Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 6S
Impacting Management Skills on Business Efficiency: A Case Study of Small and Medium Enterprise in Ho Chi Minh City
Nguyen Phan Thu Hang, Saigon University (SGU)
Abstract
The widespread of Covid-19 and economic uncertainties have brought many challenges to society and enterprises. In addition to the impact on people, Covid-19 has been rapidly causing disruptions in business and consumption. Besides, business efficiency is always the top concern of every business because business efficiency reflects the ability to combine inputs, minimizing operating costs and interaction to achieve profit goals. Thereby, business efficiency will reflect the leader’s ability to perform the enterprise’s leadership function, use resources to accomplish goals, and complete the highest efficiency in business activities. Businesses are constantly improving business efficiency, especially in the context of increasingly fierce global competition today. Therefore, the paper aims to find out how management skills impact the business efficiency of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Ho Chi Minh City. The author surveyed 700 managers related to SMEs and applied structural equation modeling (SEM). The findings of the paper had the management skills affected business efficiency with 1% significance. Based on the results, the author gave several recommendations to improve business efficiency at SMEs.
Keywords
Management, Skills, Business, Efficiency, SMES and SGU
Introduction
During the 4th outbreak of the Covid-19 epidemic, the number of businesses that will stop production or go bankrupt will increase unpredictably. Primarily, there are many small and medium enterprises. Due to their deep integration into the global value chain, which is now closed to the public, larger enterprises will face many difficulties. The number of businesses that have to reduce production will increase rapidly. Most companies said that the Covid-19 epidemic had negatively affected their production and business activities by Karmel (2020). Unable to reach customers, broken supply chain, sharply reduced revenue, had to lay off many workers, still struggling. Due to the impact of the Covid-19 epidemic, the production and business situation in most industry groups was difficult, along with the fear and caution of investors when the epidemic was complicated, so the number of newly established enterprises decreased significantly.
In addition, due to the epidemic’s impact, many businesses had to stop doing business or dissolve. The number of enterprises that have completed dissolution procedures in 2020 is more than 10.000 SMEs. Most of them are enterprises operating in accommodation and catering services, education and training, employment and tourism services, and the real estate business. Besides, Vietnam joins the globalization and international economic integration trend that has significantly impacted Vietnam’s economic development, including the business community. It causes SMEs to face differences in many aspects related to business and commercial activities such as business thinking, perception, beliefs, customer psychology, and behavioral culture. In particular, the business community is being significantly affected, especially for small and medium enterprises. Many businesses have rapidly transformed models, reorganized production, and adapted to the global pandemic struggling because of the epidemic. Therefore, each SME needs to effectively use the support solutions of the State, the social community, and the SMEs themselves to develop sustainably and adapt to the requirements of the new context by Fox all, (2019). Therefore, the author studied the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs by Haleem, Jehangir & Ullah (2019). Based on the research results, the author proposed four groups of recommendations to help improve the business efficiency of small and medium enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City.
Literature Review
Management Skill (MS)
According to Salman, Arshad & Bakar (2016), management skill is the ability and proficiency to conduct a particular activity by applying acquired knowledge to complete assigned tasks. According to Gunawardena & Fonseka (2018), management skill is the ability to use the acquired knowledge in a particular field applied in business practice. Besides, management skill is the ability to perform an intellectual activity that contributes to the adequate efficiency of a job task in business by Hudson & Bourne (2019).
Haq (2018) argued that management skills are the ability to perform tasks, turn knowledge into actions of leaders. Leaders in enterprises have to perform many different functions, so they need many other skills. Besides, management skills demonstrate the leader’s proficiency in applying the acquired knowledge to perform leadership functions and achieve the set goals.
Sedmunds (2019) showed that management skills are the ability to recognize, operate and master specific management tasks to achieve success at work. Management skills require you to apply your knowledge and skills to solve situations that arise at work with and through different individuals and groups of resources.
Business Efficiency (BE)
Sharif & Juhdi (2019) studied the business efficiency of an enterprise as the combination of input factors to minimize costs in business activities to achieve worthwhile goals in business. Achieving profitable business goals means achieving expected results; achieving goals with minimal costs means attaining high productivity by Sotterman (2016).
Taas (2017) studied business efficiency as a measure that reflects the extent to which resources achieve defined business objectives. Wago (2019) showed that profitability goals include financial and non-financial. Only business enterprises aim to maximize profits and therefore need to evaluate business efficiency by Zaccaro & Palmon (2020).
Walovey (2019) showed that worthwhile goals in business are not merely profits but also economic benefits and social benefits that companies want to achieve. Economic benefits got through financial indicators and business development by Sudd (2017). Social benefits are associated with the obligations of enterprises such as tax obligations, obligations related to the rights and interests of employees, obligations related to the interests of customers and consumers by Yuklee (2019). Enterprises need to assess efficiency in many aspects, such as economic efficiency and production activities linked to customers and workers by Platts (2015).
Cognitive Skills (CS)
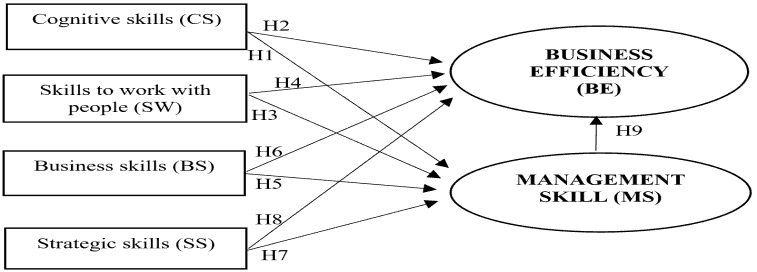
Kiambati & Itunga (2016) showed that cognitive skills are the foundational skills of leadership requirements. These include basic cognitive abilities such as information gathering, information processing, information dissemination, and learning by Yasin & Wisboa (2019). These are the basic skills required for a large part of the activities of leaders by Adebisi & Akeke (2018). This skill is related to the leader’s basic cognitive abilities. Speaking skills allow leaders to communicate effectively by Marks (2017). Listening skills help leaders gain a comprehensive understanding of the wants and problems of others, and reading comprehension skills help leaders understand complex written information. Active learning skills enable leaders to work with new information and grasp its implications by Saleem & Saeed (2017). These skills would allow leaders to adapt behaviors and strategies to deal with their work’s urgent, infrequent, and dynamic elements by Rago (2017). And finally, critical thinking skills enable leaders to comprehensively and rationally analyze the strengths and limitations of different work-related approaches, thereby helping the leader make informed decisions, sound decisions. Therefore, the proposed research hypotheses are:
Hypothesis H1: Cognitive Skills (CS) has a positive effect on management skill of SMEs.
Hypothesis H2: Cognitive Skills (CS) has a positive effect on the business efficiency of SMEs.
Skills to Work with People (SW)
Sorgeson (2017) showed that people skills are social skills and are related to interacting with and influencing others to achieve business goals. These include social awareness, coordination skills, negotiation skills, and persuasion skills. Social awareness is a leader’s perception of the reactions of others and understanding why others act the way they do. According to Tee (2018), people skills help leaders understand, motivate and motivate individuals and groups in the enterprise. People skills are social skills and skills related to interacting with and influencing others to achieve business goals Hasheed (2018) showed that people skills are critical and significantly affect the business efficiency of enterprises. Leaders must often deal with internal and external conflicts. Leaders work in an interactive world environment, the interactions with each other by Ahmad & Ahmad (2018). Therefore, leaders need to devote themselves to building community, resolving polarization, creating solid linkages between departments, and linking the business with external systems. To accomplish these tasks, leaders require social skills by Jones (2017). Leaders with persuasive skills will influence others to achieve organizational goals more effectively. Therefore, the proposed research hypotheses are:
Hypothesis H3: Skills to work with people (SW) positively affect the management skill of SMEs.
Hypothesis H4: Skills to work with people (SW) positively affect the business efficiency of SMEs.
Business Skills (BS)
Kaiser (2015) showed that business skills are necessary for enterprises’ production and processes. They are related to leaders’ specific functional activities, including skills in business analysis, human resource management skills, financial resource management, and other physical resources management skills for the production and business process by Kehinde, Jegede & Akinlabi (2012). These skills are those related to the specific functional activities of leaders, including skills in analyzing activities in the business, skills related to human resource management, skills associated with the management of financial resources, and skills related to the direction of the physical resources of the business by Anderson (2017). The skills of business analysis allow leaders to grasp the business activities of the company. From there, better meet customer needs, improve production processes, improve progress in production and business activities and improve efficiency in production and business of enterprises by Hall (2015). Chatterjee & Das (2016) showed that human resource management skills allow leaders to identify the right personnel, motivate employees, develop employees and facilitate career advancement. This factor has a significant influence on employees’ job satisfaction, increases productivity, and contributes to improving the business efficiency of enterprises. Therefore, the proposed research hypotheses are:
Hypothesis H5: Business Skills (BS) has a positive effect on management skill of SMEs.
Hypothesis H6: Business Skills (BS) have a positive effect on the business efficiency of SMEs.
Strategic Skills (SS)
Lapsinger (2015) studied the leader made to draw lessons from experience. Leaders have to perform some tasks such as: formulating visions and setting goals, planning and developing action programs, make changes following the changes of the environment, ensuring the existence and development of enterprises by Finch (2016). To accomplish these tasks, leaders require strategic skills. Strategic skills are skills related to planning a vision, systematically understanding the business, evaluating the company. Besides, the leader needs to identify the enterprises’ problems and assess the solutions that what needs. Freelance (2018) showed that the skill is to build a systematic vision and awareness of the business that would involve planning the basics of the company. Allowing the leader to create the business’s image in the future and identify when material changes to the business’s operations have occurred or are likely to occur by Bradley & Mecklenburg (2018). Strategic skills help leaders achieve business efficiency today and aim to achieve business efficiency in the future. Therefore, the proposed hypotheses are:
Hypothesis H7: Strategic Skills (SS) has a positive effect on management skill of SMEs.
Hypothesis H8: Strategic Skills (SS) has a positive effect on the business efficiency of SMEs.
Research on the relationship between management skills and business efficiency of SMEs is one of the main branches of research related to enterprises’ leadership skills and business efficiency by Fuadahet (2020). Besides, management skills have a positive influence on the business efficiency of SMEs. Therefore, the proposed research hypothesis is:
Hypothesis H9: Management Skills (MS) have a positive effect on the business efficiency of SMEs.
(Source: The author discovered)
Methods of Research
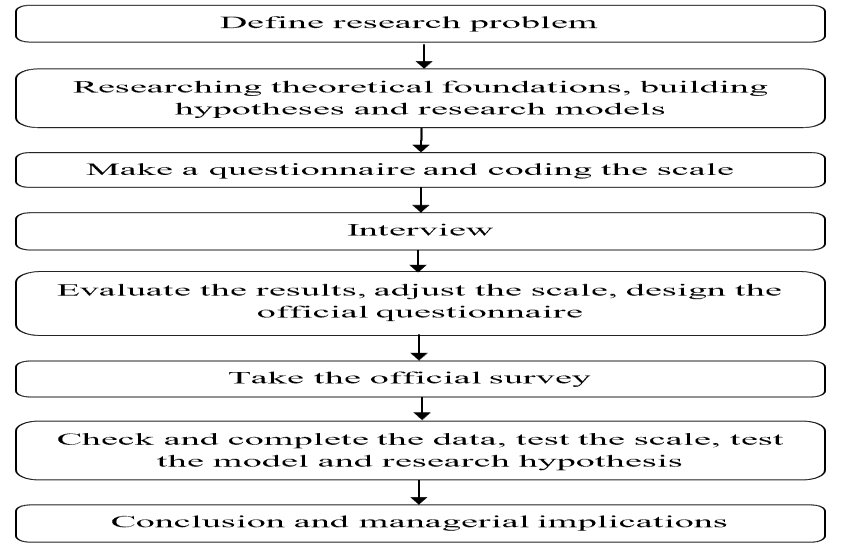
This paper applied methods according to the research process, including three stages and detailed steps as follows.
(Source: The author proposed)
Stage 1: Building and coding the scale: Phase 1 of the research paper includes the following steps: defining research objectives and tasks; research on a theoretical basis, build research models and hypotheses; construction and scale and coding of the scale by Hair, J., Anderson, Tatham & Black (2010). The author used analysis, synthesis, and rational thinking to study the overview of the research situation and determine the research objectives and tasks of the research paper. To carry out this research, the author first researched documents related to the research topic of the research paper, including reports and published scientific research articles. At the same time, the study also synthesized theoretical bases related to leader’s skills and business efficiency of enterprises, proposed hypotheses, and research models.
Stage 2: Qualitative research, qualitative research can have the following main objectives: building theory - model; help to understand more deeply the nature of the problem; service to preliminarily verify the appropriateness of the model and the scale; help explain quantitative research results. In this study, the author collected qualitative data through interviews with 11 experts in business management. After interviewing experts, the author evaluated the effects, adjusted the scale, and designed the official questionnaire.
Stage 3: Quantitative research, the survey method by questionnaire was used for 700 business managers, corresponding to 700 small and medium enterprises in HCMC, and data applied an online survey by Hair, Anderson, Tatham & Black (2010) but 677 samples applied by using SPSS 20.0, Amos tools to measure Cronbach’s alpha, Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), Confirmation Factor Analysis (CFA), and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Finally, the author had conclusions and policy recommendations to enhance business efficiency at SMEs in HCMC.
Research Results
Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for the Management Skills Affecting the Business Efficiency
| Table 1 Testing of Cronbach’s Alpha for The Management Skills Affecting The Business Efficiency |
||
|---|---|---|
| No. | Items | Cronbach’s alpha |
| Cognitive Skills (CS) | 0.886 | |
| CS1 | Business leaders always have listening and speaking skills | 0.862 |
| CS2 | Business leaders always have active learning skills | 0.823 |
| CS3 | Business leaders always have critical thinking skills | 0.879 |
| CS4 | Business leaders always have active questioning skills | 0.852 |
| Skills to Work with people (SW) | 0.967 | |
| SW1 | Business leaders always have socially Aware leadership | 0.945 |
| SW2 | Business leaders always have the leadership with coordination Skills | 0.962 |
| SW3 | Business leaders with negotiation Skills | 0.967 |
| SW4 | Business leadership with Persuasion Skills | 0.949 |
| Business Skills (BS) | 0.962 | |
| BS1 | Leaders have business analysis skills | 0.947 |
| BS2 | Leaders have skills to motivate and guide employees | 0.957 |
| BS3 | Leaders have skills to train and develop employees | 0.957 |
| BS4 | Leaders have skills in managing tangible and financial resources | 0.940 |
| Strategic Skills (SS) | 0.861 | |
| SS1 | Leaders have visionary and systematic skills | 0.809 |
| SS2 | Leaders have skills to evaluate business results system | 0.820 |
| SS3 | Leaders are skilled to identify root causes and solve problems | 0.853 |
| SS4 | Leaders have skills to evaluate effective business solutions | 0.811 |
| Management Skill (MS) | 0.945 | |
| MS1 | Cognitive Skills (CS) affecting management skills such as operating, organizing work, and planning general strategies | 0.929 |
| MS2 | Skills to Work with people (SW) affecting management skills such as communication skills | 0.887 |
| MS3 | Business Skills (BS) and Strategic Skills (SS) affecting management skills such as strategic thinking planning and human resources | 0.941 |
| Business Efficiency (BE) | 0.886 | |
| BE1 | The business meets the targets of the financial aspect | 0.871 |
| BE2 | The business achieves the targets of the customer-aspect such as increased customer satisfaction | 0.818 |
| BE3 | The business meets the internal process aspect indicators such as the number of new initiatives/improvements increased | 0.882 |
| BE4 | The enterprise achieves the targets of the learning and development aspect, such as increased productivity/work completion level of employees. | 0.843 |
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0)
Table 1 showed that all of Cronbach’s alpha is more than 0.6 for the Cognitive Skills (CS), the Skills to Work with people (SW), the Business Skills (BS), the Strategic Skills (SS), the Management Skill (MS), and the Business Efficiency (BE).
| Table 2 KMO and Bartlett’s Test for All of The Components |
||
|---|---|---|
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.840 | |
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 15276.666 |
| Df | 253 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings are cumulative % | 82.199 | |
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0)
Table 2 showed that KMO and Bartlett’s test is more than 0.840 (>0.6) for all components. And extraction sums of squared loadings that are cumulative % is 82.199 (>60%).
Testing CFA for the Management Skills Affecting the Business Efficiency of SMEs
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
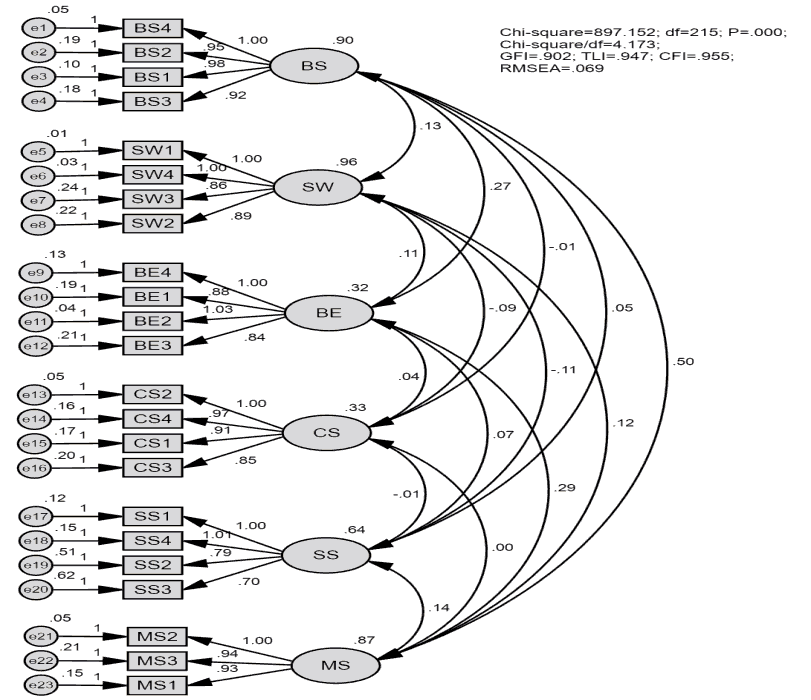
Figure 3 showed that the assessment of the CFA for the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs includes the following elements: CMIN/DF=4.173 (<5.0), GFI=0.902 (>0.8), TLI=0.947 (>0.9), CFI=0.955 (>0.9), and RMSEA=0.069 (<0.08).
| Table 3 Test CMIN/DF for All of The Components |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NPAR | CMIN | DF | P | CMIN/DF | GFI | TLI | CFI |
| Default model | 73 | 543.963 | 203 | 0.000 | 2.680 | 0.938 | 0.972 | 0.978 |
| Saturated model | 276 | 0.000 | 0 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||
| Independence model | 23 | 15459.245 | 253 | 0.000 | 61.104 | 0.285 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
Table 3 showed that the assessment of the scale of the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs includes the following elements: CMIN/DF=2.680 (<5.0), GFI=0.938 (>0.8), TLI=0.972 (>0.9) and CFI=0.978 (> 0.9), and RMSEA=0.050 (< 0.08).
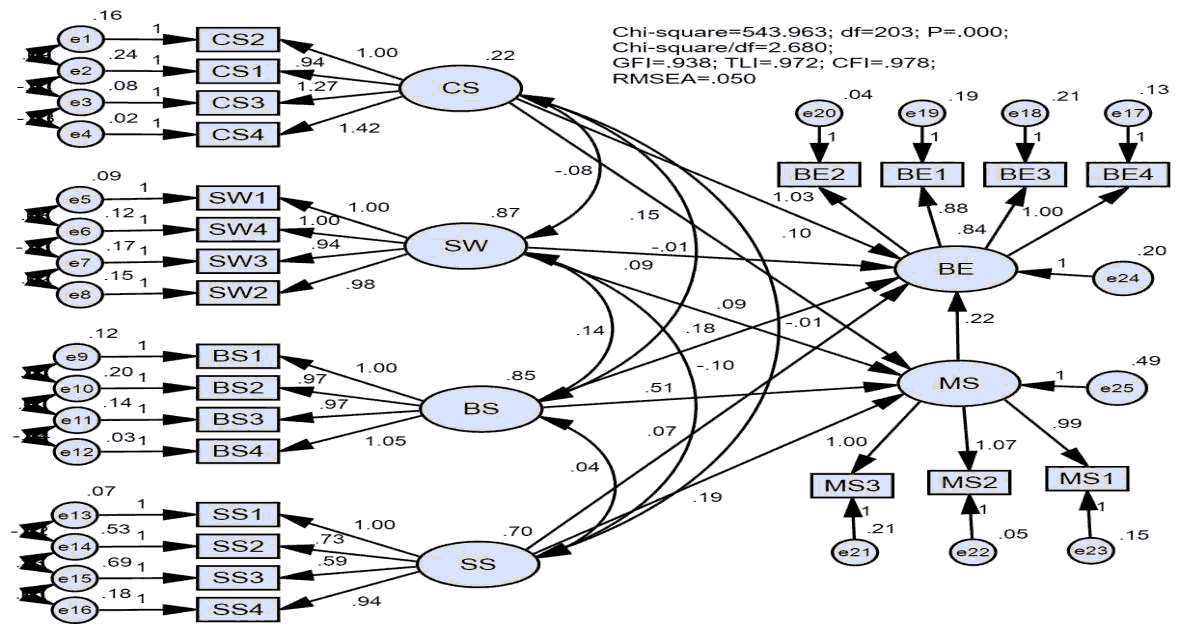
Besides, the results tested the research model and research hypothesis through SEM. The test results showed that the research model is suitable, and the research hypotheses are accepted. And bootstrap analysis demonstrated that business skills, strategic skills, skills to work with people, and cognitive skills positively affect the business efficiency of small and medium enterprises in HCMC with the standardized coefficient of 0.539, respectively; 0.178; 0.096, and 0.079.
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
Figure 4 showed that the SEM assessment had all four factors affecting the management skills and the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs in HCMC with 1% significance. Four factors included Cognitive Skills (CS), the Skills to Work with people (SW), Business Skills (BS), the Strategic Skills (SS).
Besides, the results of testing the official scale through Cronbach’s alpha test showed that the variables meet the requirements from the research model before performing the next test step. EFA and CFA tests showed that the model variables are suitable and can measure the management skills and business efficiency of small and medium enterprises in HCMC.
| Table 4 Testing Coefficients for The Management Skills Affecting The Business Efficiency of SMEs |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relationships | UnstandardizedEstimate | StandardizedEstimate | SE. | CR. | P | Hypothesis | ||
| MS | <--- | CS | 0.147 | 0.079 | 0.057 | 2.606 | 0.009 | Accepted |
| MS | <--- | SW | 0.090 | 0.096 | 0.032 | 2.791 | 0.005 | Accepted |
| MS | <--- | BS | 0.512 | 0.539 | 0.033 | 15.311 | *** | Accepted |
| MS | <--- | SS | 0.187 | 0.178 | 0.037 | 5.041 | *** | Accepted |
| BE | <--- | SS | 0.069 | 0.101 | 0.024 | 2.881 | 0.004 | Accepted |
| BE | <--- | BS | 0.177 | 0.287 | 0.025 | 7.069 | *** | Accepted |
| BE | <--- | SW | 0.086 | 0.141 | 0.021 | 4.017 | *** | Accepted |
| BE | <--- | CS | 0.100 | 0.082 | 0.037 | 2.675 | 0.007 | Accepted |
| BE | <--- | MS | 0.225 | 0.345 | 0.028 | 8.075 | *** | Accepted |
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
Table 4 showed that four factors affecting the management skills and management skills affected SMEs’ business efficiency in HCMC with 1% significance. Four factors included Cognitive Skills (CS), the Skills to Work with people (SW), Business Skills (BS), the Strategic Skills (SS).
| Table 5 Testing Bootstrap With 30.000 Samples for The Management Skills Affecting The Business Efficiency of SMEs |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | SE | SE-SE | Mean | Bias | SE-Bias | ||
| MS | <--- | CS | 0.083 | 0.001 | 0.119 | -0.028 | 0.001 |
| MS | <--- | SW | 0.030 | 0.000 | 0.089 | -0.001 | 0.000 |
| MS | <--- | BS | 0.041 | 0.000 | 0.509 | -0.002 | 0.001 |
| MS | <--- | SS | 0.040 | 0.000 | 0.185 | -0.002 | 0.001 |
| BE | <--- | SS | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.067 | -0.002 | 0.000 |
| BE | <--- | BS | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.176 | -0.001 | 0.000 |
| BE | <--- | SW | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.085 | -0.001 | 0.000 |
| BE | <--- | CS | 0.058 | 0.001 | 0.102 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| BE | <--- | MS | 0.032 | 0.000 | 0.227 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
(Source: Data processed by SPSS 20.0 and Amos)
Table 5 showed that the bootstrap test results are very good with a sample of 30.000 managers. These results indicated four factors affecting the management skills and the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs in HCMC with 1% significance. Four factors included Cognitive Skills (CS), the Skills to Work with people (SW), Business Skills (BS), the Strategic Skills (SS).
The research results showed that leaders’ leadership skills are essential and affected the business efficiency of small and medium enterprises in HCMC. At the same time, leadership skills had four main skill groups: cognitive skills, skills to work with people, business skills, strategic skills, and each group of skills. However, the level of implementation of these skills is still the low limit. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze and evaluate each skill in detail, helping leaders at small and medium enterprises in HCMC know their limitations as essential information to perfect and develop the skills of leaders at SMEs in HCMC.
Conclusions & Managerial Implications
Conclusions
Data surveyed 700 managers related to SMEs faced difficulties and temporarily suspended their operations, especially in the large market of Ho Chi Minh City. The author recognized this importance. The study collected 700 observations in small and medium enterprises. It tested through the SEM model the relationship of the impact of management skills on SMEs’ business efficiency in HCMC. These results indicated four factors affecting the management skills and the management skills affecting the business efficiency of SMEs in HCMC with 1% significance. Four factors included cognitive skills (0.079), the skills to work with people (0.096), business skills (0.539), and strategic skills (0.178) - the balanced scorecard perspective in small and medium enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City. Enterprise’s director has a better response level of leadership capabilities. The business efficiency will also be better. The research results had made specific contributions in clarifying the management skills and the business efficiency, thereby forming the basis for SMEs. Finally, research results showed a close relationship between management skills and business efficiency with 1.0 percent significance. Research results and discussions showed that leadership skills have a significant influence and a positive influence on the business efficiency of small and medium enterprises.
Managerial Implications
Based on the research results, some recommendations proposed to contribute to promoting the development of management skills and business efficiency in the future, specifically:
- Managerial implications improving the business skills (0.539). Developing management skills through training programs is a widely used solution in developing leadership skills in enterprises. Enterprises should organize training programs or send leaders to another enterprise to improve leadership skills. SME owners have business skills, cope with the market by themselves, and learn from practice, especially having their capacity from family traditions. To improve business owners’ education level, they need to be proactive and active in learning to enhance their qualifications through courses, training sessions, or business associations to learn from each other’s experiences. Regularly understand the mechanisms and policies of international organizations, especially the world economic organizations that Vietnam joined. The government should have its training program, especially studying and visiting abroad help SMEs in Vietnam have more capacity to manage enterprises. Financial management is about “looking after” money, the difference between spending and income. Periodic budgeting and financial reporting requirements are critical. Therefore, the key to this skill is to interpret and analyze the report to identify the factors that negatively affect the business’s profit.
- Managerial implications improving the strategic skills (0.178). Leadership is one of the necessary management skills, motivating team members in the same direction and towards common goals. This skill often appears in people with foresight and strategic ability, predicting significant changes and opportunities in the future. The key to success is building lasting relationships and influencing current and future customers, suppliers, employees, and investors. Strategic planning is a highly influential management function, which plays a role in ensuring that employees and stakeholders work together towards common goals, reaching an agreement on the direction of operations before the end of the year market volatility. This activity applied an effort to make fundamental decisions and actions of a defining nature, orienting the business towards the vision and mission. Whether strategic planning has good results depends on how the company had expected to operate in 3 to 5 years, along with detailed business plans. The key in sales and marketing skills is creating and conveying attractive messages and sayings to the right target and audience. In this skill, analyzing market competition and industry trends contributes significantly to promoting marketing strategy.
- Managerial implications improving the skills to work with people (0.096). Every business wants to make the most profit. However, this depends a lot on the diplomacy and negotiation skills of businesspeople in the market. Negotiation is understood as a “reciprocal” communication process between two parties to reach mutual agreements. The crux of the matter is that leaders need to know how to develop a mutually beneficial negotiation that ensures the best outcome for the business. When leaders want to solve any problem at work, analytical skills are fundamental. With today’s technological advancement, the demand for this skill is also higher. Besides, analysis is the act of approaching the business situation of an enterprise most comprehensively and comprehensively, deciding what actions are necessary to achieve growth in the future. It’s crucial that you collect, review, and evaluate the data leader need to build compelling arguments. Team building and teamwork skills are about establishing and maintaining positive collaborative relationships with people. In today’s modern workplace, this skill is essential. People thinking together will find more optimal solutions than an individual working independently.
- Managerial implications improving the cognitive skills (0.079). Practical communication skills are always needed in any situation and are considered critical in developing a person. The leader will find that most of the things you do require this skill. For a successful business, good communication skills are essential. However, good communication is not talking a lot but a way of conveying a message that needs to be light and concise so that the majority can understand and grasp information quickly and accurately. The leader must know how to connect your vision with passions and beliefs effectively. Overall management skill is the direction and control of a group of employees working together. Besides, expertise in implementing and directing human resources, finance and science, and technology is also part of the overall management skills. This skill requires leaders to develop and run a working system that can manage day-to-day operations, take care of stakeholders, and support business growth. SMEs need to increase investment and application of technology in making accounting books, electronic tax and customs declaration, and internet banking transactions to reduce transaction costs and connect and share information. Financial information with credit institutions to gradually make financial information transparent, creating trust in the market. Improve the quality and level of corporate governance, risk management, and financial management. Participate in business associations to access information on policies and support programs for SMEs of the Government, the State, and credit institutions. The leader needs to complete the production process, improving product quality to meet significant partners’ supply chain participation standards, especially the ability to participate in the global supply chain.
References
- Adebisi, O.S., & Akeke, N.I. (2018). Managerial determinants of organizational efficiency in Nigeria: Evidence from the banking sector. Journal of Management and Society, 1(2), 10-15.
- Ahmad, I., & Ahmad, S. (2018). Multiple skills and medium enterprises’ performance in Punjab Pakistan: A pilot study. Journal of Social Sciences Research, 4(1), 44-49.
- Anderson, J.G. (2017). An updated paradigm for scale development incorporating unidimensionality and its assessment. Journal of marketing research, 5(2), 86-92.
- Bradley, R.H., & Mecklenburg, G.J. (2018). Developing leadership skills in business administration: A competency assessment tool/practitioner application. Journal of Healthcare Management, 6(3), 188-197.
- Chatterjee, N., & Das, N. (2016). A study on the impact of critical entrepreneurial skills on the business success of Indian micro-entrepreneurs: A case of Jharkhand Region. Global Business Review, 17(1), 226-237.
- Finch, H.F. (2016). Comparison of the efficiency of varimax and Promax rotations: Factor structure recovery for dichotomous items. Journal of Educational Measurement, 3(1), 39-52.
- Foxall, G.H. (2019). Construct validation of a measure of adaptive-innovative cognitive styles in consumption. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 13(3), 21-33.
- Freelance, R.M. (2018). Insights into the skill development issues of management jobs: A study on RMG and textile sectors of Bangladesh. Asian Social Science, 4(2), 12-23.
- Fuadah, L.L., Safitri, R.H., Yuliani, Y., & Arisman, A. (2020). Determinant factors’ impact on managerial performance through management accounting systems in Indonesia. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(10), 109-117.
- Gunawardena, M.K., & Fonseka, A.T. (2018). Leadership and innovation in the garment industry of Srilanka. International Journal of Management Research, 4(2), 15-26.
- Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., & Black, W. (2010). Multivariate data analysis with readings. US: Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
- Haleem, F., Jehangir, M., & Ullah, Z. (2019). Strategic planning and SMEs performance: A developing country’s perspective. Journal of Business & Economics, 11(2), 33-49.
- Hall, R.J. (2015). Identity, deep structure, and the development of leadership skills. The Leadership Quarterly, 6(4), 91-105.
- Haq, S.D. (2018). Ethics and leadership skills in the public service. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 1(5), 92-103.
- Hasheed, M.Y. (2018). Impacting management skills on SMEs efficiency: A case study of Pakistan. Interdisciplinary journal of contemporary research in business, 4(1), 39-53.
- Hudson, M.A., & Bourne, M.H. (2019). Theory and practice in SME efficiency measurement systems. International journal of business management, 5(2), 9-18.
- Jones, J.S. (2017). The importance of leadership skills and self-perceived proficiency of leadership skills college of agriculture academic program leaders. Academy of Educational Leadership Journal, 6(4), 39-48.
- Kaiser, M.B. (2015). What we know about leadership. Review of general psychology, 9(2), 69-80.
- Karmel, B.J. (2020). Leadership: A challenge to traditional research methods and assumptions. Academy of Management Review, 13(3), 75-86.
- Kehinde, J.S., Jegede, C.A., & Akinlabi, H.B. (2012). Impact of leadership skill and strategies on banking sector efficiency: A survey of selected consolidated banks in Nigeria. Journal of Business & Management Review, 3(1), 313-324.
- Kiambati, K., & Itunga, J. (2016). Managerial skills and corporate strategic planning. International Journal of Management Science and Business Administration, 2(8), 16-23.
- Lapsinger, R.F. (2015). Factors affecting management skills and business efficiency at small and medium enterprises in Thailand. International Business Research, 5(3), 17-26.
- Marks, M.K. (2017). Exploring the relationship of leadership skills and knowledge to leader efficiency. The Leadership Quarterly, 11(1), 65-86.
- Platts, K.H. (2015). Efficiency measurement system design: a literature review and research agenda. International journal of management review, 5(4), 81-96.
- Rago, H.G. (2017). Leadership: Perspectives in theory and research. Management Science, 2(3), 35-46.
- Saleem, S.G., & Saeed, B.S. (2017). Corporate governance and firm efficiency: A case study of Karachi stock market. International Journal of Trade, Economics, and Finance, 2(1), 39-52.
- Salman, R., Arshad, D., & Bakar, L.J.A. (2016). Factors contributing to SMEs innovative culture in Punjab, Pakistan: A pilot study. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 6(8), 54-64.
- Sedmunds, H.L. (2019). Content, concurrent, and construct validity of the leadership skills inventory. International journal of business review, 2(4), 81-94.
- Sharif, S.B., & Juhdi, N.B. (2019). Soft skills practiced by managers for employee job efficiency in Ready Made Garments (RMG) sector of Bangladesh. Journal of International Business and Management, 3(4), 11-25.
- Sorgeson, F.P. (2017). Leadership skills: Leadership skill requirements across organizational levels. The Leadership Quarterly, 19(4), 154-166.
- Sotterman, J.K. (2016). Leadership versus management: What’s the difference? The Journal for Quality and Participation, 9(2), 13-25.
- Sudd, R.D. (2017). Leadership skills and competencies for extension directors and administrators. Journal of Business Research, 5(3), 24-36.
- Taas, R.A. (2017). School principals’ leadership skills: Measurement equivalence across cultures. Journal of Comparative and International Education, 7(2), 27-42.
- Tee, M.L. (2018). Development and evaluation of cognitive and metacognitive measures for predicting leadership potential. The Leadership Quarterly, 11(1), 35-53.
- Wago, A.S. (2019). Leadership: Perspectives in theory and research. Management Science, 2(3), 15-36.
- Walovey, P.H. (2019). Emotional intelligence and the construction and regulation of feelings. Asian Social Science, 7(3), 112-133.
- Yasin, T.M., & Wisboa, J.V. (2019). Efficiency measurement practices in manufacturing firms revisited. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 3(1), 5-20.
- Yuklee, G.H. (2019). Managerial leadership skills: A review of theory and research. Journal of Management, 15(2), 51-69.
- Zaccaro, S.J., & Palmon, R.F. (2020). Development of leadership skills: Experience and timing. InternationalJournal of Business & Management Research, 6(2), 33-45.