Research Article: 2022 Vol: 28 Issue: 5S
Key Constraints for MBA Students to Become Entrepreneur, An Empirical Analysis of Jamshoro and Hyderabad Business Schools
Amanullah Parhyar, Government College University
Waqar Ahmed Sethar, Mehran University
Muhibullah, Shaheed Benazir Bhutto University
Ahmed Raza Hafeez, Shaheed Benazir Bhutto University
Muhammad Shoiab Khan Pathan, Government College University
Citation Information: Parhyar, A., Ahmed Sethar, W., Muhibullah, Hafeez, A.R., & Khan Pathan, M.S. (2022). Key constraints for mba students to become entrepreneur, an empirical analysis of Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 28(S5), 1-11.
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the constraints and hurdles being faced by MBA students to become an entrepreneur. The target population of this study includes Jamshoro and Hyderabad Business schools. The selection of samples (targets) especially focuses on MBA (Master of Business Administration) final year students. The study includes the sample of 182 MBA students of Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools which includes five leading universities namely MUISTD, MUET, Sindh University IBA Jamshoro, Isra University Hyderabad, SZABIST Hyderabad, and HIAST Hyderabad. For this study, a quantitative approach is used to collect the data. The research was conducted by collecting the primary data through structure-based variables. The collected data was analyzed through SPSS, with the help of cross-tabulation, bar charts, and pie charts. The questionnaire consists of different variables to know the interest and hurdles faced by MBA students to become an entrepreneur. This research lead to some important recommendations which can build the interest of MBA students in making decision regarding being entrepreneur or doing for job which includes the role of universities, government steps and support to entrepreneurship, Bank loans and incubation centers at the workplace. Further, it is identified that 62.45% of the respondents are willing to do business and consider their career choice as an entrepreneur. While on the other side only 37.55% of the respondents are willing to do jobs. So, it is identified that MBA students do have interest to become entrepreneurs but due to some constraints, overall 60% of the MBA students respond that the major constraint for starting their own business is initial investment, 46.07% respondent said that lack of practical knowledge and experience is a major constraint and 31.32% of students said family resistance is key constraint. Therefore, due to these constraints MBA students change their career decision.
Keywords
Entrepreneurship, Key Constraints, Career Decisions, Entrepreneur.
Introduction
Today entrepreneurship is the most important for the success and economic growth of any society around the globe. Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in Germany, Ireland, Norway, and Mexico in their capital growth and development due to promoting entrepreneurship in their countries. While, on the other hand in Pakistan, Iran and Egypt the entrepreneurship score is very low in these countries. So, it is very essential for developing countries to promote culture of entrepreneurship in their countries for the development and the growth of the economy (Mian & Qureshi, 2010).
Therefore, for the economic development one of the most important field is “Entrepreneurship”. The importance of entrepreneurship can be examined by the several entrepreneurs to make the contribution in the field of economic growth and development of the country (Yanan, 2016). However, on the other side business student taking part in entrepreneurship development are the essential source of prosperity and the growth within the society and across the globe (Mohar & Kamal, 2007).
The focus of this study is to investigate the key constraints facing by MBA students to become an entrepreneur in Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools. Therefore, once the key factors are identified this study has to find out decision influence of MBA students to choose their career path who aim to do jobs and who aim to become an entrepreneur (Moutray, 2008). During this chapter, analysis is being represented, defined Entrepreneurship, significant of Entrepreneurship in the world and scope of Entrepreneurship in Pakistan (Michaela, 2010).
Problem Statement
To determine the key constraints that hinders the entrepreneurship in Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools.
Main Objectives of this Study are
1. To identify the major factors which influence the decision of MBA final year students to become an entrepreneur.
2. To investigate the hurdles faced by MBA final year students to become an entrepreneur.
Literature Review
The literature review section will present the previous research studies related to identifying the key constraint for MBA students to become an entrepreneur. The literature will focus on the intention of MBA students and also review the hurdles faced by the MBA students to become an entrepreneur.
According to, there are more than 20 thousand Pakistani’s living in Sweden, mostly people arrive here on a student visa and after getting opportunities they plan to settle here. According to Raza & Raza (2018) for the entrepreneurs of Pakistan with the collaboration of some mainstream Pakistani entrepreneur’s and advisory committee from Sweden, they have made a proper business channel “Pakistan Sweden Business council” which aims to provide strong relations of trade and investment between both countries, will help to explore and limit the challenges and create a strategic alliance for business among both countries. Here they value business contacts, business relations, trade regulations and promote young entrepreneurs on both sides.
Kuratko (2005) There are certain challenges faced by Pakistani entrepreneurs while doing start-ups in their home country as well as in their host country (Sweden), need to do a comparison from different entrepreneurial perspective to know more about problems faced by Pakistani entrepreneurs (Raza & Raza, 2018).
According to, it is identified that, it is very necessary to understand the factors which influence the intention of MBA students to become an entrepreneur (Scarborough, 2003). However, in the depth literature, it is identified that entrepreneurship emphasizes and focus on intention models for the business students. According to, it is very important to understand essentional elements of entrepreneurial intention from the perspective of an integrated framework. They also give the focus on the effort to fill entrepreneurship literature, the present study seeks to understand the influence of three of the most important situational and contextual factors, viz. (a) endogenous barriers, (b) exogenous environment and (c) university environment and support on the entrepreneurial intention among management students (Alistair, 2011).
Furthermore, entrepreneurship research, studies on entrepreneurship can be broadly classified into three categories, i.e. what happens when the entrepreneur's act, why they act, and how they act. According to the argue that out of these three categories, why they act, i.e. entrepreneurial intentions, is one of the most important streams of research as it enables researchers to understand the process of entrepreneurship (Kuratko & Hodgetts, 2007). Moreover, in the previous research studies, many authors have provided empirical evidence about various factors affecting entrepreneurial intention based upon comparable studies. These studies have provided new insights into entrepreneurship educators. However, within this subfield of enquiry, a number of scholars have broadly explored students’ career intentions of becoming entrepreneurs Ackroydand (1981).
The literature also found that the university can play an important role in stimulating entrepreneurship. Similarly, according to it is identified the impact of education and university environment on the creation of future entrepreneurs and the link between university assistance and support and the creation of new ventures have been the subject of much discussion in the academic community (Sujani, 2011). Furthermore, found that university environment and support positively influences perceived behavioral control in three country sample (Schaper, 2004). However, found a positive association between entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurial intention among Chinese students. Similarly, found university significantly influencing entrepreneurial intent among students. Suggested that expanding the scope of the university from traditional knowledge) generating to more of an enabler of entrepreneurial eco-system providing the concept of an entrepreneurial university (Dinis et al., 2013).
As per (David, 2012) it was also inspected the thought of planning and creating connected, industry-drew in learning conditions that grasp vagueness and vulnerability in defeating academic idleness in teaching your business people and trend-setters. The expertise and ability advancement of enterprise understudies, and also the positive effects upon self-assurance and self-viability, bolsters the methodology embraced in moving past the business arranging worldview into quick development prototyping. The examination reports that the critical triangulated proof is given; which approves the proposed dynamic and industry-connected with learning model (Davis, 2011).
As indicated by it is expressed that business instruction has made a momentous advancement after some time and the number of enterprise course books increased and supported the enthusiasm for business programs in HEIs (John, 1999). The outcomes recommend that most course readings give noteworthy inclusion of such points as the idea of enterprise, strategies for success, financing, advertising, and cases (OoiYeng et al., 2011). The investigation not just uncovers the territories that are secured by existing course readings yet additionally subjects that future reading material and research could cover to address the difficulties of future enterprise instruction (Cindy, 2010).
So also, as inspected the extent of advanced education graduates in Norway who have attempted diverse types of business enterprise training and how complete the enterprise instruction has been. The investigation showed that enterprise graduates, to a specific degree, are more intrigued by setting up their very own organization, later on, however, this propensity is much lower than what is found in other European examinations (Dugassa, 2012).
As per it is identified likewise conceptualized out of the blue the linkage between three components of business enterprise readiness and understudy pioneering mentality. The discoveries revealed that understudies were more arranged to higher enterprising outlook when they had collected more association pioneering readiness resource. Review data from 189 understudies from three colleges in Ukraine was gathered (Postigo et al., 2002). Various leveled different conventional slightest squares relapse examination and incline investigation were utilized to test displayed theories (Alain, 2013).
Methodology
Landstrom (2005) the following research consists ordinal research methodology that includes the quantitative data. Hence, by analyzing the research data gathered from the primary source, it evaluated key constraints for MBA students to become an entrepreneur within the Jamshoro and Hyderabad, Sindh. Another purpose of this methodology was to elect is that quantitative analysis is wide utilized in political economy, sociology, and scientific discipline and as our topic relates to the subsequent field it's additional probably that additional correct results are often obtained victimization this methodology (Kolvereid, 1997). The main target of the analysis is on Master in Business final year students of Jamshoro and Hyderabad Business faculties Saad & Hasnu (2016). A survey is conducted from five key universities of Jamshoro and Hyderabad Business schools to gather a spread of knowledge which might facilitate to capture respondents overall assessment concerning constraints faced by them to become entrepreneurs. The tool that's used to collect the data is structured based questionnaire, because it may be a quicker way to collect an outsized range of quantitative data and analyzed correct results (Altonji, 2016).
Data Analysis
Tables 1&2 According to the nature of ordinal data, with the help of SPSS the mean, standard deviation and the cross tabulation of the frequencies have been applied and mainly the data is presented in the tabular and graphical form (Scott, 2003). Therefore, with the help of SPSS, the ordinal data has been analyzed clearly (Mann, 1995). On the other hand, categorical analysis has been implemented for analyzing data for evaluating the key constraints for MBA students to become an entrepreneur in business schools of Jamshoro and Hyderabad.
| Table 1 Targeted Textile Mills | |
| University Name | Number of Samples |
| MUISTD, MUET, Jamshoro | 15 |
| University of Sindh Jamshoro | 48 |
| Isra University Hyderabad | 44 |
| SZABIST Hyderabad | 54 |
| HIAST Hyderabad | 21 |
| Total | 182 |
| Table 2 What is your field of Interest? Statistics |
|
| Valid | 182 |
| Mean | 1.3736 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.48510 |
Analysis and Discussion
Tables 3&4 in the findings and analysis chapter, the key constraints for MBA students are analyzed with the help of SPSS to investigate the correct results and recommended practices for the business students to become an entrepreneur. The demographic outcome of this researches investigating the key constraints for MBA students to become an entrepreneur. Therefore, the total number of participants was 182 for the research from the five key universities of Jamshoro and Hyderabad region including MUISTD, MUET, University of Sindh, Isra University Hyderabad, SZABIST Hyderabad, and HIAST.
| Table 3 The Number of MBA Students have Interests in Doing their own Business | ||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Starting your own business | 114 | 62.6 | 62.6 | 62.6 |
| doing job | 68 | 37.4 | 37.4 | 100.0 |
| Total | 182 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Table 4 Owning Business Provide more Authority than a job Statistics |
|
| Valid | 182 |
| Mean | 3.1923 |
| Std. Deviation | 1.31349 |
Field of Interest
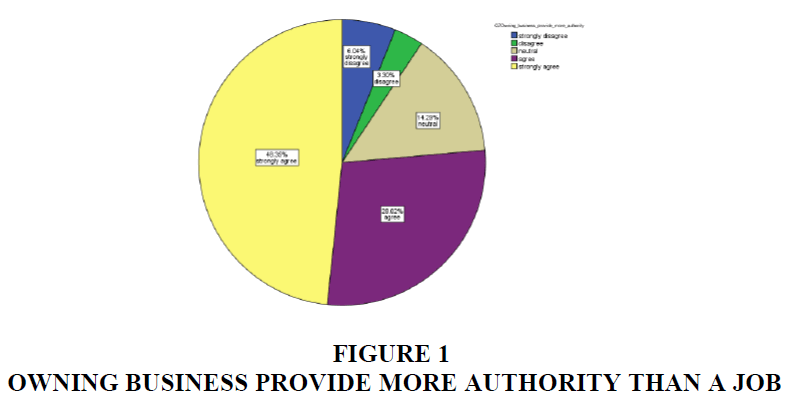
Figure 1 shows that 37.55% of the respondents have been interested aim to get the jobs. Whereas, 62.45% of the respondents have been interested in doing the business after completing their MBA degree. So, the number of MBA students have interests in doing their own business shows in Tables 5&6.
| Table 5 Owning Business | ||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Strongly disagree | 19 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 10.4 |
| Disagree | 48 | 26.4 | 26.4 | 36.8 |
| Neutral | 31 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 53.8 |
| Agree | 47 | 25.8 | 25.8 | 79.7 |
| Strongly agree | 37 | 20.3 | 20.3 | 100.0 |
| Total | 182 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| Table 6 Constraints Due to Which you Would find Starting up Business Difficult Statistics | |
| Valid | 182 |
| Mean | 1.4835 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.42342 |
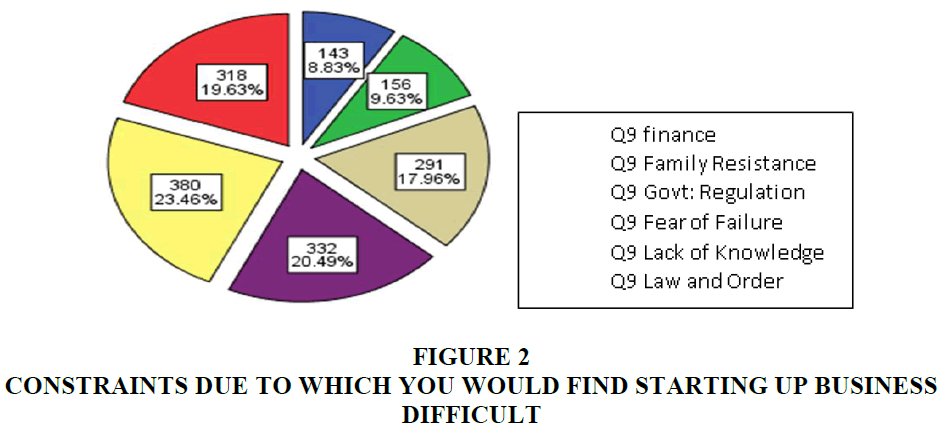
The Figure 2 shows that there are certain causes that restrain the entrepreneurship within the Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools. It indicates these causes are effecting the entrepreneurship and MBA students for making decision regarding being entrepreneur. Most of the students agree with this statement that these above cause creating difficulties to open up new businesses shows in Tables 7&8.
| Table 7 Starting Up Your Own Business | ||||
| Q1FIELD_INT | Total | |||
| Starting your own business | doing job | |||
| Q9 Constraints_newbusiness_finance | No | 25 | 14 | 39 |
| Yes | 89 | 54 | 143 | |
| Total | 114 | 68 | 182 | |
| Table 8 Case Processing Summary | ||||||
| Cases | ||||||
| Valid | Missing | Total | ||||
| N | Percent | N | Percent | N | Percent | |
| Q9Constraints_newbusiness_finance * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
| Q9Constraints_newbuiness_familyresistance * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
| Q9Constraints_newbuiness_Govtregulation * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
| Q9Constraints_newbuiness_fearoffailure * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
| Q9Constraints_newbuiness_lackofknowledge * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
| Q9Constraints_newbuiness_lawandorder * Q1FIELD_INT | 182 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 182 | 100.0% |
After conducting the research and analyzing the data collected, the outcome of this study explains the magnitude ratio of MBA students who aim to become an entrepreneur and from those who are willing to do jobs in Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools. This research has discussed the term entrepreneurship, scope of entrepreneurship and the importance of entrepreneurship globe and as well as in Pakistan. The main focus of this research is to investigate the elements which cause hinder entrepreneurship in Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools. Therefore, for this study, I have used the quantitative and qualitative research design. For collecting the research data I have adopted the questionnaire based on close ended question and filled that questionnaire by MBA student’s five well known universities including Jamshoro and Hyderabad. This research is also to find out issues faced by the MBA students in starting their own business. For this purpose, I have used the the stratified the random sampling technique. The results of this study show that 37% of the MBA students are willing to get the jobs while 62% of the MBA students are interested in doing their own business. The research findings suggest that salary is not sufficient to meet up the expenditure that’s why business money motivate the MBA students to become an entrepreneur.
The study indicates that 43.96% agrees and 36% strongly agrees that entrepreneurial studies help to develop the abilities and skills that play a significant role to contribute the stating up a successful business. So, the MBA students are much confidence that needs of skills and experience than those who are willing to do the job. This study also indicates that overall 31.32% of students agree while 18.13% of students strongly agree with this statement that their family pressurizes them to do jobs instead of doing business.
Constraints of Entrepreneurship that Forced MBA Students to Choose Jobs as their Carrier
Discussion of Findings
From the above question, it indicates the most important constraints that hinder entrepreneurship in Jamshoro and Hyderabad business schools.
To open up the new venture initial investment is too high entrepreneurs cannot afford the business expenses. From the above discussion and results, it is identified that there is too much investment needed to open up new venture the bank's policies are too difficult for MBA students to obtain the loan from the bank. This is the major constraint of entrepreneurship for MBA students to become an entrepreneur and also restrain them to do business.
31.32% students agree while 18.13% are strongly agreed, 25.27% responses are neutral, 17.58% students disagree and only 7.69% of students strongly disagree that their families pressurize them to do the jobs. This is again a major constraint for MBA students to become an entrepreneur. If they will know the pros and cons of entrepreneurship then they will allow their children to start their business as the business provides more profits and benefits to the owner as compared to the job.
36.26% respondents are agreed, 24.73% respondents strongly agree, 15.38% respondents are neutral, 17.58% respondents disagree and only 6.04% respondents strongly disagree with this statement that law and order situation is not suitable in the country that’s why students are not willing to do business. It is identified from the above question that law and order situation is not suitable for the business students that why they change their decision. This element not only effects the entrepreneurship but also effecting the current business.
29.67% students are agreed, 19.23% students are strongly agreed, 23.06% students are neutral, 18.13% students disagree and only 9.89% students strongly disagree with this statement that economy does not support starting up business. So, the economy plays an important role in starting up the new ventures and making them successful. Pakistan economy is not in good condition to start up new ventures. Entrepreneurship plays a significant role in the growth of the economy, if the Government make favorable policies then students can contribute to making the economy healthy.
38.46% students are agreed, 25.82% students strongly agree, and 18.66% students are neutral. 9.89% of students disagree and only 7.14% of students strongly disagree. Therefore, it is clear that the majority of the students are willing to do business but due to limited knowledge and experience, they change their career decision.
Factors that Influence the Decision of MBA Students to Become Entrepreneur
Discussion of Findings
The above question reveals number of elements to encourage the MBA students to start their own business these are as follows.
50% of the MBA students think that owning a business provide more authority than doing the job. Therefore, the business not only providesrecognition in society but also create employment opportunities for others as well. They also think that business provides the economic support and growth in the country.
Majority of MBA students think that due to less emloyment opportunities than business opportunities. Therefore, 65% of MBA students chose entrepreneurship over the job. There are not sufficient jobs in the job market and all the MBA students cannot get the job. So, the entrepreneurship is the best solution to overcome this constraint.
One of the most important elements identified in this study that due to the lack of merit in the job market business students prefer to do their own business. This element can much encourage business students to become an entrepreneur.
It is also identified from this study that a large number of MBA students think that the job salary is not much enough to meet up the expenditure. So, this element motivatesto business students to become an entrepreneur.
Overall a large number of students think that if the number of entrepreneur increase it will also increase the economy. Therefore, it will also support the economic development of Pakistan. As we all know that the current economic position of Pakistan is not good. So, entrepreneurship can play a significant role to support the economic growth and development.
Research Questions Answered
Factors that Influence the Decision of MBA Students
MBA students who want to start up their own business are influenced by
1. All jobs do not provide job security
2. Lack of merit in the job market
3. Salary not sufficient to meet up expenditures
4. Fewer job opportunities than business opportunities
5. Entrepreneurship will support the economy of Pakistan
6. Owning a business is a better option than doing a job
7. Owning a business provides more authority than a job
MBA students who are seeking jobs are influenced by
1. Getting a job is easier than owning a business
2. Law and order situation is not suitable
3. Too much investment needed to open up the business
4. There is the family pressure of getting the job
5. Limited entrepreneurship knowledge and experience
6. The job provides retirement benefits
7. The economy does not support starting up business
Constraints Faced by MBA Students to Become Entrepreneur
1. Overall 60% of the MBA students said that the major constraint for starting their own business is initial investment.
2. 36% of the MBA students think that law and order situation is a most important constraint to entrepreneurship.
3. 46.07% of the students think that Lack of practical knowledge and experience is a most important constraint for MBA students.
4. 31.32% of students think that family resistance is a major constraint.
Conclusion
For this research, the main universities of Jamshoro & Hyderabad were selected and the usage of smaller sample size can leads towards the mass generalization because the population is much bigger and large in the higher education institutes of Pakistan. Furthermore, time forces restrict the research study only to the region of Jamshoro & Hyderabad business schools. Similarly, the financial resources and inaccessibility of the other regions were also one of the most important limitations to conduct this research within the region of Jamshoro & Hyderabad.
References
Ackroydand, S.J.A.H. (1981). Data Collection in Context Longman (Book) Sarfaraz A Mian and M Shahid Qureshi, “Global Entrepreneurship Monitor Pakistan Report 2010 (GEM)”.
Alain, N. (2013). Challenges and perspectives facing the development of entrepreneurship education and training in South Africa. World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development, 9(2/3), 2042-5961.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Alistair, A.R. (2011). The university's role in developing Chinese entrepreneurship. Journal of Chinese Entrepreneurship, 3(3), 175-184.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Altonji, J.C., Cattan, S., & Ware, I. (2016). Identifying sibling influence on teenage substance use. Journal of Human Resources, 111(1), 209–223.
Indexed at, , Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Cindy, M. (2010). Entrepreneurship among business graduates: does a major in entrepreneurship make a difference, Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 17, 4.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
David, G.H. (2012). From chalk and talk to walking the walk: Facilitating dynamic learning contexts for entrepreneurship students in fast?tracking innovations., 54(2/3), 152–166.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Davis, S. (2011). Social entrepreneurship: Towards an entrepreneurial culture for social and economic development.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dinis, A., Arminda, D.P., Ferreira, G., & Ricardo. (2013), Psychological characteristics and entrepreneurial intentions among secondary students. Education + Training, 1(1), 763-780.
Indexed at, ,Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Dugassa, T.G. (2012). The context of entrepreneurship education in Ethiopian universities, Management Research Review, 35(3/4), 2040-8269.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
John, M., Aberdeen University, (1999). Evaluation Cookbook, advantages and disadvantages of the questionnaire.
Kolvereid, L., & Moen. (1997). Entrepreneurship among business graduates: does a major in entrepreneurship make a difference? Journal of European Industrial Training, 21(4), 154.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kuratko, D.F. (2005). The development of entrepreneurship education: development, trends, and challenges. Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice, 29(5), 577-598.
Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2007). Entrepreneurship: Theory, process, and practice. 7th edition., Thomson Learning, Ohio, US.
Landstrom, H. (2005). Pioneers in entrepreneurship and small business research. Springer Science and Business Media .
Mann, P.S. (1995). Introductory statistics., Wiley .
Michaela, M. (2010). Quantitative and qualitative research, 2010 widget, LLC dba, surveygizmo.
Mohar,Y.S.M.S., & Kamal, K.K. (2007). ‘Relationship between psychological characteristics and entrepreneurial inclination: A case study of students at University Tun Abdul Razak (Unitar), Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability.1-10.
Moutray (2008). An Office of Advocacy Working Paper, “the most important challenges faced by small business owners and entrepreneurs”.
OoiYeng Keat, Selvarajah, C., & Meyer, D. (2011). Inclination towards entrepreneurship among university students: An empirical study of Malaysian university students. International Journal of Business and Social Science. 2(4).
Postigo, S., Kantis, H., Federico, J., & María, F. (2002). The emergence of university graduate entrepreneurs: What makes the different? Empirical evidences from a research in Argentina. 20-22.
Raza & Raza, H. (2018). Home-Pakistan Sweden Business Council. [online] Pakistan Sweden Business Council. Available at: http
Saad, A., & Hasnu, S.A.F. (2016). Distinctive limitations are featured in the investigation because of which business graduates falter to end up a business visionary, in addition to significance level of every imperative is likewise computed in the examination.
Scarborough, N.M., & Zimmerer, T.W. (2003) ‘Effective small business management: An entrepreneurial approach.
Scott, A.S. (2003). A general theory of entrepreneurship: The individual-opportunity nexus. Edward Elgar Publishing:1843769964.
Sujani, S.T. (2011). The Determinants of Entrepreneurial Intention among Academics in Sri Lanka. International Conference on Economics and Finance Research IPEDR, IACSIT Press, Singapore.
Received: 01-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-22-11648; Editor assigned: 03-Mar-2022, PreQC No. AEJ-22-11648(PQ); Reviewed: 21-Jan2022, QC No. AEJ-21-10320; Revised: 26-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. AEJ-21-10320(R); Published: 30-Mar-2022