Research Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 5
Impact of Digital Marketing on Online Consumer Buying Behaviour in the Post Covid -19 Period
Uttera Choudhary, Amity University, Mohali, Punjab
Neeraj, Geeta University, Panipat
Citation Information: Choudhary, U., & Neeraj. (2024). Impact of digital marketing on online consumer buying behaviour in the post covid -19 period. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(5), 1-10.
Abstract
Internet performs very significant functions in today’s digital age and it is accessed by a large number of people, business entities and service companies for diverse purposes. A very important element of internet is the digital marketing. Digital marketing focusses on formulating and implementing the marketing strategies of a business firm by utilising digital media channels. Digital marketing includes online Shopping, wherein the customers immediately purchase the goods and services at any time from any place and with wide options available in the shortest period. The past few years have experienced a very significant transition in the modern business world because of the Covid-19 pandemic. The Covid -19 virus caused many uncertainties for consumers as well as marketers, which led to behavioural changes like working remotely, spending a lot of time indoors, avoiding crowded areas, increasing social media engagement, shifting towards online content, etc. and all of these had an immense impact on the buying pattern of the consumers. Due to increased online engagement of the people business firms can utilise digital platforms for attracting and retaining consumers by putting digital marketing tactics into practice. The main goal of this research study is to investigate the impact of digital marketing on the online buying behaviour of consumers post Covid-19 period using the Exploratory Factor Analysis Approach. For this purpose, a self-administered questionnaire was prepared and circulated among 150 respondents who were college students. The responses received were analysed by applying Exploratory factor analysis and multiple regression analysis in IBM SPSS.
The results of exploratory factor analysis have suggested five important digital marketing factors, which play a very significant role in influencing the buying behaviour of consumers. The impact of those factors was further studied by utilising multiple regression analysis, which shows 81% of the total variance in buying behaviour is explained by the derived factors and the rest is because of other factors which are not part of this research study.
Keywords
Consumer Buying Behaviour, Covid-19, Digital marketing, Pandemic.
Introduction
Consumer buying Behaviour
Consumer buying behaviour refers to the actions and decisions made by individuals or households when purchasing goods or services for personal consumption. It encompasses a range of factors such as the customer's needs and preferences, the influence of external factors such as marketing and advertising, and the customer's past experiences with the product or brand. Consumer buying behaviour is the practice adopted when individuals, groups or firms select, use or dispose of the product, services and experiences to cater to their needs and requirements” (Judge,1993); Khan et al. (2021).
Blackwell (2001) suggested that consumer buying behaviour entails a series of activities undertaken by an individual in the procedure of acquiring and using products and services. The researcher further stated that perception, attitude, awareness and learning are the main components of consumer buying behaviour of users throughout the purchase of products and services. The study of buying behaviour is a lengthy process, it entails selection, and evaluation by exploring all the requisite information about the product. It is only after the analysis of the product that the decision to purchase is made. Overall, understanding consumer buying behaviour is critical for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies and increase their sales and profits.
Covid -19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 outbreak has abruptly disrupted the global political and economic order significantly impacting consumer services sectors such as retailing, hospitality, and tourism (Pantano et al., 2020); Zhao et al. (2020). The pandemic has resulted in unprecedentedly large-scale lockdowns across the world (Kuckertz et al., 2020), severely restricting people’s daily activities. As a result, more consumer services companies are experimenting with new technologies and platforms to meet the changing consumer demands, leading to new consumption patterns. To cope with the restrictions, some consumer services companies have developed alternative business models, such as “contactless delivery” and “social cinema.
Factors that affect changes in purchase behaviour include social factors, cultural factors, demographic factors, and situational factors (Cici and Bilginer Özsaatci, 2021). Therefore, the COVID-19 pandemic as a social factor is also affecting different changes in purchase behaviour. Scholars generally believe that a large number of consumers showed panic buying behaviour or impulsive buying behaviour in the early stage of the COVID-19 pandemic, and even accompanied by compulsive buying behaviour. While purchase behaviour in the middle of the COVID-19 pandemic is characterized by mobility. The application of digital technology has created favourable conditions for consumers to participate in online shopping, and consumers’ online purchase activities have increased significantly (Jiang and Stylos, 2021). However, the changes in purchase behaviour in the above literature focus on changes in a single dimension, and do not systematically sort out the changes in consumer purchase behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Therefore, according to the basic theory of marketing, this study systematically sorts out the multiple dimensions of changes in consumer purchase behaviour under the COVID-19 pandemic, and improves the items of the purchase behaviour changes in each dimension, to provide supplements for the theory of consumer behaviour.
Review of Literature
In recent years, digital marketing has emerged as an important tool for businesses to reach their target audience. With the growth of social media and e-commerce websites and other digital platforms, many businesses are using digital marketing to target their potential customers. One of the key benefits of digital marketing is that it allows businesses to reach consumers cost-effectively and efficiently. This literature review examines the impact of digital marketing on the buying behaviour of consumers post covid-19 period.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted consumer behaviour, with many consumers shifting their shopping habits online due to safety concerns and social distancing measures.
As a result, the use of digital marketing has become even more important for businesses to reach their target audiences. Here is a review of some recent literature on the impact of digital marketing on consumer buying behaviour post-COVID-19.
The research study by Dash & Chakraborty (2021) found that the use of digital marketing channels such as social media, email marketing, and search engine marketing had a significant positive impact on consumer behaviour during the pandemic. They also found that the use of digital marketing increased the likelihood of consumers making online purchases. Another study found that the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital marketing and e-commerce, with consumers increasingly relying on digital channels for information and purchases. They also found that the use of digital marketing strategies such as personalization, social media marketing, and influencer marketing had a significant impact on consumer behaviour.
A study analysed the impact of social media marketing on consumer behaviour during the pandemic. The study found that social media marketing had a significant positive impact on consumer behaviour, especially for products that consumers were not familiar with. The study also found that the use of social media influencers had a significant impact on consumer behaviour with consumers more likely to make purchases based on influencer recommendations.
The research study examined the impact of digital marketing on consumer behaviour in the fashion industry during the pandemic. They found that digital marketing strategies such as social media marketing, search engine optimization, and email marketing had a positive impact on consumer behaviour, with consumers increasingly relying on digital channels for product information and purchases. Another research study examined the impact of digital marketing on consumer behaviour in the food and beverage industry during the pandemic. They found that digital marketing strategies such as social media marketing, mobile marketing, and email marketing had a positive impact on consumer behaviour, with consumers increasingly relying on digital channels for information and purchases.
Another research study undertaken examined the impact of online reviews on consumer behaviour during the pandemic. The study found that online reviews had a significant positive impact on consumer behaviour, with consumers more likely to make purchases based on positive online reviews. The study also found that the perceived trustworthiness of online reviews had a significant impact on consumer behaviour. Various other research studies also supported the fact that there is a strong influence of digital marketing strategies on the buying decisions of consumers specifically post Covid-19 period which includes a research study by Niazi and Hussain (2021).
Overall, these studies suggest that the use of digital marketing channels has become even more important for businesses in the post-COVID-19 era, with consumers increasingly relying on digital channels for product information and purchases. The use of digital marketing strategies such as social media marketing, personalization, and influencer marketing can have a significant impact on consumer behaviour and help businesses increase their sales and profits. However, businesses must be careful not to overuse digital marketing channels and to maintain the trust of their target audience. Future research should continue to explore the impact of digital marketing on consumers and identify best practices for businesses to effectively target this important consumer segment.
Research Methodology
Research Objective
To study the impact of digital marketing on online consumer buying behaviour post-Covid-19.
Hypothesis Formulation
H0: The independent variables (X1, X2, X3, X4 X5) do not have a significant influence on the dependent variable (Y).
Ha: The independent variables (X1, X2, X3, X4, X5) do have a significant influence on the dependent variable (Y).
1. Determining the degree of confidence of 95% (α = 0.05)
2. Determine the significance - The value of significance (p-value) <0.05 then H0 is rejected and Ha accepted. If the value of significance (p-value)> 0.05 then H0 is accepted and Ha is rejected.
Making Inferences/Conclusion
When (p-value) <0.05 then H0 is rejected and Ha is accepted. This means that the independent variable affects the dependent variable. –
When (p-value)> 0.05 then H0 is accepted and Ha is rejected. This means that the independent variables do not affect the dependent variable.
Sample and Data Collection
A self-administered questionnaire was framed for collecting the primary data for the present research study. A total of 29 survey items were there which were framed based on a detailed literature review from past studies in the relevant field. The research instrument comprised statements that aim to identify the factors which influence the online buying behaviour of consumers. A Five-point Likert scale was utilised to gather the responses, where “1 stands for strongly disagree 2 for disagree, 3 for neutral, 4 for agree and 5 stands for strongly agree”. The total number of respondents for the present study was 150 respondents. A convenience sampling technique was used to collect the data.
Research Tools Used
In the present study firstly, Exploratory Factor Analysis was used to explore the various factors that influence the buying behaviour of consumers online. Further, Multiple Regression Analysis was used to study the impact of those derived factors on buying behaviour of the consumers.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Reliability Analysis
The objective behind conducting the reliability analysis is to check the internal consistency of scales. The value of Cronbach’s Alpha of this study was .927 (Table 1) of 29 statements. The minimum acceptable value to check the reliability of data should be more than 0.6. (Mohd Salleh Abu and ZaidatunTasir 2001).
| Table 1 Reliability Statistics | |
| Cronbach's Alpha | No of Items |
| 0.927 | 29 |
So, the reliability analysis of this study shows that there is a good consistency of scale. In this research study value of Cronbach’s alpha of different variables like consumer buying behaviour (CBB) was 0.815, product information (PI) .910, feedback (FE) .699, brand image (BI) .826, convenience (CO) .837 and social factors (SF) .659 were within the acceptable limit.
Factor Analysis
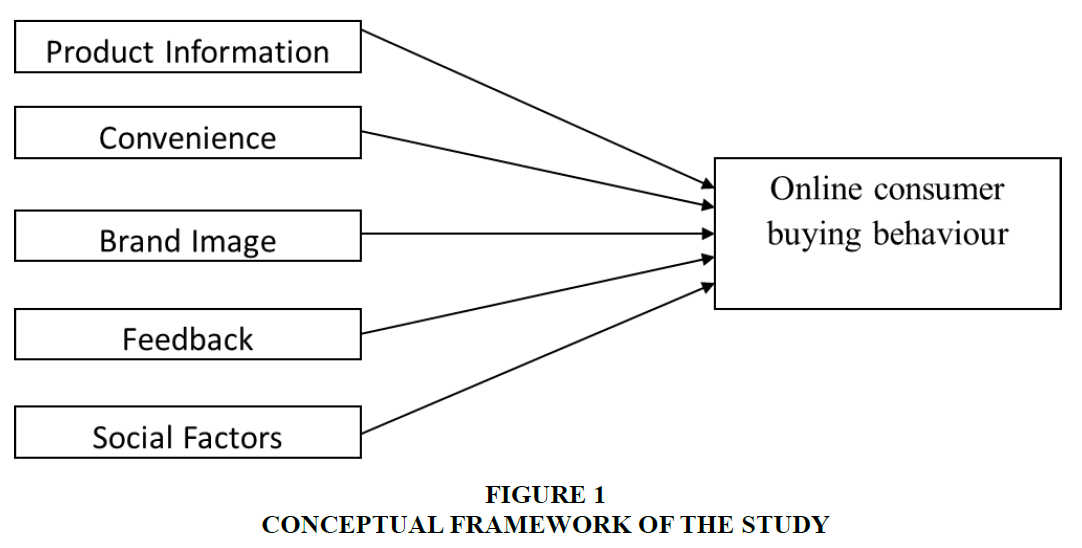
Factor analysis is a technique used for the reduction and summarization of data by recognizing the latent variables. To find out the different digital media-based factors, which influence online consumer buying behaviour post-covid-19, exploratory factor analysis was executed by the technique of dimension reduction in SPSS. The Value of KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin) which is the measure of the adequacy of the sample was .711 shown in (Table 2) and it shows that factor analysis results were significant as it is above the recommended value. Values between (0.5-1.0) indicate that the results of factor analysis were significant (Coakes & Ong 2011). Two items, which showed low factor loadings of less than 0.50, were removed and factor analysis was executed again. The results of factor analysis Table 3 extracted five factors, which together explained 65% of the variance. Extracted factors were labelled as product information, convenience, brand image, feedback and social factors. In the current research Bartlett’s test of sphericity is also found to be significant Tables 4-7.
| Table 2 Reliability Statistics of Constructs | ||
| Constructs | No. of items | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| Product Information | 12 | .910 |
| Convenience | 5 | .837 |
| Brand Image | 5 | .826 |
| Feedback | 4 | .699 |
| Social Factors | 3 | .659 |
| Table 3 KMO and Bartlett's Test | ||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.711 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 3181.827 |
| df | 351 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Table 4 Total Variance Explained | |||||||||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 10.163 | 37.642 | 37.642 | 10.163 | 37.642 | 37.642 | 5.525 | 20.462 | 20.462 |
| 2 | 2.376 | 8.801 | 46.443 | 2.376 | 8.801 | 46.443 | 3.640 | 13.482 | 33.944 |
| 3 | 2.097 | 7.765 | 54.208 | 2.097 | 7.765 | 54.208 | 3.147 | 11.655 | 45.599 |
| 4 | 1.657 | 6.138 | 60.346 | 1.657 | 6.138 | 60.346 | 2.922 | 10.822 | 56.421 |
| 5 | 1.417 | 5.249 | 65.595 | 1.417 | 5.249 | 65.595 | 2.477 | 9.174 | 65.595 |
| 6 | 1.271 | 4.707 | 70.302 | ||||||
| 7 | .984 | 3.645 | 73.947 | ||||||
| 8 | .880 | 3.257 | 77.204 | ||||||
| 9 | .822 | 3.045 | 80.249 | ||||||
| 10 | .741 | 2.745 | 82.994 | ||||||
| 11 | .671 | 2.484 | 85.478 | ||||||
| 12 | .572 | 2.118 | 87.597 | ||||||
| 13 | .539 | 1.998 | 89.595 | ||||||
| 14 | .455 | 1.684 | 91.279 | ||||||
| 15 | .423 | 1.567 | 92.847 | ||||||
| 16 | .371 | 1.374 | 94.221 | ||||||
| 17 | .275 | 1.020 | 95.240 | ||||||
| 18 | .241 | .892 | 96.132 | ||||||
| 19 | .211 | .782 | 96.914 | ||||||
| 20 | .191 | .708 | 97.622 | ||||||
| 21 | .161 | .595 | 98.218 | ||||||
| 22 | .133 | .492 | 98.710 | ||||||
| 23 | .109 | .404 | 99.114 | ||||||
| 24 | .094 | .347 | 99.461 | ||||||
| 25 | .064 | .239 | 99.700 | ||||||
| 26 | .047 | .174 | 99.874 | ||||||
| 27 | .034 | .126 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | |||||||||
| Table 5 Factor Loadings of the Items in EFA | ||
| Constructs | Items Code | Factor Loading |
| Product Information (PI) | PI1 | 0.570 |
| PI2 | 0.789 | |
| PI3 | 0.613 | |
| PI4 | 0.502 | |
| PI5 | 0.801 | |
| PI6 | 0.546 | |
| PI7 | 0.515 | |
| PI8 | 0.733 | |
| PI9 | 0.611 | |
| PI10 | 0.647 | |
| PI11 | 0.66 | |
| PI12 | 0.774 | |
| Convenience (CO) | CO1 | 0.562 |
| CO2 | 0.799 | |
| CO3 | 0.800 | |
| CO4 | 0.710 | |
| CO5 | 0.536 | |
| Brand Image (BI) | BI1 | 0.870 |
| BI2 | 0.737 | |
| BI3 | 0.711 | |
| BI4 | 0.734 | |
| Social Factors (SF) | SF1 | 0.536 |
| SF2 | 0.546 | |
| SF3 | 0.605 | |
| Feedback (FE) | FE1 | 0.587 |
| FE2 | 0.674 | |
| FE3 | 0.679 | |
| Table 6 Model Summary | ||||
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. The error in the Estimate |
| 1 | .908a | .824 | .818 | .23861 |
| a. Predictors: (Constant), Product information, convenience, brand image, feedback, social factors | ||||
| Table 7 Anovaa | ||||||
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 38.2 | 5 | 7.64 | 134.189 | .000b |
| Residual | 8.142 | 143 | 0.057 | |||
| Total | 46.342 | 148 | ||||
Regression Analysis
The present study has utilised multiple regression analysis to measure the impact of various digital media-based factors on online consumer buying behaviour. In research where there are two or more independent variables are studied to have an impact on one or more dependent variables multiple regression analysis is used.
Here consumer buying behaviour was taken as the dependent variable(y) and product information (X1), convenience (X2), brand image (X3), feedback (X4), and social factors(X5) were the independent variables. The main aim of the study was to examine the impact level of various independent variables on the dependent variable i.e., online consumer buying behaviour.
In this model, the dependent variable Y was the consumer buying behaviour whereas independent variables were X1, X2, X3, X4, and X5 which were product information, convenience, brand image, feedback and social factors respectively. So, the estimated regression model is as follows
Y = β0 + β1 X1 + β2 X2 + β3 X3 + β4 X4 + β5 X5
Y (Consumer buying behaviour) =X1(product information) +X2(convenience) +X3(brand image) +X4(feedback) + X5(social factors)
According to model summary Table 8 which describes the criteria for the correlation between independent variables and dependent variable, it can be understood that independent variables have a high correlation with the decision for 82.4% and from the coefficient of determination that is the square of the correlation coefficient (R2) is equal to 0.818 which indicates 81.8% of the variation that occurs in the consumer buying behaviour is described by all of the independent variables which were product information, convenience, brand image, feedback and social factors respectively. From the analysis Table 9, it was observed that the results of all 5 independent variables were significant as their P value was less than 0.05.
| Table 8 Coefficients | |||||||
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||||
| 1 | (Constant) | .218 | .138 | 1.578 | .117 | ||
| Product Information | .434 | .044 | .502 | 9.852 | .000 | ||
| Convenience | .106 | .036 | .147 | 2.969 | .004 | ||
| Brand Image | .225 | .040 | .336 | 5.651 | .000 | ||
| Feedback | .176 | .032 | .216 | 5.473 | .000 | ||
| Social factors | .238 | .046 | .282 | 5.157 | .000 | ||
| a. Dependent Variable: consumer buying behaviour | |||||||
| Table 9 Results of the Study | ||
| Variables | P value | Results |
| Product information | .000 | Significant |
| Convenience | .004 | Significant |
| Brand Image | .000 | Significant |
| Feedback | .000 | Significant |
| Social factors | .000 | Significant |
The results of the regression analysis provide that there is a significant impact of digital marketing on online consumer buying behaviour. So, the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative hypothesis is accepted, and it is concluded that at a 5% level of significance, R square is statistically significant. The final regression equation of this study is as follows: -
Y=.218+ .434(X1) + .106(X2) + .225(X3) + .176(X4) + .238(X5)
Therefore, it was derived that there is a strong positive impact of different digital marketing factors on online consumer buying behaviour post covid -19 Figure 1.
Results and Discussion
a) The product information (X1) variable has a P value (.000). This result shows that the regression coefficient of this variable is significant. The information available about the product and services being offered by a brand is one of the main determinants which has a strong positive influence on consumer buying behaviour. In the era of digitalisation digital media platforms are the most reliable and effective mode of circulating relevant information about the different products and services and persuading the consumer to purchase your product and services.
b) The convenience (X2) variable has a P value (.004). This result shows that the regression coefficient of this variable is significant. Convenience in getting a product or a service is a very significant factor which guides the decision-making process of the consumer. Easy accessibility of products in the online world makes it convenient for consumers to make a purchase decision. Digital platforms provide the convenience of time, place and effort.
c) The brand image (X3) has a P value (.000). This result shows that the regression coefficient of this variable is also significant. The brand image comprises the online image of the brand in the minds of the consumers, which includes impression, awareness, opinion, or consciousness about a product or company, and it is highly influenced by digital marketing. A positive brand image plays a significant role in persuading a consumer to buy a product or service.
d) The feedback (X4) variable has a P value (.000). This result shows that the regression coefficient of this variable is also significant. A consumer always makes a buying decision of whether to buy or not to buy the product after analysing all the information regarding the product. Digital platforms provide the opportunity for consumers to have an insight into the reviews, comments, tweets and opinions posted by the consumers and can make their purchase decisions accordingly.
e) The social factor X5 (.000) has P value. This result shows that the regression coefficient of this variable is also significant. The findings of this study reveal that a consumer’s buying decision is highly influenced by his/her social groups on digital platforms. Consumers can utilise the suggestions, referrals and opinions of their social groups in the digital world before making a final purchase decision.
Several debates are happening to discuss the relevance of digital media marketing in the domain of marketing specifically after the covid-19. The business world has seen a lot of transitions after the covid-19 pandemic which summed up that digital marketing is the future and it is going to stay for a very long period. The outcomes of the present research study are in parallel with the existing research studies of Song, (2001), and Suginraj, (2017) who believed that digital marketing has an impact on the purchase decisions of consumers. The findings are further supported by some latest research studies and who strongly advocated that digital media marketing has a strong positive impact on consumer buying behaviour post covid-19.
So, it is concluded from the results that digital media marketing has a strong impact on buying behaviour of consumers.
Limitations and Scope of Future Research
Irrespective of these contributions, there can be additional contributions too as digital marketing and consumer buying behaviour both are very vast fields and there is an increase in the number of people, who are utilising digital platforms after covid 19. The primary limitation of this research was the limited number of dependent and independent variables. As it was unable to cover the entire range of factors of digital media which can have a very strong impact on online consumer buying behaviour. Future researchers should try to discover more possible significant factors. Another limitation could be the sample size of the study although it was adequate for the statistical investigations it can be increased to have more generalise results, as there are millions of digital media users. The period available for the research was also one of the main constraints and this is the reason an in-depth study of variables could not take place.
Conclusion
The findings of this study provide an overview of the different factors, which have an impact on consumer buying behaviour. The results of factor analysis and regression analysis provide a framework to understand what impact digital marketing has on the online buying decision of consumers specifically post Covid-19. The impact can be studied by analysing the different factors which are derived in the current research study. The findings of the study provide us with various factors, which have a strong positive impact on buying behaviour of consumers. The factors so derived can be summed up as product information, convenience, brand image, feedback and social factors. The outcomes of this study can be helpful for marketers who are trying to understand the decision-making process of consumers. It will provide them with a base to formulate and implement their marketing strategies in a way so that they can have a hold on the needs and preferences of their consumers because it is essential to understand the needs and preferences of consumers first then only their buying behaviour can be studied. In this study, the hypothesis that digital marketing has an impact on online consumer buying behaviour post-covid-19 is accepted, as the results were significant.
References
Blackwell Roger, D., Miniard Paul, W., & Engel James, F. (2001). Consumer behaviour. Thomson. South Western.
CICI, E. N., & ÖZSAATCI, F.G.B. (2021). The impact of crisis perception on consumer purchasing behaviours during the COVID-19 (coronavirus) period: research on consumers in Turkey. Eskisehir Osmangazi Üniversitesi Iktisadi ve Idari Bilimler Dergisi, 16(3), 727-754.
Coakes, S. J., & Ong, C. (2011). SPSS version 18.0 for windows (version 18.0). Australia: John Wiley and Sons.
Dash, G., & Chakraborty, D. (2021). Digital transformation of marketing strategies during a pandemic: Evidence from an emerging economy during COVID-19. Sustainability, 13(12), 6735.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Jiang, Y., & Stylos, N. (2021). Triggers of consumers’ enhanced digital engagement and the role of digital technologies in transforming the retail ecosystem during COVID-19 pandemic. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 172, 121029.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Judge, K., & Solomon, M. (1993). Public opinion and the National Health Service: patterns and perspectives in consumer satisfaction. Journal of Social Policy, 22(3), 299-327.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Khan, K. I., Niazi, A., Nasir, A., Hussain, M., & Khan, M. I. (2021). The effect of COVID-19 on the hospitality industry: The implication for open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), 30.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kuckertz, A., Brändle, L., Gaudig, A., Hinderer, S., Reyes, C. A. M., Prochotta, A., & Berger, E.S. (2020). Startups in times of crisis–A rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Business Venturing Insights, 13, e00169.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Pantano, E., Pizzi, G., Scarpi, D., & Dennis, C. (2020). Competing during a pandemic? Retailers’ ups and downs during the COVID-19 outbreak. Journal of Business Research, 116, 209-213.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Zhao, S., Lin, Q., Ran, J., Musa, S. S., Yang, G., Wang, W., & Wang, M. H. (2020). Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. International journal of infectious diseases, 92, 214-217.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Received: 30-Jan-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14377; Editor assigned: 31-Jan-2024, PreQC No. AMSJ-24-14377(PQ); Reviewed: 30- Mar-2024, QC No. AMSJ-24-14377; Revised: 29-Jun-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-24-14377(R); Published: 09-Jul-2024