Research Article: 2022 Vol: 26 Issue: 3S
Key Factors Motivating on Online Buying Behaviour-An Empirical Study
Jahangir Y, Associate Professor, Dept of Mba Osmania University
Citation Information: Jahangir, Y. (2022). Key factors motivating on online buying behaviour – an empirical study. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 26(S3), 1-8.
Abstract
The present conditions of busy work life and hectic work schedules provoking the consumers to cut short their shopping time for daily needs and fashion needs. Most of the young and emerging consumers are depending heavily on online shopping for their daily grocery to clothing, fashion, foot wear and their family members and kid needs. By casing this intention all major retail shops created their own online shopping apps for better and timely shopping with attractive offers. The anytime shopping concept is an emerging fashion in nowadays for white-collar jobbers in the market. Virtual market sellers are efficiently using the space to make sales by attracting the present generation buyers who are surviving just by technology for their daily needs and wants. Young generation are updating themselves about the new products and services online and are even purchasing them online. The virtual space is providing a lot of scope for sellers to apply their strategies to motivate internet users by way of various applications and setting forth lucrative offers.
Keywords
Purchase Intention, Income, Behaviour, Digital Marketing.
Introduction
Online buying is a phenomenal change in the buying life of consumer, it is read in many books and journals, that buying is depends on various aspects, personal, environmental and so on, slow beginning of online buying early days, a rapid growth in currently, pandemic and Covid protocol also surged a rise in online buying, there are several motives that inducing the consumers and non-consumers buy things online, once online buying was a dreadful trade, lot of disbelief but today a highly convincing and convenient trade, it is observed in all sections of people a crazy attitude towards online trade, the point arises what pushing the user to buy things online several factors were observed like, low price, money back, ease of trade many more, The online trading platforms are advertising widely reaching target customers on their personal gadgets, say it could be social media or emails, The million offer concept attracting the younger generation to buy online, The youth are relying more on online trade rather than neighbourhood, a few years back shopping was an exotic experience but post pandemic 2019 days more congenial and affordable for online trade (Nayak et al., 2022).
Majority computer literates are highly addict to internet browsing and online trading, it is also observed from my experience and interaction with youth that buying shares online increased in recent past, a drastic increase in opening of Demat Accounts also proves my observation right (Svatosova, 2013). Thus, after a good number of observations it is decided to conduct a research on the motives of online buyers.
Review of Literature
(Gu et al., 2021) found that, the web traffic amid the coronavirus pandemic showed a jump in visits to online supermarkets. This finding indicated the commitment of online shoppers to daily shopping. The pandemic thus stimulated online shoppers to show a constancy of buying behaviour (Roh et al., 2022). The correlation analysis revealed an increasingly strong association between online shopping activity and factors of a reflexive consumer. The relationship between the investigated factors also showed a tendency to grow stronger.
Author identified that the customers are segregating information online about various products, offers, varities and going for a purchasing decision. The identified gaps in online marketing and suggested that consumer should be provided end to end shopping experience. The success of online shopping remains at product return or replacement policy he mentioned in his research Veith e al., (2022).
Vrender (2016) Day-by-day taste, preference and choices are varying regarding different factors such as the Internet emergence. However, this development needs some more understanding related to the consumer’s behaviour. Consumer behaviour research identifies a general model of buying behavior that depicts the processes used by consumers in making a purchase decision. (Singh, 2014) the author made a study is to understand what motivates consumers to buy online and the way they are collecting information from different websites and how they are enjoying at the time of shopping online. Simultaneously the sellers are developing brand equity and loyalty. Svatosova (2013) the author made a study on the B2C Business and said about the current trends in the development of online markets.
The major study was conducted with Maslow hierarchy theory where the customers are fulfilling their goals by making purchases online. (Close & Kukar-Kinney, 2010) the author explained about the powerful motivational factors is making the customers to buy or add the products to purchase at future due to the price promotions online. They are segregating information about products from various sources along with entertainment online.
Objectives of the Study
1. To know the buying motives of online buyers
2. To identify the major influencing factors
3. To understand the current buying scenario
Hypothesis
H1: There is no relationship between offers and online buying.
H2: There is no relation between ratings of past buyers on potential buyers.
Research Methodology
The Methodology adopted for conducting this study was through a sample survey which is administered offline and online, a structured questionnaire was supplied to the target respondents of younger age. A descriptive and analytical research design was implemented to complete the study that is suitable to identify the factors influencing online buying.
Study Area
The study area is covering three districts of Telangana state, it is conducted online with Google form questionnaire to collect the data by using referral sampling method (Snow Ball), the questionnaire is sent to their respective mobiles and email id’s.
Sample Size
The online questionnaire is sent to 100 people, finally 50 responses received so the sample size is 50 respondents.
Sources of Data
Primary data: Primary data is collected through respondent’s opinions through a well-structured questionnaire.
Secondary data: It is collected from various sources such as official URLs, websites, articles, journals published and other prominent literary sources.
Tools of Data Collection
Tools used in research are questionnaire that include personal information of respondent and standardised scale is used to assess their opinions, articulations and perceptions. Opinions of the respondents were categorised and summarised based on scores.
Data Processing and Analysis
Data collected from the respondents are categorized and assigned values and entered into MS-Excel spread sheet and statistical tests are applied to analyse the data Figure 1.
Data Analysis
Interpretation
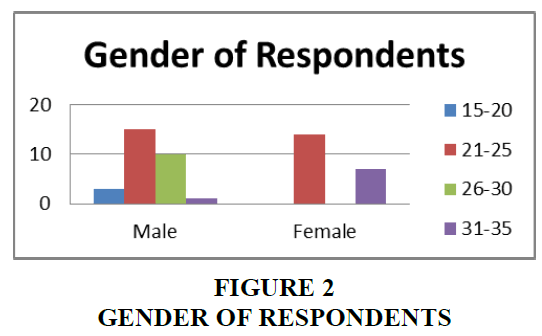
It is found from the above Table 1, and chart that the majority of respondents prefering online shopping whos age group is between 21-25 years compared to other ages, males respondents prefering online buying compare to female counterparts Table 2. More so the tendency of online shopping steadily increasing Figures 2 & 3.
| Table 1 Respondents Gender and AGE | |||
| Gender/Age | Male | Female | Total |
| 15-20 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 21-25 | 15 | 14 | 29 |
| 26-30 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 31-35 | 1 | 7 | 8 |
| Total | 29 | 21 | 50 |
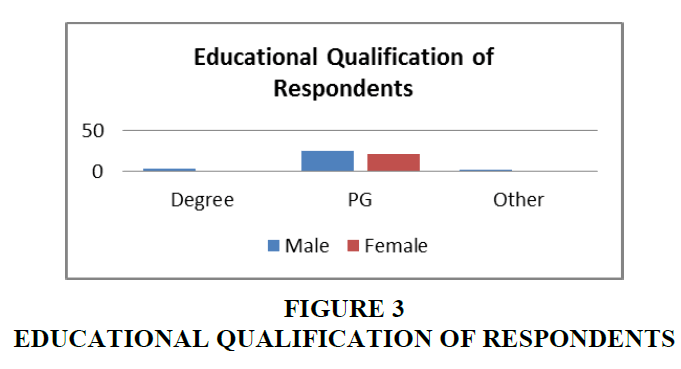
| Table 2 Respondents Educational Qualifications | |||
| Gender/Education | Male | Female | Total |
| Degree | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| PG | 25 | 21 | 46 |
| Other | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 29 | 21 | 50 |
Interpretation
The above Table 3, presents the education qualifications of respondents and it can be understand that the majority of the respondents are Post –Graduates and Graduate degree holders are involved in online shopping Vieth et al., (2022). It showcases the trending of the current generation.
| Table 3 Respondents Opinion on Motivating Factors to Purchase Online | |||
| Gender/ Motivators | Male | Female | Total |
| Offers | 19 | 14 | 43 |
| Discounts | 13 | 5 | 18 |
| Benefits | 12 | 0 | 12 |
| Redeemable points | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| Product/ Service Availability | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Emotional Taglines | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pricing Strategies | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Reviews | 29 | 21 | 50 |
| Total Count | 91 | 47 | 138 |
Interpretation
Among the genders the preference towards online buying is different both are not showing same intrest towards online shopping as the Z-Test reveals that there is a significance of difference between genders as (0.5<0.62) the p-value is greater the Table 4, value so it is significant Tables 3,4.
| Table 4 Z-Test: Two Sample for Means | ||
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | |
| Mean | 7.25 | 3.875 |
| Known Variance | 38.18 | 21.85 |
| Observations | 8 | 8 |
| Hypothesized Mean Difference | 0 | |
| z | 1.232068 | |
| P(Z<=z) one-tail | 0.108962 | |
| z Critical one-tail | 1.644854 | |
| P(Z<=z) two-tail | 0.217924 | |
| z Critical two-tail | 1.959964 | |
Interpretation
Males and females have no significance of difference towards factors that motivate to buy online Table 5. Z-Test also reveals that there is no significance of difference at genders as (0.5>0.21) the p-value is greater the significance value Table 6.
| Table 5 Source of Online Motives Information | |||
| Gender/ Source of Information | Male | Female | Total |
| Internet Browsing | 14 | 10 | 24 |
| E-Mails | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| SMS | 12 | 0 | 12 |
| Pop-Ups | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Social Media | 5 | 16 | 21 |
| Print Media | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Audio / Video Modes | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Celebrity Advertisements | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Total | 44 | 36 | 80 |
| Table 6 Z-Test: Two Sample for Means | ||
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | |
| Mean | 5.5 | 4.5 |
| Known Variance | 22.75 | 30.5 |
| Observations | 8 | 8 |
| Hypothesized Mean Difference | 0 | |
| z | 0.387601 | |
| P(Z<=z) one-tail | 0.349156 | |
| z Critical one-tail | 1.644854 | |
| P(Z<=z) two-tail | 0.698311 | |
| z Critical two-tail | 1.959964 | |
Interpretation
Males and females have significance of difference towards source of online information to buy online as they are using different applications for their purposes. Z-Test also reveals that there is a significance of difference at genders as (0.5<0.69) the p-value is greater the significance value Table 7.
| Table 7 Respondnets Opinion on Purchases Based on Ratings from Previous Sales | |||
| Gender/Offers | Male | Female | Total |
| Strongly Agree | 12 | 4 | 25 |
| Agree | 8 | 13 | 48 |
| Neutral | 1 | 4 | 18 |
| Disagree | 8 | 0 | 2 |
| Strongly disagree | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Total | 29 | 21 | 50 |
H0: There is no variation in purchase based on ratings.
H1: There is variation in purchase based on ratings.
Interpretation
The above table presents about the purchasing online based on ratings from previous sales Table 8. The chi square tests resulted (0.04<0.05) that is there is a no variation in purchasing according to genders based on the ratings thery are purchasing by considering review rating while buying online Yu & Huang (2022) the alternate hypothesis is accepted.
| Table 8 Chi- Square Test | |||
| Significance | D O F | C V | P-V |
| 0.05 | 4 | 9.49 | 0.04 |
Findings
1. It is found that the majority of respondents buying grocery, fashionables over online shopping portals, whos age is noted between 21-25 years.
2. The online buying showed no gender difference both males and females performing online shopping.
3. It also interesting observation that respondents educational qualifications are Post –Graduation and Graduation degree.
4. The purchasing preferences of gooda are different between the study genders.
5. Motivational factors are having similar impact on the both genders.
6. The information sources are similar for both the genders and online shopping experience is different however they are using multiple applications.
7. The purchasing based on the ratings phenomenally increased in recent past.
8. The online buying is emerging as an alternate shopping experience than traditional.
9. The majority respondents are also influenced by offers, discounts and trade day special discounts and many more.
10. It is concluded that the young generation more inclined towards technology run trading than visiting shop physically.
Conclusion
The motivational factors are playing a key role in the online shopping like the cash back, redeemable points, discounts, different products varieties and models availability and many more, all these are being sourced to the customers via various platforms online where the customers remaining online for their purposes that may be entertainment, social media, websites etc. The younger generation are showing more interest in the online shopping than the traditional shopping. They are comparing the markets and performing shopping that are beneficial to them with information search. It is important to remember that the amount of time spent by consumers on digital flat forms increasing significantly in self-isolation mode, and this leads to a decrease in the cost of attracting customers, so innovative entrepreneurs need to take advantage of this and improve their own websites, update their social network accounts, actively maintain their profiles, and reasonably spend their marketing budget on this to stay connected to young minds.
References
Close, A.G., & Kukar-Kinney, M. (2010). Beyond buying: Motivations behind consumers' online shopping cart use. Journal of Business Research, 63(9-10), 986-992.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gu, S., ?lusarczyk, B., Hajizada, S., Kovalyova, I., & Sakhbieva, A. (2021). Impact of the covid-19 pandemic on online consumer purchasing behavior. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(6), 2263-2281.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Lim, Y.J., Osman, A., Salahuddin, S.N., Romle, A.R., & Abdullah, S. (2016). Factors influencing online shopping behavior: the mediating role of purchase intention. Procedia economics and finance, 35, 401-410.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nayak, S., Suhan, M., Nayak, R., Spulbar, C., Birau, R., & Gull, S.M. (2022). Antecedents to purchase intention in virtual market space in India: an empirical investigation. Cogent Business & Management, 9(1), 2003502.
Roh, T., Yang, Y.S., Xiao, S., & Park, B.I. (2022). What makes consumers trust and adopt fintech? An empirical investigation in China. Electronic Commerce Research, 1-33.
Singh, D.P. (2014). Online shopping motivations, information search, and shopping intentions in an emerging economy. Asian Journal of Business Environment, 4(3), 5-12.doi: 10.13106/eajbm.2014.vol4.no3.5.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Svatosová, V. (2013). Motivation of online buyer behavior. Journal of competitiveness, 5(3).
Veith, C., Vasilache, S.N., Ciocoiu, C.N., Chi?imiea, A., Minciu, M., Manta, A.M., & Isbaita, I. (2022). An Empirical Analysis of the Common Factors Influencing the Sharing and Green Economies. Sustainability, 14(2), 771
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Vrender.(2016). Importance online shopping.
Yu, N., & Huang, Y.T. (2022). Why do people play games on mobile commerce platforms? An empirical study on the influence of gamification on purchase intention. Computers in Human Behavior, 126, 106991.
Received: 01-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11563; Editor assigned: 03-Feb-2022, PreQC No. AMSJ-22-11563(PQ); Reviewed: 17-Feb-2022, QC No. AMSJ-22-11563; Revised: 21-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. AMSJ-22-11563(R); Published: 24-Feb-2022