Research Article: 2021 Vol: 13 Issue: 1
Impact of Training & Development on Job Satisfaction: A Study on Paramedical Staff of Public Sector Hospitals
Rimjhim, Amity University Madhya Pradesh
Devendra Kumar Pandey, Amity University Madhya Pradesh
Anil Singh Parihar, Amity University Madhya Pradesh
Manoj Pandey, Amity University Madhya Pradesh
Abstract
Health is most important for any individual, society or nation. Govt of every nation keeps high focus on healthcare sector of their country. Govt. of India also focuses on Healthcare sector. The health-care sector is growing at a very fast rate, in terms of employee and revenue generation also. Govt. of India and all State Govt. focus on keeping their employees motivated, well trained and updated with the new technologies and process of treatments. This research is conducted, to study the practices related to Training & development and the job satisfaction level of Paramedical staff in public sector hospitals of Gwalior-Chambal Region. The study also aims to analyse the impact of various training & development programs on Job-satisfaction of paramedical staffs in public-sector hospitals of Gwalior and Chambal region.
Keywords
Training & Development, Job Satisfaction, Hospital Sector, Paramedical Staffs.
Introduction
Healthcare sector is one of fast growing and larges sectors of India. The reasons behind the growth of this sector are increasing income level of individuals and society, continuously changing lifestyle, growing rate of population. Govt. of India is also focusing on this sector. According to IBEF (Indian Brand Equity Forum), the Government of India has aimed to increase the spending and budget in healthcare to 3% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by the year 2022.
Training and Development
Training & development Practices are related with development of positive- attitude towards the work in staffs. Training & Development programs are also organized to correct and enhance working style of employees, behavioural and interpersonal skills. Development programs are generally prepared for middle level management.
Job Satisfaction
Job-Satisfaction is an important attitude of employees to be studied by all types of organizations.
Described as a positive feeling of staff members about their jobs. Paramedical Staff also called as paramedics. They are trained professionals responsible for providing clinical and other related services to the patients, under the supervision of doctors. The services provided by paramedics includes sanitization, maintaining hygiene, pharmacy related services, physiotherapy related services, exercise related to ongoing therapy etc.
Objective
This study aims to analyse the impact of Training & Development practices on Job Satisfaction of Paramedical staffs of Gwalior and Chambal Region.
Originality
Very few studies and research are conducted for analysing the relationship and impact of Training & Development and Job-Satisfaction in Paramedical Staffs of public sector hospitals of Gwalior-Chambal Region.
Material and Methods
The research is based on primary and secondary data. Data is collected through self- structured- questionnaire. The study was conducted on Paramedical staffs from various public hospitals of Gwalior and Chambal Region. Secondary data was used for literature review.
Literature Review
Training & Development
Sharma et al. (2020) discussed about stressful environment in hospitals are developed in emergency area, eg ICU etc. This stressful environment can create dissatisfaction in employees. Sajai (2020) concluded Job insecurity as one if the important factors of Job satisfaction. Taamneh et-al. (2018) argued effective HR Practices eg training & development, staffing etc as a tool to gain competitive advantage Shah et-al. (2018) studied about demographical variables to measure job satisfaction in lecturers Albrecht et al. (2015) suggested training & development as “efforts to be taken by any organization for improving the skill-set of the employees.” Jiang et al. (2012) argued training & development as strategy and effort made by any organization in order to improve abilities, skills, and knowledge of employees. Noe et al. (2010) discussed the relationship of attitude and effectiveness of the training program. A strong relation was found in these variables Kabene et al. (2006) argued importance HRM Practices in healthcare in global aspect. The study was done on secondary database. Gould-Williams (2003): Studied about the effect of various HRM practices on Job satisfaction in Govt organizations of UK. There was a direct association between Job Satisfaction employee commitment, Perceived organizational support and trust etc Pareek (2018) discussed on planning for training & development programs. Whether it is on job training or off-the-job training, planning makes it effective Kydd (1990) found some common HR practices eg Training and development program associated with innovation and commitment. Secondary data was used for the study David & Stephen (1989) argued training and the experience pf learning leads to a change in behaviour which is permanent. It increases the ability performing jobs in individuals. Oatey (1970); Discussed about the importance of training & development. Training was found helpful in development of employees mentally, intellectually and socially. Which leads to create a happy workforce.
Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction measures an employee's cognition and evaluation, mental status, and emotional experience with their job as-well -as all related aspects Singh (2013) identified and argued about the factors of job satisfaction, in Manipur of India. It was found that the factors of job satisfaction. Pay and compensation was found most important factor of Job satisfaction in that study. They also found a positive co relation with training and development program and Pay and compensation Johari (2013) analysed the relationship between job-satisfaction and Job- Performance of employees. They worked on four factors: Work Comfort, Salary, Work- Treatment and Job Performance. The study was done in Govt hospitals of Libya. It was concluded that the staffs not satisfied with factors of job satisfaction shown a poor Job performance. It can be enhanced when employees will be well treated by their managers and will also receive god salary and incentives Bhatnagar & Srivastava (2011) studied to develop a scale which can measure job satisfaction of medical teachers. They identified Job Reward, motivation, work enthusiasm, welfare-measures, social-support, job-competency. It was developed for measuring the job satisfaction level of health care employees of India Yang (2001) Job satisfaction is a measurement of employee’s attitude and cognition. It also measures the mental status and their experience towards job on emotional aspect O’Berien (1993) Researched about the effect of gender of paramedics of public hospitals on job satisfaction. It was found that male staffs were more satisfied than female paramedics Spencer & Byrne (2016) identified the managerial level and job satisfaction. The study found a high job satisfaction level in senior level management, in comparison with junior level managers in any organization Monga et al. (2015) studied about salary and pay, social association, the attitude of senior employees, surroundings of workplace, teamwork, personal contacts have bearing on workplace satisfaction of employees. Lu, et al. (2005) also identified wages, job work environment, social-aspects and social-recognition as determinant factors of job satisfaction Stewart (2007) researched about effect of work environment on employee job satisfaction. Work environment may include cleanliness, noise also apart from other factors Bokti & Talib (2009) discussed about influence of friendly nature of co-workers and social factors on employee motivation Hesketh & Fleetword (2009) also identified incentives and social recognition boosts employee recognition. Social recognition may include “Employee of the month award” or promotions etc Brush & Solchalski (2007) researched poor relationship between nurses, physicians and management of the hospitals are the main factors which cause low morale in the employees of medical or healthcare system.
Research Methodology
Research Design
Exploratory and Descriptive design were adopted according to the nature of the study. In case where problems are not identified, and not studied clearly, we use an exploratory research, and to describe and study the characteristics of the population a descriptive research is used.
Problem Statement
Managing employees effectively and efficiently is the biggest challenge for organizations. It needs to manage the human aspect also which includes their attitude towards job, behaviour, motivation, learning, perception etc. These are related to the HR practices and being run in the organization e.g., Recruitment, Selection, Induction, Training & Development etc. Public hospitals also organize training and development programs for every staffs, including paramedical staffs. It is very important to run the Training & Development program effectively and efficiently. The present study focuses on the impact of Job-Satisfaction and Training & Development related practices for Paramedical staffs in public hospitals.
Research Questions
Q1: What types of Training & Development Programs exist in Public Hospitals?
Q2: What is the level of Job Satisfaction of Paramedical Staffs in Public Hospitals?
Q3: Are Training & Development Programs and Job Satisfaction related?
Objectives of the Study
Current Research has the Following Objectives
1. To, study the Training & Development practices for Paramedical staffs in public sector Hospitals.
2. To study the level-of Job-Satisfaction of Paramedical staffs in public sector hospitals.
3. To study the impact of Training & Development programs on job-satisfaction level of Paramedical staffs in public sector Hospitals.
Hypothesis Formulation
H1: There is not any significant impact of Training & Development on the Job Satisfaction level of Paramedical Staffs of Public Hospitals.
Instrumentation
The survey questionnaire instruments were used. The design of questionnaire has been through formulated after discussion with well-known HRD and HRM experts and academicians and also by referring to extensive literature and a self-structured questionnaire based on previous research, prepared by the researcher was distributed to the paramedical staffs of Public Hospitals in target area. A list of total 46 statements measured on a 5-point Likert scale was prepared in Tables 1 & 2.
| Table 1 Instrumentalization | |||
| S. No. | Variable Name | No of Items | Source |
| 1 | Training & Development | 7 | Demo et al (2012) |
| 2 | Teamwork and Trust | 6 | Schultz et al (2011) and Danial et. Al (2014) |
| 3 | Flexible Job Assignment | 4 | O'Neal, Angela D (2012). |
| 4 | Employment Security | 6 | Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire (Weiss et al. in 1967 ) |
| 5 | Organizational Support | 5 | Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire (Weiss et al. in 1967 |
| 6 | Communication | 5 | JSS by Spector (1994) |
| 7 | Salary | 5 | Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire, Wakil Ajibola-asekun(2015) |
| 8 | Relationship-with supervisor and co-workers | 4 | Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire (Weiss et al. in 1967) |
| 9 | Job itself | 4 | Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire (Weiss et al. in 1967) |
| Table 2 Variable Wise Reliability Statistics | ||
| S. No. | Variable Name | Cronbach's Alpha |
| 1 | Training & Development | 0.717 |
| 2 | Teamwork and Trust | 0.829 |
| 3 | Flexible Job Assignment | 0.78 |
| 4 | Employment Security | 0.737 |
| 5 | Organizational Support | 0.876 |
| 6 | Information Sharing(Communication) | 0.856 |
| 7 | Salary | 0.795 |
| 8 | Relationship with - supervisor and co-workers | 0.828 |
| 9 | Job itself | 0.848 |
Data Analysis
Reliability Statistics
Factor wise analysis (Job Satisfaction)
Following factors of Job satisfaction were analyzed
Factor 1: Teamwork and Trust
This factor has emerged as an important determinant of Job Satisfaction, It consist of 6 variables, and explains 12.132% of variance.
Factor 2: Flexible Job Assignment
This is another determinant of Job Satisfaction, consists of 4 variables, and explained 11.883% of variance.
Factor 3: Employment Security
The next important determinant of Job satisfaction is Employment Security comprising of 6 variables. It explains 9.655% of variance on job satisfaction.
Factor 4: Organizational Support
Another important determinant of Job Satisfaction is organizational support, explaining 8.534% of variance and comprising of 5 variables.
Factor 5: Communication (Information sharing)
Communication is explaining 7.041% of variance on job satisfaction. This is also emerged as a determinant of Job Satisfaction. It has 5 variables.
Factor 6: Salary
This factor has 4 variables, explaining 10.877% of variance. It is an important determinant of Job satisfaction.
Factor 7: Relationship with Supervisor and co-workers
Another determinant emerged for Job satisfaction is Relationship with Supervisor and co-workers. Explaining variance of 6.682%. It has 4 variables.
Factor 8: Job itself
The Job itself also a determinant of job satisfaction, explaining 7.697% of variance and consisting 4 variables in Tables 3 & 4.
| Table 3 Total Variance Explained Job Satisfaction | ||||||||||
| Component | Initial Eigen values | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | |||||||
| Total | % of Varianc e |
C Cumulative % | Total | % of Varianc e |
C Cumulative % | Total | % of Varia nce |
C cumulative % | ||
| Dimensions | 1 | 12.774 | 32.754 | 32.754 | 12.77 4 |
32.754 | 32.754 | 4.731 | 12.13 2 |
12.132 |
| 2 | 4.256 | 10.913 | 43.667 | 4.256 | 10.913 | 43.667 | 4.634 | 11.88 3 |
24.015 | |
| 3 | 3.381 | 8.668 | 52.335 | 3.381 | 8.668 | 52.335 | 4.242 | 10.87 7 |
34.892 | |
| 4 | 2.391 | 6.132 | 58.467 | 2.391 | 6.132 | 58.467 | 3.765 | 9.655 | 44.547 | |
| 5 | 2.037 | 5.223 | 63.690 | 2.037 | 5.223 | 63.690 | 3.328 | 8.534 | 53.081 | |
| 6 | 1.773 | 4.545 | 68.236 | 1.773 | 4.545 | 68.236 | 3.002 | 7.697 | 60.778 | |
| 7 | 1.287 | 3.300 | 71.536 | 1.287 | 3.300 | 71.536 | 2.746 | 7.041 | 67.819 | |
| 8 | 1.156 | 2.965 | 74.501 | 1.156 | 2.965 | 74.501 | 2.606 | 6.682 | 74.501 | |
| 9 | 0.935 | 2.397 | 76.898 | |||||||
| 10 | 0.852 | 2.185 | 79.083 | |||||||
| 11 | 0.770 | 1.975 | 81.058 | |||||||
| 12 | 0.706 | 1.810 | 82.868 | |||||||
| 13 | 0.632 | 1.620 | 84.487 | |||||||
| 14 | 0.610 | 1.563 | 86.050 | |||||||
| 15 | 0.526 | 1.348 | 87.398 | |||||||
| 16 | 0.511 | 1.311 | 88.709 | |||||||
| 17 | 0.469 | 1.202 | 89.911 | |||||||
| 18 | 0.429 | 1.100 | 91.011 | |||||||
| 19 | 0.363 | 0.930 | 91.941 | |||||||
| 20 | 0.341 | 0.876 | 92.816 | 9 | ||||||
| 21 | 0.318 | 0.815 | 93.631 | |||||||
| 22 | 0.301 | 0.771 | 94.402 | |||||||
| 23 | 0.268 | 0.687 | 95.090 | |||||||
| 24 | 0.249 | 0.639 | 95.728 | |||||||
| 25 | 0.229 | 0.586 | 96.314 | |||||||
| 26 | 0.213 | 0.546 | 96.860 | |||||||
| 27 | 0.191 | 0.490 | 97.350 | |||||||
| 28 | 0.171 | 0.438 | 97.789 | |||||||
| 29 | 0.160 | 0.409 | 98.198 | |||||||
| 30 | 0.145 | 0.372 | 98.570 | |||||||
| 31 | 0.140 | 0.360 | 98.930 | |||||||
| 32 | 0.124 | 0.318 | 99.248 | |||||||
| 33 | 0.082 | 0.209 | 99.458 | |||||||
| 34 | 0.060 | 0.153 | 99.611 | |||||||
| 35 | 0.057 | 0.146 | 99.757 | |||||||
| 36 | 0.037 | 0.094 | 99.851 | |||||||
| 37 | 0.022 | 0.056 | 99.907 | |||||||
| 38 | 0.021 | 0.053 | 99.960 | |||||||
| 39 | 0.016 | 0.040 | 100.000 | |||||||
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | ||||||||||
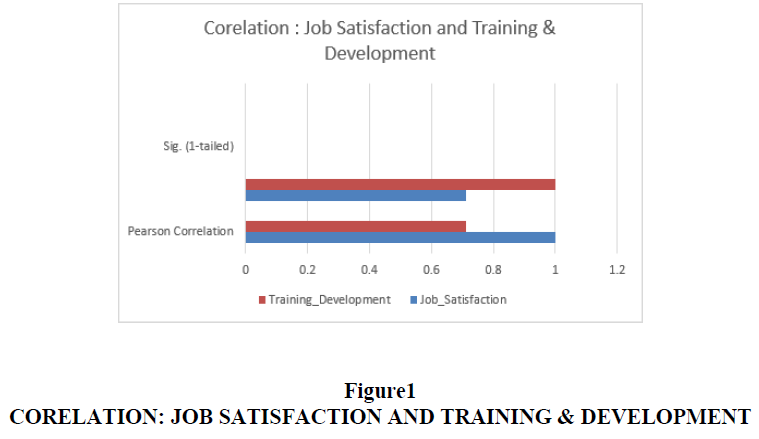
| Table 4 Corelation | |||
| Job_Satisfaction | Training_Development | ||
| Pearson Correlation | Job_Satisfaction | 1 | 0.711 |
| Training_Development | 0.711 | 1 | |
| Sig. (1- tailed) |
Job_satisfaction | . | 0 |
| Training_Development | 0 | . | |
Correlation
Regression Analysis
Conclusion
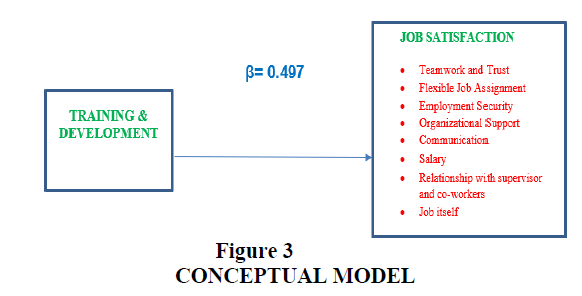
Factors of Job satisfaction were identified by factor analysis of Job Satisfaction. Total 8 factors of Job Satisfaction were identified. All the factors of Job Satisfaction were strongly co- related with Training & Development programs. Teamwork and Trust explained 12.132% Flexible Job Assignment explained 11.883%, Employment Security expalined 9.655% Organizational Support explained 8.534% Communication (Information sharing) explained 7.041%, Salary 10.877%, Relationship with Supervisor and co-workers explained 6.682%, Job itself explained 7.697% of variance in Figures 1 & 2. The regression analysis shows an overall impact of 49.7% by Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction of Paramedical staffs. If the management identifies the training needs in proper way, and provide the required training to their paramedical staffs, the staff will show a higher job satisfaction. The senior level employees will develop more trust on the trained staffs, which in turn will increase the teamwork. Increased teamwork is a factor of Job Satisfaction in Table 5. Fully trained staffs need less supervision, so jobs can be assigned to them according to their flexible time, which will again lead to higher Job Satisfaction. Trained employees can show better performance, which increase employment security and employment security will lead to high job satisfaction. Training & development programs are also perceived as organizational support by the employees, and by providing quality training their perceived organizational support will be satisfied. Well trained employees can understand the jargons easily and understand the process with fast speed, so the communication will be better and leading to increased job satisfaction. Training enhances good relationship with supervisor and subordinate, as the tasks will be completed by the employees in better way, this is important for job satisfaction. After attending good training programs, the efficiency of staffs will increase, and it will lead to their salary increment which ultimately is a reason of job satisfaction. Well trained employees will enjoy their job. A workforce with high level of job-satisfaction contributes to minimize the employee turnover ratio. The management team of any hospital must focus on increasing job satisfaction amongst all staffs especially paramedical staffs, to minimize the employee turnover ratio in Figure 3.
| Table 5 Model Summary | ||||||||
| Model | R | R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Change Statistics | Durbin- Watson | |||
| R Square Change |
F Change |
Sig. F Change | ||||||
| dimension0 | 1 | 0.711a | 0.505 | 0.497 | 0.505 | 62.255 | 0 | 2.19 |
Conceptual Model
Limitations
The study contains few constraints and limitations; those could not be controlled and not be ignored as well.
1. The data was collected from Gwalior and Chambal Region only
2. This study is restricted only to those hospitals which had the capacity of minimum 10 beds.
3. Time Constraint
Future Scope of Study
1. A study on impact pf Training &Development practices on Job-satisfaction of Paramedical staffs on Contractual basis in Public sector Hospitals of Gwalior and Chambal Region
2. A Study on Training & Development of Paramedical staffs in Private hospitals of Gwalior and Chambal Region
3. A study on Training & Development practices and its impact on Job satisfaction in Private Hospitals of Gwalior and Chambal Region
References
- Albrecht, S.L., Bakker, A.B., Gruman, J.A., Macey, W.H., & Saks, A.M. (2015). Employee engagement, human resource management practices and competitive advantage. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, 2(1), 7-35.
- Bhatnagar, K., & Srivastava, K. (2011). A Preliminary Study to Measure and Develop Job Satisfaction Scale for Medical Teachers. Industrial Psychiatry Journal, 20(2).
- Bokti, N.L., Talib, M.A. (2009). A preliminary study on occupational stress and job satisfaction among male navy personnel at a naval base in Lumut, Malaysia. The Journal of International Social Research. 2(9), 299-307.
- Brush, B.L., & Sochalski J. (2007). International nurse migration: Lessons from the Philippines. Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice, 8(1), 37-46|.
- Carol, S.F. Kerth, O., Jon J. & Terri, A.S. (1993) Job satisfaction of paramedics: The effects of gender and type of agency of employment, Annals of Emergency Medicine, (22), 4, 657-662.
- David, A., & Cenezo, D. (1989). Personnel/Human resource management. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India. Elarabi, H.M., & Johari, F. (2014). The Determinant Factors Effecting the Job Satisfaction and Performance in Libyan Government Hospital. Asian Social Science, 10(8), 55–65.
- Gould-Williams, J. (2003). The importance of HR practices and workplace trust in achieving superior performance: a study of public-sector organizations. International journal of human resource management, 14(1), 28-54.
- Hesketh, A., & Fleetwood, S. (2009). Explaining the performance of human resource. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Jiang, K., Lepak, D.P., Han, K., Hong, Y., Kim, A., & Winkler, A.L. (2012). Clarifying the construct of human resource systems: Relating human resource management to employee performance. Human Resource Management Review, 22(2), 73-85.
- Kabene, S.M., Orchard, C., Howard, J.M., Soriano, M.A., & Leduc, R. (2006). The importance of human resources management in health care: a global context. Human Resources for Health, 4(1), 20.
- Kydd, C.T., & Oppenheim, L. (1990). Using human resource management to enhance competitiveness: Lessons from four excellent companies. Human Resource Management, 29(2), 145-166.
- Lu J, Shi K, Yang J. (2001) Structures and methods for job satisfaction evaluation. Human Res Dev China. 1:15–7.
- Lu, H., & While, K., Bariball, K. (2005). Job satisfaction among nurses: a literature review. Int J Nurs Stud.; 42:211–27.
- Monga, A., Verma, N., & Monga, O.P. (2015). A Study of Job Satisfaction of Employees of ICICI Bank in Himachal Pradesh. Human Resource Management Research, 5(1), 18-25.
- Nima Sajai, (2020). Comparative study to assess the level of job satisfaction among the nursing professionals working in certain hospitals & academic institutions at asir region, kingdom of Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(7), 4800-4813.
- Noe, R., Hollenbeck, J., Gerhart, B. & Wright, P. (2010) Human Resource Management: Gaining a Competitive Advantage. McGraw Hill, New York.
- Oatey, M. (1970). The economics of training with respect to the firm. British Journal of Industrial Relations, 8(1), 1-21.
- Pareek, L.U., & Purohit, S. (2018). Training Instruments in HRD and OD. SAGE Publishing India.
- Shah, H.S.A., & Khan, M.A. (2018). Leadership effectiveness in relation with job satisfaction. International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Scientific Research 1(5), 50-57.
- Sharma, A., Kaushal, V., Pandey, N., Arora, P., Thiyagarajan, A., & Bhattacharya, S. (2020). Assessment of job satisfaction among nursing officers working at a tertiary care hospital in Northern India. CHRISMED Journal of Health and Research, 7(1), 35-41.
- Singh, R.G. (2013). Factors Explaining Job Satisfaction Among Hospital Employees. OPUS: Annual HR Journal, 29-43.
- Spencer, R.J., & Byrne, M.K. (2016). Relationship between the extent of psychopathic features among corporate managers and subsequent employee job satisfaction. Personality and Individual Differences, 101, 440-445.
- Stewart, M.B. (2007). The interrelated dynamics of unemployment and low-wage employment. Journal of Applied Econometrics 22(3), 511-531.
- Taamneh, A., Alsaad, A.K., & Elrehail, H. (2018). HRM practices and the multifaceted nature of organization performance. EuroMed Journal of Business , 13(3), 315-334.