Research Article: 2025 Vol: 29 Issue: 3
Impact of E-Crm on E - Loyalty in Online Retailing
Neelam Raut, Prin. L.N. Welingkar Institute of Management Development & Research, Mumbai
Shubham Saxena, International School of Business and Media, Pune
Divya Bharathi, Christ University, Bengaluru
Jayashree Patole, Ramachandran International Institute of Management (RIIM), Pune
Ameya Patil, Dr. Viswanath Karad MIT World Peace University, Pune
Mohit Kant Kaushik, Dr. Viswanath Karad MIT World Peace University, Pune
Citation Information: Raut, N., Saxena, S., Bharathi, D., Patole, J., Patil, A., & Kaushik, M.K. (2025). Impact of e - crm on e - loyalty in online retailing. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 29(3), 1-9.
Abstract
With the rise of online retailing, businesses are increasingly adopting Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) strategies to enhance customer loyalty in the digital marketplace. E-CRM encompasses various elements that help businesses build and maintain relationships with customers, ultimately fostering Electronic Loyalty (E-Loyalty). Despite its growing significance, there is a need to better understand which E-CRM constructs most effectively contribute to customer retention in online retailing. The objective of the present research study is to examine the impact of five key E-CRM constructs i.e. Trust, Communication, Technology, Service Quality, and Commitment on E-Loyalty in online retail. Primary data was collected from 160 online retail customers through a structured questionnaire, and the relationships between the variables were analyzed using multiple regression analysis. The findings reveal that Service Quality, Technology, Trust, and Communication play a significant role in shaping E-Loyalty, while Commitment has a negligible impact. The Adjusted R² value of 0.627 indicates that a substantial proportion of E-Loyalty is explained by E-CRM constructs, reinforcing their importance in customer relationship management strategies.
Key Words
E-CRM, E-Loyalty, Online Retailing, Multiple Regression Analysis, Descriptive Research.
Introduction
The increasing influence of the internet, along with evolving lifestyles, has transformed every walks of our lives (Gaurav et. al., 2025). Currently, consumers are favoring online shopping over traditional in-store purchasing methods. Simultaneously, organizations throughout the industry are transitioning from conventional commercial practices to contemporary electronic commerce procedures. The e-commerce and online retailing industry is expanding at an unprecedented rate, attracting the interest of investors and enterprises, resulting in heightened rivalry. The Indian e-commerce business has been undergoing significant expansion, transforming the manner in which individuals do transactions online. Competition is intensifying, and market power is transitioning from manufacturers to consumers as the latter get access to a growing array of options within the same product category. Customer expectations are becoming rigorous; meeting these demands has become more intricate, challenging, and at times unmanageable. Currently, organizations face the problem of attracting and retaining loyal consumers, as such customers frequently contribute to a sustainable competitive advantage (Gaurav, 2008). Organizations within the business frequently endeavor to establish and sustain enduring, lucrative connections with their clients. Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist of French origin, illustrated that a corporation generates 80% of its revenue from 20% of its clientele. Reichheld and Sasser (1990) observed that a 5 percent enhancement in customer retention can lead to a profitability rise ranging from 25 percent to 85 percent (in net present value), contingent upon the industry. Loyal consumers exhibit reduced price sensitivity and are more cost-effective to retain than new customers. Ball, et al. (2004) noted that client loyalty and retention represent the primary issues encountered by Chief Executive Officers globally.
Marketing has been shifted from “transaction marketing to relationship marketing” (Lindgreen, 2001). In recent time, Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) has surfaced as an online marketing strategy employed by firms to find and attract potentially profitable clients (Usman et al., 2012). Moreover, E-CRM enables clients to access the business and its offerings from an expanding number of locations, as internet connection points proliferate daily. Recently, corporations have recognized that continuous and frequent interactions are essential for understanding customers’ wants and desires to create and maintain strong relationships with them. E-CRM is frequently regarded as a collection of activities, tools, and technology, including websites, email, and communication platforms, utilized to establish and strengthen enduring relationships with clients via the Internet (Abbott, 2001). The primary objective of E-CRM is to proficiently manage distinct relationships with all clients and engage in individualized communication with them. E-CRM is crucial in ascertaining an organization’s overall success, especially within the realm of internet shopping.
At this backdrop, the present research study seeks to examine the influence of E-CRM on E-Loyalty in online retailing within the Indian setting.
Literature Review
E-Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM)
E-CRM is the process of developing and maintaining successful customer relationships in a profitable manner. It has become an essential element in modern business, ensuring long-term sustainability by enhancing customer retention and satisfaction (Kımıloğlu andZaralı, 2009). Given that serving customers is the core activity of any business, companies cannot survive without a strong customer relationship management system. The rising competition in the e-commerce sector has driven online retailers to strengthen their customer engagement strategies to retain e-loyalty. The rapid advancement of technology and internet penetration has further compelled businesses to shift their focus toward e-loyalty by leveraging E-CRM.
E-retailing has witnessed significant growth due to its competitive advantages over traditional brick-and-mortar stores, including greater flexibility, lower cost structures, faster transactions, broader product lines, and increased convenience. Consequently, businesses are increasingly adopting E-CRM strategies to foster customer loyalty and sustain their competitive advantage in the online marketplace (Lee-Kelley, Gilbert, and Mannicom, 2003).
Determinants of E-CRM Success
Feinberg and Kadam (2002) highlights the significance of website design in maintaining successful customer relationships. He argues that a company’s website should avoid offensive content or any elements that might negatively impact a customer’s societal perception. His study, which focuses on the retail industry, finds a strong positive correlation between e-CRM website features and customer retention, with 90% of retailers demonstrating improved business performance through enhanced online engagement.
Nguyen,Sherif andNewby (2007) further supports the notion that customers are central to business success and emphasizes the need for effective resource utilization in relationship management. He notes that CRM tools are increasingly wireless-enabled, with mobile sales force automation and digital communication methods (e.g., SMS and email) playing a crucial role in improving customer engagement. However, he also acknowledges that implementing CRM strategies comes with challenges, as business variables are dynamic and require continuous adaptation.
Strategic Implementation of E-CRM
Bull (2003) highlights the importance of leadership in CRM implementation, arguing that organizations should adopt a holistic approach that places CRM at the heart of business operations. He conceptualizes CRM beyond a front-end contact management system, incorporating operational, analytical, and collaborative elements. A holistic approach enables organizations to coordinate multiple customer touch points effectively, ensuring a seamless customer experience across all communication channels. However, the study also identifies potential challenges, such as channel conflicts that may arise when customer experiences differ across various sales channels.
E-Loyalty and Its Significance in Online Shopping
E-loyalty refers to the likelihood that a customer will return to the same company for repeated purchases. It is a key predictor of customer lifetime value, influencing long-term business success. Chen and Ching (2006) define e-loyalty as a customer’s commitment to a brand’s products or services over time. In their study involving 96 students, they employed hypothesis testing to establish a positive relationship between e-loyalty and E-CRM, indicating that improved E-CRM practices enhance customer retention.
Customer loyalty can be categorized into two categories: long-term loyalty and short-term loyalty. Long-term loyalty represents a stable, unwavering commitment to a brand, whereas short-term loyalty is influenced by situational factors and competitive offerings. Gaurav, Nerlekar, Srinivas, and Ray (2024) noted that the customers are rational decision-makers, and companies must adopt strategic retention practices to minimize customer attrition. Gaurav and Khan (2013) further suggest that loyal customers not only make repeat purchases but also act as brand advocates, recommending the company to others.
The Impact of E-CRM on E-Loyalty
The primary goal of marketing is twofold: attracting new customers by offering superior value and retaining existing customers through continuous satisfaction. Companies create value for customers by building strong relationships, which, in turn, fosters brand loyalty (Gaurav, 2016).
Khalafinezhad and Sang Long (2013) suggest that E-CRM has a significant positive impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty. They argue that customer anxiety serves as a moderating variable that influences the relationship between E-CRM and customer satisfaction.
E-loyalty plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between businesses and their customers. Ramaj and Ismaili (2015) assert that CRM implementation should prioritize customer retention and profit maximization. A well-executed CRM strategy not only improves profitability but also provides a competitive advantage by enhancing customer engagement.
E-CRM functions as an information system that tracks customer interactions, allowing businesses to access critical customer data, including past purchases, service records, and unresolved issues. By centralizing this data, companies can align their sales, marketing, and customer service efforts, ensuring a seamless customer experience. Ultimately, E-CRM serves as a strategic tool for sustaining customer loyalty and driving long-term business success (Lee-Kelley, et al. 2003).
Research Methodology
The present research is an empirical study that follows a descriptive research design and is entirely based on primary data collected from online retail customers across various regions of India. A convenience sampling method was employed to select respondents, ensuring accessibility and ease of data collection. This approach enables a structured analysis of E-CRM’s impact on E-Loyalty while capturing consumer perceptions and experiences in the online retail sector.
A structured questionnaire containing 26 statements (21 for E-CRM variables and 5 for customer loyalty) was developed and administered to 160 online retail customers for the purpose of data collection. All items were measured using a five-point Likert Scale, where responses ranged from 1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree. Various items considered for the questionnaire were identified with the help of exhaustive literature review (Churchill and Surprenant, 1982; Morgan and Hunt, 1994; Ramaj and Ismaili, 2015; Lee-Kelley, Gilbert, and Mannicom, 2003; Gaurav, 2016).
For the purpose of data analysis, a multiple regression analysis (Ray, Patil, Bhatt, Randive and Gaurav, 2024) was employed to understand the impact of E-CRM on E-Loyalty. In the multiple regression model, various constructs of E-CRM i.e. trust, communication, technology, service quality and commitment were considered as independent variables whereas customer loyalty was considered as dependent variable. This study uses average scores of different items associated with various constructs of E-CRM and E-Loyalty in order to estimate E-CRM and E-Loyalty for employing the multiple regression analysis.
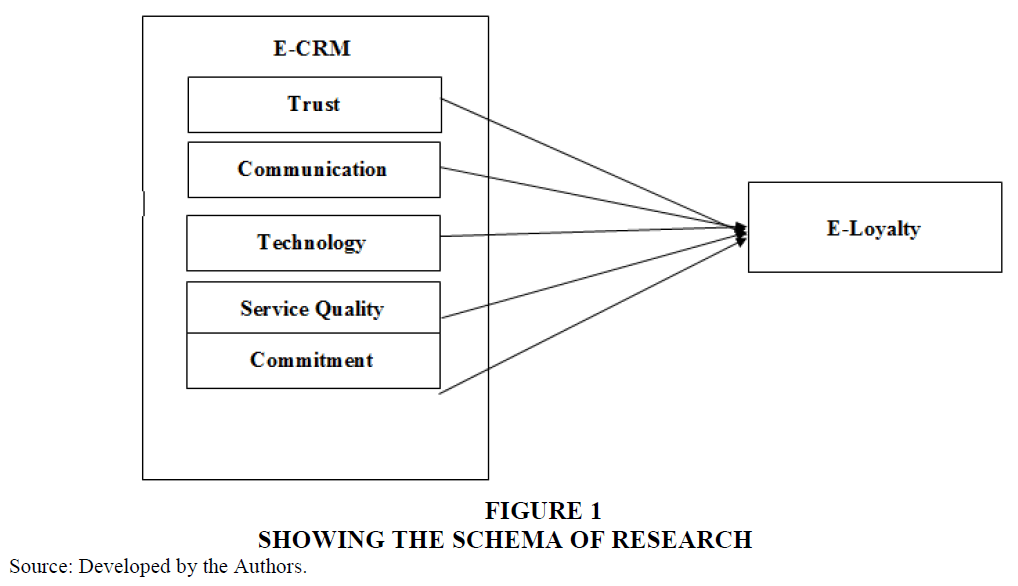
Schema of Research
The present research study relies upon the following schema of research (Figure 1) in order to employ multiple regression analysis in order to understand the impact of E-CRM on E-Loyalty in online retailing within the Indian setting.
Data Analysis
Multiple Regression Analysis (MRA) is a statistical method used to examine the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables (Gaurav and Ray, 2020). This technique is particularly useful for quantifying the combined impact of multiple influencing factors on a single dependent variable. In this study, MRA has been utilized to assess the effect of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) on Electronic Loyalty (E-Loyalty) in the context of online retailing, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of how various E-CRM constructs collectively contribute to customer loyalty.
The following multiple regression equation is developed in order to examine the impact of influence of electronic customer relationship management (E-CRM) on electronic loyalty (E-Loyalty).
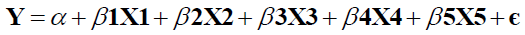
Where,
Y represents electronic loyalty the α coefficient represents the intercept;
X1 , X2 , X3 , X4 and X5 represents different constructs of electronic customer relationship management viz. trust, communication, technology, service quality and commitment;
β1, β2, β3,β4 and β5 denotes strength of different constructs of electronic customer relationship management viz. trust, communication, technology, service quality and commitment; and
Є represents the error term.
On the basis of data analysis, the overall multiple regression model was found to be significant (F = 54.521, p<0.0) at 5% level of significance. This implies that all the independent variables (constructs of E-CRM) considered in this multiple regression model are significant in determining dependent variable i.e. E-Loyalty.
The model’s coefficient of determination (R²) is 0.639, while the Adjusted R² is 0.627, indicating a strong explanatory power. The R² value, when multiplied by 100, suggests that 63.9% of the variance in the dependent variable (E-Loyalty) is accounted for by the independent variables (E-CRM constructs: Trust, Communication, Technology, Service Quality, and Commitment). However, to adjust for potential errors and overfitting, the Adjusted R² value of 0.627 is considered a more reliable measure, implying that the joint effect of E-CRM elements explains 62.7% of the variance in E-Loyalty (Table 1).
| Table 1 Model Summary | ||||||||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | Durbin- Watson | ||||
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | ||||||
| 1 | .799a | .639 | .627 | .39088 | .639 | 54.521 | 5 | 154 | .000 | 1.792 |
b. Dependent Variable: e-loyalty
Source: Developed by the Authors.
This result indicates that electronic customer relationship management plays a significant role in shaping electronic loyalty among online retail customers. However, the remaining 37.3% of the variance in E-Loyalty is attributed to other factors not included in this model, such as pricing strategies, brand perception, external competition, and personal customer experiences. Future studies could explore additional factors that contribute to e-loyalty beyond E-CRM.
The overall F-test for model significance further confirms the appropriateness of the regression model, reinforcing that the selected E-CRM constructs have a statistically significant impact on customer loyalty in online retailing.
On the basis of the result of multiple regression analysis, multiple regression model can be written as follows;
Electronic Loyalty = 3.494 + (0.135) Trust + (0.076) Communication + (0.338) Technology + (0.352) Service Quality + (0.20) Commitment
As per the Table 2, the intercept (B = 3.494, p = 0.000) is highly significant, indicating that when all E-CRM constructs are at zero, the baseline value of E-Loyalty is 3.494. The beta coefficient is measured in ‘standard deviation’ units, and is a measure of how robustly the independent variable influences the dependent variable. The multiple regression analysis results indicate that Service Quality (β=0.352,p=0.000) and Technology (β=0.338,p=0.000) are the most significant predictors of E-Loyalty, demonstrating their crucial role in fostering customer retention in online retailing. Trust (β=0.135,p=0.000) and Communication (β=0.076,p=0.016) also have a positive and statistically significant impact on E-Loyalty, though their influence is relatively lower. The Commitment construct (β=0.020,p=0.513) was found to be statistically insignificant, indicating that it does not meaningfully contribute to electronic loyalty.
| Table 2 Regression Coefficients | |||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95.0% Confidence Interval for B | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| (Constant) | 3.494 | .031 | 113.082 | .000 | 3.433 | 3.555 | |
| Trust | .135 | .031 | .211 | 4.349 | .000 | .074 | .196 |
| Communication | .076 | .031 | .118 | 2.444 | .016 | .015 | .137 |
| Technology | .338 | .031 | .527 | 10.893 | .000 | .276 | .399 |
| Service quality | .352 | .031 | .549 | 11.342 | .000 | .290 | .413 |
| Commitment | .020 | .031 | .032 | .656 | .513 | -.041 | .082 |
Source: Developed by the Authors.
Conclusion
The findings of this research study highlight the significant impact of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) constructs on Electronic Loyalty (E-Loyalty) in online retailing. Among the five E-CRM elements examined, Service Quality emerged as the most influential factor, followed by Technology, Trust, and Communication, all of which showed a statistically significant positive relationship with customer loyalty. This indicates that online retailers who prioritize high-quality customer service, user-friendly and reliable technology, and transparent communication are more likely to enhance customer retention and long-term engagement. However, Commitment was found to have an insignificant impact on E-Loyalty, suggesting that it may not be a key driver of customer retention in the online retail sector. The multiple regression model, with an Adjusted R² of 0.627, demonstrates that E-CRM constructs explain 62.7% of the variance in E-Loyalty, reinforcing the critical role of relationship management strategies in fostering loyalty. The remaining 37.3% variance suggests the presence of other influencing factors, such as pricing strategies, brand reputation, and external competition, which future research could explore. Based on these insights, online retailers should focus on enhancing Service Quality, Technology, Trust, and Communication to strengthen customer relationships and improve E-Loyalty, while reconsidering the emphasis placed on Commitment in their CRM strategies.
Limitations and Future Directions
While this study provides valuable insights into the impact of Electronic Customer Relationship Management (E-CRM) constructs on Electronic Loyalty (E-Loyalty) in online retailing, certain limitations must be acknowledged. First, the study is based on primary data collected from 160 respondents, which may not fully represent the broader population of online shoppers. A larger and more diverse sample size across different demographics and geographic locations would enhance the generalizability of the findings.
Second, the study focuses on five key E-CRM constructs - Trust, Communication, Technology, Service Quality, and Commitment - as independent variables. However, other potential factors, such as pricing strategies, promotional offers, user experience design, social media engagement, and brand perception, may also influence customer loyalty. Future research should consider incorporating these additional elements to provide a more comprehensive model of E-Loyalty determinants.
Third, this study employs cross-sectional data, capturing customer perceptions at a single point in time. However, consumer behavior and loyalty are dynamic and may evolve over time due to market trends, technological advancements, and changing customer expectations. Longitudinal studies could be conducted to observe how E-CRM practices impact customer loyalty over an extended period.
Finally, this research is limited to the online retail sector, and the results may not be directly applicable to other industries such as banking, hospitality, or healthcare, where customer relationship management operates differently. Future studies could explore sector-specific variations in E-CRM effectiveness to gain industry-specific insights.
Despite these limitations, this study lays a strong foundation for understanding the role of E-CRM in fostering customer loyalty and provides practical recommendations for online retailers. Future research can build upon these findings to develop more holistic models, industry-specific strategies, and longitudinal insights into customer loyalty in the digital era.
References
Abbott, J. (2001). Data data everywhere – and not a byte of use? Qualitative Market Research, 4(3), 182-192.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ball, D. (2004). The role of communication and trust in explaining customer loyalty: An extension to the ECSI model. European Journal of Marketing, 38(9/10), 1272-1293.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Bull, C. (2003). Strategic issues in customer relationship management (CRM) implementation. Business Process Management Journal, 9(5), 592-602.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Chen, J.-S., & Ching, R. (2006). The study of mobile customer relationship management and loyalty. 2006 International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, 67-72.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Churchill, G. A., & Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research, 19(4), 491-504.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Feinberg, R., & Kadam, R. (2002). E-CRM web service attributes as determinants of customer satisfaction with retail web sites. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 13(5), 432-451.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gaurav, K. (2008). Impact of relationship marketing strategy on customer loyalty. The Icfaian Journal of Management Research, 7(11), 7-21.
Gaurav, K. (2016). Impact of relationship marketing on customer loyalty: Evidence from the Indian automobile industry. Purusharta, 9(1), 1-17.
Gaurav, K., & Khan, K. (2013). Impact of relationship marketing and perceived service quality on customer loyalty: An agenda for inquiry. The International Journal of Management, 2(3), 46-52.
Gaurav, K., & Ray, A. S. (2022). Impact of social media advertising on consumer buying behavior in Indian E-commerce industry. Sumedha Journal of Management, 9(1), 41–51.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Gaurav, K., Mahato, M., Raut, N., & Patil, A. (2025). Exploring internet trends: An empirical study of usage patterns among Indian millennials. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Computing and Expert Technology. Taylor & Francis.
Gaurav, K., Nerlekar, V. S., Srinivas, K., & Ray, A. S. (2024). Impact of customer relationship management (CRM) on customer loyalty in Indian organized retailing – An agenda for inquiry. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(2), 1-11.
Khalafinezhad, R., & Sang Long, C. (2013). Customer satisfaction and loyalty: A review in the perspective of CRM. Jurnal Teknologi, 64.
Kimiloglu, H., & Zarali, H. (2009). What signifies success in e-CRM? Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 27(2), 246-267.
Lee-Kelley, L., Gilbert, D., & Mannicom, R. (2003). How e-CRM can enhance customer loyalty. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 21(2), 239-248.
Lindgreen, A. (2001). A framework for studying relationship marketing dyads. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal, 4(2), 75-87.
Morgan, R. M., & Hunt, S. D. (1994). The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. Journal of Marketing, 58(3), 20-38.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Nguyen, T. H., Sherif, J. S., & Newby, M. (2007). Strategies for successful CRM implementation. Information Management & Computer Security, 15(2), 102-115.
Ramaj, A., & Ismaili, R. (2015). Customer relationship management, customer satisfaction, and loyalty. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 4(3) 594-599.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Ray, A. S., Patil, A., Bhatt, A., Randive, K., & Gaurav, K. (2024). Analysing the influence of service quality on customer experience in the life insurance industry: A quantitative study. Journal of Informatics Education and Research, 4(3), 49–60.
Reichheld, F., & Sasser Jr, W. (1990). Zero defections: Quality comes to services. Harvard Business Review, 68(5), 105-111.
Usman, U., Usman, Z., Jalal, A., & Alhaji Musa, M. (2012). The impact of electronic customer relationship management on consumer’s behavior. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, 3(1), 500-504.
Received: 25-Feb-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15715; Editor assigned: 26-Feb-2025, PreQC No. AMSJ-25-15715(PQ); Reviewed: 02- Mar-2025, QC No. AMSJ-25-15715; Revised: 10-Mar-2025, Manuscript No. AMSJ-25-15715(R); Published: 13-Mar-2025