the individual or team to think outside the box (Heller & Weisberg, 2018), as creativity needs In organizations to individuals, they possess many advantages that distinguish them from their peers, and they also possess a rich sum of knowledge related to the desired field of work with skills that provide a stimulating core work, leading to distinguished and unconventional organizational performance accompanied by wide openness to the experiences of others (Beheshtifar & Kamani-Fard, 2013).
The Impact of Organizational Culture on Organizational Performance
From the point of view of Bulach, Lunenburg, & Potter, 2012 the impact of organizational culture on the organization’s performance can be summarized through:
1. Knowledge of an organization's culture allows employees to understand each organization's history and appropriate current methods of operation.
2. Understanding organizational culture contributes to enhancing commitment to the organization's philosophy and values and in turn creates shared feelings of working toward common goals.
3. Organizational culture governs behaviors in a way that supports required and acceptable behaviors, and in return is supported by recruitment and selection of employees who retain the best values that fit with the organization’s values.
4. It contributes to reaching a higher level of effectiveness and greater productivity (Victoria et al., 2021).
The Practical Aspect of the Research
This paragraph will discuss the research procedures adopted by the researcher in order to achieve and test the goals that the research seeks to achieve, including a description of the research sample, appropriate statistical methods for analyzing data, and testing hypotheses. The procedures mentioned will be reviewed in the paragraphs below.
Descriptive Analysis of the Research
In the paragraphs shown below, the responses of the research sample individuals will be analyzed on both research variables represented by (organizational culture, organizational performance) as follows:
Analyzing the Responses of Sample Members Regarding the Organizational Culture Variable
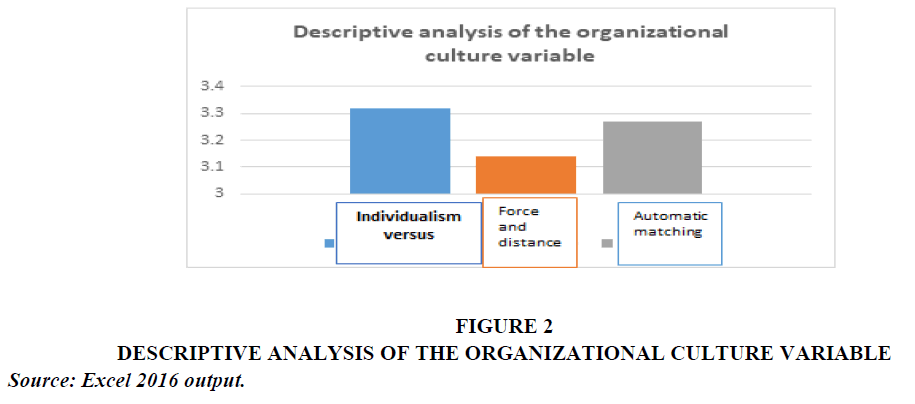
Through the process of analyzing the data of the responses of the research sample individuals, on the questionnaire items related to the variable (organizational culture), the following results appeared in Table 2 and Figure 2.
| Table 2 Descriptive Analysis of the Organizational Culture Variable | ||||||
| Dimensions | Sample | Arithmetic mean | standard deviation | The importance of the ratio | Arrangement | |
| Individualism versus collectivism | 67 | 3,32 | 0.685 | 66 % | The first | |
| The power of distance | 67 | 3,14 | 0.790 | 63 % | The third | |
| Cultural congruence | 67 | 3.27 | 0.723 | 65 % | The second | |
| Total organizational culture | 67 | 3.24 | 0.694 | 65 % | ||
Through the Results of Table 2 above, we have the following:
• The arithmetic mean for the total organizational culture reached (3.24), which is higher than the hypothesized mean of (3), which is used to test the response levels of the research sample members. The standard deviation for the same variable reached (.694), and its relative importance reached (65%).
• The arithmetic mean for the individualism versus collectivism dimension was (3.32), and the standard deviation was (0.685), and the relative importance of this dimension was (66%), which is the highest relative importance among the dimensions, which means that this dimension came in first place.
• The arithmetic mean for the cultural compatibility dimension was (3.27), and the standard deviation was (0.723), and the relative importance of this dimension was (65%), which is lower than the relative importance of the first dimension, which means that this dimension ranked second.
• The arithmetic mean of the power distance dimension was (3.14), and the standard deviation was (0.790), and the relative importance of this dimension was (63%), which is lower than the relative importance of the two dimensions above, which means that this dimension ranked third and last.
• The aforementioned results indicate that employees in private sector banks in Thi-Qar Governorate have a clear understanding of the nature of the organizational culture variable and its sub-dimensions, and how the presence of the dimensions of this culture can affect the performance of individual employees and how it is reflected in the overall performance of the organization. This was demonstrated by the extent to which individual employees responded to the questionnaire questions, which measure the independent variable (organizational culture).
Analyzing the Responses of Sample Members Regarding the Organizational Performance Variable
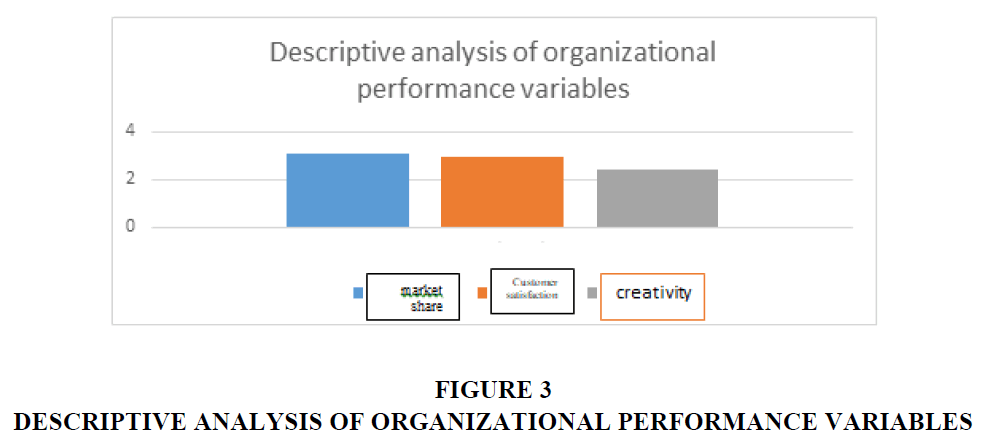
Through the process of analyzing the data of the responses of the research sample individuals, on the questionnaire items related to the variable (organizational performance), the following results appeared in Table 3 and Figure 3:
| Table 3 Descriptive Analysis of the Organizational Performance Variable | |||||
| Dimensions | Sample | Arithmetic mean | Standard deviation | Percentage importance | Arrangement |
| Market Share | 67 | 3,08 | 0.782 | %62 | First |
| Customer satisfaction | 67 | 2,93 | 0.814 | %59 | Second |
| Creativity | 67 | 2,44 | 0.937 | %49 | Third |
| Total organizational performance | 67 | 2,82 | 0.853 | %56 | |
Through the Results of Table (3) above, we have the following
• The arithmetic mean for the total organizational performance reached (2.82), which is less than the hypothesized mean of (3), which is used to test the response levels of the research sample members. The standard deviation for the same variable reached (0.853), and its relative importance reached (56%).
• The arithmetic mean for the market share dimension was (3.08), and the standard deviation was (0.782), and the relative importance of this dimension was (62%), which is the highest relative importance among the dimensions, which means that this dimension came in first place.
• The arithmetic mean of the customer satisfaction dimension was (2.93), and the standard deviation was (.814), and the relative importance of this dimension was (59%), which is lower than the relative importance of the first dimension, which means that this dimension ranked second (Kaplan, 1992).
• Dr. The arithmetic mean for the creativity dimension was (2.44), and the standard deviation was (0.937), and the relative importance of this dimension was (49%), which is lower than the relative importance of the two dimensions above, which means that this dimension ranked third and last (Schuldt & Gomes, 2020).
The aforementioned results indicate that employees in private sector banks in Dhi Qar Governorate have a clear understanding of the nature of the organizational performance variable and its sub-dimensions, and how the presence of dimensions of this type of performance can affect the sustainability of the organization and its continuity in providing its services and achieving profits. This was demonstrated by the extent to which individual employees responded to the questionnaire questions related to measuring the dependent variable (organizational performance).
Testing Research Hypotheses
This paragraph of the research will be divided into two parts. The first section is concerned with testing the hypotheses of the main correlation relationships between the main research variables and their sub-dimensions, while the second section will deal with testing the influence relationships between the main research variables and their sub-dimensions as well, as follows:
Testing the Hypotheses of Correlations
Correlation hypotheses state that there is a significant correlation between organizational culture and its dimensions and organizational performance in its dimensions. The acceptance or denial of these hypotheses will be proven through the results shown in Table 4 below, which are as follows:
| Table 4 The Results of the Correlations between Organizational Culture and Organizational Performance | |||
| Hypotheses | Hypothesis Text | Correlation Coefficient | The Result |
| The first sub-hypothesis | There is a significant correlation between the dimension of individualism versus collectivism and organizational performance | 0.603* | Accept the hypothesis |
| The second sub-hypothesis | There is a significant correlation between the dimension of individualism versus collectivism and organizational performance | 0.592* | Accept the hypothesis |
| The third sub-hypothesis | There is a significant correlation between the dimension of individualism versus collectivism and organizational performance | 0.587* | Accept the hypothesis |
| Main hypothesis | There is a significant correlation between organizational culture and organizational performance | 0.618* | Accept the hypothesis |
It is clear from the results of table 4 above, that all the hypotheses of the main and sub-correlation relationships are accepted, as they came at a significant level (0.012), which is less than the level of significance assumed by the researcher (0.05), and thus all hypotheses of the correlation relationships are accepted at the level of this research.
Testing the Main Effect Hypothesis
The main effect hypothesis states that (there is a significant effect of organizational culture on organizational performance), and the sub-hypotheses emanating from it will be verified and tested, respectively, according to what was clarified in the hypothetical research scheme. After working on testing and measuring the effect between the two research variables, the following results were obtained, which are shown in Table 5 below
| Table 5 Testing the Effect of Organizational Culture on Organizational Performance | ||||||
| Dependent variable | organizational performance | |||||
| Independent variable | Impact factor ß | T value | Coefficient of determination R2 | F value | level of significance | The result |
| Organizational culture | 618.0 | 60.312 | 328, | 9,541 | 0012, | Accept the hypothesis |
Through the results of table 5 above, it has been shown that there is a significant effect of organizational culture on organizational performance, since the level of significance has reached (0.012), and that this percentage is less than the level of significance that the researcher presumed, which is (0.05). The regression slope coefficient was (0.618). It is worth noting that the interpretation coefficient, which is symbolized by (R2), amounted to (0.382), and this means that the organizational culture variable explains (0.382) from the variation that can occur in the dependent variable represented by organizational performance, and based on the calculated (F) value that It reached (9.541), which is greater than its tabular value of (4.00), so it is acceptable. By relying on these results, it is possible to acknowledge the acceptance of the main influence hypothesis at the level of the current research.
Testing the Impact Sub-Hypotheses
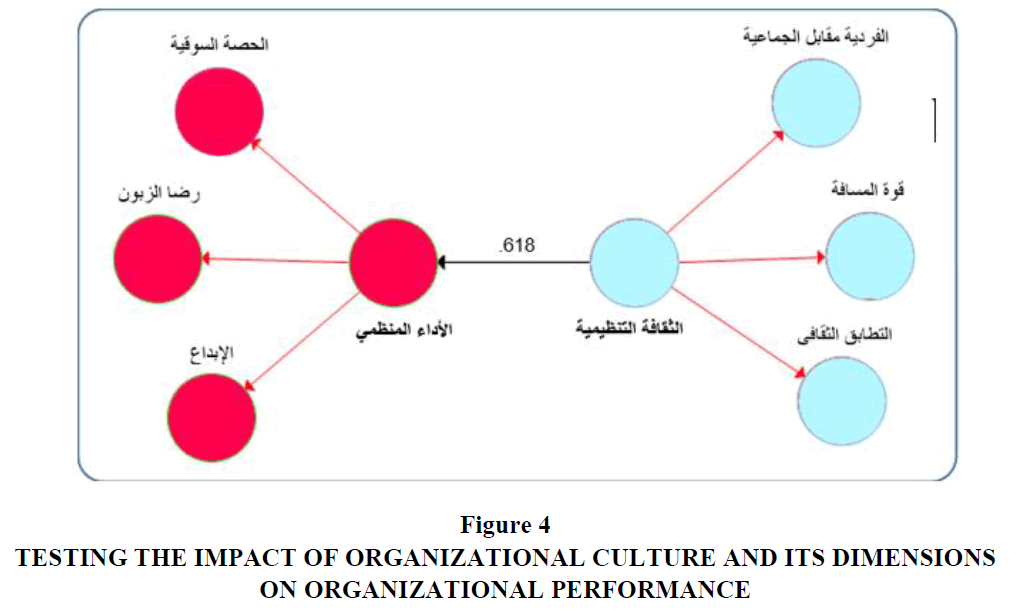
In the effect sub-hypotheses, it was hypothesized that there is a significant effect of the dimensions of organizational culture (individual versus group, power of distance, cultural conformity) on organizational performance. This indicates that the dependent variable, represented by organizational performance, is a real function of the constituent dimensions of the independent variable represented by organizational culture. If any change occurs in the dimensions of organizational culture, this will lead to an inevitable change in organizational performance. Table 6 and Figure 4 show the results of testing the impact sub-hypotheses, as follows
| Table 6 Examining the Impact of Organizational Culture Dimensions on Organizational Performance | ||||||
| Dependent variable | organizational performance | |||||
| Dimensions of organizational culture | Impact factor ß | T value | Coefficient of determination R2 | F value | level of significance | The result |
| Individualism versus collectivism | 0.603 | 50.504 | 364 | 80.411 | 012.0 | Accept the hypothesis |
| The power of distance | 0.592 | 40.836 | 351 | 70.950 | 012.0 | Accept the hypothesis |
| Cultural congruence | 0.587 | 40.259 | 345 | 60.883 | 0.012 | Accept the hypothesis |
| Main hypothesis | 0.618 | 60.312 | 382 | 90.541 | 0.012 | Accept the hypothesis |
Through the Results of Table (6) above, we find the Following:
Figure 4 Testing the Impact of Organizational Culture and its Dimensions on Organizational Performance
• The first sub-hypothesis of influence: This hypothesis assumes that there is a significant effect of the dimension of individualism versus groupness on organizational performance, and the results of Table 6 show that there is a significant effect of the dimension of individuality versus groupness on organizational performance, because the level of significance has reached (0.012), which is Less than the level of significance assumed by the researcher (0.05), and the value of the regression coefficient for this dimension was (0.603), and based on these results, the first sub-hypothesis of influence is accepted.
• The second sub-hypothesis of effect: This hypothesis assumes that there is a significant effect of the distance strength dimension on organizational performance, and the results of Table 6 show that there is a significant effect of the distance strength dimension on organizational performance, because the level of significance has reached (0.012), which is less than The level of significance that the researcher assumed was (0.05), and the regression coefficient for this dimension was (0.592). Based on these results, the second sub-hypothesis of influence is accepted.
• The third sub-influence hypothesis: This hypothesis assumes that there is a significant effect of the cultural congruence dimension on organizational performance. The results of Table 6 show that there is a significant effect of the cultural congruence dimension on organizational performance, because the level of significance has reached (0.012), which is less than The level of significance assumed by the researcher is (0.05), and the regression slope coefficient for this dimension was (0.587). Based on these results, the third sub-hypothesis of influence is accepted.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusions
A Set of Conclusions Related to the Current Research were Reached, Which are as Follows
1. Research and studies on organizational culture indicate that it is an important and critical factor in the success of business and non-profit organizations. It can influence the behaviors of individual employees and their job satisfaction, as well as loyalty to the organization in which they work.
2. Organizational culture can provide an environment that supports innovation and creativity among employees in order to create a competitive advantage in the market or industry in which the organization operates.
3. Research on organizational performance indicates that it is affected by factors such as force distance, leadership characteristics, and organizational linkages. Individual values and needs can influence performance management systems.
4. Through the results of the applied side of the research, it was found that there is a positive and significant effect of organizational culture in its dimensions on organizational performance in private sector banks in Thi - Qar Governorate.
Recommendations
By Relying on the Conclusions Reached by the Researcher, A Number of Recommendations Were Proposed, as Follows
Private sector banks in Thi- Qar Governorate must enhance the organizational culture in their corridors by creating meaningful values and communicating them to all employees.
Private sector banks in Thi - Qar Governorate must build and develop an organizational culture that supports innovation and creativity based on the beliefs and values in which they believe.
Senior management in private sector banks in Thi- Qar Governorate must ensure that its organizational culture expresses goals through values and beliefs, and directs its activities through shared assumptions and group rules in line with its strategy.
If private sector banks in Thi - Qar Governorate want to enhance organizational performance, they must adopt, work with, and strengthen the organizational culture with its sub-dimensions.
References
Alvesson, M. (2012). Understanding organizational culture. Understanding Organizational Culture, 1-248.
Ambroz, M., Praprotnik, M. (2008). Organisational effectiveness and customer satisfaction” organizacija, 41 (5), 161-173.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Beheshtifar, M., & Kamani-Fard, F.B. (2013). Organizational creativity: A substantial factor to growth. International journal of academic research in business and social sciences, 3(3), 98.
Ghosh, A. (2011). Power distance in organizational contexts-a review of collectivist cultures. Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, 89-101.
Hartung, F. (2000). How individualist and collectivist organizational cultures influence work processes, outcomes, and cooperation.
Heller, J., & Weisberg, J. (2018). Creativity, innovation and organizational performance: does hrm bind them together?. Kindai management review/The Institute for Creative Management and Innovation, Kinki University, 6, 46-63.
Hsu, T. (2022). Market share as a performance measure: a conceptual framework. Management and Business Research,(21), 24-34.
Kaplan, R. S. (1992). The balanced scorecard measures that drive performance. Harvard business review.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2000). Marketing Management Prentice Hall. Inc, New Jersey, USA.
Kumar, A. (2016). Redefined and importance of organizational culture. Global Journal of Management and Business Research, 16(4), 14-18.
LeFebvre, R., & Franke, V. (2013). Culture matters: Individualism vs. collectivism in conflict decision-making. Societies, 3(1), 128-146.
Morrison, J. M., Brown, C. J., & Smit, E. V. D. M. (2006). A supportive organisational culture for project management in matrix organizations: a theoretical perspective. South African Journal of Business Management, 37(4), 39-54.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Olanipekun, A. O., Abiola-Falemu, J. O., & Aje, I. O. (2014). Dimensions of organisational culture in quantity surveying firms in Nigeria. Australasian Journal of Construction Economics and Building, The, 14(4), 54-70.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Palthe, J. (2014). Cross-level cultural congruence: Implications for managing diversity in multinational corporations. Journal of Diversity Management (JDM), 9(1), 51-62.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Schuldt, K. S., & Gomes, G. (2020). Influence of organizational culture on the environments of innovation and organizational performance. Gestão & Produção, 27, e4571.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Shah, S.N.A., & Dubey, S. (2013). Market orientation and organizational performance of financial institutions in United Arab Emirates. Journal of Management and Public Policy, 4(2), 17.
Singh, S., Darwish, T. K., & Potocnik, K. (2016). Measuring organizational performance: A case for subjective measures. British Journal of Management, 27(1), 214-224.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Uzun, T. (2020). Relationships between power distance, organizational commitment, and trust in schools. Educational Policy Analysis and Strategic Research, 15(3), 359-371.
Victoria O., Akpa; Olalekan U., Asikhia; Evangeline, Nneji (2021). Organizational culture and organizational performance: a review of literature. International Journal of Advances in Engineering andManagement (IJAEM), 3 (1), 360-372.
Received: 1-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-14103; Editor assigned: 03-Oct-2023, Pre QC No. JMIDS-23-14103(PQ); Reviewed: 17- Oct-2023, QC No. JMIDS-23-14103; Revised: 18-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. JMIDS-23-14103 (R); Published: 23-Oct-2023