Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 6S
Organization of Control Over Labor Safety during Manitenance and Repairs of Tractors and Combines at the Agro-Industrial Enterprises
Igor.E. Lipkovich, Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrar-ian University in Zernograd
?aksim. ?. Ukraintsev, Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrarian University in Zernograd
Irina.V. Egorova, Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrari-an University in Zernograd
Nadezhda V. Petrenko, Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrarian University in Zernograd
Sergei.?. Pyatikopov, Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrarian University in Zernograd
Abstract
The research is aimed at creating a correct world-view about the labor protection of the agro-industrial technical and engineering employees who carry out the repairs and maintenance of tractors and combines.
The major method is an analysis and conditions of carrying out the operations on repairs and maintenance of tractors and combines, on basis of which it is getting necessary to correctly organize the supervisory activities over labor safety.
As a result, aspects of the work made by a labor protection specialist and the organization of his/her activities on supervision over the labor safety were developed and formulated, and obligations of the technical and engineering employees in respect to this aspect are stated.
This research will be of use to masters and postgraduate students studying the organization of maintenance and repairs of the tractors and combines, and to the agro-industrial technical and engineering employees.
Keywords:
Tractor, Combine, Safety, Maintenance, Repairs, Organization
Introduction
Manufacturing of the competitive agricultural products is based on the use of advanced machine technologies, which are based on the technical facilities. In this connection, the agricul-ture is reequipped technologically and technically, the agricultural machine building is modern-ized, the state-of-the-art equipment is supplied in larger quantities. The machines operation is accompanied by wear-out processes as well as by wear and tear and obsolescence. As a result, the technical and economic performance of the equipment used becomes worse. In order to keep the machines in good repair, it is necessary to control their technical state, to carry out their maintenance and repairs qualitatively and in a timely manner, to implement the equipment stor-age (Lipkovich, Egorova, Petrenko & Gayda, 2019).
In order to perform all these tasks, it is necessary to create a technical service system, which would include all the stages aimed at keeping the equipment in proper working order dur-ing the entire service life.
Technical service in the Agro-industrial complex is a package of services for supplying the needs related to operation of the machines, equipment and other technical facilities used in the agriculture and its production infrastructure.
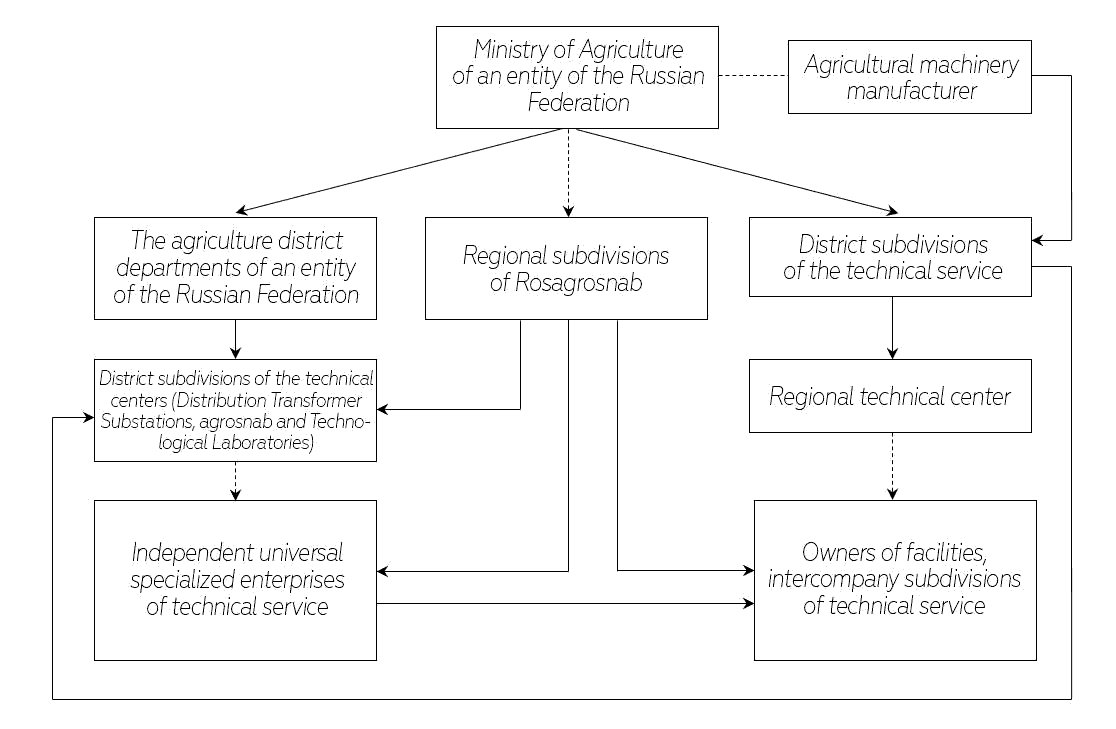
Figure 1 shows a tentative diagram of a system of the technical service of an entity of the Russian Federation, which makes it clear that direct interaction of the technical service with the operated technical facilities is implemented at levels of the mechanic means owners by means of their resources and the service enterprises located in the administrative districts (Lipkovich, Egorova & Petrenko, 2020; Lipkovich, Egorova & Petrenko, 2019).
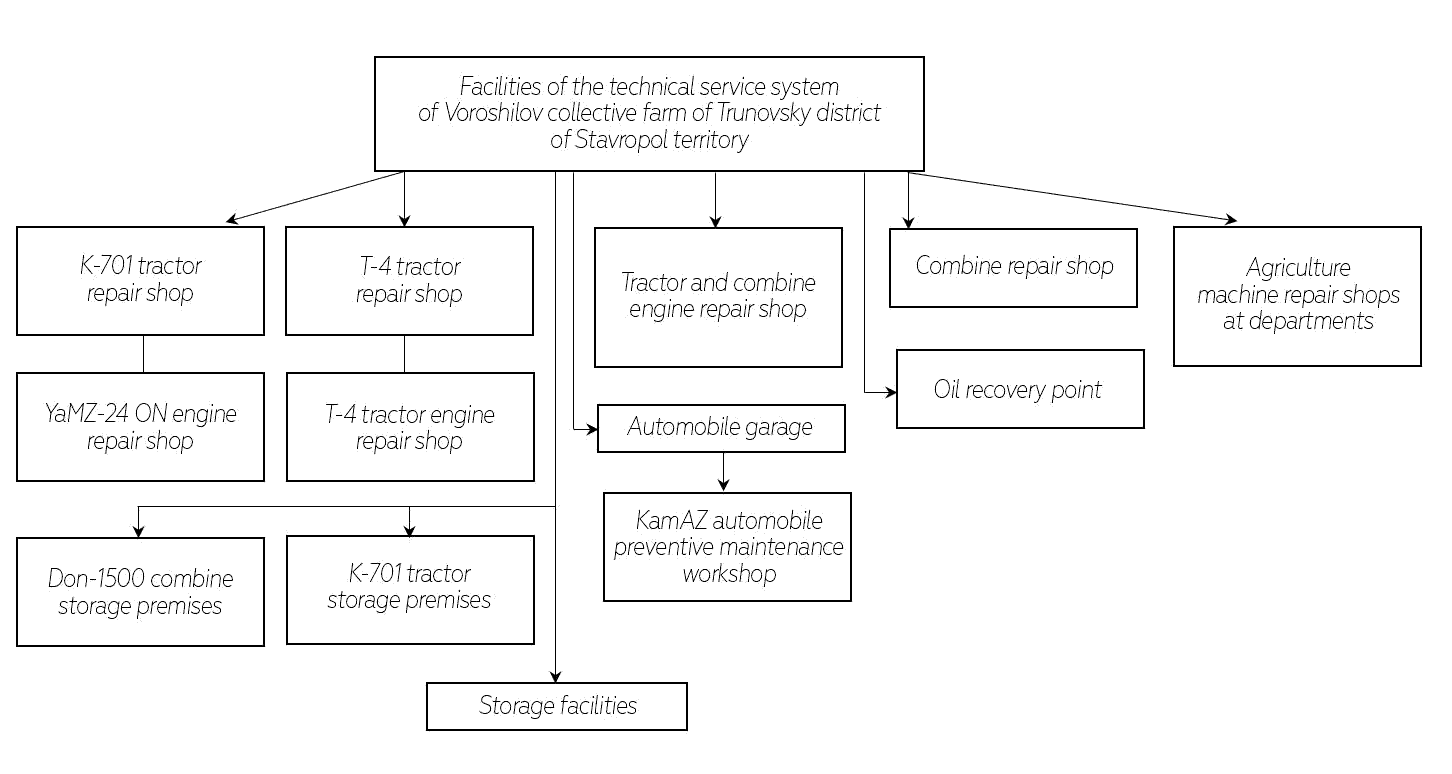
Figure 2 shows a diagram of the technical service system of a major agricultural enter-prises of Stavropol territory of the Russian Federation (Vedenyapin, 1968).
Figure 2:Diagram of the Technical Service System of a Major Agricultur- Al Enterprise of Stavropol Territory of the Russian Federation
Figure 2 shows that the technical service system of this enterprise is quite self-sufficient and is able to carry out the maintenance and repairs in full. In the long run, the authors would like to see such a system of the technical service of the mobile agricultural equipment at each agricultural enterprise or in a group of small enterprises (Ageev, 1978; Lipkovich, Egorova, Petrenko, Sergeev & Pyatikopov, 2019).
Materials and Methods
The maintenance includes the following major operations: cleaning-washing, control-inspection, diagnostic, fastening, installation-dismantling, fuelling, lubrication, adjustment opera-tions, etc. While developing the technologies of the agricultural equipment maintenance, it is nec-essary to adhere to the following principles (Lipkovich & Egorova, 2016):
1. To carry out the maintenance with account taken of assessment of their technical state;
2. To divide and to specialize the labor during carrying out the maintenance;
3. To ensure the work sequence;
4. To apply the mechanic means.
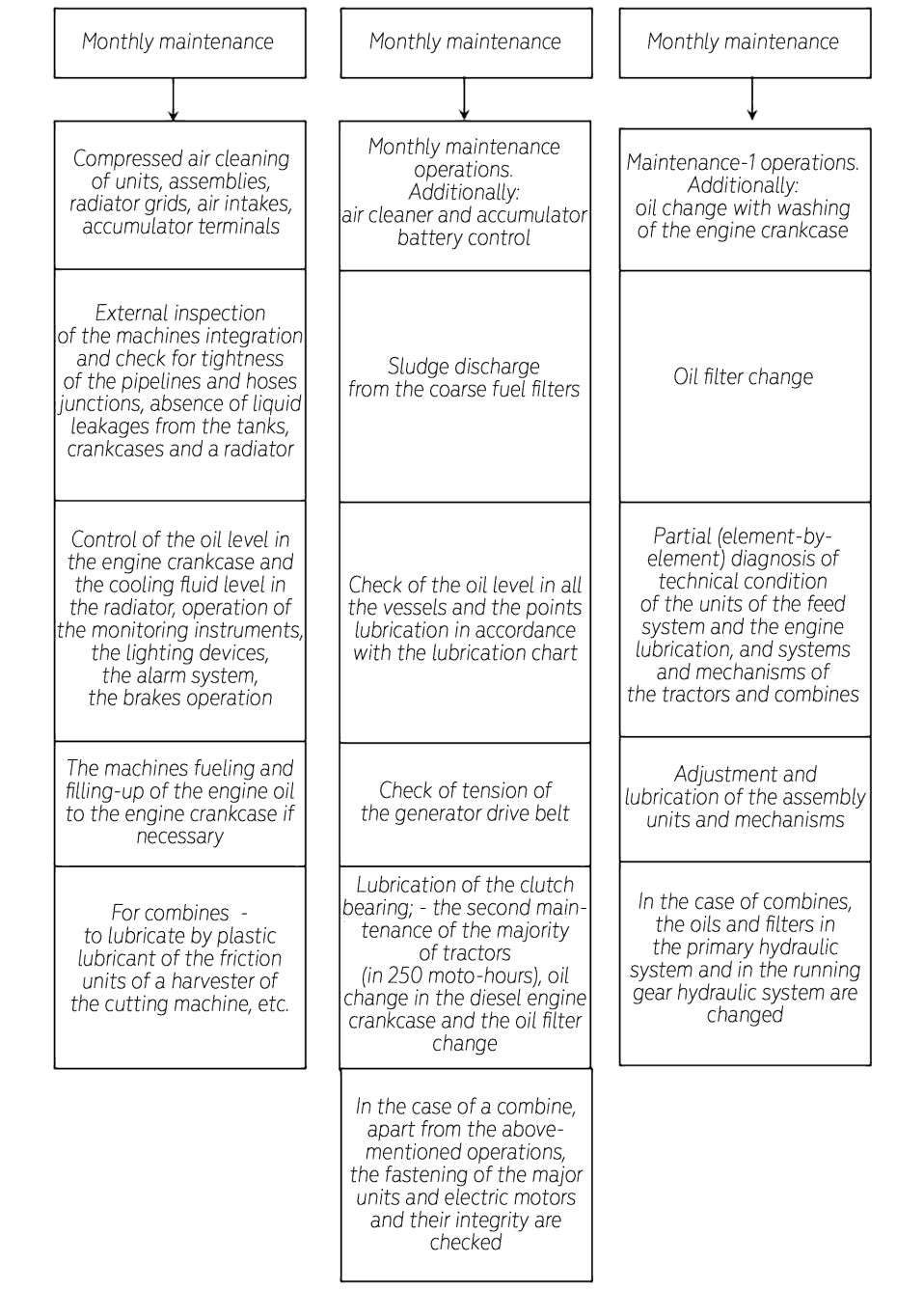
Periodicity of the tractors and combines maintenance was established in moto-hours of the service. Periodicity and conditions of carrying out the tractors and combines maintenance are stated in Tables 1 and 2 (Anasica & Sweta Batra, 2020; Drincha, 2002).
| Table 1 Periodicity and Conditions of Carrying out the Tractors Maintenance |
|
|---|---|
| Maintenance | Periodicity, conditions of carrying out the maintenance |
| Before-sale | During preparation for sale by the dealer enterprises |
| During the operational breaking- in | During preparation, implementation and finishing of the breaking-in |
| Monthly maintenance | In 8-10 moto-h |
| Maintenance-1 | In 125 moto-h |
| Maintenance-2 | In 500 moto-h |
| Maintenance-3 | In 1000 moto-h |
| Season maintenance-Spring- Summer | At a steady-state mean daily ambient air temperature of higher than 5 °c |
| Season maintenance-Autumn- Winter | At a steady-state mean daily ambient air temperature of lower than 5 °c |
| In special operation conditions | During operation in deserts and on sand soils; at long-term low and high tem- peratures; on stony soils; on boggy soils |
| During preparation for the long- term storage | Within 10 days of the use finishing |
| In the process of long-term stor- age | Once a month- during the outdoors and under shelter storage; once every two months- during the indoors storage |
| During removing from the long- term storage | 15 days before the beginning of use |
| Table 2 Periodicity and Conditions of Carrying out the Maintenance of Combines and Other Agricultural Machines |
|
|---|---|
| Maintenance | Periodicity, conditions of carrying out the maintenance |
| Before-sale | During preparation for the machine sale |
| During the operational breaking- in | During preparation, implementation and finishing of the machines breaking-in |
| Monthly maintenance | In 10 hours (monthly) for all kinds of agricultural activities |
| Maintenance-1 | 60 moto-h of service- for combines and complicated self-propelled fixed ma- chines, units and complexes |
| Maintenance-2* | 240 moto-h of service – for combines and complicated self-propelled ma- chines |
| Postseason maintenance | After completion of operation of the simple agricultural machines |
| Before the beginning of the oper- ation season | For the seasonal complicated agricultural machines |
| During preparation for the long- term storage | Within 10 days of the use period finishing |
| In the process of long-term stor- age | Once a month- during the outdoors and under shelter storage; once every two months- during the indoors storage |
| During removing from the long- term storage | 15 days before the beginning of use |
The tables show that all the work, which is related to the tractor and combine mainte-nance, is strictly regulated in time.
A volume of operations of the periodic maintenances increases with the increase of the maintenance number. In addition, each subsequent maintenance contains all the operations of the previous maintenance and additional operations.
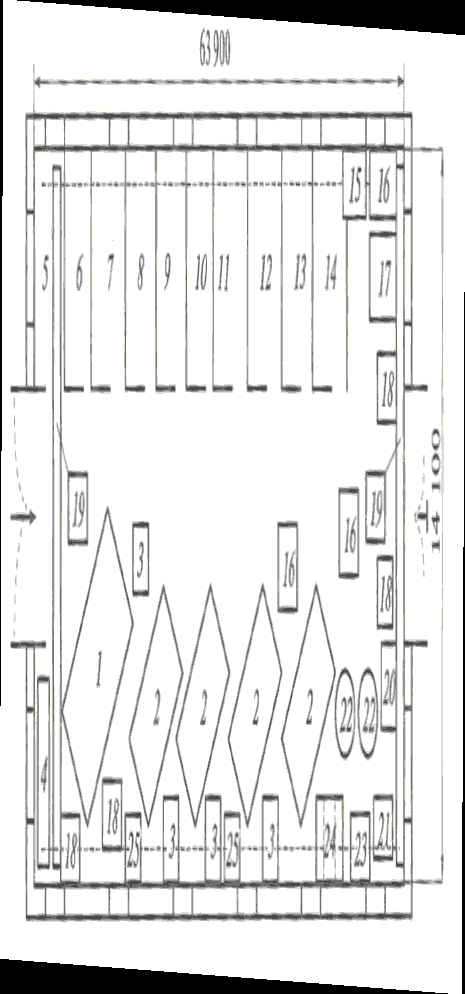
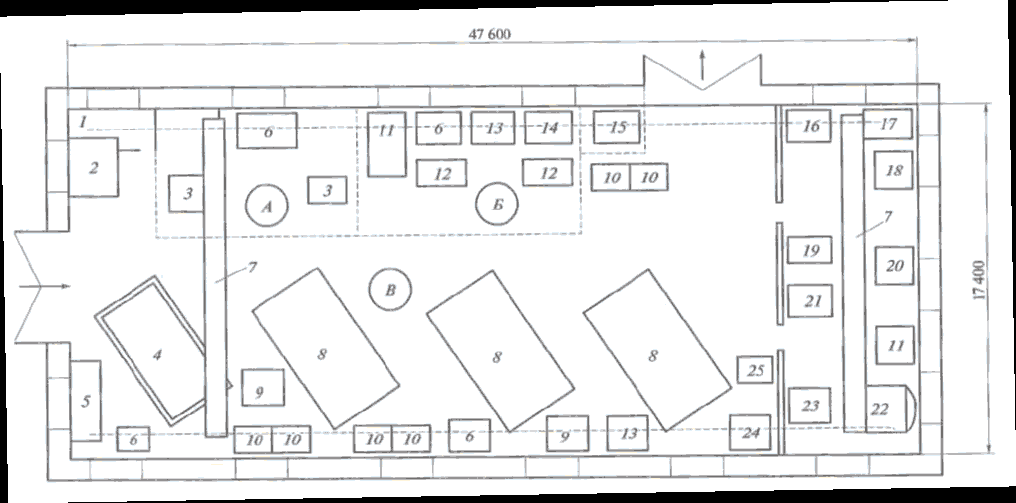
Content of the agricultural equipment maintenance operations, which are performed in the stationary points, (Figures 3 and 4) and the mobile units (Figure 5) is represented at the dia-gram (Figure 6).
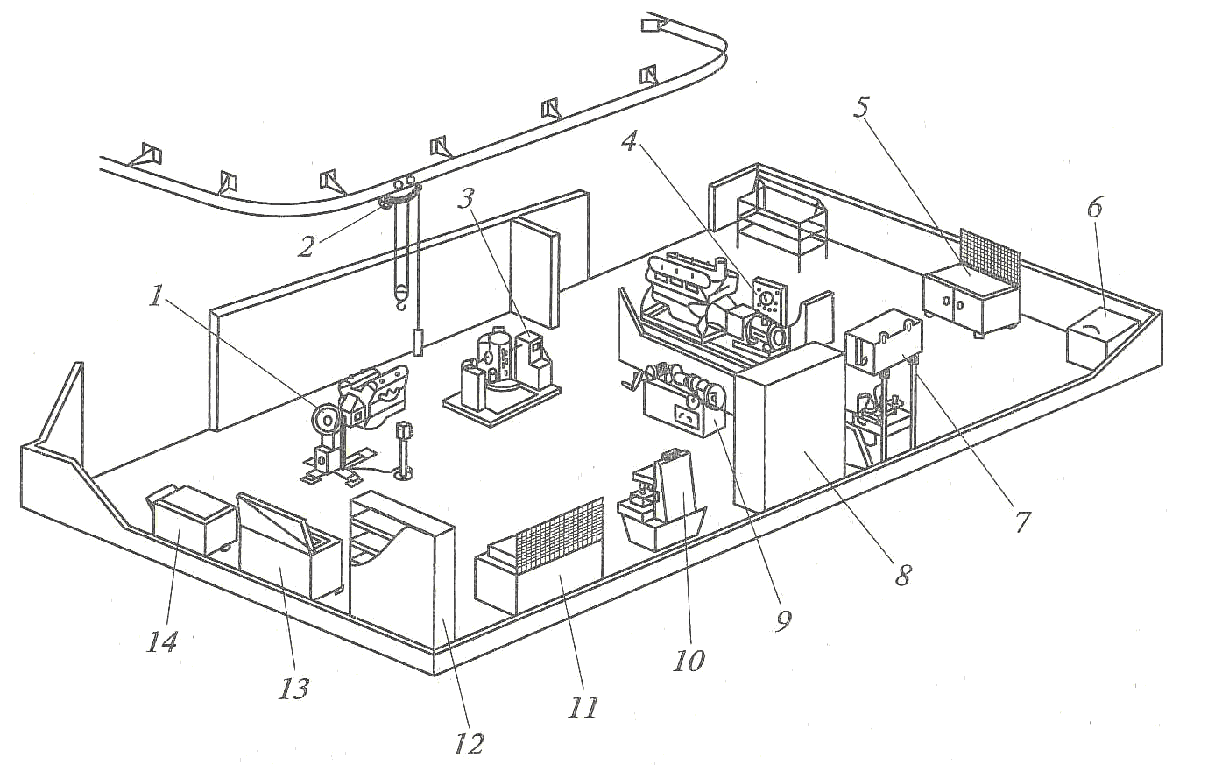
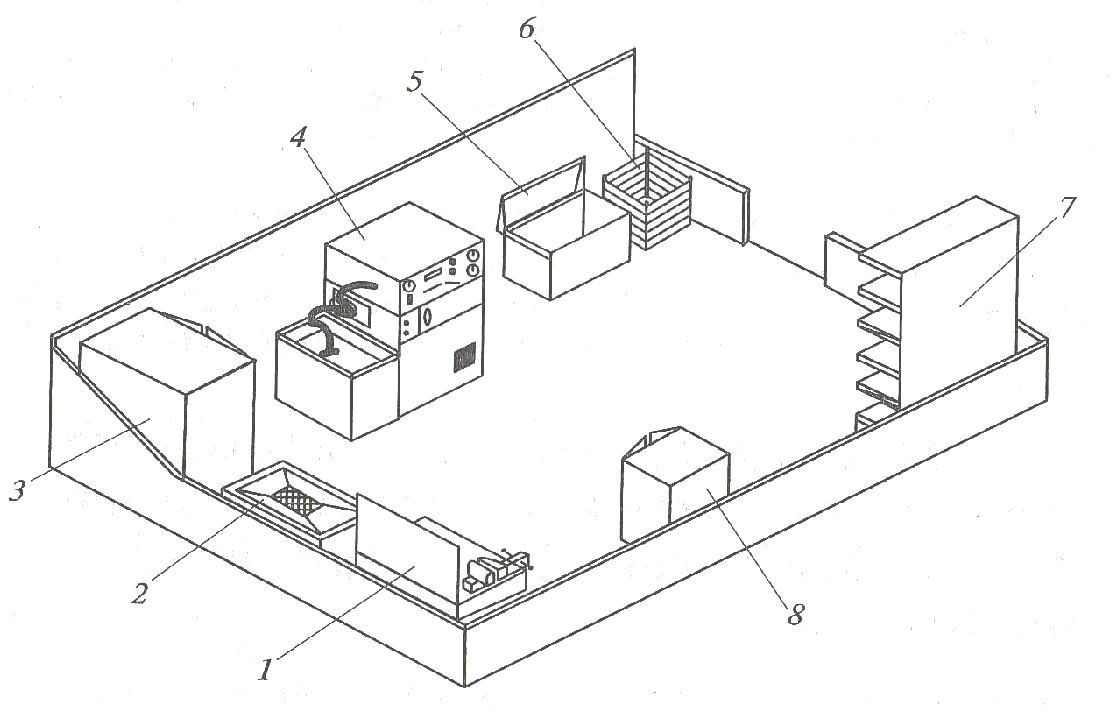
Figure 3: Layout of a Building for Maintenance and Repairs of Tractors, Trailers and Detachable Equipment
1 – diagnosis platform; 2 – tractors and trailers maintenance and repairs rooms; 3 – workbench or trolley for tools; 4 – diagnostic devices cabinet or rack; 5 – technical and engi-neering employees office; 6 – gas welding and electrical welding area; 7 – part reconditioning area; 8 – coper-canned area; 9 – diesel fuel equipment repairs area; 10 – hydraulic system units repairs area; 11 – electrical equipment repairs area; 12 – unit repairs area; 13, 14 – metalwork areas; 15 – compressor room; 16 – toilet room and wash stand; 17 – workers’ locker room; 18 – lubrication area; 19 – overhead-track hoist; 20 – rough grinding machine; 21 – hydraulic press area; 22 – washing bathtub; 23 – drilling machine; 24 – trolley jack; 25 – transmission poles for removing and putting the units
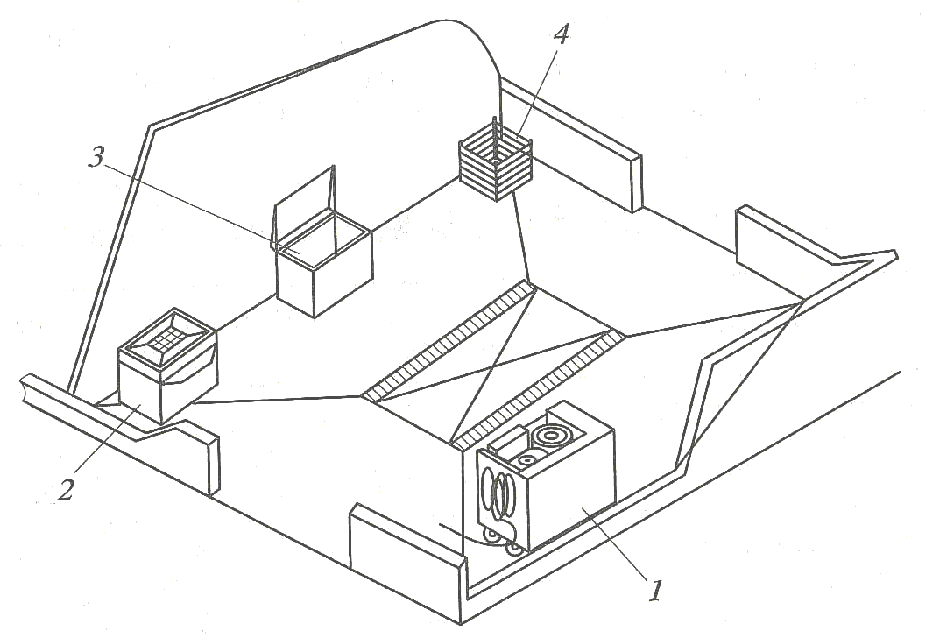
? – disassembly-assembly area; ? – engine repairs area; ? – Zone of diagnosis, mainte-nance and routine repairs of combines; 1 – workers’ locker room; 2 – technical and engineering employees office; 3 – unit disassembly and assembly stand; 4 – unit adjustment and diagnosis room; 5 – instrument cabinet-rack; 6 – metalwork and mounting table; 7 – overhead-track hoist; 8 – combine repairs and maintenance room; 9 – trolley jack; 10 – lubrication and cooling fluid change plant; 11 – pivot block workbench; 12 – engine disassembly-assembly stand; 13 – mov-able tool carriage; 14 – hydraulic press; 15 – compressor; 16 – controlling and measuring appa-ratus cabinet; 17 – upright drilling machine; 18 – part movement trolley; 19 – rack-workbench; 20 – wheel removal and installation trolley; 21 – metalwork bench; 22 – part inspection table; 23 – washing machine; 24 – mobile welding plant; 25 – rough grinding machine
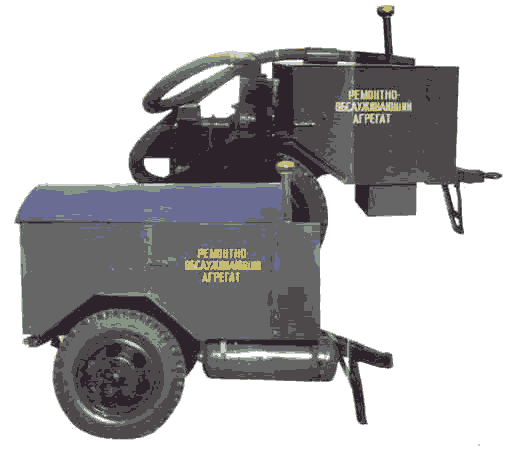
The trailed repairs-maintenance unit PROA-1 is intended for the tractor and combine maintenance in the field, and for wielding, metalwork and other operations during the equipment malfunction repair in the mobile-engineering formations. Its equipment is placed on the two-wheeled trailer frame, on the drop-side container, and it makes it possible to clean the machines, their assemblies and units with compressed air, to inflate the tyres, to perform the dismantling, installation and metalwork operations, adjustment operations, metal welding and cutting, as well as the oil products fuelling and the low-pressure gun filling (Lipkovich, 2019; Vedenyapin, 1968; Shabanov, 2018; Iofinov, 1974).
Figure 6: Diagram of Content of the Agricultural Equipment Maintenance Operations, Which are Performed on the Fixed Maintenance Points and by Means of the Mobile Maintenance Unit Proa-1
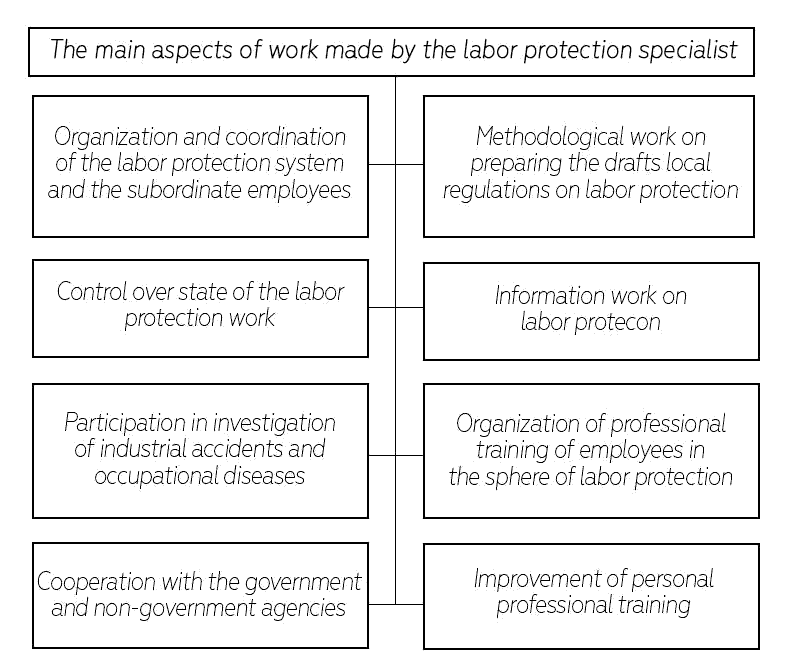
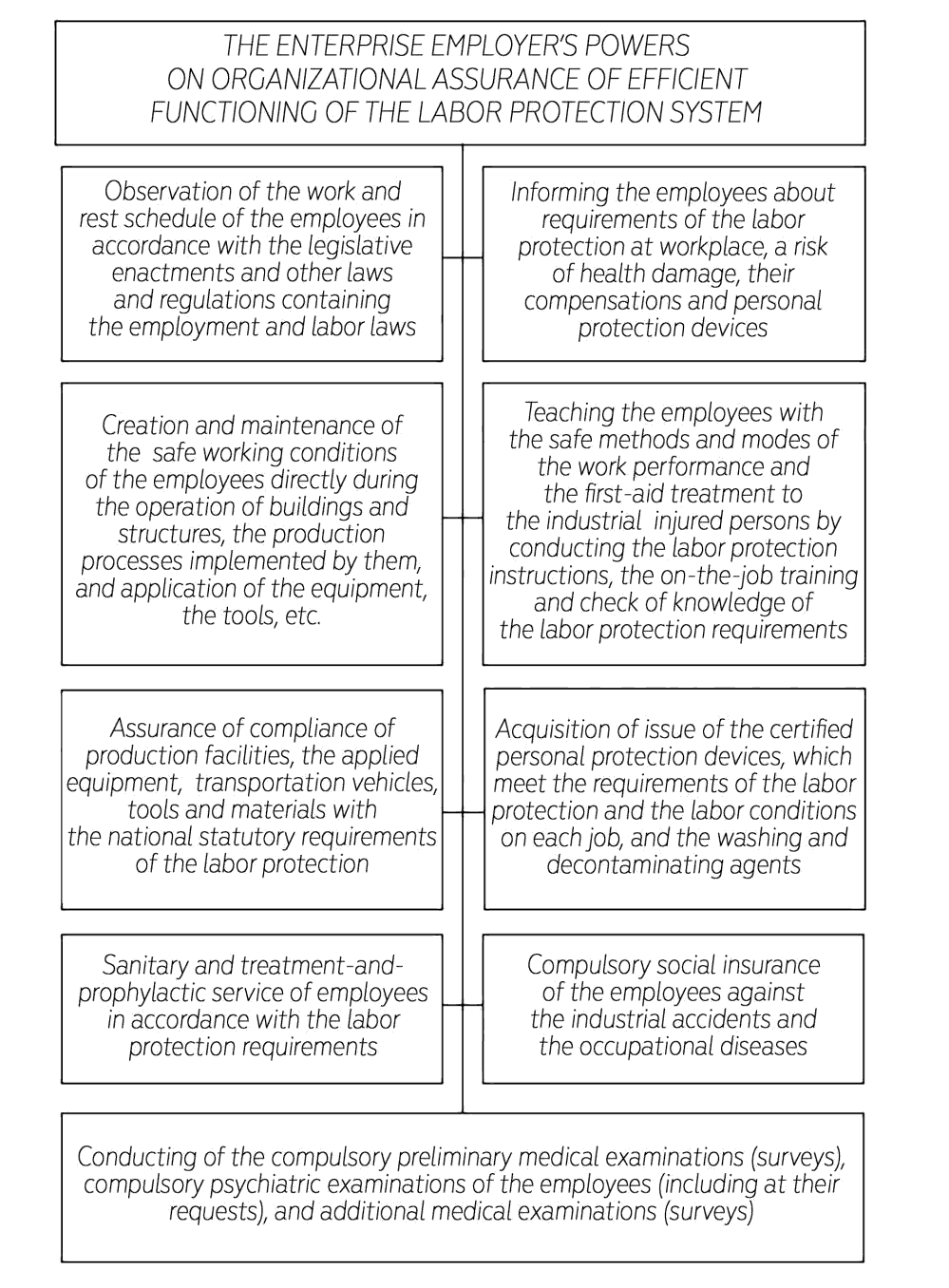
While analyzing the agricultural enterprise activities in the field of the tractors and com-bines maintenance and repairs, it is possible to see a large range of operations performed in the fixed rooms and in the field. In this connection, a problem arises, which it related to ensuring the safety of carrying out the operations, and which is expressed in a necessity of strict control ex-erted by the officials. In accordance with Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federa-tion, in order to enforce the labor safety requirements, to control their fulfillment, each employer establishes a labor safety service, or introduces a position of the labor protection specialist who is trained in an appropriate manner or has a work experience in this sphere (Iofinov, 1982). As-pects of work made by the labor protection specialist are stated in Figure 7.
Results
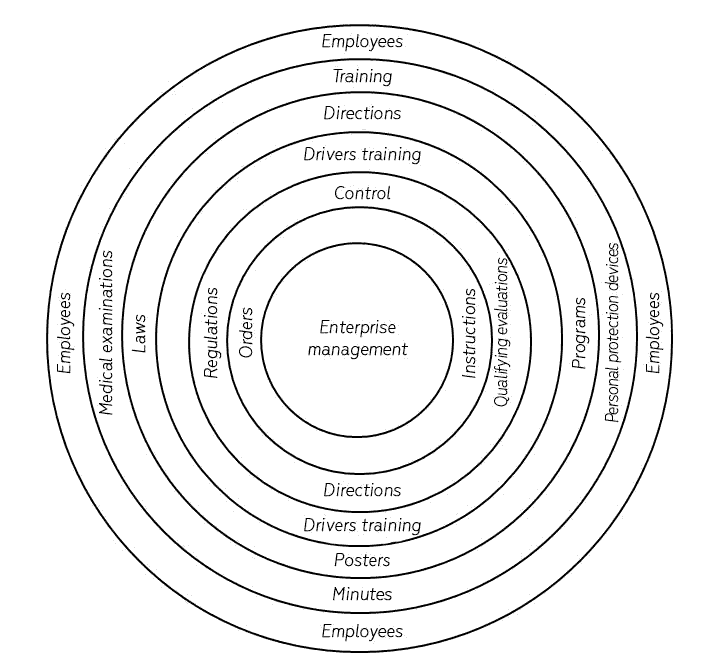
For visual clarity, let's represent a diagram of organizing the work made by the labor pro-tection specialist at an agricultural enterprise (Figure 8), where the main area is an area of or-ders, instructions and standards of the enterprise. In accordance with functions and tasks of the labor protection management, the employer determines obligations of each subdivision of the enterprise and introduces them into the job descriptions of the subdivisions managers. The em-ployer’s powers on organizing the labor protection work are stated on the diagram (Figure 9) (Sinyakov, 1971; Bekey, 1970; Lipkovich, 2017).
Figure 8: Diagram of Organizing the Work Made by the Labor Protection Specialist in An Agricultural Enterprise
At the same time, the authors consider it necessary to pay attention to the following pe-culiarity of any agricultural enterprise activities: as a rule, in the field, the majority of operations are performed at a considerable distance from populated areas, and the enterprise facilities have quite a wide geography of location, which makes a process of control over the operation safety less efficient (Caplan, 1975; Lipkovich, 2015). Apart from that, there are kinds of operations that require a permanent control over their performance safety, while a representative of the la-bor protection service cannot be at several facilities simultaneously because they are located at a distance from each other. This bolsters a role of the technical and engineering employees in su-pervisory activities over safety of works on maintenance and repairs of the combines and trac-tors. Engineering employees, who maintain and repair the agricultural equipment, follow the legislative government regulations, orders, instructions and directions by heads of the enterpris-es in the their labor protection work, they are responsible for the labor protection state in the ar-eas, which they control, and they are obliged: to ensure the employees’ health and safe labor conditions on workplaces, the fulfillment of the applicable standards, rules and regulations on the labor protection and the fire protection, directions and proposals of the supervisory agencies, the labor protection engineer; the control over ventilation, lighting and heating; to control the timely tests, engineering certification and registration of the boiler plants and other equipment, which is subject to periodical testing and examination; to suspend the work if the people’s life and health risks arise; to take part in conditioning of a janitorial state of departments, work-shops, facilities, in developing and fulfilling the comprehensive plans of improving the labor protection conditions and the sanitary measures, and relevant sections of the collective contract (agreement for special issues and labor protection); to forbid the persons, who did not reach a necessary age, who have no certificates and did not undergo the qualifying evaluations, to man-age the electro-mechanization means, boilers, pressure vessels, lifting machines and other plants and units; jointly with the chief specialists, to draw up the applications for personal protection devices.
In addition, the engineering employee, jointly with the labor protection specialist and other enterprise administration employees, organizes the maintenance and keeping of the fol-lowing documents:
In the enterprise personnel department- orders made by the head of the enterprise (Lip-kovich & Bondarenko, 2016; Lipkovich & Bondarenko, 2017):
• on labor protection and fire safety;
• on appointment of the officials responsible for check of technical conditions of the machines during their setting out on a trip or for performing the work;
• on allocating machines to tractor drivers (drivers);
• on allocating the utility facilities and territories to officials;
• on organizing the supervision over the use of measurement means;
• In the control point room:
• trip ticket forms;
• tractor trip tickets;
• tractor-driver’s registration form;
• registers:
a) Trip ticket register;
b) Machine going and returning register;
c) Occupational labor protection briefing register;
d) Automotive vehicle drivers briefing register;
e) Register of pre-trip medical examinations conducted as per instructions;
f) Automotive vehicle pre-trip technical inspection register.
• evacuation plan of tractors and combines in case of fire.
Discussion
The authors believe that one of the main obligations of the engineering employees, in terms of ensuring the personnel safety, during the tractor and combine maintenance and repairs, is layout and organization of workplaces.
The workplace layout is characterized by placement of equipment, devices, tools and other objects over area and in space in order to ensure the convenience and safety of the work performance. The main requirements for the workplace layout consist in observance of the op-timal working zone and rational placement of equipment, rigging and the labor volumes.
The rational workplace layout makes it possible to remove the losses of working time on superfluous movements during the work, which increases labor productivity.
The rational sizes of the workplace area are determined by a possibility of convenient and safe work performance. A work objects quantity in the workplace must not exceed the shift demand.
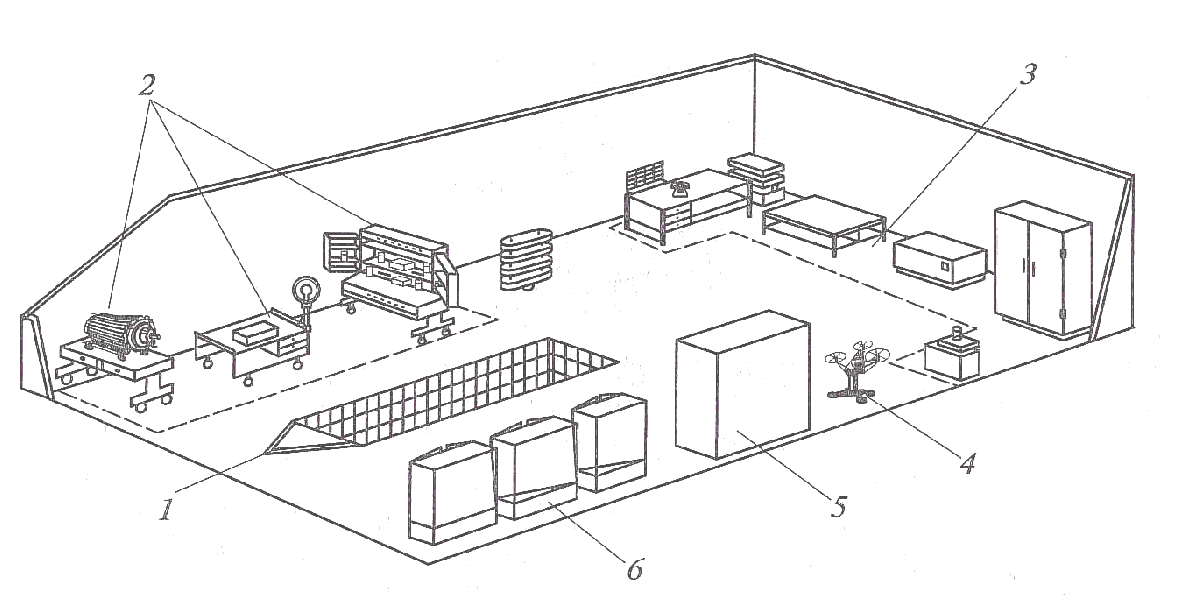
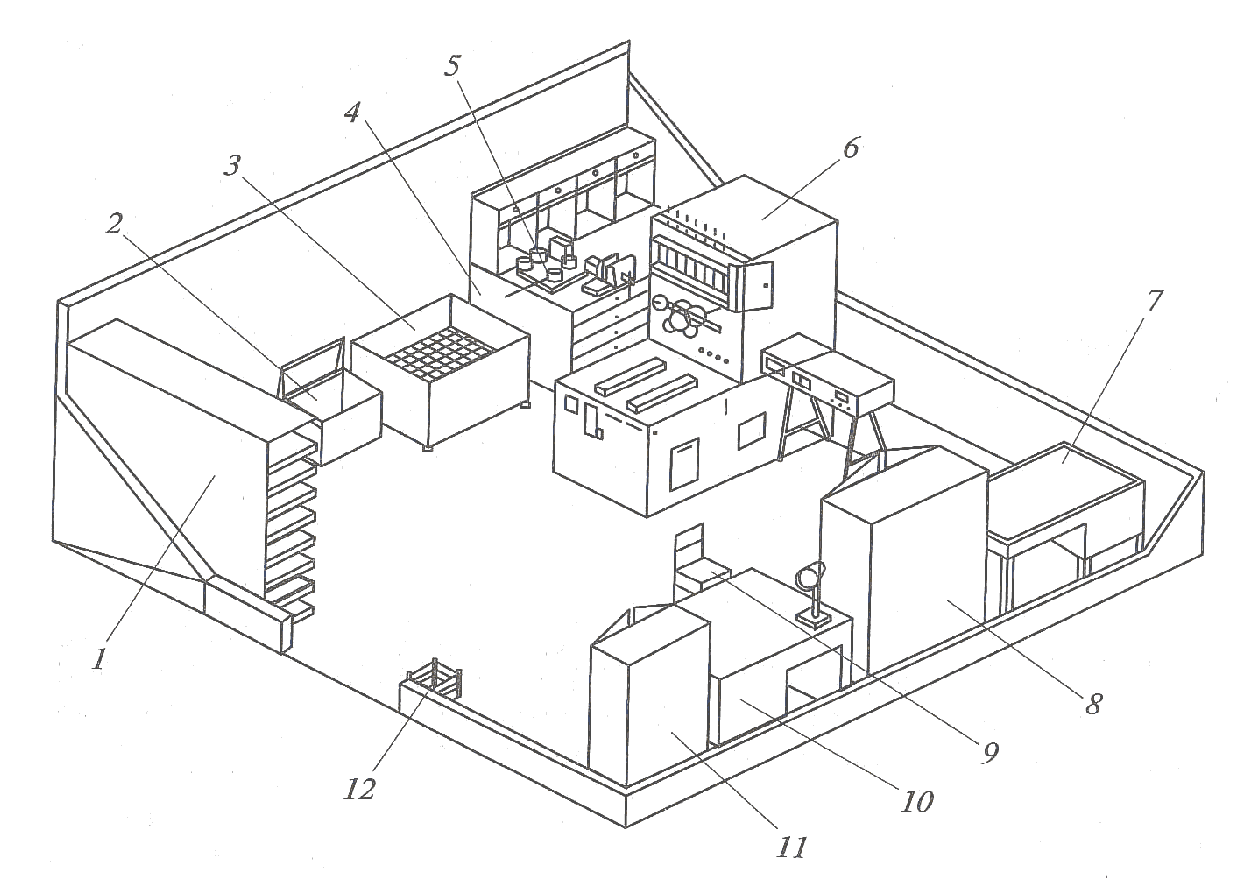
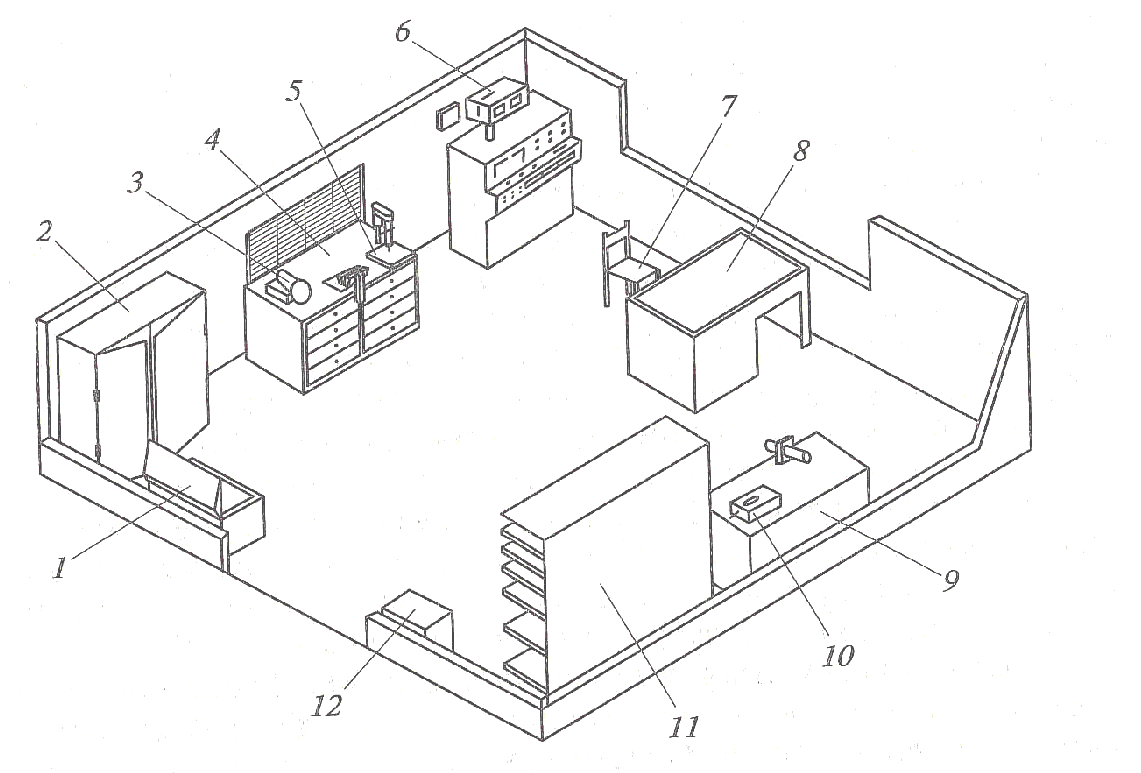
Let’s give examples of layout of some workplaces (areas) of buildings for repairs and maintenance of the tractors and combines (Figure 10-15) (Lipkovich, 2015; Sinyakov, 1991).
1 – inspection pit; 2 –fixed set of diagnostic tools; 3 – the fixer’s rigging set; 4 – electri-cal lubricant injector S-321 ?; 5 – parts rack; 6 – plants for lubricating and filling the machines, collecting the waste oils and filling with transmission oils
1 – universal stand for disassembly-assembly of diesel engines OPR-5557; 2 – electric hoist TE-200-5211; 3 – stand for disassembly-assembly of V- parts KI-5500; 4 – breaking-in and brake stand KI-5543?; 5 – workbench for a workplace ORG-1468-05320; 6 – sand box; 7 – weighing device for a stand; 8 – rack ORG-1468-05320; 9 – valve grinding stand R-186; 10 – valve setting device ?-177; 11 – workbench ORG-5365 with controlling plate; 12 – rack ORG-1468-05320; 13 – movable washing bathtub ??-1316; 14 – hydroficated rigging for engines routine repairs 70-7823-3709
1 – rack for repair stock and finished products ORG-1468-05-230?; 2 – hopper for wip-ing material ORG-5133; 3 – washing bathtub ??-5365; 4 – metalwork bench ORG-5365; 5 – instrument for testing and adjustment of fuel equipment KI-15706; 6 – stand for testing and ad-justment of fuel equipment KI-15711?; 7 – atomizer processing table; 8 – rigging storage rack ORG-1468-05-230?; 9 – chair; 10 – executive desk; 11 – clothes locker; 12 – sand box
1– metalwork bench for a workplace ORG-1468-01-060; 2 – movable washing bathtub ??-1316; 3 – rigging set for current repairs of hydraulic units ORG-12510; 4 – stand for testing of the hydraulic drive units KI-4815?; 5 – hopper for wiping material ORG 5133; 6 – sand box; 7 – rack for units and assemblies ORG1468-05-230?; 8 – tool cupboard
1 – cleaning and washing area; 2 – movable washing bathtub ??-1316; 3 – hopper for wiping materials ORG-5133; 4 – sand box ORG-5139
1 – hopper for wiping materials; 2 – cabinet for tools and mounting facilities; 3 – bench tool-grinding machine 3?631; 4 – metalwork bench ?RG-5365; 5 – bench drilling machine R-105 or 2?112; 6 – stand for check and adjustment of motor-and-tractor electrical equipment KI-968; 7 – chair; 8 – one-drawer executive desk; 9 – metalwork bench ORG-5101; 10 – set of in-struments for checking and cleaning the sparking plugs E-203; 11 – unit storage rack; 12 – sand box
Conclusion
Thus, one can note that the technical and engineering employees, who organize the trac-tors and combines repairs and maintenance, must fulfill their professional duties honestly and in a competent manner, but they must also have a correct world-view in the sphere of the labor protection, its organization and promotion, and be ready to partially fulfill the duties of a labor protection specialist, considering a specific character of the agricultural enterprise activities, as noted above. Thus, the agricultural complex system must have the employees who have a good command of methods and means of keeping the machines in good repair, techniques of diagno-sis, maintenance and repairs, storage of machines, reconditioning and strengthening of parts, and who know the necessary rules and regulations on the labor protection, who know the methods of training the personnel with safe modes of the work performance, who are able to choose, operate and maintain the lighting, ventilation and heating systems of production rooms, who organize the work on fire safety on agricultural facilities, etc.
References
- Lipkovich, I.E., Egorova, I.V., Petrenko, N.V., & Gayda, A.S. (2019). Influence of the Human-Machine Systems (HMS) operation mode on the increase of grain-harvesting aggregates productivity. Journal of mechanical engineering research and developments, 3, 10-14.
- Lipkovich, I.E., Egorova, I.V., & Petrenko, N.V. (2020). Assessment characteristics of some parameters of labor conditions of the self-propelled agricultural machines operators. Bulletin of agricultural science of Don: journal, 1(49), 72-81.
- Lipkovich, I.E., Egorova, I.V., & Petrenko, N.V. (2019). Endurability of work of the man-machine systems opera-tor, as a characteristic property of labor conditions. Bulletin of agricultural science of Don: journal, 1(45), 91-98.
- Vedenyapin, G.V. (1968). Operation of machine and tractor fleet.
- Ageev, L.?. (1978). Fundamentals of calculation of optimal and permissible operating modes of machine and trac-tor units.
- Lipkovich, I.E., Egorova, I.V., Petrenko, N.V., Sergeev, N.V., & Pyatikopov, S.M. (2019). Traffic safety funda-mentals of track-type tractors on the on-farm roads of agricultural enterprises. Asia life sciences: journal, 1, 205-228.
- Lipkovich, I.E. (2016). Influence of external environment upon a human operator managing the agricultural unit via a man-machine system. Bulletin of agricultural science of Don: journal, 3(35), 86-92.
- Anasica, S., & Sweta, B. (2020). Analysing the factors involved in risk management in a business. International Journal of New Practices in Management and Engineering, 9(03), 05-10.
- Drincha, V.?. (2002). Development of agrien-gineering science and prospects of agri-technologies
- Shabanov, N.I., Lipkovich, I.E., Petrenko, N.V., Pyatikopov, S.M., Pikalov, ?.V., Egorova, I.V., & Gayda, A.S. (2018). Ergonomics and psychophysiological fundamentals of labor safety in the agri-engineering sphere: monograph. Azov-Black-Sea Engineering Institute of Don State Agrarian University in Zernograd, 265.
- Iofinov S.?. Operation of machine and tractor fleet. - ?.: Kolos, 1974.[ Iofinov S.?. Ekspluatatsia mashinno-traktornogo parka. - ?.: Kolos, 1974.] ??????? ?.?. ???????????? ???????-??????????? ?????. - ?.: ?????, 1974.
- Iofinov S.?. Fundamentals of operation of machine and tractor fleet. - ?.: Kolos, 1982.[Iofinov S.?. Osnovy teknicheskoi ekspluatatsii mashinno-traktornogo parka. - ?.: Kolos, 1982.] ??????? ?.?. ?????? ??????????? ???????????? ???????-??????????? ?????. - ?.: ?????, 1982.
- Sinyakov, V.?. (1991). Assessment of labor conditions of the tractor operators. Tractors and agricultural machines. 10.
- Bekey, G.A. (1970). The human operator in control systems ? De Green K.B., Systems psychology.New York: Mc Graw. Hill.
- Caplan, R.D. (1975). Job demands and worker health. Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- Lipkovich, E.I., Bondarenko, A.M., & Lipkovich, I.E. (2016). Ecological balance of technogenic processes and tractors of fifth generation. Research journal of pharmaceutical, biological and chemical sciences: journal 7(3), 751-760.
- Lipkovich, E.I., Bondarenko, A.M., & Lipkovich, I.E. (2017). Distribution of masses and technological schemes of agricultural combines. Journal of industrial pollution control: journal, 33(1), 1163-1170.
- Lipkovich, I.E., Egorova, I.V., & Pikalov, ?.V. (2015). Activities of a labor protection engineer at the automobile transport enterprises. Freight and passenger motor transport establishment, 9, 36-42.
- Sinyakov, V.?. (1991). Assessment of labor conditions of tractor operators. Tractors and agricultural machines, 10.
- Lomov, B.F. (1967). A man in management systems. Knowledge.