Research Article: 2021 Vol: 25 Issue: 1S
Influencing of Collaboration and Communication with Community besides Interaction of Government Intervention to Improve the Police Innovative Services in Dubai
Khalid Khalifa Fadhel Khalifa Almazrooei, University in Changlun
Muhammad Fuad bin Othman, University in Changlun
Mohammed R A Siam, University in Changlun, Kedah
Keywords
Community Collaboration, Community Communication, Government Intervention, Police Innovative Services, Dubai Police.
Abstract
The aim of study is to examine the impact of the community collaboration and community communication on the innovative services delivery by surveying stockholders in relation to the Dubai Police in the UAE. The study population equates to the total number of civil servants excepts those in police or security agencies that knew much about the security developments in Dubai. The philosophy behind this is to investigate the unbiased. The actual sample size for this study is 344 which is collected in face-to-face collection technique by using a printed copy. The samples are collected from different location to have the best diversity in locations and duty among the population. The results show that the proposed model is successful because it can explain 40.34% of the innovative police services. The two variables community collaboration and community communication are both good predictors and have significant relationships with the innovative police services. For government intervention, it seems that the more interact the stronger relationship between community collaboration and innovative police services but not community communication.
Introduction
The concept of innovativeness in recent times has gained numerous attentions from different scholars. Thus, innovativeness had been argued to be key to sustainability practices, effective and efficient service delivery (Shahzad et al., 2020). Moreover, the innovativeness specifically the use of artificial intelligence had also been argued to have reduced cost and increase the revenue (Cam et al., 2019). Although the importance of innovativeness has been widely unveiling, the factors that trigger innovation in organizations to date remain vague specifically in the police force (Pasha, 2019). Some of the arguments given that causes innovativeness include the interplay between several actors in society (Gallouj et al., 2018). While scholars believed that advancement in technology has spurred global innovation (Isaac et al., 2019). So, what led to innovation specifically remains vague, to answer this question, the researcher feels the urge to embark on empirical investigation.
Nevertheless, there has been continuous innovation in the police force specifically in the Dubai police servicing to the extent that Dubai was awarded as the most innovative country based on human capital and research; infrastructure; market sophistication; business sophistication; knowledge and technology outputs; and creative outputs (Abbas, 2019). With this, the police department argues that their technological innovation had solved some crimes issues that might be left unsolved if not for their technological innovation (Shrouk, 2017). Also, from the available pieces of literature, there are indications that factors such as technological advancement had prompted innovativeness specifically the adoption of artificial intelligent in the business model as well as in the police force (Cam et al., 2019).
In business, there are indications that the adoption of artificial intelligence has been beneficial whereas, there is contempt the contribution of artificial intelligent pertaining to police service innovativeness (Delle et al., 2018).
On a contrary, academics and practitioners identified that the innovativeness embarked on by the police to keep the community safe using artificial intelligence alone without the collaboration and communication with the community does not really work at most times (Dinnen & Peake, 2015). To support this, evidence from the Crime and Safety report (2019) listed that despite the innovativeness ongoing in the police force service in Dubai, the street is arguably not 100% safe for United State citizens visiting Dubai. The crimes like pickpocketing, ATM scams and Fraud, shoplifting and on rare occasions, the criminals committing crime uses weapons (OSAC, 2019). So, the question is, if innovativeness in policing service is effective why crime still exists in the street specifically, the street of Dubai. To answer this rhetoric question, the researcher considers empirical investigation on the perceptions of the community towards the effectiveness of innovativeness in policing services in Dubai.
Similarly, there have been ongoing arguments about the effectiveness of police-community collaboration in assuring and delivering effective policing services. For example, the study of Jackson (2015), argue that to deliver an innovative effective policing service, to ensure transparency, trust, and usefulness, the police need to collaborate and communicate with the community. The contrary to this, believes that caution needed to be taken so that juveniles are protected from policing abuse (Bleakley, 2020). However, the considering this, it is paramount for the researcher to examine the perceived effectiveness of communication and collaboration in policing service as part of innovativeness in policing service in Dubai. This is because this area of research is yet to gain attention from scholars and practitioners. Despite the rampant innovation happening around the globe, there are indications that the observed innovativeness will not be possible if there no backing from the government via supportive policies (Shumetie & Watabaji, 2019).
The aim of study is to examine the impact of the community collaboration and community communication on the innovative services delivery by surveying stockholders in relation to the Dubai Police in the UAE.
Literature Review
Innovation in the Service Industry
The objective of innovation is to provide customers with good services and enhanced products as well improving customers’ experiences which in turn lead to business success (Keiningham et al., 2020). Therefore, from this definition, it is not bad to promptly argue that innovation in the service industry has a significant impact on business success (Wallenburg et al., 2019). Using a case study approach to examine the factors that contributes to service innovativeness, factors such as environment, government intervention via policy employee, customers and expert ideas were reported by earlier studies to significantly contribute to positive or intend service innovation result (Singh et al., 2020). Other factors earlier investigations argue to enhance service innovativeness includes legal protection, patents, and trade secrets (Morikawa, 2019). Although, arguing that service innovation is essential to business success, nevertheless, the author argues that for this to be achieved, all the business employees needed to be tune in to the objective of the innovation (Shafi, 2020).
Furthermore, Jahanshahi, et al., (2020), argues that the innovation outcome must be customer-oriented. Moreover, to support this stance, using an experimental approach to compare expert and customers’ approaches to customers’ needs, the customers are more innovative in-service delivery, while, experts’ innovative approach is quite easy to implement (Rai, 2016). According to the (Salunke et al., 2019), argue that technically suggest customers’ input during service innovation plans to enhance innovation quality. Moreover, to achieve significant service innovativeness, the employee must be given some amount of autonomy to achieve creativity and innovativeness (Peñate et al., 2020). Meanwhile, the conceptual investigation exploiting and including knowledge-intensive business offerings significant to innovativeness itself during the implementation of the service innovation process (Winneberger & Hengsteler, 2020).
History of Police Services
Police are set of individuals empowered by the state to control crimes enhance peace, harmony, and progress among the people of the community residing within the pre-defined jurisdiction (Babatunde, 2017). Other functions of the police in society include the protection of the elderly from being victims of crime (Xie & Baumer, 2019), disciplinary control and the knowledge and regulation of populations (Stenson, 1993). According to Goerger, et al., (2020), police are the verifiable public agency in charge of crime control policymaking and implementation. History has it that policing service start as a volunteerism job as those who join the police at the early time, did it out of the zeal to keep the community safe, therefore they are not being paid for the job done (Dwyer et al., 2020). The needs arise from a population explosion around that time and several public unrests and rioting rocking most cities in the United States of America (USA) and the United Kingdom (UK) (Gaffikin & Warf, 2002).
Community Collaboration and Innovative Police Service
Community Police Cooperation
A collaborative partnership between your law enforcement agency and the individuals and organizations it serves is essential to finding answers to community problems (Dlamini, 2020; Mitchell, 2016). So that, and according to many researchers such as (Currie & Sellassie, 2019; Harkin, 2018; Melvin-Campbell, 2019; Monteoliva-García, 2020) they found out that a better community-Police collaboration will defiantly lead to a better and effective police service delivery (Currie & Sellassie, 2019; Mitchell, 2016) and based on that the researcher is expecting significant positive direct effect of Community-Police collaboration in the police force on effective police service delivery. As this hypothesis is compatible with other hypothesis in others studies such as; (Buffone et al., 2017; Christensen et al., 2018; Currie & Sellassie, 2019; Harkin, 2018; Melvin-Campbell, 2019).
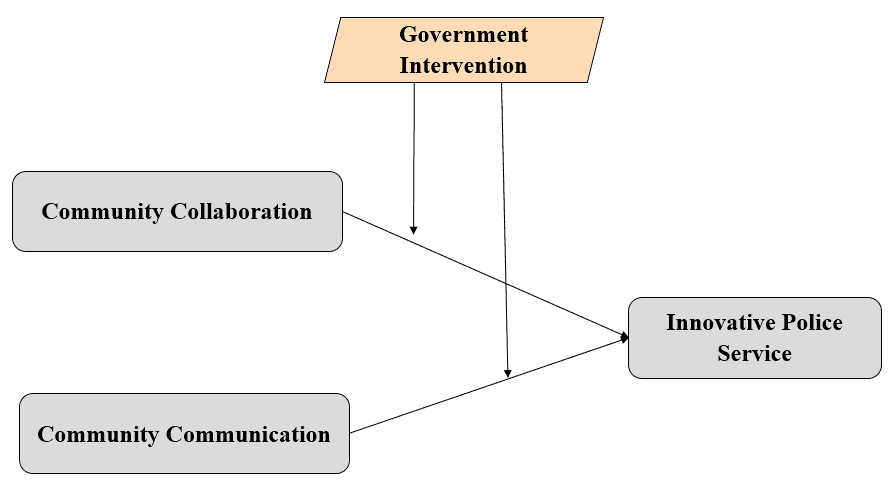
Hypothesis 1 Community Collaboration has a significant relationship to the innovative service delivery in Dubai police.
Community Communication and Innovative Police Service
Community-Police communication is the channels and tools to make two ways communication between the police and community to solve the community problems (Stawnicka & Klonowska, 2018; Strudwick et al., 2019). So that, and according to many researchers such as (Fray, 2017; Lu, 2019; Nawab et al., 2019; Strudwick et al., 2019) they found out that a better community-Police communication will lead to a better chemistry and enhance the coordination as well which will lead at the end and to a better and effective police service delivery (Dlamini, 2020; Pridmore et al., 2019) and based on that the researcher is expecting significant positive direct effect of Community-Police communication in the police force on effective police service delivery. As this hypothesis is compatible with other hypothesis in others studies such as; (Dlamini, 2020; Lu, 2019; Mitchell, 2016; Monteoliva-García, 2020; Pridmore et al., 2019; Strudwick et al., 2019).
Hypothesis 2 Community Communication a significant relationship to the innovative service delivery in Dubai police.
Government Intervention Moderation 1
As has been defined before, government intervention is kind of instructions and laws imposed by government to seek some changes like social or economic (Droste et al., 2016; Huang & Du, 2017; Zhang & Yousaf, 2020). On the other hand, and as has been explained before about the significant relationships between the community-police collaboration in the police agency and effective police service delivery (Deng et al., 2017; Sinayi & Rasti-Barzoki, 2018; Wang, 2018). Other researchers such as (Abdulhabib & Al-Dhaafri, 2019; Buffone et al., 2017; Christensen et al., 2018; Deng et al., 2017; Melvin-Campbell, 2019; Mitchell, 2016; Sinayi & Rasti-Barzoki, 2018; Wang, 2018) also discussed and emphasized on the important positive moderating role of the government intervention in the relationships of this study independent and deepened variable (Abbas, 2020; Palladan, 2017) based on that the researcher is expecting that government intervention significantly moderates the relationship between community-police collaboration and effective police service delivery. As this hypothesis is compatible with other hypothesis in others studies such as; (Abbas & Policek, 2020; Flom, 2020; Hendrix et al., 2018; Skrbiš & Laughland?Booÿ, 2019; Young & Ready, 2018).
Hypothesis 3 Government intervention significantly moderates the relationship between community collaboration and the innovative service delivery in Dubai police.
Government Intervention Moderation 2
Government intervention is the process or roles that are imposed by the government to make some changes in certain situations where the intervention is needed (Howell et al., 2019; Mahmoudi & Rasti-Barzoki, 2018; Wang, 2018). On the other hand, and as has been explained before about the significant relationships between the community-police communication in the police agency and effective police service delivery (Maclean, 2017; Margraf, 2019). Other researchers such as (Abbas & Policek, 2020; Flom, 2020; Musgrave, 2020; Nowicka-Skowron, 2018; Vanharanta, 2019) also discussed and emphasized on the important positive moderating role of the government intervention in the relationships of this study independent and deepened variable (Alosani et al., 2020; Kawiana et al., 2018; Kombo, 2018; Willis et al., 2016) based on that the researcher is expecting that government intervention significantly moderates the relationship between community-police communication and effective police service delivery. As this hypothesis is compatible with other hypothesis in others studies such as; (Al-Ali et al., 2017; Chatman & O’Reilly, 2016; Del-Rosario & René, 2017; Paro & Gerolamo, 2017) (Figure 1).
Hypothesis 4 Government intervention significantly moderates the relationship between community communication and the innovative service delivery in Dubai police. Emotional intelligence has a significant mediating effect in the relation between attributed charisma and employees’ commitment in UAE banks.
Methodology
The study follows systematic steps to achieve the desired objectives in a scientific approach. The study is allocated as deductive approach because it is based on hypothesis evaluation. In addition the study is quantitative methods because the design is based in numerical data and statistical analysis as well. The data used for this study is original collected in a cross-sectional time horizon in 2019 by using a questionnaire that adapted from previous studies.
The study population equates to the total number of civil servants excepts those in police or security agencies that knew much about the security developments in Dubai. The philosophy behind this is to investigate the unbiased. The actual sample size for this study is 344 which is collected in face-to-face collection technique by using a printed copy. The samples are collected from different location to have the best diversity in locations and duty among the population.
The survey was organized to ask question in likert-5 format. Likert 5 questionnaire style has been used in social science studies for long time and proved to be a suitable style for measuring human perceptions. Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) techniques are used for statistical data analysis via the SmartPLS software package, which is used in management and social science studies such as (Salem & Alanadoly, 2020; Salem & Salem, 2018).
The items used in measuring community-police collaboration were adapted from the studies of (Carter & Radelet, 2002; Fridell & Lim, 2016; Pickett & Roche, 2016; Nagin et al., 2015). In general, six items were used in measuring community-police collaboration.
• I believed collaborating with the community is the best strategy to prevent crime in my society
• I perceived that community partnership with police force enhance community security.
• In my own opinion, I believed the police department gather more information about potential crime in the community
• The minority races are subjected to police brutality due to community policing.
• I perceived community policing to be harsh on minority race in area where the minority race has history of crime
• The police need to collaborate with the minority ethnics to make them feel safe.
The items used in measuring community-police communication were adapted from the studies of (Cam et al., 2019; Mokyr, 2018; Maguire & John, 2006; Williams et al., 2018). In general, seven items were used in measuring community-police communication.
• Communicating with the community enhance strategic policing policies formulation.
• Interaction of police department and the community enhance policy and community priorities mitigations.
• Having civilian police among the society will help to prevent unforeseen crime.
The awareness that people are working for police make it difficult for crime offenders to commit crime.
• Collaborating with police will leads to power abuse by those collaborating with police officers.
• The minority race will suffer from the joint civilian police collaborations.
• Reporting anonymous case with precise location has help improve communication between community and police officers.
The items used in measuring government intervention were adapted from the studies of (Gayadeen & Phillips, 2014; Morikawa, 2019; De-Fuentes et al., 2001; Cheurprakobkit & Puthpongsiriporn, 2005). Therefore, to measure the moderating role of government intervention in this research, a 9 items were developed to capture the perception of the masses on the issues raised in this research.
• I believed the government provides resources ‘finance’ needed to support police-community partnership innovation.
• The provision made by the government promotes innovation in delivering effective police service
• The provision made by the government inhibit innovation in delivering effective police service.
• I believe the role government can enhance service innovativeness between the police and the community by formulating and implementing policy that encourage such innovativeness.
• I believe it is the duty of the government to create awareness about the police-community collaboration.
• It is the duty of the government to create awareness about several channels of effective policing strategies.
• Through unbiased service policy from the government, the interest of the minority race can be protected can be protected against community policing abuse of power.
• Through unbiased service policy from the government, the civil rights of the minority race can be protected against community policing abuse of power.
• Overall, the intervention of government to enhance police innovation had made significant impact.
The items measuring service quality were adapted in this research because it had been widely adapted in social science researches and confirmed to be reliable and valid (Cronin & Taylor, 1992, Gronroos, 1988; Lien & Zhou, 2017; Napitupulu et al., 2018; Santos, 2003). Eight questions are adapted for this scale.
• In recent times, Dubai Police are proactive in preventing crimes.
• With the technology adoptions, the police response time has significantly improved.
• Several innovativeness embarked upon by the policing agency meets the needs of the society
• The police agency successfully integrates the society into the security team.
• The recent innovativeness in the policing agency protect the Dubai citizens from domestic crime.
• The recent innovativeness in the policing agency protect the Dubai citizens from international crime.
• Overall, I perceived that the police service quality has significantly improved.
• Overall, the communities are satisfied with the recent policing services delivery.
Findings
Validity and Reliability of Constructs
The proposed model of this research is cause-effect model to interconnect between community collaboration, community communication, government intervention, and innovative police services. Such designs need to be tested for validity and reliability before proceeding to the relationships evaluation.
Several measures have been conducted such as composite reliability, outer loading, convergent validity, and discriminant validity to ensure reliability and validity of the measurement model (Hair, Hult, Ringle & Sarstedt, 2016; Sekaran & Bougie, 2016). As shown in Tables 1 composite reliability is measured by Cronbach’s Alpha and all values are above the cut-off value of 0.70.
Therefore, the reliability of measurement model is achieved. In addition, outer loading for all the items are above 0.708 with no cross loading from foreign item, therefore indicator reliability is achieved. The Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values are above 0.5, therefore convergent validity is achieved.
Finally, Table 1 shows the matrix of Fornell-Larcker criterion, which indicates that no discriminate validity issues are. Some items were eliminated based on the rule of thumb for outer loading and cross loading.
| Table 1 Construct Reliability and Validity |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construct | Item | Loading | AVE | Cronbach’s alpha |
| Community Collaboration (CCR) | CCR1 | 0.744 | 0.607 | 0.869 |
| CCR2 | 0.827 | |||
| CCR3 | 0.874 | |||
| CCR4 | 0.769 | |||
| CCR5 | 0.759 | |||
| CCR6 | 0.689 | |||
| Community Communication (CCU) | CCU1 | 0.827 | 0.622 | 0.877 |
| CCU2 | 0.75 | |||
| CCU3 | 0.84 | |||
| CCU4 | 0.737 | |||
| CCU5 | 0.862 | |||
| CCU6 | 0.701 | |||
| Government Intervention (GI) | GI1 | 0.725 | 0.567 | 0.856 |
| GI2 | 0.742 | |||
| GI3 | 0.79 | |||
| GI4 | 0.763 | |||
| GI5 | 0.891 | |||
| GI6 | 0.717 | |||
| GI7 | 0.758 | |||
| GI8 | 0.779 | |||
| GI9 | 0.725 | |||
| Innovative Police Service (IPS) | IPS1 | 0.738 | 0.606 | 0.906 |
| IPS2 | 0.714 | |||
| IPS3 | 0.708 | |||
| IPS4 | 0.795 | |||
| IPS5 | 0.797 | |||
| IPS6 | 0.801 | |||
| IPS7 | 0.844 | |||
| IPS8 | 0.819 | |||
This roadmap for examining the validity and reliability are applied in social science studies such as Salem & Alanadoly (2020) and Salem & Salem (2018). ( Table 2 )
| Table 2 Discriminant Validity – Fornell-Larcker Criterion |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCR | CCU | GI | IPS | |
| CCR | 0.779 | |||
| CCU | 0.187 | 0.788 | ||
| GI | 0.292 | 0.175 | 0.736 | |
| IPS | 0.572 | 0.374 | 0.487 | 0.778 |
Structural Model
The model of innovative police services can explain 40.34% of its variance based on the prediction of community collaboration and community communication. The purpose of assessing the power of the model construct is to devalue the success of the model based on predictive power R2 (Hair et al., 2016). The results of the hypothesized relationships are also tabulated in Table 3. The table shows that two direct relationships are accepted.
| Table 3 Structural Relationships and Hypothesis Testing |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path Coefficient | Standard Error | T Statistics | P Value | Effective Size f2 | Relationship | |
| Community collaborationà Innovative Police Services | 0.369 | 0.036 | 10.184 | 0 | 0.27 | Significant |
| Community communication à Innovative Police Services | 0.206 | 0.035 | 5.824 | 0 | 0.093 | Significant |
The threshold for accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is p-value value, which is supposed to be less than 0.05 (significance at 5% level). Community collaboration has the highest impact with path coefficient score of 0.369 and effective size of 0.270. Community communication has the second impact with path coefficient score of 0.206 and effective size of 0.093.
For the moderation affect, Table 4 shows the moderation of government innovation in the two relationships. Government intervention interact in the relationship between community collaboration and innovative police services is not significant is significant with P value=0.003 and path coefficient of 0.599. However, government interventions interact in the relationship between community communication and innovative police services is not significant because the P value: 0.205.
| Table 4 Moderation Assessment of Government Intervention (GI) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path Coefficient | Standard Deviation | T Statistics | P Value (one tailed) | Status | |
| CCR * GI-> IPS | 0.599 | 0.197 | 3.042 | 0.003 | Significant |
| CCU * GI-> IPS | 0.259 | 0.204 | 1.27 | 0.205 | Non-Significant |
Discussions and Conclusions
The aim of study is to examine the impact of the community collaboration and community communication on the innovative services of the Dubai Police; besides to the interaction of the government intervention. The results show that the proposed model is successful because it can explain 40.34% of the innovative police services. The two variables community collaboration and community communication are both good predictors and have significant relationships with the innovative police services. For government intervention, it seems that the more interact the stronger relationship between community collaboration and innovative police services but not community communication.
The study contributes to the knowledge of prediction of the innovative police services in Dubai. The proposed combination of variables and inclusion of government intervention as a moderator is significant contribution to academic research.
This study is limited to the empirical examination of Dubai Police and the replication of the same conceptual model in different countries or even in other organizations will be beneficial to the generalization of the relationships in the model. In addition, the model can explain 40.34% of the variance but by adding more variables the explanation for sure will be better. The rejection of the interaction of government intervention in the relationship from technology use is rational but need more investigation.
References
- Abbas, N. (2020). Fit and appropriation model for training: An action research study to advance mobile technology training in police forces. Lancaster University.
- Abbas, N., & Policek, N. (2020). ‘Don’t be the same, be better’: An exploratory study on police mobile technology resistance. Police Practice and Research, 1–20.
- Abdulhabib, A.A.A., & Al-Dhaafri, H.S. (2019). The moderating role of training on the relationship between strategy management, information technology management and organizational performance of Sharjah police. People: International Journal of Social Sciences, 5(1).
- Afshar-Jahanshahi, A., Al?Gamrh, B., & Gharleghi, B. (2020). Sustainable development in Iran post?sanction: Embracing green innovation by small and medium?sized enterprises. Sustainable Development, 28(4), 781-790.
- Al-Ali, A.A., Singh, S.K., Al-Nahyan, M., & Sohal, A.S. (2017). Change management through leadership: The mediating role of organizational culture. International Journal of Organizational Analysis.
- Alosani, M.S., Yusoff, R.Z., Al-Ansi, A.A., & Al-Dhaafri, H.S. (2020). The mediating role of innovation culture on the relationship between Six Sigma and organisational performance in Dubai police force. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma.
- Bleakley, P. (2020). The cult of corruption: Reframing organizational frameworks of police corruption from a cultic perspective. Deviant Behavior, 1–13.
- Brynjolfsson, E., Rock, D., & Syverson, C. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the modern productivity paradox: A clash of expectations and statistics. In The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda. University of Chicago Press, 23-57.
- Buffone, S., Chenier, A., Schulenberg, J.L., & Sycz, D. (2017). Improving the police complaints system: Stakeholder collaboration as a vehicle for systems change. American Journal of Criminal Justice, 42(2), 293–313.
- Chatman, J.A., & O’Reilly, C.A. (2016). Paradigm lost: Reinvigorating the study of organizational culture. Research in Organizational Behavior, 36, 199-224.
- Cheurprakobkit, S., & Puthpongsiriporn, S. (2005). Service culture for the implementation of community policing: A case study of the Malaysian police. International Journal of Police Science & Management, 7(4), 286-299.
- Christensen, T., Lægreid, P., & Rykkja, L.H. (2018). Reforming the Norwegian police between structure and culture: Community police or emergency police. Public Policy and Administration, 33(3), 241–259.
- Cronin, J.J., & Taylor, S.A. (1992). Measuring service quality: A re-examination and extension. Journal of marketing, 56(3), 55-68.
- Currie, M., & Sellassie, A. (2019). Innovative collaboration to further community self-determination.
- Del-Rosario, R.S.M., & René, D.P. (2017). Eco-innovation and organizational culture in the hotel industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 65, 71–80.
- Delle-Donne, J., & Fortin, F. (2018). Innovation and policing: Factors influencing the adoption of social medias by members of Quebec police organizations. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice.
- Deng, L., Jiang, P., Li, S., & Liao, M. (2017). Government intervention and firm investment. Journal of Corporate Finance, 101231.
- Dinnen, S., & Peake, G. (2015). Experimentation and innovation in police reform: Timor-Leste, Solomon Islands and Bougainville. Political Science, 67(1), 21-37.
- Dlamini, S. (2020). A comparative analysis of the quality of community police forums in local Cato Manor & Glenwood communities, South Africa. Cogent Social Sciences, 6(1), 1809141.
- Droste, N., Hansjürgens, B., Kuikman, P., Otter, N., Antikainen, R., Leskinen, P., … & Pitkänen, K. (2016). Steering innovations towards a green economy: Understanding government intervention. Journal of Cleaner Production, 135, 426–434.
- Dwyer, A., Ball, M., Lee, M., Crofts, T., & Bond, C. (2020). Barriers stopping LGBTI people from accessing LGBTI police liaison officers: Analysing interviews with community and police. Criminal Justice Studies, 1-20.
- Flom, H. (2020). Controlling bureaucracies in weak institutional contexts: The politics of police autonomy. Governance, 33(3), 639–656.
- Fray, C. (2017). Narrative in police communication: The art of influence and communication for the modern police organization.
- Fridell, L., & Lim, H. (2016). Assessing the racial aspects of police force using the implicit-and counter-bias perspectives. Journal of Criminal Justice, 44, 36-48.
- Gaffikin, F., & Warf, B. (2002). Urban policy and the post-Keynesian state in the United Kingdom and the United States. The City: Land use, structure, and change in the Western city, 2(3), 238.
- Gallouj, F., Rubalcaba, L., Toivonen, M., & Windrum, P. (2018). Understanding social innovation in services industries. Industry and Innovation, 25(6), 551-569.
- Gayadeen, S.M., & Phillips, S.W. (2014). The innovation of community policing and the COPS Office: does diffusion of innovation theory hold in a manipulated environment? International Journal of Police Science & Management, 16(3), 228-242.
- Goerger, S., Mummolo, J., & Westwood, S.J. (2020). Which police departments want reform? Barriers to Evidence-Based Policymaking.
- Gronroos, C. (1988). Service quality: The six criteria of good perceived service. Review of business, 9(3), 10.
- Harkin, D. (2018). Community safety partnerships: The limits and possibilities of ‘policing with the community.’ Crime Prevention and Community Safety, 20(2), 125–136.
- Hendrix, J.A., Taniguchi, T.A., Strom, K.J., Barrick, K.A., & Johnson, N.J. (2018). The eyes of law enforcement in the new panopticon: Police-community racial asymmetry and the use of surveillance technology. Surveillance & Society, 16(1), 53–68.
- Hidalgo-Peñate, A., Nieves, J., & Padrón-Robaina, V. (2020). The influence of employees’ knowledge, organisational commitment, and culture on the innovativeness of vocational educational. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 1-12.
- Howell, T.R., Noellert, W.A., Kreier, J.G., & Wolff, A.W. (2019). Steel and the state: Government intervention and steel’s structural crisis. Routledge
- Huang, Z., & Du, X. (2017). Government intervention and land misallocation: Evidence from China. Cities, 60, 323–332.
- Isaac, V.R., Borini, F.M., Raziq, M.M., & Benito, G.R. (2019). From local to global innovation: The role of subsidiaries’ external relational embededness in an emerging market. International Business Review, 28(4), 638-646.
- Jackson, B.A. (2015). Strengthening trust between police and the public in an era of increasing transparency. Arlington, VA: RAND Corporation.
- Kawiana, I.G.P., Dewi, L.K.C., Martini, L.K.B., & Suardana, I.B.R. (2018). The influence of organizational culture, employee satisfaction, personality, and organizational commitment towards employee performance. International Research Journal of Management, IT and Social Sciences, 5(3), 35–45.
- Keiningham, T., Aksoy, L., Bruce, H.L., Cadet, F., Clennell, N., Hodgkinson, I.R., & Kearney, T. (2020). Customer experience driven business model innovation. Journal of Business Research, 116, 431-440.
- Kenny, J.F. (2020). Hiding in plain sight: Deceptive tactics and the criminal victimization process. Palgrave Macmillan.
- Kombo, P. (2018). An inquiry into youth innovativeness in radicalization and extremism: The case of the recent Manchester city Bombing and Al-Shabaab activity in Kenya.
- Lien, C.H., Cao, Y., & Zhou, X. (2017). Service quality, satisfaction, stickiness, and usage intentions: An exploratory evaluation in the context of We Chat services. Computers in Human Behaviour, 68, 403-410.
- Lu, J. (2019). Discussion on Community Policing and Police-citizen Communication Ethics. The 4th International Conference on Economy, Judicature, Administration and Humanitarian Projects.
- Maclean, M. (2017). Social capital, innovativeness and performance of micro and small family businesses in Ghana.
- Maguire, M., & John, T. (2006). Intelligence led policing, managerialism and community engagement: Competing priorities and the role of the National Intelligence Model in the UK. Policing & society, 16(1), 67-85.
- Mahmoudi, R., & Rasti-Barzoki, M. (2018). Sustainable supply chains under government intervention with a real-world case study: An evolutionary game theoretic approach. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 116, 130–143.
- Margraf, P. (2019). Diffusion of frugal innovation and innovativeness in low-income contexts.
- Melvin-Campbell, K.M. (2019). Who is talking with whom? Community policing and inter-agency collaboration in a rustbelt secondary city: A case study. Case Western Reserve University.
- Merenda, F., Trent, J., Rinke, C.R., & Buchanan, M. (2020). Understanding citizen satisfaction with the police: results from a community survey. Police Practice and Research, 1-19.
- Mitchell, F. (2016). Policing culturally-linguistically diverse communities in an era of terrorism: Improving community policing as a counter-terrorism strategy at the grassroots community police level. Countering Terrorist Recruitment in the Context of Armed Counter-Terrorism Operations, 125, 212.
- Mokyr, J. (2018). The past and the future of innovation: Some lessons from economic history. Explorations in Economic History, 69, 13-26.
Monteoliva-García, E. (2020). Interpreting or other forms of language support? Experiences and decision-making among response and community police officers in Scotland. Translation & Interpreting, 12(1), 37. - Musgrave, P. (2020). Bringing the state police in: The diffusion of US statewide policing agencies, 1905–1941. Studies in American Political Development, 34(1), 3–23.
- Nagin, D.S., Solow, R.M., & Lum, C. (2015). Deterrence, criminal opportunities, and police. Criminology, 53(1), 74-100.
- Napitupulu, D., Rahim, R., Abdullah, D., Setiawan, M.I., Abdillah, L.A., Ahmar, A.S., ... & Pranolo, A. (2018, January). Analysis of student satisfaction toward quality of service facility. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series: IOP Publishing, 954, 012019.
- Nawab, B., Ullah, S., Nyborg, I.L.P., & Maqsood, T. (2019). Community-oriented policing: Political, institutional and technical reforms in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa police.
- Nowicka-Skowron, M. (2018). Paradigms of management of innovativeness in concepts of maria romanowska, doctor honoris causa of the cz?stochowa university of technology, 7.
- Otieno, F.O. (2019). Counterterrorism strategies and performance of the national police service in managing terrorism in lamu county, Kenya Fredrick Okoth (Doctoral dissertation, MMUST).
- Palladan, A.A. (2017). Effects of strategic leadership, organizational innovativeness, information technology capability on effective strategy implementation. Universiti Utara Malaysia.
- Paro, P.E.P., & Gerolamo, M.C. (2017). Organizational culture for lean programs. Journal of Organizational Change Management.
- Pasha, O. (2019). Does substandard performance encourage innovation adoption? The American Review of Public Administration, 49(5), 572-584.
- Peerally, J.A., De-Fuentes, C., & Figueiredo, P.N. (2019). Inclusive innovation and the role of technological capability-building: The social business Grameen Danone Foods Limited in Bangladesh. Long Range Planning, 52(6), 101843.
- Pickett, J.T., & Roche, S.P. (2016). Arrested development: Misguided directions in deterrence theory and policy. Criminology & Public Policy, 15(3), 727-751.
- I.P. (2017). Law and innovation: Evidence from state trade secrets laws. Review of Economics and statistics, 99(1), 167-179.
- Pridmore, J., Mols, A., Wang, Y., & Holleman, F. (2019). Keeping an eye on the neighbours: Police, citizens, and communication within mobile neighbourhood crime prevention groups. The Police Journal, 92(2), 97-120.
- Rai, R.S. (2016). Innovating in practice: A practice-theoretical exploration of discontinuous service innovations.
- Rehman, A.U., Alam, I., Abbas, S., Mujahid, A.U., & Iqbal, S. (2019). Assessing psychological problems of women policing and its effects on their performance in district peshawar khyber pakhtunkhwa. Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities, 3(1 & 2), 84-98.
- Salem, S.F., & Alanadoly, A.B. (2020). Personality traits and social media as drivers of word-of-mouth towards sustainable fashion. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management.
- Salem, S.F., & Salem, S.O. (2018). Self-identity and social identity as drivers of consumers’ purchase intention towards luxury fashion goods and willingness to pay premium price. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 23(2).
- Salunke, S., Weerawardena, J., & McColl-Kennedy, J.R. (2019). The central role of knowledge integration capability in service innovation-based competitive strategy. Industrial Marketing Management, 76, 144-156.
- Santos, J. (2003). E?service quality: A model of virtual service quality dimensions. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal.
- Shafi, M. (2020). Sustainable development of micro firms: Examining the effects of cooperation on handicraft firm's performance through innovation capability. International Journal of Emerging Markets.
- Shahzad, M., Qu, Y., Zafar, A.U., Rehman, S.U., & Islam, T. (2020). Exploring the influence of knowledge management process on corporate sustainable performance through green innovation. Journal of Knowledge Management.
- Shrouk, A.A. (2017). Dubai police: Era of innovative policing begins: Smart police stations, robocops, futuristic vehicles and artificial intelligence will help Dubai Police do their job better.
- Sinayi, M., & Rasti-Barzoki, M. (2018). A game theoretic approach for pricing, greening, and social welfare policies in a supply chain with government intervention. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196, 1443–1458.
- Singh, S., Akbani, I., & Dhir, S. (2020). Service innovation implementation: A systematic review and research agenda. The Service Industries Journal, 40(7-8), 491-517.
- Skrbiš, Z., & Laughland?Booÿ, J. (2019). Technology, change, and uncertainty: maintaining career confidence in the early 21st century. New Technology, Work and Employment, 34(3), 191–207.
- Stawnicka, J., & Klonowska, I. (2018). The role of a community police officer in shaping the security of local communities--considerations in the context of the first national surveys of community police officers (2017). Internal Security, 10(1).
- Stenson, K. (1993). Community policing as a governmental technology: Community policing as a governmental technology. Economy and Society, 22(3), 373-389.
- Strudwick, K., Jameson, J., & Rowe, J. (2019). Developing volunteers in policing: Assessing the potential volunteer police community police officer. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice, 13(4), 397–410.
- Vanharanta, O. (2019). Innovativeness contested–discrepancies between managerial ideals and employee identities.
- Wallenburg, C.M., Johne, D., Cichosz, M., Goldsby, T.J., & Knemeyer, A.M. (2019). Alignment mechanisms for supplier-initiated innovation: Results from the logistics service industry. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 25(5), 100575.
- Wang, J. (2018). Innovation and government intervention: A comparison of Singapore and Hong Kong. Research Policy, 47(2), 399–412.
- Williams, C.B., Fedorowicz, J., Kavanaugh, A., Mentzer, K., Thatcher, J.B., & Xu, J. (2018). Leveraging social media to achieve a community policing agenda. Government Information Quarterly, 35(2), 210-222.
- Willis, C.D., Saul, J., Bevan, H., Scheirer, M.A., Best, A., Greenhalgh, T., … & Jenkins, E. (2016). Sustaining organizational culture change in health systems. Journal of Health Organization and Management.
- Winneberger, N., & Hengsteler, M.J. (2020). In the pursuit of competitive advantage-A single case study investigating how the deployment of product innovations is challenged within knowledge-intensive business service firms.
- Xie, M., & Baumer, E.P. (2019). Neighbourhood immigrant concentration and violent crime reporting to the police: A multilevel analysis of data from the National Crime Victimization Survey. Criminology, 57(2), 237-267.
- Young, J.T.N., & Ready, J.T. (2018). A longitudinal analysis of the relationship between administrative policy, technological preferences, and body-worn camera activation among police officers. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice, 12(1), 27–42.
- Zhang, X., & Yousaf, H.M.A.U. (2020). Green supply chain coordination considering government intervention, green investment, and customer green preferences in the petroleum industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 246, 118984.