Research Article: 2022 Vol: 25 Issue: 4S
Innovation and challenges in human resource management in the 21st century
Julaluck Punthung, Walailak University
Kittachet Krivart, Walailak University
Citation Information: Punthung, J., & Krivart, K. (2022). Innovation and challenges in human resource management in the 21st century. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 25(S4), 1-8.
Keywords
Innovation, Innovative organization, Human Resource Management
Abstract
The 21st century is the era of free trade where technology and innovation play an important role in the working world. Especially in the part of human resource management is a significant structural transition from a labor resource-based economy to a knowledge-based, technology-based economy and innovation. It is a great challenge for the organization to see it as a threat “disruption” or as an “opportunity”. Therefore, to drive towards an innovative organization, it is essential to manage human capital to be able to think analytically, plan, develop creativity with universal potential to create maximum value and be ready for the influx of people for the flow of change that will take place. The human resource department is an important front line that must be proactive in recognizing the presence of HR Innovation and upgrading to HR Tech or Digital HR in 4 main dimensions: (1). Innovative Recruitment & Selection. (2) Innovative Training & Development. (3) Innovative Compensation & Employee Relation. (4) Innovative Human Resource Information System: HRIS. To prepare personnel who can competently compete professionally to meet the needs of working for the organization. In particular, the contributing factors to this success include Innovative Leadership, Design of innovative human resource management practices; HR practices. Values â??â??that support the creation of an innovative culture in the organization; Values.
Introducation
Past and present, the concept of human resource management is constantly evolving and changing. The impact of the three waves from the agricultural era, the industrial era to the information and communication technology era (Toffler, 1980), which makes a major transformation towards the “modern digital human resource management” model. As a result, human resource management strategies have rapidly adapted to the three eras, as HR circles call this era VUCA era, meaning the era of Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity (Hrnote,2019).
In human resource management to achieve “innovation”, the organization needs to create new things while the management itself has to keep up with the modern times. Creating such changes is not easy and takes time. Because it concerns individuals, top executives must use Innovative Leadership rather than Management as a key to driving the organization by recognizing three key factors: (1) Determining the direction of the organization in terms of innovation: For example, promoting participation and setting a shared vision by leaders of organizational design that facilitates innovation, personnel at all levels contribute to innovation-building activities. (2) Continuing innovation: For example, having an efficient operation team, having a long-term training and development plan, communicating in all directions, being open to external perspectives, exploring opportunities and threats, and seeking new opportunities for innovation. (3) Creating Sustainable Innovation: For example, creating an organizational culture that fosters creativity, a sense of organizational awareness, building a knowledge management system and a learning organization, and continuous improvement (Woottirong, 2016). An innovative leader must have the leadership traits that create a strategic engine that generates internal competitive advantage to accommodate external change, to be consistent with the radical innovation changes and difficult to compete with the form of the original strategy so that the work can cope with the current changing conditions effectively (Pochjanart & Chienwattanasook, 2020).
However, Thummachote(2018) has pointed out that innovations in human resource management should take a broader perspective rather than solely adopting technology, such as talent management with the Dashboard for comprehensive work including Using technology to help manage feedback and suggestions in real-time 360 degrees, etc. But it is important to consider the cost-effectiveness and appropriateness following the corporate culture context to achieve sustainable competitive advantage, in line with the concept of Conner and Ulrich(2016) which discusses the integration of technology to lead Come to help in personnel management in many forms, each of which will be used in different situations, resulting in more flexibility in operations.
HR Innovation, or HR Innovation, not only includes motivating personnel to attract competence to be able to invent new work processes, projects, activities, or design guidelines for human capital competency development in new ways. Distinction from the traditional conceptual framework only enhances competitive advantage “Applying from Best Practice” to simulate a new model of success following the organizational context, Or bring a case study to think and build on the original concept concretely and practically, it can be considered as the use of "HR innovation or HR Innovation" as well.
When considering the dimension of human resource management by motivating personnel to pull competence to be able to invent new work processes, projects, activities, It is even possible to design other forms of human capital competency development that stand out from the traditional framework and enhance competitive advantage. It can be said that another interesting and widely used method today is “adapting from best practice” to adapt it to a new model of success following the organizational context, or to use it for further thinking. The balance from the original conceptual framework that is concrete can be put into practice. It can be counted as the use of “HR Innovation or HR Innovation” as well. In addition, another challenge on the ladder to HR Innovation is the shared commitment of key people who dare to change to an innovation organization, including (1) Innovator, which is the first and important group in the creation of innovation. (2) Group of Directors (Facilitator). (3) Supporter groups. (4) The group of customers or users who, if developed as a prototype work, have never been put into practice and do not dare to take risks and accept the results. Organizations will not develop and cannot create innovations (Traipopsakul & Pitchayangkool, 2021), As the saying goes, “As long as you trampling in your place or stalking others' footsteps, there will be no footprints of your own.”
In this article, the author's objective is to discuss the application of innovation in human resource management, which is a challenge of modern organizations that must adapt in the 21st century, both the concept of innovation in human resource management and the drive of innovation in the organization through Human resource development towards Innovative Organization. Another important point is that the author aims to present innovative approaches to human resource management which can be divided into 4 groups: (Rhecsenanth, 2003) Group 1 Innovative Recruitment & Selection. Group 2 Innovative Training & Development. Group 3 Innovative Compensation & Employee Relation. And Group 4 Innovative Human Resource Information System: HRIS. Including presenting the concept of the HR Innovation Model that is challenging in the 21st century or the “HR Innovation Windmill Model” which the author has designed to be applied to both small and large organizations to be appropriate.
Innovation In Human Resource Management
Innovation is creative destruction. It is the cornerstone of sustainable organizational success, derived from the Latin word “Innovare” which means “to make something new”. Whereas Peter F. Drucker (1998) referred to “innovation” from an entrepreneurial point of view as a unique tool used to exploit change and opportunities to create new businesses and services that differentiate themselves from their competitors. This is in line with Michal E. Porrter (1990) concept of creating a competitive advantage of business organizations through innovation processes, both using new technologies and creating new operating methods. In addition, innovation is something that has never been seen before in an organization, organization. in the country or the world. Including must be practical to create economic, social benefits (Wutthirong, 2020). This concept is consistent with the National Innovation Agency that has defined innovation as “New things arising from the use of knowledge and creativity with economic and social benefits” as well (National Innovation Agency, 2010).
Therefore, the author concludes that “innovation” means creating new things in different dimensions, Both concepts and methods for producing products or services are unique, based on the knowledge base, creativity, and generating utility both at the individual and international level. Innovation factors can be classified into two types: (Dwivedi, 1985): (1) Radical Innovation is the process of introducing something truly new to society by completely changing the Value, Belief, Value System of society. (2) Gradual innovation is the discovery process or the invention of Invent by applying New Ideas or New Knowledge that has a continuous nature
Meanwhile, the National Innovation Agency has classified innovation into two categories: (National Innovation Agency, 2010). (1) product innovation that consists of innovation of Tangible product and Intangible product. (2) process innovation, which consists of technological process innovation and organizational process innovation.
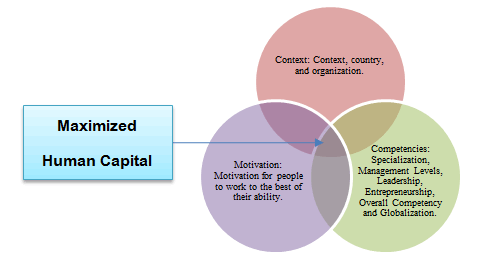
Modern human resource management maintains four main tasks: recruitment and selection, development, maintenance, and utilization of human resources, which are at the heart of human resource work. Circle (Hongladarom, 2018), which is a key concept in Human Resource Management: HRM, found that successful organizations from both domestic and foreign countries consist of three factors:
1. The context of the organization is to arrange the organization to be agile, livable, and modern, both administratively and overall environment following growth and achieving goals that may change in the future.
2. The quality of human capital in the organization is the development of the competence and capabilities of personnel in the organization. Organizations need to define knowledge, skills, abilities, attitudes, and behaviors for each job position. Identify the level of competency in each competency according to the role or position assigned. In a nutshell, which position requires which level of competence, If comparing the criteria that the organization needs and the person does not meet the expectations (Gap), then they need to train and develop them to be competent and good human capital in the organization.
3. Motivation and motivation for people to work with full efficiency, good management principles must manage and manage people because the morale and morale of each person are different, creating incentives that are well-matched to their needs will encourage people to work to their full potential.
Figure 1: Theory 3 Circles (Hongladarom, 2018)
However, when considering the issue of human resource management, the following five objectives are identified (Yoonyong, 2020).
1. To provide personnel to perform tasks according to the qualifications required by the organization effectively.
2. To use human resources to the maximum benefit by human beings as administrative capital that has been exhausted due to retirement, resignation, the need to leave the organization, there must be a process for personnel to be able to practice work for the benefit of the organization as much as possible.
3. To develop skills and abilities of personnel to be the most efficient, ready, and capable of performing such tasks.
4. To keep the competent personnel with the organization as long as possible, there must be motivation and create a feeling of commitment to the organization, willingness to devote physical and mental effort to produce excellent results for the organization.
5. To communicate the human resource management policy to personnel so that the organization has a work plan that is in the same direction.
While (Yotsomsak, 2006) mentions that human resource management has three objectives:
The first is Society's Requirements.
Secondly, in response to Management's Expectations, the human resource management agency must ensure that the organization has the right level of knowledge, skills, and competence to work with the organization.
And finally, to respond to Employee's Needs, by focusing on the development of work processes and enhancing the happiness of working in line with Werther & Keith (1993) who outlined the four objectives of human resource management:
1. Organizational objectives to help increase the efficiency of the organization to achieve its goals.
2. Societal objective to support the organization to have social responsibility with ethics, good governance, and mutual benefits.
3. Personal objective to support personnel to achieve the goal of motivating and maintaining the organization to treat personnel with corporate governance following the Labor Relations Act.
4. Functional objective, the mission meets the needs of the organization with the expectation that the person can work effectively.
Discussion
In today's world that relies on innovation as an economic driver, organizations that are prepared to adapt, flexibly, and continually innovate have a competitive advantage. Therefore, innovation is a new strategic tool that every organization seeks and builds for sustainable development (Dessler, 2003). Technological advances have affected many aspects of human resource management. Many organizations are adopting artificial intelligence (AI), and robots to replace human workers. However, the work of executives, planners, creative designers, or some types of skilled workers still relies on the knowledge and skills of human resources. Sensitive, flexible, creative, or empathetic administration and understanding complex behaviors comparable to human beings. Because in the end, Human Capital is the guiding force of technology. Therefore, it can be said that intelligence, knowledge, skills, and abilities of human resources are the key to building efficiency and driving the organization to grow steadily (Phonanan, 2003). Human resource management for innovation requires both "science" and "art" to obtain guidelines for developing personnel to create innovation, motivation, and motivation to create innovation for the organization, including executives must have the Committed to bringing the organization to an atmosphere of innovation, coupled with the effect of human resource management that will enable personnel to work appropriately for the job and continually develop themselves. This will result in the ability to use the potential of human resources appropriately to work for the organization to achieve its goals (Tienphut, 1996). In line with Pochjanart & Chienwattanasook (2020) discussing Innovative Leadership, which is the key to driving an innovative organization, emphasizing the alignment of organizational strategies with modernity and technological advancement along the way, it must not focus in any direction or stick to past successful actions and strategies.
However, driving innovation in the organization through human development cannot be successful without supporting factors such as
1. The innovative vision of personnel in the organization from executives to employees at all levels, especially the human resource department that plays an important role in adjusting human resource strategies to keep up with the dynamics of the world.
2. Adjust the organization structure to be Flexible according to the key concept of Agile, which emphasizes product and service development, works without attachments as quickly as possible, and adjusts one by one to foster an innovative culture.
3. New human resource management strategies in innovation HR INNOVATION, parallel to the use of technology intelligently to facilitate HR work that is suitable for the organization.
4. Exchange of knowledge, build a strong learning organization foundation by building knowledge, linking as a network between internal and external teams, accepting new perspectives from Outside-in, blending internal ideas to form an organization. of innovation in the end.
It can be seen that both domestic and international case studies such as Siam Commercial Bank (SCB), and Tesla Company (Tesla) have all applied innovations in human resource management. The SCB has developed upskilling for employees at the Bank-wide level, including building Employer Branding to the general public through a project to promote data analysis skills for personnel and manpower for Data Analytics for Upskilling. It is also creating a Data Champion or leadership in creating an organizational culture in using data to create success for the organization. At the same time, Tesla is a clear example of an organization that has achieved innovation in electric vehicle manufacturing and Artificial Intelligence: AI, that is, it has achieved both product innovation and process innovation, which consists of technological process innovation and organizational process innovation, with the key factor being the strong support of leaders with Growth Midset to drive the organization towards a truly innovative organization. The success of these two organizations would not be possible without the creation of a foundation for human resource management in an organization that is ready to continuously learn, in which the correct learning consists of: learning new things (Learn), not sticking to what has been learned or dared to erase the same (Unlearn), including learning what we already know from a new perspective, and realizing The value of the knowledge we gain from that perspective (Relearn).
At present, innovation in human resource management consists of 4 main dimensions:
1. Recruiting and selecting qualified personnel through the use of AI and modern technology to help facilitate the reduction of Hallo effect or Cognitive Bias of HR on applicants using various social media channels, either Facebook or LinkedIn. etc. Particularly noteworthy is that Facebook's rebranding to Meta marks a new step towards the future vision of the Metaverse, a "virtual environment" that connects virtual communities. Users can meet, work, play, shop online or social media through Virtual Reality (VR), and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies. Including applications on mobile phones or other devices is a significant change in which in the future we will be able to teleport to sit and work in the office in a hologram format without having to travel (Thaipbs, 2021).
2. Training and personal development must adhere to the principle of learning center with learners as the main (Learner – Center Training), through group activities Exchanging opinions, suggestions as well as being able to use techniques such as AAR, Show and Share, Reflection to reflect the exchange of ideas to conclude about new creative ideas that lead to innovation.
3. Compensation and employee relations, should use various incentive methods, adhere to Worker Wellbeing principles such as hybrid working model, reduce working hours to allow employees more time to do their work. Creative or self-development activities in areas of interest that may not be directly related to the job, or change the stressful work atmosphere to do some stress-relieving activities during the working hours of the day, for example.
4. Collecting information about human resources, using the Human Resource Information System: HRIS came to help as a database that organizations use to collect and analyze employee information, Focus is used to improve the quality of life and working conditions of employees rather than control. This system is like a repository of various organizational data, including promotion information. Transfers, payroll information, profits, absenteeism and leave, performance appraisal information, administrative development information about training and development, etc. The functionality of the system tracks the skills and experiences of all employees, as well as evaluates their development, which helps management in anticipating career success, making effective planning decisions, and scheduling necessary training and development. and most appropriate for the time. In the organizational transformation era, it is very necessary to develop a database of management development, a large amount of manpower data to determine which skills are suitable for the new structure or which skills need to be improved. This automated system processes information for top executives to find them quickly and easily and make effective decisions. (Thamviriyavong, 2021). In short, HRIS is an application system used for collecting information related to all human resources of an organization such as recruiting and recruiting, creating training activities, and developments that will stimulate operational innovation.
While Conner & Ulrich (1996) offer a modern perspective on human resource management, the technology used in human resource management practice is available according to the following objectives (Siririn, 2019)
1. Application Service Providers (ASP) is a computer system that is applied to apply for a job through online control.
2. Web Portals is a website that collects information related to human resource management.
3. Streaming PC Video is software used for remote training.
4. Wirelessor Mobile Tools are devices connected to the wireless and mobile networks to facilitate employees to access the activities of the organization.
5. Personal Digital Assistants is an application used to assist human resource managers to facilitate the management of modern human resources.
6. Monitoring Software is a program used to track the work on the Internet, receiving and sending e-mails, including the performance of employees in matters related to personnel management, etc.
In addition, Prakash Rao (2021) mentioned
1. Digital Transformation in the work of HR, which combines HR Applications with the cloud or digital platform. platform) that allows shorter recruitment cycles and can be updated in real-time about the recruitment process through software such as ATS (Application Tracking System).
2. The concept of Outcomes Over Efforts is used to work in the WFH model, causing organizations to change the concept to focus on Outcomes. The new standard of assessment of employee efficiency and effectiveness is focused on considering the results and outcomes that are. more concrete
3. Implementing objective key results: OKRs help align personnel performance with business goals by linking them to Key KPIs (focusing on Outcomes) and Action Plans (focusing on Efforts), by defining Key Results based on the objectives following the important goals set by the organization, In short, OKRs are goal-setting methods to measure success by defining the objectives we want to achieve and defining the key result or outcomes to be measured to know whether we have achieved the objectives or not.
It can be seen that all this is a stepping stone to change in the modern world. However, the important role of Innovative HR is not only being a strategic consultant to the organization but also focusing on creating and maintaining high-performing culture, up-skilling and reskilling of employees at all levels, as well as having to use innovations and learn about modern technology professionally, such as applications that are useful for HR departments to programs that help work of the HR department is more efficient to adapt to help facilitate and speed up work to keep pace with the changing world. Build Know-How, your own body of knowledge and practical knowledge in human resource management, including recruiting and selection, human resource development, welfare and labor relations, to various strategies related to human resources, etc. Having a strong own Know-How is one of the keys to a successful organization.
Conclusion
The dynamics of the economy and industrial society in the 21st century lead to an era of challenges in the digital world of the future by connecting with the power of technological advancements in all dimensions, whether it is Cloud Computing, Big Data, Blockchain., or modern financial management in a cashless society such as financial transactions through banking applications on smartphones, various cryptocurrencies, as well as connecting innovations and new technologies such as AI, AR, VR, Robots. These changes range from the management of global corporate information to the household economy, which is a significant change to organizations and people around the world, building knowledge and adapting to change. It is therefore essential to the work of human resource management in the organization which is transforming from an ongoing 'disruption' to a 'new step of innovation growth'.
An organization that will survive is an organization that lays the foundation for building itself into an innovative organization, Innovators are human resources that are in an organization based on key drivers: leadership's vision, human resource potential, work environment, and organizational culture that encourages innovation. All dimensions are committed to continuous creative development, dare to think, dare to say, dare to do new things. By relying on knowledge capital, skill capital, wisdom capital, happiness capital. Organizational leaders have to have a Growth Mindset, to recruit, create and maintain that capital in human resources. However, it was found that innovation in HR Innovation focuses on four key pillars: Innovations in recruiting and selection, innovations in training and development, innovations in compensation and labor relations, as well as innovations in the use of HRIS information technology systems.
However, the study found that what has changed in the subject of HR Innovation in this new era is Flexible according to the key concepts of Agile from system structure, personnel development, and knowledge management, including various technologies, as long as the organization can create a leadership image as well as create its own body of innovation knowledge, it reflects a strong foundation in HR Innovation that can draw out the potential of the personnel to create the highest efficiency. more concretely. And of course, this important step is a success in management and transcending the transformation towards excellence, creating a stable competitive advantage at the international level.
Recommendation
From this study on innovation and challenges in human resource management, the conclusions were drawn for the benefit of organizational operations and human resource operations.
Policy Commendation
1. There should be a network of innovation cooperation in human resource management between organizations to upgrade products or services to have more innovative value, able to learn, exchange and share success for continuous development.
2. Government organizations and educational institutions should consider the development of key ideas in promoting innovation in educational curricula by laying the foundation from elementary school to university by adjusting them to keep up with the times and in line with the national strategy because good seeds are It creates a thriving tree that means innovation in human resources as well.
Finding Using Recommendation
1. Innovative evaluation, HR should consider 360 degrees as traditional assessment methods may not be comprehensive or have gaps in some areas, or different work processes and measurements should be used between general tasks and tasks. It is Innovation, which on the other hand measures the results of the organization's innovation team. It is also classified as Innovation in HR as well.
2. Encourage agencies in the organization to create innovations in their work by setting quality standards of organizations with innovation excellence in comparison with successful models or in the same organization by promoting incentives as incentives. In a more diverse form to bring innovation, success is to compete nationally or internationally.
Acknowledgment
This paper belongs to Dr. Julaluck Punthung, his e-mail: julaluck.nk@gmail.com. And the Corresponding author is Dr. Kittachet Krivart, School of Political Science and Laws, Walailak University, Thailand, e-mail: kittachet.kr@wu.ac.th.
References
Alvin, T. (1980). The third wave. New York: William Marrow.
Conner, J., & Ulrich, D. (1996). Human resource roles: Creating value, not rhetoric. Human Resource Planning, 19(3), 38 - 49.
Dessler, G. (2003). Transition to effective management with INSEAD executive education. New York: McMillan.
Drucker, P.F. (1998). “The coming of the new organization.” Harvard Business Review on Knowledge Management. Boston: Harvard Business School Publishing. 1-19.
Dwivedi, R.S. (1985). Management of human resources. New Delhi: Oxford & IBH Publishing.
Hongladarom, C. (2018). Theory of 3 Circles.
Hrnote. (2019). New Roles of HR in the Digital Age.
Michael, E.P. (1990). The competitive advantage of nations: With a new introduction. Eleventh printing: Free Press Business & Economics.
National Innovation Agency. (2010). Innovation Management Executives (IMEs). Bangkok: National Innovation Agency.
Phonanan, T. (2003). Focus human resource management in the guidelines to employee satisfaction. (2th ed.). Bangkok: Yellow pages.
Pochjanart, P., & Chienwattanasook, K. (2020). “Innovative leadership for the competitive advantage of the organization in the 21st Century”, Journal of Management Science Review. 23(1), 241-253.
Prakash Rao. (2021). A KPI Driven HR Leader's Toolkit for 2021.
Rhecsenanth, N. (2003). Human resource management. Bangkok: SE-ED Book Center.
Siririn, J. (2019). HRM 5.0 “Human Resource Management” 5G Era (End).
Thaipbs, (2021). Facebook changes company name to “Meta” Enters the Metaverse World.
Thamviriyawong, P. (2021). “The guide to innovative human resource management”, Dusit Thani College Journal. 15(1), 516-528.
Thummachote, R. (2018). “Innovative human resource management of Thailand to create competitive advantages in the ASEAN community: A case study of siam cement Thailand public company limited and advanced info service public company limited”, Rajapark journal. 12(26), 186-197.
Tienphut, D. (1996). Human resource management in the next decade. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Traipopsakul, S., & Pitchayangkool, C. (2021). Innovation Management. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Werther, W.B., & Kieth, D. (1993). Human Resource and Personnel Management. New York: McGraw – Hill.
Wutthirong, P. (2016). HR in the next decade. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Wutthirong, P. (2020). Innovation management: Resource Learning Organization and Innovation. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
Yoonyong, T. (2020). Human Resource Management. Tak: Northernprint, 541.
Yotsomsak, S. (2006). Human Resource Management. Bangkok: M.T.Press.
Received: 20-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. JMIDS-21-10031; Editor assigned: 22-Dec-2021; PreQC No. JMIDS-21-10031(PQ); Reviewed: 7-Jan-2022, QC No. JMIDS-21-10031; Revised: 15-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. JMIDS-21-10031(R); Published: 20-Jan-2022