Short commentary: 2021 Vol: 13 Issue: 1
Is Big Basket A Preferred Site for Indian Online Shoppers?
Anjali Agarwal, Xavier Institute of Management & Entrepreneurship, Electronics City Phase 2, Bangalore
Dhanush S, Xavier Institute of Management & Entrepreneurship, Electronics City Phase 2, Bangalore
Namrata Agarwal, Xavier Institute of Management & Entrepreneurship, Electronics City Phase 2, Bangalore
Pooja Agarwal, Xavier Institute of Management & Entrepreneurship, Electronics City Phase 2, Bangalore
Abstract
Big Basket is into delivering everyday cooking essentials like ghee (clarified butter), diced coconut and fragrant basmati rice and over 18,000 other items from bread to detergent for customers at their doorstep. Their motive is to enable the convenience of doing grocery shopping online to avoid traffic and therefore the drudgery of supermarket runs.To explore new opportunities, the company has also launched 3 new businesses BB Daily, BB Instant and BB Beauty. BB Daily is a subscription-based service that permits customers to order milk and groceries. Customers have to place the order before 10 PM, and get the goods delivered with 5AM - 7AM the next day.BB instant is Big BasketâÂ?Â?s unmanned vending machines that are mostly available in corporate offices, tech parks, and apartment buildings in Tier I cities. While BB Beauty that allows the consumers to choose from a wide range of beauty and personal care products online. Bigbasket allows customers to simple relaxed way of browsing and buying groceries and discover new products with its smart monthly shopping list, is now available online at bigbasket.com, IndiaâÂ?Â?s best online grocery. They currently operate in about 15 leading cities and expanding its wings.
Introduction
The Founders
Big Basket was founded by Sudhakar, Hari Menon, Ramesh, Vipul Parekh and Abhinay Choudhari in 2011. Before Big Basket, the founders also founded Fabmart.com, a web platform that sold books, toys, and groceries within the year 1999. Fabmart was sold to a grocery chain in 2006. Mr V S Sudhakar is the founder and CEO of Fabmall, a number one online and physical retail business. Before Bigbasket, Sudhakar was the CEO of Planetasia, the primary online focused services business within the country. Mr V S Ramesh is the Head of Logistics & Supply Chain at Bigbasket.com. He was also a Co-founder at Fabmall. Before Fabmall, he ran the operations and logistics for an outsized fleet of ships for shipping major. He has over 21 years of experience within the Indian Navy handling Operations and Logistics. Mr Vipul Parekh is the current Head of Finance & Marketing and earlier was an investment Director at Peepul Capital, a number one Private Equity Fund. Abhinay Choudhari is the Head of latest Initiatives at BigBasket. Besides working with leading IT companies like iGATE & Infosys, Abhinay also founded Stylecountry.com, one among India's first online fashion retail stores.
How did Big Basket Start?
All of this began when the Big Basket founders decided to make a singular website that was never done before. Fabmart.com was a web platform that sold books, toys, and groceries within the year 1999. Back then, only within a couple of months, that they had realized that not just our country but the entire world wasn't able to take this buzz of digitization. within the year 2006, Fabmart was merged with a physical grocery chain and the founders sold their stake.
Then came the golden year of 2011, when the team reunited and began re-evaluating the thought of again arising with something new and exciting. Despite all the criticism, they stood very strong on the very fact that the time to try something that’d put them on the map was then. In 2011, the smartphone market was booming and anything and everything was available except groceries, of course and that, right there was their Eureka moment.
BigBasket - User Acquisition
Big Basket keeps into account the changing needs and diverse shopping propensities of its clients. The group expanded the verdant greens numbers in Mumbai, provided a unique sort of rice (called Sona Masoori) in Bangalore and went similarly as giving eight different types of eggplants to fastidious clients. They formulated a model of modified programming that naturally directs drivers to their customer locations.
Business Model
There was a time when Indians only bought their vegetables and fruits directly at the public market. BigBasket standardized this experience and gives consistent pricing for all items in a given city. In recent months, the company has added efficient delivery fleet and after the covid situation things have changed more drastically as to avoid the contact less and fast delivery. The business model of Big Basket ensures encompasses two elements- inventory model and hyperlocal delivery model. A robust product catalogue and customer service has helped them to gain the market share. They have a mobile app and a website, which generates about 70% of their revenue.
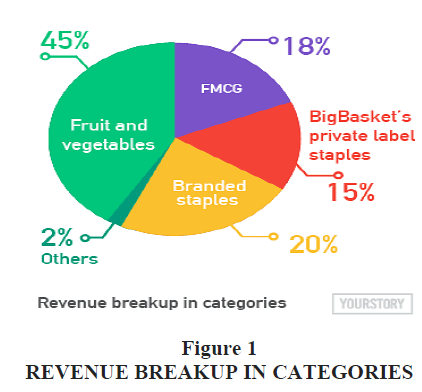
The remaining part comes from the other businesses including hotels, restaurants as well as offline retail brands in Figure 1. Big Basket buys products from some of the best and largest brands of the country like P&G, HUL, and from mills and farmers as well. There are perishables and non-perishable products. Although the company wastes around 5% of their total revenue on perishables, but it is not a very significant amount when compared to their overall profits. BigBasket has tied up with more than 1800 local stores with a delivery chain that promises the perfect delivery. It used to take delivery charge of Rs. 30 and now waived the same due to synergy with small local retailer
Managing the Risks of Perishable Products
Perishable products are procured only on order. This reduced their loss of stock by 3-4%. It requires high investment to build the business infrastructure (Supply chain, storage facilities and delivery systems). Also, selling groceries is a low margin business. To have a better control and better margins, big-basket worked with its own fleet. Big basket initially started with marketplace model, it shifted to mixed model (Inventory model + Hyper local model) to achieve economies of scale.
Procurement Capabilities
BB procures packaged items directly from big firms. Procurement of fresh produce is done from farmers (70%), vendors (20%) and national sourcing (10%). BB makes 20,000 products available with 90-minute express delivery. About 70% of BigBasket’s sales come from the portal. The app is compatible across all smartphones. By incorporating a referral marketing promotion, the company was able to increase the user base very rapidly.
Competitive Landscape
The direct competitors of Big Basket are Grofers, Ninjakart and Nature Basket. Big giants like Reliance, Amazon have all recently launched their grocery Business.
Grofers
Grofers is the biggest low-cost online supermarket in the grocery sector in India and is the main competitor for Bigbasket. It was started in 2013. The firm utilizes its in-house technology platform to manage a network of over 5,000 partner stores that enable the company to operate fast and lean supply chain–from manufacturers straight to customers in 27+ cities and currently focuses on private labels, Subscription based, Open more offline stores and the like.
Ninjacart
Ninjacart, started in 2015 is India's largest fresh-produce supply chain connects food producers directly to retailers, restaurants and service providers using in-house applications. At present, their supply Chain is prepared to transfer 1400 tons of perishables from farms to businesses every day in less than 12 hours.
Nature Basket
Nature's Basket is India's leading food destination through physical retail stores, online portals and mobile apps. Nature Basket was started in 2005. Ninjacart's presence is currently expanded to over 36 neighborhood convenience stores in Mumbai, Pune and Bangalore with a wide range of items, including fresh fruit and vegetables, fish and meat, homemade breads, FMCG and staples.
Financials
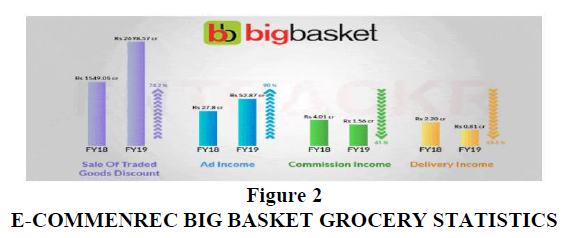
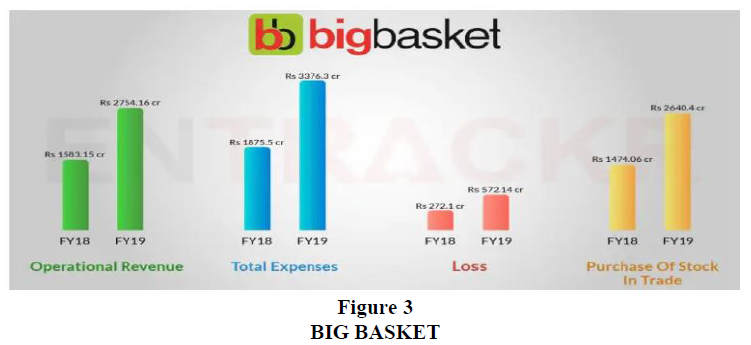
Bigbasket is backed by Alibaba and is burning cash just to grow in the market. Its revenue from operations has jumped from Rs 1,583 crore in FY 18 to Rs 2,754 crore in FY 19. Bigbasket earns 98% of its revenue from sales of goods on its platform and rest from advertising. However the income from deliveries and commission decreased in FY 19 (Table 1). Even though the company’s revenue is increasing it is not earning profit because of high operating costs. Expense of the organization increased by 80% in FY 19 from Rs 1,877 crore in FY 18 to Rs 3,376 crore FY 19. This was done to fuel the demand for the platform but this in turn resulted in the company bearing loss. Due to the increasing demand in FY 19 the company spent approximately Rs 98 crore on packaging and transportation as compared to Rs 44 crore in FY 18. Total outstanding loss of the company as of FY 19 is Rs 2,247 crore. Loss for FY 19 amounted to Rs 572 crore which is 2.1X as compared to Rs 272 crore as of FY 18 (Exhibit 2). With recent funding of $150 million BigBasket has made its way to India’s unicorn club. Bigbasket currently holds nearly 50% of India’s $1.20 billion E-commerce grocery retail and plans to reach $1 billion out of $2.50 billion in 2020 in Figure 2 & Figure 3.
References
- https://www.digitalvidya.com/blog/case-study-bigbasket-online-grocery-marketplace-digital-marketing/
- https://www.icmrindia.org/casestudies/catalogue/Business%20Strategy/BSTR581.htm
- https://www.themarcomavenue.com/blog/how-big-basket-became-peoples-favourite-online-grocery-marketplace/
- https://entrackr.com/2019/12/bigbasket-spent-rs-3376-cr-to-earn-revenues-of-rs-2754-cr-fy19/
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/small-biz/startups/newsbuzz/bigbasket-targets-revenue-of-rs-6300-crore-infy20/articleshow/69344488.cms?from=mdr