Research Article: 2021 Vol: 20 Issue: 4
Implementing Total Quality Management in a Retail Bank in the Kingdom of Bahrain
Minwir M. Al-Shammari, University of Bahrain
Sleh Isa, University of Bahrain
Abstract
The study's primary purpose was to investigate the implementation of total quality management (TQM) in a retail bank in the Kingdom of Bahrain. The study used a random sampling method to distribute 131 questionnaires, out of which 120 have been returned. The findings indicated that the proper TQM within the organization ensures better operations and functions through employee participation and training. The study recommends that employees in the banking sector in Bahrain need to maintain the quality standards and provide them with regular exercise and education to participate in quality care.
Keywords
TQM, Retail Bank, Bahrain.
Introduction
In this current world of advanced technology and increased globalization, it has become necessary for all organizations to study their customers and potential customers to understand their needs. Customers are the significant factors for the survival of each organization. Most organizations cannot face their competitors because they have not successfully presented appropriate services to their customers (Hosseini et al., 2015). Quality is one of the fastest-growing customer-centric strategies in all organizations, and it has become one of the industry's survival and success requirements (Mauch, 2010).
Organizations strive to excel in quality by performing the right thing and employing the right resources to add value to the services rendered to the customers. The total quality management (TQM) concept successfully meets the business goals by designing and supplying the products and facilitating customer satisfaction at the most economical level. The former name of this concept was total quality control, which later on was revised to TQM. This term refers to the philosophy of corporate business management that helps recognize the needs of the customers and the inseparable goals of the business organization (Jain, 2001).
TQM is a strategic management system for the satisfaction of customers. Strategic management is an essential part of today's dynamic and competitive environment that helps managers evaluate external environments. The effective strategy allows them to optimize their organizational resources and creates the ability to extract opportunities and limit threats to achieve competitive advantage (Salamzadeh et al., 2016).
The paper is structured as follows. It begins with the objectives and contribution of the study, followed by a literature review. Then, it describes the research methodology and results. Finally, the paper discusses the research results and ends up with conclusions, recommendations, and limitations.
Research Objectives
This study's primary focus was to analyze the TQM program in a retail bank in Bahrain. The specific objectives of the study are:
1. To investigate the relationship between employee involvement and TQM in a local Bahraini bank.
2. To study the relationship between employee training and TQM in a local Bahraini bank.
3. To explore the relationship between strategic planning and TQM in a local Bahraini bank, and
4. To study the relationship between the commitment of the top management and TQM in the Bahraini local bank.
Theoretical Contribution
Despite the growing importance of TQM as a field, examining a previously tested theory in a new context adds to theoretical contribution (Salamzadeh, 2020), especially in developing countries. The current research aims to bridge this literature gap on the role of TQM in an emerging economic setting, viz. implementing TQM in a retail bank in the Kingdom of Bahrain. The progress of the quality issue has become a matter of concern for the local banking sectors. The study has examined several areas concerning the maintenance and valuing of quality issues. The study has also been extended in collecting the primary data and statistical analysis so that practitioners and policymakers can make use of actual and accurate materials.
Literature Review
TQM deals with management techniques used to improve the profitability and quality of organizations. TQM is a way of thinking that guides organizations to achieve success. This technique helps the company produce quality products and services, thus meeting its requirements and needs. TQM contributes to creating a culture of teamwork, quality, and participation among the employees and contributes to the organization's success (Dale, 2015).
TQM signifies the approach that aims to create the optimal conditions and similar environment for the organization and economies for the permanent development through the efficient combination of the body's several functions and the formulation of the best possible use of the skills, knowledge, and expertise of the workforce. For the successful performance and management of the quality control programs, the organization requires many additional costs such as the formulation of innovative strategies, the increment of the infrastructures, and the arrangement of the latest and advanced forms of training and development programs. All these costs need to be bear by the organization before arranging and implementing the quality control and management programs (Iyida, 2012).
Elements of TQM
TQM is a management concept that originated in the 1950s and became familiar in the 1980s. TQM describes the organization's attitude and culture to deliver a quality product to the customers, thus meeting the clients' needs. In all aspects of the organization's operation, the culture requires quality, detects defects, and eliminates process errors (Padhi, 2016).
As per the Study of Padhi (2016), the eight critical elements of TQM, which direct the organization towards success, are communication, ethics, integrity, leadership, recognition, teamwork, training, and trust. TQM described that quality is the giving force behind guidance, preparation, and enhancement. The eight essential elements have their significance in the process and techniques of managing the TQM within the organization. Whether at a lower, middle, or higher management level, communication among all the employees is essential to ensure proper and efficient management of the quality issues and measures. On the other hand, ethics and integrity are also equally crucial because they make the employees competent enough to efficiently carry forward organizational culture and structure. Similarly, leadership is the other critical factor that can motivate the employees to move on to the correct path of the administrative systems (Padhi, 2016).
TQM elements are again categorized under four influential groups to be quickly, efficiently implemented, and applied in coherence with the organization's various quality issues and management. This fact was also supported by several scholars such as Prajogo & Sohal (2006); Wind & Mahajan (1997); Tidd et al. (1997); Slater & Narver (1998); Kim & Marbougne (1999); and Fotopoulos & Psomas (2009). Furthermore, Padhi (2016) categorized the TQM elements into the binding mortar, building bricks, foundation, and roof.
Binding Mortar – Communication
Communication refers to the understanding between the sender and the receiver. A successful TQM requires active communication between the employees, customers, and suppliers. Mainly, there are three types of communication: downward communication, upward communication, and sideways communication.
Building Bricks –Teamwork, Training, and Leadership
This category includes elements such as teamwork, training, and leadership. Collaboration ensures the smooth running of the organization. People feel free to bring challenges, and the management gets help from the operators in finding out the solution. Successful companies in the future encourage teamwork, cooperation, and connection of employees to their business partners and clients and provide greater inclusion of employees in the company's development activities (Radovic-Markovic et al., 2019).
Similarly, training is essential to increase the productivity of the employees. It helps employees to improve their skills and such as problem-solving, decision making, etc. The learning or training curve can be improved using a short creation period, seminars and courses, co-working space, divided teams, cohort peers, and mentorship (Salamzadeh & Radovic-Markovic, 2018).
Leadership is one of the essential elements in TQM. The supervisor led the employee to the strategic direction of the company. The leader understands the concept of TQM and teaches the employees through their daily practices.
Foundation – Integrity, Ethics, and Trust
Under this category come integrity, ethics, and trust. Integrity specifically discusses or includes the factors such as morale, value, and honesty. On the other hand, ethics are related to the discipline maintained in bad or good situations. Personnel decisions are related to the standards. Trust is the output of integrity and trust. The framework of the TQM is built based on faith. It encourages ownership and commitment. Trust ensures customer participation and makes the company environment suitable to work.
Roof –Recognition
In the complete system, acceptance is the final step. It provides individual and group recommendations, recognition, and acceptance to the employees trying to receive credit for their group and themselves. This job is the responsibility of the supervisor to recognize the contributors of individuals.
Models of TQM
TQM can also be described as the set of procedures and techniques that can be utilized to reduce or eliminate the variation from the production process or the service delivery system to improve reliability, efficiency, and quality. TQM can also be quoted as the integrative philosophy of the management for the continuous improvement of the process and product quality. In this section of the study, some of the major frameworks of TQM have been explained. Joseph et al. (1999) developed a model of TQM with ten principal factors of TQM, namely organizational commitment, supplier integration, human resource management, quality policy, the role of the quality department, product design, quality information systems, training, utilization of technology and procedures of operating. This study also came up with the measurement that can be used to evaluate how several of TQM can be deployed within the organization. According to these measurements, there are four major factors for building TQM and top management commitment: process management, employee training, quality control, and analysis and focus of the customers.
According to Sila & Ebrahimpour (2002), a TQM model was constructed that consists of eleven significant dimensions, namely leadership and top management commitment, employee involvement, employee empowerment, education and training, teamwork, customer focus, process management, strategic planning, open organization, information and analysis system, and service culture.
Methodology
Instrument
A five-point Likert scale questionnaire was designed and divided into two parts. The first part of the questionnaire contained a brief explanation of the research and the respondents' demographic profile. The other part of the questionnaire included the questions related to the variables identified in the study. The questionnaires were distributed to the respective respondents through Google forms survey allocation using a five-point Likert scale.
Sampling Method
This study adopted the simple random sampling technique that provides the foundation for all the complex sampling designs based on probability sampling. It also determines all the possible samples taken from the population for the study, which possesses a similar probability of being selected for the research and belongs to the same range of the categories (Barreiro & Albandoz, 2001). The primary intention for using the sampling technique was that it is straightforward to implement, and it requires minimal knowledge about the population in advance (Frerichs, 2008).
The methods of collecting and sending questionnaires were email and telephone interviews. The questionnaires were prepared using Google forms, and the web link was distributed by email to the randomly selected employees in the bank.
Sample Size
The respondents were of a local bank in Bahrain under which all the managers, executives, and middle-level employees. The following formula has been used to estimate the sample size:
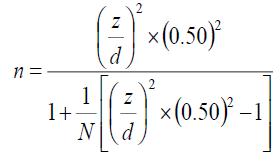
Source: Smith (2009)
Since:
z: Standard value, it equals 1.96 at 0.05 significance level.
d: maximum error allowed (we have taken 0.08).
N: Population Size (996).
n= 131
The questionnaires were distributed to the respective respondents to collect the primary data. Out of these 131 questionnaires, 120 were returned. Thus, it could be said that the response rate for this study was 91.60%. The demographic profile of the respondents was analyzed based on three factors such as gender, occupation level, and several experience years. The tabular and graphical representation for each of the demographic factors of the respondents was as follows:
Research Variables
The variables used in this study were as follows:
TQM
The organization's management approach focuses on quality based on the participation of all the organization members for meeting the objectives of long-term success through customer satisfaction and organizational benefits.
Employee involvement
For the participation of organization members in the quality control process, all employees need to participate. It will result in the assurance of a proper TQM process.
Strategic planning
The availability of adequate physical resources is also an essential element for reasonable quality control assurance. For the proper management of the quality within organizations, there must be sufficient material resources to ensure the necessary quality control and management strategies.
Employee training
It helps the employees understand the need to maintain the organization's quality issues. Training has always been an important tool to motivate employees to control and manage quality problems and factors. It makes the employees responsible enough to accomplish all of their duties to assure quality control and leadership within the organizational aspects.
The Commitment of top management
Top management is the major one responsible for maintaining and looking after all the issues related to quality management. They need to govern all the other members in ensuring proper administration of the TQM of the organization. The top administration of the organization is the one that can make the other employees indulge and be motivated towards the proper management and control of all the quality issues.
Results
Table 1 indicates that the respondents who participated in the survey were primarily females with 50.83% of the interviewees, then males with 49.17%. This representation of the data concerning gender shows that banks and many other workplaces were highly motivated towards empowering women through equal participation in the job market. Table 2 indicates that the respondents who participated in the survey regarding the occupation level were mostly assistants (36.67%). In comparison, the supervisors were only (35%) of the respondents, managers (20%), and executive managers were only (8.33%).
| Table 1 Frequencies and Percentages for Gender Categories | ||
| Categories | Frequencies | Percent |
| Female | 61 | 50.83% |
| Male | 59 | 49.17% |
| Total | 120 | 100% |
| Table 2 Frequencies and Percentages for Occupation Categories | ||
| Categories | Frequencies | Percent |
| Assistant | 44 | 36.67% |
| Supervisor | 42 | 35% |
| Manager | 24 | 20% |
| Executive manager | 10 | 8.33% |
| Total | 120 | 100% |
Table 3 indicates that the respondents who participated in the survey about the number of years of experience; the majority were employees with (more than seven years, 43.33%). The employees who had 5-7 years of experience were (24.17%) of the respondents, then came the employees with 3-5 years with (20%) The minority were the employees with less working experience (less than three years, 12.50%). The most significant feature from the study of the demographic analysis was that most of the respondents had total work experience of more than seven years.
| Table 3 Frequencies and Percentages for Experience Categories | ||
| Categories | Frequencies | Percent |
| More than 7 years | 52 | 43.33% |
| 5-7years | 29 | 24.17% |
| 3-5 years | 24 | 20% |
| Less than 3 years | 15 | 12.50% |
| Total | 120 | 100% |
Reliability and Internal Consistency
Table 4 provides the Cronbach's alpha test results for 120 participants using the SPSS version 20. According to Tavakol & Dennick (2011), the value of Cronbach's alpha is more significant than 0.7 is considered acceptable, and the higher value of Cronbach's alpha indicates the good internal consistency of the items in the scale. Table 4 demonstrates that Cronbach's alpha for the questionnaire's variables is more than 0.7 with a minimum being 0.733 and maximum being 0.953, along with Cronbach's alpha value for all questionnaires was 0.975.
| Table 4 Reliability and Internal Consistency | |||
| Construct | No. of questions | Items | Cronbach's Alpha (Reliability) |
| TQM | 4 | Q1-Q4 | 0.808 |
| Employee involvement | 4 | Q5-Q8 | 0.733 |
| Employee training | 4 | Q9-Q12 | 0.953 |
| Strategic planning | 4 | Q13-Q16 | 0.952 |
| The commitment of top management | 4 | Q17-Q20 | 0.951 |
Item to Item Spearman's Correlation Coefficient Test
The results of the Spearman correlation coefficient test are documented in Table 5. All coefficients exceeded 0.7, referring to high relationships between the study variables, in addition to the p-values, which were lesser than 0.05. The employee involvement, employee training, strategic planning, and top management commitment showed significant relationships with the TQM.
| Table 5 Item-to-Item Spearman's Correlation Coefficient Results | ||||||
| Correlations | TQM | Employee Involvement | Employee Training | Strategic Planning | The Commitment of Top Management | |
| TQM | Spearman's ρ | 1.000 | ||||
| Employee Involvement | Spearman's ρ | 0.894** | 1.000 | |||
| Employee Training | Spearman's ρ | 0.916** | 0.871** | 1.000 | ||
| Strategic Planning | Spearman's ρ | 0.917** | 0.858** | 0.921** | 1.000 | |
| The Commitment of Top Management | Spearman's ρ | 0.935** | 0.902** | 0.968** | 0.934** | 1.000 |
Perceptions of TQM
Table 6 compiles the general mean score of 3.08 since at the first place was the statement “All the employees of the bank strive to meet their needs and expectations” with a mean equals to 3.55, followed by “Quality is the key strategic factor in the achievement of business success” with a mean equals to 3.30. The statement “TQM is the procedure or technique for improving the reliability, efficiency, and quality of the bank” with a mean equal to 2.99. Finally, “TQM is that management approach all the bank adopts” equals 2.48.
| Table 6 Perceptions of TQM | |||||||
| Question | Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | Mean | Std |
| All the employees of the banks strive to meet their needs and expectations | 0 | 28 | 18 | 54 | 20 | 3.55 | 1.03 |
| Quality is the key strategic factor in the achievement of business success | 0 | 33 | 18 | 69 | 0 | 3.3 | 0.88 |
| TQM is the procedure or technique for improving the reliability, efficiency, and quality of the bank. | 0 | 41 | 39 | 40 | 0 | 2.99 | 0.82 |
| TQM is that management approach which is adopted by all the organizations | 19 | 25 | 76 | 0 | 0 | 2.48 | 0.76 |
| Total | 3.08 | 0.69 | |||||
Employee Involvement
Table 7 shows the general mean of the section as 3.81. In contrast, the mean of the statement “Employees of the bank always involved in offering a high quality of work” was 4.53, followed by “Participation of all the organization members determines high quality in the group” with a mean of 4.50. Then “The involvement of employees is also the primary element of TQM” had a mean equals to 3.27. Finally, “Employees are the primary determinant to maintain and assure quality in the organization,” with a mean equivalent to 2.96.
| Table 7 Perceptions of Employee Involvement | |||||||
| Question | Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | Mean | Std |
| Employees of the bank always involve in showing the high quality of work | 0 | 10 | 4 | 19 | 87 | 4.53 | 0.91 |
| Participation of all the members of the organization determines high quality in the organization | 0 | 10 | 5 | 20 | 85 | 4.5 | 0.92 |
| Involvement of employees is also the major element of TQM | 0 | 28 | 37 | 50 | 5 | 3.27 | 0.87 |
| Employees are the primary determinant to maintain and assure quality in the organization | 19 | 22 | 34 | 35 | 10 | 2.96 | 1.21 |
| Total | 3.81 | 0.68 | |||||
Employee Training
Table 8 shows the general mean of the section was 3.82. The mean average of the statement “Training will also make them aware of the need for quality control for ensuring proper organizational proceedings” was 4.25. Then “Training and development programs help the employees to know about their goals and objectives in the organization” with a mean of 4.18.
Then, “Training that can make employees understand about the need of managing quality within the organization” with mean equals to (3.94), and finally “All the employees of the bank are provided with training for showing high-quality performance” with mean equals to (2.91).
| Table 8 Perceptions of Employee Training | |||||||
| Question | Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | Mean | Std |
| Training will also make them aware of the need for quality control for ensuring proper organizational proceedings | 0 | 5 | 5 | 65 | 45 | 4.25 | 0.72 |
| Training and development programs help the employees to know about their goals and objectives in the organization | 0 | 5 | 23 | 37 | 55 | 4.18 | 0.89 |
| Training that can make employees understand the need for managing quality within the organization | 0 | 5 | 32 | 48 | 35 | 3.94 | 0.85 |
| All the employees of the bank are provided with training for showing high-quality performance | 0 | 46 | 39 | 35 | 0 | 2.91 | 0.82 |
| Total | 3.82 | 0.77 | |||||
Strategic Planning
Table 9 indicates that the general mean of the section was 4.09. The mean average was 4.58 for the statement “TQM is the strategic planning that involves continuous improvement of product quality to achieve customer satisfaction”, followed by a mean average of 4.53 for the statement “TQM strategic planning of the organization”. Then, “Strategic planning accomplishes the primary task or duty of maintaining quality issues within the organization” with a mean equals 3.69. Finally, the statement “For ensuring proper TQM process in the organization, it is vital to synchronize TQM and strategic planning” with a mean equals to 3.55.
| Table 9 Perceptions of Strategic Planning | |||||||
| Question | Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | Mean | Std |
| TQM is the strategic planning that involves continuous improvement of product quality to achieve customer satisfaction | 0 | 0 | 14 | 23 | 83 | 4.58 | 0.69 |
| TQM is also an essential part of strategic planning of the organization | 0 | 10 | 4 | 19 | 87 | 4.53 | 0.91 |
| Strategic planning accomplishes the primary task or duty of maintaining quality issues within the organization | 0 | 14 | 19 | 77 | 10 | 3.69 | 0.79 |
| For ensuring proper TQM process in the organization, it is essential to synchronize TQM and strategic planning | 0 | 28 | 18 | 54 | 20 | 3.55 | 1.03 |
| Total | 4.09 | 0.81 | |||||
The Commitment of Top Management
Table 10 shows that the general mean of the section was 3.32. “The top management of the organization needs to make their subordinates understand the need to maintain the quality” had a mean score of 3.69, followed by a mean score of 3.46 for “Top-level management of the organization arranges for organizational innovation can ensure high-quality work”. The statement “A bank follows TQM programs with the help of top management support” had a mean score of 3.18, and finally, “All the organization members are responsible for maintaining high-quality products and services for gaining customer satisfaction” had a mean score of 2.96.
| Table 10 Frequencies for Commitment of Top Management | |||||||
| Question | Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | Mean | Std |
| The top management of the organization needs to make their subordinates understand the need for maintaining the quality | 0 | 14 | 19 | 77 | 10 | 3.69 | 0.79 |
| Top-level management of the organization arranges for organizational innovation that can ensure high quality work | 0 | 14 | 37 | 69 | 0 | 3.46 | 0.7 |
| A bank follows TQM programs with the help of top management support | 14 | 19 | 18 | 69 | 0 | 3.18 | 1.08 |
| All the members of the organization are responsible for maintaining high-quality products and services for gaining customer satisfaction | 19 | 22 | 34 | 35 | 10 | 2.96 | 1.21 |
| Total | 3.32 | 0.9 | |||||
Discussion
This study focused on implementing TQM in a Bahraini local bank and the analysis of this implementation. TQM had become one of the significant elements to enhance and enforce organizational policies and procedures so that customers could get the most attractive benefits and raise their satisfaction. Employees showed satisfaction with TQM as a strategic management technique to improve the profitability and quality of the bank. This result was consistent with Hosseini et al. (2015) on the role of service quality in attaining sustainable advantage.
The correlation between employee involvement and TQM provided a positive result, signifying a high explanation value for the model developed with employee involvement and the TQM variables. This result is quite similar to that of the study of (Fotopoulos & Psomas, 2009), which explained that employees were the major determinant that helps the organization maintains its quality issues and control the maintenance of the quality of the services and its products.
The correlation between employee training and TQM provided a positive result, which stated a high explanation value between employee training and TQM variables. Providing proper training and development programs for the employees is one of the bank's significant responsibilities and higher-level managers. This result was consistent with Padhi (2016), Salamzadeh et al. (2016); Salamzadeh & Radovic-Markovic (2018); and Radovic-Markovic et al. (2019) who explained that training is crucial to increasing employees' productivity. Training helps employees improve their skills, such as problem-solving, decision-making, etc. Management competencies and skills help to handle TQM issues through the proper skills and knowledge. Knowledge development and human resource capabilities are essential and necessary because increasing human resource capabilities play a significant role in achieving strategic objectives and public satisfaction.
The correlation between strategic planning and TQM provided a positive relationship between these two variables, namely strategic planning and TQM. Strategic planning has a significant role in assuring and managing all the quality issues within the bank. According to Sallis (2014), TQM is a management strategy that incorporates quality elements in the organization's management process. The concept of TQM needs to be nurtured within the culture of organizations. The organization needs to have specific strategies to raise its standards in the policies and procedures related to its quality issues.
The correlation between top management and TQM commitment again provided a positive result that said top management and TQM commitment variables had a positive and significant relationship. The commitment of the top management in the cases of quality management is of high importance as that of the participation of them in the quality control issues. It is the highest required duty that needs to be accomplished by the top managers in the maintenance of quality control, which in return will again motivate the other employees of similar banks also to take the initiative in the maintaining of quality issues. Furash (1999) also found that top management had a unique role in maintaining and managing the TQM programs.
Conclusion
There is a great need to develop TQM programs in the operations and functions, considering the competitive environment in the banking sector. All employees are trying their best to offer a high quality of services to its customers. Through the concept of TQM, a local bank in Bahrain can be encouraged to maintain its standards and bring in development in customer needs satisfaction.
TQM deals with management techniques used to improve the profitability and quality of the organization. TQM involves several principles that aim to continuously improve the employees and the organization, such as process-centered, customer-focused, integrated system, total development of the employee, systematic and strategic progress, communication, continuous improvement, and fact-based decision-making.
In the banking sector, service quality is an important aspect. The successes of the business depend upon the effective ways adopted for improving the performance of the organization. If the TQM is framed and practiced, it gives a clear vision to the marketer to identify the bank's elements as the first choice for new customers and existing customers.
Quality needs to be the top priority of the administration. To build a service quality culture in any organization, the leadership and participation of the management play a crucial role. Thus, this study came up with the combined result that TQM issues need to take particular concern over the factors such as employee involvement, training of the employees, strategic planning, and commitment level of the bank’s top management.
Practical Implications
The management of the banks needs to ensure the creation of more awareness among the staff about the strategic role of TQM in creating the bank’s sustainable competitive advantage. The employees need to be provided with regular training and education on the TQM practices that can change their beliefs, attitude, and behavior.
Employees need to be aware of the importance of human resource initiatives, and employees' involvement needs to be encouraged. There is also a need to introduce rewards and recognition for the employees’ involvement in improving quality. The TQM practices of the bank need to be regularly evaluated and constantly improved.
Limitations of the Study
The restricted period for the completion of the study was one of the significant limitations of this study. The study would have become more comprehensive if there was more time for its completion. The selected research context, i.e., a local retail bank, does not allow a broad coverage for the collected data. Meeting with the desired officials for the primary data collection was troublesome, as they could not give enough time for the study.
References
- Barreiro, P.L., & Albandoz, J.P. (2001). Population and sample. Sampling techniques. Management. United Kingdom: Mathematics for European Schools.
- Dale, B. (2015). Total quality management. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- Fotopoulos, C.B., & Psomas, E.L. (2009). The impact of "soft" and "hard" TQM elements on quality management results. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 26(2), 150-163.
- Frerichs, R.R. (2008). Simple random sampling. United States: Rapid Surveys.
- Furash, E. (1999). Internet strategy: why banks may be getting it wrong, and how to get it right. Journal of Retail Banking Services, 21(2), 37-42.
- Hosseini, M.H., Meymand, M.M., & Heidarvand, S. (2015). Examining the patient's satisfaction from hospital service quality using the CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Model. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Business and Economics , 3(2), 16-40.
- Iyida, I. (2012). Total quality management in the banking industry, A Case Study of Zenith Bank Nigeria Plc, MBA Project, University Of Nigeria, Enugu Campus. pp. 1-85.
- Jain, J.P.L. (2001). Quality control and total quality management. New Jersey: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
- Joseph, I.N., Rajendran, C., & Kamalanabhan, T.J. (1999). An instrument for measuring total quality management implementation in manufacturing-based business units in India. Internal Journal of Production Research, 37, 2201-2215.
- Kim, W.C., & Marbougne, R. (1999). Strategy, value innovation, and the knowledge economy. Sloan Management Review, (Spring), 41–54.
- Mauch, P.D. (2010). Quality management: Theory and application. CRC Press.
- Padhi, N., (2016). The eight elements of TQM. Retrieved from https://www.isixsigma.com/methodology/total-quality-management-tqm/eight-elements-tqm/
- Prajogo, D.I., & Sohal, A.S. (2006).The integration of TQM and technology /R&D management in determining quality and innovation performance. The International Journal of Management Science, Omega, 34, 296-312.
- Radovic-Markovic, M., Salamzadeh, A., & Vujicic, S. (2019). Selection of organization models and creation of competencies of the employed people for the sake of competitiveness growth in global business environments. International Review, (1-2), 64-71.
- Salamzadeh, A. (2020). What constitutes a theoretical contribution? Journal of Organizational Culture, Communications and Conflicts , 24(1), 1-2.
- Salamzadeh, A., & Radovic-Markovic, M. (2018). Shortening the learning curve of media start-ups in accelerators: Case of a developing country. In Evaluating Media Richness in Organizational Learning (pp. 36-48). IGI Global.
- Salamzadeh, Y., Yousefnia, M., Radovic-Markovic, M. & Salamzadeh, A. (2016). Strategic management development: The role of learning school on promotion of managers' competence. Economía y Sociedad, 21(50), 1-25.
- Sallis, E. (2014). Total quality management in education. United States: Routledge.
- Sila, I., & Ebrahimpour, M. (2002). An investigation of the TQM survey-based research published between 1989 and 2000- a literature review. International Journal ofQuality& Reliability Management , 19(7), 902-970.
- Slater, S.F., & Narver, J.C. (1998). Customer-led and market-led: Let's not confuse the two. Strategic Management Journal , 19(10), 1001-1006.
- Smith, S.M. (2009). Determining sample size. Retrieved from https://success.qualtrics.com/rs/qualtrics/images/Determining-Sample-Size.pdf
- Tavakol, M., & Dennick, R., (2011). Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. International Journal of Medical Education, 2, 53-55.
- Tidd, J., Bessant, J., & Pavitt, K. (1997). Managing innovation: Integrating technological, market, and organizational change. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- Wind, J., & Mahajan, V. (1997). Issues and opportunities in new product development: An introduction to the special issue. Journal of Marketing Research , 34(1), 1-12.