Research Article: 2021 Vol: 24 Issue: 6S
Governance and Its Impact on the Restructuring Processes of Some Iraqi Public Banks
Naji Shayeb Al-rikabi, Baghdad College of Economic Sciences University
Abstract
Bank governance is one of the important tools that contribute to the success of the restructuring operations of some public banks, because these banks constitute a great importance in the infrastructure for the development of the country, which requires their preparation to suit the requirements of sustainable development in terms of work methods, technology used, management philosophy, etc., and the researcher believes The appropriate way to develop these banks so that their strategic goals are achieved and their activities become economically feasible and contribute to the sustainable development of the country is the restructuring of these banks based on the governance of banks. For this purpose, I took a random sample from the Rafidain and Rashid banks and distributed the questionnaire prepared for the purpose of measuring the impact of corporate governance of the independent variable on the restructuring of the dependent variable banks and by 30 questionnaires distributed equally among the employees of these two banks. The measurement results were as follows: 1 - The correlation coefficient between the two variables is the governance of banks (the independent variable) and the restructuring of operations (the dependent variable) is 0.862 and this indicates that the correlation is direct and strong. 2 - The determination coefficient is 0.742, meaning that the governance of the independent variable banks affects the restructuring of the dependent variable banks by 74.2%. The rate is high and the remaining 25.8% is the ratio of the influence of other variables that may be because to regulatory, legal or other factors outside the scope of the research.
Keywords
Bank Governance, Restructuring Processes
Introduction
Different developing and developed countries seek to continue development and growth, but what distinguishes the developed countries provides the appropriate infrastructure. Thus, the trends of the development of these countries focus on preserving scientific and technological excellence and entering into new fields or delving into scientific progress rings. As for developing countries, including Iraq, the pattern of their development It differs from those countries and lives in a state of confusion and experimentation and searches for finding a suitable ground for its development. Usually, it is looking for preparing and configuring the infrastructure for this desired development that expands in size or shrinks according to each developing country and in the Arab world, where the transformation the countries from rely on public activities to what resembles western countries and to focus on private activity and investment in various types and forms, this requires the creation of infrastructure in all legal, regulatory, financial and technological areas.
In this research, banks are an important pillar of the infrastructure for the development of the country, which requires its preparation to suit the requirements of this development in terms of working methods, technology used, management philosophy and others. The restructuring of these banks based on bank governance contribute to attract investment, and that the restructuring in the traditional way is not enough and may lead to just deleting some activities or reducing some procedures, either linking the restructuring of banks to governance is not limited to mere change or re-engineering of operations despite its importance, but rather charts the correct paths that link the banks to their goals in addition to that, banks governance is one of the proven tools and proven to be successful globally in various activities.
Research Problem
The current procedures of Iraqi public banks constitute an obstacle to domestic and foreign investments to Iraq, which requires the restructuring of these banks to achieve the economic feasibility of its activities and makes them effective tools in the development and advancement of the sociality. And banks constitute the infrastructure for any investment activity, whether internal or external. At the present time the public banks In Iraq are unable to operating with efficiently and effectively because virtue of its legislative, legal, and administrative legacy, as the public banks are unable alone to carry out this large task, to keep pace with the development taking place in the world in the field of preparing the appropriate grounds to attract investments to Iraq, Actually, The private banks sector is an important pillar of development and economic development in Iraq.
Research Hypothesis
The Research is Based on Testing the Following Hypothesis
The use of bank governance leads to the success of the restructuring operations of Iraqi state-owned banks in order to achieve the efficiency and effectiveness required for banking work and makes the banking activity economically feasible, reduces the cost of services provided by the banks to customers, improves their performance and contributes to attracting investments.
Research Importance
While discussions and studies are conducted on ways to advance the state-owned banking activity and try to define possible paths and mechanisms to achieve this goal, the research topic constitutes a vision that helps decision-makers in developing mechanisms appropriate for this purpose by linking the mechanism of restructuring the banking activity and governance mechanisms and adapting them to achieve the goals of the activity The bank, the restructuring of the bank means the economic operation of the banking activity, while governance means ensuring the success of the operations of structuring public banks in a manner that leads to the adoption of modern methods of work and the introduction of advanced technology leading to the adoption of recommendations for Basel 2006 related ISO banking.
Research Goals
The research goals are to highlight the importance of using the banks governance to succeed restructuring operations of Iraqi banks, and this is achieved through:
1. Knowing the banks governance and their mechanisms of applying governance.
2. The use mechanisms for banks governance in restructuring the Iraqi public banking sector.
Search Limits
The research includes studying the reality of public banks owned by the state (Rafidain and Al-Rasheed banks) with the aim of contributing to the success of the restructuring operations using the governance of banks by preparing the questionnaire list to contain two groups of paragraphs the first focuses on restructuring and the second is concerned with banks governance as a proven mechanism and contributed to the success of many public and private companies in Various countries in the world.
Research Society and Sample
The research community consists of public banks owned by the Iraqi state, Al-Rafidain and Al-Rasheed banks. As for the research sample, the department concerned with restructuring banks in the general management of Al-Rafidain and Al-Rasheed banks was chosen. (34) Questionnaires were distributed to (department head, senior manager, director, assistant director) with the exception of (4) questionnaires because they were not valid for statistical analysis, and thus the number of questionnaires that were subjected to statistical treatment becomes (30) questionnaires, that is (88,235%) of Distributed questionnaires.
Sources of Information Collection
The research data was collected from the following main sources:
1. Books, scientific periodicals, references, available websites and studies related to the research topic.
2. The questionnaire, as one of the statistical methods commonly used by researchers, distributed the questionnaire to the sample chosen from the Rafidain and Rashid banks, as shown in the practical side later.
Theoretical Framework for Banking Governance
Concept Governance Banks
The concept of corporate governance was initially associated with shareholding companies and was called corporate governance or good management for corporate, and then the use of this concept spread in other economic and financial sectors, including banks, and it was called bank governance, and in general there are many institutions, including the International Finance Corporation, which has defined corporate governance as " It is the system by which companies are managed or their businesses are controlled " As for the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, corporate governance has been defined as" a set of relationships between those who manage the company from the board of directors, shareholders and other shareholders " (Youssef, 2007) Accordingly, bank governance aims to achieve a high level of transparency, disclosure, justice, and accountability of board directors bank when it acts in a manner that strikes the interests of other parties related to the bank, protecting the rights of shareholders and depositors, and at the same time ensuring workers ’rights and as a result attracting investments, developing savings and maximizing the profitability of the bank.
Banking Governance Standards
Banking standards constitute a mixture of the principles and mechanisms of corporate governance, the recommendations of the Basel Committee for Banking Work that were issued in 1999 and the subsequent modifications for 2005, 2006, in addition to the instructions and directives issued by the International Finance Corporation. Here is a summary of these standards:
First: The members of the bank’s board of directors enjoy the appropriate qualification, skills and experience that enable them to develop strategies for banking business activities and this board is responsible for managing the bank’s affairs in a way that achieves its general goals and guarantees the rights for shareholders, depositors, employees and to ensure the integrity of the bank’s financial position (Haddad, 2008, 13).
Second: Establishing an organizational structure commensurate with the nature of the bank’s work so that the business is described and duties are distributed and responsibilities are defined for the bank’s board of directors, executive management, managers and employees to ensure the application of the principle of responsibility accountability in a specific and clear manner (Macey & O’Hara, 2003, 13)
Third: The independence of internal and external auditing, given that the supervisory work constitutes the core of the banks ’governance, and that the board of directors evaluates the performance of internal control and makes sure the financial statements represent the actual activity of the bank and at the same time that the audit committee coordinates between the actors of the bank.
Fourth: The wages and bonuses policy coincides with the bank’s long-term strategy, and the incentives of the bank’s board members, the executive directors, from cash and shares are consistent with the goals of the bank’s governance.
Fifth: The importance of transparency, adequate disclosure in financial statements of important information to members of the Board of Directors and executives fairly among shareholders and stakeholders as an important principle for successful governance in banks.
Sixth: The bank’s board of directors must understand the legislative environment in which the bank operates, and the executive management must abide by the structure of the bank’s business functions without engaging in activities that might expose the bank to risks.
The Advantages of Governance in Iraqi Banks
Iraqi banks achieve many advantages when applying bank governance, the most important of which are:
1. Improving the performance of Iraqi banks, which leads to achieving their strategic objectives.
2. Effective control over the performance of Iraqi banks.
3. Ensures that qualified qualifications are available at high quality levels.
4. It provides workers with adequate protection when preparing reports on illegal and unethical practices with the aim of reducing financial and administrative corruption cases in Iraqi banks.
5. Affirms that wage and bonus policies are in line with the bank’s culture, goals and strategy.
6. Achieving transparency, justice and protecting the rights of stakeholders through creating rules, regulations and controls for the Central Bank on the one hand, and the bank’s management on the other.
7. Attracting investments, whether foreign or local, and limiting the flight of Iraqi capital abroad.
8. Regulating the work of Iraqi banks and controlling them according to high-quality rules, standards and mechanisms of work, and granting the right to hold the bank’s management fully transparent to limit the abuse of power in a way other than the public interest.
9. Developing deposits and savings for depositors by building confidence in Iraqi banks among members of society.
10. It works to stabilize the stock markets and improve the economic system.
11. Achieve sufficient disclosure of information describing risk management processes, internal control procedures, policies for social and environmental responsibility towards society.
12. Applying modern banking systems and using technologies and information technology.
13. Improving the competitiveness of Iraqi banks and increasing their value.
14. Activating the role of the external auditor in adding confidence and credibility to the financial statements.
(Klapper & love, 2002; Coleman & Biekp, 2006; Aikleng, 2004; Hamady, 2005)
Accounting Mechanisms for Bank Governance
The effective application of the concept of corporate governance in banks requires working mechanisms that are "the set of methods that are applied at the level of banks to solve banking problems” (Omron, 2008). There are many mechanisms that contribute to the success of corporate governance, including accounting, legal, Organizational, economic, and social, as the accounting mechanisms of governance receive more attention and occupy the largest part of the various procedures and methods for applying governance. These mechanisms include:
The Board of Directors
The Board of Directors is an effective tool that exercises leadership and directs and works for the benefit of the bank and stakeholders and exercise accountability and control in a transparent and responsible manner through the formation of a group of committees from among members its executive and non-executive, where the committees as the following: (Al-Fade, 2007)
The Audit Committee
The Audit Committee emanates from the Board of Directors, and its primary duties are to prepare financial reports, achieve confidence in accounting information, follow-up and evaluation of the internal control system, and follow up on the work of the external auditor, and the committee must have sufficient independence and have the necessary expertise to carry out its duties and responsibilities effectively and as required.
The Rewards Committee
Its duties and functions are focused on determining salaries, bonuses and benefits for senior management, reviewing and approving them.
Risk Management Committee
It supervises the senior management systems in relation to credit, liquidity, market risk management and other different types of risks.
Internal Auditing
Internal auditing is one of the monitoring mechanisms within the governance structure, whereby the internal auditor, through the activities he carries out, increases credibility and fairness, improves the behavior of employees working in banks, reduces risk, especially in terms of ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial reports and preventing and detecting cases of fraud and fraud (Gleam, 2004).
The External Audit
The external audit is the cornerstone of public banks governance and private, where the external auditor plays a role in improving the quality of financial statements. To achieve this, the Audit Committee should discuss the quality of the statements, and the external auditor helps banks achieve accountability and integrity and improve operations in them. It promotes trust between stakeholders and citizens in general, and it helps governments oversee, prevent, and discover administrative and financial corruption (Al-Hanafi, 2005).
Disclosure and Transparency
Disclosure and transparency represents the presentation of financial and non-financial information that depend and that not depend on the generally accepted accounting principles and standards and legislative requirements in financial reports in a timely and accurate manner to provide users with the information they need to make their decisions. That is so main principles and pillars on which banks governance is based to achieve the interests of the various parties (Robert, 2005).
Other Mechanisms
There are other mechanisms that affect the effectiveness of banks governance in important and complement it ways and other mechanisms in protecting stakeholders in banks, such as financial analysts, the International Standards Board, and some international organizations, as an World Transparency Organization, the World Trade Organization and the Basel Committee for Banking Supervision.
Theoretical Framework for the Restructuring of Banks
Concept Restructuration of Banks
The term Restructuring consists of two parts: The first part (Re) means (restoration), the second part (structuring) means (rebuilding) or (raising efficiency) or (scientific re-design). For the purpose of giving a clear idea about the concept of bank restructuring, it is necessary to review the concept of restructuring mentioned by writers and researchers, and it defined by (Claudia & Celia, 1998) restructuring as "one of the pressures that organizations face due to continuous change in a complex environment in order to achieve survival, continuity and success, also defined from (Kotler, 2000), it as "a way to achieve the goals of the organization efficiently and effectively and aims to find the best compatibility between organizational building and the use of modern, advanced and effective means", and he emphasized (Parker, 1998) that restoring The restructuring is "part of the reengineering and aims to abandon old means, and push organizations to Using new methods to satisfy customers. "As for the concept of restructuring banks, it has been defined (Al-Hourly, 2011) as" a deliberate process of change of official relations between the various organizational components of the bank in order to improve performance efficiency", as defined by (Waxman, 1998 as a set of strategies, plans, programs and policies developed by the bank's management in order to improve the performance of banks", (Fahmy, 1992) believes that restructuring the banking sector is "a set of activities and processes designed to increase the efficiency of the bank And achieve competitive advantage. " After reviewing a number of definitions of restructuring, it becomes evident that all of them agree on the following:
1. Making a change in the working style of the bank.
2. Adopting a new method, and that the change be basic, comprehensive, and has value and depends on information technology.
3. The results of the change are substantial and comprehensive.
The restructuring of banks aims to make the necessary correction for the technical, economic and financial structures in a manner that enables them to remain in the business world and continue successfully through studying problems, whether technical, technological, economic, financing, regulatory, etc. And that the restructuring of the banks be in accordance with modern international banking standards and requirements, which generally focus on supporting internal banking oversight of its various types, and setting the organizational structure of the bank in a manner consistent with national standards and requirements issued by central banks with specifying the powers and duties of the committees and for each job level and the various functions in banks (Qaddara, 2007).
The Reasons that Lead Banks to Adopt a Restructuring Strategy
1. The problem of surplus employment resulting from the policies adopted in the bank
2. Technological development and the replace of advanced technology for the technology used
3. Failure to achieve goals
4. Failure to take advantage of external opportunities and reduce threats
5. Inefficiency and low profitability
6. Conditions of general recession
7. Privatization
8. Increasing competition between banks (Barker, 1998).
Requirements for Successful Bank Restructuring
For the purpose of successful restructuring, banks are required to take the following procedures and policies (Qattara, 2007):
1. There is a clear and transparent real political will to carry out this process, and it is necessary to carry out the restructuring process in a timely manner and in a period of financial of relative calm for banking activity.
2. Carrying out a financial restructuring that includes commitment to the minimum capital of bank, as well as reviewing the credit portfolio and improving and developing its management.
3. Strengthening the internal control system, monitoring compliance, and setting the required policies in accordance with the Banking Law and the central bank’s regulations.
4. Consider the type of services provided, their development, and implement them as quickly as possible.
5. The need to reduce liabilities and transfer what is possible of amounts to increase the capital.
6. Reconsidering the specialized banks and merging them into one specialized bank.
7. Reducing operational costs and using modern methods in providing banking services.
8. Setting a well-studied plan and expeditious work by all those connected to this bank.
Restructuring the Iraqi Public Banks
Concept and Goals
The banking system is an active sector in managing the economy and keeping pace with developments, and the main role of this system is to provide the necessary channels and institutional frameworks to mobilize savings and direct them towards real investment in supporting the sustainable development process, and in light of the rapid change in the environment business, the banking system must face the challenges and threats and keep abreast of developments in the field of banking And technology with a view to survival and continuity, however, the Iraqi public banks stayed on the same where traditional activities and it is unable to face challenges and threats and keep pace with developments in the field of business banking and technology, because of the constraints imposed on them under laws and legislations and not adopting policies to introduce modern banking services as well as the weak banking awareness in Iraqi society, so the Iraqi banks should adopt a restructuring as a method to achieve radical improvements to operations to comply with the new environment, and the Iraqi banking expert, Dr. Kamal Al-Basri, defined the banking restructuring as "Reorganization of human resources and financial, technological and material assets in order to improve the performance of banks and bring them to the level of the modern global banking industry in a manner consistent with the requirements of the growing Iraqi economy and economic relations International ", (Al-Basri, 2007) where of the goal of restructuring banks in Iraqi as following (Al-Mulla, 2011):
1. Developing its performance in order to provide banking services to the government, institutions and individuals according to the requirements of the economic development.
2. The banking sector plays an important role in international economic and financial relations. Therefore, it is receiving international attention and the banking sector must have the accuracy and responsibility in carrying out these transactions.
3. Eliminating the problems that banks suffer from in order to ensure accuracy the local and international transactions.
Actually, The Iraqi banks needs a comprehensive restructuring through a set of multiple and overlapping operations and activities that include identifying financial losses and financial liabilities, restructuring the operation and rebuilding a legal, accounting and regulatory system to raise its efficiency and improve the banking environment in which it operates.
The Strategy of Restructuring the Iraqi Banks
Iraqi banks play the mediator role between available resources and their investment aspects, and thus contribute to increased employment and economic growth, and the efficiency of the Iraqi banking system is measured by its ability to achieve its goals and providing the best services and at a lower cost, and to achieve these goals a comprehensive strategy must be developed to develop and restructure Iraqi banks, where that this strategy include the following stages (Saleh, 2009):
First: Diagnosing the reality of these banks and identifying the difficulties they face.
Second: Developing executive programs to achieve these goals.
First: Diagnosing the reality of these banks and identifying the difficulties they face
Iraqi banks suffer from structural weaknesses that can be summarized in the following points:
Non-Performing Loans
The accumulation of nonperforming loans has limited the ability of banks to perform brokerage functions by reducing their liquidity and increasing the cost of their operations.
Weak Disclosure and Control
Iraq lacks the minimum level of disclosure, which makes it difficult to make a comparison between it and international banks, as well as the banking data varies in its comprehensiveness and accuracy between one bank and another, which weakens disclosures.
Weak Technical Efficiency
Iraq needs to keep pace with the modern banking work through the communications network and the systems that work in the field of modern payment systems in the internal and external devices and systems using modern technologies increases the diversity of services and its speed, Dissemination of all information.
A Move Away from Directed Credit
We note the demand for bank credit because of the high interest rates charged by banks that reflect negatively on the overall investment activity.
Shortcomings in Human Resources Management
Lack of keeping pace with the Iraqi banking sector for modern developments.
Imbalance in the Pattern of Ownership
Their part of the financial services that provide them with support from the Central Bank of Iraq and this affects their efforts to combat corruption.
Second: Setting the executive programs to achieve these goals
(Al-Nasser Program: 2011, 68-70):
A program for the restructuring of Iraqi banks as following:
1. Restructuring the banks themselves administratively, financially and operationally and supporting them with advanced risk management systems.
2. Restructuring the supreme supervisory and supervisory authority over these banks.
3. Developing appropriate regulations to regulate the work of banks, based on the various Basel agreements, with a view to exercising the oversight role consistent with international standards.
4. Reconsidering the relevant Iraqi laws, especially the Banking Law No. 24 of 2004 and making adjustments to them in line with the requirements of the transitional phase that the economy and the banking system in Iraq are going through.
5. Restructuring the methodology of thinking for workers in the banking industry to align with the requirements of restructuring banks and the tasks of the banking industry in the economy and bank management in all financial, human and material aspects.
Challenges Facing the Iraqi Banking Sector
The global banking sector has witnessed tremendous developments, including technological advances in the banking industry and the development of new financial tools in addition to the phenomenon of banking integration between banks, and the banking industry is one of the industries most affected by economic and technological developments, hence the importance of restructuring Iraqi banks to strive to develop themselves quickly to meet challenges Future, and that the efficient management of any bank must have a clear strategy that takes into account financial and banking developments, whether local or global, and that affect the banking sector, and from here it can be identified the most important challenges The Iraqi banking sector may face:
Globalization of Banking Services
The most important challenges facing Iraqi banks represent how to respond and adapt to change as a result of the globalization. The primary problem is how to absorb changes and developments in their systems, structures and operations and move to the best by exploiting resources and capabilities and entering the new banking world by developing their work methods to be able to play their role by providing better Banking services (Al-Houry, 2011).
The Increasing and Diversifying Risks that Face the Work of Banks
The banking environment has become suffering from a lot of risks stemming from uncertainty, as this negatively affects profits, and banks face many risks such as credit, liquidity, interest rates, exchange rates, operating, solvency, political risks and other risks that may affect the bank’s profits and economic value. So the bank should be has a risk management system with an emphasis on the necessary of risk control (Al-Khatib, 2008).
Interbank Merger
Banking merger is the abandonment by the merged bank of its license, name, assets and liabilities to the merged bank, which leads to support for the financial position, by increasing capital and improving the level of banking services and raising the level of the bank's technology to keep pace with international standards and diversification of banking services and activities (Naji, 2006).
Information Technology and Innovation Revolution
Many challenges lie with the banks in order to apply banking technology and invent modern financial tools in light of increased global competition, as technological progress has led to changes and developments in banking business that affect the efficiency of implementation and banking performance, because technology imposes on Iraqi banks provide new financial services for customers in the banking market, which leads to innovation and add new banking services appropriate to the desires of those dealing with banks (Al-Qatanani, 2004).
The Privatization Policy
Privatization is one of the products of globalization, and the banks' tendency towards privatization in countries within the economic reform program to convert to market mechanisms through restructuring the administrative system and human resources (Belhawy, 2011).
Programs to be Implemented to restructure and Develop Iraqi Banks
Improving the Mechanisms of Providing Banking Services
This includes the development and modernization of banking operations management through:
• Restructuring of clearing and collection operations, loan operations and follow-up of accounts payable.
• Accurate re-description of procedures for carrying out every banking operation.
• Improved tracks the flow of banking operations through the use of electronic forms.
• Create a comprehensive customer service and ATM function.
The Development of Technological Infrastructure
This includes the development of technological infrastructure through:
• Development of banking systems and communication infrastructure.
• Developing the control structures so that they depend on the method of auditing and monitoring through accounting information Systems.
• Adopt a high-tech programs and integrated software package.
• Preparing and qualifying human cadres to operate, maintain and support these systems.
• Modernizing the banking business in line with these systems.
Financial and Administrative Restructuring
This includes financial restructuring and administrative and organizational through:
A. Financial Restructuring Including:
• Reclassification, treatment and allocation of debts in accordance with international standards.
• Ensure the application of international accounting standards in force globally.
• Supporting the means of internal control and establishing internal audit committees.
• Increase the capital of banks.
• Deposit insurance.
• Supporting electronic payment systems.
B. The Administrative and Organizational Structure Including:
• Developing information systems and technology and automating the branches.
• Establishing and developing risk, credit, inspection and the money laundering departments.
• Modernizing management systems and selecting competent banking leaderships.
• Attention to raise the efficiency of workers through training and rehabilitation.
Human Resources
This aims to focus on the human element through:
• Activating training courses for workers.
• Building a banking culture for workers.
• Activating the incentive system to be linked to the size of the achievement.
• Building modern administrative structures to define job levels.
• Applying transparency and communication with workers to understand their needs and develop their sense of belonging to organization or bank.
Controlling and Supervision
With regard to the subject of supervision of banks through:
• Determining the minimum capital adequacy standard.
• Determining the liquidity and reserve ratio.
• Ensure that banks comply with risk management control.
• Define rules for disclosure and transparency.
Risk and Credit Management
This includes monitoring risk and credit management through:
• Define risk and credit management standards.
• Credit risk assessment.
• Supervising the follow-up and implementation of the decisions of the Basel Committee.
• Developing policies for investing money based on cost rates and risks.
• The involvement of risk management in measuring credit risk
• Determining the maximum facilities granted to clients.
The Practical Framework for Research
Study of the relationship between the independent variable, bank governance and the dependent variable, restructuring of the Rafidain and Rashid banks, as the Rafidain Bank was established in 1941 and has 171 branches inside and outside Iraq, while the Rashid Bank is also public and was established in 1988 and has 138 branches inside and outside Iraq.
Data Collection Methods
To achieve the main objective of this research, a sample consisting of (30) employees from both banks and by (15) employees from each bank was taken and they were chosen as an intentional sample in order to achieve the goals of the research and after that a questionnaire was designed consisting of two parts, the first part is composed of four questions Related to general information about the employees, the sample of the research, and the second part of the questionnaire included (50) questions that formed in their entirety the two axes of bank governance and the restructuring of banks, and a five point Likert Scale was used. Table (1) illustrates this.
Description of General Information for the Selected Sample
| Table 1 Sample description |
||
|---|---|---|
| Academic Qualification | Number | Percentage (%) |
| Diploma | 2 | 6,6 |
| Bachelor | 9 | 30 |
| Higher Diploma | 15 | 50 |
| M.A. or MSc | 3 | 10 |
| Ph.D. | 1 | 3,4 |
| Total | 30 | 100 |
| Job Title | Number | Percentage (%) |
| Head of the Department | 15 | 16 |
| Manager | 6 | 8,23 |
| Associate Director | 3 | 7,39 |
| Senior manager | 6 | 5,20 |
| Total | 30 | 100 |
| Specialty field | Number | Percentage (%) |
| Accounting | 10 | 33,4 |
| Banking management | 11 | 36,6 |
| Economic | 6 | 20 |
| Statistic | 2 | 6,6 |
| Computer Engineering | 1 | 3,4 |
| Total | 30 | 100 |
| Service years | Number | Percentage (%) |
| 1- 5 years | __ | __ |
| 6 - 10 years | 3 | 10 |
| 11 - 15 years | 6 | 20 |
| 16 - 20 years | 6 | 20 |
| More than 20 years | 15 | 50 |
| Total | 30 | 100 |
The first section of the questionnaire included information describing some of the characteristics of the sample and table No. (1) Gives a description of the sample. It was found that the holders of higher certificates obtained by the elements of the sample constituted (63.3%) of the research sample, which indicates the scientific level of the selected sample, Also, the leadership category on which the main role falls in achieving the strategic goals of the banks constitutes (90%) of the sample size, noting that those who occupy jobs with a manager assistant level reach 10% of the sample size, as it is clear from the above table that the individuals who They hold scientific specializations in banking and accounting (70%), which is a good percentage for obtaining answers to issues Consciousness on the research questionnaire, as it is clear from Table No. 1 that (90%) of the sample population has a number of years of service from 11 years to more than 20 years, and this ratio indicates that the number of years of service is a key role in shaping the acquired practical experience with The workers, and according to this information where he notes the diversity of the demographic characteristics of the sample in a way that reflects the reality of the society that was taken from it.
Validity and Reliability Test of the Research Questionnaire
Content Validity Test
It means the ability of the questionnaire to express the goal that was designed for the sake of it. There are several statistical methods for measuring the validity of the questionnaire, and the most important, most common and accurate is the method of the Comparison of Extreme Groups. This idea of this method is summarized by arranging the results of questionnaire in ascending order and divided into two groups, then a choice 27% of the highest scores as a first group and 27% of the lowest scores as a second group, and the test (t) is calculated according to the following formula:
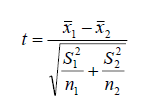
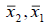 They are the average of the first group and the average of the second group, respectively.
They are the average of the first group and the average of the second group, respectively.
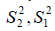 They are the variance of the first group and the variance of the second group, respectively.
They are the variance of the first group and the variance of the second group, respectively.
Then we compare the calculated value of t (10.328 ) with the tabular value (1.761 ) at the significance level of 0.05 and the degree of freedom (1,28) where the calculated value is greater than the tabular value so there are differences between the two averages and the questionnaire is true in its measurement and vice versa.
Test Questionnaire Stability
Stability means that the scale of the questionnaire gives the same results to the dates of its application to the same study population after a period of time. There are several statistical methods to show the extent of the stability of the questionnaire scale, all of which depend on the idea of the correlation coefficient. Among the most important and most common formulas is the (Guttmann L.A.) formula:
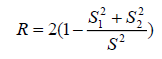
R Coefficient of stability
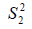 Varying the degrees of doubles questions
Varying the degrees of doubles questions
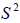 Variation in the degrees of all questions
Variation in the degrees of all questions
| Table 2 The Table Shows the Results of Validity and Coefficient of Stability |
||
|---|---|---|
| Questionnaire Axes | t- Calculated | Coefficient of Stability (R) |
| Banking Governance | 10.328 | 0,946 |
| Restructuring the banks | 10.162 | 0,975 |
As it becomes clear that the calculated value was greater than the tabular (1.761) for the two variables studied and this confirms the validity of the questionnaire scale. The stability coefficient is more than 0.5, and this confirms the stability of the resolution scale of the studied variables.
Test the Difference in the Opinions of the Research Sample when Answering the Questionnaire Questions
| Table 3 Difference in Opinions of the Research Sample When Answering the Questionnaire Paragraphs |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| The scale/Axis | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation |
| Banking Governance | 4.4 | 0.667 | 15.1593 |
| Restructuring the banks | 4.44 | 0.669 | 15.067 |
Table (3) shows the degree of difference in the views of the research sample with respect to each axis of the questionnaire, as the degree of difference in the views of the research sample for the axis of bank governance was 15,153 while the coefficient of difference for the axis of restructuring the banks was 15,067 and the reason for the difference in the views of the research sample Both axes of the questionnaire are due to the difference in the scientific and practical backgrounds of the individual sample and its effect on their opinions.
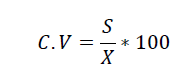
Whereas:
C.V – Coefficient of variation
S – Standard deviation
X – Mean
Analyze the Answers of the Research Sample
The Mean, Percentage Weight and Standard Deviation
Table (4) shows the analysis of the answers of the research sample to the axis of banking governance, as this analysis shows the agreement of the opinions of the research sample with what the researcher proposed to define the characteristics of banking governance that will contribute to the success of the restructuring operations of the Rafidain & Rashid banks, and the mean of the question number (6) was ( 4.7) which states (The members of the bank’s board of directors must be qualified and able to manage the bank’s business and develop an appropriate strategy for the bank’s work and take decisions related to various activities, including the soundness of the bank’s financial position) and the mean of question number (16) is (3.8) which states (in order to ensure Safety performance should be determined by an equivalent system Board of Directors and incentives so as to be in cash and shares. This means that they will serve our shareholders and this is very important to remove the gap between the owners and the executive management of the bank) and weight percentage ranges between 76%, 94 % respectively.
| Table 4 Weighted Mean, Proportional Weight, and Standard Deviation of the Bank Governance Axis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | Details | Weighted mean | Proportional weight | standard deviation |
| 1 | Applying the principles of banking governance in a proper way ensures the success of the restructuring operations of Iraqi banks Rafidain and AlRashid banks and provides the appropriate environment to attract foreign and local investment. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 2 | Adopting appropriate procedures for banking governance, including providing information, applying international accounting standards, paying attention to training and raising the level of human resources, will contribute to reassuring relevant parties whether they are depositors or shareholders, and others. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| 3 | Setting a regulatory framework for the bank that guarantees the integration of work between the board of directors and the external audit and auditing committee, so that it leads to the integration of the work and at the same time achieving the sequential and organized oversight work. The audit committee monitors the actions of the board and the external auditor examines the work. The general authority of the bank supervises all activities | 4.3 | 86% | 0.915 |
| 4 | The Central Bank of Iraq monitors the banks in a manner that achieves supervision and guarantees the proper performance of its work and plays its role in development and keeps it away from speculation and not be an entry for money laundering and at the same time determining the size and scope of the activity of each bank and the required liquidity and reserve ratio. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.712 |
| 5 | The Central Bank of Iraq is preparing an additional supervisory mechanism to be added to the mechanisms adopted in the governance of banks by setting the standard of capital adequacy, classifying assets and determining the allocations for each of them, and issuing instructions related to lending and guarantees required so that financial and administrative corruption does not occur. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.959 |
| 6 | The members of the bank’s board of directors must be qualified and able to manage the bank’s business and develop an appropriate strategy for the bank’s work and take decisions related to various activities, including the safety of the bank’s financial position | 4.7 | 94% | 0.651 |
| 7 | The board of directors is responsible for ensuring the rights of shareholders, depositors and other parties dealing with the bank, and at the same time preparing the appropriate organizational structure for the bank’s work, consistent with the principles of governance, so that the principle of accountability is adopted. | 4.2 | 84% | 0.61 |
| 8 | One of the main basic of banking governance is the formation of the audit committee by the bank’s board of directors, and it consists of nonexecutive members who have knowledge and experience in the field of accounting and auditing in addition to high independence and coordinates the bank’s various operations with related parties. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 9 | The audit committee is important to the following parties: | 4.2 | 84% | 0.761 |
| 1.Board of Directors through: | ||||
| · Helping executive members. | ||||
| · Coordination between the Board of Directors and the internal audit. | ||||
| 2. External auditor through: | ||||
| · Strengthening its independence. | ||||
| · Solving problems. | ||||
| · Review its reports. | ||||
| 3. The internal auditor through: | ||||
| · Enhancing independence and providing resources. | ||||
| · Activate the internal audit. | ||||
| 4. External parties through: | ||||
| · Increased transparency. | ||||
| · Commitment to bank governance. | ||||
| · Creating stock market requirements. | ||||
| 10 | The core of bank governance is focused on internal and independent external audit, as they contribute to the integrity of the bank’s work and keeping the rights of related parties. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.508 |
| 11 | The external auditor's commitment to high quality in examinations, audits, impartiality and neutrality in detecting errors and fraud and submitting his reports to the bank’s board of directors with a right to call the bank’s general assembly meeting in cases of high materiality. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.508 |
| 12 | Adoption of the principle of transparency and disclosure and the application of international accounting principles in the field of banking, particularly the decisions of the Basel Committee in the field of bank governance issued in 1999 and subsequent amendments in 2005, 2006. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| 13 | The application of the principles of corporate governance in banking will enhance the role of banks by: | 4.5 | 90% | 0.508 |
| · Fighting financial and administrative corruption. | ||||
| · Contribute to the stability of financial markets. | ||||
| · Reducing the costs of bank investments. | ||||
| · Reducing potential risks to bank work | ||||
| 14 | The bank’s board of directors must create an efficient internal control system that protects investments, and examines the efficiency of this system to include auditing systems related to financial control, process control and risk management systems. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.508 |
| 15 | Bank governance focuses on the independence of nonexecutive board members and independent members of audit committees as it is a watchdog on the work of the board of directors from executives. | 4.2 | 84% | 0.761 |
| 16 | In order to ensure the safety of performance, the system of bonuses and incentives for the Board of Directors must be defined so that they are in cash and shares and this means that they will be as shareholders and this is very important to eliminate the gap between the owners and the executive management of the bank. | 3.8 | 76% | 0.996 |
| 17 | Bank governance provides many advantages to parties related to governance: | 4.1 | 82% | 0.712 |
| The bank: by increasing the value of shares and reducing capital costs. | ||||
| Investors: by protecting their rights and reducing risks. | ||||
| The State: by improving economic activity. | ||||
| 18 | The audit committee sets the necessary procedures to implement the internal control system and the internal audit and to meet separately with the external and internal auditors and management to discuss the strength or weakness of the disclosure policy and the internal control system. | 3.9 | 78% | 0.712 |
| 19 | Discussion of management, internal auditor and external auditor on the policies and procedures that have been taken to face the risks facing the bank such as business risks and risks related to noncompliance with the principles of professional behavior. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.845 |
| 20 | Follow up on the extent to which the administration is implementing the observations and recommendations made by the internal and external auditor. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.794 |
| 21 | The Audit Committee evaluates the work of the internal audit in terms of the efficiency and adequacy of employees in proportion to the workload required to be accomplished and the expected risks. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.712 |
| 22 | Management's discussion of the bank's procedures related to how to discover various risks, including noncompliance with laws that affect the bank's work and financial statements. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 23 | Discussion of the external auditor and management on the quality of the accounting standards applied in the bank and their impact on preparing annual statements and the external auditor's observations on them. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 24 | The audit committee responsible for the external auditor with regard to the appointment, separation and determination of fees, at the same time, is the supervisor of his work and resolves the differences between the external auditor and the bank management. | 3.9 | 78% | 0.844 |
| 25 | The Audit Committee requests the external auditor to submit a report clarifying: | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| · The efficiency of the internal control procedures | ||||
| · the extent of cooperation with the administration | ||||
| · Accounting problems that are still pending with the administration | ||||
| 26 | The audit committee evaluates the independence, impartiality, efficiency, and integrity of the external auditor and this reflects on the evaluation of the bank's activities. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.814 |
| 27 | The audit committee examines the annual report submitted by the management, the internal auditor's report, and the external auditor's report to ensure compliance with laws and professional codes of conduct. | 4.3 | 80% | 0.788 |
| 28 | The financial statements are important to the following external parties: | 4.4 | 88% | 0.674 |
| · Current and prospective investor. | ||||
| · Current and prospective lender. | ||||
| · Suppliers. | ||||
| · Customers and employees. | ||||
| 29 | The objectives of the financial statements under governance are as follows: | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| · Provide appropriate information to the relevant parties. | ||||
| · Measuring the periodic income of the bank. | ||||
| · Provide information on cash flows. | ||||
| · Provide information on the bank's economic resources and sources. | ||||
| 30 | The responsibility of the audit committees in preparing the financial statements is as follows: | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| · Carry out a financial statements examination, whether quarterly or annual. | ||||
| · Auditing the applied accounting policies. | ||||
| · Check the internal control system. | ||||
| · Evaluate the possibility of fraud. | ||||
| 31 | The responsibility of the audit committee with respect to the external auditor is determined by the following: | 4.2 | 84% | 0.761 |
| · Make a recommendation to appoint an external auditor. | ||||
| · Determining the fees of the external auditor. | ||||
| · Ensure its independence. | ||||
| · Resolving disputes between management and the external auditor | ||||
| · Supervising other services provided by the auditor. | ||||
| 32 | The responsibility of the audit committee with respect to the internal auditor is determined by the following: | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| · Activating the role of internal audit. | ||||
| · Emphasizing the independence of the internal audit. | ||||
| · Create adequate resources. | ||||
| · Examination of internal audit activities. | ||||
| · Appointing the head of the Internal Audit Department. | ||||
Below is Table (5) Analysis of the answers of the research sample to the axis of restructuring banks, as this analysis shows the agreement of the opinions of the research sample with what the researcher proposed about banking governance and its positive impact on the restructuring of banks as whenever banks are used efficiently, this leads to a high efficiency of restructuring operations Banks and the mean arithmetic for this axis ranged between (4.8) for the question No (18) (improving the level of control and developing accounting systems so that they are transparent and clear, even if the banking supervision process and accounting systems are combined with international accounting standards) and (4.1) for the question No (7) (Restructuring the government banking sector to operate according to the method of profit and loss and stopping the banks ’dependence on government support and dependence on the state through integration in banking services).
| Table 5 The Weighted Mean, Proportional Weight, and Standard Deviation of the Banks Restructuring Axis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | Details | Weighted mean | Proportional weight | standard deviation |
| 1 | Restructuring the banks means formulating a vision for the banks, making a comprehensive change in the activities of the banks, establishing specialized departments to provide new services and applying the principles of governance in accordance with international standards. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| 2 | The restructuring of banks in accordance with international requirements requires the support of various types of banking control and the development of the organizational structure of banks in line with national and international standards and requirements issued by the central bank with the determination of the powers and duties of the committees and each job level | 4.4 | 88% | 0.674 |
| 3 | Among the requirements for the restructuring of banks is strengthening the internal control system, establishing audit committees and monitoring compliance with the required policies and procedures in accordance with the Banking Law and the central bank’s regulations. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| 4 | Raising efficiency and improving the banking environment through multiple and interrelated processes that include rebuilding a legal, accounting, control and technological system. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.814 |
| 5 | According to the different Basel agreements, strengthening the role of the Central Bank of Iraq in controlling and supervising the activities of Rafidain and Al-Rasheed banks is one of the important steps to restructure the banks. | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 6 | Restructuring the boards of directors of banks and other committees to be more in line with the requirements of the market economy approach and mechanisms and the requirements of the global banking industry. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.814 |
| 7 | Restructuring the government banking sector to operate according to the method of profit and loss and stopping the banks ’dependence on government support and dependence on the state through integration in banking services. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.242 |
| 8 | Activating the bank's credit role with the aim of providing the necessary loans to encourage investment and increase the efficiency of economic activity. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.682 |
| 9 | The necessity for the central bank to compel all banks to apply international standards, including the criterion of capital adequacy and weighted risk ratios according to the decisions of the Basel Committee (3) for banking supervision, as well as the announcement issued at the end of 2010 | 4.3 | 86% | 0.651 |
| 10 | Finding a legislative and control environment that regulates the work of banks according to an appropriate investment vision consistent with the international requirements and practices of modern banks by introducing substantive amendments to the Central Bank of Iraq law regarding monetary policy and also reviewing the financial legislation governing the banking sector. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.498 |
| 11 | Work to reduce restrictions and procedures on financial activity to encourage non-banking institutions to enter the competition market in order to stabilize financial markets. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.675 |
| 12 | Making changes in the human resources management system with the aim of making optimal use of the human element by defining recruitment requirements and the qualities that must be available in human resources and the incentives system and coordination between planning, training, qualification and development and building a banking culture for workers. | 4.5 | 90% | 0.508 |
| 13 | Strengthening the banking supervision of the Central Bank over public banks through an independent and impartial supervisory system in line with approved international practices. | 4.7 | 94% | 0.466 |
| 14 | The necessity of setting a strategic plan to develop the techniques used in control and auditing by using modern banking systems, communication network, information systems and the Internet. | 4.6 | 92% | 0.498 |
| 15 | Establish a system for managing credit risks, market risks, liquidity, interest rates, exchange rates, operation and solvency, political risks, risks of electronic banking activities and other risks that may affect the bank's profits and its economic value. | 4.7 | 94% | 0.651 |
| 16 | One of the methods of restructuring banks is privatization and mergers with foreign banks, which requires Iraqi banks to change the composition of their administrative boards in line with the market economy policy. | 4.1 | 82% | 0.959 |
| 17 | The restructuring of banks includes laying the foundations for managing and controlling risks through the participation of several parties, including:- Observers by setting a risk management framework.- Shareholders through the selection of members of the Board of Directors.- The Board of Directors through setting the strategy, appointing employees, and setting policies and procedures.- Executive management through applying policies and procedures.- The Internal Audit and Auditing Committee by ensuring that the bank adheres to internal control systems and efficient information systems.- External auditors through their role in evaluating risk management information processes.- The public or customers of the bank through asking the bank management to disclose and transparency. | 4.4 | 88% | 0.498 |
| 18 | Improving the level of control and developing accounting systems so that they are transparent and clear, even though the process of banking control and accounting systems approaches international accounting standards. | 4.8 | 96% | 0.407 |
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is used to study the variables of each axis of the questionnaire and then the formation of several groups for each axis and this formation depends on the values of those groups and at the same time it shows the relationship of the relationship of each variable (question) with its group, then the relationship may be positive, which has a direct effect, or the relationship is negative, any effect Reverse, and also shows the importance of each question within the group from the point of view of the research sample.
Table (6) showed that the factor analysis formed seven groups for the axis of banking governance, whose total value ranges between (15.146) for the first group and (1.049) for the seventh group and with cumulative percentages ranging between (47.330%) for the first group and (96.727%) for the seventh group.
| Table 6 The Sequence of the Seven Groups is Shown According to their Value and the Cumulative Proportions of their Variation in the Banking Governance Axis |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group Sequence | Total Values for Each Group | The Ratio of Group Variance to the Total | Cumulative Proportions |
| 1 | 15.146 | 47.33 | 47.33 |
| 2 | 4.84 | 15.84 | 62.455 |
| 3 | 3.599 | 11.24 | 73.703 |
| 4 | 2.882 | 9.006 | 82.709 |
| 5 | 2.237 | 6.99 | 89.699 |
| 6 | 1.2 | 3.751 | 93.45 |
| 7 | 1.049 | 3.277 | 96.727 |
Table (7) shows the variables of the first group, arranged according to the degree of saturation of each variable, or according to the degree of correlation of the variable with its group for the axis of bank governance. That is, the table shows the importance of the questions from the point of view of the research sample and not based on their arrangement as stated in the questionnaire.
| Table 7 It Shows the Most Influential Variables (Questions) in the Banking Governance Axis from the Point of View of the Research Sample |
||
|---|---|---|
| Sequence according to importance | First group variables | Amount of saturation |
| 9 | The necessity for the central bank to compel all banks to apply international standards, including the criterion of capital adequacy and weighted risk ratios according to the decisions of the Basel Committee (3) for banking supervision, as well as the announcement issued at the end of 2010. | 0.917 |
| 19 | Discussion of management, internal auditor and external auditor on the policies and procedures that have been taken to face the risks facing the bank such as business risks and risks related to non-compliance with the principles of professional behavior. | 0.917 |
| 24 | The audit committee responsible for the external auditor with regard to the appointment, separation and determination of fees, at the same time, is the supervisor of his work and resolves the differences between the external auditor and the bank management. | 0.914 |
| 17 | Bank governance provides many advantages to parties related to governance: | 0.876 |
| The bank: by increasing the value of shares and reducing capital costs. | ||
| Investors: by protecting their rights and reducing risks. | ||
| The state: by improving economic activity. | ||
| 29 | The objectives of the financial statements under governance are as follows: | 0.843 |
| · Provide appropriate information to the relevant parties. | ||
| · Measuring the periodic income of the bank. | ||
| · Provide information on cash flows. | ||
| · Provide information on the bank's economic resources and sources. | ||
| 31 | The responsibility of the audit committee with respect to the external auditor is determined by the following: | 0.835 |
| · Make a recommendation to appoint an external auditor. | ||
| · Determining the fees of the external auditor. | ||
| · Ensure its independence. | ||
| · Resolving disputes between management and the external auditor | ||
| · Supervising other services provided by the auditor. | ||
| 3 | Setting a regulatory framework for the bank that guarantees the integration of work between the board of directors and the external audit and auditing committee, so that it leads to the integration of the work and at the same time achieving the sequential and organized oversight work. The audit committee monitors the actions of the board and the external auditor examines the work. The general authority of the bank supervises all activities. | 0.806 |
Table (7) shows that the influencing questions are (26) only from the total number of questions of thirty-two for the axis of banking governance, and it has been proven in the above table seven questions with the highest saturation.
Studying the Direct Impact Ratio of the Independent Variable (x) Bank Governance on the Dependent Variable (y) Restructuring the Banks
Table (8) shows the effect of bank governance on the restructuring of banks for the research sample, as the percentage of the coefficient of determination was 74.2%, and this indicates that the independent variable (bank governance) has an impact on the dependent variable (bank restructuring) at 74.2%, and this represents a high impact rate The complement of the ratio is due to the influence of other unknown factors on the dependent variable.
| Table 8 It Shows the Effect of Banking Governance on Restructuring of Rafidain and Al-Rasheed Banks |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Coefficient of Determination ( R) | Coefficient of Determination Square (R Square) | Square of the Adjusted Coefficient of Determination |
| The research sample | 86.20% | 74.20% | 73.30% |
As for Table (9), it shows the analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the calculated value of (F) reached (80,640) with a degree of freedom (1.28) and at a significant level (0.05), whereas the value of F is a table (4.196), which means that) F) The computation is greater than the new (F) and this indicates that the bank governance variable directly affects the restructuring of banks variable.
| Table 9 Analysis of Variance (Anova) for Multiple Linear Regressions Shows the Effect of the Variable, Bank Governance in the Variable, Bank Restructuring |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Variance Analysis | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Average Squares | Computed F |
| research sample | Regression | 8.907 | 1 | 8.907 | 80.64 |
| ---------- | The rest | 3.093 | 28 | 0.11 | --------- |
| ---------- | Total | 12 | 29 | ---------- | --------- |
Conclusions
1. Rafidain and Rashid banks suffer from the low level of services provided to its customers and the high cost of these services and the limited use of modern technology in activity in addition to the deterioration of the banking infrastructure in Iraq and this matter requires the restructuring of operations in public banks.
2. There is a clear rise in the costs of banking services and the delay in providing them, as workers ’wages and debts arising from both banks increase from the previous period, which constitutes a pressure factor for restructuring the Rashid and Rafidain banks.
3. The restructuring of Al-Rasheed and Al-Rafidain banks is an absolute necessity to create the appropriate environment for development Sustainable and attracting internal and external investment, and for the restructuring of banks to be effective, banks must be governed.
Recommendations
1. Table No. (3) shows that the mean of the bank restructuring axis (4.44) as well as the standard deviation (0.669) of the research sample and this means that the views of the research sample for this axis are consistent with the researcher went to that the restructuring of banks leads to raising the level of banking services Through the introduction of modern technology in the banking industry.
2. Take practical measures to prepare and train bank employees in a way that is commensurate with the actual need of the bank and at the same time to be allocate part of the state’s general budget to compensate for bad debt by establishing a bank for this purpose as some countries have done to cover bad debts from this bank, then to start working away from the effect of obligations previous period.
3. Table No. (8) Shows that the coefficient of determination square is 74.4%, and this indicates that bank governance affects at a high rate on banks restructuring operations, which leads to the success of restructuring operations and then creates the appropriate environment for investment whether internal and external.
4. It requires a fundamental change in the banks ’departments, reforming the legal and organizational system and enhancing the supervisory capacity, and to qualifying the right people of managing change in the culture of banks to meet the needs of their customers and to comply with modern requirements banking.
References
- Al-Basra, K. (2007). Banking Reform Thesis, Workshop. “Baghdad – Iraq”.
- Al-Hefnawi, S., & Abdul, A. (2005). Corporate governance and its accounting, administrative and economic dimensions. “Baghdad – Iraq”.
- Al-Houry, A.Q., & Itani, M. (2011). Adopting the foundations of modern banking and enhancing confidence in the banking system and Arab and international outreach. Union of Arab Banks.
- Al-Khatib, S. (2004). Measuring and managing bank risks, a practical approach and a scientific application (Second Edition). Alexandria: Egypt.
- Al-Fadl, M.A. (2007). The relationship between institutional governance and the value of the establishment: A case study of Jordan. Journal of Economic Horizons, Federation of Chambers of Commerce and Industry in the United Arab Emirates.
- Al-Qatanani, K.M. (2004). The impact of the characteristics of the technical environment and information technology on the risks of operational control (An Analytical Study in Jordanian Banks). Jordan.
- Al-Mulla, A. (2011). The Arab Portal, Al-Sabah Newspaper. “Baghdad- Iraq”.
- Al-Nusseery, S. (2011). The banking sector reform in Iraq, Union of Arab Banks. “Baghdad-Iraq”.
- Aik, L. (2004). The impact of corporate governance practices on Firm’s financial performance: Evidence from Malaysian companies. SEAN Economic Bulletin: Malaysia.
- Bank of Alexandria (2005). Economic Review, 37, 1-93.
- Belhawi, H.K. (2011). Privatization as a model for economic reform in Iraq. Waist University: Waist Journal for humanities.
- Ciaudia, D., & Ceyla, P.B. (1998). Lesson from systemic bank restructuring. International Monetary fund published.
- Coleman, A.K., & Biekpe, N. (2006). The link between corporate governance and performance of the non-traditional export sector: evidence from Ghana. Corporate Governance, 6(5), 609-623.
- Fahmy, H.K. (1992). Toward restructuring of the Islamic banking system. Saudi Arabia: Journal of King Abdulaziz University, Islamic Economics.
- Haddad, M. (2008). Corporate governance and its role in economic reform. First Scientific Conference, Damascus University: Syria.
- Hammad, A. (2005). Corporate governance, corporate governance applications in Banks, University House. Alexandria: Egypt.
- Irvin, N.G. (2004). Internal audit role in governance, risk control. Gleam publication Inc.
- Jonathan R.M., & Maureen, O. (2003). The corporate governance of banks, FRBNY Economic Policy Review, Cornell University’s Samuel Curtis Johnson. New York, U.S.A.
- Klapper, L., & Love, I. (2002). Corporate governance, investor protection and the performance of emerging markets. Working Paper 2818, World Bank Policy research.
- Kotler (2000). Marketing Management prentice. Hall International.
- Margery, W.A. (1998). Framework for systemic bank restructuring.
- Naji, F.A. (2006). Banking, merger an appropriate model for merging Yemeni Banks. Yemen.
- Omran M.M, Bolbol, A., & Fatheldin (2008). Corporate governance and firm Performance in Arab equity markets: Does ownership concentration matter? International Review of Law and Economics, 28, 32-45.
- Parker (1998). Globalization and Business practice. Sage public cations.
- Robert, M.B. (2005). What determines financial reporting? Healthcare financial management, 59, 58-65.
- Qaddara, F.O. (2007). Development and restructuring of Libyan commercial banks. Libya.
- Saleh, M.M., & Al-Basri, K.A.N. (2009). Walid Idi, Evaluation of banking reform policy in Iraq. “Baghdad- Iraq”.
- Tanui, P.J., & Serebemuom, B.M. (2021). Corporate diversification and financial performance of listed firms in Kenya: Does firm size matter? Journal of Advanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(2), 65-77.
- Tanui, D.P.J., Katana, H., Alosi, G., Khahenda, L., & Adhiambo, V.E. (2021). Ownership structure and financial performance of listed firms in Kenya: Mediation role of corporate diversification. Journal of Advanced Research in Economics and Administrative Sciences, 2(2), 16-34.