Research Article: 2020 Vol: 19 Issue: 2
Guidelines for Developing the Desirable Competencies of Operational Labors in the Petrochemical Industry
Obrom Aranyapruk, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Sakrapee
Worawattanaparinya, King Mongkut’s University of Technology
Abstract
Aim: This research aims at investigating guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in petrochemical industry.
Methodology: The study has been designed as a mixed method by developing the analysis of structural equation model through qualitative data and the quantitative data were derived from the survey of 500 managers in petrochemical industry.
Finding: The results revealed that: 1) the guidelines to develop competencies consist of 4 variables, i.e. knowledge management, characteristics of professional labors, resource based management, and teamwork. The managers from plastic industries and those from injection molding and packaging industries gave the important on the guidelines at high level with 3.77 and 3.74 respectively. When considering on each variable, it was found that every variable was rated at high level. 2) The development of the SEM Model passed the criteria and congruent with the empirical data with the Chi-Square Probability level of 0.081, Relative Chi-Square was 1.204, the goodness of fit index of 0.970 and root mean square error of approximation of 0.020. And 3) the hypothesis test showed that the resource based management variable had direct influence on knowledge management with the factor loading of 0.96. The resource based management variable had direct influence on teamwork with the factor loading of 0.83. The knowledge management variable had direct influence on characteristics of professional labors with the factor loading of 0.75. The teamwork variable had direct influence on characteristics of professional labors with the factor loading of 0.30. The statistically significant level was 0.001
Conclusion: The guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry consist of 4 variables which all are important for developing competencies of both plastic industries and injection molding and packaging industries. The factor is ranked according to their important levels referred to as Likert scale as follows: knowledge management, characteristics of professional labors, resource based management and teamwork respectively. Both types of industries gave the most important factor on teamwork variable in order to be a guideline for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry. The evaluation of the SEM Model showed passing the criteria of the model fitting with the empirical data. It was found that Chi-Square Probability Level was 0.081, Relative Chi-square was 1.204, Goodness of fit Index was 0.970 and Root Mean Square Error of approximation was 0.020.
Keywords
Petrochemical Industries, Desirable Competencies, Developing Labor Competencies, Structural Equation Modeling.
Introduction
The economic structure of Thailand consists of service industrial sector, agricultural sector, and industrial sector that can create high value added for the country. According to the report from the Office of National Economics and Social Development Council (NESDC) of 2016 the ratio of industrial production and GDP of the country was 28% of which petrochemical industries play the important part. Moreover, the report from Petroleum Institute of Thailand in 2017 revealed that the amount of petrochemical products was as high as 10.6 million tons per annum equal with the economic value of investment of 992,000 million baht creating income of 919,000 million baht or 8% of the country GDP. Furthermore, petrochemical industries lead to several other related industries using petrochemicals as their raw components (Piyachat, 2015). It can be seen that petrochemical industries are high potential industries, which can compete, with other global industries in the era of technological change and innovation. Thus, it can be predicted that the industrial sector will have high needs on professional labors to cope with the future change.
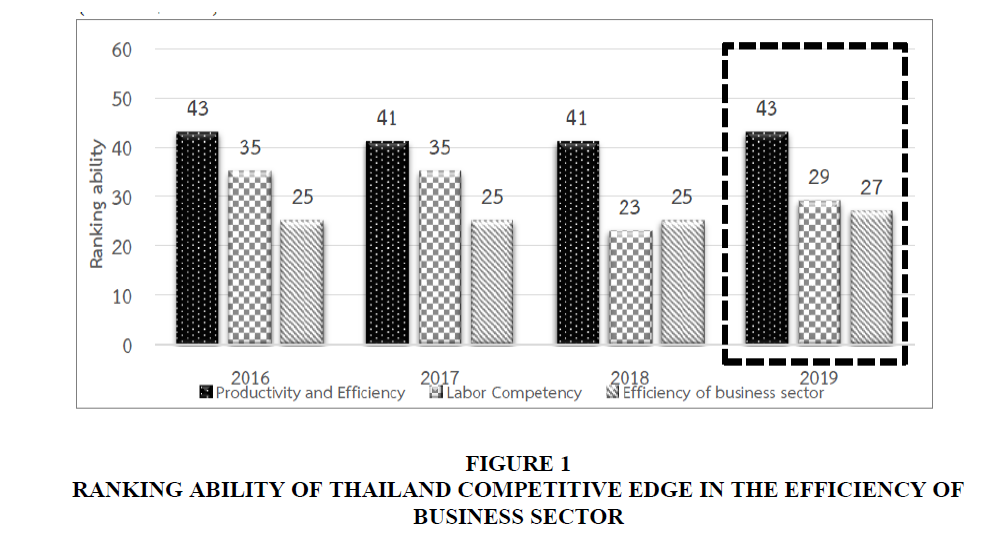
It is challenging to develop competencies of human resource particularly in petrochemical industries to meet the requirement of the industrial sector. The organization should be aware of the importance on developing labor competencies, which result in higher quality of the products (Thailand Management Association, 2016). At the same time, our country faces the problem on human resource competencies in several areas such as science, technology and innovation, foreign language including the ability on analysis and problem solving. These problems have the impact on the productivity issue and product quality together with high production cost which result in the decrease of competitive edge and sustainable development (Stefan & Craciuneanu, 2014) of the country. According to the Thailand Management Association (2019) together with IMD International Institute for Management Development, it was found that the growth rate of productivity and efficiency of the country was low with no positive developing trend. The results in 2017 showed that Thailand was ranked the 43rd and then the 41st in 2018 but was lower to the 43rd again in 2019 On the ranking of working skill competencies, it was found that in 2017 Thailand was ranked the 35th, with a better record in 2018 at the 23rd but in 2019 was the 29th When considering the overall of the country business efficiency, in 2018 the country was ranked the 25th and became the 27th in 2019 showing the problems on both productivity and the efficiency of the labor competencies affecting directly on the general efficiency of the country business as shown in Figure 1. In addition, based on the report by the Global Competitiveness Report World Economic Forum (2019), the knowledge index of Thai labors was in a low level.
Thus, the successful organization of industrial business sector must give the importance on human resource (Bagie?ska, 2015) because human resource can be developed to become higher quality, competencies, knowledge, skills, and characteristics required by the needs of industries (Pande & Joshi, 2013). That is to say the development of human resources in industrial business sector is very crucial (Sattabut, 2012).
From the information and problems mentioned above, the researcher was interested in studying guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry by investigating overall crucial variables affecting the development of labor competencies. This will result in successful in industrial business management and increase the competitive edge. The 4 important variables are knowledge management, characteristics of professional labors, resource based management and teamwork. The results of the study can be used as guidelines to develop the potential and increase the strength of the petrochemical industries of the country.
Knowledge Management
KM is the process of creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. Moten (2011) presented the research about the problems of insufficient operation skills of labors that directly affected the industrial products. The results showed that to be able to survive in new business era, knowledge management about human resource is the key strategy. The labors must understand their responsible jobs and be able to make decision when facing the operation problems. The trend of human resource in the future is the labor with higher professional skills and knowledge. According to the research by Kuo (2013) on the benefit and expectation influencing the knowledge sharing stated that reliance in workplace directly affected internal communication in the organization. Moreover, reliance in workplace had direct influence on knowledge sharing among the staffs of the organization. At the same time, Mendoza (2017) studied the evaluation of knowledge management efficiency in government sector revealing that knowledge management strategy has been used to drive the organization effectively creating higher productivity and competitive edge.
Characteristics of Professional Labors
The characteristics of professional labor must have a good attitude. Responsible, morality and ethics be honestly able to work well with a team. Pierre (2017) conducted a research on recruiting strategy for production personnel and found that the organization requires high skilled staffs. Thus, the recruiting strategy plays an important role on the first step of management in industrial business. Jackson (2016) presented the research on leadership core competencies in managing industrial business of medium and small industries for sustainable management. The results showed that the expertise in particular field leads to strategic decision and knowledge management and planning of knowledge management will result in sustainability. Effective communication and relationship among staffs including skills and characteristics of staffs are important variables in sustainable development of organization.
Resource Based Management
Prioritizing or focusing on resources and the ability to manage resources within the organization need to be effective in creating a competitive advantage. Levius (2016) studied on IT and communication strategies for country development and increasing the competitive edge of the organization. It was found that based on the concept of resource management, IT and communication strategies are necessary to increase competition potential particularly in the international business. Godwin-Opara (2016) also studied the strategic viewpoint about the financial resource of small business finding that the capital is crucial fundamental resource using for exchange. The business that is lack of financial liquidity might face the business failure problem. Accessing external capital resource and gaining external fund are crucial.
Teamwork
Teamwork is generally understood as the willingness of a group of people to work together to achieve a common aim Mak (2017) investigated guidelines in teamwork adjustment by giving the importance on workload to develop teamwork skill. The research found that training should focus on both skill development and teamwork. The success of team depends on the ability of the team members, cooperative work, and effective knowledge sharing and integrating. Understanding the problems together can help the team find the effective solution. Daniel (2010) studied on the spirit of workplace that affects the teamwork efficiency. The results showed that the spirit of workplace is the importance factor of organizational culture, which is crucial for the efficiency of teamwork particularly on trust, faith, innovation, and people respect.
Related Research
Bunsueb (2015) studied on the development of indicators for professional characteristics of vocational graduates of Thailand. The purpose of this research is to study the indicators for professional characteristics of vocational graduates of Thailand and found that there were 5 components, i.e. knowledge (intellectual, thinking), working, mind and attitude, life skills including happiness life, and communication with 17 sub-components and 66 indicators.
Don-Serge (2019) conducted the research about the future competencies of medium skilled labors of electrical automotive industry. The purpose of this study is to investigate the future competencies of medium skilled labors of electrical automotive industry with the results that the necessary competencies include the fundamental competencies on skills and operation and technical knowledge. The desirable personality includes human relationship, self-development, good personality, and moral and ethics.
Dean (2017) investigated the curriculum for developing the competencies of Thai youths in the future with the aims at: 1) describing the trend of Thai society in the future, 2) defining desirable competencies of Thai youths in the future (2015-2034), and 3) developing the curriculum for developing the competencies of Thai youths in the future. The results revealed that there will be a change in Thai society such as smaller family, increasing issues, lower fertility, decreasing working generation, increasing senior citizen, more urbanization, giving more importance on the 2nd language, more difficult to corrupt, more city migration, emerging of foreign culture, more advanced technology in industrial sector, more requirement of higher skilled labors, and higher competition with foreign countries.
Sujiraporn (2017) studied on the guidelines in developing labor potential of production industries in Pathumthani Province with the purposes to: 1) study the needs in developing labor potential of production industries in Pathumthani Province, 2) compare the needs on the guidelines in developing labor potential of production industries in Pathumthani Province according to types of products, and 3) find the guidelines in developing labor potential of production industries in Pathumthani Province. It was found that there was a high need in developing the labor potential of production industries with no difference among types of industries. The guidelines in developing labor potential of production industries showed that the organization focused on developing personnel related with their positions. In the future, the training will be conducted through websites or E training, which is congruent with the research on the fundamental resource and knowledge management. These are important components in developing labor competencies leading to the increasing of competitive edge potential of industrial sector.
Objective
The objective of this study is to investigate guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry.
Hypothesis
There were 4 hypotheses testing in this study.
H1 Resource based management variable has direct influence on knowledge management variable
The important variable to increase the capability in competitive edge is knowledge management and knowledge sharing through the management of resources based management (Connell et al., 2014). Resource based management is necessary process, which is a part of knowledge management, which can facilitate, encourage, and support internal communication resulting in effective teamwork and reducing risk. The process is useful for data searching with fast and accurate business operation (Chadha, 2014).
H2 Resource based management variable has direct influence on teamwork variable
In the era of world economic change on innovation and technology including high business competition, an organization needs to be prepared for teamwork adjustment to increase its efficiency. The organization has to provide resource based management, innovation, information technology, communication, and work cooperation (Robinson, 2015). Those factors will help in knowledge sharing and create relationship among colleagues, which is very important process to help staffs adjust themselves as an effective teamwork (Sundaravej, 2014).
H3 Knowledge management variable has direct influence on characteristics of professional labors variable
Knowledge management plays an important role during globalization period. The severe competition causes an organization to adjust itself to cope with the global change (Staples, 2013). To achieve the success, an organization must develop its staffs for intellectual capital, perception of business ownership, and leadership personality. Good knowledge management will result in intellectual capital leading to high skilled staffs with appropriate knowledge for their operation causing the organization increase its productivity and competition potential (Moten, 2011).
H4 Teamwork variable has direct influence on characteristics of professional labors variable
Cooperation in working is a part of teamwork that increases work quality and efficiency. Labor must possess the characteristics of advanced professional workers. That is to say, labors need to have knowledge, capability, skills, and good attitude when working with others. It is important to develop their attitudes to feel like one team and direct the team to achieve the set target. An organization with capable personnel can create effective teamwork rather than individual success (Jankovic, 2015). Effective teamwork makes an organization achieve their target successfully and create characteristics of professional labors (Erdo?an & Çelik, 2016).
Methodology
This study has been designed as an inductive research with mixed methodology
1. The qualitative research data were derived from an in-depth interview with 9 specialists consisting of 3 administrators or managers, 3 entrepreneurs or stakeholders or managing directors or CEO and 3 academic experts in the field of human resource management. The structured interview consists of 4 variables, i.e. knowledge management, characteristics of professional labors, resource based management and teamwork variables. The results of the congruence evaluation between research questions and the research objective or Index of Item Objective Congruence (IOC) ranged between 0.60-1.00 (> 0.5). Then, the 100 items of questions were tried-out to find the discrimination value and reliability with the Chronbach alpha equaled 0.987 (> 0.8). The discrimination value of the items which were in the form of checklist gained the Standard Deviation (S.D.) between 0.546-2.113. The items with rating scales were analyzed to find Corrected Item-Total Correlation ranging between 0.353-0.840.
2. The Quantitative Research data were derived from 500 samplings who were operational managers from petrochemical industries registered with Thai Plastic Industry Association or with the enterprises registered with the data analysis center of Plastic Intelligence Unit through random sampling technique (Comrey & Lee, 1992). They were divided into 2 groups (Thai Plastic Institute, 2019), i.e. 250 samples from plastic industries and 250 from injection molding and packaging industries. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics by SPSS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis which was developed to SEM Model by AMOS program. The Evaluating of the Data-Model Fit criteria consisted of 4 values 1) chi-square probability > 0.05 2) Relative chi-square (CMIN/DF) < 2 3) Goodness of fit index (GFI) > 0.90 and 4) Root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) < 0.08 (Arbuckle, 2011).
3. The guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry were certified by 7 specialists through focus group.
Results
The managers of plastic industries and injection molding and packaging industries gave high importance on the guidelines for developing labor competencies as shown in Table 1.
| Table 1: Importance level of the desirable competencies of Operational Labors in the Petrochemical Industry according to types of Industrial Business | ||||||
| Guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in the petrochemical industry |
Types of industrial business | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic industries | Injection Molding and packaging industries |
|||||
| S.D. | Significant Level |
S.D. | Significant Level |
|||
| Overall | 3.77 | 3.69 | High | 3.74 | 3.67 | High |
| 1. Knowledge management | 3.66 | 3.81 | High | 3.60 | 3.78 | High |
| 2. Characteristics of professional labors | 3.66 | 3.77 | High | 3.71 | 3.77 | High |
| 3. Resource based management | 3.87 | 3.74 | High | 3.76 | 3.66 | High |
| 4. Teamwork | 3.88 | 3.67 | High | 3.90 | 3.64 | High |
1. The results of the analysis of the importance level on the guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in petrochemical industry showed that the overall importance reported by plastic industries was 3.77 and that of injection molding and packaging industries was 3.74. When considering on each variable, it was found that plastic industries gave high importance on every variable with the highest value on teamwork (mean =3.88) followed by resource based management (mean = 3.87), characteristics of professional labors (mean = 3.66), and knowledge management (mean =3.66) respectively. The managers of the molding and packaging industries gave the importance on the 4 variables at high level with the highest value on teamwork (mean = 3.90) followed by resource based (mean = 3.76), characteristics of professional labors (mean = 3.71), and knowledge management (mean =3.60) respectively.
2. The results of the analysis on the guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in petrochemical industry between the two types of industrial business showed no statistically significant level at 0.05. In other words, the managers of the two groups of industries gave the important on developing labor competencies at the same level.
3. The results of the SEM evaluation before the adjustment showed that Chi-Square Probability Level (CMIN- ρ) =0.000, relative chi-square (CMIN\DF) = 4.750, Goodness of fit index (GFI) =0.437, and Root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.087 did not pass the criteria of empirical data.
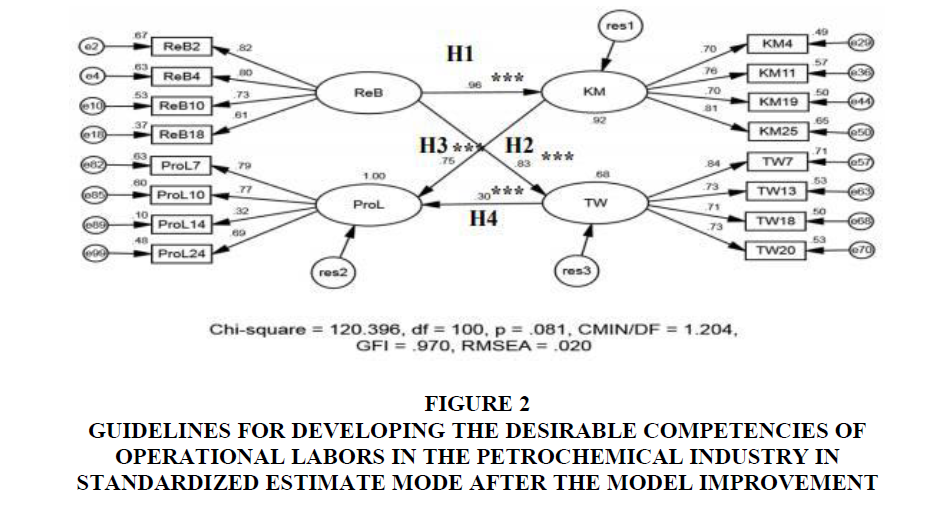
Therefore, the researcher improved the model by considering Modification Indices by Arbuckle (2011). After the model improvement, it was found that Chi-Square Probability Level (CMIN- ρ) = 0.081>0.05 showing no statistically significant level, relative chi-square (CMIN\DF) = 1.204 < 2, Goodness of fit index (GFI) = 0.970 > 0.90 and Root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.020 < 0.08. This can be concluded that the 4 statistical values passed the criteria as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of Operational Labors in the Petrochemical Industry in standardized estimate mode after the model improvement
Structural Equation Model for the Guidelines Developing the Desirable Competencies of Operational Labors in the Petrochemical Industry
The results of the hypothesis testing to analyze causal relationship between variables for developing labor competencies in the petrochemical industries revealed 4 hypotheses as follows.
1. H1: Resource based management variable has direct influence on knowledge management variable at the statistically significant level of 0.001 with factor loading of 0.96.
2. H2: Resource based management variable has direct influence on teamwork variable at the statistically significant level of 0.001 with factor loading of 0.83
3. H3: Knowledge management variable has direct influence on characteristics of professional labors variable at the statistically significant level of 0.001 with factor loading of 0.75.
4. H4: Teamwork variable has direct influence on characteristics of professional labors variable at the statistically significant level of 0.001 with factor loading of 0.30, as shown in Table 2.
| Table 2: Statistical Analysis of structural equation model for the development of the Desirable Competencies of Operational Labors in the Petrochemical Industry in standardized estimate model | |||
| Variable | Estimate Regression Weight | Square Multiple Correlation (R²) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Based Management | |||
| Knowledge Management | 0.96 | 0.92 | *** |
| Teamwork | 0.83 | 0.68 | *** |
| Knowledge Management | |||
| Characteristic of Professional Labor |
0.75 | 1.00 | *** |
| Teamwork | |||
| Characteristic of Professional Labor |
0.30 | 1.00 | *** |
| Resource Based Management |
|||
| ReB2 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| ReB4 | 0.80 | 0.63 | *** |
| ReB10 | 0.73 | 0.53 | *** |
| ReB18 | 0.61 | 0.37 | *** |
| Characteristic of | |||
| Professional Labor | |||
| ProL7 | 0.79 | 0.63 | *** |
| ProL10 | 0.77 | 0.60 | |
| ProL14 | 0.32 | 0.10 | *** |
| ProL24 | 0.69 | 0.48 | *** |
| Knowledge Management | |||
| KM4 | 0.70 | 0.49 | *** |
| KM11 | 0.76 | 0.57 | *** |
| KM19 | 0.70 | 0.50 | |
| KM25 | 0.81 | 0.65 | *** |
| Teamwork | |||
| TW7 | 0.84 | 0.71 | |
| TW13 | 0.73 | 0.53 | *** |
| TW18 | 0.71 | 0.50 | *** |
| TW20 | 0.73 | 0.53 | *** |
Structural equation model for the guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in petrochemical industry after the model improvement consisted of 4 latent variables and 1 Exogenous Latent Variable, i.e. resource based management variables and 3 Endogenous Latent Variables, i.e. knowledge management, characteristics professional labors, and teamwork.
The resource based management variables consisted of 4 observed variables arranged according to the factor loading, i.e. providing facility to develop labors (ReB2) with the factor loading of 0.82, providing specialists for consultancy on knowledge and skills (ReB4) with factor loading of 0.80, surveying the needs on equipment and tools for labors (ReB10) with factor loading of 0.73, and appointing purchasing committee for equipment and tools (ReB18) with factor loading of 0.61.
The characteristics of professional labors variables consisted of 4 observed variables arranged from the factor loading, i.e. encouraging gifted labors to become specialists with higher salary (ProL7) with factor loading of 0.79, providing self-assessment for labors to set own development target (ProL10) with factor loading of 0.77, labors must strictly obey organizational values (ProL24) with factor loading of 0.69, and setting plan for career development (ProL14) with factor loading of 0.32.
The knowledge management variables consisted of 4 observed variables arranged from the factor loading, i.e. trying innovation that benefits the organization (KM25) with factor loading of 0.81, collecting statistics as a database for problem solving (KM11) with factor loading of 0.76, providing learning through experience telling with tape recording and rearranging into knowledge (KM19) with factor loading of 0.70, and providing job rotation in operation to create knowledge (KM4) with factor loading of 0.70.
Teamwork variables consisted of 4 observed variables arranged from the factor loading, i.e. understanding the individual difference (TW7) with factor loading of 0.84, team members must correct their own weak points (TW20) with factor loading of 0.73, good relationship among groups to get rid of the operation obstacles (TW13) with factor loading of 0.73, and open discussion (TW18) with factor loading of 0.71.
Conclusion and Discussion
It can be concluded that the guidelines for developing the desirable competencies of operational labors in petrochemical industry consist of 4 variables which all are important for developing competencies of both plastic industries and injection molding and packaging industries. The variables include knowledge management, characteristics of professional labors, resource based management, and teamwork. Both types of industries gave the most importance on teamwork variables.
After the improvement of the model, it was found that resource based management variables has direct influence on knowledge management at the statistically significant level 0.001 with Standardized Regression Weights = 0.96 and has direct influence on teamwork at the statistically significant level 0.001 with the Standardized Regression Weights = 0.83. Knowledge management variables direct influence on characteristics of professional labors at the statistically significant level 0.001 with the Standardized Regression Weights = 0.75. Teamwork variables direct influence on characteristics of professional labors at the statistically significant level 0.001 with the Standardized Regression Weights = 0.30.
Guidelines for developing the desirable competencies with the highest ranking was teamwork (mean = 3.89) because under the high competition situation, effective teamwork will result in strategic innovation to gain the market share and profit. This was in line with the research by Matthews & McLees (2015) studying the construction of effective teamwork which revealed that it is important to have effective leadership with good understanding about skills and capacity of the teamwork. Also, the research by Whetten et al. (2007) states that the management in developing skills in the organization finding that increasing team efficiency and unity of the team results in the organization success particularly in the severe competition of disruptive technology era.
The highest variable in the development of operational labors was on being unbiased of the management team and supervisors of all levels with the mean of 4.13. The researcher believes that supervisors or leaders must have accumulated arts of managerial skills to gain faith and influence, which was congruent with the research by Singhry (2018) studying on the justice perception for change leaders and work satisfaction in public organization finding that staff relationship and justice in data informing among leaders affects directly on staff satisfaction.
Suggestions
It is essential to design the human-machine interface and therefore it could be presented to the workforce as a mock or simulation model. By doing so, the operators should be able to view the map, which shows the control and functioning of the factory. The mock model will be vital for the diagnostic purposes and the management of information, such as scheduled maintenance procedures, logistical information, etc.
It is evident that industries in Thailand are facing a labour shortage and there is an urgent need to establish learning and development facilities to better understand “Industrial 4.0”.
It is also important that the Thai government assist in increasing the number of technicians to work in the operating department, within the manufacturing industry.
In addition, there is a need to develop programs for teachers and expert trainers in the manufacturing industry (Industry 4.0), to have an overall benefit in the economy.
There is a need for cooperation between industries and the educational system, which will prove beneficial in allowing skills and knowledge to be passed on at the tertiary level of education. A bilateral education management system is required between industries and educational institutions. Lastly, a review on the education curriculum to make editions where it is deemed suitable, in order to produce technicians that is capable to handle Industry 4.0.
References
- Arbuckle, J.L. (2011). IBM® SPSS® AmosTM 20 users guide. Chicago, IL: AMOS Development Corporation.
- Bagie?ska, A. (2015). Measurement and analysis of the efficiency of human capital in a small enterprise in Poland. e-Finanse, 11(2), 1-9.
- Bunsueb, P. (2015). Development of professional labor indicator of graduates in the vocational education system of Thailand. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Silpakorn University.
- Chadha, S.K., & Saini, R. (2014). Information technology support to knowledge management practices: A structural equation modeling approach. IUP Journal of Knowledge Management, 12(1).
- Comrey, A. L., & Lee, HB (1992). A first course in factor analysis, 2.
- Connell, J., Gough, R., McDonnell, A., & Burgess, J. (2014). Technology, work organisation and job quality in the service sector: An introduction.
- Daniel, J. L. (2010). The effect of workplace spirituality on team effectiveness. Journal of Management Development.
- Dean, S. A. (2017). Soft skills needed for the 21st century workforce.
- Don-Serge, H. M. O. (2019). The role of knowledge creation, sharing and utilization to the resource based view of competitive advantage. Global Journal of Management and Business Research.
- Erdo?an, P., & Çelik, A. (2016). Relationship between morale and motivation in teamwork environments: A research in the health sector. Journal of Human Sciences, 13(1), 1433-1451.
- Godwin-Opara, M. N. (2016). A resource-based perspective on financial resource strategies for small business sustainability.
- Jackson, A.W. (2016). Core leader competencies for implementing sustainability strategies in small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Jankovic, R. (2015). Teamwork Behavior: Measurement and Links to Outcomes. Hofstra University.
- Kuo, T. H. (2013). How expected benefit and trust influence knowledge sharing. Industrial Management & Data Systems.
- Levius, S. (2016). Information and communication technology strategies to improve international competitiveness in a Barbados organization. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Walden University.
- Mak, S. (2017). Adaptive Guidance with Teams: Shifting from Taskwork to Teamwork. Michigan State University. Psychology.
- Matthews, R., & McLees, J. (2015). Building effective projects teams and teamwork. Journal of Information Technology and Economic Development, 6(2), 20.
- Mendoza, C., Bischoff, J., & Willy, C. (2017). Measuring the Value of Knowledge Management Practices at Government Research and Development Centers. Knowledge and Process Management, 24(1), 14-22.
- Moten, K. W. (2011). The impact of industrial technician skill losses at a west Tennessee manufacturer.
- Pande, S., & Joshi, G. (2013). Competency Model at Adeco Industry (P) Ltd. Drishtikon: A Management Journal, 5(1).
- Pierre, M. W. (2017). Recruitment Strategies for Manufacturers in Northwest Louisiana.
- Piyachat, B., & Chanongkorn, K. (2015). Guidelines for improving productivity, inventory, turnover rate, and level of defects in thailand plastic industry. Indian Journal of Management Science, 5(2), 65.
- Robinson, C. D. (2015). Successful virtual teams: Collaboration and influence as drivers of team success. University of Pennsylvania.
- Sattabut, T. (2012). A study of competency needs of human resource staff for industry sector. Veridian E-Journal, 5 (2), 426-448.
- Singhry, H. B. (2018). Perceptions of leader transformational justice and job satisfaction in public organizations. International Journal of Public Leadership.
- Staples, G. A. (2013). The efficacy of strategic human resource development on followership. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Phoenix.
- Stefan, D. L., & Craciuneanu, V. (2014). Labor's Flexibility-Boost of the Productivity's Growth. Knowledge Horizons. Economics, 6(4), 113.
- Sujiraporn, F. (2017). Guidelines for potential development of industrial workers in pathum thani province. Academic Journal Bangkokthonburi University, 6 (1), 114-124.
- Sundaravej, T. (2014). Synchronous and asynchronous collaboration technology use in teamwork.
- The Petroleum Institute of Thailand. (2017). http://www.ptit.org/ptit_medias/arlcat_a01d3582860bfcfc97eb220b1fdb0c9e.pdf
- Whetten, D. A., Cameron, K. S., & Woods, M. (2007). Developing management skills. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- World Economic Forum. (2019). Global Competitiveness Report. Retrieved from http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf