Research Article: 2023 Vol: 27 Issue: 5
Municipal Solid Waste Management: A Futuristic Research Direction using Bibliometric Analysis
Surjit Kumar Kar, ICFAI Business School, Hyderabad
Debasmita Panigrahi, IMIS B School, Bhubaneswar
Harshita Kulla, ICFAI Business School, Hyderabad
Ambika Singh, ICFAI Business School, Hyderabad
Shilpa Samanta, ICFAI Business School, Hyderabad
Citation Information: Kar, Surjit K., Panigrahi, D., Kulla, H., Singh, A., & Samanta, S. (2023). Municipal solid waste management: a bibliometric analysis concerning marketing & sustainability. Academy of Marketing
Studies Journal, 27(5), 1-8.
Abstract
With sustainability in business marketing being the new buzz word, diverse research has been going on across various domains, to make processes environment friendly. The movement towards greener lifestyles requires everyone to be socially conscious and contribute to the environmental, social and governance framework, to create a sustainable environment. Among these everyday issues, municipal waste management has been one of the significant areas that is critical to add value in this search for a greener world. In this study, bibliometric analysis of the literature related to municipal solid waste management across the world, was performed using the visualisation tool, the VOSviewer. Meaningful and relevant collection of literature was sourced from the Scopus database, to obtain network and density visualisation, in addition to word cloud and graphs citing publications. Based on the research, results suggested that the importance and publication around these topics have been following an increasing trend, except in 2022, where researchers diverted to the study about the pandemic significantly. Hence, the conclusion of this study reveals potential research scope and future research direction, on a similar topic in which demanding sustainable value could be added. Amongst keywords, “sustainable development” remained the most occurred, followed by “climate change”. “Solid waste management”, however, had less frequency of occurrence in comparison to the former.
Keywords
Sustainable, Development, Climate Change Solid Waste Management, Environment, Green Marketing.
Introduction
Municipal solid waste is defined as commercial and domestic waste generated in municipal or notified areas in either solid or semi-solid form, excluding industrial hazardous waste but including treated bio-medical waste. Municipal solid waste (MSW) generation is increasing globally as a result of rapid population growth, increased economic development and industrialization, urbanisation, and rising consumerism in society Gupta et al. (2015).
Municipal solid waste has a complicated composition and is typically generated by households and commercial enterprises. Municipal solid waste includes various types of paper, bottles, plastics, garden waste, discarded foods, furniture, clothing, appliances, and even batteries. To reduce the negative and harmful nature of this waste stream, it is critical to effectively manage it from its origin to the point of final disposal, treatment, or recycling. MSW is a complex procedure that includes numerous steps such as waste collection routes, temporary storage points, waste treatment, disposal, energy recovery strategies, and recycling, with the primary goal of improving environmental protection, public health, and the need to comply with local government regulatory requirements. Effective solid waste management is also one of the issues that are relevant in meeting the targets for the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 11, which involves working to achieve sustainable cities and communities Korman et al. (2021).
Taking the critical issue of MSW into account, many studies and research are being conducted on the sustainable development of MSW. To keep track of the geographical distribution of MSWM knowledge generation and research trends, a bibliometric analysis of existing knowledge on MSWM globally was conducted Mao et al. (2020).
A bibliometric analysis is a quantitative examination of metadata from various written sources in order to assess the interdependence and impact of publications within a specific field of study. In this case, bibliometric analysis was the most useful tool for analysing the future trends of MSWM research Maphosa (2020).
Methodology
Data Extraction: The bibliometric analysis in this study was derived from data in the Scopus database. This database's data was extracted using the MSWM keyword. Authors, Title, Year, Source title, Volume, Issue, Cited by, Document Type, Publication Stage, Open Access, Source, ID were all considered in the search. However, some filters were used to limit the results to articles written in English and from the Arts, Humanities, and Management disciplines Marinello (2020).
Data Processing: After exporting the data in comma-separated values (CSV) format. VOSviewer was then used to investigate it. VOSviewer is well-known for its high-quality visualisation capabilities as well as its ease of use.
Data Analysis: The number of authors and the co-occurrence of keywords were two of the parameters examined by VOSviewer Minghua et al. (2009).
Limitations: The current study focused on peer-reviewed articles and book chapters from the Scopus database. Some important literature from conference papers and technical papers may have been overlooked. Other authors who conducted bibliometric analysis have also reported on this.
Results
Bibliometric Analysis of the Co-Authorship
A total of 504 authors have participated in the publication of the solid waste management papers. Among which we have identified. A total of 159 authors worldwide have contributed about scientific articles with a focus on Municipal solid waste management and others are on sustainability and risk management. The number of articles, authors with the most publications, countries that lead in scientific production, and keyword co-occurrence were among the parameters examined by VOS viewer Nanda & Berruti (2021).
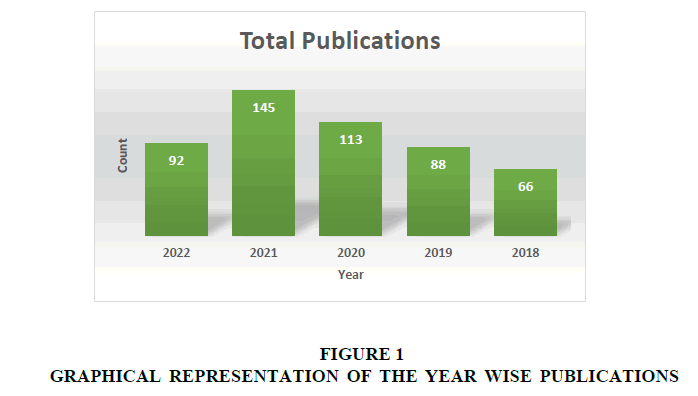
The year wise publications are depicted in the table (Table 1) and are shown in the clustered graph (Figure 1). This trend may be attributed to the rapidly growing importance of MSWM challenges that many countries are facing Rajkumar & Ahmad (2016).
| Table 1 Number Of Publications Per Year |
|
|---|---|
| Year Wise | Total Publications |
| 2022 | 92 |
| 2021 | 145 |
| 2020 | 113 |
| 2019 | 88 |
| 2018 | 66 |
The estimated growth is identified based on a time series analysis statistical application and will be expected in solid waste management research publications in the year 2025 is around 720 and in the year 2030 is around 820 Vergar & Tchobanoglous (2012).
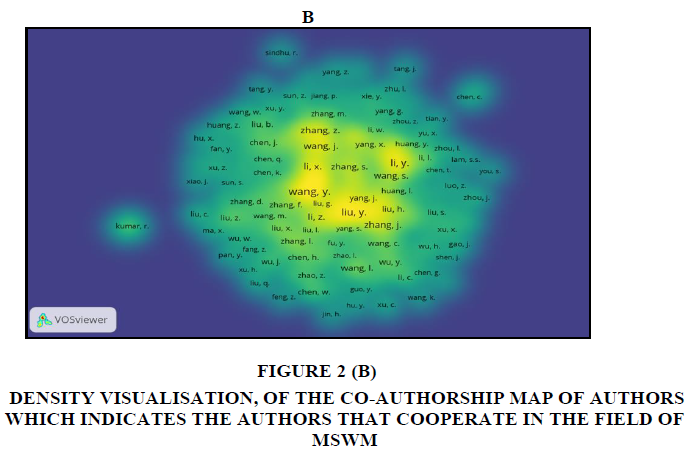
The clusters in the output obtained from VOSviewer (Figure 2A, 2B) shows that t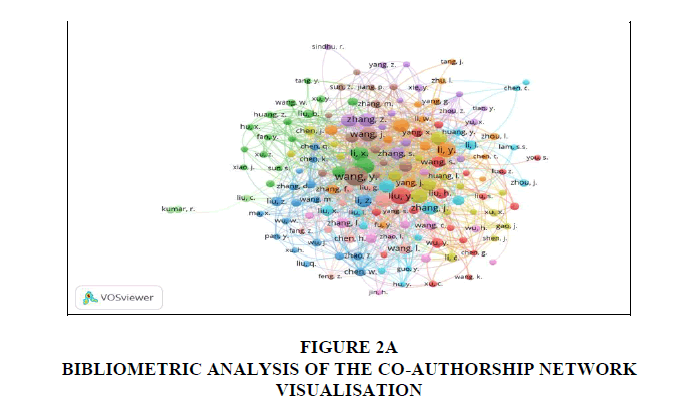 he author Wang, y has major papers published focusing on the sustainable development and Solid waste management.
he author Wang, y has major papers published focusing on the sustainable development and Solid waste management.
Figure 2a: Bibliometric Analysis Of The Co-Authorship Network Visualisation.
Figure 2b: Density Visualisation, Of The Co-Authorship Map Of Authors Which Indicates The Authors That Cooperate In The Field Of Mswm.
A search of the domestic and international literature reveals that few organizations have published related papers.
The clusters shows that highly cited top 20 solid waste management research publications during the selected 5-year study period. Furthermore, some of the local universities are researching the characterization, recovery, and recycling potential of solid waste.
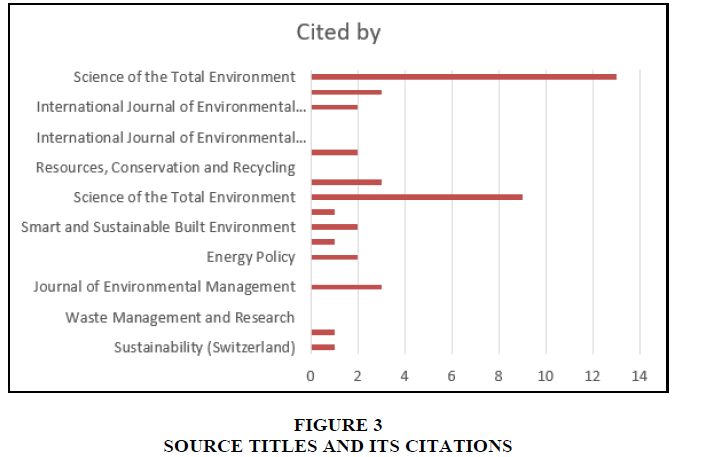
The source titles have been taken into consideration for research and the citations made were in between 4-14. The graph (Figure 3) is for the year 2022 and the title science of the total environment has the highest citation in solid waste journal papers.
Bibliometric Analysis of the Keywords
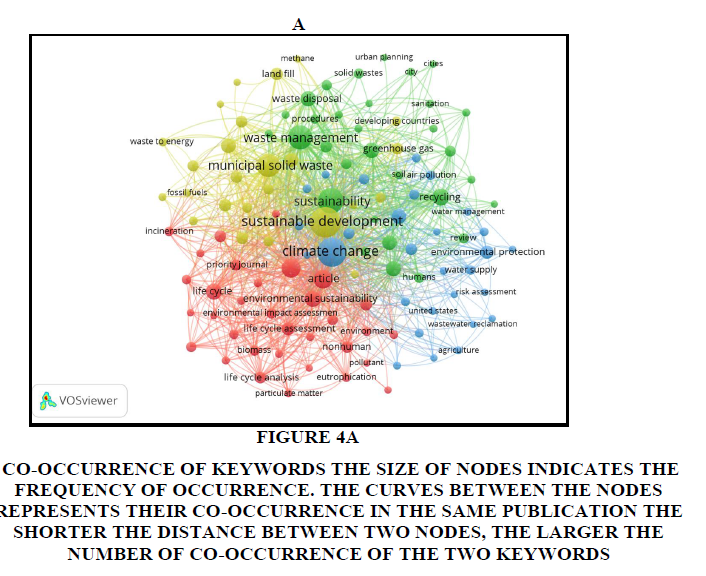
Keywords provided by authors of the paper, as well as the index keywords that occurred for more than 5 times in the fetched Scopus database file, were enrolled in the final analysis. Of the 2,095 keywords, 118 met the threshold. The keywords that appeared most were “sustainable development” (total link strength 1,161) and “climate change” (total link strength 1,094) which had a strong link to “sustainability” and “municipal solid waste” (Figure 4A). For the primary keyword, “solid waste” and “solid waste management” the total link strength was more than 350, touching 400. “Urban planning” and “groundwater” were the keywords with the least link strength of 29 and 43 respectively.
Figure 4a: Co-Occurrence Of Keywords The Size Of Nodes Indicates The Frequency Of Occurrence. The Curves Between The Nodes Represents Their Co-Occurrence In The Same Publication The Shorter The Distance Between Two Nodes, The Larger The Number Of Co-Occurrence Of The Two Keywords.
The unit of analysis was ‘all keywords’ inclusive of Author Keywords, as well as Index Keywords. In addition, the type of analysis picked was co-occurrence, which defines the relatedness of items based on the number of documents in which they occur together. Each co-occurrence link has the same weight, due to which the full counting method has been chosen. For each of the 118 keywords, the total strength of co-occurrence links with other keywords was calculated.
A word cloud was also created to show the frequency of the keywords, having the total link strength of more than 200, that occurred for more than 12 times. It was indicated that “sustainable development” was the most frequent followed by “climate change” and “sustainability” (Figure 4B).
Figure 4b:Word Cloud 28 Keywords Which Occurred For More Than 12 Times Were Enrolled. The Font Size Represents The Frequency Of Occurrence. Keywords Such As “Sustainable Development”, “Climate Change” And “Sustainability” Occurred Most Common “Greenhouse Effect” And “Landfill” Are Rare.
Conclusion
This paper performed a bibliometric analysis of the available scientific literature on Municipal solid waste management on a global scale, using data from the Scopus database. With such analysis, it was possible to identify existing patterns and trends in solid waste management research while revealing similarities and differences on a global scale. WTE technologies, sustainable development, risk management, and life-cycle assessment were among the keywords used in the research clusters worldwide.
During the overall 5-year study period, the contribution of solid waste management research publications from the SCOPUS database has been increasing and decreasing, and this study was completed using various bibliometric tools. According to this study, more than 88% of research publications have multiple authors. The majority of research is done in collaboration between various authors, institutions, and countries. In the future, many more research activities in the field of solid waste management research will be developed by research scholars, scientists, and research institutes in order to save the environment from pollution.
Acknowledgement
"Note: This research article is a working paper series from the project funded by The Research Committee, IFHE- A Deemed to be University u/s 3 of The UGC Act, 1956 (NAAC A++), Donthanapally, Shankarpally Road, Hyderabad - 501 203, Telangana, India."
References
Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V. (2015) A review on current status of municipal solid waste management in India. J. Environ Sci. 37, 206–217.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Korman?áková, M.; Remešová, M.; Vanc?ová, T. (2021) Food waste in municipal mixed waste produced at household level: Empirical evidence from the Czech Republic. J. Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23, 1348–1364.World Bank.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Mao, G.; Hu, H.; Liu, X.; Crittenden, J.; Huang, N. (2020) A Bibliometric Analysis of Industrial Wastewater Treatments from 1998 to 2019. Environ Pollut, 275, 115785.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Maphosa, V.; Maphosa, M. (2020) E-waste management in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic literature review. Cogent Bus. Manag. 7, 1814503.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Marinello, F. (2020) Bibliometric Analysis of Trends in Biomass for Bioenergy Research. Energies 13, 3714.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Minghua, Z.; Xiumin, F.; Rovetta, A.; Qichang, H.; Vicentini, F.; Bingkai, L.; Giusti, A.; Yi, L. (2009) Municipal solid waste management in Pudong New Area, China. Waste Manag, 29, 1227–1233.
Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. (2021) Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 1433–1456.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Rajkumar, J.; Ahmed, S. (2016) Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: A review. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2, 1139434.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Vergara, S.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. (2012) Municipal Solid Waste and the Environment: A Global Perspective. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 37, 277–309.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 11-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13465; Editor assigned: 12-Apr-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-13465(PQ); Reviewed: 08-May-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-13465; Revised: 20-Jun-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-13465(R); Published: 22-Jul-2023