Research Article: 2022 Vol: 21 Issue: 2S
Impact of Transformational Leadership on the Job Satisfaction With the Moderating Role of Organizational Commitment: Case of Uae and Jordan Manufacturing Companies
Abdelwahhab I. Allozi, Abu Dhabi University
Muhammad Alshurideh, The University of Jordan & University of Sharjah
Ahmad Qasim AlHamad, University of Sharjah
Barween Hikmat Al Kurdi, The Hashemite University
Keywords
Transformational Leadership, Job Satisfaction, Comparative Study, Organizational Commitment, Moderating Variable, Manufacturing Companies
Citation Information
Allozi, A.I., Alshurideh, M., AlHamad, A.Q., & Al Kurdi, B.R. (2022). Impact of Transformational Leadership on the Job Satisfaction With the Moderating Role of Organizational Commitment: Case of UAE and Jordan Manufacturing Companies. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 21(S2), 1-13
Abstract
This research was conducted to investigate the importance of transformational leadership on job satisfaction by focusing on two countries which are UAE and Jordan. The study has also incorporated organizational commitment as a moderating variable to determine its importance in respect to the connection of transformational leadership and job satisfaction. The primary data source used in this study is the questionnaire survey which includes the questions asked from the respondents for the different variables of the study. The questionnaire has been responded by 314 participants from Jordan and UAE. The data analysis technique involved in this study is statistical data analysis technique which is conducted through the use of SmartPLS. The structural equation modelling has been used in this data analysis along with confirmatory factor analysis. The study has revealed that there is no significant comparative difference among the two countries based on the results. Furthermore, the transformational leadership was determined to have significant and positive effect on job satisfaction whereas organizational commitment was identified to have insignificant moderating effect. This study is particularly emphasized in the context of UAE and Jordan which leads to limiting the results from the aspect of two countries. Hence, future researches can be conducted by emphasizing on focusing on different countries.
Introduction
The role of leadership in the conglomerates cannot be denied in the contemporary world (Alameeri et al., 2020; Al-Dhuhouri et al., 2020; AlShehhi et al., 2020). Some CEOs and Chairmen have taken the corporates to the pinnacle of innovation and creation (Ghannajeh et al., 2015; Al Naqbia et al., 2020; Almaazmi et al., 2020; Alameeri et al., 2021; Nuseir et al., 2021; Obeidat et al., 2021). To name a few, Steve Jobs, Jack Ma, Sundar Pichai and Thomas J. Watson redefined the landscape of their business models. They did not only foster the growth but generated an inclusive culture that is intact to date. Basically, transformational leadership has been the main approach in promoting creativity among the employees (Gumusluoglu & Ilsev, 2009; Alsuwaidi et al., 2020; Al Suwaidi et al., 2020; Odeh et al., 2021). The leadership style involves the participation of a leader with the employees and subordinates to guide their course of actions at the work. It also propounds on the inspirational motivation and idealized attitudes that influence employees and aggrandize their prospects of job satisfaction (Alshurideh et al., 2012; Alshurideh, 2014; Alshraideh et al., 2017; Aburayya et al., 2020; Alketbi et al., 2020; Alzoubi et al., 2020; Al-Dmour et al., 2021; Hayajneh et al., 2021). Assertively, transformational leadership is integral to employee retention as it generates a sense of belonging. Besides, it also challenges the conventional work relationship of a boss and his subordinates that undermine freedom of expression too (Alshurideh et al., 2015; Ammari et al., 2017; Al Kurdi et al., 2020; Kurdi et al., 2020; Al Shebli et al., 2021).
Problem Statement
The Middle East has been considered the main oil hub of the world. It is also a considerable fact that the region supplies around 27% of oil to the world (the U.S. Energy Information Administration). In turn, the manufacturing companies are further developed in terms of energy infrastructure and seamless flow of crude oil for production. The petroleum boom occurred after the discovery of oil in the 1950s. Presently, the UAE and Jordan both are facing issues of employee satisfaction. Meanwhile, the UAE's manufacturing sector is mostly concerned with oil, aluminum, and fertilizer production. Jordan mainly deals with textiles, pharmaceuticals, jewelry and electrical appliances. Both countries have different dynamics of job satisfaction and organizational commitment (Alkalha et al., 2012; Al-dweeri et al., 2017; Al-Khayyal et al., 2020; Sultan et al., 2021). In petroleum, the employees tend to be concerned more about safety. Whereas the textile industry often faces issues pertaining to meager salaries and harsh working conditions. Therefore, this study aims to comprehend the role of transformational leadership in creating employee satisfaction while maintaining the organizational commitment among them (Alshurideh, 2010; Alshamsi et al., Alsharari & Alshurideh, 2020; 2020; Aburayya et al., 2020). It will also explore the perspectives from both countries that will support the motivating and commitment dynamics of leadership.
Aims and Objectives
The basic aim of this research is to delineate the influence of transformational leadership over job satisfaction functions. In this regard, organizational commitment has been designated as a moderating variable. Thus, the following objectives have been devised accordingly:
• To comprehend the role of transformational leadership in enhancing the job satisfaction.
• To understand the influence of transformational leadership towards the generation of organizational commitment.
Research Questions
The following questions have been devised keeping in view the above objectives:
• What is the role of transformational leadership that promotes job satisfaction?
• How transformational leadership keeps employee motivation while generating their organizational commitment?
Significance of the Study
The UAE and Jordan both are constitutional monarchies that are devoid of democratic culture. The throne is usually passed between intra or inter-family members in both of the countries. Therefore, the growth of leadership, in general, is unwary there. Emphatically, a large number of Diasporas works in the UAE, specifically in Dubai. It has made the population highly diverse (Al-Sadi et al., 2013). The case in Lebanon is also the same, although the extent of intra-nationalities is less there. In such circumstances, the leaders need to evolve their approaches to promote an inclusive culture within their organizations. On the other hand, the leadership capabilities of both countries are solely based on the petroleum-supported wealth in the UAE and services-supported revenue in Jordan. Hence, this study will significantly determine the parameters of transformational leadership with regard to the retention of employees.
Literature Review
The Concept of Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership is a newer leadership style that focuses on how leaders can help their followers change for the better. James MacGregor Burns introduced the concept of transformational leadership in his study of political leaders, which is now used to analyze corporations (Goethals & Allison, 2016). Burns classified leadership as transactional or transformational. Fast forward, almost 30 years of studies correlating transformative leadership to high-performance results at the individual, group, and organizational levels. It also highlighted the need to study leadership supporters. Transformative leadership was the first philosophy shown to emphasize morals and values in leadership. However, a multifactor management questionnaire gives conflicting results. In this regard, top executives were likewise heavily researched. It was found that the leaders may "fake" transformation leadership. Still, transformational leadership is a strong and widely used technique of leadership learning and teaching.
Impact of Transformational Leadership on Job Satisfaction
Transformational leadership has a substantial beneficial effect on workplace empowerment. Meanwhile, by increasing job satisfaction and reducing the incidence of bad outcomes, job satisfaction can be secured. Subsequently, work satisfaction is mostly associated with less unfavourable events (Boamah et al., 2018). On the other hand, Puni, et al., (2018) found that there are favorable links between the transformative leadership component and work satisfaction which are enhanced by contingent compensation. However, idealized influence and intellectual stimulation are regulated by the contingent incentive, meaning that these transformative leadership characteristics can have a beneficial effect on the happiness of employees by providing a contingent reward in the banking industry.
Influence of Transformational Leadership on the Organizational Commitment
Organizational commitment is directly associated with the leadership capabilities that create a sense of recognition among employees. The leadership also promotes a culture that aligns employee goals and perspectives with regard to the workplace. Contrarily, the success of an organization is dependent on many factors, from outside to within, and the workforce is considered one of the most important determinants of the competitiveness of the organization. The commitment of employees towards the organization reduces their intention to leave the organization and remain part of the group to work more effectively and loyally (Paille et al., 2011). The study by Marques De Lima Rua, et al., (2016) analyzed how organizational commitment mediates the relationship between transformative leadership and organizational trust in Porto, Portugal. The results revealed that transformative leadership improves organizational confidence favorably. But transformative leadership and corporate confidence are not impacted much by corporate engagement.
Hypothesis Based Literature
Transformational leadership is mainly reflected to a relational leadership style where the followers have strong trust and respect for its leaders and have high motivation towards the achievement of organizational goals (Boamah et al., 2018; Puni, Mohammed & Asamoah, 2018). There are several researches that have been undertaken by other researchers in investigating the importance of transformational leadership on job satisfaction (Dappa, Bhatti & Aljarah, 2019; Lan et al., 2019; Luu & Phan, 2020). In respect to the study conducted by Dappa, Bhatti & Aljarah (2019), it was emphasized in evaluating the influence of transformational leadership on job satisfaction in North Cyprus. The questionnaire was adopted in the study where the results of regression revealed that transformational leadership has a significant and positive influence on the employee satisfaction. In addition to this, the study conducted by Alshehhi, Abuelhassan & Nusari (2019) has investigated the influence of transformational leadership on the job satisfaction of the public employees of the UAE. The findings from the regression analysis have revealed that the transformational leadership has positive effect on job satisfaction of the employees. Based on the results of the prior studies, the following hypothesis is developed for the research and represents the first hypothesis:
H1 Transformational leadership has a significant and positive influence on the job satisfaction in the manufacturing companies of UAE and Jordan.
In respect to organizational commitment, it is referred to the stage where the employee has strong willingness to stay at the organization which also reflects to the loyalty of the employees (Eliyana & Ma’arif, 2019; Chai, Hwang & Joo, 2017). The research conducted by Lim, Loo & Lee (2017) has conducted a research as whether organizational commitment significantly moderates between leadership and job performance. The results have indicated that organizational commitment significantly moderates between leadership and job performance. In addition, to this, the research conducted by Sungu, Weng & Xu (2019) has also found that organizational commitment plays a major role towards boosting the job satisfaction of the employees. Therefore, as per the empirical evidence, the following represents the second hypothesis of the study (Figure 1).
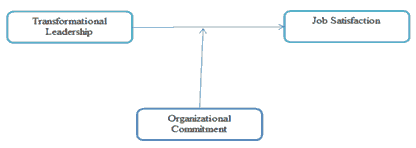
H2 Organizational commitment significantly and positively moderating between the transformational leadership and job satisfaction of the manufacturing companies of UAE and Jordan.
Figure 1 represents the conceptual framework of the research where there are particularly three types of variables that are involved which are independent, dependent and moderating variable. The independent variable that is involved in the research is transformational leadership where the job satisfaction is the dependent variable. Hence, the study seeks to evaluate the influence of transformational leader on job satisfaction. In addition to this, the organizational commitment is considered to be the moderating variable where its moderating effects are evaluated between transformational leadership and job satisfaction. Furthermore, the conceptual framework is studied under two countries where first country represents UAE and second country reflects to Jordan. Hence, the research emphasizes the effect of transformational leadership from the context of UAE and Jordan on the satisfaction of the employee.
Methodology
Data Collection and Participants
The research is being conducted through the quantitative research design which implies that the research would use the numerical data for the purpose of analysis. The data in the study has been converted into the numerical form so that it can be quantified. The data collection in this study has been conducted from the primary sources of the data. The primary source of data implies that the data is collected through the direct interaction of the researcher with the respondents or participants of the study. It is the original sources of the data. The primary data source used in this study is the questionnaire survey which includes the questions asked from the respondents for the different variables of the study. The questionnaire has been developed using the Likert Scale on the scale of 1 to 5 where 1 indicates the highly disagree and 5 shows the highly agree to the statement. The questionnaire was distributed to the different participants through the online survey link and through the direct interaction with them.
The participants of the study are the managers of the manufacturing companies of Jordan and UAE. The managers were selected based on their different designations in the companies and the two countries have been selected for developing the better comparison and to gain the larger sample size for better analysis. The questionnaire has been responded by 314 participants from the both countries and hence it is the sample size of this study.
Data Analysis
The data analysis technique involved in this study is statistical data analysis technique which is conducted through the use of SMART PLS. The structural equation modelling has been used in this data analysis. The study of Kline (2015) has indicated that for ordinal data where there is the non-normal PLS-SEM the SEM is most effective technique for analysing the data and producing the efficient results. It further includes the Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) in which the indicators underlying has been tested for the relevance whereas the latent constructs are evaluated for reliability and their validity. The data analysis includes discriminant validity and reliability. It also involves the convergent validity, composite reliability and the Cronbach’s alpha for evaluating the reliability. Furthermore, the quality of the model is also tested using the R-Squared and Q-Square measures obtained through the SMART PLS. The analysis further includes the path analysis which evaluates the hypothesis of the study. The path analysis shows the direct, indirect and specific effect within the model. The hypothesis is then accepted or rejected based on the P-values obtained through the path coefficient analysis in SMART-PLS. This technique has been indicated to be providing the efficient results and better analysis.
Results
Convergent Validity and Reliability Assessment
As indicated in the methodology, the software that is used for producing the results is SmartPLS where there are mainly two techniques that are applied with the support of SmartPLS which are Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and the Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). The section mainly covers the results of CFA in terms of evaluating the validity and reliability of the constructs. There are four techniques that are used for assessing the reliability and validity of the constructs as indicated in Table 1. The first technique represents the outer loading where the purpose of the technique is to assess the absolute contribution of the items in respect to their relevant constructions. For instance, the items JS1, JS2 and JS3 represent the items of job satisfaction. The threshold criteria of the outer loading technique are the value must be above 0.6 for represents the contribution of the indicator (Khoi & Van Tuan, 2018; Nugraheni & Bayastura, 2021). As shown in the results, the item’s outer loading values are above 0.6 and thus show that the items are making proper contribution in terms of their variables. The next two techniques represent the reliability assessment tools which are Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability. The purpose of both techniques is to evaluate the internal consistency of the responses where it is vital that the responses are internally consistent with each other for representing reliable data. The threshold criteria for both the technique are that the value of the constructs should be above 0.7 (Purwanto et al., 2020; Purwanti, 2021). As shown in Table 1, the value of the constructs in respect to the Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability is above 0.7 and therefore suggests that the constructs are reliable. The last technique is the average variance extracted or also referred to as AVE which investigates the validity of the constructs. The value of the constructs in terms of AVE is that it must be above 0.5 for indicating that the constructs are valid (Nasution, Fahmi & Prayogi, 2020; Pham et al., 2018). As per the results, the value of AVE is above 0.5 for all constructs and therefore, the results indicate the variable is valid. In terms of the overall analysis, it is found that the variables of the research are reliable and valid (Table 1).
| Table 1 Confirmatory Factor Analysis |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Items | Outer loadings | Cronbach's Alpha | Composite Reliability | AVE |
| Job Satisfaction | JS1 | 0.874 | 0.883 | 0.928 | 0.81 |
| JS2 | 0.921 | ||||
| JS3 | 0.905 | ||||
| Organizational Commitment | OC1 | 0.893 | 0.771 | 0.866 | 0.686 |
| OC2 | 0.892 | ||||
| OC3 | 0.681 | ||||
| Transformational Leadership | TL1 | 0.894 | 0.902 | 0.939 | 0.836 |
| TL2 | 0.911 | ||||
| TL3 | 0.938 | ||||
| TL*OC | Transformational Leadership * Organizational Commitment | 1.376 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Discriminant Validity
The discriminant validity is a technique that is applied from the SmartPLS where the function of the test is to examine the validity in terms of discriminant. As per the study of Ramayah, et al., (2017), it is crucial for evaluating the discriminant validity of the dataset as it determines the degree of distinctness among the variables. The variables of the study should have a certain degree of differences as the highly correlated variables leads to the issue of multicollinearity. In terms of discriminant validity, the study of Ab Hamid, et al., (2017) has demonstrated that there are several techniques that are available to the researcher for measuring the discriminant validity which includes Fornell and Larcker criterion, cross-loading or HTMT ratio (Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio of Correlations). In respect to the following study, the technique that is used for evaluating the discriminant validity is the HTMT ratio where the results of the test are provided in Table 2. Basheer, et al., (2021) has indicated that the criterion for accepting the discriminant validity through the HTMT is that the value must be below 0.9. As per the results in Table 2, the correlation value of the constructs is below 0.9 where the highest value is 0.588 that is between organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Therefore, as per the results of the discriminant validity, it is confirmed that the constructs are discriminant valid and the regression analysis technique is feasible with the dataset.
| Table 2 Discriminant Validity (Htmt Ratio) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Job Satisfaction | OC*TL | Organizational Commitment | |
| Job Satisfaction | 0.033 | |||
| OC*TL | 0.036 | 0.155 | ||
| Organizational Commitment | 0.049 | 0.588 | 0.376 | |
| Transformational Leadership | 0.021 | 0.466 | 0.357 | 0.572 |
Effect Size
The effect size of the constructs is measured from F-square where it has become critical in the current studies for the researchers to examine the effect size (Ramayah et al., 2017). The threshold criteria for effect size is that the f-square value 0.02, 0.15 and 0.35 represents small, medium and large effect of the variables (Sénquiz-Díaz, 2021). As per the results in Table 3, there are 3 constructs effect size investigated which includes organizational commitment, transformational leadership and moderating effect of organizational commitment with transformational leadership on job satisfaction. The F-square of OC*TL is computed as 0.01 which is below 0.02 and therefore, it suggests that it does not have any effect on job satisfaction. In terms of transformational leadership, its value of F-square is observed to be 0.06 and therefore, the value being above 0.02 indicates a small effect of the variable. Lastly, the organizational commitment value of F-square is calculated as 0.17 and is above 0.15; therefore, this suggests that organizational commitment has medium effect (Table 3).
| Table 3 Effect Size (F-Square) |
|
|---|---|
| Effect Size | Job Satisfaction |
| OC*TL | 0.01 |
| Organizational Commitment | 0.17 |
| Transformational Leadership | 0.06 |
Path Coefficient Analysis
With the constructs and items meeting the threshold criteria of reliability and validity testing, the regression analysis among the variables can be performed for evaluating the influence and testing the hypothesis. The regression analysis or also referred to as the path coefficient analysis is the technique that is applied through SmartPLS and is considered to be the part of the SEM. The analysis is reflected as the main technique of the statistical test where it is applied for evaluating the influence of the independent variable on the dependent variable. In respect to the following research, it is used for evaluating the influence of transformational leadership on job satisfaction along with testing the moderating role of organizational commitment. In addition to this, the comparative analysis is also conducted among UAE and Jordan which is measured by the dummy variable that is ‘Country’. The path coefficient analysis mainly evaluates two aspects which are the beta and p-value. The purpose of the beta is to signify as whether the results have positive or negative effect and by how many units. The p-value on the other hand measures the significance of the variable influence where there are 3 confidence interval for identifying the significance of the variables which includes 99% (0.01), 95% (0.05) and 90% (0.10). If the country variable is found to be significant then it would justify that there is a significant difference among UAE and Jordan in terms of performance management from the perspective of transformational leadership influence on job satisfaction.
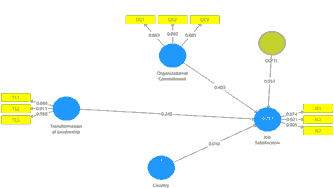
The result of the path coefficient analysis is provided in Table 4 where the first variable evaluates country influence on job satisfaction. The p-value is computed as 0.829 which is above 0.10; therefore, this suggests that the country variable has insignificant influence on job satisfaction. This implies that the performance management of both UAE and Jordan does not significantly differ with each other in terms of transformational leadership influence on job satisfaction. The second element is the moderating effect of organizational commitment with transformational leadership on job satisfaction. The p-value is observed to be 0.573 and is above 0.10; hence, this indicates that the organizational commitment does not significantly moderating between transformational leadership and job satisfaction. The third aspect that is evaluated is the organizational commitment [B=0.403; P=0.000] influence on job satisfaction. The p-value being 0.000 indicates that the organizational commitment has significant influence on job satisfaction. The beta value computed as 0.403 indicates that organizational commitment has positive influence on job satisfaction. With every unit change to organizational commitment will cause a positive change to job satisfaction by 0.403. The fourth aspect that is evaluated is the transformational leadership [B=0.245; P=0.000] influence on job satisfaction. The p-value being 0.000 indicates that the transformational leadership has significant influence on job satisfaction. The beta value computed as 0.245 indicates that transformational leadership has positive influence on job satisfaction. With every unit change to transformational leadership will cause a positive change to job satisfaction by 0.245 (Table 4).
| Table 4 Path Coefficient Analysis |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | T-statistics | P-value | |
| Country --> Job Satisfaction | 0.01 | 0.216 | 0.829 |
| OC*TL --> Job Satisfaction | 0.051 | 0.564 | 0.573 |
| Organizational Commitment --> Job Satisfaction | 0.403*** | 5.138 | 0 |
| Transformational Leadership --> Job Satisfaction | 0.245*** | 4.276 | 0 |
Model Summary and Predictive Relevance
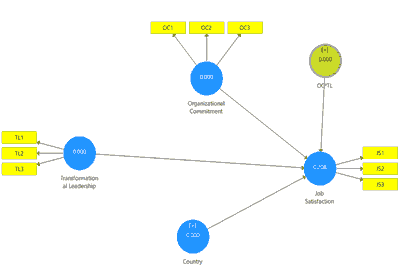
The model summary is examined through the R-square where it determines the level of variance that is captured in the model. The model is developed based on the influence of transformational leadership on job satisfaction with the moderating effect of organizational commitment. Table 5 represents the model summary results where the R-square value is computed as 29.33% which demonstrates that the transformational leadership is able to explain or predict job satisfaction by 29.33%. In addition to this, the predictive relevance of the model is measured through Q-square in which the value must be greater than zero (Sakinah et al., 2020). As per the results, the Q-square is computed as 0.208 and is above 0; therefore, the model is identified to be predictively relevant (Figure 3).
| Table 5 Model Summary and Predictive Relevance |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| R Square | R Square Adjusted | Q-square | |
| Job Satisfaction | 29.33% | 28.42% | 0.208 |
Hypotheses Summary
| H.# | Hypothesis | Beta and Significance | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Transformational leadership has a significant and positive influence on the job satisfaction in the manufacturing companies of UAE and Jordan | B=0.245; P=0.000 | Accepted |
| H2 | Organizational commitment significantly and positively moderating between the transformational leadership and job satisfaction of the manufacturing companies of UAE and Jordan | B= 0.051; P=0.573 | Rejected |
Conclusion
The role of leaders is highly important in the contemporary business environment as highly skilled leaders are able to boost the overall performance of the organization through increasing the motivation and morale of the employees. The following research was conducted to investigate the importance of transformational leadership on job satisfaction by focusing on two countries which are UAE and Jordan. The study has also incorporated organizational commitment as a moderating variable to determine its importance in respect to the connection of transformational leadership and job satisfaction. The questionnaire survey was developed and was distributed among the employees and managers of manufacturing companies that are working in UAE and Jordan. The findings of the study have revealed that there is no significant comparative difference among the two countries based on the results. Furthermore, the transformational leadership was determined to have significant and positive effect on job satisfaction whereas organizational commitment was identified to have insignificant moderating effect.
Limitations and Future Implications
The limitations that are identified in the study are that the research is particularly emphasized in the context of UAE and Jordan which leads to limiting the results from the aspect of two countries. Hence, future researches can be conducted by emphasizing on focusing on different countries such as making comparison of Western and Eastern countries for identifying as whether there is a difference influence of transformational leadership on job satisfaction due to different culture. In addition to this, the following research was conducted through only quantitative research design where the future implication of the study can be through focusing on qualitative approach for gaining in-depth information about the difference of performance management of the two identified countries.
References
Ab Hamid, M.R., Sami, W., & Sidek, M.M., (2017) Discriminant validity assessment: Use of Fornell & Larcker criterion versus HTMT criterion. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 890(1), 012163.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alameeri, K., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). The effect of work environment happiness on employee leadership. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, 668-680.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alameeri, K.A., Alshurideh, M.T., & Al Kurdi, B. (2021). The effect of Covid-19 pandemic on business systems’ innovation and entrepreneurship and how to cope with it: A theatrical view. The Effect of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) on Business Intelligence, 334, 275-288.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Al-Dhuhouri, F.S., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). Enhancing our understanding of the relationship between leadership, team characteristics, emotional intelligence and their effect on team performance: A critical review. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Springer, Cham.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Al-Dmour, R., AlShaar, F., Al-Dmour, H., Masa’deh, R., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2021). The effect of service recovery justices strategies on online customer engagement via the role of “customer satisfaction” during the Covid-19 Pandemic: An empirical study. The Effect of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) on Business Intelligence, 334, 325-346.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Al-dweeri, R.M., Obeidat, Z.M., Al-dwiry, M.A., Alshurideh, M.T., & Alhorani, A.M. (2017). The impact of e-service quality and e-loyalty on online shopping: Moderating effect of e-satisfaction and e-trust. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 9(2), 92-103.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alkalha, Z., Al-Zu’bi, Z., Al-Dmour, H., Alshurideh, M., & Masa’deh, R. (2012). Investigating the effects of human resource policies on organizational performance: An empirical study on commercial banks operating in Jordan. European Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Sciences, 51(1), 44-64.
Al-Khayyal, A., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Aburayya, A. (2020). The impact of electronic service quality dimensions on customers' e-shopping and e-loyalty via the impact of e-satisfaction and e-trust: A qualitative approach. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 14(9), 257-281.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alketbi, S., Alshurideh, M., & Al Kurdi, B. (2020). The influence of service quality on customers ‘retention and loyalty in the UAE hotel sector with respect to the impact of customer ‘satisfaction, trust, and commitment: A qualitative study. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 17(4), 541-561.
Al Kurdi, B., & Alshurideh, M. (2020). Employee retention and organizational performance: Evidence from banking industry. Management Science Letters, 10(16), 3981-3990.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Almaazmi, J., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). The effect of digital transformation on product innovation: A critical review. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics (731-741). Springer, Cham.
Al Naqbi, E., Alshurideh, M., AlHamad, A., & Al Kurdi, B. (2020). The impact of innovation on firm performance: a systematic review. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 14(5), 31-58.
Al-Sadi, A.M., Al-Wehaibi, A.N., Al-Shariqi, R.M., Al-Hammadi, M.S., Al-Hosni, I.A., Al-Mahmooli, I.H., & Al-Ghaithi, A.G., (2013). Population genetic analysis reveals diversity in Lasiodiplodia species infecting date palm, Citrus, and mango in Oman and the UAE. Plant Disease, 97(10), 1363-1369.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alshamsi, A., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). The influence of service quality on customer retention: a systematic review in the higher education. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Springer, Cham.
Alsharari, N.M., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2020). Student retention in higher education: The role of creativity, emotional intelligence and learner autonomy. International Journal of Educational Management, 35(1), 233-247.
Al Shebli, K., Said, R.A., Taleb, N., Ghazal, T.M., Alshurideh, M.T., & Alzoubi, H.M. (2021). RTA’s employees’ perceptions toward the efficiency of artificial intelligence and big data utilization in providing smart services to the residents of Dubai. In The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, Springer, Cham.
Alshehhi, S., Abuelhassan, A.E., & Nusari, M., (2019). Effect of transformational leadership on employees' performances through job satisfaction within public sectors in UAE. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8, 588-597.
AlShehhi, H., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). The impact of ethical leadership on employees performance: A systematic review. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Springer, Cham.
Alshraideh, A.T.R., Al-Lozi, M., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2017). The impact of training strategy on organizational loyalty via the mediating variables of organizational satisfaction and organizational performance: An empirical study on Jordanian agricultural credit corporation staff. Journal of Social Sciences (COES&RJ-JSS), 6(2), 383-394.
Alshurideh, M. (2010). Customer service retention–A behavioural perspective of the UK mobile market (Doctoral dissertation, Durham University).
Alshurideh, M. (2014). The Factors Predicting Students’ Satisfaction with Universities’ Healthcare Clinics’ Services. Dirasat. Administrative Sciences, 41(2), 451-464.
Alshurideh, M., Alhadid, A.Y., & Barween, A. (2015). The effect of internal marketing on organizational citizenship behavior an applicable study on the University of Jordan employees. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 7(1), 138-145.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Alshurideh, M., Masa'deh, R.M.D.T., & Alkurdi, B. (2012). The effect of customer satisfaction upon customer retention in the Jordanian mobile market: An empirical investigation. European Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Sciences, 47(12), 69-78.
Alsuwaidi, M., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). Performance appraisal on employees’ motivation: A comprehensive analysis. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Springer, Cham.
Al Suwaidi, F., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., & Salloum, S.A. (2020). The impact of innovation management in SMEs performance: A systematic review. In International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Springer, Cham.
Alzoubi, H., Alshurideh, M., Kurdi, B., & Inairat, M. (2020). Do perceived service value, quality, price fairness and service recovery shape customer satisfaction and delight? A practical study in the service telecommunication context. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 8(3), 579-588.
Aburayya, A., Alshurideh, M., Albqaeen, A., Alawadhi, D., & Ayadeh, I. (2020). An investigation of factors affecting patients waiting time in primary health care centers: An assessment study in Dubai. Management Science Letters, 10(6), 1265-1276.
Aburayya, A., Alshurideh, M., Alawadhi, D., Alfarsi, A., Taryam, M., & Mubarak, S. (2020). An investigation of the effect of lean six sigma practices on healthcare service quality and patient satisfaction: Testing the mediating role of service quality in Dubai primary healthcare sector. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems, 12(8), 56-72.
Ammari, G., Alkurdi, B., Alshurideh, A., & Alrowwad, A. (2017). Investigating the impact of communication satisfaction on organizational commitment: A practical approach to increase employees’ loyalty. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 9(2), 113-133.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Basheer, M.F., Saleem, M., Hameed, W.U. & Hassan, M.M., (2021). Employee voice determinants and organizational innovation: Does the role of senior manager matter?Psychology and Education Journal, 58(3), 1624-1638.
Boamah, S.A., Laschinger, H.K.S., Wong, C., & Clarke, S. (2018). Effect of transformational leadership on job satisfaction and patient safety outcomes. Nursing outlook, 66(2), 180-189.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Chai, D.S., Hwang, S.J., & Joo, B.K., (2017). Transformational leadership and organizational commitment in teams: The mediating roles of shared vision and team-goal commitment. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 30(2), 137-158.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Dappa, K., Bhatti, F., & Aljarah, A., (2019). A study on the effect of transformational leadership on job satisfaction: The role of gender, perceived organizational politics and perceived organizational commitment. Management Science Letters, 9(6), 823-834.
Eliyana, A., & Ma’arif, S., (2019). Job satisfaction and organizational commitment effect in the transformational leadership towards employee performance. European Research on Management and Business Economics, 25(3), 144-150.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Ghannajeh, A.M., AlShurideh, M., Zu'bi, M.F., Abuhamad, A., Rumman, G.A., Suifan, T., & Akhorshaideh, A.H.O. (2015). A qualitative analysis of product innovation in Jordan's pharmaceutical sector. European Scientific Journal, 11(4), 474-503.
Goethals, G.R., & Allison, S.T., (2016). Transforming motives and mentors: The heroic leadership of James MacGregor Burns. In Politics, Ethics and Change: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gumusluoglu, L., & Ilsev, A. (2009). Transformational leadership, creativity, and organizational innovation. Journal of business research, 62(4), 461-473.
Harahsheh, A.A., Houssien, A.A., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2021). The effect of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) on business intelligence.
Hayajneh, N., Suifan, T., Obeidat, B., Abuhashesh, M., Alshurideh, M., & Masa’deh, R. (2021). The relationship between organizational changes and job satisfaction through the mediating role of job stress in the Jordanian telecommunication sector.Management Science Letters, 11(1), 315-326.
Khoi, B.H., & Van Tuan, N., (2018). Using SmartPLS 3.0 to analyse internet service quality in Vietnam. In International Econometric Conference of Vietnam, Springer, Cham.
Kline, R.B., (2015). Principles and practice of structural equation modelling. Guilford publications.
Kurdi, B., Alshurideh, M., & Alnaser, A. (2020). The impact of employee satisfaction on customer satisfaction: Theoretical and empirical underpinning. Management Science Letters, 10(15), 3561-3570.
Lan, T.S., Chang, I., Ma, T.C., Zhang, L.P., & Chuang, K.C. (2019). Influences of transformational leadership, transactional leadership, and patriarchal leadership on job satisfaction of cram school faculty members. Sustainability, 11(12), 1-13.
Lim, A.J.P., Loo, J.T.K., & Lee, P.H. (2017). The impact of leadership on turnover intention: The mediating role of organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Structural Equation Modelling, 1(1), 27-41.
Luu, D.T., & Phan, H.V. (2020). The effects of transformational leadership and job satisfaction on commitment to organisational change: A three-component model extension approach. The South East Asian Journal of Management, 14(1), 106-123.
Martins Marques De Lima Rua, O.M., & Costa Araújo, J.M. (2016). Linking transformational leadership and organizational trust: Has organizational commitment a mediating effect on it?
Nasution, M.I., Fahmi, M., & Prayogi, M.A. (2020). The quality of Small and Medium Enterprises Performance Using the Structural Equation Model-Part Least Square (SEM-PLS). In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1477(5), 052052.
Nikpour, A., (2017). The impact of organizational culture on organizational performance: The mediating role of employee’s organizational commitment. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 6, 65-72.
Nugraheni, D.M.K., & Bayastura, S.F. (2021). Analysis of factors that influence satisfaction and usefulness for attendance system with the Delone & McLean model (Case study: attendance system at Diponegoro University). Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 1943(1), 012108.
Nuseir, M.T., Aljumah, A., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2021). How the business intelligence in the new startup performance in UAE during COVID-19: The mediating role of innovativeness. The Effect of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) on Business Intelligence, 334, 79-63.
Odeh, R.B.M., Obeidat, B.Y., Jaradat, M.O., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2021). The transformational leadership role in achieving organizational resilience through adaptive cultures: The case of Dubai service sector. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management.
Paillé, P., Fournier, P.S., & Lamontagne, S., (2011). Relationships between commitments to the organization, the superior and the colleagues, and the intention to leave among truckers. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 19(2), 92-108.
Pham, Q.T., Tran, X.P., Misra, S., Maskeliunas, R., & Damaševicius, R., (2018). Relationship between convenience, perceived value, and repurchase intention in online shopping in Vietnam. Sustainability, 10(1), 1-14.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Puni, A., Mohammed, I., & Asamoah, E. (2018). Transformational leadership and job satisfaction: The moderating effect of contingent reward. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 39(4), 522-537.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Purwanto, A., Wirawati, S.M., Arthawati, S.N., Radyawanto, A.S., Rusdianto, B., & Yunanto11, D.A., (2020). Lean six sigma model for pharmacy manufacturing: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(8), 304-313.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Purwanti, Y. (2021). The influence of digital marketing & innovasion on the school performance. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(7), 118-127.
Ramayah, T., Yeap, J.A., Ahmad, N.H., Halim, H.A., & Rahman, S.A., (2017). Testing a confirmatory model of Facebook usage in SmartPLS using consistent PLS. International Journal of Business and Innovation, 3(2), 1-14.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Sakinah, U., Ridzwan, C.R., Ramlee, M., & Zaliza, H., (2020). Career challenges model among female engineers: PLS-SEM analysis. Malaysian Journal of Public Health Medicine, 20(Special1), 243-250.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Sénquiz-Díaz, C. (2021). Effect size of logistics: Evidence from selected countries. LOGI–Scientific Journal on Transport and Logistics, 12(1), 123-134.
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Sultan, R.A., Alqallaf, A.K., Alzarooni, S.A., Alrahma, N.H., AlAli, M.A., & Alshurideh, M.T. (2021). How students influence faculty satisfaction with online courses and do the age of faculty matter. In The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, Springer, Cham.
Sungu, L.J., Weng, Q., & Xu, X. (2019). Organizational commitment and job performance: Examining the moderating roles of occupational commitment and transformational leadership. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 27(3), 280-290.
U.S. Energy Information Administration (2021). What countries are the top producers and consumers of oil?
Crossref, GoogleScholar, Indexed at
Received: 06-Nov-2021, Manuscript No. asmj-21-8742; Editor assigned: 11- Nov -2021, PreQC No. asmj-21-8742 (PQ); Reviewed: 20- Nov -2021, QC No. asmj-21-8742; Revised: 04-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. asmj-21-8742 (R); Published: 03-Jan-2022