Research Article: 2019 Vol: 18 Issue: 2
Motivational Monitoring as a Component of Effective Human Resource (HR) Strategy of Company
Valeriy Nykyforenko, Odessa National University of Economics
Vira Kravchenko, Odessa National University of Economics
Tetiana Zbrytska, Odessa National University of Economics
Marina Kryvtsova, Odessa National University of Economics
Liliya Svorobovich, Odessa National University of Economics
Abstract
The approach to Human Resource (HR) management has been justified based on the change of motivational stimulations during the staff life cycle. It makes possible to analyze employee activity on the basis of related functions and to increase economic behavior in accordance with value orientations, expectations for ensuring an increase in the level of productivity. It has been proved that motivation monitoring is a key aspect of building HR strategy of company. According to the results of the expert analysis, maps of motivators and demotivators have been built, on the basis of which the motivational profile of the workers has been constructed. The remedial measures have been determined in order to prevent the reasons for HR demotivation on the basis of selection of influence groups onto internal motivation with the appropriate means of stimulation, namely material, organizational, professional and social one.
Keywords
Map of Motivators, Human Resource (HR) Strategy, Competitive Advantages, Motivational Profile, Human Capital.
JEL Classifications
M5, Q2.
Introduction
Matters of particular importance are emphasized by the issues of comprehensive HR development as the implementer of administrative initiatives in the practical activity of the enterprise. Especially, they are expressed in the current context of development of economic relations, characterized by growing influence of globalization processes in all terms of the enterprise activity, increasing role of social responsibility of management and permanent updating of approaches to management. Existing approaches and HR management tools are aimed at solving current tasks. Under such conditions, the urgency of the tasks for the formation of a reasonable and effective HR strategy is increased. This ensures the direction of management activity to create sustainable competitive advantages and achieve the efficiency of management in the long run.
The purpose of the work is to substantiate the theoretical and methodological approaches and the development of scientific and practical recommendations on the formation of an economic incentive mechanism for enterprise personnel. In order to achieve this purpose the following tasks were set and solved in the paper: to substantiate the personnel management system using general scientific approaches; to improve the conceptual model of personnel incentives; to analyze the economic incentive mechanism for the personnel of enterprises, to determine its structure and fields for improvement; to predict the impact of personnel incentives on labor productivity; to make deeper the scientific and methodological approach to assessing the effectiveness of the implementation of the economic incentive mechanism for personnel.
Literature Review
All scientists and practitioners point out the exclusiveness of the HR role, its special nature due to the presence of psychological and social aspects that are not inherent in other resources and capital types of the enterprise. Such a special HR role and its specific nature leads to the complication of its management, high uncertainty in the decision-making process, which, according to the authors, leads to a variety of approaches to the determination of the essence of the HR strategy and its place in the strategic set of the enterprise.
As a result, there are some differences regarding the place and role of HR strategy in the enterprise management system.
According to the HR strategic positioning regarding general corporate strategic guidelines, it is possible (Dong & Ibrahim, 2017) to conditionally divide into three groups: the concept of strategic subordination, the concept of strategic dominance, and the concept of strategic parity.
In turn, Lakshman et al. (2017) distinguish offensive, offensive-defensive (stabilization strategy), and defensive (survival strategy) groups.
Distinguish the following varieties of HR strategies in accordance with the corporate strategy of functioning as an orientation towards attracting and securing large-scale middle-level professionals; orientation towards the narrow specialization HR and the highest qualification HR; orientation towards the narrow specialization HR; and according to development strategies.
Onyeukwu & Ekere (2018) defines the types of HR strategy according to the dynamics of enterprise targets (development strategy, functional strategy, reduction strategy), depending on the type of competitive strategy (innovative, quality-oriented, reduction-oriented costs), according to the overall strategy (entrepreneurial, of dynamic growth, of profitability, liquidation and cyclical).
But in our opinion, the analysis of the influence of key destructive and demotivating factors on the activities of enterprises should take a priority in the development of the HR strategy (Nykyforenko, 2016). The establishment of these factors can be obtained through interviews, surveys, anonymous questionnaires of employees, boxes of offers and wishes, etc.
Methodology
In the process of study, general scientific and special methods of scientific knowledge were used, namely: critical analysis, scientific abstraction and generalization of the scientific experience of modern theoretical studies; analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction, system analysis (in order to study the theoretical aspects of the economic mechanism for providing incentives for the personnel of enterprises); qualimetric assessment and expert method (to assess the effectiveness of personnel incentives).
In order to assess the factors that primarily affect the HR incentive, taking into account the criterion for cost minimization, the maps of motivators are used. The maps of motivators are based on such well-known techniques described in the works:
1. S.T.A.R. technique (Situation, Task, Action, Result), based on building open questions that provide information on how the situation faced by an employee in the performance of his duties (Herzberg, 2017).
2. A case interview based on the development of certain situations, after which the candidate is asked to describe the model of his behavior or the solution of a particular situation (Korlén et al., 2018).
3. Projective techniques in interviews, the essence of which is that the questions are constructed in such a way as to offer the candidate an estimate not himself but a character (Leon, 2018).
4. Testing provides information on the definition of labor motivation: instrumental, professional, economic, patriotic and lumpenized types (Rocha & Brymer, 2017).
In order to identify behavioral models, there is a technique of asking questions. The STAR questioning technique is built on 4 components: Situation (Give an example of the situation in which you...), Target (What was the purpose for which you did it?), Actions (What did you do? Resources), Results (What result did you get? What has changed?). The questions are aimed at understanding how and with what result the candidate displayed this or that competence (interpersonal skills, leadership, ability to motivate, work in a team, responsibility, etc.)
Results And Discussion
Hence, we get a number of motivators, which the candidate states. These are most often referred to as: material incentives, social security after completion of work, career prospects, job evaluation-that is, material, social, professional and organizational incentives. The map of motivators is based on questions. The most important thing when applying this technique is to recognize the current motivator for all the answers received.
Both managerial and industrial-productive HR of enterprise PJSC Farlep Invest (Kyiv, Ukraine) participated in the projective express survey. PJSC Farlep Invest is one of the leaders in the field of wire telecommunications, the size of the authorized capital at the end of 2018 is 30.5 million dollars. The HR number is 4000 people, that is, the company is large according to the criteria of the types of economic entity. This makes it possible to implement the proposed methodology for assessing HR incentives.
In total, 600 questionnaires were received (7.1% of the work force). In this case, the scale was used, namely from 1 to 10 points, where 10 points is a maximum result.
According to the results of the survey, a map of motivators has been constructed, in which the rank and the main motivator are determined, namely the most important factor of HR stimulation. In order to achieve maximum results, it is a prerequisite to create an individual motivation model for each enterprise and specific unit.
This may lead to the following consequences: the negative attitude of the staff to the management and the enterprise as a whole in the event of problems, the employee’s refusal to participate in informal meetings, indicating the emotional disunity in the team; the next step may be an open protest, namely a reluctance to perform duties, covert sabotage, negative perception by employees of changes in the activities of the enterprise. Also, the reason for HR demotivation is “willingness to do their own business” (6.7% of the respondents). These are employees under the age of 35 who believe that the best work is “work for them” and feel insufficient selfrealization at the enterprise.
Self-triggering of demotivators often occurs in the absence of a clear link between the outcome of work and the opportunities for professional growth in the team.
After constructing the maps of motivators and demotivators, one can build a worker’s motivational profile. In this case, the significance of the factor of motivation is determined by the results of the study of the maps of motivators, and the degree of satisfaction of needs is determined by the results of the study of maps of demotivators. The qualitative values of the factors of motivation at PJSC Farlep Invest are listed in the Table 1.
| Table 1: Qualitative Significance Of Factors Of Motivation And Their Satisfaction | ||||
| Factor of Motivation | Number of Factor | Significance of Factor | Degree of Satisfaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before the implementation of HR strategy | After the implementation of HR strategy | |||
| High level of wages | 1 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| Material remuneration, allowances, additional payments | 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Medical and social insurance | 3 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Non-state pension insurance | 4 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.7 |
| Granting loans for housing | 5 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Staff development | 6 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Internship abroad | 7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Provision of social privileges and guarantees | 8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Promotion | 9 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Paying for results | 10 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Working conditions | 11 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Self-realization, stability | 12 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Microclimate in the team | 13 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Authorization | 14 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Social contacts | 15 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Interesting job | 16 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Penalties for non-fulfillment of the production plan | 17 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
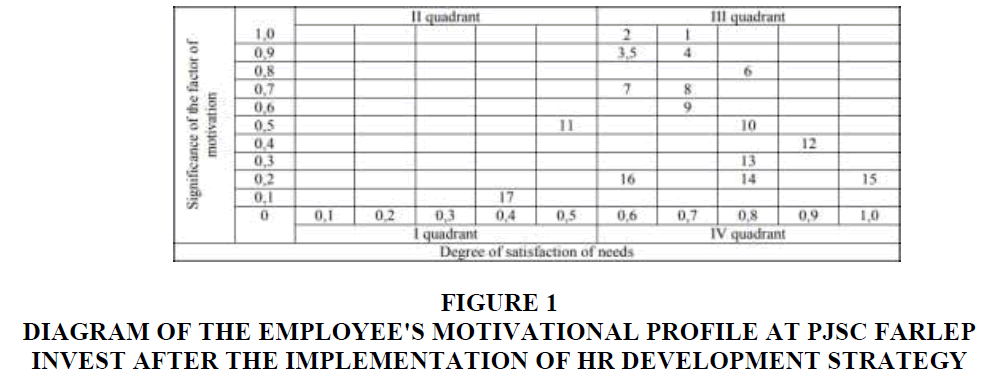
In order to improve the system of HR incentives at PJSC Farlep Invest, it is necessary to pay attention to the factors located in the quadrant I-“High level of wages”, “Material remuneration, allowances, additional payments” and “Non-state pension insurance”. The diagram of the employee's motivational profile at PJSC Farlep Invest after the implementation of HR development strategy is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.Diagram Of The Employee's Motivational Profile At Pjsc Farlep Invest After The Implementation Of Hr Development Strategy.
After the implementation of HR development strategy at PJSC Farlep Invest, there were changes in the quadrants of the employee's motivational profile diagram: there were no factors of motivation in the quadrant I; the following factors are added: quadrant II- “High level of wages”, “Material remuneration, allowances, additional payments”, “Non-state pension insurance”, “Staff development” and square IV- “Paying for results”.
The benefits of non-state pension provision for the employee:
1. Economic welfare-pension contributions and received investment income are recorded in his personal account and are the property of the employee and are an additional source of income after retirement.
2. Motivation-paying pension benefits in favor of their employees, showing interest in providing a future employer emphasizes the importance and evaluation of their work. The employee forms a loyal attitude to the enterprise, which cares about its employees.
3. Tax privileges for personal income tax.
The results of our study are confirmed by the following studies. As a result of the study at the enterprises, it was revealed that the motivation system can be constructed through express surveys and by means of maps of motivators (Tetiana et al., 2018a; Tetiana et al., 2018b and Stoyanov, 2014).
Conclusion
In each company, of course, HR strategies must have their “differences”, since these or other contradictions require the strengthening of the role of certain influential factors and staff levers in order to eliminate or mitigate the manifestation of these contradictions. In the interests of achieving optimal results in the field of view of the HR manager, one must constantly keep in mind the range of actions of all internal and external factors that determine the dynamics of company growth. Thus, the above said stresses that only a comprehensive vision of the process of developing and implementing a HR strategy is most appropriate for managing the competitiveness of HR and organizations in general. The prospects for further study are related, in our opinion, to the development of methodological approaches to assessing the effectiveness of HR strategies and effective mechanisms for HR competence management.
Recommendations
As a matter of particular importance in the development of HR strategies, we recommend the implementation of motivational monitoring, namely a system of periodic observations on the state of HR motivation to effective work, manifestation of creativity. Such monitoring involves the questionnaire of employees in order to clarify the range of their needs, the degree of their satisfaction through work, dominant motives, factors that positively and negatively influence the creative attitude to fulfilling their duties, manifestation of initiative, self-development of the individual, professional growth. We believe that the results of monitoring, taking into account the results of the implementation of other components of the strategy, should provide the necessary basis for improving staff work, forecasting staff turnover, adequate changes in the system of incentives, tangible and intangible incentives, closely related to the achievement of the organization’s objectives in the market.
References
- Dong, J., & Ibrahim, R. (2017).Flexible workers or full-time employees? On staffing service systems with a blended workforce. Northwestern University, Working Paper.
- Herzberg, F. (2017).Motivation to work. Routledge.
- Hilorme, T., Nazarenko, I., Okulicz-Kozaryn, W., Getman, O., & Drobyazko, S. (2018b). Innovative model of economic behavior of agents in the sphere of energy conservation. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal,24(3).
- Korlén, S., Essén, A., Lindgren, P., & Amer-Wåhlin, I. (2018). Leaders as intermediates between economic incentive models and professional motivation.Lakartidningen.
- Lakshman, S., Lakshman, C., & Estay, C. (2017). The relationship between MNCs’ strategies and executive staffing.International Journal of Organizational Analysis,25(2), 233-250.
- Leon, J. (2018). Is praise the best motivation for staff?DIY Trade News.
- Nykyforenko, V.G. (2016). Transformation management system development of human resources in Ukraine. Economics and Finance, 3, 40-48.
- Onyeukwu, P.E., & Ekere, N.E. (2018). Evaluation of staff motivation strategies on the productivity of Nigerian banking industry.International Journal of Innovation and Economic Development,4(1), 51-59.
- Rocha, V., & Brymer, R.A. (2017). Entrepreneurial founders’ imprints, human capital sourcing, and firm performance. In5th Linked Employer-Employee Data Workshop.
- Stoyanov, I.T. (2014). Metodological and managerial aspects of team coaching. Economics and Finance, 5.
- Tetiana, H., Chorna M., Karpenko L., Milyavskiy, M., & Drobyazko, S. (2018a). Innovative model of enterprises personnel incentives evaluation. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 17(3).